Outcomes of Kidney Perfusion Techniques in Transplantation from Deceased Donors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Search Strategy
- Keywords for the search:
- Kidney/renal perfusion
- Kidney/renal preservation
- Kidney/renal transplantation/transplant/graft/allograft
- The specifics of the search strategy are outlined in Supplementary Table S9.
- Last search was performed on 30 November 2022.
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Data Extraction and Selection
- A comparison between the outcomes (DGF) related to one of the machine perfusion techniques and SCS (i.e., randomized controlled trials, case control trials and observational studies) is included;
- The results in the form of mean and standard deviation are published or can be obtained from median and range [26].
- Secondary studies such as systematic reviews and meta-analyses, as this would lead to duplication in data;
- Pre-clinical studies such as animal and laboratory studies as well as letters to the editor and published protocols;
- Case reports, abstracts, and publications that missed the minimum required data for reporting.
- Suitable studies were identified, and full text analysis was performed. Discrepancies between reviewers were resolved after discussion between them and the senior authors.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
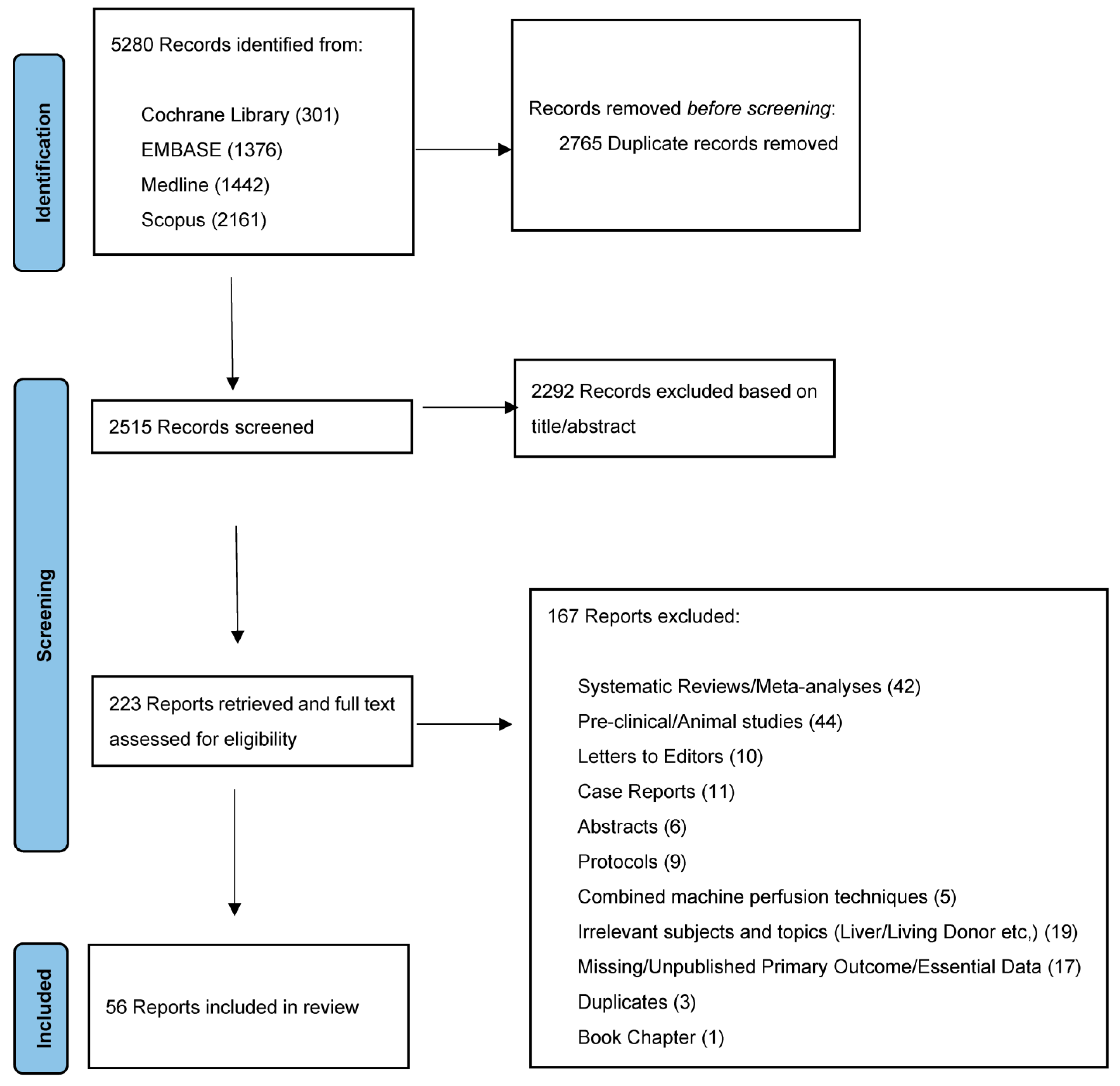
3.1. Literature Search and Systematic Review
3.2. Hypothermic Machine Perfusion (without Oxygen) (HMP)
3.2.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2.2. Meta-Analysis
3.3. Hypothermic Oxygenated Machine Perfusion (HMP + O2)
3.3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.3.2. Comparative Studies
3.4. Normothermic Machine Perfusion (NMP)
Descriptive Statistics
3.5. Normothermic Regional Perfusion (NRP)
3.5.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.5.2. Comparative Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CIT | Cold Ischemia Time |
| DBD | Donation after Brain Death |
| DCD | Donation after Circulatory Death |
| DGF | Delayed Graft Function |
| ECD | Extended Criteria Donors |
| ECMO | Extra-Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation |
| HMP | Hypothermic Machine Perfusion |
| HOPE | Hypothermic Oxygenated Perfusion |
| ICP | In situ Cold Perfusion |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| NMP | Normothermic Machine Perfusion |
| NRP | Normothermic Regional Perfusion |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PNF | Primary Non-Function |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| RR | Relative Risk |
| SCD | Standard Criteria Donors |
| SCS | Static Cold Storage |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| uDCD | uncontrolled Donation after Cardiac Death |
References
- Wolfe, R.A.; Ashby, V.B.; Milford, E.L.; Ojo, A.O.; Ettenger, R.E.; Agodoa, L.Y.C.; Held, P.J.; Port, F.K. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.W.; Manninen, D.L.; Garrison, L.P.; Hart, L.G.; Blagg, C.R.; Gutman, R.A.; Hull, A.R.; Lowrie, E.G. The Quality of Life of Patients with End-Stage Renal-Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 312, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaubel, D.; Desmeules, M.; Mao, Y.; Jeffery, J.; Fenton, S. Survival experience among elderly end-stage renal disease patients. Transplantation 1995, 60, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, R.A.; Delmonico, F.L.; Feng, S.; Port, F.K.; Wynne, J.J.; Merion, R.M. Expanded criteria donors for kidney transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2003, 3, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, M.; Diena, D.; Dellepiane, S.; Guzzo, G.; Lo Sardo, L.; Fop, F.; Segoloni, G.P.; Amoroso, A.; Magistroni, P.; Biancone, L. Long-Term Outcomes and Discard Rate of Kidneys by Decade of Extended Criteria Donor Age. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosengard, B.R.; Feng, S.; Alfrey, E.J.; Zaroff, J.G.; Emond, J.C.; Henry, M.L.; Garrity, E.R.; Roberts, J.P.; Wynn, J.J.; Metzger, R.A.; et al. Report of the crystal city meeting to maximize the use of organs recovered from the cadaver donor. Am. J. Transplant. 2002, 2, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, S.; Clayton, P. DCD ECD Kidneys—Can You Make a Silk Purse from a Sow’s Ear? Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 249–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsis, V.; Dounousi, E.; Mitsis, M. Hypothermic Machine Perfusion of Kidney Transplant: A Mini-Review. Transpl. Proc. 2021, 53, 2793–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karangwa, S.A.; Dutkowski, P.; Fontes, P.; Friend, P.J.; Guarrera, J.V.; Markmann, J.F.; Mergental, H.; Minor, T.; Quintini, C.; Selzner, M.; et al. Machine Perfusion of Donor Livers for Transplantation: A Proposal for Standardized Nomenclature and Reporting Guidelines. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 2932–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosgood, S.A.; Nicholson, H.F.L.; Nicholson, M.L. Oxygenated Kidney Preservation Techniques. Transplantation 2012, 93, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kron, P.; Schlegel, A.; de Rougemont, O.; Oberkofler, C.E.; Clavien, P.A.; Dutkowski, P. Short, Cool, and Well Oxygenated—HOPE for Kidney Transplantation in a Rodent Model. Ann. Surg. 2016, 264, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochmans, I.; Brat, A.; Davies, L.; Hofker, H.S.; van de Leemkolk, F.E.M.; Leuvenink, H.G.D.; Knight, S.R.; Pirenne, J.; Ploeg, R.J.; Collaboration, C.T.; et al. Oxygenated versus standard cold perfusion preservation in kidney transplantation (COMPARE): A randomised, double-blind, paired, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosgood, S.A.; Nicholson, M.L. Normothermic kidney preservation. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2011, 16, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosgood, S.A.; Thompson, E.; Moore, T.; Wilson, C.H.; Nicholson, M.L. Normothermic machine perfusion for the assessment and transplantation of declined human kidneys from donation after circulatory death donors. Brit. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosgood, S.A.; van Heurn, E.; Nicholson, M.L. Normothermic machine perfusion of the kidney: Better conditioning and repair? Transpl. Int. 2015, 28, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oniscu, G.C.; Randle, L.V.; Muiesan, P.; Butler, A.J.; Currie, I.S.; Perera, M.T.; Forsythe, J.L.; Watson, C.J. In situ normothermic regional perfusion for controlled donation after circulatory death—The United Kingdom experience. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 2846–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, M.; Coll, E.; Fernandez-Perez, C.; Pont, T.; Ruiz, A.; Perez-Redondo, M.; Oliver, E.; Atutxa, L.; Mancino, J.M.; Daga, D.; et al. Improved short-term outcomes of kidney transplants in controlled donation after the circulatory determination of death with the use of normothermic regional perfusion. Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 21, 3618–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minambres, E.; Suberviola, B.; Dominguez-Gil, B.; Rodrigo, E.; Millan, J.C.R.S.; Juan, J.C.R.S.; Ballesteros, M.A. Improving the Outcomes of Organs Obtained from Controlled Donation After Circulatory Death Donors Using Abdominal Normothermic Regional Perfusion. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delsuc, C.; Faure, A.; Berthiller, J.; Dorez, D.; Matillon, X.; Meas-Yedid, V.; Floccard, B.; Marcotte, G.; Labeye, V.; Rabeyrin, M.; et al. Uncontrolled donation after circulatory death: Comparison of two kidney preservation protocols on graft outcomes. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moers, C.; Smits, J.M.; Maathuis, M.H.; Treckmann, J.; van Gelder, F.; Napieralski, B.P.; van Kasterop-Kutz, M.; van der Heide, J.J.; Squifflet, J.P.; van Heurn, E.; et al. Machine perfusion or cold storage in deceased-donor kidney transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, J.M.; Knight, S.R.; Morgan, R.D.; Morris, P.J. Preservation Solutions for Static Cold Storage of Kidney Allografts: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Transplant. 2012, 12, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, J.M.; Pall, K.T.; Pengel, L.H.M. Cope. Supplemental oxygen during hypothermic kidney preservation: A systematic review. Transplant. Rev. 2017, 31, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jochmans, I.; Moers, C.; Smits, J.M.; Leuvenink, H.G.D.; Treckmann, J.; Paul, A.; Rahmel, A.; Squifflet, J.P.; van Heurn, E.; Monbaliu, D.; et al. The Prognostic Value of Renal Resistance During Hypothermic Machine Perfusion of Deceased Donor Kidneys. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 2214–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissolati, M.; Pindozzi, F.; Guarneri, G.; Adamenko, O.; Giannone, F.; Mazza, M.; Maggi, G.; Rosati, R.; Secchi, A.; Socci, C. Hypothermic Machine Perfusion as an Alternative to Biopsy Assessment in Transplantation of Kidneys Donated After Cardiocirculatory Death: A Pilot Study. Transpl. Proc. 2019, 51, 2890–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021, 71, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozo, S.P.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/online-learning/core-software/revman (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Jochmans, I.; Moers, C.; Smits, J.M.; Leuvenink, H.G.; Treckmann, J.; Paul, A.; Rahmel, A.; Squifflet, J.P.; van Heurn, E.; Monbaliu, D.; et al. Machine perfusion versus cold storage for the preservation of kidneys donated after cardiac death: A multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Surg. 2010, 252, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abboud, I.; Antoine, C.; Gaudez, F.; Fieux, F.; Lefaucheur, C.; Pillebout, E.; Viglietti, D.; Serrato, T.; Verine, J.; Flamant, M.; et al. Pulsatile perfusion preservation for expanded-criteria donors kidneys: Impact on delayed graft function rate. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2011, 34, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treckmann, J.; Moers, C.; Smits, J.M.; Gallinat, A.; Maathuis, M.H.; van Kasterop-Kutz, M.; Jochmans, I.; Homan van der Heide, J.J.; Squifflet, J.P.; van Heurn, E.; et al. Machine perfusion versus cold storage for preservation of kidneys from expanded criteria donors after brain death. Transpl. Int. 2011, 24, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallinat, A.; Moers, C.; Treckmann, J.; Smits, J.M.; Leuvenink, H.G.; Lefering, R.; van Heurn, E.; Kirste, G.R.; Squifflet, J.P.; Rahmel, A.; et al. Machine perfusion versus cold storage for the preservation of kidneys from donors >/= 65 years allocated in the Eurotransplant Senior Programme. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 4458–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Chen, M.; Zhang, K.; Fu, Y. Hypothermic Machine Perfusion in DCD Kidney Transplantation: A Single Center Experience. Urol. Int. 2016, 96, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xie, D.W.; Hu, X.P.; Yin, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.D. Effect of Hypothermic Machine Perfusion on the Preservation of Kidneys Donated After Cardiac Death: A Single-Center, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Artif. Organs 2017, 41, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Rosen, L.M.; Tan, H.P.; Fishbein, J.; Wu, C.M.; Donaldson, O.B.; Stuart, S.; Shah, N.A.; McCauley, J.; Humar, A.; et al. Outcomes of Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation Using Expanded Criteria Donor Kidneys Following Pulsatile Preservation. Cureus 2019, 11, e5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.J.E.; Wells, A.C.; Roberts, R.J.; Akoh, J.A.; Friend, P.J.; Akyol, M.; Calder, F.R.; Allen, J.E.; Jones, M.N.; Collett, D.; et al. Cold Machine Perfusion Versus Static Cold Storage of Kidneys Donated After Cardiac Death: A UK Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, R.M.; Brock, G.N.; Garrison, R.N.; Smith, J.W.; Marvin, M.R.; Franklin, G.A. To pump or not to pump: A comparison of machine perfusion vs cold storage for deceased donor kidney transplantation. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2013, 216, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedigh, A.; Tufveson, G.; Backman, L.; Biglarnia, A.R.; Lorant, T. Initial experience with hypothermic machine perfusion of kidneys from deceased donors in the Uppsala region in Sweden. Transplant. Proc. 2013, 45, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dion, M.S.; McGregor, T.B.; McAlister, V.C.; Luke, P.P.; Sener, A. Hypothermic machine perfusion improves Doppler ultrasonography resistive indices and long-term allograft function after renal transplantation: A single-centre analysis. Bju Int. 2015, 116, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, J.C.; Shields, W.P.; Azhar, M.; Daly, P.J.; Zimmermann, J.A.; Smyth, G.P.; Eng, M.P.; Power, R.E.; Mohan, P.; Hickey, D.P.; et al. Single centre experience of hypothermic machine perfusion of kidneys from extended criteria deceased heart-beating donors: A comparative study. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 185, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlaban, M.; Barreda, P.; Ballesteros, M.A.; Rodrigo, E.; Suberviola, B.; Valero, R.; Minambres, E.; Ruiz-San Millan, J.C. Static Cold Storage vs Ex Vivo Machine Perfusion: Results from a Comparative Study on Renal Transplant Outcome in a Controlled Donation After Circulatory Death Program. Transpl. Proc. 2019, 51, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszyna, T.; Richter, P. Hypothermic Machine Perfusion of Kidneys Compensates for Extended Storage Time: A Single Intervention with a Significant Impact. Transpl. Proc. 2021, 53, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Lan, J.; Ye, S.; Liu, Z.; Fan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Qiao, B.; Shiu-Chung Ko, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Outcome Improvement for Hypothermic Machine Perfusion Versus Cold Storage for Kidneys from Cardiac Death Donors. Artif. Organs 2017, 41, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husen, P.; Boffa, C.; Jochmans, I.; Krikke, C.; Davies, L.; Mazilescu, L.; Brat, A.; Knight, S.; Wettstein, D.; Cseprekal, O.; et al. Oxygenated End-Hypothermic Machine Perfusion in Expanded Criteria Donor Kidney Transplant A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama Surg. 2021, 156, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, F.A.; Czigany, Z.; Rietzler, K.; Miller, H.; Reichelt, S.; Liu, W.J.; Boecker, J.; Moeller, M.J.; Tolba, R.H.; Hamesch, K.; et al. Decrease of renal resistance during hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion is associated with early allograft function in extended criteria donation kidney transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravaioli, M.; De Pace, V.; Angeletti, A.; Comai, G.; Vasuri, F.; Baldassarre, M.; Maroni, L.; Odaldi, F.; Fallani, G.; Caraceni, P.; et al. Hypothermic Oxygenated New Machine Perfusion System in Liver and Kidney Transplantation of Extended Criteria Donors: First Italian Clinical Trial. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiselle, J.; Augusto, J.F.; Videcoq, M.; Legeard, E.; Dube, L.; Templier, F.; Renaudin, K.; Sayegh, J.; Karam, G.; Blancho, G.; et al. Transplantation of kidneys from uncontrolled donation after circulatory determination of death: Comparison with brain death donors with or without extended criteria and impact of normothermic regional perfusion. Transpl. Int. 2016, 29, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.; Geddes, C.; Mark, P.; Clancy, M.; Asher, J. Transplantation of kidneys after normothermic perfusion: A single center experience. Clin. Transplant. 2021, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, D.M.; Watson, C.J.E.; Pettigrew, G.J.; Johnson, R.J.; Collett, D.; Neuberger, J.M.; Bradley, J.A. Kidney donation after circulatory death (DCD): State of the art. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Farney, A.C.; Rogers, J.; Zuckerman, J.; Reeves-Daniel, A.; Hartmann, E.; Iskandar, S.; Adams, P.; Stratta, R.J. Kidney transplantation from donation after cardiac death donors: Lack of impact of delayed graft function on post-transplant outcomes. Clin. Transplant. 2011, 25, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijkse, E.; Ceuppens, S.; Qi, H.C.; IJzermans, J.N.M.; Hesselink, D.A.; Minnee, R.C. Implementation of donation after circulatory death kidney transplantation can safely enlarge the donor pool: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 92, 106021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, T.D.; Thacker, L.R.; Jeon, H.; Lucas, B.A.; Ranjan, D. Sensitivity of expanded-criteria donor kidneys to cold ischaemia time. Clin. Transplant. 2004, 18, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, J.; Zamora, J.; Pirsch, J.D. A systematic review of kidney transplantation from expanded criteria donors. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 52, 553–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarlagadda, S.G.; Coca, S.G.; Formica, R.N.; Poggio, E.D.; Parikh, C.R. Association between delayed graft function and allograft and patient survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedland, S.J.; Shoskes, D.A. Economic impact of delayed graft function and suboptimal kidneys. Transplant. Rev. 1999, 13, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Tsapepas, D.; King, K.L.; Husain, S.A.; Corvino, F.A.; Dillon, A.; Wang, W.; Mayne, T.J.; Mohan, S. Financial impact of delayed graft function in kidney transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2020, 34, e14022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kron, P.; Schlegel, A.; Muller, X.; Gaspert, A.; Clavien, P.A.; Dutkowski, P. Hypothermic Oxygenated Perfusion: A Simple and Effective Method to Modulate the Immune Response in Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2019, 103, E128–E136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaths, J.M.; Hamar, M.; Echeverri, J.; Linares, I.; Urbanellis, P.; Cen, J.Y.; Ganesh, S.; Dingwell, L.S.; Yip, P.; John, R.; et al. Normothermic ex vivo kidney perfusion for graft quality assessment prior to transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sandes-Freitas, T.V.; Costa, S.D.; de Andrade, L.G.M.; Girao, C.M.; Fernandes, P.; de Oliveira, C.M.C.; Esmeraldo, R.M. The Impact of Hypothermic Pulsatile Machine Perfusion Versus Static Cold Storage: A Donor-Matched Paired Analysis in a Scenario of High Incidence of Delayed Kidney Graft Function. Ann. Transplant. 2020, 25, e927010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, A.C.C.; Requiao Moura, L.R.; Borrelli, M.; Nogueira, M.; Clarizia, G.; Ongaro, P.; Durao, M.S.; Pacheco-Silva, A. Impact of machine perfusion after long static cold storage on delayed graft function incidence and duration and time to hospital discharge. Clin. Transplant. 2018, 32, e13130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, A.; McGrogan, D.; Inston, N.; Ready, A. Hypothermic machine perfusion permits extended cold ischemia times with improved early graft function. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2015, 13, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Ciancio, G.; Gaynor, J.J.; Sageshima, J.; Chen, L.; Roth, D.; Kupin, W.; Guerra, G.; Tueros, L.; Zarak, A.; Hanson, L.; et al. Favorable outcomes with machine perfusion and longer pump times in kidney transplantation: A single-center, observational study. Transplantation 2010, 90, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingle, S.J.; Figueiredo, R.S.; Moir, J.A.; Goodfellow, M.; Talbot, D.; Wilson, C.H. Machine perfusion preservation versus static cold storage for deceased donor kidney transplantation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 3, CD011671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darius, T.; Gianello, P.; Vergauwen, M.; Mourad, N.; Buemi, A.; De Meyer, M.; Mourad, M. The effect on early renal function of various dynamic preservation strategies in a preclinical pig ischemia-reperfusion autotransplant model. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutkowski, P.; Polak, W.G.; Muiesan, P.; Schlegel, A.; Verhoeven, C.J.; Scalera, I.; DeOliveira, M.L.; Kron, P.; Clavien, P.A. First Comparison of Hypothermic Oxygenated PErfusion Versus Static Cold Storage of Human Donation After Cardiac Death Liver Transplants an International-matched Case Analysis. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEvoy, C.M.; Clotet-Freixas, S.; Tokar, T.; Pastrello, C.; Reid, S.; Batruch, I.; RaoPeters, A.A.E.; Kaths, J.M.; Urbanellis, P.; Farkona, S.; et al. Normothermic Ex-vivo Kidney Perfusion in a Porcine Auto-Transplantation Model Preserves the Expression of Key Mitochondrial Proteins: An Unbiased Proteomics Analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2021, 20, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasile, L.; Stubenitsky, B.M.; Booster, M.H.; Arenada, D.; Haisch, C.; Kootstra, G. Hypothermia—A limiting factor in using warm ischemically damaged kidneys. Am. J. Transplant. 2001, 1, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, M.L.; Hosgood, S.A. Renal Transplantation After Ex Vivo Normothermic Perfusion: The First Clinical Study. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandak, P.; Phillips, B.L.; Uwechue, R.; Thompson, E.; Bates, L.; Ibrahim, I.; Sewpaul, A.; Figueiredo, R.; Olsburgh, J.; Hosgood, S.; et al. Dissemination of a novel organ perfusion technique: Ex vivo normothermic perfusion of deceased donor kidneys. Artif. Organs 2019, 43, E308–E319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steichen, C.; Erpicum, P. Combining cell-based therapy and normothermic machine perfusion for kidney graft conditioning has gone one step further. Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 21, 1359–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosgood, S.A.; Bagul, A.; Kaushik, M.; Rimoldi, J.; Gadepalli, R.S.; Nicholson, M.L. Application of nitric oxide and carbon monoxide in a model of renal preservation. Brit. J. Surg. 2008, 95, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.B.; Plotkin, J.S.; Howell, C.D.; Njoku, M.J.; Kuo, P.C.; Bartlett, S.T. Successful emergency transplantation of a liver allograft from a donor maintained on extracorporeal, membrane oxygenation. Transplantation 1997, 63, 910–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznik, O.; Bagnenko, S.; Scvortsov, A.; Loginov, I.; Ananyev, A.; Senchik, K.; Moysyuk, Y. The use of in-situ normothermic extracorporeal perfusion and leukocyte depletion for resuscitation of human donor kidneys. Perfusion 2010, 25, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, A.; Fulceri, G.E.; Lazzeri, C.; Bonizzoli, M.; Li Marzi, V.; Serni, S.; Cirami, L.; Migliaccio, M.L. Delayed graft function and perfusion parameters of kidneys from uncontrolled donors after circulatory death. Perfusion 2021, 36, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, G.; Cerami, C.; Facchini, F.; Fontana, F.; Alfano, G.; Giovanni, R.; Cappelli, G. Kidney Transplantation from Circulatory Death Donors: Monocentric Experience. Transplant. Proc. 2019, 51, 2865–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaioli, M.; De Pace, V.; Comai, G.; Capelli, I.; Baraldi, O.; D’Errico, A.; Bertuzzo, V.R.; Del Gaudio, M.; Zanfi, C.; D’Arcangelo, G.L.; et al. Preliminary experience of sequential use of normothermic and hypothermic oxygenated perfusion for donation after circulatory death kidney with warm ischemia time over the conventional criteria—A retrospective and observational study. Transpl. Int. 2018, 31, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matillon, X.; Danjou, F.; Petruzzo, P.; Thaunat, O.; Rimmele, T.; Delsuc, C.; Faure, A.; Rabeyrin, M.; Yedid, V.M.; Hanf, W.; et al. Hypothermic pulsatile preservation of kidneys from uncontrolled deceased donors after cardiac arrest—A retrospective study. Transpl. Int. 2017, 30, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatev, H.; von Horn, C.; Kaths, M.; Paul, A.; Minor, T. Clinical use of controlled oxygenated rewarming of kidney grafts prior to transplantation by ex vivo machine perfusion. A pilot study. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2022, 52, e13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtzager, J.H.E.; Hemelrijk, S.D.; Post, I.C.J.H.; Idu, M.M.; Bemelman, F.J.; van Gulik, T.M. The Use of the Oxygenated Airdrive(TM) Machine Perfusion System in Kidney Graft Preservation: A Clinical Pilot Study. Eur. Surg. Res. 2021, 61, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznik, O.; Bagnenko, S.; Skvortsov, A.; Ananyev, A.; Senchik, K.; Loginov, I.; Moysyuk, Y. Rehabilitation of Ischemically Damaged Human Kidneys by Normothermic Extracorporal Hemoperfusion in situ with Oxygenation and Leukocyte Depletion. Transpl. Proc. 2010, 42, 1536–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Utrera, N.; Medina-Polo, J.; Pamplona-Casamayor, M.; Passas-Martinez, J.B.; Rodriguez-Antolin, A.; Kehrmann, F.D.; Duarte-Ojeda, J.M.; Tejido-Sanchez, A.; Auba, F.V.; Belmonte, A.A. Uncontrolled non-heartbeating donors (types I-II) with normothermic recirculation vs. heartbeating donors: Evaluation of functional results and survival. Actas Urol. Esp. 2015, 39, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catena, F.; Gazzotti, F.; Amaduzzi, A.; Fuga, G.; Montori, G.; Cucchetti, A.; Coccolini, F.; Vallicelli, C.; Pinna, A.D. Pulsatile Perfusion of Kidney Allografts With Celsior Solution. Transpl. Proc. 2010, 42, 3971–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarrera, J.V.; Goldstein, M.J.; Samstein, B.; Henry, S.; Reverte, C.; Arrington, B.; Brown, T.; Coleman, T.K.; Mattei, G.; Mendez, N.; et al. ‘When good kidneys pump badly’: Outcomes of deceased donor renal allografts with poor pulsatile perfusion characteristics. Transpl. Int. 2010, 23, 444–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuno, N.; Konno, Y.N.O.; Jyojima, Y.; Akashi, I.; Iwamoto, H.; Hama, K.; Hiirano, T.; Nagao, T. Machine Perfusion Preservation for Kidney Grafts with a High Creatinine from Uncontrolled Donation After Cardiac Death. Transpl. Proc. 2010, 42, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moers, C.; Varnav, O.C.; van Heurn, E.; Jochmans, I.; Kirste, G.R.; Rahmel, A.; Leuvenink, H.G.; Squifflet, J.P.; Paul, A.; Pirenne, J.; et al. The value of machine perfusion perfusate biomarkers for predicting kidney transplant outcome. Transplantation 2010, 90, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciancio, G.; Gaynor, J.J.; Sageshima, J.; Roth, D.; Kupin, W.; Guerra, G.; Tueros, L.; Zarak, A.; Hanson, L.; Ganz, S.; et al. Machine perfusion following static cold storage preservation in kidney transplantation: Donor-matched pair analysis of the prognostic impact of longer pump time. Transpl. Int. 2012, 25, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Pankewycz, O.G.; Weber-Shrikant, E.; Zachariah, M.; Kohli, R.; Nader, N.D.; Laftavi, M.R. Effect of Increased Pressure During Pulsatile Pump Perfusion of Deceased Donor Kidneys in Transplantation. Transpl. Proc. 2012, 44, 2202–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogland, E.R.; de Vries, E.E.; Christiaans, M.H.; Winkens, B.; Snoeijs, M.G.; van Heurn, L.W. The value of machine perfusion biomarker concentration in DCD kidney transplantations. Transplantation 2013, 95, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagelschmidt, M.; Minor, T.; Gallinat, A.; Moers, C.; Jochmans, I.; Pirenne, J.; Ploeg, R.J.; Paul, A.; Treckmann, J. Lipid peroxidation products in machine perfusion of older donor kidneys. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 180, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wszola, M.; Kwiatkowski, A.; Diuwe, P.; Domagala, P.; Gorski, L.; Kieszek, R.; Berman, A.; Perkowska-Ptasinska, A.; Durlik, M.; Paczek, L.; et al. One-year results of a prospective, randomized trial comparing two machine perfusion devices used for kidney preservation. Transpl. Int. 2013, 26, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, I.; Bhangoo, R.; Reese, P.; Doshi, M.; Weng, F.; Hasz, R.; Goldstein, M.; Schroppel, B.; Parikh, C. Glutathione S-Transferase Iso-Enzymes in Perfusate From Pumped Kidneys Are Associated With Delayed Graft Function. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, A.J.; Nath, J.; Cobbold, M.; Ludwig, C.; Tennant, D.A.; Inston, N.G.; Ready, A.R. Metabolomic Analysis of Perfusate During Hypothermic Machine Perfusion of Human Cadaveric Kidneys. Transplantation 2015, 99, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloyo, S.; Sageshima, J.; Gaynor, J.J.; Chen, L.D.; Ciancio, G.; Burke, G.W. Negative impact of prolonged cold storage time before machine perfusion preservation in donation after circulatory death kidney transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2016, 29, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, C.R.; Hall, I.E.; Bhangoo, R.S.; Ficek, J.; Abt, P.L.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Lin, H.; Bimali, M.; Murray, P.T.; Rao, V.; et al. Associations of Perfusate Biomarkers and Pump Parameters With Delayed Graft Function and Deceased Donor Kidney Allograft Function. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 1526–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.D.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, L.H.; Yuan, X.P.; Qiu, J.; Wang, C.X.; He, X.S.; Chen, L.Z. Evaluation of quality of kidneys from donation after circulatory death/expanded criteria donors by parameters of machine perfusion. Nephrology 2018, 23, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.G.; Tian, P.X.; Ding, X.M.; Xiang, H.L.; Li, Y.; Tian, X.H.; Han, F.; Tai, Q.H.; Liu, Q.L.; Zheng, J.; et al. Beneficial Effect of Moderately Increasing Hypothermic Machine Perfusion Pressure on Donor after Cardiac Death Renal Transplantation. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 2676–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kox, J.; Moers, C.; Monbaliu, D.; Strelniece, A.; Treckmann, J.; Jochmans, I.; Leuvenink, H.; Van Heurn, E.; Pirenne, J.; Paul, A.; et al. The Benefits of Hypothermic Machine Preservation and Short Cold Ischemia Times in Deceased Donor Kidneys. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Nath, J.; Hodson, J.; Inston, N.; Ready, A. Outcomes of donation after circulatory death kidneys undergoing hypothermic machine perfusion following static cold storage: A UK population-based cohort study. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoylova, M.L.; Nash, A.; Kuchibhatla, M.; Barbas, A.S.; Brennan, T.V. Machine perfusion of donor kidneys may reduce graft rejection. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinc, M.; Stamp, S.; Ling, J.; Carter, N.; Talbot, D.; Sheerin, N.S. Comparison of the Outcome of Kidney Transplant After Pulsatile or Continuous Ex Vivo Hypothermic Machine Perfusion of Kidneys Donated After Cardiac Death: Analysis of Kidney Pairs. Transpl. Proc. 2019, 51, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wszola, M.; Domagala, P.; Ostaszewska, A.; Gorski, L.; Karpeta, E.; Berman, A.; Sobol, M.; Durlik, M.; Chmura, A.; Kwiatkowski, A. Time of Cold Storage Prior to Start of Hypothermic Machine Perfusion and Its Influence on Graft Survival. Transpl. Proc. 2019, 51, 2514–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, V.; Wunsch, S.; O’Connor, K.; Souter, M. Variation in Hypothermic Machine Perfusion Utilization and Clinical Outcomes for Deceased-Donor Kidneys. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 982. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Logan, A.; Schenk, A.; Bumgardner, G.; Brock, G.; El-Hinnawi, A.; Rajab, A.; Washburn, K. Machine perfusion of kidney allografts affects early but not late graft function. Am. J. Surg. 2022, 223, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghoneima, A.S.; Sousa Da Silva, R.X.; Gosteli, M.A.; Barlow, A.D.; Kron, P. Outcomes of Kidney Perfusion Techniques in Transplantation from Deceased Donors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3871. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123871
Ghoneima AS, Sousa Da Silva RX, Gosteli MA, Barlow AD, Kron P. Outcomes of Kidney Perfusion Techniques in Transplantation from Deceased Donors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):3871. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123871
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhoneima, Ahmed S., Richard X. Sousa Da Silva, Martina A. Gosteli, Adam D. Barlow, and Philipp Kron. 2023. "Outcomes of Kidney Perfusion Techniques in Transplantation from Deceased Donors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 3871. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123871
APA StyleGhoneima, A. S., Sousa Da Silva, R. X., Gosteli, M. A., Barlow, A. D., & Kron, P. (2023). Outcomes of Kidney Perfusion Techniques in Transplantation from Deceased Donors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 3871. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123871













