Impairment of Mesenteric Perfusion as a Marker of Major Bleeding in Trauma Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting the Aim
2.2. Data Collection Methods
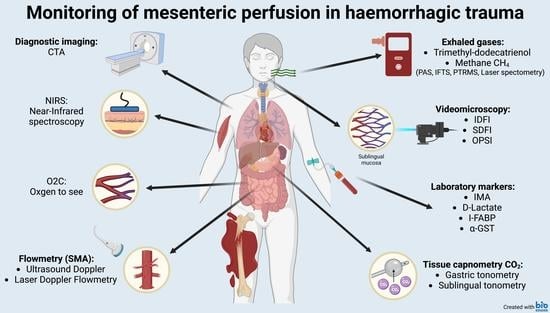
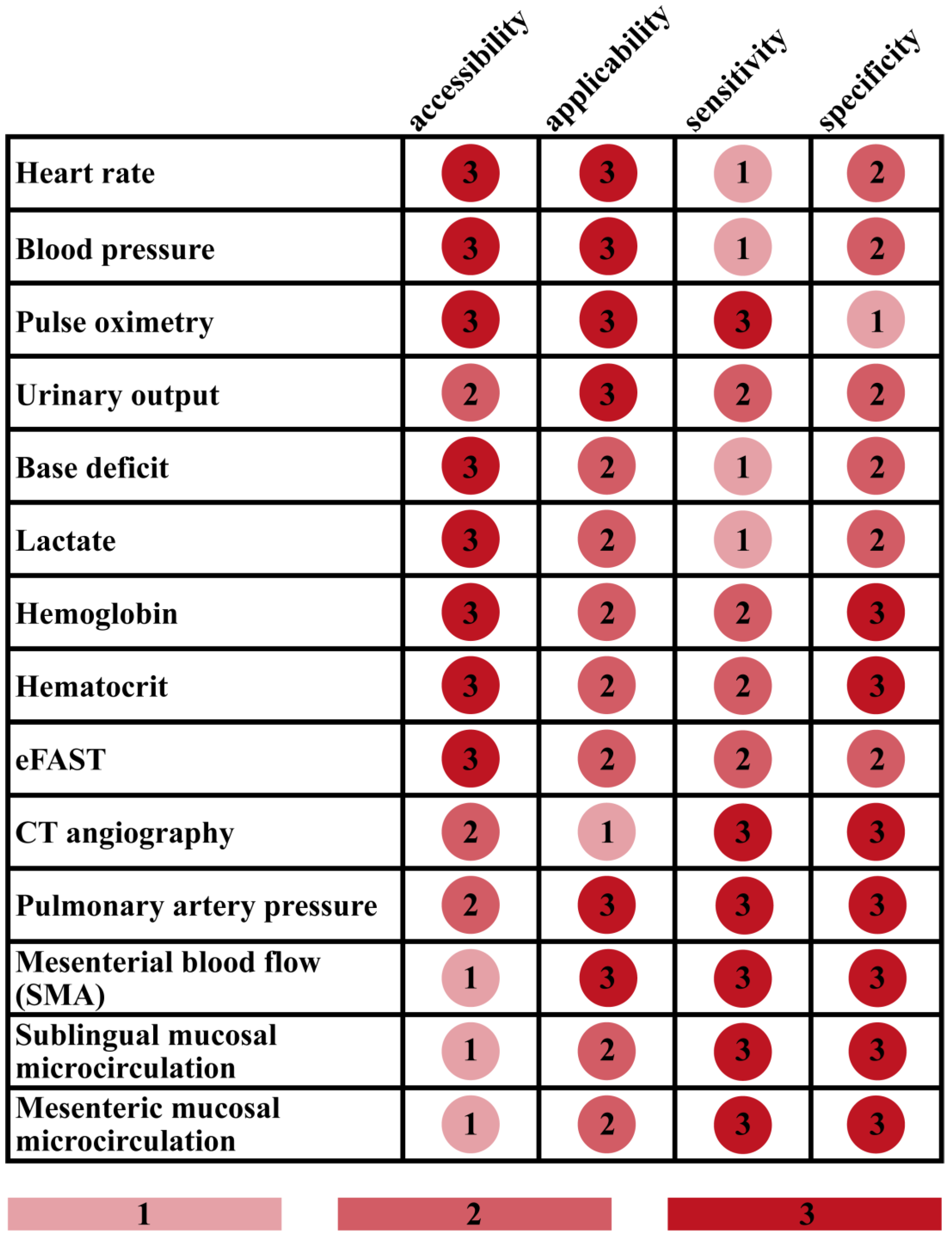
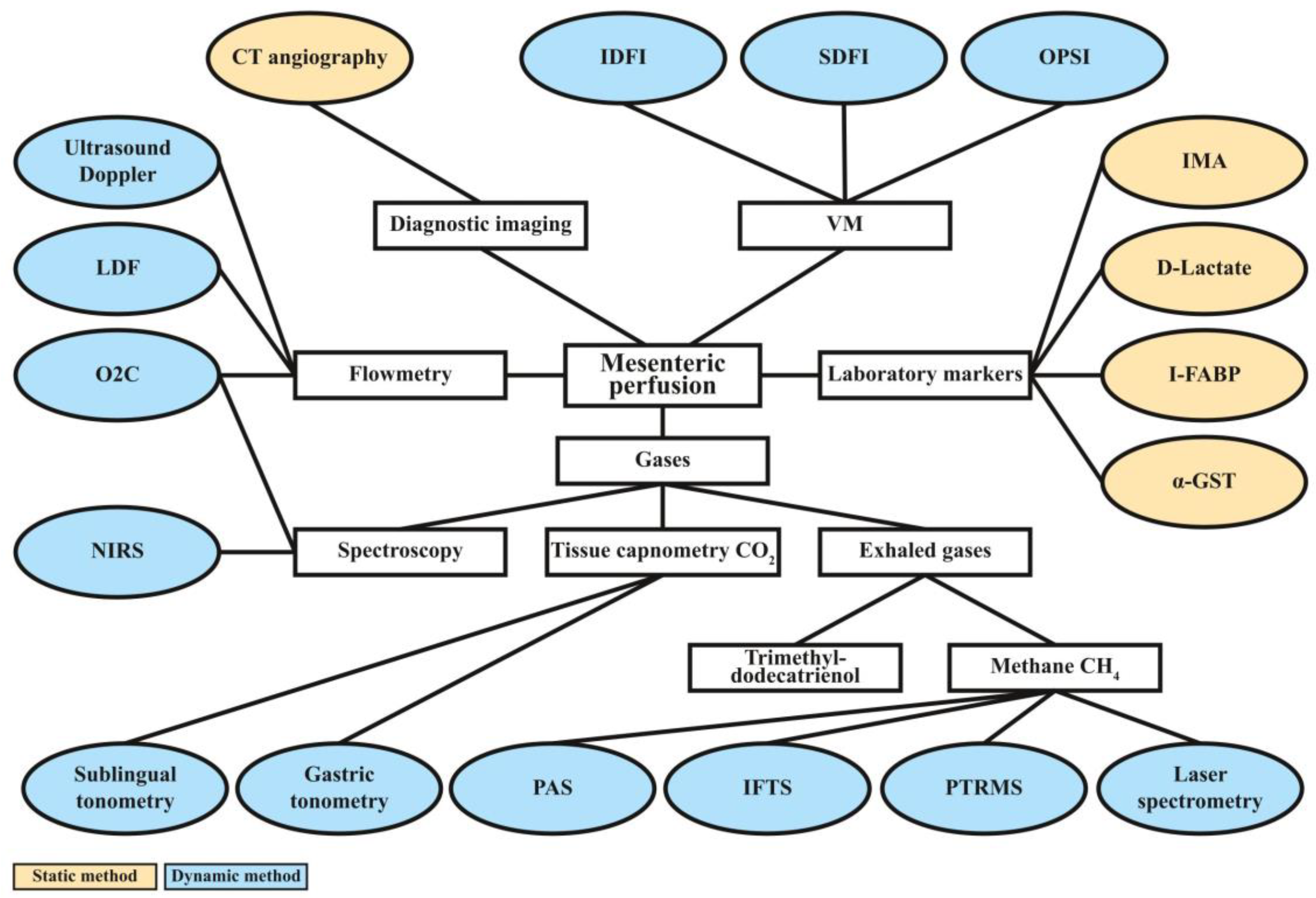
3. Results
3.1. Diagnostic Imaging
3.2. Doppler Ultrasound and Laser Doppler Flowmetry
3.3. Videomicroscopic Approaches
3.4. Laboratory Markers
3.5. Measurements of Gas Tensions in Tissues and Exhaled Air
3.5.1. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
3.5.2. Micro-Lightguide Spectrophotometry (“Oxygen-to-See”/O2C)
3.5.3. Tissue Capnometry
3.5.4. Detection of Exhaled Gases
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eastridge, B.J.; Holcomb, J.B.; Shackelford, S. Outcomes of Traumatic Hemorrhagic Shock and the Epidemiology of Preventable Death from Injury. Transfusion 2019, 59, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Eastridge, B.J.; Holcomb, J.B. Remote Damage Control Resuscitation in Austere Environments. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2017, 28, S124–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jávor, P.; Hanák, L.; Hegyi, P.; Csonka, E.; Butt, E.; Horváth, T.; Góg, I.; Lukacs, A.; Soós, A.; Rumbus, Z.; et al. Predictive Value of Tachycardia for Mortality in Trauma-Related Haemorrhagic Shock: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e059271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooke, M.; Yeung, L.; Miraflor, E.; Garcia, A.; Victorino, G.P. Lactate Predicts Massive Transfusion in Hemodynamically Normal Patients. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 204, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutschler, M.; Nienaber, U.; Brockamp, T.; Wafaisade, A.; Fabian, T.; Paffrath, T.; Bouillon, B.; Maegele, M. Renaissance of Base Deficit for the Initial Assessment of Trauma Patients: A Base Deficit-Based Classification for Hypovolemic Shock Developed on Data from 16,305 Patients Derived from the TraumaRegister DGU®. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Surgeons Shock. Advanced Trauma Life Support: Student Course Manual; American College of Surgeons: Chicago, IL, USA, 2018; pp. 42–61. [Google Scholar]
- Jávor, P.; Csonka, E.; Butt, E.; Rárosi, F.; Babik, B.; Török, L.; Varga, E.; Hartmann, P. Comparison of the Previous and Current Trauma-Related Shock Classifications: A Retrospective Cohort Study from a Level I Trauma Center. Eur. Surg. Res. 2021, 62, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raux, M.; Le Manach, Y.; Gauss, T.; Baumgarten, R.; Hamada, S.; Harrois, A.; Riou, B.; Duranteau, J.; Langeron, O.; Mantz, J.; et al. Comparison of the Prognostic Significance of Initial Blood Lactate and Base Deficit in Trauma Patients. Anesthesiology 2017, 126, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, M.L.; Hollosi, S.; Chumbe, J.T.; Samanta, D.; Modak, A.; Bethea, A. The Effect of Ethanol on Lactate and Base Deficit as Predictors of Morbidity and Mortality in Trauma. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, H.K.; Dechert, T.A.; Wolfe, L.; Aboutanos, M.B.; Malhotra, A.K.; Ivatury, R.R.; Duane, T.M. Lactate in Trauma: A Poor Predictor of Mortality in the Setting of Alcohol Ingestion. Am. Surg. 2011, 77, 1576–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.W.; Kaups, K.L. Base Deficit in the Elderly: A Marker of Severe Injury and Death. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 1998, 45, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.K.; Ryan, K.L.; Rickards, C.A.; Hinojosa-Laborde, C.; Pamplin, J.C.; Patel, S.S.; Herold, T.S.; Convertino, V.A. Progressive Reduction in Central Blood Volume Is Not Detected by Sublingual Capnography. Shock 2012, 37, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavijo-Alvarez, J.A.; Sims, C.A.; Pinsky, M.R.; Puyana, J.C. Monitoring Skeletal Muscle and Subcutaneous Tissue Acid-Base Status and Oxygenation during Hemorrhagic Shock and Resuscitation. Shock 2005, 24, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuster, M.; Exadaktylos, A.; Schnüriger, B. Non-Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring in Trauma Patients. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2015, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, U.G.; Schiller, H.J.; Carney, D.E.; Kilpatrick, J.; Gatto, L.A.; Paskanik, A.M.; Nieman, G.F. Invasive Arterial BP Monitoring in Trauma and Critical Care: Effect of Variable Transducer Level, Catheter Access, and Patient Position. Chest 2001, 120, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, S.; Taconet, C.; Harrois, A.; Hamada, S.; Gauss, T.; Raux, M.; Duranteau, J.; Attias, A.; Ausset, S.; Boutonnet, M.; et al. How Useful Are Hemoglobin Concentration and Its Variations to Predict Significant Hemorrhage in the Early Phase of Trauma? A Multicentric Cohort Study. Ann. Intensive Care 2018, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acker, S.N.; Petrun, B.; Partrick, D.A.; Roosevelt, G.E.; Bensard, D.D. Lack of Utility of Repeat Monitoring of Hemoglobin and Hematocrit Following Blunt Solid Organ Injury in Children. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015, 79, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehtabchi, S.; Sinert, R.; Goldman, M.; Kapitanyan, R.; Ballas, J. Diagnostic Performance of Serial Haematocrit Measurements in Identifying Major Injury in Adult Trauma Patients. Injury 2006, 37, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, V.; Shahi, V.; Mower, W.R. Using Serial Hemoglobin Levels to Detect Occult Blood Loss in the Early Evaluation of Blunt Trauma Patients. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 55, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opreanu, R.C.; Arrangoiz, R.; Stevens, P.; Morrison, C.; Mosher, B.D.; Kepros, J.P. Hematocrit, Systolic Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Are Not Accurate Predictors for Surgery to Control Hemorrhage in Injured Patients. Am. Surg. 2010, 76, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Chang, P.Y.; Lien, W.C. Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma. J. Med. Ultrasound 2023, 29, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richards, J.R.; McGahan, J.P. Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma (FAST) in 2017: What Radiologists Can Learn. Radiology 2017, 283, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bársony, A.; Vida, N.; Gajda, Á.; Rutai, A.; Mohácsi, Á.; Szabó, A.; Boros, M.; Varga, G.; Érces, D. Methane Exhalation Can Monitor the Microcirculatory Changes of the Intestinal Mucosa in a Large Animal Model of Hemorrhage and Fluid Resuscitation. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 567260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubin, A.; Pozo, M.O.; Ferrara, G.; Murias, G.; Martins, E.; Canullán, C.; Canales, H.S.; Kanoore Edul, V.S.; Estenssoro, E.; Ince, C. Systemic and Microcirculatory Responses to Progressive Hemorrhage. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadian, M.; Pinsky, M.R. Evidence-Based Review of the Use of the Pulmonary Artery Catheter: Impact Data and Complications. Crit. Care 2006, 10 (Suppl. 3), S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorson, C.M.; Van Haren, R.M.; Ryan, M.L.; Pereira, R.; Olloqui, J.; Guarch, G.A.; Barrera, J.M.; Busko, A.M.; Livingstone, A.S.; Proctor, K.G. Admission Hematocrit and Transfusion Requirements after Trauma. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2013, 216, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijboer, J.M.M.; Van Der Horst, I.C.C.; Hendriks, H.G.D.; Ten Duis, H.J.; Nijsten, M.W.N. Myth or Reality: Hematocrit and Hemoglobin Differ in Trauma. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2007, 62, 1310–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Shinozaki, F.; Hasegawa, R.; Shirai, Y.; Motoyoshi, Y.; Sugiyama, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Ishige, N. Low Hemoglobin Levels Are Associated with Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, B.; Lindsey, M.; Rowe, K.; Brown, S.; Minei, J.P.; Gentilello, L.M.; Shafi, S. Hemoglobin Drops within Minutes of Injuries and Predicts Need for an Intervention to Stop Hemorrhage. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2007, 63, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubran, A. Pulse Oximetry. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, S.M.; Tenhunen, J.J.; Laitinen, S.; Heino, A.; Alhava, E.; Takala, J. Effects of Systemic Arterial Hypoperfusion on Splanchnic Hemodynamics and Hepatic Arterial Buffer Response in Pigs. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 280, G819–G827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, S.M. Clinical Review: Splanchnic Ischaemia. Crit. Care 2002, 6, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Y.; Chan, K.C.; Cheng, Y.J.; Yeh, Y.C.; Chien, C.T. Effects of Different Types of Fluid Resuscitation for Hemorrhagic Shock on Splanchnic Organ Microcirculation and Renal Reactive Oxygen Species Formation. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eipel, C.; Abshagen, K.; Vollmar, B. Regulation of Hepatic Blood Flow: The Hepatic Arterial Buffer Response Revisited. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2010, 16, 6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, K.; Malitan, H.; Lehmann, C. Imaging of the Intestinal Microcirculation during Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Biology 2020, 9, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Kelly, C.J.; Colgan, S.P. Physiologic Hypoxia and Oxygen Homeostasis in the Healthy Intestine. A Review in the Theme: Cellular Responses to Hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2015, 309, C350–C360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, I.B.; Davarpanah, A.H.; Rybicki, F.J.; Desjardins, B.; Flamm, S.D.; Francois, C.J.; Gerhard-Herman, M.D.; Kalva, S.P.; Ashraf Mansour, M.; Mohler, E.R.; et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Imaging of Mesenteric Ischemia. Abdom. Imaging 2013, 38, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangemi, J.R.; Picco, M.F. Intestinal Ischemia in the Elderly. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 38, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szucs, S.; Bari, G.; Ugocsai, M.; Lashkarivand, R.A.; Lajkó, N.; Mohácsi, Á.; Szabó, A.; Kaszaki, J.; Boros, M.; Érces, D.; et al. Detection of Intestinal Tissue Perfusion by Real-Time Breath Methane Analysis in Rat and Pig Models of Mesenteric Circulatory Distress. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, e403–e411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trompeter, M.; Brazda, T.; Remy, C.T.; Vestring, T.; Reimer, P. Non-Occlusive Mesenteric Ischemia: Etiology, Diagnosis, and Interventional Therapy. Eur. Radiol. 2002, 12, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perko, M.J. Duplex Ultrasound for Assessment of Superior Mesenteric Artery Blood Flow. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2001, 21, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarabin, J.; Bere, Z.; Hartmann, P.; Tóth, F.; Kiss, J.G.; Rovó, L. Laser-Doppler Microvascular Measurements in the Peri-Implant Areas of Different Osseointegrated Bone Conductor Implant Systems. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 272, 3655–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limjeerajarus, C. Laser Doppler Flowmetry: Basic Principle, Current Clinical and Research Applications in Dentistry. CU Dent. J. 2014, 37, 123–136. [Google Scholar]
- Corbett, E.J.; Barry, B.N.; Pollard, S.G.; Lodge, J.P.A.; Bellamy, M.C. Laser Doppler Flowmetry Is Useful in the Clinical Management of Small Bowel Transplantation. The Liver Transplant Group. Gut 2000, 47, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urboniene, A.; Palepsaitis, A.; Uktveris, R.; Barauskas, V. Doppler Flowmetry of the Superior Mesenteric Artery and Portal Vein: Impact for the Early Prediction of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Neonates. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2015, 31, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, T.; Kuzuhara, K.; Nishimori, S.; Kurooka, Y.; Yamada, A.; Harihara, Y.; Ogura, Y.; Otsubo, O.; Inou, T. Evaluation of Laser Doppler Flowmetry in Renal Transplantation. J. Clin. Laser Med. Surg. 1994, 12, 231–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifalian, A.M.; Mallet, S.V.; Rolles, K.; Davidson, B.R. Hepatic Microcirculation during Human Orthotopic Liver Transplantation. Br. J. Surg. 2005, 84, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanavičius, L.; Pattyn, P.; Van de Putte, D.; Venskutonis, D. How to Assess Intestinal Viability during Surgery: A Review of Techniques. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2011, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karliczek, A.; Benaron, D.A.; Baas, P.C.; Zeebregts, C.J.; Wiggers, T.; van Dam, G.M. Intraoperative Assessment of Microperfusion with Visible Light Spectroscopy for Prediction of Anastomotic Leakage in Colorectal Anastomoses. Color. Dis. 2010, 12, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greksa, F.; Butt, E.; Csonka, E.; Jávor, P.; Tuboly, E.; Török, L.; Szabo, A.; Varga, E.; Hartmann, P. Periosteal and Endosteal Microcirculatory Injury Following Excessive Osteosynthesis. Injury 2021, 52 (Suppl. 1), S3–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzeciak, S.; Cinel, I.; Dellinger, R.P.; Shapiro, N.I.; Arnold, R.C.; Parrillo, J.E.; Hollenberg, S.M. Resuscitating the Microcirculation in Sepsis: The Central Role of Nitric Oxide, Emerging Concepts for Novel Therapies, and Challenges for Clinical Trials. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2008, 15, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, A.; Edul, V.S.K.; Eguillor, J.F.C.; Ferrara, G. Monitoring Microcirculation: Utility and Barriers—A Point-of-View Review. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2020, 16, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezemer, R.; Bartels, S.A.; Bakker, J.; Ince, C. Clinical Review: Clinical Imaging of the Sublingual Microcirculation in the Critically Ill--Where Do We Stand? Crit. Care 2012, 16, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilty, M.P.; Guerci, P.; Ince, Y.; Toraman, F.; Ince, C. MicroTools Enables Automated Quantification of Capillary Density and Red Blood Cell Velocity in Handheld Vital Microscopy. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uz, Z.; Ince, C.; Guerci, P.; Ince, Y.; Araujo, R.P.; Ergin, B.; Hilty, M.P.; van Gulik, T.M.; de Mol, B.A. Recruitment of Sublingual Microcirculation Using Handheld Incident Dark Field Imaging as a Routine Measurement Tool during the Postoperative De-Escalation Phase—A Pilot Study in Post ICU Cardiac Surgery Patients. Perioper. Med. 2018, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdant, C.L.; De Backer, D.; Bruhn, A.; Clausi, C.M.; Su, F.; Wang, Z.; Rodriguez, H.; Pries, A.R.; Vincent, J.L. Evaluation of Sublingual and Gut Mucosal Microcirculation in Sepsis: A Quantitative Analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 2875–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, C. Hemodynamic Coherence and the Rationale for Monitoring the Microcirculation. Crit. Care 2015, 19, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Backer, D.; Durand, A. Monitoring the Microcirculation in Critically Ill Patients. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2014, 28, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, D.N.; Mellis, C.; Smith, I.M.; Mamuza, J.; Skene, I.; Harris, T.; Midwinter, M.J.; Hutchings, S.D. Safety and Feasibility of Sublingual Microcirculation Assessment in the Emergency Department for Civilian and Military Patients with Traumatic Haemorrhagic Shock: A Prospective Cohort Study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e014162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezemer, R.; Goedhart, P.; Khalilzada, M.; Ince, C. Sidestream Dark-Field Imaging versus Orthogonal Polarization Spectroscopic Imaging: A Comparative Study. Crit. Care 2008, 12, P63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykut, G.; Veenstra, G.; Scorcella, C.; Ince, C.; Boerma, C. Cytocam-IDF (Incident Dark Field Illumination) Imaging for Bedside Monitoring of the Microcirculation. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2015, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, M.J.; Shapiro, N.I. A Guide to Human in Vivo Microcirculatory Flow Image Analysis. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero, O.; Ónody, P.; Kovács, T.; Molnár, D.; Lotz, G.; Tóth, S.; Turóczi, Z.; Fülöp, A.; Garbaisz, D.; Harsányi, L.; et al. Impaired Intestinal Mucosal Barrier upon Ischemia-Reperfusion: “Patching Holes in the Shield with a Simple Surgical Method”. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 210901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camara-Lemarroy, C.R.; Escobedo-Zúñiga, N.; Guzmán-de la Garza, F.J.; Castro-Garza, J.; Vargas-Villarreal, J.; Góngora-Rivera, F. D-Lactate and Intestinal Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Are Elevated in Serum in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2021, 121, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, M.; He, X.; Jiang, C.; Liu, R. Functional Changes of Intestinal Mucosal Barrier in Surgically Critical Patients. World J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 1, 205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levitt, M.D.; Levitt, D.G. Quantitative Evaluation of D-Lactate Pathophysiology: New Insights into the Mechanisms Involved and the Many Areas in Need of Further Investigation. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, S.; Nilsson, T. Current Status on Plasma Biomarkers for Acute Mesenteric Ischemia. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2012, 33, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, I.E.; Ceyhan, G.O.; Friess, H. Beyond Lactate: Is There a Role for Serum Lactate Measurement in Diagnosing Acute Mesenteric Ischemia? Dig. Surg. 2012, 29, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voth, M.; Lustenberger, T.; Relja, B.; Marzi, I. Is I-FABP Not Only a Marker for the Detection Abdominal Injury but Also of Hemorrhagic Shock in Severely Injured Trauma Patients? World J. Emerg. Surg. 2019, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Heijkant, T.C.; Aerts, B.A.C.; Teijink, J.A.; Buurman, W.A.; Luyer, M.D.P. Challenges in Diagnosing Mesenteric Ischemia. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 1338–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMonagle, M.P.; Halpenny, M.; McCarthy, A.; Mortell, A.; Manning, F.; Kilty, C.; Mannion, D.; Wood, A.E.; Corbally, M.T. Alpha Glutathione S-Transferase: A Potential Marker of Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury of the Intestine after Cardiac Surgery? J. Pediatr. Surg. 2006, 41, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S.; Corbally, M.T.; Manning, F.; Armenise, T.; Kierce, B.; Kilty, C. Glutathione S-Transferase: A Potential New Marker of Intestinal Ischemia. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2002, 37, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treskes, N.; Persoon, A.M.; van Zanten, A.R.H. Diagnostic Accuracy of Novel Serological Biomarkers to Detect Acute Mesenteric Ischemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2017, 12, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnana, M.; Danese, E.; Lippi, G. Biochemical Markers of Acute Intestinal Ischemia: Possibilities and Limitations. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, A.; Turedi, S.; Mentese, A.; Altunayoglu, V.; Turan, I.; Karahan, S.C.; Topbas, M.; Aydin, M.; Eraydin, I.; Akcan, B. Ischemia-Modified Albumin Levels in Cerebrovascular Accidents. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2008, 26, 874–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türedi, S.; Şahin, A.; Akça, M.; Demir, S.; Köse, G.D.R.; Çekiç, A.B.; Yıldırım, M.; Yuluğ, E.; Menteşe, A.; Türkmen, S.; et al. Ischemia-Modified Albumin and the IMA/Albumin Ratio in the Diagnosis and Staging of Hemorrhagic Shock: A Randomized Controlled Experimental Study. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2020, 26, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uygun, M.; Yilmaz, S.; Pekdemir, M.; Duman, C.; Gürbüz, Y.S. The Diagnostic Value of Ischemia-Modified Albumin in a Rat Model of Acute Mesenteric Ischemia. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2011, 18, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerman, A.; Wouters, P. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) Monitoring in Contemporary Anesthesia and Critical Care. Acta Anaesthesiol. Belg. 2010, 61, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gruszecka, A.; Gruszecki, M.; Neary, J.P.; Singh, J.; Teckchandani, T.; Waskow, M.; Wszedybyl-Winklewska, M.; Guminski, W.; Frydrychowski, A.F.; Rumiński, J.; et al. Comparison of near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) and near-Infrared Transillumination-Backscattering Sounding (NIR-T/BSS) Methods. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikala, R.V. Modified Beer’s Law-Historical Perspectives and Relevance in near-Infrared Monitoring of Optical Properties of Human Tissue. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2010, 40, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkin, S.L.; Spencer, S.A.; Dimmock, P.W.; Wickramasinghe, Y.A.B.D.; Rolfe, P. A Comparison of Pulse Oximetry and near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) in the Detection of Hypoxaemia Occurring with Pauses in Nasal Airflow in Neonates. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 1999, 15, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.E.; Simonson, S.G. Use of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy to Monitor Tissue Oxygenation. New Horiz. 1996, 4, 420–425. [Google Scholar]
- Sakudo, A. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Medical Applications: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 455, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, K.; Yamada, K.; Tsenkova, R.; Wang, Y.; Ozaki, Y. Near-Infrared Spectra of Serum Albumin and γ-Globulin and Determination of Their Concentrations in Phosphate Buffer Solutions by Partial Least Squares Regression. Vib. Spectrosc. 1998, 18, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.W.; Pollard, A. Near-Infrared Spectroscopic Determination of Serum Total Proteins, Albumin, Globulins, and Urea. Clin. Biochem. 1993, 26, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.W.; Pollard, A. Near-Infrared Spectrophotometry: A New Dimension in Clinical Chemistry. Clin. Chem. 1992, 38, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirosawa, N.; Sakamoto, Y.; Katayama, H.; Tonooka, S.; Yano, K. In Vivo Investigation of Progressive Alterations in Rat Mammary Gland Tumors by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 305, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peuchant, E.; Salles, C.; Jensen, R. Determination of Serum Cholesterol by Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1987, 59, 1816–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarti, S.; Srivastava, S.; Mittnacht, A.J.C. Near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) in Children. Semin. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2008, 12, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohler, E.R.; Lech, G.; Supple, G.E.; Wang, H.; Chance, B. Impaired Exercise-Induced Blood Volume in Type 2 Diabetes with or without Peripheral Arterial Disease Measured by Continuous-Wave near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1856–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bank, W.; Chance, B. An Oxidative Defect in Metabolic Myopathies: Diagnosis by Noninvasive Tissue Oximetry. Ann. Neurol. 1994, 36, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, B.; Porcelli, S.; Marzorati, M.; Lanfranconi, F.; Vago, P.; Marconi, C.; Morandi, L. Metabolic Myopathies: Functional Evaluation by Analysis of Oxygen Uptake Kinetics. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 2120–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch Gwen Lech, D.R.; Farmer, J.M.; Balcer, L.J.; Bank, W.; Chance, B.; Wilson, R.B. Near Infrared Muscle Spectroscopy in Patients with Friedreich’s Ataxia. Muscle Nerve 2002, 25, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, B.; Marzorati, M.; Lanfranconi, F.; Ferri, A.; Longaretti, M.; Stucchi, A.; Vago, P.; Marconi, C.; Morandi, L. Impaired Oxygen Extraction in Metabolic Myopathies: Detection and Quantification by near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Muscle Nerve 2007, 35, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Sánchez, F.; Galvez-Sola, L.; Martínez-Nicolás, J.J.; Muelas-Domingo, R.; Nieves, M.; García-Sánchez, F.; Galvez-Sola, L.; Martínez-Nicolás, J.J.; Muelas-Domingo, R.; Nieves, M. Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Agricultural Systems. In Developments in Near-Infrared Spectroscopy; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, J.E.; Cohn, S.M.; Giannotti, G.D.; Dolich, M.O.; Ramon, H.; Wiseberg, J.A.; McKenney, M. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Reflects Changes in Mesenteric and Systemic Perfusion during Abdominal Compartment Syndrome. Surgery 2001, 129, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, S.M.; Varela, J.E.; Giannotti, G.; Dolich, M.O.; Brown, M.; Feinstein, A.; McKenney, M.G.; Spalding, P. Splanchnic Perfusion Evaluation during Hemorrhage and Resuscitation with Gastric Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2001, 50, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, J.E.; Cohn, S.M.; Diaz, I.; Giannotti, G.D.; Proctor, K.G. Splanchnic Perfusion during Delayed, Hypotensive, or Aggressive Fluid Resuscitation from Uncontrolled Hemorrhage. Shock 2003, 20, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, A.N.; Lazar, D.A.; Stoll, B.; Naik-Mathuria, B.; Mushin, O.P.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Burrin, D.G.; Olutoye, O.O. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Measurement of Abdominal Tissue Oxygenation Is a Useful Indicator of Intestinal Blood Flow and Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Premature Piglets. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledo, A.; Aguar, M.; Núñez-Ramiro, A.; Saénz, P.; Vento, M. Abdominal Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Detects Low Mesenteric Perfusion Early in Preterm Infants with Hemodynamic Significant Ductus Arteriosus. Neonatology 2017, 112, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheeren, T.W.L.; Schober, P.; Schwarte, L.A. Monitoring Tissue Oxygenation by near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS): Background and Current Applications. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2012, 26, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crookes, B.A.; Cohn, S.M.; Bloch, S.; Amortegui, J.; Manning, R.; Li, P.; Proctor, M.S.; Hallal, A.; Blackbourne, L.H.; Benjamin, R.; et al. Can Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Identify the Severity of Shock in Trauma Patients? J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2005, 58, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatous, S.B.; Mammen, P.P.A. Regulation of Myoglobin Expression. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 2741–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, G.; Wittenberg, B.A.; Jue, T. Myoglobin’s Old and New Clothes: From Molecular Structure to Function in Living Cells. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyldenlove, T.; Jorgensen, L.P.; Schroeder, T.V. Micro-Lightguide Spectrophotometry (O2C) for Lower Limb Perfusion: Effects of Exercise Walking in Claudicants. Int. J. Angiol. 2019, 28, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, B.; Kreuzer, M.; Bischoff, B.; Wolf, D.; Schmitt, H.; Eyupoglu, I.Y.; Rössler, K.; Buchfelder, M.; Ganslandt, O.; Wiendieck, K. Combined Laser-Doppler Flowmetry and Spectrophotometry: Feasibility Study of a Novel Device for Monitoring Local Cortical Microcirculation during Aneurysm Surgery. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2017, 78, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckert, S.; Witte, M.B.; Königsrainer, A.; Coerper, S. The Impact of the Micro-Lightguide O2C for the Quantification of Tissue Ischemia in Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2863–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirle, E.; Wogatzki, A.; Kunzmann, R.; Schoenfelder, A.M.; Litzke, L.F. Correlation between Capillary Oxygen Saturation and Small Intestinal Wall Thickness in the Equine Colic Patient. Vet. Rec. Open 2017, 4, e000197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Weil, M.H.; Sun, S.; Noc, M.; Gazmuri, R.J.; Bisera, J. Gastric Intramural PCO2 as Monitor of Perfusion Failure during Hemorrhagic and Anaphylactic Shock. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994, 76, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palágyi, P.; Kaszaki, J.; Rostás, A.; Érces, D.; Németh, M.; Boros, M.; Molnár, Z. Monitoring Microcirculatory Blood Flow with a New Sublingual Tonometer in a Porcine Model of Hemorrhagic Shock. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 847152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlesso, E.; Taccone, P.; Gattinoni, L. Gastric Tonometry. Minerva Anestesiol. 2006, 72, 529–532. [Google Scholar]
- Bar, S.; Fischer, M.O. Regional Capnometry to Evaluate the Adequacy of Tissue Perfusion. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, S1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett-Guerrero, E.; Panah, M.H.; Bodian, C.A.; Methikalam, B.J.; Alfarone, J.R.; DePerio, M.; Mythen, M.G. Automated Detection of Gastric Luminal Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide during Cardiovascular Surgery Using the Tonocap. Anesthesiology 2000, 92, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xuan, W.; Yin, P.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Wu, Q. Gastric Tonometry Guided Therapy in Critical Care Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton-Davies, C.; Mythen, M.G.; Salmon, J.B.; Jacobson, D.; Shukla, A.; Webb, A.R. Comparison of Commonly Used Clinical Indicators of Hypovolaemia with Gastrointestinal Tonometry. Intensive Care Med. 1997, 23, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mythen, M.G. Does Gastric Tonometry-Guided Therapy Reduce Total Mortality in Critically Ill Patients? Crit. Care 2015, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creteur, J.; De Backer, D.; Vincent, J.L. Monitoring Gastric Mucosal Carbon Dioxide Pressure Using Gas Tonometry: In Vitro and In Vivo Validation Studies. Anesthesiology 1997, 87, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öz, B.; Akyüz, M.; Emek, E.; Sözüer, E.; Akyildiz, H.; Akcan, A.; Ok, E. The Effectiveness of Gastric Tonometry in the Diagnosis of Acute Mesenteric Ischemia in Cases Where a Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography Cannot Be Obtained. Turk. J. Surg./Ulus. Cerrahi Derg. 2015, 31, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.A.; Baker, S. Orogastric Tube Placement during Trauma Arrest. J. Am. Coll. Emerg. Physicians Open 2020, 1, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipov, E.G.; Sosis, M.B. Safe Nasogastric Tube Placement in a Patient with a Basal Skull Fracture. Anesthesiology 1993, 78, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Weil, M.H.; Tang, W.; Sun, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Jin, X.; Bisera, J. Sublingual Capnometry for Diagnosis and Quantitation of Circulatory Shock. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 1838–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creteur, J.; De Backer, D.; Sakr, Y.; Koch, M.; Vincent, J.L. Sublingual Capnometry Tracks Microcirculatory Changes in Septic Patients. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rózsavölgyi, Z.; Boda, D.; Hajnal, A.; Boda, K.; Somfay, A. A Newly Developed Sublingual Tonometric Method for the Evaluation of Tissue Perfusion and Its Validation In Vitro and in Healthy Persons In Vivo and the Results of the Measurements in COPD Patients. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 534130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povoas, H.P.; Weil, M.H.; Tang, W.; Moran, B.; Kamohara, T.; Bisera, J. Comparisons between Sublingual and Gastric Tonometry during Hemorrhagic Shock. Chest 2000, 118, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, M.H.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tang, W.; Sato, Y.; Ercoli, F.; Finegan, R.; Grayman, G.; Bisera, J. Sublingual Capnometry: A New Noninvasive Measurement for Diagnosis and Quantitation of Severity of Circulatory Shock. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 27, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, S.A.; Scalea, T.M. Sublingual Capnometry: An Alternative to Gastric Tonometry for the Management of Shock Resuscitation. AACN Clin. Issues 2003, 14, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Weil, M.H.; Sun, S.; Tang, W.; Bisera, J.; Mason, E.J. Decreases in Organ Blood Flows Associated with Increases in Sublingual PCO2 during Hemorrhagic Shock. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 1998, 85, 2360–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattas, D.; Ayer, R.; Suntharalingam, G.; Chapman, M. Carbon Dioxide Monitoring and Evidence-Based Practice-Now You See It, Now You Don’t. Crit. Care 2004, 8, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marik, P.E. Sublingual Capnography: A Clinical Validation Study. Chest 2001, 120, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marik, P.E.; Bankov, A. Sublingual Capnometry versus Traditional Markers of Tissue Oxygenation in Critically Ill Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackow, E.C.; O’Neil, P.; Astiz, M.E.; Carpati, C.M. Sublingual Capnometry and Indexes of Tissue Perfusion in Patients with Circulatory Failure. Chest 2001, 120, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, A.T.; Creteur, J.; Vincent, J.L. Tissue Capnometry: Does the Answer Lie under the Tongue? Intensive Care Med. 2004, 30, 2157–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvet, X.; SáDelgado, J.; Montserrat, A.; Lario, S.; Ramírez-Lázaro, M.J.; Quesada, M.; Casalots, A.; Suárez, D.; Campo, R.; Brullet, E.; et al. Accuracy of Diagnostic Tests for Helicobacter Pylori: A Reappraisal. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, D.; Conklin, J.; Pimentel, M. Lactose Intolerance and the Role of the Lactose Breath Test. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1726–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.V.; Malik, A. Hydrogen Breath Tests in Gastrointestinal Diseases. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 29, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauling, L.; Robinson, A.B.; Teranishi, R.; Cary, P. Quantitative Analysis of Urine Vapor and Breath by Gas-Liquid Partition Chromatography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 2374–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.C.; Delano, F.; Wilson, J.M.; Kokubun, B.A.; Bennion, R.S.; Thompson, J.E.; Schmid-Schonbein, G.; Saltzman, D.J. Analysis of Exhaled Volatile Compounds Following Acute Superior Mesenteric Artery Occlusion in a Pilot Rat Study. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 25, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jávor, P.; Rárosi, F.; Horváth, T.; Török, L.; Varga, E.; Hartmann, P. Detection of Exhaled Methane Levels for Monitoring Trauma-Related Haemorrhage Following Blunt Trauma: Study Protocol for a Prospective Observational Study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e057872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J. Methane Medicine: A Rising Star Gas with Powerful Anti-Inflammation, Antioxidant, and Antiapoptosis Properties. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1912746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poles, M.Z.; Juhász, L.; Boros, M. Methane and Inflammation-A Review (Fight Fire with Fire). Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2019, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mészáros, A.T.; Szilágyi, Á.L.; Juhász, L.; Tuboly, E.; Érces, D.; Varga, G.; Hartmann, P. Mitochondria as Sources and Targets of Methane. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boros, M.; Ghyczy, M.; Irces, D.; Varga, G.; Tokés, T.; Kupai, K.; Torday, C.; Kaszaki, J. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Methane. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, A.; Unterkofler, K.; Mochalski, P.; Jandacka, M.; Ruzsanyi, V.; Szabó, G.; Mohácsi, Á.; Teschl, S.; Teschl, G.; King, J. Modeling of Breath Methane Concentration Profiles during Exercise on an Ergometer. J. Breath Res. 2016, 10, 017105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, A.; Ruzsanyi, V.; Unterkofler, K.; Mohácsi; Tuboly, E.; Boros, M.; Szabó, G.; Hinterhuber, H.; Amann, A. Exhaled Methane Concentration Profiles during Exercise on an Ergometer. J. Breath Res. 2015, 9, 016009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuboly, E.; Molnár, R.; Tokés, T.; Turányi, R.N.; Hartmann, P.; Mészáros, A.T.; Strifler, G.; Földesi, I.; Siska, A.; Szabó, A.; et al. Excessive Alcohol Consumption Induces Methane Production in Humans and Rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelovas, P.P.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.G.; Xanthos, T.T. A Comparative Anatomic and Physiologic Overview of the Porcine Heart. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2014, 53, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- von Trotha, K.T.; Butz, N.; Grommes, J.; Binnebösel, M.; Charalambakis, N.; Mühlenbruch, G.; Schumpelick, V.; Klinge, U.; Neumann, U.P.; Prescher, A.; et al. Vascular Anatomy of the Small Intestine-a Comparative Anatomic Study on Humans and Pigs. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2015, 30, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jávor, P.; Donka, T.; Horváth, T.; Sándor, L.; Török, L.; Szabó, A.; Hartmann, P. Impairment of Mesenteric Perfusion as a Marker of Major Bleeding in Trauma Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3571. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103571
Jávor P, Donka T, Horváth T, Sándor L, Török L, Szabó A, Hartmann P. Impairment of Mesenteric Perfusion as a Marker of Major Bleeding in Trauma Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(10):3571. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103571
Chicago/Turabian StyleJávor, Péter, Tibor Donka, Tamara Horváth, Lilla Sándor, László Török, Andrea Szabó, and Petra Hartmann. 2023. "Impairment of Mesenteric Perfusion as a Marker of Major Bleeding in Trauma Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 10: 3571. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103571
APA StyleJávor, P., Donka, T., Horváth, T., Sándor, L., Török, L., Szabó, A., & Hartmann, P. (2023). Impairment of Mesenteric Perfusion as a Marker of Major Bleeding in Trauma Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(10), 3571. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103571