Whether Renal Pathology Is an Independent Predictor for End-Stage Renal Disease in Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients with Nephrotic Range Proteinuria: A Biopsy-Based Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Clinical, Laboratory, and Pathologic Characteristics
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Clinical and Pathologic Characteristics
3.2. Associations between the Histopathological and Clinical Findings
3.3. Clinical and Pathological Risk Factors for ESRD
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Name |
| ESRD | end-stage renal disease |
| DKD | diabetic kidney diseases |
| IFTA | interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| UACR | urine albumin/create ratio |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| DR | diabetic retinopathy |
| Hb | hemoglobin |
| HbA1c | Glycosylated Hemoglobin, Type A1C |
| RAAS | renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system |
| ACEI | angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors |
| ARBs | angiotensin II receptor blockers |
| EPO | erythropoietin |
| ESAs | erythropoiesis stimulating agents |
| HIF-PHI | hypoxia inducible factor proline hydroxylase inhibitor |
| SGLT2 | Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| SBP | systolic pressure |
| DBP | diastolic blood pressure |
| Cys-C | Cystatin C |
| BUN | blood urea nitrogen |
| HDL-C | High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| LDL-C | Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| NDRD | non diabetic renal disease |
References
- International Diabetes Federation. Available online: http://www.diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Umanath, K.; Lewis, J.B. Update on Diabetic Nephropathy: Core Curriculum 2018. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Bakris, G.L.; Bilous, R.W.; Chiang, J.L.; de Boer, I.H.; Goldstein-Fuchs, J.; Hirsch, I.B.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Narva, A.S.; Navaneethan, S.D.; et al. Diabetic kidney disease: A report from an ADA Consensus Conference. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 64, 510–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Xu, F.; Le, W.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, M.; Chen, H.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. Renal histologic changes and the outcome in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2015, 30, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, S14–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Diabetes Work Group. KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, S1–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, A.; Bavanandan, S.; Prasad, N.; Wong, M.; Chang, J.; Eiam-Ong, S.; Hao, C.; Lim, C.; Lim, S.; Oh, K.; et al. Asian Pacific Society of Nephrology Clinical Practice Guideline on Diabetic Kidney Disease. Nephrology 2020, 25, 12–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossing, K.; Christensen, P.; Hovind, P.; Parving, H. Remission of nephrotic-range albuminuria reduces risk of end-stage renal disease and improves survival in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 2241–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2017 Abridged for Primary Care Providers. Clin. Diabetes 2017, 35, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tervaert, T.W.; Mooyaart, A.L.; Amann, K.; Cohen, A.H.; Cook, H.T.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Ferrario, F.; Fogo, A.B.; Haas, M.; de Heer, E.; et al. Pathologic classification of diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, M.; Shimizu, M.; Yamanouchi, M.; Toyama, T.; Hara, A.; Furuichi, K.; Wada, T. Trajectories of kidney function in diabetes: A clinicopathological update. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Yang, Q.; Chen, L.; Tang, S.; Liu, W.; Yu, X. Renal pathological change in patients with type 2 diabetes is not always diabetic nephropathy: A report of 52 cases. Clin. Nephrol. 2007, 67, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Guo, R.; Yin, Q.; Yang, L.; Yue, R.; Su, B.; Huang, S.; et al. Renal pathological implications in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with renal involvement. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, T.; Nagao, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Nagaoka, Y.; Wada, T.; Nakao, T. Histological predictors for renal prognosis in diabetic nephropathy in diabetes mellitus type 2 patients with overt proteinuria. Nephrology 2012, 17, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.W.; Kim, S.; Na, K.Y.; Chae, D.W.; Kim, S.; Jin, D.C.; Chin, H.J. Clinical implications of pathologic diagnosis and classification for diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 97, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottl, A.K.; Gasim, A.; Schober, F.P.; Hu, Y.; Dunnon, A.K.; Hogan, S.L.; Jennette, J.C. Segmental Sclerosis and Extracapillary Hypercellularity Predict Diabetic ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.I.; Park, J.T.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, S.J.; Oh, H.J.; Yoo, D.E.; Han, S.H.; Yoo, T.H.; Kang, S.W. Renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes with or without coexisting non-diabetic renal disease. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 92, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, M.; Bolignano, D.; Tesar, V.; Pisano, A.; Biesen, W.V.; Tripepi, G.; D’Arrigo, G.; Gesualdo, L. Renal biopsy in patients with diabetes: A pooled meta-analysis of 48 studies. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2017, 32, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.G.; Bomback, A.S.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Herlitz, L.C.; Stokes, M.B.; Markowitz, G.S.; D’Agati, V.D. The modern spectrum of renal biopsy findings in patients with diabetes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Choi, P.C.; Szeto, C.C.; To, K.F.; Tang, N.L.; Chan, A.W.; Li, P.K.; Lai, F.M. Renal outcome in type 2 diabetic patients with or without coexisting nondiabetic nephropathies. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leehey, D.J.; Kramer, H.J.; Daoud, T.M.; Chatha, M.P.; Isreb, M.A. Progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes—Beyond blood pressure control: An observational study. BMC Nephrol. 2005, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Tomonaga, O.; Hirayama, M.; Ishii, A.; Takeda, M.; Babazono, T.; Ujihara, U.; Takahashi, C.; Omori, Y. Predictors of the progression of diabetic nephropathy and the beneficial effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in NIDDM patients. Diabetologia 1997, 40, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.H.; Kim, D.K.; Park, J.T.; Kang, E.W.; Yoo, T.H.; Kim, B.S.; Choi, K.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Han, D.S.; Shin, S.K. Influence of ketoanalogs supplementation on the progression in chronic kidney disease patients who had training on low-protein diet. Nephrology 2009, 14, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.C.; Brownlee, M.; Susztak, K.; Sharma, K.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.A.; Zoungas, S.; Rossing, P.; Groop, P.H.; Cooper, M.E. Diabetic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanram, A.; Zhang, Z.; Shahinfar, S.; Keane, W.F.; Brenner, B.M.; Toto, R.D. Anemia and end-stage renal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentata, Y.; Haddiya, I.; Latrech, H.; Serraj, K.; Abouqal, R. Progression of diabetic nephropathy, risk of end-stage renal disease and mortality in patients with type-1 diabetes. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2013, 24, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, S.; Makkar, B.M.; Abichandani, V.K.; Talwalkar, P.G.; Saboo, B.; Srikanta, S.S.; Das, A.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Krishnan, P.V.; Shah, A.; et al. Management of anemia in patients with diabetic kidney disease. A consensus statement. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 20, 268–281. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, B.; Fried, L.; Orchard, T. Hemoglobin and overt nephropathy complications in type 1 diabetes. Ann. Epidemiol. 2008, 18, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Babazono, T.; Hanai, K.; Suzuki, K.; Kiuchi, Y.; Inoue, A.; Tanaka, M.; Tanaka, N.; Hase, M.; Ishii, A.; Iwamoto, Y. Lower haemoglobin level and subsequent decline in kidney function in type 2 diabetic adults without clinical albuminuria. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossing, K.; Christensen, P.K.; Hovind, P.; Tarnow, L.; Rossing, P.; Parving, H.H. Progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.F.; Tarng, D.C. Anemia in patients of diabetic kidney disease. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2019, 82, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.C. Anemia in diabetes: Marker or mediator of microvascular disease? Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2007, 3, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minutolo, R.; Locatelli, F.; Gallieni, M.; Bonofiglio, R.; Fuiano, G.; Oldrizzi, L.; Conte, G.; De Nicola, L.; Mangione, F.; Esposito, P.; et al. Anaemia management in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients: A multicentre prospective study in renal clinics. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2013, 28, 3035–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Chen, N. Roxadustat for Anemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, e3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Hao, C.; Liu, B.C.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Xing, C.; Liang, X.; Jiang, G.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Roxadustat Treatment for Anemia in Patients Undergoing Long-Term Dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, T.; Mimura, I.; Tanaka, T.; Nangaku, M. Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: Current and Future. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiendacz, H.; Nabrdalik, K.; Stompór, T.; Gumprecht, J. What do we know about biomarkers in diabetic kidney disease? Endokrynol. Pol. 2020, 71, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansevoort, R.T.; Matsushita, K.; van der Velde, M.; Astor, B.C.; Woodward, M.; Levey, A.S.; de Jong, P.E.; Coresh, J.; Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium. Lower estimated GFR and higher albuminuria are associated with adverse kidney outcomes. A collaborative meta-analysis of general and high-risk population cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.; Matsushita, K.; Woodward, M.; Bilo, H.; Chalmers, J.; Heerspink, H.; Lee, B.; Perkins, R.; Rossing, P.; Sairenchi, T.; et al. Associations of kidney disease measures with mortality and end-stage renal disease in individuals with and without diabetes: A meta-analysis. Lancet 2012, 380, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Huang, R.; Kavanagh, J.; Li, L.; Zeng, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, P. Efficacy and Safety of Dual Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2019, 19, 259–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.M.; Cooper, M.E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Keane, W.F.; Mitch, W.E.; Parving, H.H.; Remuzzi, G.; Snapinn, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Shahinfar, S.; et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.; Mavridis, D.; Navarese, E.; Craig, J.C.; Tonelli, M.; Salanti, G.; Wiebe, N.; Ruospo, M.; Wheeler, D.C.; Strippoli, G.F. Comparative efficacy and safety of blood pressure-lowering agents in adults with diabetes and kidney disease: A network meta-analysis. Lancet 2015, 385, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, E.; Hunsicker, L.; Clarke, W.; Berl, T.; Pohl, M.; Lewis, J.; Ritz, E.; Atkins, R.; Rohde, R.; Raz, I. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Total (n = 199) | Non-ESRD Group (n = 86) | ESRD Group (n = 113) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (male) | 58 (29.1) | 27 (31.4) | 31 (27.4) | 0.651 |
| Age (years) | 51.49 ± 9.12 | 52.22 ± 9.81 | 50.93 ± 8.57 | 0.372 |
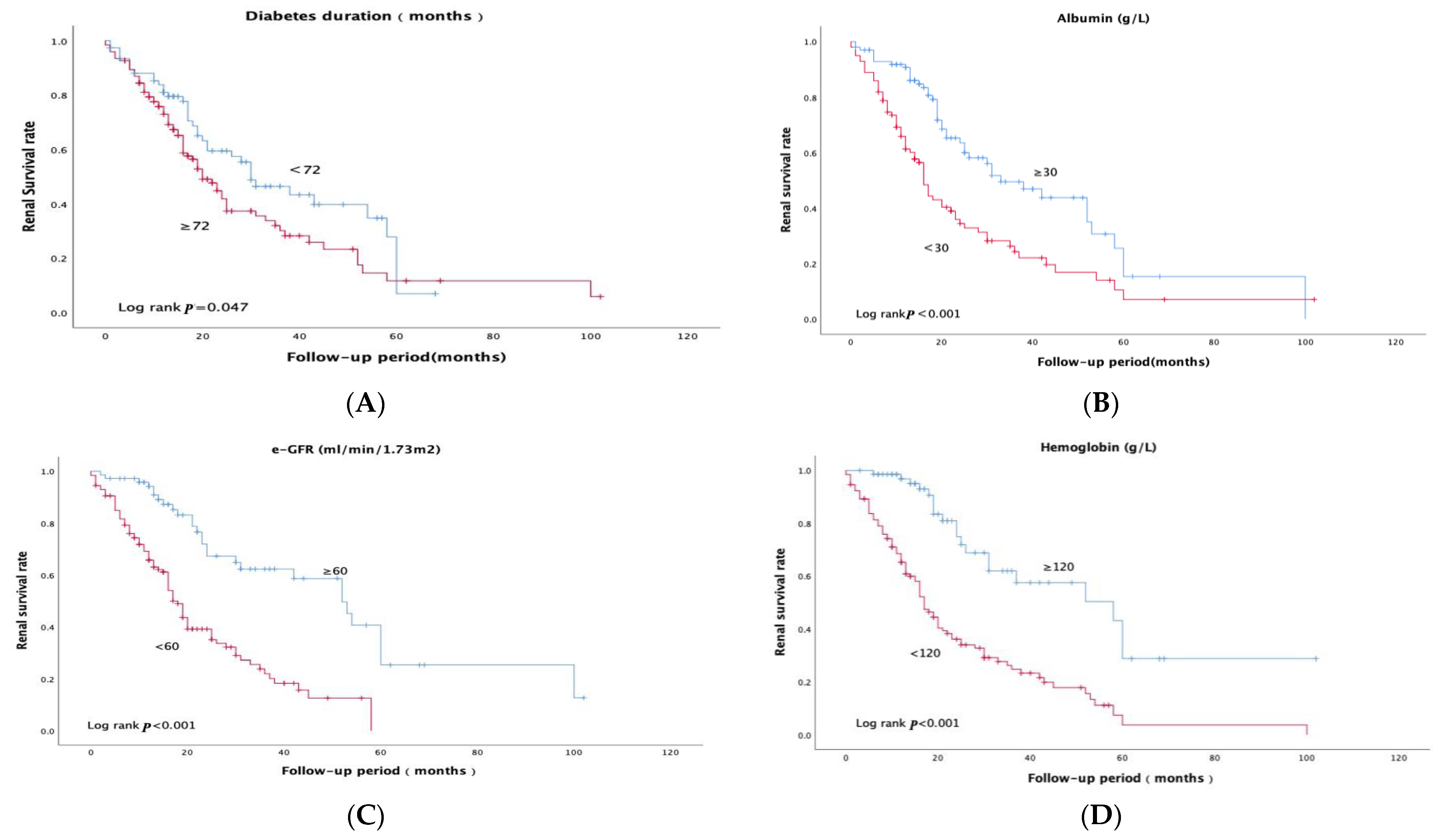
| Duration of diabetes (m) | 96 (36–132) | 84 (36–120) | 120 (36–144) | 0.066 |
| Cigarette smoking (%) | 100 (50.3) | 41 (47.7) | 59 (52.2) | 0.623 |
| Hypertension (%) | 180 (90.5) | 80 (93) | 100 (88.5) | 0.405 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 149.94 ± 23.52 | 150.17 ± 24.41 | 149.77 ± 22.92 | 0.906 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 87.96 ± 13.57 | 89.64 ± 14.09 | 86.68 ± 13.08 | 0.132 |
| e-GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 51.31 (36.15–81.54) | 61.15 (45.28–93.30) | 43.4 (27.57–59.74) | <0.001 * |
| Serum creatinine (umol/L) | 139 (97–187) | 108.5 (74.5–145.7) | 156 (115–245.8) | <0.001 * |
| Stage 1,2,3a,3b,4,5 CKD (KDIGO) | 33/42/47/38/32/7 | 19/13/21/17/15/1 | 14/29/26/21/17/6 | 0.157 |
| Cys-C (mg/L) | 1.72 (1.38–2.23) | 1.41 (1.13–1.81) | 1.93 (1.58–2.65) | <0.001 * |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 8.2 (6.30–12.30) | 7 (5.80–10.74) | 9.31 (7.05–13.99) | <0.001 * |
| Uric acid (umol/L) | 378 (327–428) | 379 (320.5–418.5) | 377.2 (329.5–435) | 0.898 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.24 (4.45–6.46) | 5.17 (4.42–6.20) | 5.24 (4.48–6.49) | 0.448 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.29 (1.04–1.59) | 1.16 (1.05–1.5) | 1.31 (1.04–1.67) | 0.320 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 3.13 (2.47–4.11) | 3.07 (2.45–3.85) | 3.14 (2.51–4.16) | 0.686 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.86 (1.35–2.45) | 1.92 (1.4–2.42) | 1.83 (1.27–2.53) | 0.526 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 30.04 ± 6.34 | 31.64 ± 6.21 | 28.83 ± 6.20 | <0.001 * |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 7.64 (5.5–10.16) | 7.93 (6.43–10.21) | 7.59 (5.13–10.18) | 0.329 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.35 (6.3–8.6) | 7.6 (6.7–8.8) | 7.1 (6.0–8.4) | 0.014 * |
| Proteinuria (g/24 h) | 6.78 (4.8–9.75) | 6.34 (4.46–9.32) | 7.14 (5.01–10.17) | 0.145 |
| Hematuria (%) | 145 (72.7) | 62 (72.1) | 83 (73.5) | 0.958 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 111 (98–129) | 124 (109–143.5) | 106 (90–116) | <0.001 * |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 2.08 ± 0.16 | 2.11 ± 0.14 | 2.06 ± 0.18 | 0.043 * |
| Phosphorus (mmol/L) | 1.26 ± 0.27 | 1.22 ± 0.25 | 1.29 ± 0.29 | 0.062 |
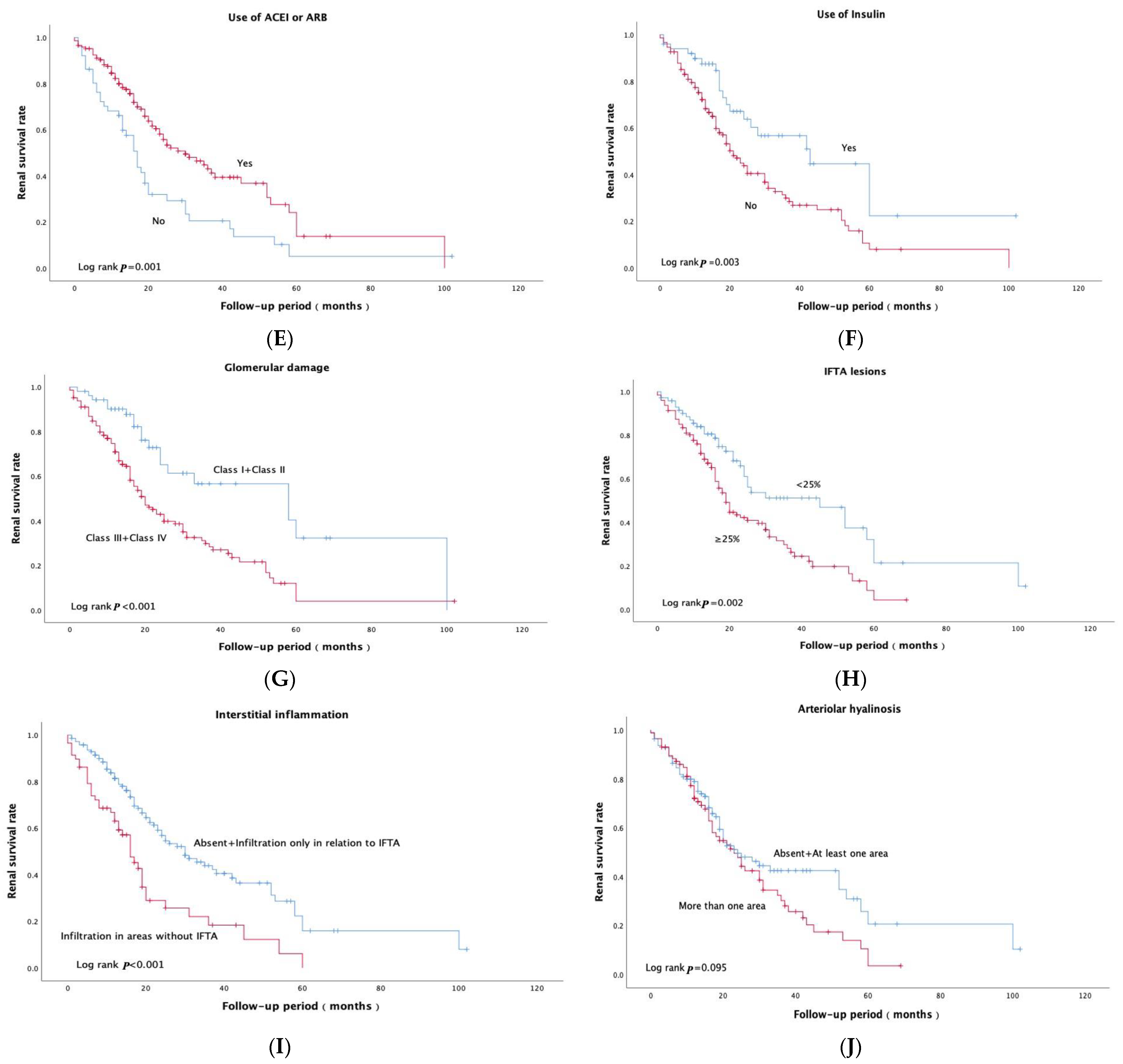
| Use of ACEI/ARB (%) | 180 (90.5) | 80 (93.0) | 100 (88.5) | 0.405 |
| Use of Statin (%) | 122 (61.3) | 53 (61.6) | 69 (61.1) | 0.935 |
| Use of Insulin (%) | 149 (74.9) | 56 (65.1) | 95 (82.3) | 0.008 * |
| Pathological Lesions | Total (n = 199) | Non-ESRD Group (n = 86) | ESRD Group (n = 113) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glomerular class | <0.001 * | |||
| I | 2 (1.00) | 2 (2.32) | 0 (0) | |
| IIa | 28 (14.07) | 21 (24.42) | 7 (6.19) | |
| IIb | 23 (11.56) | 11 (12.79) | 12 (10.62) | |
| III | 108 (54.27) | 38 (44.19) | 70 (61.95) | |
| IV | 38 (19.10) | 14 (16.28) | 24 (21.24) | |
| IFTA | 0.047 * | |||
| 0 | 1 (0.50) | 1 (1.16) | 0 (0) | |
| 1 | 71 (35.68) | 38 (44.19) | 33 (29.20) | |
| 2 | 96 (48.24) | 34 (39.53) | 62 (54.87) | |
| 3 | 31 (15.58) | 13 (15.12) | 18 (15.93) | |
| Interstitial inflammation | 0.003 * | |||
| 0 | 8 (4.02) | 7 (8.14) | 1 (0.89) | |
| 1 | 133 (66.83) | 62 (72.09) | 71 (62.83) | |
| 2 | 58 (29.15) | 17 (19.77) | 41 (36.28) | |
| Arteriolar hyalinosis | 0.153 | |||
| 0 | 13 (6.53) | 7 (8.14) | 6 (5.31) | |
| 1 | 99 (49.75) | 48 (55.81) | 51 (45.13) | |
| 2 | 87 (43.72) | 31 (36.05) | 56 (49.56) |
| Pathological Immunofluorescence | Total (n = 199) | Non-ESRD Group (n = 86) | ESRD Group (n = 113) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG (%) | 30 (15.08) | 6 (6.98) | 24 (21.24) | 0.010 * |
| IgM (%) | 44 (22.11) | 12 (13.95) | 32 (28.32) | 0.025 * |
| IgA (%) | 15 (7.54) | 5 (5.81) | 10 (8.85) | 0.594 |
| C3 (%) | 33 (16.58) | 6 (6.98) | 27 (23.89) | 0.003 * |
| C4 (%) | 20 (10.05) | 4 (4.65) | 16 (14.16) | 0.049 * |
| C1q (%) | 26 (13.07) | 5 (5.81) | 21 (18.58) | 0.015 * |
| Glomerular Class | IFTA | Interstitial Inflammation | Arteriolar Hyalinosis | Albumin (g/L) | e-GFR | Hemoglobin (g/L) | Proteinuria (g/24 h) | ESRD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glomerular class | 1 | ||||||||
| IFTA | 0.450 ** | 1 | |||||||
| Interstitial inflammation | 0.241 ** | 0.508 ** | 1 | ||||||
| Arteriolar hyalinosis | 0.207 ** | 0.211 ** | 0.069 | 1 | |||||
| Albumin (g/L) | −0.072 | −0.062 | −0.079 | −0.048 | 1 | ||||
| e-GFR | −0.367 ** | −0.502 ** | −0.484 ** | −0.144 * | 0.085 | 1 | |||
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | −0.333 ** | −0.180 * | −0.180 * | −0.093 | 0.363 ** | 0.413 ** | 1 | ||
| Proteinuria (g/24 h) | 0.122 | 0.128 | 0.099 | 0.073 | −0.389 ** | −0.168 * | −0.174 * | 1 | |
| ESRD | 0.228 ** | 0.136 | 0.219 ** | 0.137 | −0.253 ** | −0.359 ** | −0.437 ** | 0.103 | 1 |
| Factors | HR | 95% Cl | p |
|---|---|---|---|
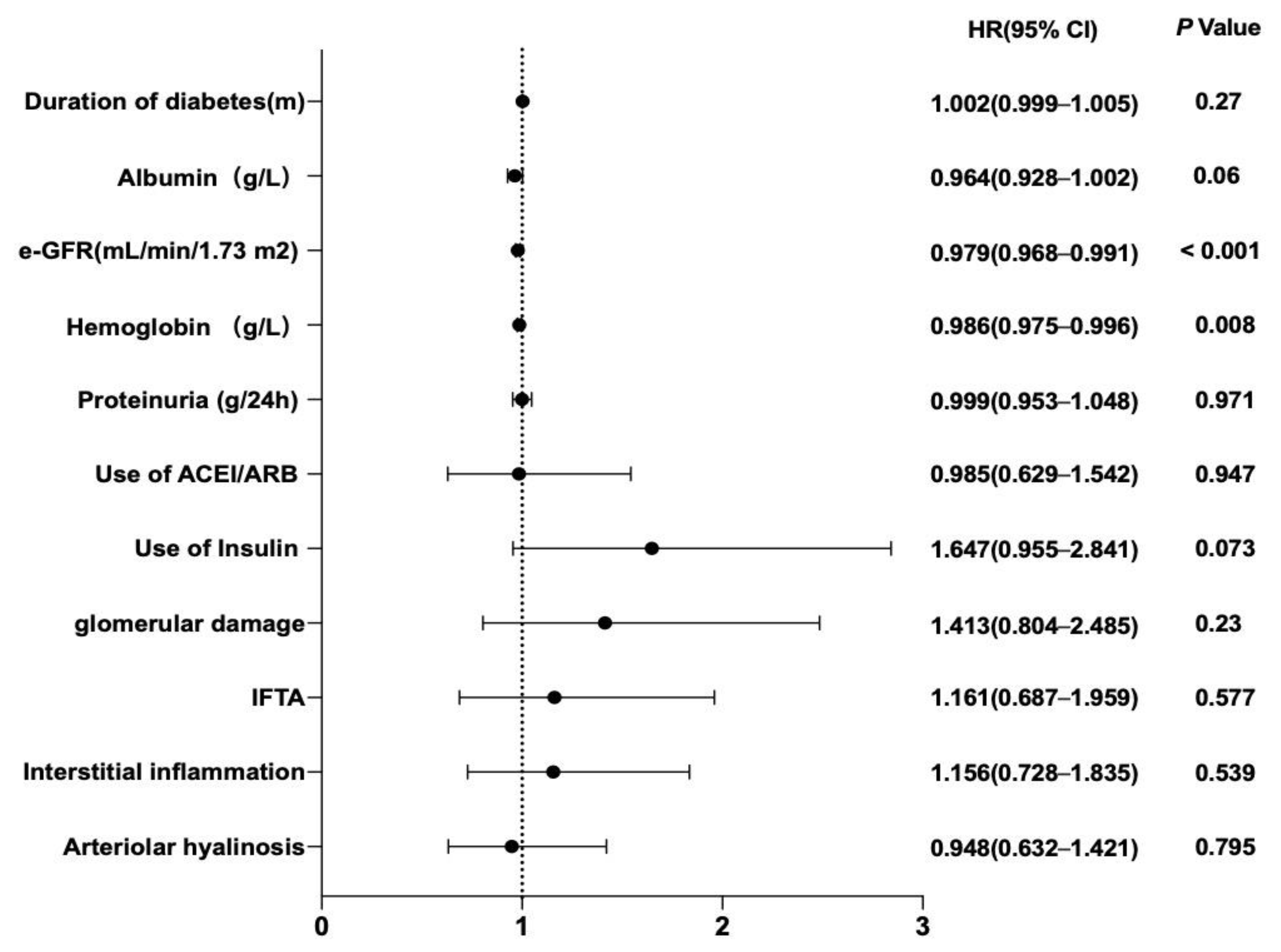
| univariate | |||
| Gender | 0.946 | 0.625–1.432 | 0.794 |
| Age (years) | 0.991 | 0.971–1.012 | 0.401 |
| Duration of diabetes (m) | 1.003 | 1.000–1.005 | 0.042 * |
| Albumin (g/L) | 0.942 | 0.914–0.970 | <0.001 * |
| e-GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 0.971 | 0.962–0.979 | <0.001 * |
| HbA1c (%) | 0.909 | 0.819–1.010 | 0.075 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 0.973 | 0.965–0.981 | <0.001 * |
| Proteinuria (g/24 h) | 1.052 | 1.015–1.091 | 0.006 * |
| Use of ACEI/ARB | 0.525 | 0.356–0.774 | 0.001 * |
| Use of Statin | 1.018 | 0.696–1.488 | 0.927 |
| Use of Insulin | 2.028 | 1.248–3.296 | 0.004 * |
| Glomerular damage | 2.480 | 1.503–4.091 | <0.001 * |
| IFTA | 1.913 | 1.260–2.903 | 0.002 * |
| Interstitial inflammation | 2.170 | 1.470–3.203 | <0.001 * |
| Arteriolar hyalinosis | 1.363 | 0.940–1.975 | 0.102 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Y.; Ren, H.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xu, H.; Chai, Z.; et al. Whether Renal Pathology Is an Independent Predictor for End-Stage Renal Disease in Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients with Nephrotic Range Proteinuria: A Biopsy-Based Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010088
Wang T, Zhang J, Wang Y, Zhao L, Wu Y, Ren H, Zou Y, Zhang R, Xu H, Chai Z, et al. Whether Renal Pathology Is an Independent Predictor for End-Stage Renal Disease in Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients with Nephrotic Range Proteinuria: A Biopsy-Based Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(1):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010088
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tingli, Junlin Zhang, Yiting Wang, Lijun Zhao, Yucheng Wu, Honghong Ren, Yutong Zou, Rui Zhang, Huan Xu, Zhonglin Chai, and et al. 2023. "Whether Renal Pathology Is an Independent Predictor for End-Stage Renal Disease in Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients with Nephrotic Range Proteinuria: A Biopsy-Based Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 1: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010088
APA StyleWang, T., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Zhao, L., Wu, Y., Ren, H., Zou, Y., Zhang, R., Xu, H., Chai, Z., Cooper, M. E., Zhang, J., & Liu, F. (2023). Whether Renal Pathology Is an Independent Predictor for End-Stage Renal Disease in Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients with Nephrotic Range Proteinuria: A Biopsy-Based Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010088





