The Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors on Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
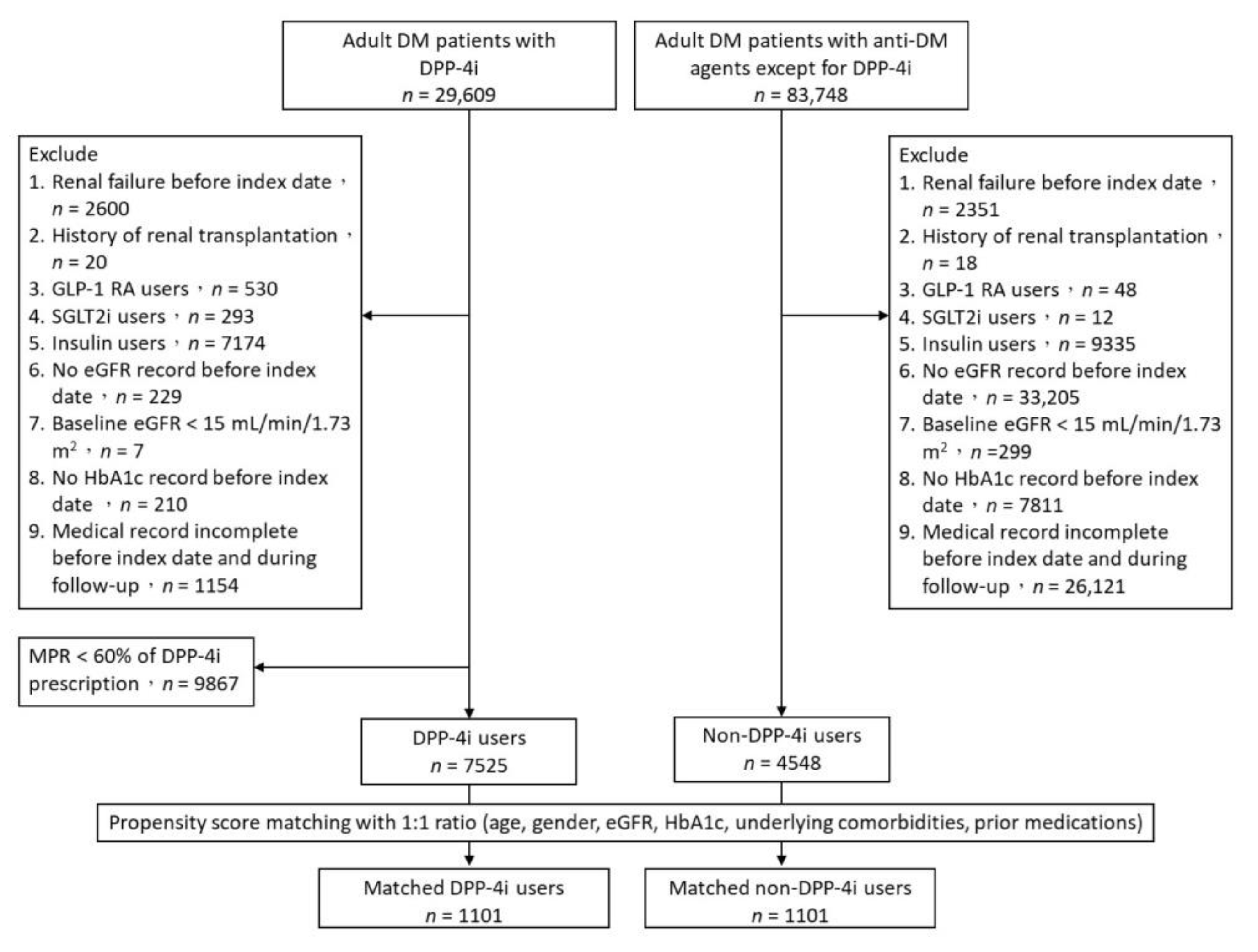
2.1. Study Design and Study Population
2.2. Outcomes
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study Patients and Baseline Characteristics
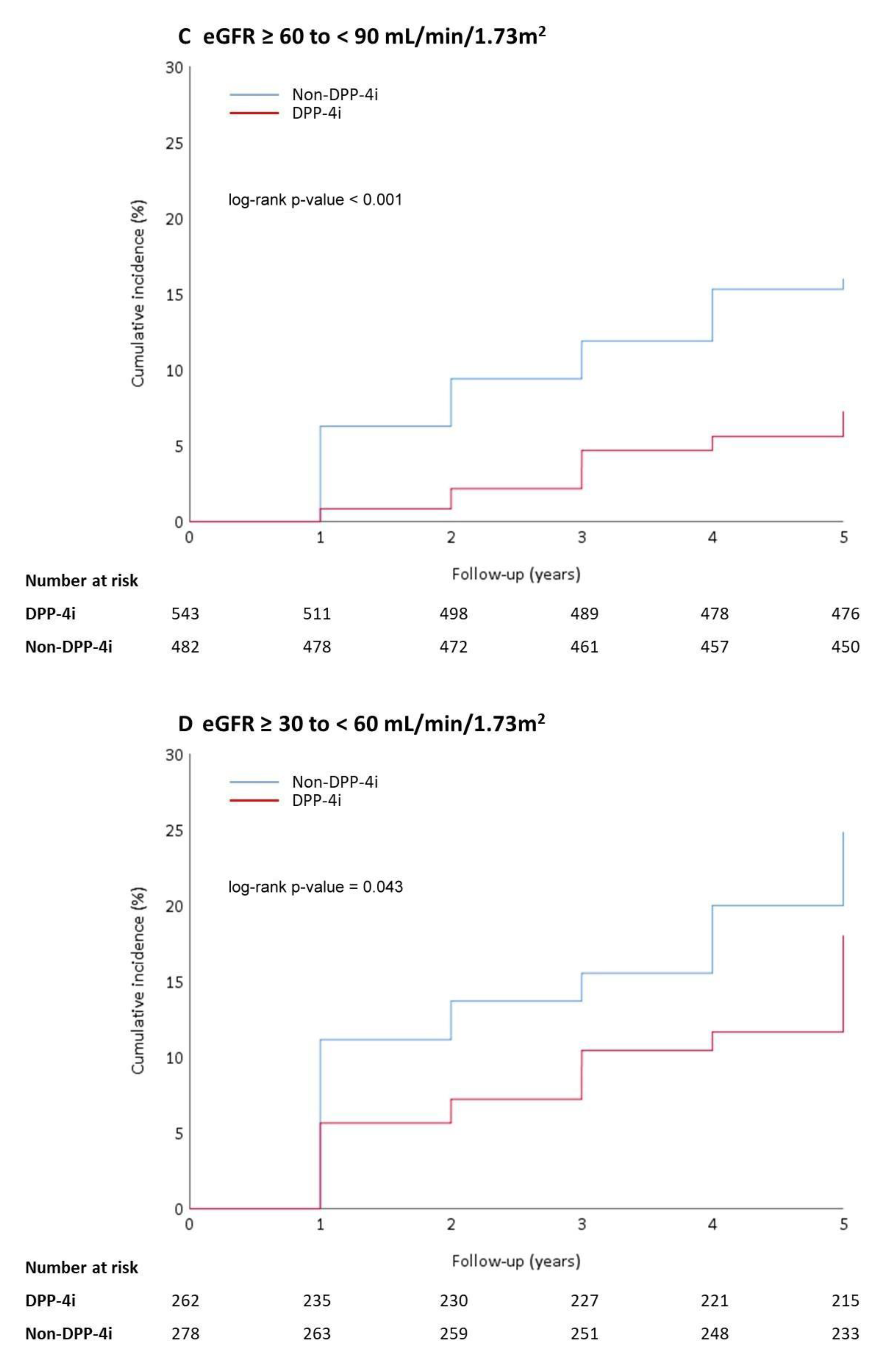
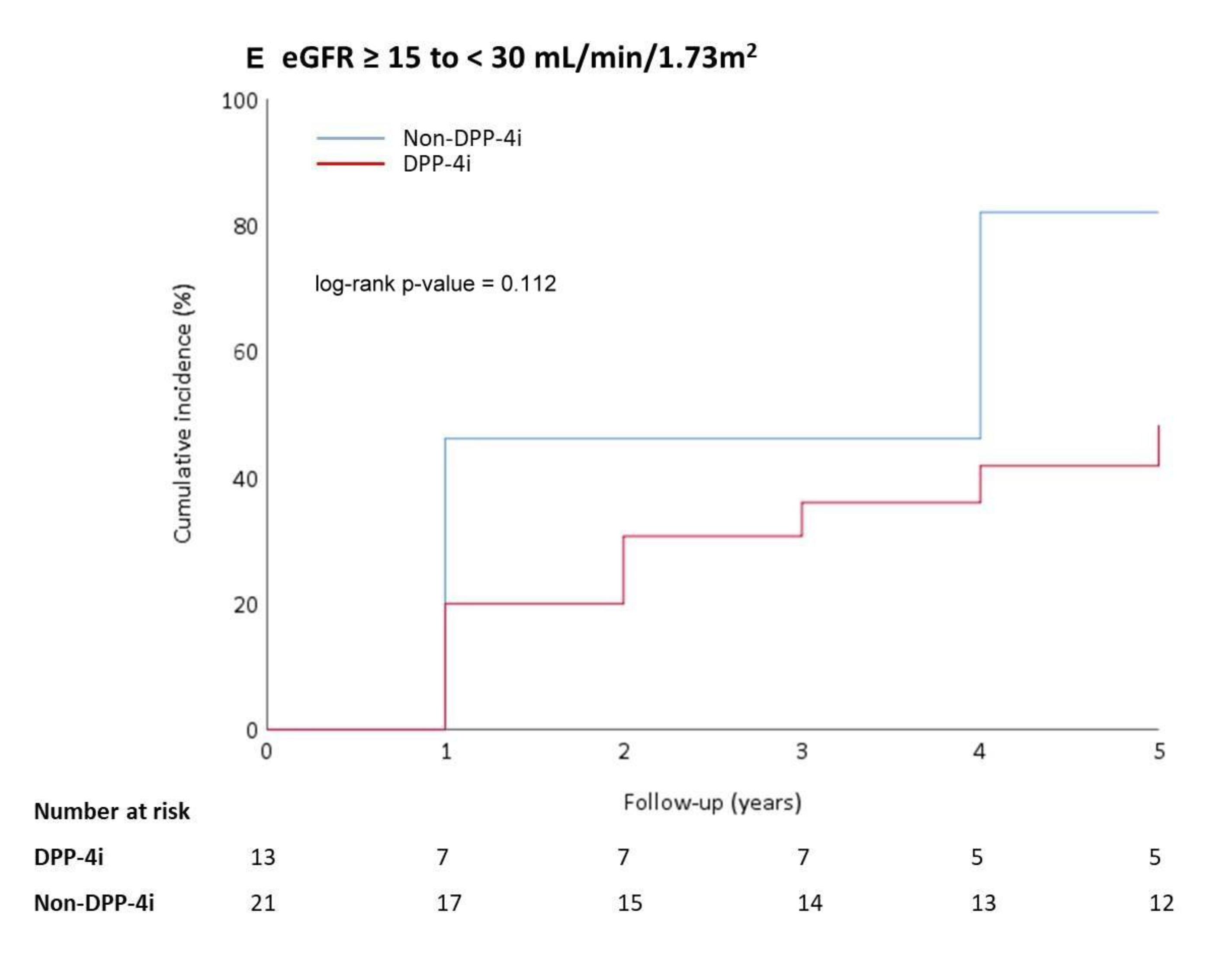
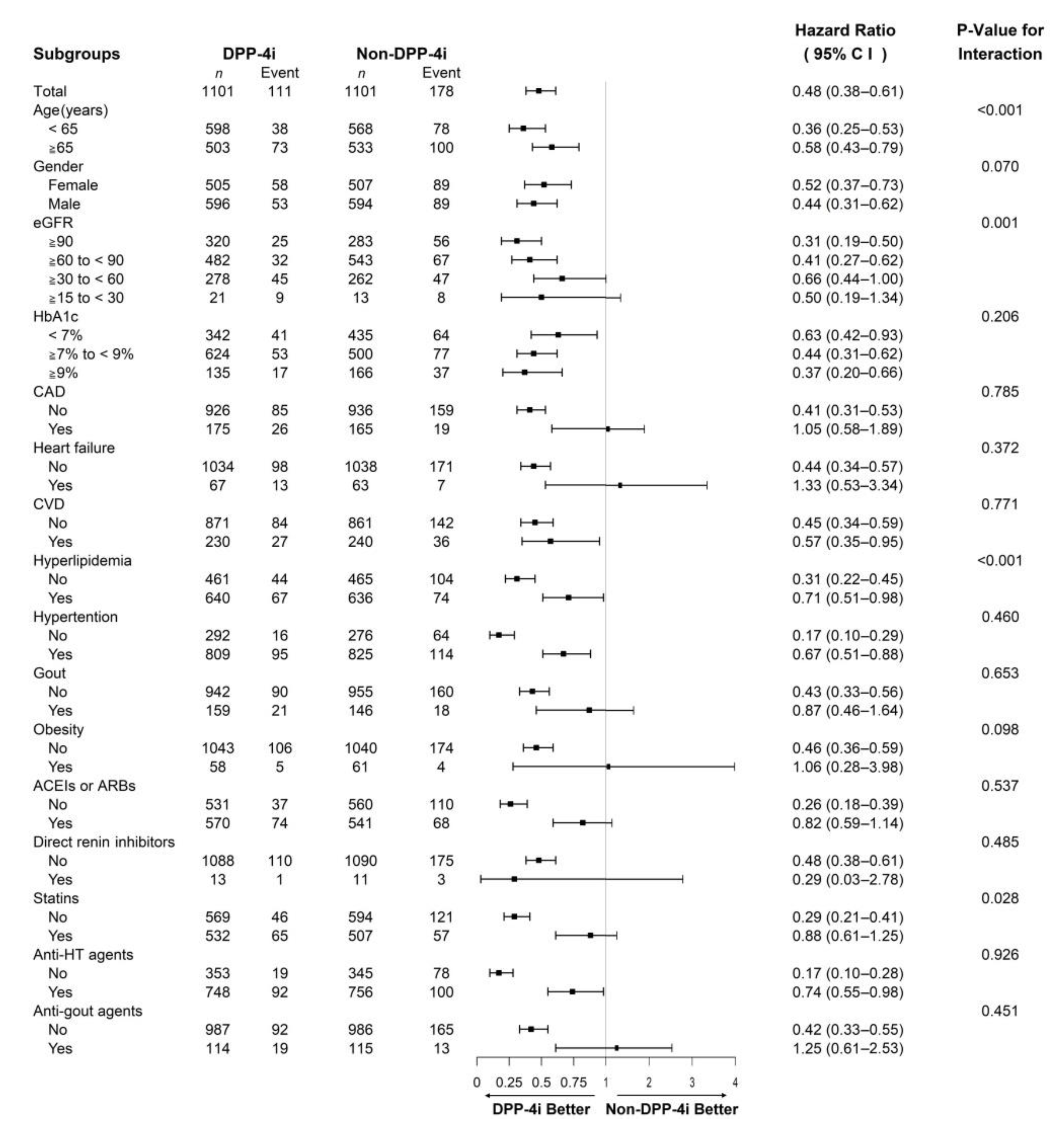
3.2. Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Bakris, G.L.; Bilous, R.W.; Chiang, J.L.; de Boer, I.H.; Goldstein-Fuchs, J.; Hirsch, I.B.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Narva, A.S.; Navaneethan, S.D.; et al. Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Report From an ADA Consensus Conference. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2864–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- American Diabetes Association. Microvascular Complications and Foot Care: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S151–S167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.S.; Matsushita, K.; Woodward, M.; Bilo, H.J.G.; Chalmers, J.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Lee, B.J.; Perkins, R.M.; Rossing, P.; Sairenchi, T.; et al. Associations of kidney disease measures with mortality and end-stage renal disease in individuals with and without diabetes: A meta-analysis. Lancet 2012, 380, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.F.E.; Ørsted, D.D.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Marso, S.P.; Poulter, N.R.; Rasmussen, S.; Tornøe, K.; Zinman, B.; Buse, J.B. Liraglutide and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eknoyan, G.; Lameire, N.; Eckardt, K.; Kasiske, B.; Wheeler, D.; Levin, A.; Stevens, P.; Bilous, R.; Lamb, E.; Coresh, J. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 3, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kosiborod, M.; Gomes, M.B.; Nicolucci, A.; Pocock, S.; Rathmann, W.; Shestakova, M.V.; Watada, H.; Shimomura, I.; Chen, H.; Cid-Ruzafa, J.; et al. Vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes: Prevalence and associated factors in 38 countries (the DISCOVER study program). Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Diabetes Association. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S125–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, I.M.; Adler, A.I.; Neil, H.A.W.; Matthews, D.R.; Manley, S.E.; Cull, C.A.; Hadden, D.; Turner, R.C.; Holman, R.R. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): Prospective observational study. BMJ 2000, 321, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, A.; MacMahon, S.; Chalmers, J.; Neal, B.; Billot, L.; Woodward, M.; Marre, M.; Cooper, M.; Glasziou, P.; Grobbee, D.; et al. Intensive Blood Glucose Control and Vascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2560–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holman, R.R.; Paul, S.K.; Bethel, M.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Neil, H.A.W. 10-Year Follow-up of Intensive Glucose Control in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baggio, L.L.; Drucker, D.J. Biology of Incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2131–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, E.V.; Russo, G.; Giandalia, A.; Viazzi, F.; Pontremoli, R.; De Cosmo, S. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Kidney Protection. Medicina 2019, 55, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drucker, D.J.; Nauck, M.A. The incretin system: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2006, 368, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzwiller, J.-P.; Tschopp, S.; Bock, A.; Zehnder, C.E.; Huber, A.R.; Kreyenbuehl, M.; Gutmann, H.; Drewe, J.r.; Henzen, C.; Goeke, B.; et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Induces Natriuresis in Healthy Subjects and in Insulin-Resistant Obese Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 3055–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H.; Morii, T.; Fujishima, H.; Sato, T.; Shimizu, T.; Hosoba, M.; Tsukiyama, K.; Narita, T.; Takahashi, T.; Drucker, D.J.; et al. The protective roles of GLP-1R signaling in diabetic nephropathy: Possible mechanism and therapeutic potential. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanozawa, K.; Noguchi, Y.; Sugahara, S.; Nakamura, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Kaneko, K.; Kono, R.; Sato, S.; Ogawa, T.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. The renoprotective effect and safety of a DPP-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, at a small dose in type 2 diabetic patients with a renal dysfunction when changed from other DPP-4 inhibitors: REAL trial. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2018, 22, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Platt, M.J.; Shibasaki, T.; Quaggin, S.E.; Backx, P.H.; Seino, S.; Simpson, J.A.; Drucker, D.J. GLP-1 receptor activation and Epac2 link atrial natriuretic peptide secretion to control of blood pressure. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muskiet, M.H.A.; Smits, M.M.; Morsink, L.M.; Diamant, M. The gut–renal axis: Do incretin-based agents confer renoprotection in diabetes? Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Mega, C.; Gonçalves, A.; Rodrigues-Santos, P.; Teixeira-Lemos, E.; Teixeira, F.; Fontes-Ribeiro, C.; Reis, F.; Fernandes, R. Sitagliptin Prevents Inflammation and Apoptotic Cell Death in the Kidney of Type 2 Diabetic Animals. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 538737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanasaki, K.; Shi, S.; Kanasaki, M.; He, J.; Nagai, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Ishigaki, Y.; Kitada, M.; Srivastava, S.P.; Koya, D. Linagliptin-Mediated DPP-4 Inhibition Ameliorates Kidney Fibrosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice by Inhibiting Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in a Therapeutic Regimen. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2120–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cornel, J.H.; Bakris, G.L.; Stevens, S.R.; Alvarsson, M.; Bax, W.A.; Chuang, L.-M.; Engel, S.S.; Lopes, R.D.; McGuire, D.K.; Riefflin, A.; et al. Effect of Sitagliptin on Kidney Function and Respective Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: Outcomes From TECOS. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2304–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mosenzon, O.; Leibowitz, G.; Bhatt, D.L.; Cahn, A.; Hirshberg, B.; Wei, C.; Im, K.; Rozenberg, A.; Yanuv, I.; Stahre, C.; et al. Effect of Saxagliptin on Renal Outcomes in the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenstock, J.; Perkovic, V.; Johansen, O.E.; Cooper, M.E.; Kahn, S.E.; Marx, N.; Alexander, J.H.; Pencina, M.; Toto, R.D.; Wanner, C.; et al. Effect of Linagliptin vs Placebo on Major Cardiovascular Events in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes and High Cardiovascular and Renal Risk: The CARMELINA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, D.V.; Parkhill, T.R.; Badve, S.V.; Jun, M.; Jardine, M.J.; Perkovic, V. The effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on kidney outcomes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.H.; Kim, S.; Park, E.-G.; Kim, S.G.; Hahn, S.; Kim, N.H. Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors on Renal Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 34, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaki, H.; Tachi, T.; Goto, C.; Sugita, I.; Kanematsu, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Saito, K.; Noguchi, Y.; Ohno, Y.; Aoyama, S.; et al. Renoprotective Effect of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brenner, B.M.; Cooper, M.E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Keane, W.F.; Mitch, W.E.; Parving, H.-H.; Remuzzi, G.; Snapinn, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Shahinfar, S. Effects of Losartan on Renal and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Diabetes Association. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S73–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| DPP-4 Inhibitor (n = 1101) | Non-DPP-4 Inhibitor (n = 1101) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) a | 63.18 ± 11.18 | 63.43 ± 12.62 | 0.623 |
| Gender [n (%)] | |||
| Female | 505 (45.87) | 507 (46.05) | 0.932 |
| Male | 596 (54.13) | 594 (53.95) | |
| Baseline eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) a | 77.84 ± 27.56 | 77.60 ± 27.19 | 0.838 |
| Baseline HbA1c (%) a | 7.59 ± 1.24 | 7.63 ± 1.47 | 0.445 |
| Underlying comorbidities [n (%)] | |||
| Coronary artery disease | 175 (15.89) | 165 (14.99) | 0.555 |
| Heart failure | 67 (6.09) | 63 (5.72) | 0.718 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 230 (20.89) | 240 (21.80) | 0.603 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 640 (58.13) | 636 (57.77) | 0.863 |
| Hypertension | 809 (73.48) | 825 (74.93) | 0.436 |
| Gout | 159 (14.44) | 146 (13.26) | 0.423 |
| Obesity | 58 (5.27) | 61 (5.54) | 0.777 |
| Prior medications [n (%)] | |||
| ACEIs or ARBs | 570 (51.77) | 541 (49.14) | 0.216 |
| Direct renin inhibitors | 13 (1.18) | 11 (1.00) | 0.681 |
| Statins | 532 (48.32) | 507 (46.05) | 0.286 |
| Antihypertensive agents | 748 (67.94) | 756 (68.66) | 0.714 |
| Anti-gout drugs | 114 (10.35) | 115 (10.45) | 0.944 |
| DPP-4 Inhibitor (n = 1101) | Non-DPP-4 Inhibitor (n = 1101) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR decline of ≥ 30% [n (%)] a | 111 (10.08) | 178 (16.17) | <0.001 |
| Time to eGFR decline of ≥ 30% (year) a,b | 2.84 ± 1.60 | 1.96 ± 1.30 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, W.-C.; Lin, C.-S.; Chen, J.-F.; Chang, C.-M. The Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors on Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092653
Hsu W-C, Lin C-S, Chen J-F, Chang C-M. The Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors on Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(9):2653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092653
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Wan-Chia, Chun-Sheng Lin, Jung-Fu Chen, and Chih-Min Chang. 2022. "The Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors on Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 9: 2653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092653
APA StyleHsu, W.-C., Lin, C.-S., Chen, J.-F., & Chang, C.-M. (2022). The Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors on Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(9), 2653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092653





