Mortality Risk Associated with Diabetic Foot Complications in People with or without History of Diabetic Foot Hospitalizations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Source
2.2. Definition and Classification of DF Complications
2.3. Outcomes and Statistical Procedures
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations and Strengths of the Study
4.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boulton, A.J.; Vileikyte, L.; Ragnarson-Tennvall, G.; Apelqvist, J. The global burden of diabetic foot disease. Lancet 2005, 366, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lazzarini, P.A.; McPhail, S.M.; van Netten, J.J.; Armstrong, D.G.; Pacella, R.E. Global disability burdens of diabetes-related lower-extremity complications in 1990 and 2016. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, D.G.; Swerdlow, M.A.; Armstrong, A.A.; Conte, M.S.; Padula, W.V.; Bus, S.A. Five year mortality and direct costs of care for people with diabetic foot complications are comparable to cancer. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2020, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.W.; Hoffstad, O.J.; Sullivan, M.O.; Margolis, D.J. Association of diabetic foot ulcer and death in a population-based cohort from the United Kingdom. Diabetes Med. 2016, 33, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, A.; Goyal, G.; Kesavan, R.; Bal, A.; Kumar, H.; Kamath, P.; Jude, E.B.; Armstrong, D.G.; Bhansali, A. Long term outcomes after incident diabetic foot ulcer: Multicenter large cohort prospective study (EDIFOCUS investigators) epidemiology of diabetic foot complications study: Epidemiology of diabetic foot complications study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyaraman, K.; Berhane, T.; Hamilton, M.; Chandra, A.P.; Falhammar, H. Mortality in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: A retrospective study of 513 cases from a single centre in the Northern Territory of Australia. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, J.A.; Jimenez, S.; Lazaro-Martınez, J.L. Mortality in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: Causes, risk factors, and their association with evolution and severity of ulcer. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbach, S.; Furchert, H.; Gröblinghoff, U.; Hoffmeier, H.; Kersten, K.; Klauke, G.T.; Klemp, U.; Roden, T.; Icks, A.; Haastert, B.; et al. Long-term prognosis of diabetic foot patients and their limbs: Amputation and death over the course of a decade. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2021–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupiter, D.C.; Thorud, J.C.; Buckley, C.J.; Shibuya, N. The impact of foot ulceration and amputation on mortality in diabetic patients. I: From ulceration to death, a systematic review. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownrigg, J.R.; Griffin, M.; Hughes, C.O.; Jones, K.G.; Patel, N.; Thompson, M.M.; Hinchliffe, R.J. Influence of foot ulceration on cause-specific mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus. J. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 60, 982–986.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheng, S.W.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Ko, Y. Healthcare costs and utilization of diabetes-related complications in Taiwan: A claims database analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, M.M.; Tell, G.S.; Riise, T.; Hanestad, B.R.; Østbye, T.; Graue, M.; Midthjell, K. History of foot ulcer increases mortality among individuals with diabetes: Ten-year follow-up of the Nord-Trøndelag Health Study, Norway. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 2193–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, R.C.; Fleetwood, K.; Wild, S.H.; Colhoun, H.M.; Lindsay, R.S.; Petrie, J.R.; McCrimmon, R.J.; Gibb, F.; Philip, S.; Sattar, N.; et al. Foot ulcer and risk of lower limb amputation or death in people with diabetes: A national population-based retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faglia, E.; Clerici, G.; Caminiti, M.; Curci, V.; Clerissi, J.; Losa, S.; Casini, A.; Morabito, A. Mortality after major amputation in diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia who did and did not undergo previous peripheral revascularization Data of a cohort study of 564 consecutive diabetic patients. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2010, 24, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopi, E.; Coppelli, A.; Goretti, C.; Bargellini, I.; Cicorelli, A.; Cioni, R.; Piaggesi, A. Effect of direct endovascular revascularization based on the angiosome model on risk of major amputations and life expectancy in type 2 diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia and foot ulceration. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2021, 111, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghieri, G.; Policardo, L.; Gualdani, E.; Anichini, R.; Francesconi, P. Gender difference in the risk for cardiovascular events or mortality of patients with diabetic foot syndrome. Acta Diabetol. 2019, 56, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gini, R.; Francesconi, P.; Mazzaglia, G.; Cricelli, I.; Pasqua, A.; Gallina, P.; Brugaletta, S.; Donato, D.; Donatini, A.; Marini, A.; et al. Chronic disease prevalence from Italian administrative databases in the VALORE project: A validation through comparison of population estimates with general practice databases and national survey. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, I.; Braga, G.A.; de Melo, F.G.; da Costa Silva Silva, A.C.C. The diabetic foot as a proxy for cardiovascular events and mortality review. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, F.L.; Maggini, M.; De Bellis, A.; Seghieri, G.; Anichini, R. Lower extremity amputations in persons with and without diabetes in Italy: 2001–2010. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Armstrong, D.G.; Liu, P.H.; Lin, C.W.; Huang, C.H.; Huang, Y.Y. Survival of patients following first diagnosis of diabetic foot complications: A nationwide 15-year longitudinal analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 801324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunir, E.; Hidayah, C.D.; Harimurti, K.; Kshanti, I.A.M. Three years survival and factor predicting amputation or mortality in patients with high risk for diabetic foot ulcer in Fatmawati General Hospital, Jakarta. J. Prim. Care Community Health 2022, 13, 21501319211063707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monge, L.; Gnavi, R.; Carnà, P.; Broglio, F.; Boffano, G.M.; Giorda, C.B. Incidence of hospitalization and mortality in patients with diabetic foot regardless of amputation: A population study. Acta Diabetol. 2020, 57, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seghieri, G.; Policardo, L.; Gualdani, E.; Francesconi, P. Gender differences in the risk of adverse outcomes after incident diabetic foot hospitalization: A population cohort study. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2021, 17, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffcoate, W.J.; Harding, K.G. Diabetic foot ulcers. Lancet 2003, 361, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| without Prior Hospitalizations for Diabetic Foot | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetic Foot Lesions | Major Amputations | Minor Amputations | Revascularizations | Gangrene | Infections | Charcot | Ulcer | Total |
| No. (%) | 143 (1.2) | 306 (2.6) | 2854 (24.7) | 6282 (54.5) | 908 (7.9) | 51 (0.4) | 985 (8.5) | 11,529 |
| Incidence rate of first hospitalization per 1000 p-y (95%CI) | 3.0 (2.5–3.5) | 6.5 (5.8–7.3) | 77.3 (74.5–80.2) | 293.2 (286–300.6) | 20.4 (19.1–21.7) | 1.1 (0.8–1.4) | 22.3 (21.0–23.8) | 4.6 (4.5–4.7) |
| Mean Age yr (SD) | 74 (12) | 68 (13) | 70 (10) | 73 (10) | 66 (13) | 62 (13) | 72 (12) | 71 (11) |
| Male Sex No. (%) | 73 (51) | 199 (65) | 1875 (66) | 3865 (54.4) | 548 (60.3) | 30 (58.8) | 518 (52.6) | 61.6 |
| Charlson index | ||||||||
| 0 No. (%) | 46 (31.2) | 145 (47.4) | 1149 (40.3) | 2364 (37.6) | 435 (47.9) | 22 (43.1) | 413 (41.9) | 39.7 |
| 1 No. (%) | 22 (15.4) | 54 (17.6) | 520 (18.2) | 1182 (18.8) | 165 (18.2) | 10 (19.6) | 188 (19.1) | 18.6 |
| 2+ No. (%) | 75 (52.4) | 107 (35.0) | 1185 (41.5) | 2736 (43.6) | 308 (33.9) | 19 (37.3) | 384 (39.0) | 41.7 |
| Therapy (%) | ||||||||
| Insulin | 14.0 | 13.4 | 12.0 | 11.9 | 10.6 | 15.7 | 13.1 | 12.0 |
| Oral | 42.7 | 41.5 | 41.5 | 44.4 | 36.6 | 29.4 | 44.2 | 42.9 |
| Insulin/oral | 10.5 | 13.1 | 11.8 | 11.8 | 13.0 | 25.5 | 15.3 | 12.3 |
| None | 32.9 | 32.0 | 34.6 | 31.9 | 39.9 | 31.4 | 27.4 | 32.8 |
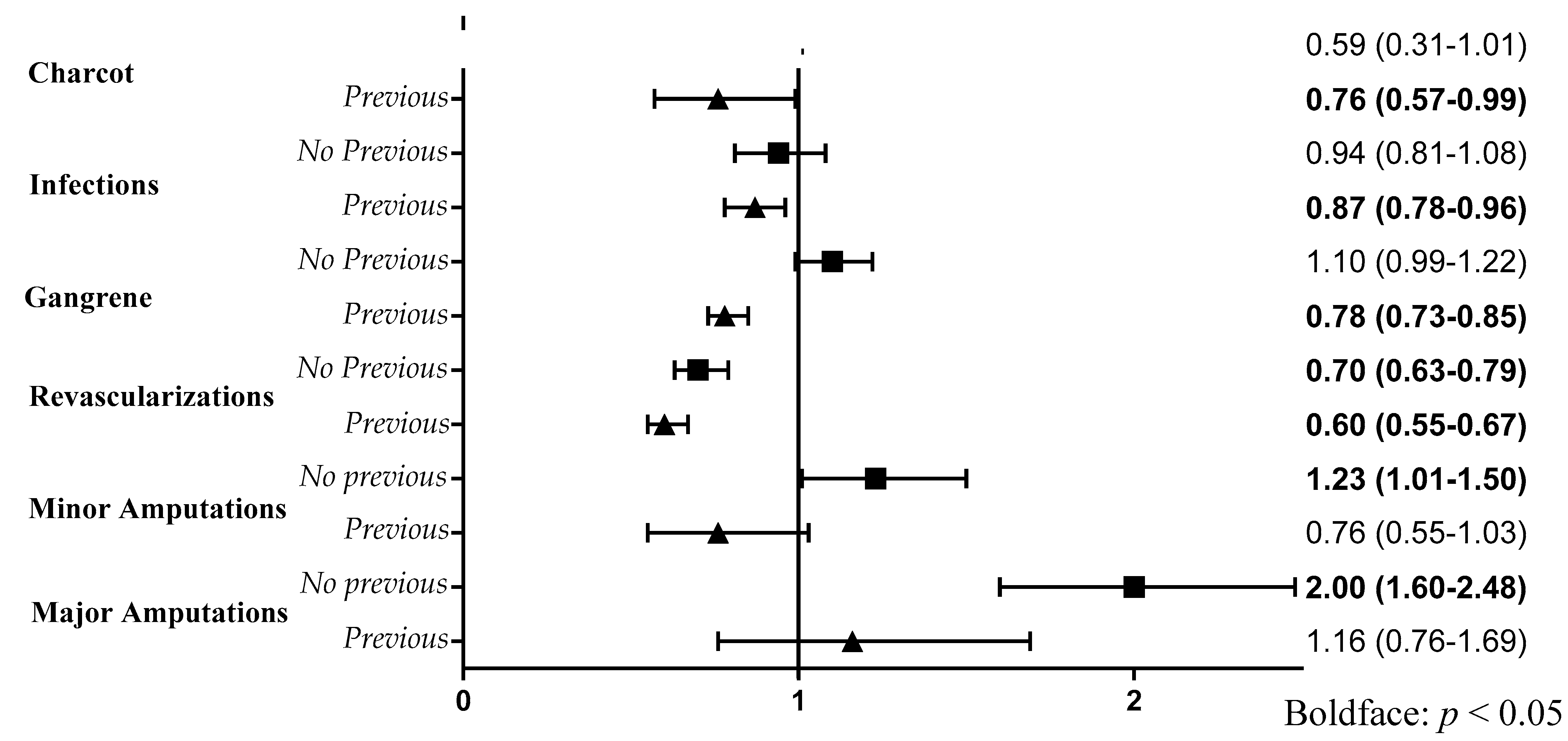
| No. of deaths; Incidence rate of death per 1000 p-y (95%CI) | 96; 1.63 (1.33–1.99) | 122; 0.58 (0.48–0.69) | 939; 0.40 (0.37–0.42) | 3087; 0.76 (0.73–0.79) | 310; 0.40 (0.36–0.45) | 12; 0.20 (0.12–0.36) | 462; 0.67 (0.60–0.74) | 5028; 0.61 (0.59–0.63) |
| with Prior Hospitalizations for Diabetic Foot | ||||||||
| No. (%) | 39 (0.3) | 86 (0.8) | 1561 (13.9) | 7049 (62.7) | 1273 (11.3) | 113 (1.0) | 1125 (10.0) | 11,246 |
| Mean Age yr (SD) | 71 (13) | 69 (14) | 74 (9) | 75 (10) | 69 (13) | 67 (14) | 73 (11) | 74 (10) |
| Male Sex (%) | 31 (72) | 54 (60) | 1099 (71) | 4822 (64.8) | 739 (58.1) | 63 (55.8) | 629 (55.9) | 66.1 |
| Charlson index (%) | ||||||||
| 0 No. (%) | 11 (25.6) | 23 (25.6) | 70 (4.5) | 440 (6.2) | 185 (14.5) | 14 (12.4) | 44 (3.9) | 7.0 |
| 1 No. (%) | 11 (25.6) | 23 (25.6) | 284 (18.3) | 1122 (15.9) | 287 (22.6) | 21 (18.6) | 183 (16.3) | 17.2 |
| 2+ No. (%) | 21 (48.8) | 44 (48.8) | 1199 (77.2) | 5487 (77.9) | 801 (62.9) | 78 (69.0) | 898 (79.8) | 75.8 |
| Therapy (%) | ||||||||
| Insulin | 16.3 | 21.1 | 14.2 | 21.4 | 25.6 | 30.1 | 34.7 | 22.3 |
| Oral | 37.2 | 35.6 | 42.6 | 37.8 | 31.8 | 23.0 | 27.7 | 36.6 |
| Insulin/oral | 9.3 | 13.3 | 9.9 | 16.3 | 17.9 | 18.6 | 22.8 | 16.2 |
| None | 37.2 | 30.0 | 33.3 | 24.5 | 24.7 | 28.3 | 14.8 | 24.9 |
| No. of deaths; Incidence rate of death per 1000 p-y (95%CI) | 22; 0.54 (0.35–0.81) | 39; 0.30 (0.22–0.40) | 818; 0.39 (0.37–0.42) | 4320; 0.56 (0.55–0.58) | 633; 0.35 (0.32–0.38) | 52; 0.30 (0.23–0.40) | 749; 0.72 (0.67–0.77) | 6633; 0.51 (0.50–0.53) |
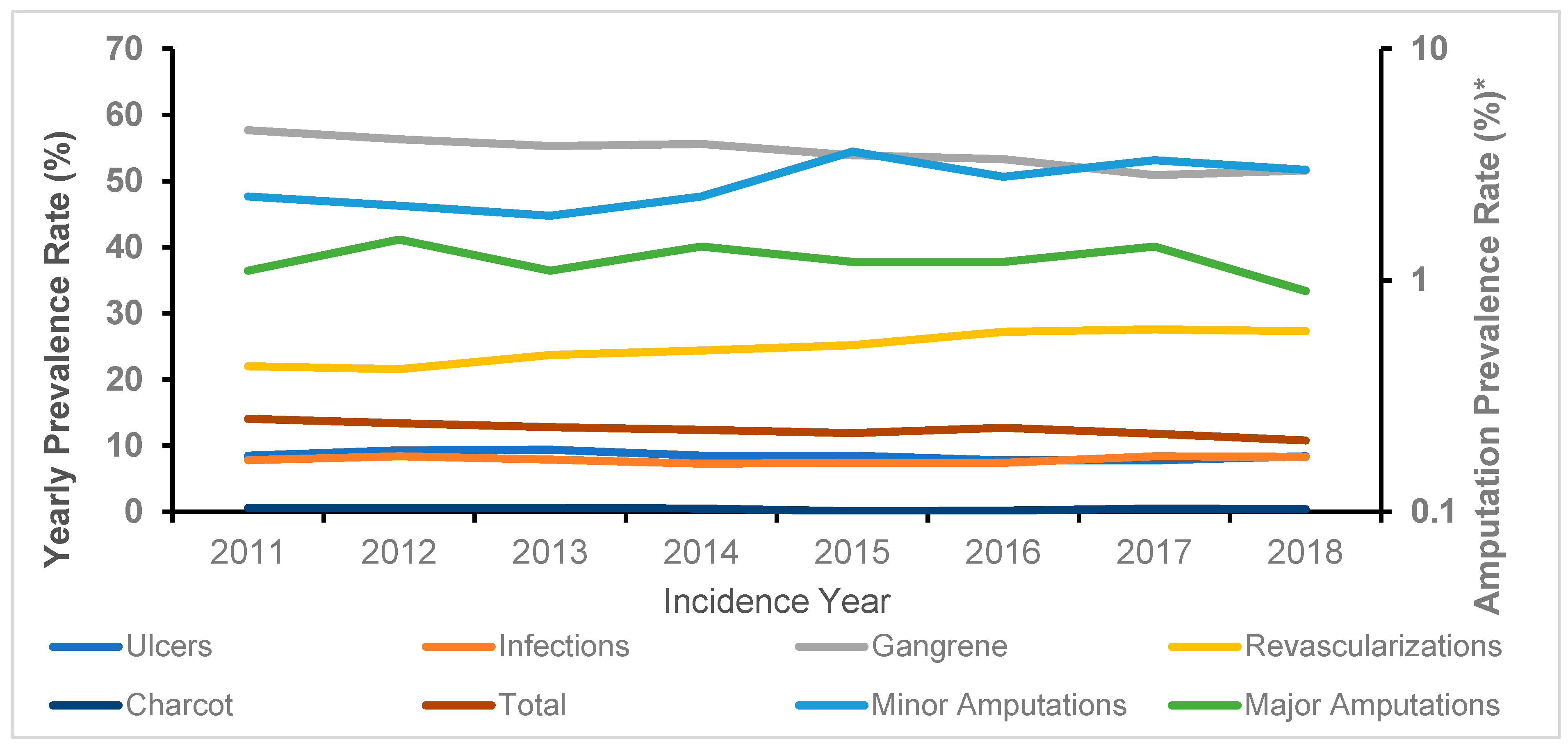
| Year | Ulcers | Infections | Gangrene | Charcot | Revascularizations | Major Amputations | Minor Amputations | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | No. (%) | No. (%) | No. (%) | No. (%) | No. (%) | No. (%) | No. (%) | |
| 2011 | 138 (8.5) | 127 (7.8) | 940 (57.7) | 9 (0.6) | 358 (22.0) | 18 (1.1) | 38 (2.3) | 1628 (14.1) |
| 2012 | 144 (9.3) | 130 (8.4) | 871 (56.3) | 10 (0.6) | 335 (2.6) | 24 (1.5) | 33 (2.1) | 1547 (13.4) |
| 2013 | 139 (9.4) | 117 (7.9) | 814 (55.3) | 9 (0.6) | 348 (23.7) | 16 (1.1) | 28 (1.9) | 1471 (12.8) |
| 2014 | 122 (8.5) | 104 (7.3) | 795 (5.6) | 7 (0.5) | 349 (24.4) | 20 (1.4) | 33 (2.3) | 1430 (12.4) |
| 2015 | 117 (8.5) | 102 (7.4) | 743 (53.9) | 1 (0.1) | 348 (25.2) | 17 (1.2) | 50 (3.6) | 1378 (11.9) |
| 2016 | 114 (7.8) | 109 (7.4) | 780 (53.3) | 3 (0.2) | 399 (27.2) | 18 (1.2) | 41 (2.8) | 1464 (12.7) |
| 2017 | 106 (7.8) | 115 (8.4) | 695 (50.9) | 7 (0.5) | 377 (27.6) | 19 (1.4) | 45 (3.3) | 1364 (11.8) |
| 2018 | 105 (8.4) | 104 (8.3) | 644 (51.6) | 5 (0.4) | 340 (27.3) | 11 (0.9) | 38 (3.0) | 1247 (10.8) |
| P for trend | NS | NS | 0.0001 | NS | <0.0001 | NS | 0.007 | 0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francia, P.; Gualdani, E.; Policardo, L.; Bocchi, L.; Franconi, F.; Francesconi, P.; Seghieri, G. Mortality Risk Associated with Diabetic Foot Complications in People with or without History of Diabetic Foot Hospitalizations. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092454
Francia P, Gualdani E, Policardo L, Bocchi L, Franconi F, Francesconi P, Seghieri G. Mortality Risk Associated with Diabetic Foot Complications in People with or without History of Diabetic Foot Hospitalizations. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(9):2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092454
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancia, Piergiorgio, Elisa Gualdani, Laura Policardo, Leonardo Bocchi, Flavia Franconi, Paolo Francesconi, and Giuseppe Seghieri. 2022. "Mortality Risk Associated with Diabetic Foot Complications in People with or without History of Diabetic Foot Hospitalizations" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 9: 2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092454
APA StyleFrancia, P., Gualdani, E., Policardo, L., Bocchi, L., Franconi, F., Francesconi, P., & Seghieri, G. (2022). Mortality Risk Associated with Diabetic Foot Complications in People with or without History of Diabetic Foot Hospitalizations. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(9), 2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092454










