Current Strategies to Optimize Nutrition and Growth in Newborns and Infants with Congenital Heart Disease: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Nutritional Challenges in CHD Patients
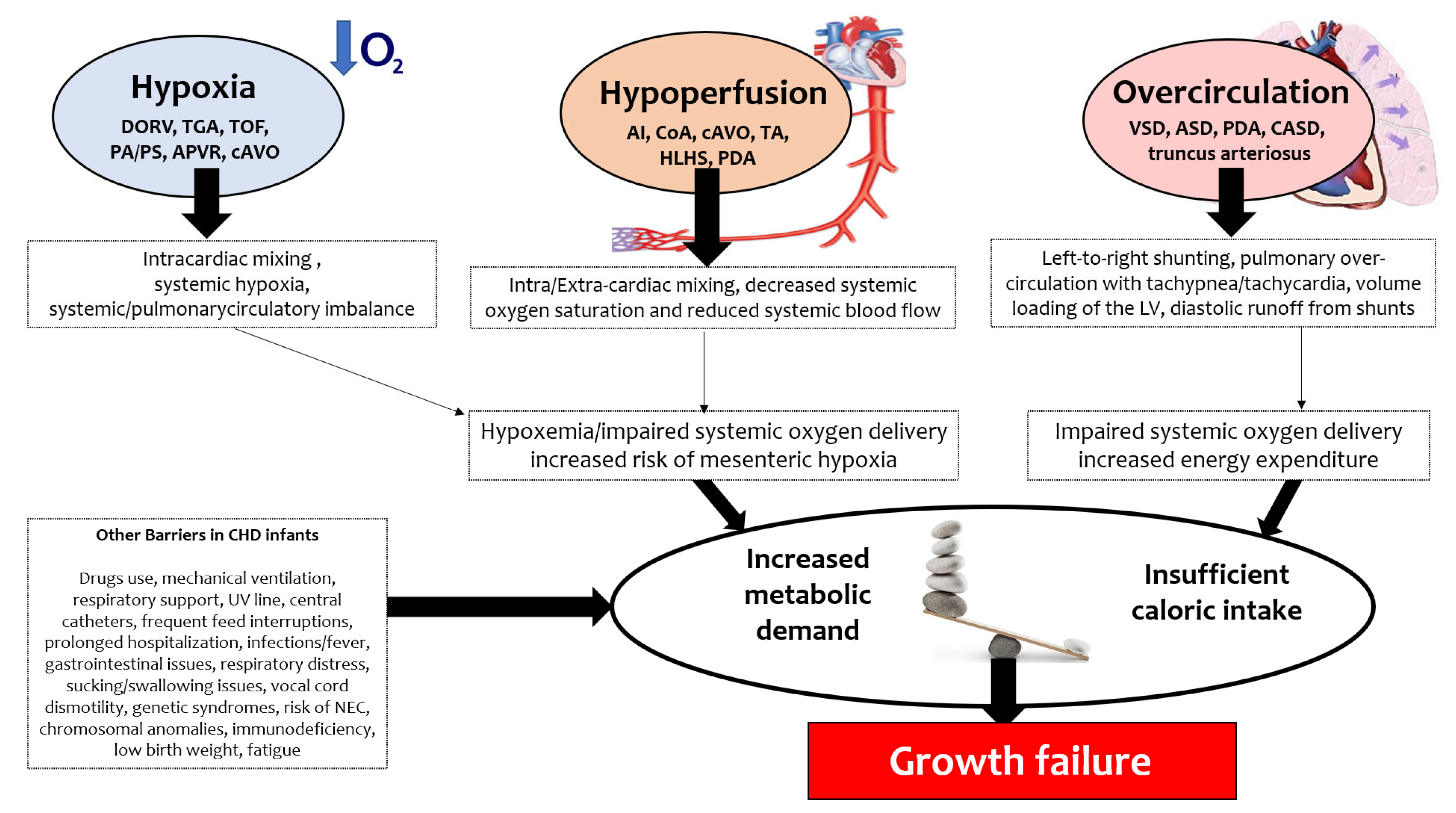
3.1. CHD Hemodynamics and the Consequences for Nutrition
- (1)
- Hypoxia, such as in double-outlet right ventricle (DORV), transposition of the great arteries (TGA), tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), pulmonary atresia/pulmonary stenosis (PA/PS), anomalous pulmonary venous return (APVR), critical aortic valve obstruction (cAVO);
- (2)
- Hypoperfusion, such as in aortic interruption (AI), aortic coarctation (CoA), cAVO, tricuspid atresia (TA), hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS), patent ductus arteriosus (PDA);
- (3)
- Overcirculation, such as in ventricular septal defect (VSD), atrial septal defect (ASD), PDA, complete atrioventricular septal defect (CASD), truncus arteriosus.
3.2. Prematurity, Low Birthweight and Genetic Anomalies
3.3. Other Clinical Barriers
3.4. Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Risks and Fear
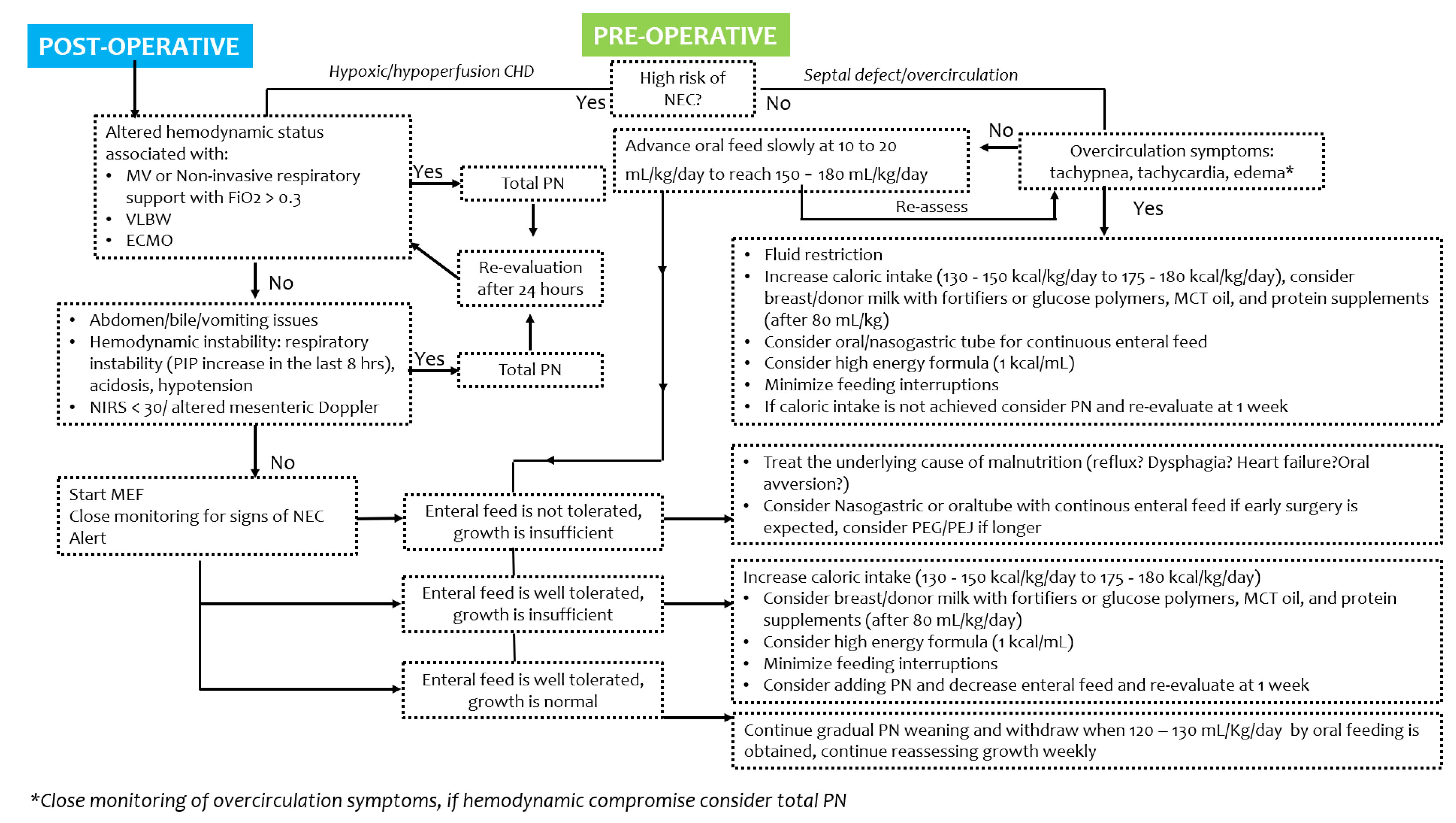
4. Pre- and Post-Operative Strategies and Recommendations
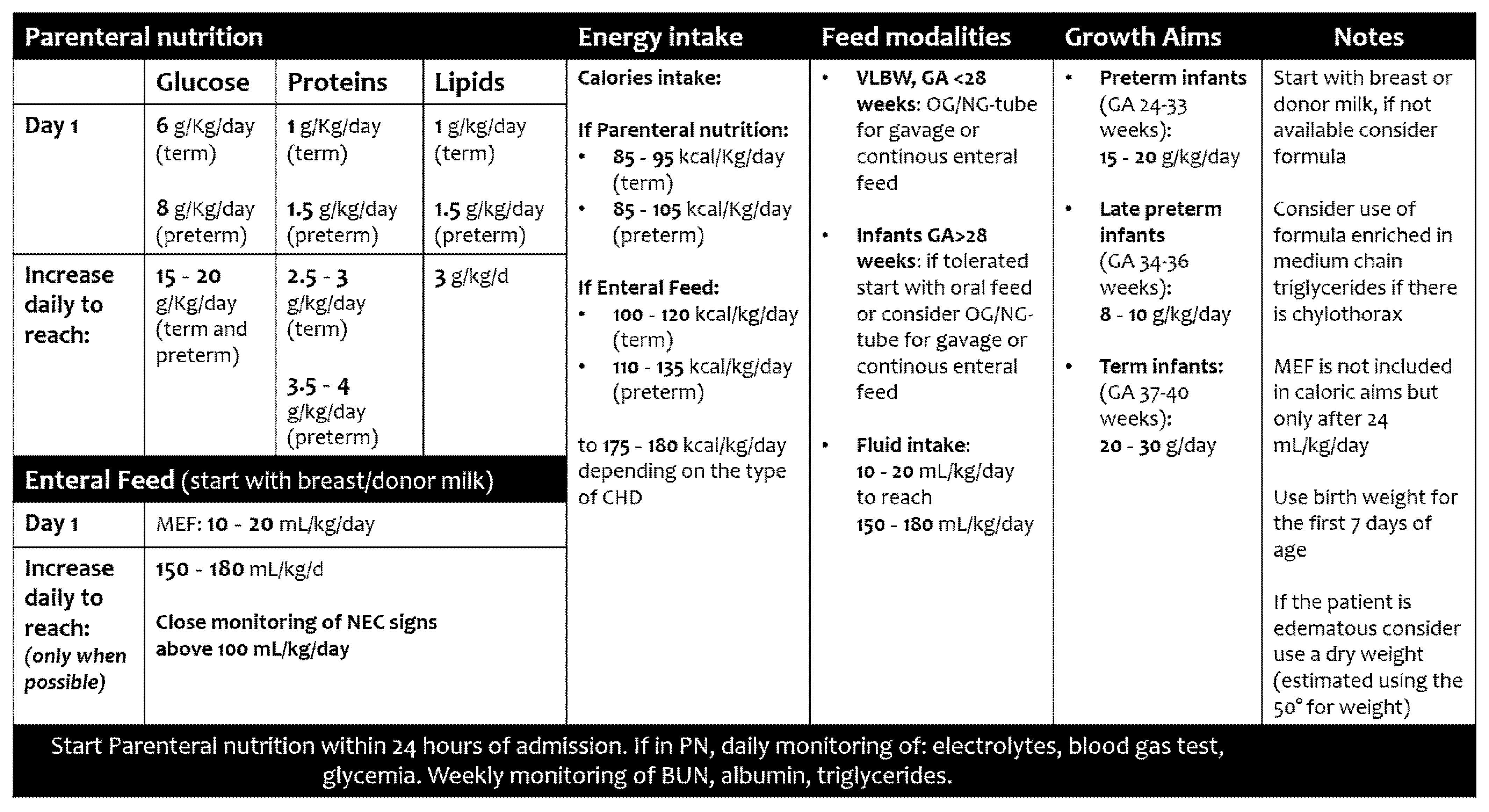
4.1. Total Nutritional Requirements
4.1.1. Fluid Volume
4.1.2. Energy Intake
4.1.3. Protein Intake
4.2. Parenteral Nutrition
4.3. Enteral Nutrition
4.3.1. Types of Feed
4.3.2. Routes
4.3.3. Short- and Long-Term Difficulties after Cardiac Surgery
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marino, L.V.; Johnson, M.J.; Hall, N.J.; Davies, N.J.; Kidd, C.S.; Daniels, M.L.; Robinson, J.E.; Richens, T.; Bharucha, T.; Darlington, A.E.; et al. The development of a consensus-based nutritional pathway for infants with CHD before surgery using a modified Delphi process. Cardiol. Young 2018, 28, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, L.V.; Johnson, M.J.; Davies, N.J.; Kidd, C.S.; Fienberg, J.; Richens, T.; Bharucha, T.; Beattie, R.M.; Darlington, A.-S.E. Improving growth of infants with congenital heart disease using a consensus-based nutritional pathway. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argent, A.C.; Balachandran, R.; Vaidyanathan, B.; Khan, A.; Kumar, R.K. Management of undernutrition and failure to thrive in children with congenital heart disease in low- and middle-income countries. Cardiol. Young 2017, 27, S22–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsintoni, A.; Dimitriou, G.; Karatza, A.A. Nutrition of neonates with congenital heart disease: Existing evidence, conflicts and concerns. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 33, 2487–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwalbe-Terilli, C.R.; Hartman, D.H.; Nagle, M.L.; Gallagher, P.R.; Ittenbach, R.F.; Burnham, N.B.; Gaynor, J.W.; Ravishankar, C. Enteral feeding and caloric intake in neonates after cardiac surgery. Am. J. Crit. Care 2009, 18, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehir, D.A.; Cooper, D.S.; Walters, E.M.; Ghanayem, N.S. Feeding, growth, nutrition, and optimal interstage surveillance for infants with hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Cardiol. Young 2011, 21, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisenga, D.; La Bastide-Van Gemert, S.; Van Bergen, A.; Sweeney, J.; Hadders-Algra, M. Developmental outcomes after early surgery for complex congenital heart disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021, 63, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpen, H.E. Nutrition in the Cardiac Newborns. Evidence-based Nutrition Guidelines for Cardiac Newborns. Clin. Perinatol. 2016, 43, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, M.; Hakansson, S.; Kusuda, S.; Vento, M.; Lehtonen, L.; Reichman, B.; Darlow, B.A.; Adams, M.; Bassler, D.; Isayama, T.; et al. Neonatal outcomes in very preterm infants with severe congenital heart defects: An international cohort study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rose, D.U.; Cota, F.; Gallini, F.; Bottoni, A.; Fabrizio, G.C.; Ricci, D.; Romeo, D.M.; Mercuri, E.; Vento, G.; Maggio, L. Extra-uterine growth restriction in preterm infants: Neurodevelopmental outcomes according to different definitions. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2021, 33, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.M.; Compher, C. ASPEN clinical guidelines: Nutrition support of the critically ill child. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2009, 33, 260–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radman, M.; Mack, R.; Barnoya, J.; Castañeda, A.; Rosales, M.; Azakie, A.; Mehta, N.; Keller, R.; Datar, S.; Oishi, P.; et al. The effect of preoperative nutritional status on postoperative outcomes in children undergoing surgery for congenital heart defects in San Francisco (UCSF) and Guatemala City (UNICAR). J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steltzer, M.; Rudd, N.; Pick, B. Nutrition care for newborns with congenital heart disease. Clin. Perinatol. 2005, 32, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.B.; Beekman, R.H., 3rd; Border, W.L.; Kalkwarf, H.J.; Khoury, P.R.; Uzark, K.; Eghtesady, P.; Marino, B.S. Lower weight-for-age z score adversely affects hospital length of stay after the bidirectional Glenn procedure in 100 infants with a single ventricle. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 138, 397–404.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toole, B.J.; Toole, L.E.; Kyle, U.G.; Cabrera, A.G.; Orellana, R.A.; Coss-Bu, J.A. Perioperative nutritional support and malnutrition in infants and children with congenital heart disease. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2014, 9, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tume, L.N.; Balmaks, R.; Da Cruz, E.; Latten, L.; Verbruggen, S.; Valla, F.V. Enteral Feeding Practices in Infants with Congenital Heart Disease Across European PICUs: A European Society of Pediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care Survey. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 19, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasquez, A.; Clouzeau, H.; Fayon, M.; Mouton, J.B.; Thambo, J.B.; Enaud, R.; Lamireau, T. Evaluation of nutritional status and support in children with congenital heart disease. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.E.; Desai, H.; Fogel, J.L.; Negrin, K.A.; Torzone, A.; Willette, S.; Fridgen, J.L.; Doody, L.R.; Morris, K.; Engstler, K.; et al. Disruptions in the development of feeding for infants with congenital heart disease. Cardiol. Young 2021, 31, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benbrik, N.; Romefort, B.; Le Gloan, L.; Warin, K.; Hauet, Q.; Guerin, P.; Baron, O.; Gournay, V. Late repair of tetralogy of Fallot during childhood in patients from developing countries. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2015, 47, e113–e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cheung, M.M.H.; Davis, A.M.; Wilkinson, J.L.; Weintraub, R.G. Long term somatic growth after repair of tetralogy of Fallor: Evidence for restoration of genetic growth potential. Heart 2003, 89, 1340–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weintraub, R.G.; Menahem, S. Growth and congenital heart disease. J. Paediatr. Child Health 1993, 29, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.J.M.; Cheifetz, I.M.; Ong, C.; Nakao, M.; Lee, J.H. Nutrition Support for Children Undergoing Congenital Heart Surgeries: A Narrative Review. World J. Pediatr. Congenit. Heart Surg. 2015, 6, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, M.; Goldenberg, N.; Bonduel, M.; Revel-Vilk, S.; Amankwah, E.; Albisetti, M. Catheter-Related Arterial Thrombosis in Neonates and Children: A Systematic Review. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tume, L.N.; Valla, F.V.; Joosten, K.; Jotterand Chaparro, C.; Latten, L.; Marino, L.V.; Macleod, I.; Moullet, C.; Pathan, N.; Rooze, S.; et al. Nutritional support for children during critical illness: European Society of Pediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC) metabolism, endocrine and nutrition section position statement and clinical recommendations. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordenström, K.; Lannering, K.; Mellander, M.; Elfvin, A. Low risk of necrotising enterocolitis in enterally fed neonates with critical heart disease: An observational study. Arch. Dis. Child.-Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2020, 105, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vari, D.; Xiao, W.; Behere, S.; Spurrier, E.; Tsuda, T.; Baffa, J.M. Low-dose prostaglandin E1 is safe and effective for critical congenital heart disease: Is it time to revisit the dosing guidelines? Cardiol. Young 2020, 31, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aykanat, A.; Yavuz, T.; Özalkaya, E.; Topçuoğlu, S.; Ovalı, F.; Karatekin, G. Long-Term Prostaglandin E1 Infusion for Newborns with Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2016, 37, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.R.; Blancha Eckels, V.L.; Crook, S.; Duchon, J.M.; Kalfa, D.; Bacha, E.A.; Krishnamurthy, G. The Risks of Being Tiny: The Added Risk of Low Weight for Neonates Undergoing Congenital Heart Surgery. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2020, 41, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanchi, A.; Derridj, N.; Bonnet, D.; Bertille, N.; Salomon, L.J.; Khoshnood, B. Children Born with Congenital Heart Defects and Growth Restriction at Birth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, A.; Allison, B.J.; Gwini, S.M.; Menahem, S.; Miller, S.L.; Polglase, G.R. Vascular aging and cardiac maladaptation in growth-restricted preterm infants. J. Perinatol. 2018, 38, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia Martins, L.; Lourenço, R.; Cordeiro, S.; Carvalho, N.; Mendes, I.; Loureiro, M.; Patrício, M.; Anjos, R. Catch-up growth in term and preterm infants after surgical closure of ventricular septal defect in the first year of life. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2016, 175, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, D.; Davis, S.; Cotman, K.; Worley, S.; Londrico, D.; Kenny, D.; Harrison, A.M. Feeding difficulties and growth delay in children with hypoplastic left heart syndrome versus d-transposition of the great arteries. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2008, 29, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangili, G.; Garzoli, E.; Sadou, Y. Feeding dysfunctions and failure to thrive in neonates with congenital heart diseases. Pediatr. Med. Chir. 2018, 40, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubberman, J.M.; Van Zoonen, A.; Bruggink, J.; Van der Heide, M.; Berger, R.; Bos, A.F.; Kooi, E.; Hulscher, J. Necrotizing Enterocolitis Associated with Congenital Heart Disease: A Different Entity? J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 54, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria-Hale, J.; Cognata, A.; Hagan, J.; Zender, J.; Sheaks, P.; Osborne, S.; Roddy, J.; Hair, A. The Relationship Between Preoperative Feeding Exposures and Postoperative Outcomes in Infants with Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 22, e91–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognata, A.; Kataria-Hale, J.; Griffiths, P.; Maskatia, S.; Rios, D.; O’Donnell, A.; Roddy, D.J.; Mehollin-Ray, A.; Hagan, J.; Placencia, J.; et al. Human Milk Use in the Preoperative Period Is Associated with a Lower Risk for Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Neonates with Complex Congenital Heart Disease. J. Pediatr. 2019, 215, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, S.; Aceti, A.; Galletti, S.; Beghetti, I.; Faldella, G.; Corvaglia, L. To feed or not to feed: A critical overview of enteral feeding management and gastrointestinal complications in preterm neonates with a patent ductus arteriosus. Nutrients 2020, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocjancic, L.; Bührer, C.; Berger, F.; Boos, V. Effect of a Dual-Strain Probiotic on Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Neonates with Ductal-Dependent Congenital Heart Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Neonatology 2021, 117, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Veldman, A.; Menahem, S. Does milk fortification increase the risk of necrotising enterocolitis in preterm infants with congenital heart disease? Cardiol. Young 2013, 23, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massolo, A.C.; Vanina Cantone, G.; Musolino, A.M.; Corsini, I.; Patel, N.; Evangelisti, M.; Monaco, F.; Villa, M.P.; Braguglia, A. Myocardial strain on admission predicts disease severity in infants hospitalized for bronchiolitis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musolino, A.M.; Buonsenso, D.; Massolo, A.C.; Gallo, M.; Supino, M.C.; Boccuzzi, E. Point of care ultrasound in the paediatric acute care setting: Getting to the ‘heart’ of respiratory distress. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2020, 57, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giliberti, P.; Mondì, V.; Conforti, A.; Lombardi, M.H.; Sgrò, S.; Bozza, P.; Picardo, S.; Dotta, A.; Bagolan, P. Near infrared spectroscopy in newborns with surgical disease. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011, 24, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, Y.; Seshia, M. A new intestinal ultrasound integrated approach for the management of neonatal gut injury. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.; Bassler, D. Practice variations and rates of late onset sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis in very preterm born infants, a review. Transl. Pediatr. 2019, 8, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong-Dillard, J.; Neary, A.; Marietta, J.; Jones, C.; Jeffers, G.; Gakenheimer, L.; Puchalski, M.; Eckauser, A.; Delgado-Corcoran, C. Evaluating the Impact of a Feeding Protocol in Neonates before and after Biventricular Cardiac Surgery. Pediatr. Qual. Saf. 2018, 3, e080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newcombe, J.; Fry-Bowers, E. A Post-operative Feeding Protocol to Improve Outcomes for Neonates with Critical Congenital Heart Disease. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2017, 35, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neal Maynord, P.; Johnson, M.; Xu, M.; Slaughter, J.C.; Killen, S. A Multi-Interventional Nutrition Program for Newborns with Congenital Heart Disease. J. Pediatr. 2021, 228, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongwer, R.C.; Gauvreau, K.; Huh, S.Y.; Sztam, K.A.; Jenkins, K.J. Impact of a Standardized Clinical Assessment and Management Plan (SCAMP) on growth in infants with CHD. Cardiol. Young 2018, 28, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, L.; Lind, T.; Wiklund, U.; Öhlund, I.; Rydberg, A. Fluid restriction negatively affects energy intake and growth in very low birthweight infants with haemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus. Acta Paediatr. 2019, 108, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cui, Y.Q.; Ma Md, Z.M.; Luo, Y.; Chen, X.X.; Li, J. Energy and Protein Requirements in Children Undergoing Cardiopulmonary Bypass Surgery: Current Problems and Future Direction. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 43, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cui, Y.Q.; Luo, Y.; Chen, X.X.; Li, J. Assessment of Energy and Protein Requirements in Relation to Nitrogen Kinetics, Nutrition, and Clinical Outcomes in Infants Receiving Early Enteral Nutrition Following Cardiopulmonary Bypass. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2021, 45, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazle, M.A.; Gajarski, R.J.; Yu, S.; Donohue, J.; Blatt, N.B. Fluid Overload in Infants Following Congenital Heart Surgery. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 13, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCammond, A.N.; Axelrod, D.M.; Bailly, D.K.; Ramsey, E.Z.; Costello, J.M. Pediatric cardiac intensive care society 2014 consensus statement: Pharmacotherapies in cardiac critical care fluid management. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 17, S35–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirleman, E.; Larson, D.F. Cardiopulmonary bypass and edema: Physiology and pathophysiology. Perfusion 2008, 23, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanot, J.; Dingankar, A.R.; Sivarajan, V.B.; Sheppard, C.; Cave, D.; Garcia Guerra, G. Fluid management practices after surgery for congenital heart disease: A worldwide survey. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 20, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.M.; Skillman, H.E.; Irving, S.Y.; Coss-Bu, J.A.; Vermilyea, S.; Farrington, E.A.; McKeever, L.; Hall, A.M.; Goday, P.S.; Braunschweig, C. Guidelines for the Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Pediatric Critically Ill Patient: Society of Critical Care Medicine and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 18, 675–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebuck, N.; Fan, C.S.; Floh, A.; Harris, Z.L.; Mazwi, M.L. A Comparative Analysis of Equations to Estimate Patient Energy Requirements Following Cardiopulmonary Bypass for Correction of Congenital Heart Disease. JPEN J. Parent. Enteral. Nutr. 2020, 44, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itkin, M.; Piccoli, D.A.; Nadolski, G.; Rychik, J.; DeWitt, A.; Pinto, E.; Rome, J.; Dori, Y. Protein-Losing Enteropathy in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 2929–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrin, G.; De Nardo, M.C.; Boscarino, G.; Di Chiara, M.; Cellitti, R.; Ciccarelli, S.; Gasparini, C.; Parisi, P.; Urna, M.; Ronchi, B.; et al. Early Protein Intake Influences Neonatal Brain Measurements in Preterms: An Observational Study. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehne, M.; Sasse, M.; Karch, A.; Dziuba, F.; Horke, A.; Kaussen, T.; Mikolajczyk, R.; Beerbaum, P.; Jack, T. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome after pediatric congenital heart surgery: Incidence, risk factors, and clinical outcome. J. Card. Surg. 2017, 32, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, J.N.; Hilkin, B.M.; Hook, J.S.; Brophy, P.D.; Davenport, T.L.; Davis, J.E.; Colaizy, T.T.; Moreland, J.G. Neutrophil Phenotype Correlates with Postoperative Inflammatory Outcomes in Infants Undergoing Cardiopulmonary Bypass. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 18, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, T.; Yoshida, M.; Arita, M. Omega-3 fatty acid-derived mediators that control inflammation and tissue homeostasis. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, L.C.; Martin, C.R. Parenteral lipid emulsions in the preterm infant: Current issues and controversies. Arch. Dis. Child.-Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2021, 106, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, B.M.; Goonewardene, L.A.; Joffe, A.R.; Van Aerde, J.E.; Field, C.J.; Olstad, D.L.; Clandinin, M.T. Pre-treatment with an intravenous lipid emulsion containing fish oil (eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acid) decreases inflammatory markers after open-heart surgery in infants: A randomized, controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fivez, T.; Kerklaan, D.; Mesotten, D.; Verbruggen, S.; Wouters, P.J.; Vanhorebeek, I.; Debaveye, Y.; Vlasselaers, D.; Desmet, L.; Casaer, M.P.; et al. Early versus Late Parenteral Nutrition in Critically Ill Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scahill, C.J.; Graham, E.M.; Atz, A.M.; Bradley, S.M.; Kavarana, M.N.; Zyblewski, S.C. Preoperative Feeding Neonates with Cardiac Disease: Is the Necrotizing Enterocolitis Fear Justified? World J. Pediatr. Congenit. Heart Surg. 2017, 8, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toms, R.; Jackson, K.W.; Dabal, R.J.; Reebals, C.H.; Alten, J.A. Preoperative trophic feeds in neonates with hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2015, 10, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, R.; Vohra, R.; Negi, M.; Joshi, R.; Aggarwal, N.; Aggarwal, M.; Joshi, R. Feasibility of initiating early enteral nutrition after congenital heart surgery in neonates and infants. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 25, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.; Sahu, M.K.; Trilok Kumar, G.; Kumar, A. Effect of energy-and/or protein-dense enteral feeding on postoperative outcomes of infant surgical patients with congenital cardiac disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, S.; Corvaglia, L.; Aceti, A.; Vitali, F.; Faldella, G.; Galletti, S. Effect of Patent Ductus Arteriosus on Splanchnic Oxygenation at Enteral Feeding Introduction in Very Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, J.; Almodovar, M.C.; Zuk, J.; Friesen, R.H. Correlation of abdominal site near-infrared spectroscopy with gastric tonometry in infants following surgery for congenital heart disease. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 9, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.A.; Spatz, D.L. Human Milk and Infants with Congenital Heart Disease: A Summary of Current Literature Supporting the Provision of Human Milk and Breastfeeding. Adv. Neonatal Care 2019, 19, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatori, G.; Foligno, S.; Occasi, F.; Pannone, V.; Valentini, G.B.; Dall’Oglio, I.; Bagolan, P.; Dotta, A. Human milk and breastfeeding in surgical infants. Breastfeed. Med. 2014, 9, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, S.L.; Lohmann, P.; Preidis, G.A.; Gordon, P.S.; O’Donnell, A.; Hagan, J.; Venkatachalam, A.; Balderas, M.; Luna, R.A.; Hair, A.B. Improved feeding tolerance and growth are linked to increased gut microbial community diversity in very-low-birth-weight infants fed mother’s own milk compared with donor breast milk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, L.M.; Serrano, F.; Shekerdemian, L.; Ravn, H.B.; Guffey, D.; Ghanayem, N.S.; Monteiro, S. Impact of feeding mode on neurodevelopmental outcome in infants and children with congenital heart disease. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2019, 14, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.A.; Fiorotto, M.L.; Suryawan, A. Bolus vs. continuous feeding to optimize anabolism in neonates. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, A.H.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Rosenthal, G.L. Arch intervention following stage 1 palliation in hypoplastic left heart syndrome is associated with slower feed advancement: A report from the National Pediatric Quality Cardiology Improvement Collaborative. Cardiol. Young 2020, 30, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slicker, J.; Hehir, D.A.; Horsley, M.; Monczka, J.; Stern, K.W.; Roman, B.; Ocampo, E.C.; Flanagan, L.; Keenan, E.; Lambert, L.M.; et al. Nutrition Algorithms for Infants with Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome; Birth through the First Interstage Period. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2013, 8, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Matisoff, A.; Deutsch, N.; Sandler, A.; Kane, T.; Petrosyan, M. A Team-Based Approach for Children with Congenital Cardiac Disease Undergoing Antireflux Procedure with Gastrostomy. Am. Surg. 2021, 87, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beers, K.M.; Bettenhausen, A.; Prihoda, T.J.; Calhoon, J.H.; Husain, S.A. Gastrostomy Tube Placement in Neonates Undergoing Congenital Heart Surgery: A Novel Assessment for Improving Utilization and Timing of Placement. World J. Pediatr. Congenit. Heart Surg. 2021, 12, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuluaga, M.T. Chylothorax after surgery for congenital heart disease. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2012, 24, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mery, C.M.; Moffett, B.S.; Khan, M.S.; Zhang, W.; Guzmán-Pruneda, F.A.; Fraser, C.D., Jr.; Cabrera, A.G. Incidence and treatment of chylothorax after cardiac surgery in children: Analysis of a large multi-institution database. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 678–686.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, K.M.; Saxena, A.K. Surgical chylothorax in neonates: Management and outcomes. World J. Pediatr. 2018, 14, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, L.; Springer, T.; Nieschke, K.; Kostelka, M.; Dähnert, I. ChyloBEST: Chylothorax in Infants and Nutrition with Low-Fat Breast Milk. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2020, 41, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiLauro, S.; Russell, J.; McCrindle, B.W.; Tomlinson, C.; Unger, S.; O’Connor, D.L. Growth of cardiac infants with post-surgical chylothorax can be supported using modified fat breast milk with proactive nutrient-enrichment and advancement feeding protocols; an open-label trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 38, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Geragotellis, A.; Singh, G.K.; Verma, D.; Ansari, D.M.; Tarmahomed, A.; Whitehall, E.; Lowe, N.; Ashry, A.; Harky, A. Vocal cord palsy as a sequela of paediatric cardiac surgery—A review. Cardiol. Young 2021, 31, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzell, S.; Joseph, R.; Ongkasuwan, J.; Bedwell, J.; Shin, J.; Raol, N. Outcomes of Vocal Fold Motion Impairment and Dysphagia after Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery: A Systematic Review. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitting, R.; Marino, L.; Macrae, D.; Shastri, N.; Meyer, R.; Pathan, N. Nutritional status and clinical outcome in postterm neonates undergoing surgery for congenital heart disease. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 16, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medoff-Cooper, B.; Ravishankar, C. Nutrition and growth in congenital heart disease: A challenge in children. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2013, 28, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fu, W.; Yang, Y.; Latour, J.M. Implementation of an Evidence-Based Guideline of Enteral Nutrition for Infants with Congenital Heart Disease: A Controlled Before-And-After Study. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 21, e369–e377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Shi, Z.; Yao, R.; Wang, D.; Tang, S. Maternal factors and preoperative nutrition in children with mild cases of congenital heart disease. Jpn. J. Nurs. Sci. 2019, 16, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.B.; Brown, D.W.; Lihn, S.; Mangeot, C.; Bates, K.E.; Van Bergen, A.H.; Rudd, N.A.; Hanke, S.; Tweddell, J.; Lannon, C. Power of a Learning Network in Congenital Heart Disease. World J. Pediatr. Congenit. Heart Surg. 2019, 10, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| “Red Flags” |
|---|
| • Hypotension during inotropes infusion |
| • Acute respiratory distress |
| • Apnoea (>2 within 2 h associated to respiratory distress and worsening) |
| • Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation |
| • Severe acidosis (pH < 7.15 for >2 h; EB > 10 mmol/L) |
| • Persistent hypoxia (PaO2 < 40 for >2 h) |
| • Clinical abdomen signs of suspected NEC |
| • Bile-colored vomiting or gastric drainage |
| • Blood in the stool/absence of stool |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salvatori, G.; De Rose, D.U.; Massolo, A.C.; Patel, N.; Capolupo, I.; Giliberti, P.; Evangelisti, M.; Parisi, P.; Toscano, A.; Dotta, A.; et al. Current Strategies to Optimize Nutrition and Growth in Newborns and Infants with Congenital Heart Disease: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071841
Salvatori G, De Rose DU, Massolo AC, Patel N, Capolupo I, Giliberti P, Evangelisti M, Parisi P, Toscano A, Dotta A, et al. Current Strategies to Optimize Nutrition and Growth in Newborns and Infants with Congenital Heart Disease: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(7):1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071841
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalvatori, Guglielmo, Domenico Umberto De Rose, Anna Claudia Massolo, Neil Patel, Irma Capolupo, Paola Giliberti, Melania Evangelisti, Pasquale Parisi, Alessandra Toscano, Andrea Dotta, and et al. 2022. "Current Strategies to Optimize Nutrition and Growth in Newborns and Infants with Congenital Heart Disease: A Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 7: 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071841
APA StyleSalvatori, G., De Rose, D. U., Massolo, A. C., Patel, N., Capolupo, I., Giliberti, P., Evangelisti, M., Parisi, P., Toscano, A., Dotta, A., & Di Nardo, G. (2022). Current Strategies to Optimize Nutrition and Growth in Newborns and Infants with Congenital Heart Disease: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(7), 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071841







