Coronary Malperfusion Secondary to Acute Type A Aortic Dissection: Surgical Management Based on a Modified Neri Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
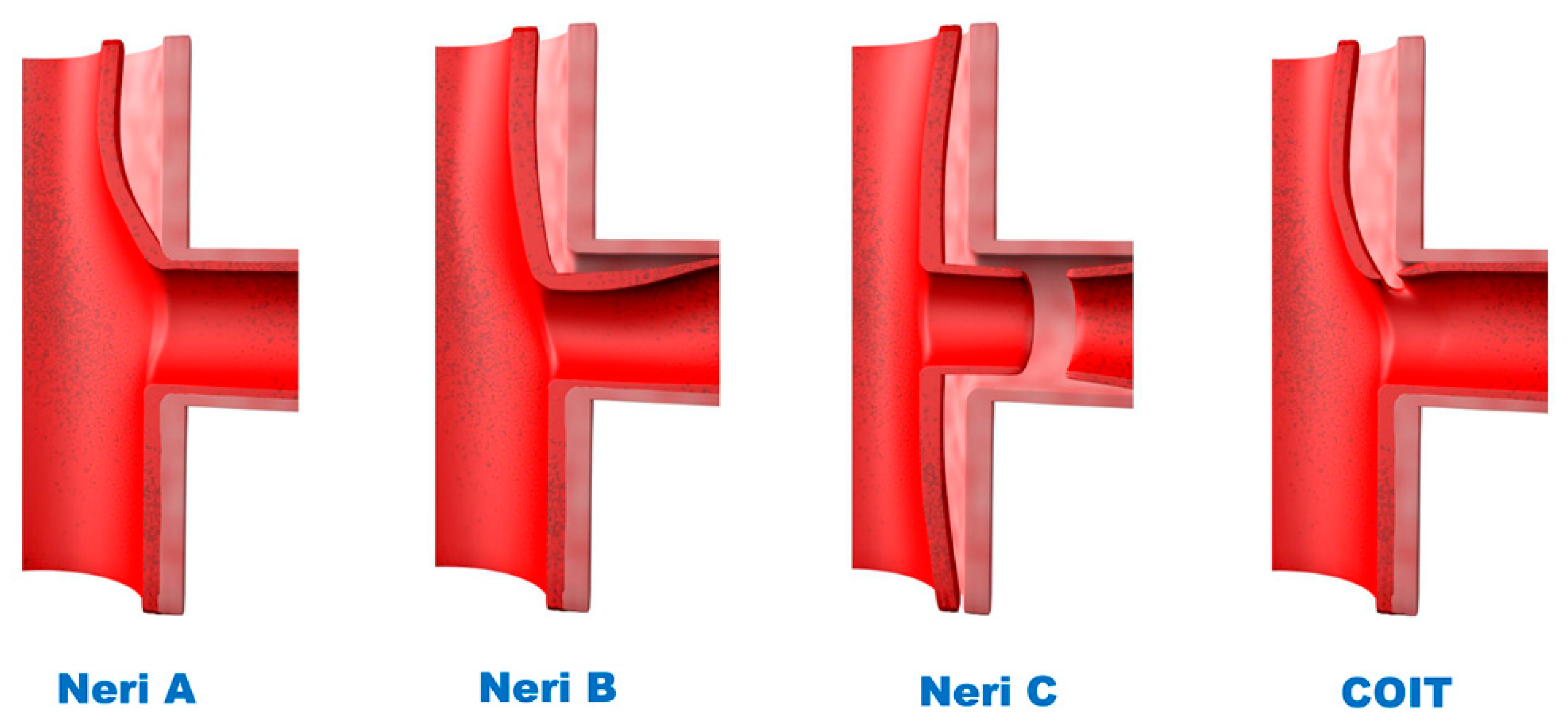
2.2. Classification of CM
2.3. Surgical Technique
2.4. Myocardial Protection and CA Repair
2.5. Clinical Endpoints
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pre- and Intraoperative Characteristics of the Entire Cohort
3.2. Outcomes of the Entire Cohort
3.3. Pre- and Intraoperative Characteristics of the CM Patients
3.4. In-Hospital Outcomes of the CM Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hagan, P.G.; Nienaber, C.A.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Bruckman, D.; Karavite, D.J.; Russman, P.L.; Evangelista, A.; Fattori, R.; Suzuki, T.; Oh, J.K.; et al. The International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD): New insights into an old disease. JAMA 2000, 283, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaisrie, S.C.; Szeto, W.Y.; Halas, M.; Girardi, L.N.; Coselli, J.S.; Sundt, T.M., III; Chen, E.P.; Fischbein, M.P.; Gleason, T.G.; Okita, Y.; et al. 2021 The American Association for Thoracic Surgery expert consensus document: Surgical treatment of acute type A aortic dissection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 162, 735–758.e732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerny, M.; Schoenhoff, F.; Etz, C.; Englberger, L.; Khaladj, N.; Zierer, A.; Weigang, E.; Hoffmann, I.; Blettner, M.; Carrel, T.P. The Impact of Pre-Operative Malperfusion on Outcome in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection: Results From the GERAADA Registry. J. Am. Coll Cardiol. 2015, 65, 2628–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirst, A.E., Jr.; Johns, V.J., Jr.; Kime, S.W., Jr. Dissecting aneurysm of the aorta: A review of 505 cases. Medicine 1958, 37, 217–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreibich, M.; Bavaria, J.E.; Branchetti, E.; Brown, C.R.; Chen, Z.; Khurshan, F.; Siki, M.; Vallabhajosyula, P.; Szeto, W.Y.; Desai, N.D. Management of Patients With Coronary Artery Malperfusion Secondary to Type A Aortic Dissection. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 107, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, E.; Toscano, T.; Papalia, U.; Frati, G.; Massetti, M.; Capannini, G.; Tucci, E.; Buklas, D.; Muzzi, L.; Oricchio, L.; et al. Proximal aortic dissection with coronary malperfusion: Presentation, management, and outcome. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2001, 121, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahito, K.; Adachi, H.; Murata, S.; Yamaguchi, A.; Ino, T. Coronary malperfusion due to type A aortic dissection: Mechanism and surgical management. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2003, 76, 1471–1476; discussion 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Chien, T.M.; Yu, C.P.; Ho, K.J.; Wen, H.; Li, W.Y.; Chen, C.W.; Huang, J.W.; Hsieh, C.C.; Chen, H.M.; et al. Acute aortic dissection type A with acute coronary involvement: A novel classification. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 4063–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imoto, K.; Uchida, K.; Karube, N.; Yasutsune, T.; Cho, T.; Kimura, K.; Masuda, M.; Morita, S. Risk analysis and improvement of strategies in patients who have acute type A aortic dissection with coronary artery dissection. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2013, 44, 419–425; discussion 424–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Variables | Total (n = 1018) | CM (n = 137) | No CM (n = 881) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | ||||
| Age (mean ± SD) | 50.5 ± 10.8 | 50.3 ± 11 | 50.5 ± 10.7 | 0.799 |
| Male (%) | 855 (84.0) | 116 (84.7) | 739 (83.9) | 0.815 |
| Cardiogenic shock(%) | 127 (12.5) | 41 (29.9) | 86 (9.8) | <0.001 |
| Tamponade/blood effusion | 122 (12.0) | 23 (16.8) | 99 (11.2) | 0.067 |
| Hypertension (%) | 617 (60.0) | 93(67.9) | 524 (59.5) | 0.061 |
| Connective tissue disorder | 46 (4.5) | 5(3.6) | 41 (4.7) | 0.825 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 23 (2.3) | 3(2.3) | 20 (2.3) | 1.000 |
| Smoking (%) | 182 (17.9) | 30 (21.9) | 152 (17.3) | 0.187 |
| History of stroke (%) | 60 (5.9) | 8 (5.8) | 52 (5.9) | 0.977 |
| Coronary heart disease (%) | 75 (7.4) | 16 (11.7) | 59 (6.7) | 0.038 |
| Chronic renal dysfunction (%) | 20 (2.0) | 3 (2.2) | 17 (1.9) | 0.743 |
| History of heart/aortic surgery (%) | 50 (4.9) | 8 (5.8) | 42 (4.8) | 0.589 |
| Atrial fibrillation (%) | 9 (0.9) | 1 (0.7) | 8 (0.9) | 1.000 |
| COPD (%) | 18 (1.8) | 2 (1.5) | 16 (1.8) | 1.000 |
| Malperfuison | ||||
| Cerebral (%) | 46 (4.5) | 4 (2.9) | 42 (4.8) | 0.505 |
| Renal (%) | 201 (19.7) | 28 (20.4) | 173 (19.6) | 0.827 |
| Gastrointestinal (%) | 60 (5.9) | 7 (5.1) | 53 (6.0) | 0.675 |
| Iliofemoral (%) | 39 (3.8) | 2 (1.5) | 37 (4.2) | 0.152 |
| Spinal (%) | 14 (1.4) | 2 (1.5) | 12 (1.4) | 1.000 |
| Variables | Total (n = 1018) | CM (n = 137) | No CM (n = 881) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proximal repair | ||||
| Supracoronary aortic replacemnt (%) | 311 (30.6) | 16 (11.7) | 295 (33.5) | <0.001 |
| Commissure suspension (%) | 249 (24.5) | 22 (16.2) | 227 (25.8) | 0.015 |
| AVR + supracoronary aortic replacement (%) | 16 (1.6) | 3 (2.2) | 13 (1.5) | 0.465 |
| Root replacement (%) | 351 (34.5) | 78 (56.9) | 273 (31.0) | <0.001 |
| sinus replacement with neomedia (%) | 37(3.6) | 8 (5.8) | 29 (3.3) | 0.138 |
| V-SARR (%) | 55 (5.4) | 11 (8.0) | 44 (5.0) | 0.013 |
| CABG (%) | 62 (7.3) | 36 (26.3) | 26 (3.6) | <0.001 |
| Arch vessels reconstruction, n (%) | ||||
| branched graft (%) | 694 (68.2) | 119 (86.9) | 575 (65.3) | <0.001 |
| En-bloc (%) | 323 (31.7) | 18 (13.1) | 305 (34.6) | <0.001 |
| FET (%) | 999 (98.1) | 137 (100) | 862 (97.8) | 0.083 |
| Time/Temperature | ||||
| CPB time (mean ± SD) | 246.1 ± 66.6 | 273.6 ± 78.8 | 241.863.5 | <0.001 |
| Aortic cross-clamp time (mean ± SD) | 131.3 ± 43.9 | 151.1 ± 48.5 | 128.242.3 | <0.001 |
| HCA time (mean ± SD) | 22.1 ± 8.4 | 21.2 ± 7.3 | 22.2 ± 8.6 | 0.198 |
| Lowest HCA temperature (mean ± SD) | 22.5 ± 3.4 | 22.3 ± 2.7 | 22.5 ± 3.5 | 0.443 |
| Variables | Total (n = 1018) | CM (n = 137) | No CM (n = 881) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In hospital mortality (%) | 94 (9.2) | 25 (18.2) | 69 (7.8) | <0.001 |
| ECMO (%) | 35 (3.4) | 15 (10.9) | 20 (2.3) | <0.001 |
| New stroke (%) | 67 (6.6) | 10 (7.3) | 57 (6.5) | 0.716 |
| Revisiting for bleeding (%) | 90 (8.8) | 17 (12.4) | 73 (8.3) | 0.114 |
| Mediastinitis (%) | 11 (1.1) | 2 (1.5) | 9 (1.0) | 0.650 |
| Paraplagia (%) | 23 (2.3) | 8 (5.8) | 15 (1.7) | 0.002 |
| CRRT (%) | 222 (21.8) | 41 (29.9) | 181 (20.5) | 0.013 |
| Tracheostomy (%) | 31 (3.0) | 6 (4.4) | 25 (2.8) | 0.329 |
| Times | ||||
| Ventilation time, d, (median [IQR]) | 4.0 [2.0, 7.0] | 5.0 [3.0, 7.5] | 4.0 [2.0, 7.0] | 0.200 |
| ICU stay, d, (median [IQR]) | 8.0 [5.0, 13.0] | 9.0 [6.0, 15.0] | 8.0 [5.0, 12.0] | 0.119 |
| Hospital stay, d, (median [IQR]) | 22.0 [17.0, 30.0] | 21.0 [14.0, 30.0] | 22.0 [17.0, 30.0] | 0.147 |
| Variables | Overall (n = 137) | Neri A (n = 68) | Neri B (n = 43) | Neri C (n = 15) | COIT a (n = 11) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | ||||||
| Age, year (median [IQR]) | 51.0 [45.0, 57.0] | 52.5 [46.0, 57.0] | 50.0 [41.0, 56.0] | 51.0 [48.0, 57.0] | 56.0 [39.0, 63.0] | 0.747 |
| Male (%) | 116 (84.7) | 56 (82.4) | 38 (88.4) | 13 (81.8) | 9 (81.8) | 0.837 |
| Hypertension (%) | 93 (67.9) | 47 (69.1) | 34 (79.1) | 8 (53.3) | 4 (36.4) | 0.029 |
| Connective tissue disorder (%) | 5 (3.6) | 2 (2.9) | 1 (2.3) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (18.2) | 0.058 |
| Smoking (%) | 107 (78.1) | 56 (82.4) | 31 (72.1) | 10 (66.7) | 10 (90.9) | 0.281 |
| CAD (%) | 16 (11.7) | 7 (10.3) | 6 (14.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (27.3) | 0.178 |
| CA malperfusion | ||||||
| Isolated left (%) | 10 (7.3) | 5 (7.4) | 4 (9.3) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (9.1) | 0.685 |
| Isolated right (%) | 99 (72.3) | 45 (66.2) | 32 (74.4) | 12 (80.0) | 10 (90.9) | 0.294 |
| Bilateral (%) | 28 (20.4) | 18 (26.5) b | 7 (16.3) c | 3 (20.0) d | 0 (0.0) | 0.187 |
| Other system malperfusion | ||||||
| Cerebral (%) | 4 (2.9) | 2 (2.9) | 2 (4.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.744 |
| Renal (%) | 28 (20.4) | 17 (25.0) | 5 (11.6) | 5 (40.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.026 |
| Gastrointestinal (%) | 7 (5.1) | 4 (5.9) | 3 (7.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.616 |
| Iliofemoral (%) | 2 (1.5) | 1 (1.5) | 1 (2.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.894 |
| Spinal (%) | 2 (1.5) | 2 (2.9) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.560 |
| Shock/Hypotension (%) | 41 (31.5) | 20 (29.4) | 10 (23.3) | 7 (46.7) | 4 (36.4) | 0.370 |
| Tamponade (%) | 23 (16.8) | 13 (19.1) | 5 (11.6) | 3 (20.0) | 2 (18.2) | 0.751 |
| Moderate to severe AI (%) | 36 (26.3) | 18 (26.5) | 10 (23.3) | 4 (26.7) | 2 (36.4) | 0.854 |
| Variables | Overall (n = 137) | Neri A (n = 68) | Neri B (n = 43) | Neri C (n = 15) | COIT (n = 11) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coronary repair, n (%) | ||||||
| Successful repair | 105 (76.6) | 67 (98.5) | 31 (72.1) | 2 (13.3) | 5 (45.5) | <0.0001 |
| Successful coronary orifice repair | 74 (54.0) | 46 (67.6) | 21 (48.8) b | 2 (13.3) a | 5 (45.5) | <0.0001 |
| Successful ST junction repair | 31 (22.6) | 21 (30.9) | 10 (23.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.016 |
| Failed repair/CABG conversion | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.3) c | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.532 |
| Primary CABG | 35 (25.5) | 1 (1.5) | 13 (30.2) | 15 (100.0) | 6 (54.5) | <0.0001 |
| Proximal repair, n (%) | ||||||
| Supracoronary aortic replacement | 16 (11.7) | 8 (11.8) | 7 (16.3) | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0.440 |
| Sinus replacement with neomedia | 8 (5.8) | 4 (5.9) | 4 (9.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.466 |
| Aortic valve resuspension | 21 (15.3) | 19 (27.9) | 2 (4.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | <0.0001 |
| Aortic root replacement | 78 (56.9) | 31 (45.6) | 25 (58.1) | 13 (86.7) | 9(81.8) | 0.008 |
| AVR + supracoronary aortic replacement | 3 (2.2) | 1 (1.5) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0.611 |
| V-SARR | 11 (8.0) | 5 (7.4) | 4 (9.3) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (18.2) | 0.394 |
| Arch vessels reconstruction, n (%) | ||||||
| branched graft (%) | 18 (13.1) | 6 (11.8) | 7 (16.3) | 2 (13.3) | 1 (9.1) | 0.887 |
| En-bloc (%) | 119 (86.9) | 60 (88.2) | 36 (83.7) | 13 (86.7) | 10 (90.9) | 0.887 |
| FET | 137 (100) | 66 (100) | 44 (100) | 20 (100) | 7 (100) | - |
| Time/Temperature | ||||||
| CPB time, min (mean ± SD) | 273.6 ± 78.8 | 243.2 ± 46.7 | 298.0 ± 95.2 | 297.6 ± 86.6 | 333.2 ± 88.0 | <0.0001 |
| ACC time, min (median [IQR]) | 151 [117, 175] | 138 [114.25, 164.75] | 158 [126, 196] | 157 [116, 184] | 175 [138, 199] | 0.024 |
| HCA time, min (median [IQR]) | 21 [17, 25] | 20 [17, 26.75] | 21 [18, 25] | 20 [15, 23] | 22 [19, 25] | 0.837 |
| Lowest HCA temperature, °C (median [IQR]) | 22.5 [20.55, 24] | 22.6 [20.625, 23.8] | 22.6 [20.9, 24.3] | 21.8 [18.7, 23.6] | 22.5 [20.5, 24.3] | 0.697 |
| Variables | Overall (n = 137) | Neri A (n = 68) | Neri B (n = 43) | Neri C (n = 15) | COIT (n = 11) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
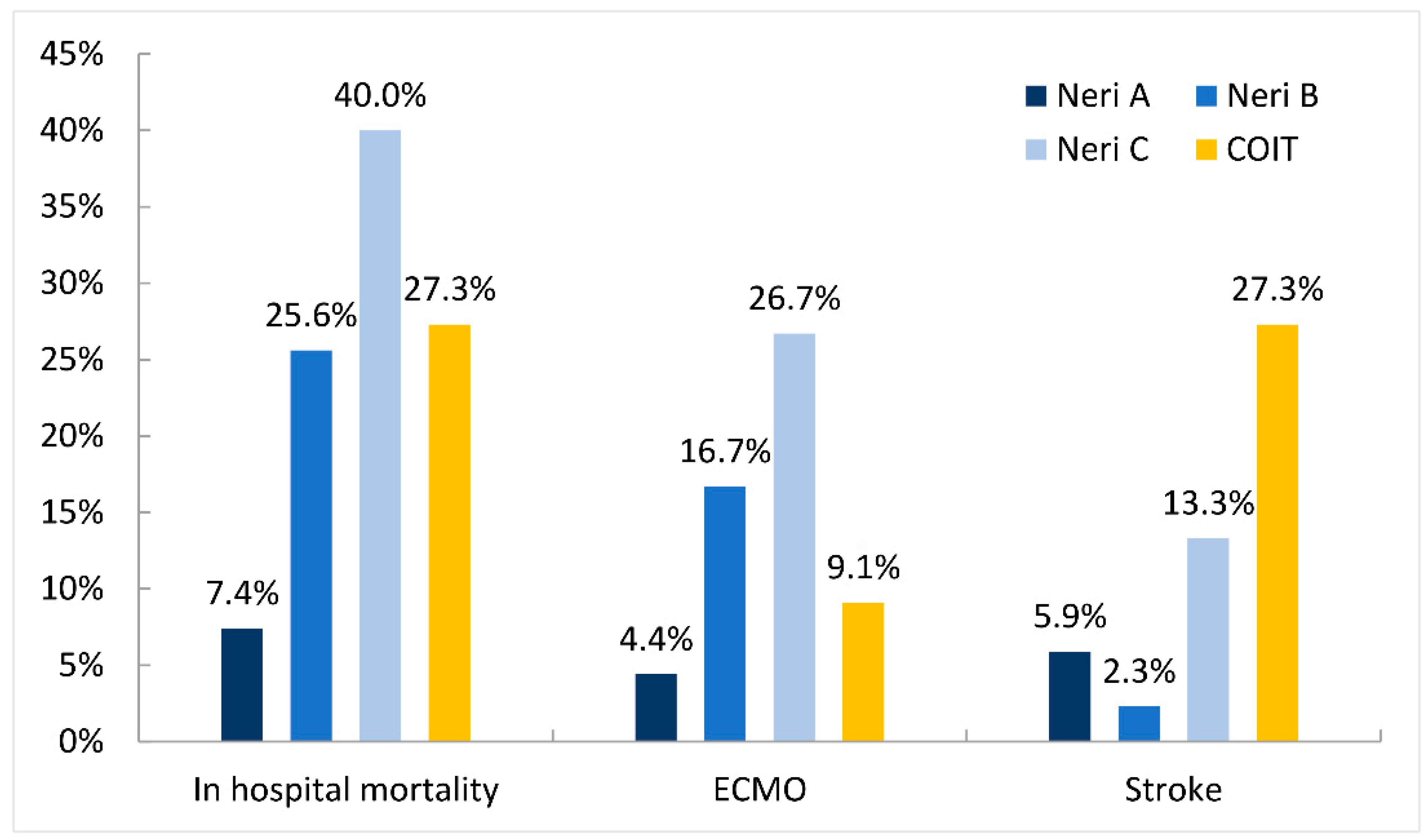
| In hospital mortality, n (%) | 25 (18.2) | 5 (7.4) | 11 (25.6) | 6 (40.0) | 3 (27.3) | 0.006 |
| ECMO, n (%) | 15 (10.9) | 3 (4.4) | 7 (16.7) | 4 (26.7) | 1 (9.1) | 0.045 |
| New Stroke, n (%) | 10 (7.3) | 4 (5.9) | 1 (2.3) | 2 (13.3) | 3 (27.3) | 0.028 |
| Revisit for bleeding, n (%) | 17 (12.4) | 5 (7.4) | 6 (14.0) | 3 (20.0) | 3 (27.3) | 0.193 |
| Mediastinitis, n (%) | 2 (1.5) | 1 (1.5) | 1 (2.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.894 |
| Paraplegia, n (%) | 8 (5.8) | 3 (4.4) | 3 (7.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (18.2) | 0.228 |
| CRRT, n (%) | 41 (29.9) | 19 (27.9) | 12 (27.9) | 7 (46.7) | 3 (27.3) | 0.522 |
| Tracheostomy, n (%) | 6 (4.4) | 4 (5.9) | 1 (2.3) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (9.1) | 0.558 |
| Composite adverse events, n (%) | 60 (43.8) | 25 (36.8) | 19 (44.2) | 10 (66.7) | 6 (54.5) | 0.167 |
| Ventilation time, d (median [IQR]) | 5.0 [3.0, 7.0] | 5.0 [2.25, 7.0] | 5 [3.0, 8] | 6.0 [2.0, 12.0] | 4.0 [2.0, 6.0] | 0.902 |
| ICU stay, d (median [IQR]) | 9.0 [6.0, 15.0] | 9.0 [6.0, 16.75] | 9 [5.0, 12.0] | 10.0 [4.0, 17.0] | 9.0 [6.0, 22.0] | 0.920 |
| Hospital stay, d (median [IQR]) | 21.0 [14.0, 30.0] | 18.5 [14.0, 30.0] | 22.0 [17.0, 32.0] | 17.0 [10.0, 26.0] | 25.0 [10.0, 34.0] | 0.571 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, G.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhuang, D.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Fan, R.; Sun, Z.; et al. Coronary Malperfusion Secondary to Acute Type A Aortic Dissection: Surgical Management Based on a Modified Neri Classification. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061693
Tong G, Wu J, Chen Z, Zhuang D, Zhao S, Liu Y, Yang Y, Liang Z, Fan R, Sun Z, et al. Coronary Malperfusion Secondary to Acute Type A Aortic Dissection: Surgical Management Based on a Modified Neri Classification. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(6):1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061693
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Guang, Jinlin Wu, Zerui Chen, Donglin Zhuang, Shuang Zhao, Yaorong Liu, Yongchao Yang, Zhichao Liang, Ruixin Fan, Zhongchan Sun, and et al. 2022. "Coronary Malperfusion Secondary to Acute Type A Aortic Dissection: Surgical Management Based on a Modified Neri Classification" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 6: 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061693
APA StyleTong, G., Wu, J., Chen, Z., Zhuang, D., Zhao, S., Liu, Y., Yang, Y., Liang, Z., Fan, R., Sun, Z., & Sun, T. (2022). Coronary Malperfusion Secondary to Acute Type A Aortic Dissection: Surgical Management Based on a Modified Neri Classification. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(6), 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061693





