The GenoDiabMar Registry: A Collaborative Research Platform of Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Registry
Medical Records and CV Risk Factors Assessment
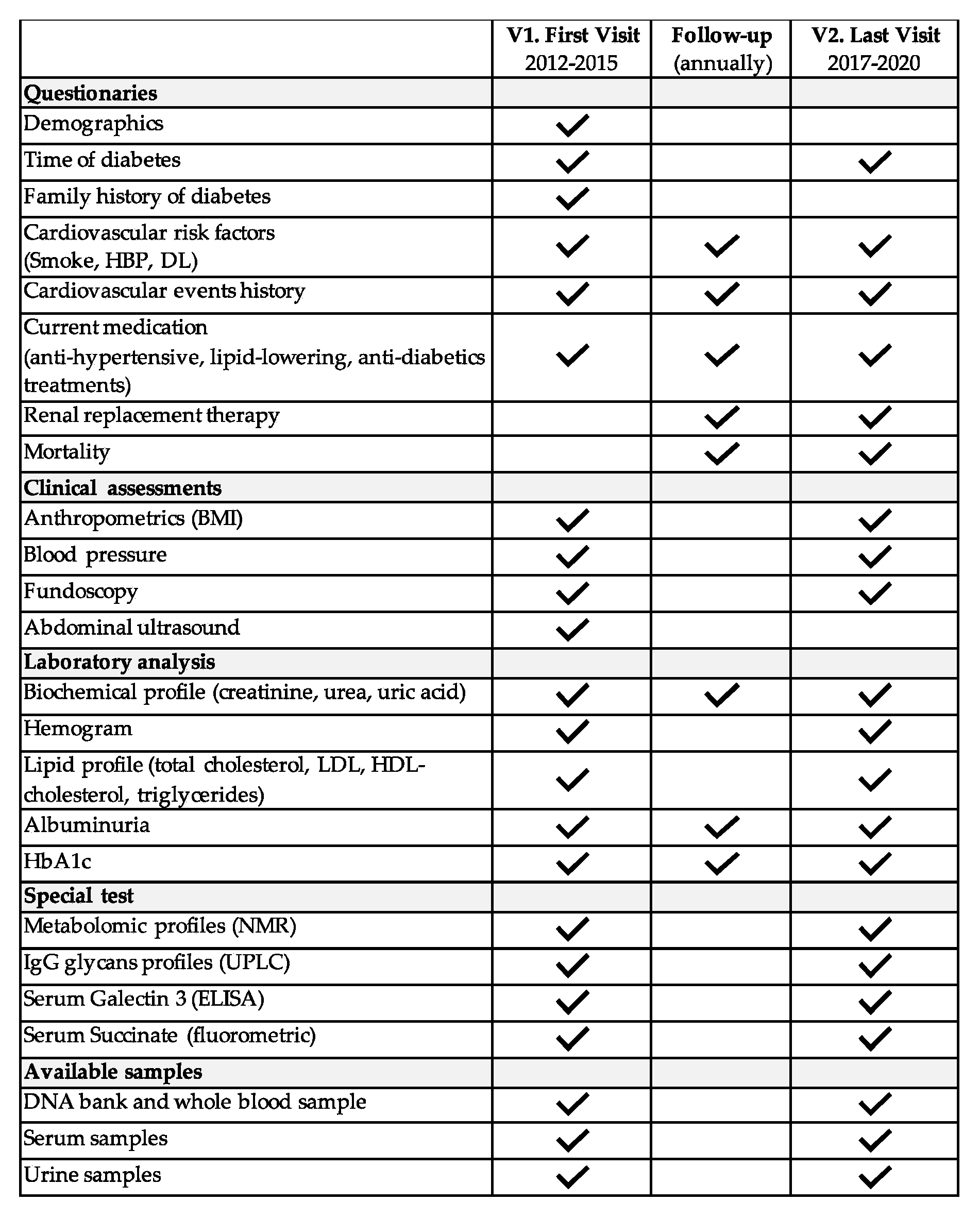
2.3. Laboratory Data and Sample Management
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
| CKD Grade | 1–2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 327 | 204 | 70 | 49 | |
| Age (years) | 67 (10) | 75 (13) | 76 (10) | 81 (22) | <0.001 |
| Time of diabetes (years) | 14 (10) | 15 (10) | 17 (12) | 14 (4) | <0.001 |
| Gender (Male/Female) (%) | 61.8/38.2 | 61.6/38.2 | 55.7/44.3 | 61.3/38.8 | 0.812 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.7 (6.8) | 30.5 (6.6) | 30.3 (7.6) | 23.4 (4) | 0.045 |
| Smokers/former smokers (%) | 24.8/34.5 | 15.2/39.2 | 4.3/45.7 | 4.1/36.7 | <0.001 |
| HBP (%) | 69.4 | 98.5 | 95.7 | 100 | <0.001 |
| Antihypertensive treatment ACEi/ARB/ACEi + ARB % | 32.7/39.7/3.1 | 35.3/45.6/2.9 | 11.4/41.4/5.7 | 14.3/49/0 | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular events history (%) | 31.5 | 46.1 | 60 | 48.9 | <0.001 |
| Ischemic cardiomyopathy | 12.8 | 26.5 | 34.3 | 28.6 | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 9.5 | 11.3 | 37.1 | 10.2 | 0.822 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 14.7 | 23 | 12.9 | 22.5 | 0.019 |
| Diabetic retinopathy (%) | 17.1 | 27.9 | 34.3 | 63.3 | <0.001 |
| Lipid-lowering therapy (statin %) | 71.8 | 80.9 | 85.7 | 85.7 | 0.002 |
| Antidiabetic treatment (%) | |||||
| Oral agents/insulin/combined | 59.3/6.1/33.9 | 43.1/28.4/26.9 | 7.3/58.6/20 | 8.1/79.6/6.1 | <0.001 |
| iDPP4/SGLT2i/GLP1-RA | 7.6/0.3/0.9 | 1.9/0.5/0.5 | 1.4/0/0 | 0/0/0 | 0.808 |
| eGFR (mL/min 71.73 m2) | 82.2 (24.1) | 42.8 (13.2) | 23.5 (19.6) | 9.14 (3.75) | <0.001 |
| Urinary albumin/creatinine (mg/g) | 9.5 (53.3) | 85.8 (434) | 465 (1574.7) | 1158 (3210.8) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 60.1 (17.9) | 60.6 (19.6) | 59.1 (19.6) | 53 (13) | 0.004 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | |||||
| Total | 173 (45) | 165 (49) | 165.5 (54) | 143 (42) | <0.001 |
| LDL | 96 (36.5) | 87 (36) | 91 (42) | 71 (35) | <0.001 |
| HDL | 45 (14) | 45.2 (19) | 42 (19) | 43 (13) | 0.665 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 129 (91.7) | 144 (86) | 141 (93) | 125 (60) | 0.072 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5.4 (1.9) | 6.6 (1.7) | 7 (1.9) | 6 (0.8) | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (mg/dL) | 13.6 (2.1) | 12.6 (1.88) | 11.5 (1.45) | 12.1 (2) | <0.001 |
| First Visit 2012–2015 | Last Visit 2017–2020 | |
|---|---|---|
| N | 650 | 442 |
| Age (years) | 69 (14) | 72.9 (13) |
| Sex (male/female %) | 61.1/38.9 | 61.5/38.8 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.9 (6.8) | 29.2 (6.2) |
| Family history of diabetes (%) | 47.1 | 53.1 |
| Cardiovascular risk factors history | ||
| Smokers/former smoker (%) | 18/37.4 | 15.8/41.4 |
| High blood pressure (%) | 91.4 | 90.9 |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 77.2 | 73 |
| Cardiovascular events history (%) | 40.5 | 41.17 |
| Myocardial infarction (%) | 20.6 | 21.3 |
| Cerebrovascular disease (%) | 10.5 | 14.3 |
| Peripheral vascular disease (%) | 19.8 | 20.4 |
| Diabetic retinopathy (%) | 25.8 | 30.5 |
| Antihypertensive treatment ACEI/ARB/ACEI + ARB (%) | 29.8/40.6/2.8 | 31/37.8/2.3 |
| Others (Calcium antagonists/ß-blockers/diuretics) (%) | 78 | 80.8 |
| Lipid-lowering therapy (%) | ||
| Statins | 72.6 | 68.1 |
| Fibrates | 10.1 | 6.8 |
| Other | 3.4 | 7.8 |
| Antidiabetic treatment | ||
| Oral agents only (%) | 46.3 | 41.2 |
| DPP4i/SGLT2i/GLP1-RA (%) | 6.1/0.3/0.6 | 21/5.9/4.3 |
| Insulin only (%) | 24.3 | 21 |
| Oral agents + insulin (%) | 28.3 | 34.6 |
| Diet (%) | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.12 (0.81) | 1.11 (0.78) |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73mt2) | 60.4 (46.5) | 57.7 (46.4) |
| Urinary albumin/creatinine (mg/g) | 34.2 (217.05) | 32.6 (219.9) |
| Hemoglobin (gr/dL) | 13 (2.2) | 13.1 (2.5) |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 59.6 (18.5) | 55.2 (18.5) |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 6.1 (2.1) | 6.6 (2.5) |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 171 (48) | 162 (57) |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 94 (39) | 89 (44) |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 45 (16) | 46 (17) |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 136 (90) | 137 (90.5) |
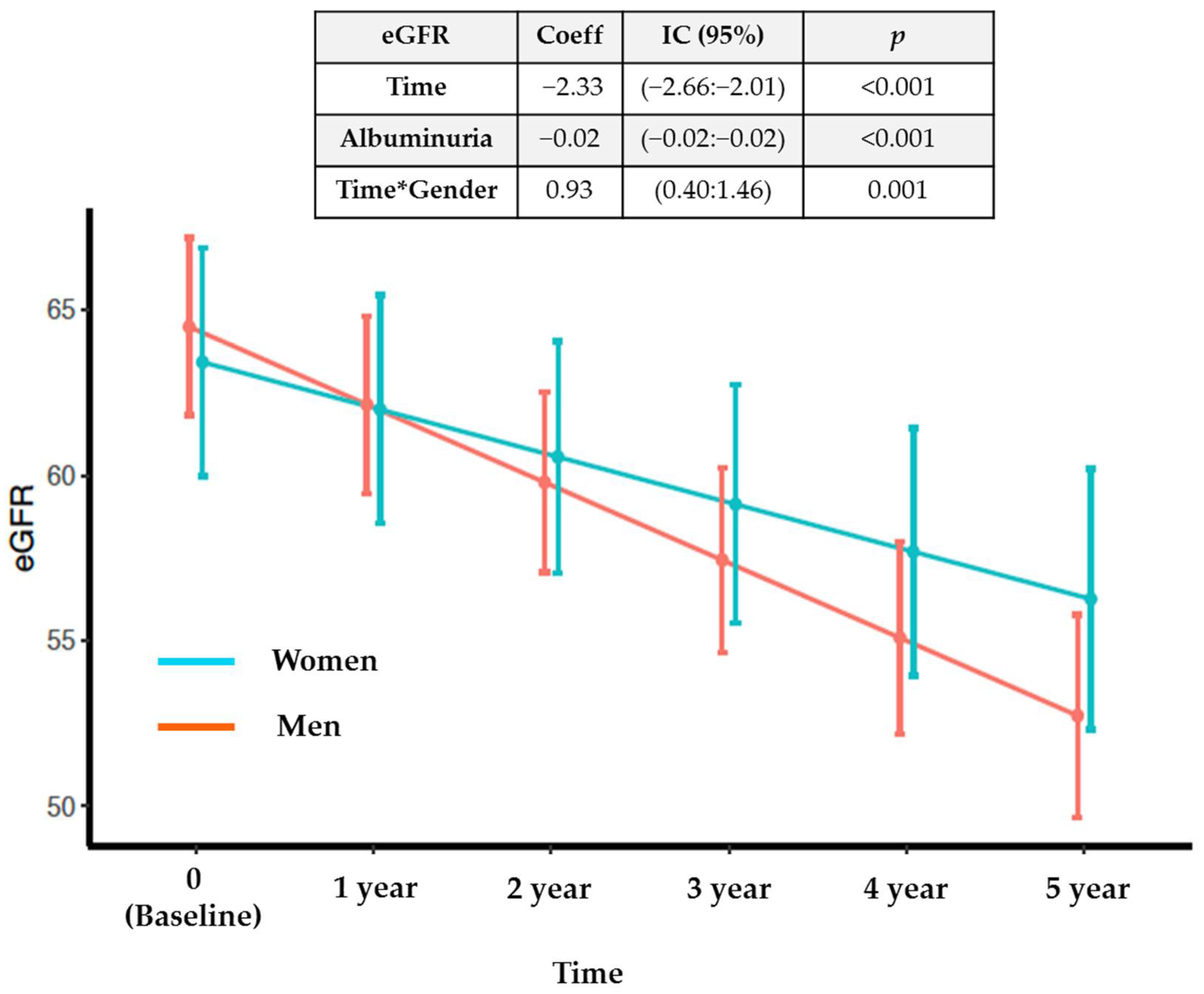
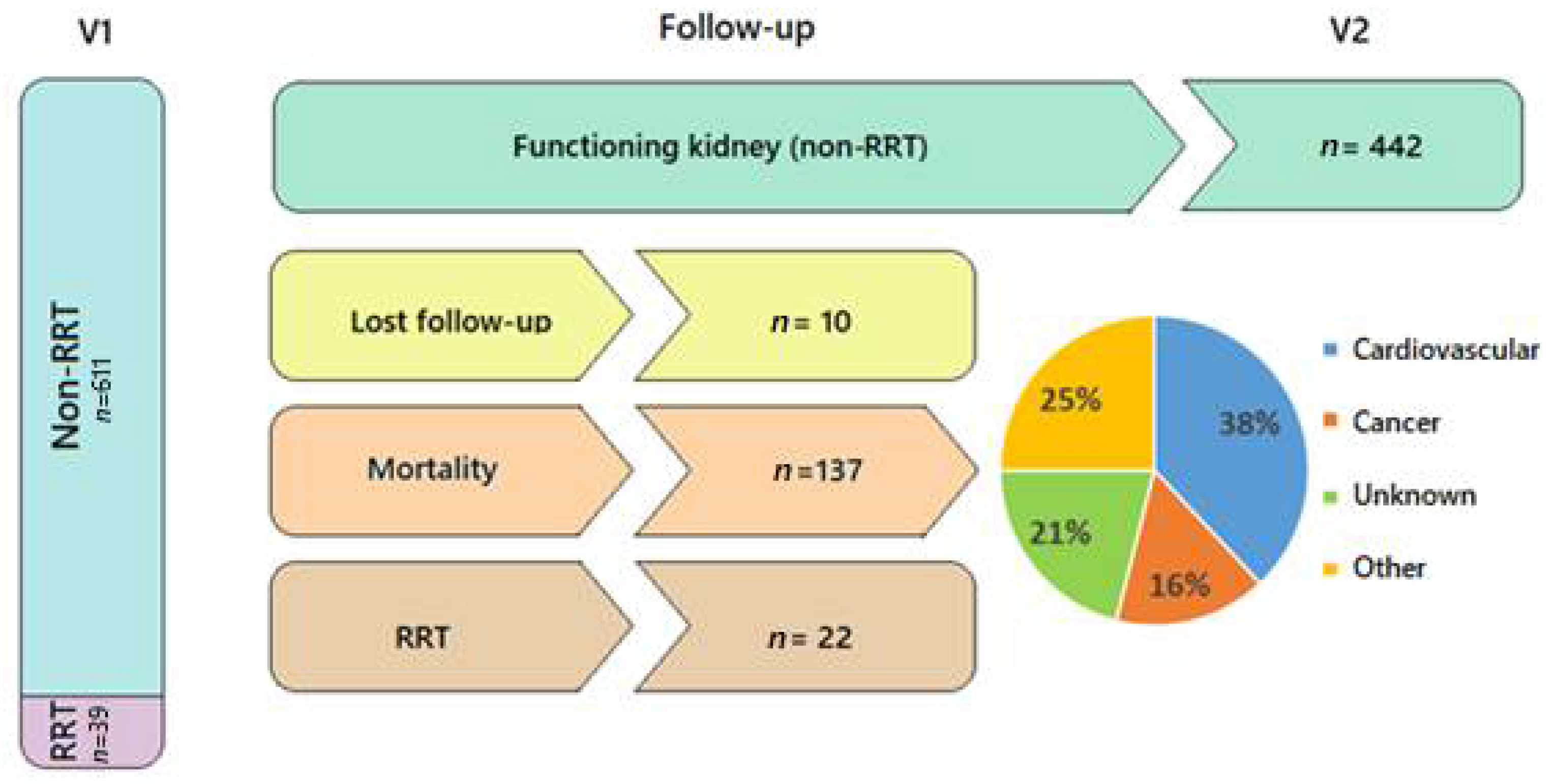
3.2. Patient Follow-Up: Renal Deterioration by Sex and Mortality
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes–Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Einarson, T.R.; Acs, A.; Ludwig, C.; Panton, U.H. Economic Burden of Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Value Health 2018, 21, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Speight, J.; Holmes-Truscott, E.; Hendrieckx, C.; Skovlund, S.; Cooke, D. Assessing the impact of diabetes on quality of life: What have the past 25 years taught us? Diabet. Med. 2019, 37, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Preston, S.H.; Choi, D.; Elo, I.T.; Stokes, A. Effect of diabetes on life expectancy in the United States by race and ethnicity. Biodemogr. Soc. Biol. 2018, 64, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaneethan, S.D.; Schold, J.D.; Jolly, S.E.; Arrigain, S.; Winkelmayer, W.C.; Nally, J.V. Diabetes Control and the Risks of ESRD and Mortality in Patients With CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 70, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, E.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Burrows, N.R.; Ali, M.K.; Rolka, D.; Williams, D.E.; Geiss, L. Changes in Diabetes-Related Complications in the United States, 1990–2010. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tancredi, M.; Rosengren, A.; Svensson, A.-M.; Kosiborod, M.; Pivodic, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Wedel, H.; Clements, M.; Dahlqvist, S.; Lind, M. Excess Mortality among Persons with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1720–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tonelli, M.; Muntner, P.; Lloyd, A.; Manns, B.J.; Klarenbach, S.; Pannu, N.; James, M.T.; Hemmelgarn, B.R. Risk of coronary events in people with chronic kidney disease compared with those with diabetes: A population-level cohort study. Lancet 2012, 380, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, C.; Pascual, J.; Otero, S.; Soler, M.J.; Rodríguez, E.; Collado, S.; Faura, A.; Mojal, S.; Navarro-González, J.; Betriu, A.; et al. Diabetic nephropathy is an independent factor associated to severe subclinical atheromatous disease. Atherosclerosis 2015, 242, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Becker, C.; Inker, L.A. Glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria for detection and staging of acute and chronic kidney disease in adults: A systematic review. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2015, 313, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inker, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Tighiouart, H.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Feldman, H.I.; Greene, T.; Kusek, J.W.; Manzi, J.; Van Lente, F.; Zhang, Y.L.; et al. Estimating Glomerular Filtration Rate from Serum Creatinine and Cystatin, C. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stevens, L.A.; Coresh, J.; Greene, T.; Levey, A.S. Assessing Kidney Function—Measured and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2473–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krolewski, A.S.; Niewczas, M.A.; Skupien, J.; Gohda, T.; Smiles, A.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Doria, A.; Warram, J.H. Early Progressive Renal Decline Precedes the Onset of Microalbuminuria and Its Progression to Macroalbuminuria. Diabetes Care 2013, 37, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferguson, T.W.; Komenda, P.; Tangri, N. Cystatin C as a biomarker for estimating glomerular filtration rate. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2015, 24, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, J.C.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.A.; Cooper, M.E. New Insights into the Use of Biomarkers of Diabetic Nephropathy. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014, 21, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G. Metabolomic biomarkers in diabetic kidney diseases—A systematic review. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, C.; Spector, T.D.; Menni, C. Blood, urine and faecal metabolite profiles in the study of adult renal disease. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 589, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekula, P.; Goek, O.-N.; Quaye, L.; Barrios, C.; Levey, A.S.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Menni, C.; Yet, I.; Gieger, C.; Inker, L.A.; et al. A Metabolome-Wide Association Study of Kidney Function and Disease in the General Population. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 27, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, C.; Beaumont, M.; Pallister, T.; Villar, J.; Goodrich, J.K.; Clark, A.; Pascual, J.; Ley, R.; Spector, T.D.; Bell, J.; et al. Gut-Microbiota-Metabolite Axis in Early Renal Function Decline. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rysz, J.; Gluba-Brzózka, A.; Franczyk, B.; Jabłonowski, Z.; Ciałkowska-Rysz, A. Novel Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease and the Prediction of Its Outcome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colhoun, H.M.; Marcovecchio, M.L. Biomarkers of diabetic kidney disease. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 996–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrios, C.; Zierer, J.; Würtz, P.; Haller, T.; Metspalu, A.; Gieger, C.; Thorand, B.; Meisinger, C.; Waldenberger, M.; Raitakari, O.; et al. Circulating metabolic biomarkers of renal function in diabetic and non-diabetic populations. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, C.; Zierer, J.; Gudelj, I.; Štambuk, J.; Ugrina, I.; Rodríguez, E.; Soler, M.J.; Pavić, T.; Šimurina, M.; Keser, T.; et al. Glycosylation Profile of IgG in Moderate Kidney Dysfunction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 27, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubin, R.F.; Rhee, E.P. Proteomics and Metabolomics in Kidney Disease, including Insights into Etiology, Treatment, and Prevention. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kidney Disease—IMIM Institut Hospital del Mar d’Investigacions Mèdiques. Available online: https://www.imim.es/programesrecerca/rct/en_nefropaties.html (accessed on 19 December 2021).
- Parc de Salut Mar’s Biobank. Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute. IMIM. Available online: https://www.imim.es/sct/biobanc/en_index.html (accessed on 19 December 2021).
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., III; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A New Equation to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E.; Bilous, R.W.; Coresh, J.; De Francisco, A.L.M.; De Jong, P.E.; Griffith, K.E.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Iseki, K.; Lamb, E.J.; et al. Kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) CKD work group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beckonert, O.; Keun, H.C.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Bundy, J.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic profiling, metabolomic and metabonomic procedures for NMR spectroscopy of urine, plasma, serum and tissue extracts. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2692–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Kettunen, J.; Würtz, P.; Haller, T.; Havulinna, A.S.; Kangas, A.; Soininen, P.; Esko, T.; Tammesoo, M.-L.; Mägi, R.; et al. Biomarker Profiling by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy for the Prediction of All-Cause Mortality: An Observational Study of 17,345 Persons. PLOS Med. 2014, 11, e1001606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinde, M.T.; Giskeødegård, G.F.; Andreassen, T.; Tessem, M.-B.; Bathen, T.F.; Moestue, S.A. Biomarker Discovery Using NMR-Based Metabolomics of Tissue. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2037, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.A.; Pereira, T.C.; Souza, A.R.; Ribeiro, P.R. 1H NMR-based metabolite profiling for biomarker identification. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 502, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T. IgG Fc Glycosylation in Human Immunity. In Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hodeib, H.; Hagras, M.M.; Abdelhai, D.; Watany, M.M.; Selim, A.; Tawfik, M.A.; Elsebaey, M.A.; Elshweikh, S.A. Galectin-3 as a prognostic biomarker for diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, S.; Habib, A.; Hussain, S.; Najmi, A.K. Potential biomarkers for early detection of diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 161, 108082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yu, D.; Mo, R.; Zhang, J.; Hua, H.; Hu, L.; Feng, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Yin, N.; et al. The Succinate Receptor GPR91 Is Involved in Pressure Overload-Induced Ventricular Hypertrophy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrienko, T.N.; Pasdois, P.; Pereira, G.; Ovens, M.J.; Halestrap, A.P. The role of succinate and ROS in reperfusion injury—A critical appraisal. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2017, 110, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mallafré, V.C.; Llauradó, G.; Keiran, N.; Benaiges, E.; Astiarraga, B.; Martínez, L.; Pellitero, S.; González-Clemente, J.M.; Rodríguez, A.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; et al. Preoperative Circulating Succinate Levels as a Biomarker for Diabetes Remission After Bariatric Surgery. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astiarraga, B.; Martínez, L.; Ceperuelo-Mallafré, V.; Llauradó, G.; Terrón-Puig, M.; Rodríguez, M.M.; Casajoana, A.; Pellitero, S.; Megía, A.; Vilarrasa, N.; et al. Impaired Succinate Response to a Mixed Meal in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Is Normalized After Metabolic Surgery. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 2581–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 6. Glycemic targets: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43 (Suppl. 1), S66–S76. [CrossRef]
- Buse, J.B.; Wexler, D.J.; Tsapas, A.; Rossing, P.; Mingrone, G.; Mathieu, C.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Davies, M.J. 2019 update to: Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2019, 63, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricardo, A.C.; Yang, W.; Sha, D.; Appel, L.J.; Chen, J.; Krousel-Wood, M.; Manoharan, A.; Steigerwalt, S.; Wright, J.; Rahman, M.; et al. Sex-Related Disparities in CKD Progression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 30, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albertus, P.; Morgenstern, H.; Robinson, B.; Saran, R. Risk of ESRD in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Mahillo, I.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, J.; Carriazo, S.; Sanz, A.B.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Ortiz, A. Gender, Albuminuria and Chronic Kidney Disease Progression in Treated Diabetic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Zanetti, K.A.; Temprosa, M.; Albanes, D.; Appel, N.; Barrera, C.B.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Boerwinkle, E.; Casas, J.P.; Clish, C.; et al. The Consortium of Metabolomics Studies (COMETS): Metabolomics in prospective cohort studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 188, 991–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unger, T.; Borghi, C.; Charchar, F.; Khan, N.A.; Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Schutte, A.E. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1334–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Patel, R.S. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Men | Women | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (IC95%) | p | OR (IC95%) | p | |
| Age | 1.01 (0.98:1.04) | 0.62 | 1.02 (0.97:1.08) | 0.48 |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 1.18 (0.61:2.23) | 0.61 | 0.99 (0.25:3.33) | 0.98 |
| Time of DM2 | 1.02 (0.99:1.06) | 0.18 | 0.97 (0.91:1.03) | 0.42 |
| BMI | 1.03 (0.96:1.10) | 0.45 | 0.97 (0.89:1.05) | 0.47 |
| Ischemic cardiopathy | 1.02 (0.53:1.88) | 0.94 | 1.16 (0.31:3.39) | 0.80 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 0.79 (0.39:1.53) | 0.49 | 3.32 (1.10:9.57) | 0.02 |
| Stroke | 1.83 (0.85:3.74) | 0.12 | 1.82 (0.38:6.21) | 0.41 |
| Albuminuria > 300 mg/g | 2.40 (1.29:4.44) | 0.005 | 0.99 (0.91:3.73) | 0.99 |
| HbA1c | 0.89 (0.71:1.11) | 0.32 | 1.14 (0.80:1.59) | 0.43 |
| Smoker | 1.03 (0.46:2.30) | 0.94 | 1.15 (0.21:4.97) | 0.86 |
| Former smoker | 0.72 (0.37:1.46) | 0.35 | 0.29 (0.02:1.62) | 0.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sierra, A.; Otero, S.; Rodríguez, E.; Faura, A.; Vera, M.; Riera, M.; Palau, V.; Durán, X.; Costa-Garrido, A.; Sans, L.; et al. The GenoDiabMar Registry: A Collaborative Research Platform of Type 2 Diabetes Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051431
Sierra A, Otero S, Rodríguez E, Faura A, Vera M, Riera M, Palau V, Durán X, Costa-Garrido A, Sans L, et al. The GenoDiabMar Registry: A Collaborative Research Platform of Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(5):1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051431
Chicago/Turabian StyleSierra, Adriana, Sol Otero, Eva Rodríguez, Anna Faura, María Vera, Marta Riera, Vanesa Palau, Xavier Durán, Anna Costa-Garrido, Laia Sans, and et al. 2022. "The GenoDiabMar Registry: A Collaborative Research Platform of Type 2 Diabetes Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 5: 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051431
APA StyleSierra, A., Otero, S., Rodríguez, E., Faura, A., Vera, M., Riera, M., Palau, V., Durán, X., Costa-Garrido, A., Sans, L., Márquez, E., Poposki, V., Franch-Nadal, J., Mundet, X., Oliveras, A., Crespo, M., Pascual, J., & Barrios, C. (2022). The GenoDiabMar Registry: A Collaborative Research Platform of Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(5), 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051431







