Liquid Biopsy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management: Building Specific Biosignatures via Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. ccfDNA Levels in T2DM Patients and Healthy Volunteers
2.2. ccfDNA Fragment Size Analysis in T2DM Patients and Healthy Volunteers
2.3. Methylation Analysis of β-Cell-Specific Genes
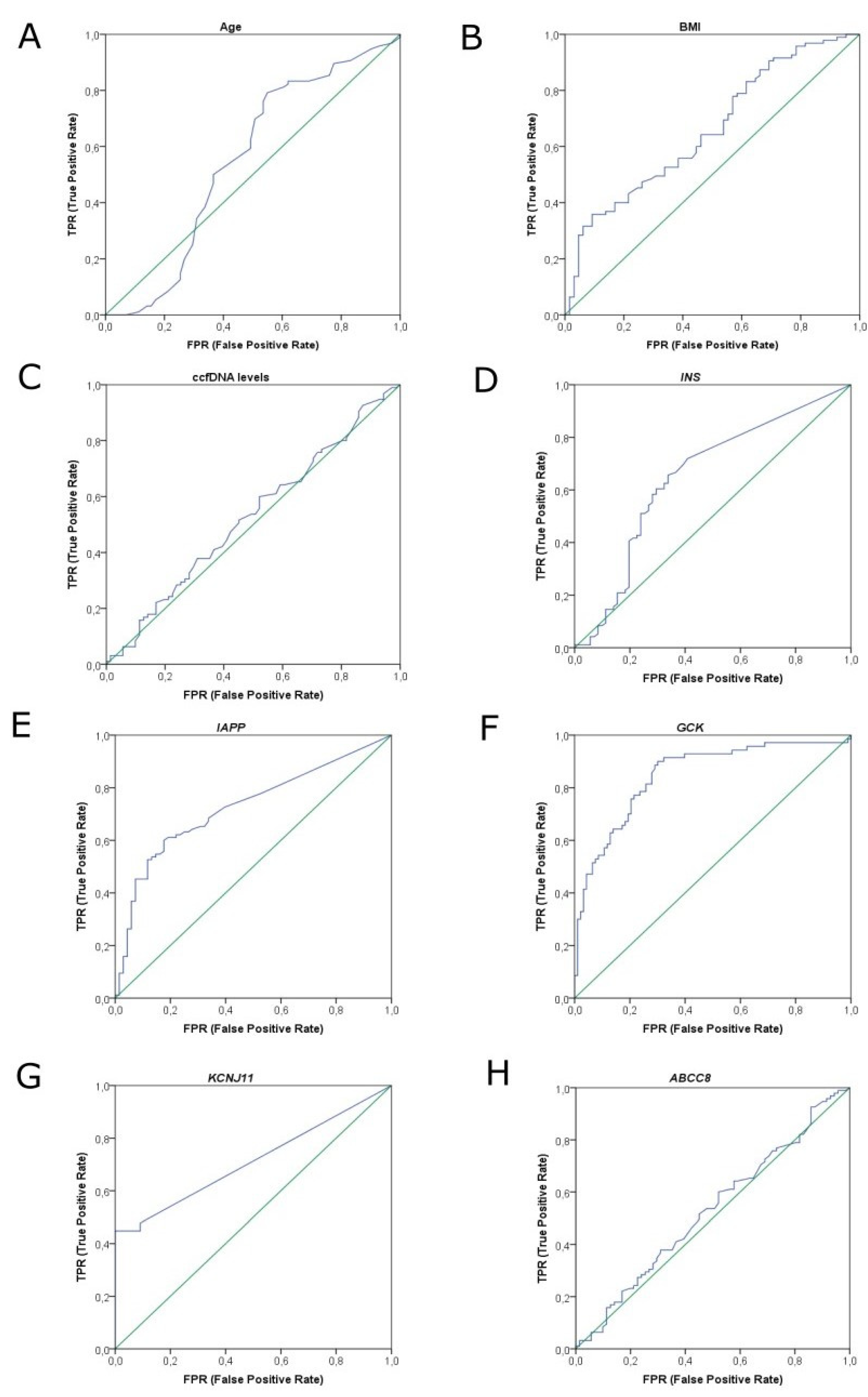
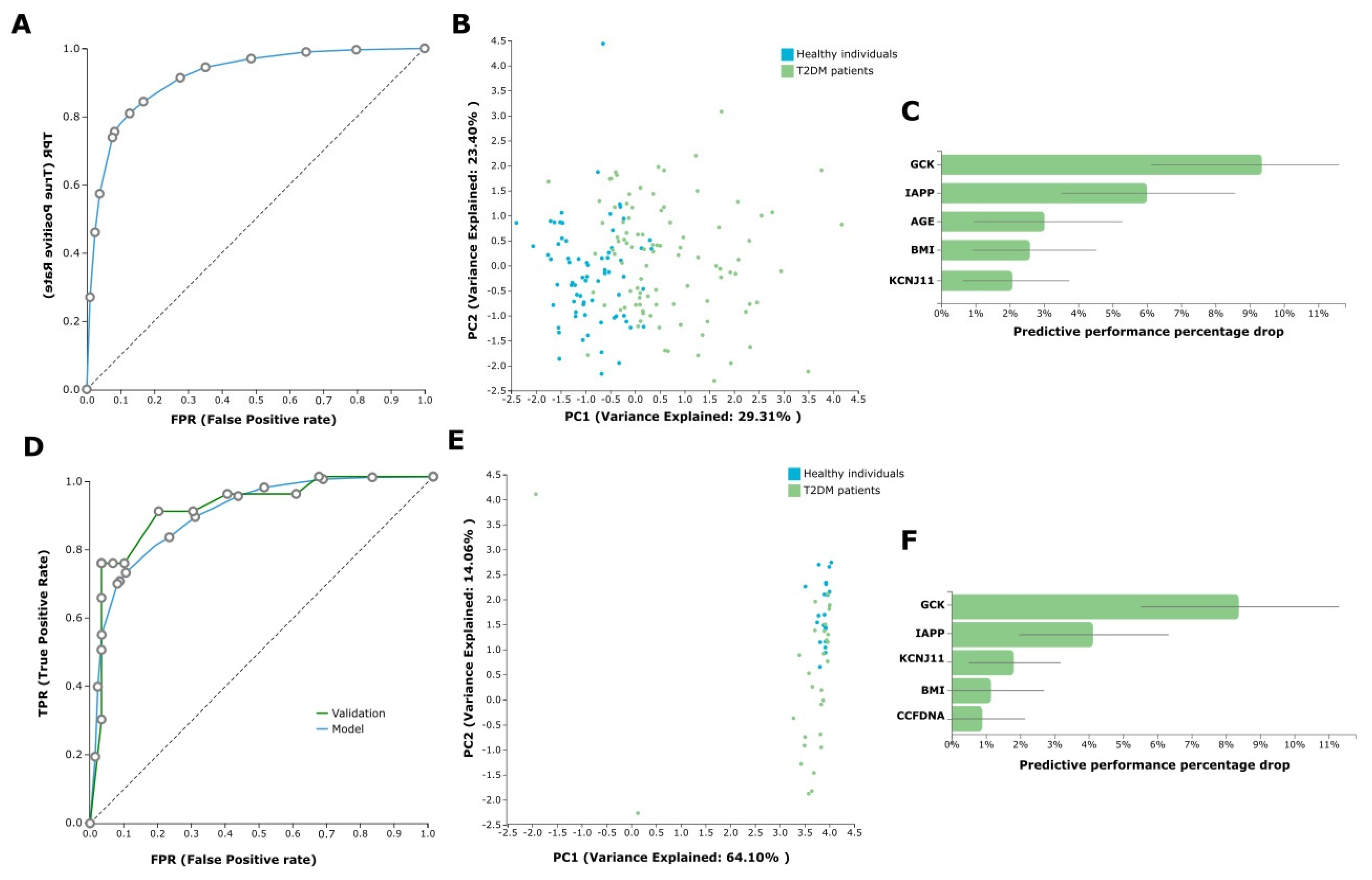
2.4. AutoML Predictive Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Groups and Serum Sampling
4.2. Direct Quantification of ccfDNA
4.3. ccfDNA Isolation
4.4. Capillary Electrophoresis of Extracted ccfDNA
4.5. Methylation Analysis
4.6. Statistics
4.7. AutoML Predictive Modelling with JADBio
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharroubi, A.T.; Darwish, H.M. Diabetes mellitus: The epidemic of the century. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 850–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahier, J.; Guiot, Y.; Goebbels, R.M.; Sempoux, C.; Henquin, J.C. Pancreatic beta-cell mass in European subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2008, 10 (Suppl. S4), 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.E.; Janson, J.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Ritzel, R.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akirav, E.M.; Lebastchi, J.; Galvan, E.M.; Henegariu, O.; Akirav, M.; Ablamunits, V.; Lizardi, P.M.; Herold, K.C. Detection of beta cell death in diabetes using differentially methylated circulating DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19018–19023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husseiny, M.I.; Kaye, A.; Zebadua, E.; Kandeel, F.; Ferreri, K. Tissue-specific methylation of human insulin gene and PCR assay for monitoring beta cell death. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, K.C.; Usmani-Brown, S.; Ghazi, T.; Lebastchi, J.; Beam, C.A.; Bellin, M.D.; Ledizet, M.; Sosenko, J.M.; Krischer, J.P.; Palmer, J.P.; et al. beta cell death and dysfunction during type 1 diabetes development in at-risk individuals. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.A.; Kenna, L.A.; Spelios, M.G.; Hessner, M.J.; Akirav, E.M. Circulating Differentially Methylated Amylin DNA as a Biomarker of beta-Cell Loss in Type 1 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklenarova, J.; Petruzelkova, L.; Kolouskova, S.; Lebl, J.; Sumnik, Z.; Cinek, O. Glucokinase Gene May Be a More Suitable Target Than the Insulin Gene for Detection of beta Cell Death. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2058–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lehmann-Werman, R.; Neiman, D.; Zemmour, H.; Moss, J.; Magenheim, J.; Vaknin-Dembinsky, A.; Rubertsson, S.; Nellgard, B.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Identification of tissue-specific cell death using methylation patterns of circulating DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1826–E1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani-Brown, S.; Lebastchi, J.; Steck, A.K.; Beam, C.; Herold, K.C.; Ledizet, M. Analysis of beta-cell death in type 1 diabetes by droplet digital PCR. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3694–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fisher, M.M.; Perez Chumbiauca, C.N.; Mather, K.J.; Mirmira, R.G.; Tersey, S.A. Detection of islet beta-cell death in vivo by multiplex PCR analysis of differentially methylated DNA. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3476–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahan, P.B. Biology of circulating nucleic acids and possible roles in diagnosis and treatment in diabetes and cancer. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2012, 12, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, Y.; Cedar, H. DNA methylation dynamics in health and disease. Nat. Struct Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, T.; Kalakota, R. The potential for artificial intelligence in healthcare. Future Healthc. J. 2019, 6, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myszczynska, M.A.; Ojamies, P.N.; Lacoste, A.M.B.; Neil, D.; Saffari, A.; Mead, R.; Hautbergue, G.M.; Holbrook, J.D.; Ferraiuolo, L. Applications of machine learning to diagnosis and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 440–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, J.; Lehne, M.; Schepers, J.; Prasser, F.; Thun, S. The use of machine learning in rare diseases: A scoping review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourou, K.; Exarchos, T.P.; Exarchos, K.P.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Fotiadis, D.I. Machine learning applications in cancer prognosis and prediction. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzaki, E.; Tsamardinos, I. Somatic copy number aberrations detected in circulating tumor DNA can hold diagnostic value for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2020, 57, 102851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Niu, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Machine learning for characterizing risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a rural Chinese population: The Henan Rural Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, L.J.; Algehyne, E.A.; Usman, S.S. Predictive Supervised Machine Learning Models for Diabetes Mellitus. SN Comput. Sci. 2020, 1, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsamardinos, I.; Charonyktakis, P.; Lakiotaki, K.; Borboudakis, G.; Zenklusen, J.C.; Juhl, H.; Chatzaki, E.; Lagani, V. Just Add Data: Automated Predictive Modeling and BioSignature Discovery. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaglani, M.; Gourlia, K.; Tsamardinos, I.; Chatzaki, E. Accurate Blood-Based Diagnostic Biosignatures for Alzheimer’s Disease via Automated Machine Learning. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markaki, M.; Tsamardinos, I.; Langhammer, A.; Lagani, V.; Hveem, K.; Røe, O.D. A Validated Clinical Risk Prediction Model for Lung Cancer in Smokers of All Ages and Exposure Types: A HUNT Study. EBioMedicine 2018, 31, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagopoulou, M.; Karaglani, M.; Balgkouranidou, I.; Biziota, E.; Koukaki, T.; Karamitrousis, E.; Nena, E.; Tsamardinos, I.; Kolios, G.; Lianidou, E.; et al. Circulating cell-free DNA in breast cancer: Size profiling, levels, and methylation patterns lead to prognostic and predictive classifiers. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3387–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagopoulou, M.; Karaglani, M.; Manolopoulos, V.G.; Iliopoulos, I.; Tsamardinos, I.; Chatzaki, E. Deciphering the Methylation Landscape in Breast Cancer: Diagnostic and Prognostic Biosignatures through Automated Machine Learning. Cancers 2021, 13, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamou, M.; Antoniou, G.; Greasidou, E.; Lagani, V.; Charonyktakis, P.; Tsamardinos, I.; Doyle, M. Toward Automatic Risk Assessment to Support Suicide Prevention. Crisis 2019, 40, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, Q.; Liu, F. Differentially methylated circulating DNA: A novel biomarker to monitor beta cell death. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2018, 32, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTaggart, J.S.; Clark, R.H.; Ashcroft, F.M. The role of the KATP channel in glucose homeostasis in health and disease: More than meets the islet. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 3201–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaglani, M.; Ragia, G.; Panagopoulou, M.; Balgkouranidou, I.; Nena, E.; Kolios, G.; Papanas, N.; Manolopoulos, V.G.; Chatzaki, E. Search for Pharmacoepigenetic Correlations in Type 2 Diabetes Under Sulfonylurea Treatment. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 127, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aucamp, J.; Bronkhorst, A.J.; Badenhorst, C.P.S.; Pretorius, P.J. The diverse origins of circulating cell-free DNA in the human body: A critical re-evaluation of the literature. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos Soc. 2018, 93, 1649–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laktionov, P.P.; Tamkovich, S.N.; Rykova, E.Y.; Bryzgunova, O.E.; Starikov, A.V.; Kuznetsova, N.P.; Sumarokov, S.V.; Kolomiets, S.A.; Sevostianova, N.V.; Vlassov, V.V. Extracellular circulating nucleic acids in human plasma in health and disease. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2004, 23, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Tarhouny, S.A.; Hadhoud, K.M.; Ebrahem, M.M.; Al Azizi, N.M. Assessment of cell-free DNA with microvascular complication of type II diabetes mellitus, using PCR and ELISA. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2010, 29, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagopoulou, M.; Karaglani, M.; Balgkouranidou, I.; Pantazi, C.; Kolios, G.; Kakolyris, S.; Chatzaki, E. Circulating cell-free DNA release in vitro: Kinetics, size profiling, and cancer-related gene methylation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, M.Y.; Ehses, J.A.; Maedler, K.; Schumann, D.M.; Ellingsgaard, H.; Eppler, E.; Reinecke, M. Mechanisms of β-Cell Death in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2005, 54, S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamardinos, I.; Greasidou, E.; Borboudakis, G. Bootstrapping the out-of-sample predictions for efficient and accurate cross-validation. Mach. Learn. 2018, 107, 1895–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borboudakis, G.; Tsamardinos, I. Extending greedy feature selection algorithms to multiple solutions. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2021, 35, 1393–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, L.; Stres, B. The Importance of Objective Stool Classification in Fecal 1H-NMR Metabolomics: Exponential Increase in Stool Crosslinking Is Mirrored in Systemic Inflammation and Associated to Fecal Acetate and Methionine. Metabolites 2021, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Á.; Ligeti, B.; Szebeni, J.; Pongor, S.; Gyrffy, B. COVIDOUTCOME-estimating COVID severity based on mutation signatures in the SARS-CoV-2 genome. Database 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaab, E.; Rauschenberger, A.; Banzi, R.; Gerardi, C.; Garcia, P.; Demotes, J. Biomarker discovery studies for patient stratification using machine learning analysis of omics data: A scoping review. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e053674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Huang, H.; Keshavjee, K.; Guergachi, A.; Gao, X. Predictive models for diabetes mellitus using machine learning techniques. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, F.; Tersey, S.A.; Turatsinze, J.V.; Felton, J.L.; Kang, N.J.; Nelson, J.B.; Sims, E.K.; Defrance, M.; Bizet, M.; Fuks, F.; et al. Circulating unmethylated CHTOP and INS DNA fragments provide evidence of possible islet cell death in youth with obesity and diabetes. Clin. Epigenetics 2020, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosemena, M.; Meah, F.A.; Mather, K.J.; Tersey, S.A.; Mirmira, R.G. Cell-Free DNA Fragments as Biomarkers of Islet β-Cell Death in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.C.; Dahiya, R. MethPrimer: Designing primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 1427–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Katsaros, D.; de la Longrais, I.A.; Sochirca, O.; Yu, H. Hypermethylation of let-7a-3 in epithelial ovarian cancer is associated with low insulin-like growth factor-II expression and favorable prognosis. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10117–10122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karaglani, M.; Panagopoulou, M.; Cheimonidi, C.; Tsamardinos, I.; Maltezos, E.; Papanas, N.; Papazoglou, D.; Mastorakos, G.; Chatzaki, E. Liquid Biopsy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management: Building Specific Biosignatures via Machine Learning. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11041045
Karaglani M, Panagopoulou M, Cheimonidi C, Tsamardinos I, Maltezos E, Papanas N, Papazoglou D, Mastorakos G, Chatzaki E. Liquid Biopsy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management: Building Specific Biosignatures via Machine Learning. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(4):1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11041045
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaraglani, Makrina, Maria Panagopoulou, Christina Cheimonidi, Ioannis Tsamardinos, Efstratios Maltezos, Nikolaos Papanas, Dimitrios Papazoglou, George Mastorakos, and Ekaterini Chatzaki. 2022. "Liquid Biopsy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management: Building Specific Biosignatures via Machine Learning" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 4: 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11041045
APA StyleKaraglani, M., Panagopoulou, M., Cheimonidi, C., Tsamardinos, I., Maltezos, E., Papanas, N., Papazoglou, D., Mastorakos, G., & Chatzaki, E. (2022). Liquid Biopsy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management: Building Specific Biosignatures via Machine Learning. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(4), 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11041045










