The Strategy against Iatrogenic Prematurity Due to True Umbilical Knot: From Prenatal Diagnosis Challenges to the Favorable Fetal Outcome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
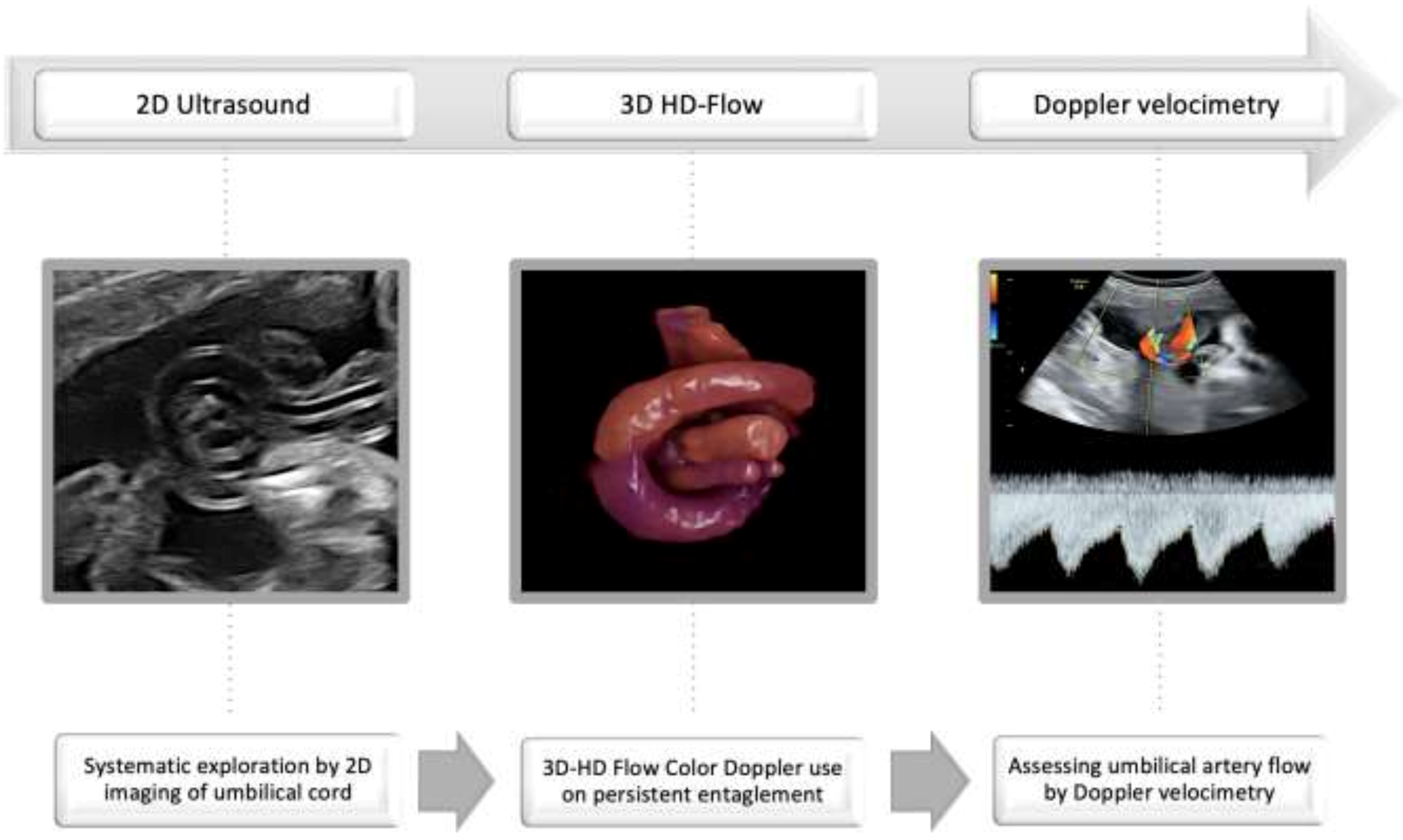
Practice Key Points
- ○
- Assess umbilical cord free loops;
- ○
- Verify the persistence of entanglement after fetal movement and repeated scan;
- ○
- Use 3D-HD-flow imaging or refer the case for diagnosis confirmation;
- ○
- Closely monitor umbilical artery flow by Doppler velocimetry.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasegawa, J. Ultrasound screening of umbilical cord abnormalities and delivery management. Placenta 2018, 62, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtman, Y.; Wainstock, T.; Landau, D.; Sheiner, E. 460: The significance of true knot of the umbilical cord. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 222, S302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S. Excessively long umbilical cord: A preventive factor of miserable outcomes of pregnancies with true umbilical cord knots. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 33, 3757–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzikowski, W.; Kowalczyk, D.; Więcek, J. Diagnosis of true umbilical cord knot. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2014, 10, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackman, F.; Capewell, V.; Gagnon, R.; Richardson, B. Fetal umbilical cord oxygen values and birth to placental weight ratio in relation to size at birth. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2001, 185, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasnoff, I.J.; Fletcher, M.A. True knot of the umbilical cord. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1977, 127, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, J.T.; Conti, J.A. A comparison of umbilical cord blood gas values between newborns with and without true knots. Obstet. Gynecol. 1996, 88, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtman, Y.; Wainstock, T.; Walfisch, A.; Sheiner, E. The Significance of True Knot of the Umbilical Cord in Long-Term Offspring Neurological Health. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räisänen, S.; Georgiadis, L.; Harju, M.; Keski-Nisula, L.; Heinonen, S. True umbilical cord knot and obstetric outcome. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2013, 122, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohîlțea, R.; Furtunescu, F.; Turcan, N.; Navolan, D.; Ducu, I.; Cîrstoiu, M. Prematurity and Intrauterine Growth Restriction: Comparative Analysis of Incidence and Short Term Complication. In Proceedings of the SOGR 2018, 17th National Congress of The Romanian Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2018, Bucharest, Romania, 4–6 October 2018; pp. 708–712. [Google Scholar]
- Salomon, L.J.; Alfirevic, Z.; Berghella, V.; Bilardo, C.; Hernandez-Andrade, E.; Johnsen, S.L.; Kalache, K.; Leung, K.-Y.; Malinger, G.; Munoz, H.; et al. Practice guidelines for performance of the routine mid-trimester fetal ultrasound scan. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 37, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Radiology. AIUM-ACR-ACOG-SMFM-SRU Practice Parameter for the Performance of Standard Diagnostic Obstetric Ultrasound Examinations. J. Ultrasound Med. 2018, 37, E13–E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauniaux, E.; Alfirevic, Z.; Bhide, A.G.; Burton, G.J.; Collins, S.L.; Silver, R.; Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Vasa Praevia: Diagnosis and Management: Green-Top Guideline No. 27b. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2019, 126, e49–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethune, M.; Alibrahim, E.; Davies, B.; Yong, E. A Pictorial Guide for the Second Trimester Ultrasound. Australas. J. Ultra Sound Med. 2013, 16, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinar, H.; Carpenter, M. Placenta and umbilical cord abnormalities seen with stillbirth. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 53, 656–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramón y Cajal, C.L.; Martínez, R.O. Four-dimensional ultrasonography of a true knot of the umbilical cord. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 195, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, A.C.; da Silveira Betat, R.; Dal Pai, T.K.V.; Arcolini, C.P.; Gobatto, A.M.; de Holleben Bicca, A.M.; Zen, P.R.G.; Rosa, R.F.M. Prenatal Diagnosis of a True Umbilical Cord Knot in a Fetus with Intrauterine Growth Restriction and Placenta Accreta. Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 55, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singh, C.; Kotoch, K. Prenatal Diagnosis of True Knot of the Umbilical Cord. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 2020, 42, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherer, D.M.; Manning, F.A. Prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis of conditions associated with potential umbilical cord compression. Am. J. Perinatol. 1999, 16, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A.; Graves, L. Four true umbilical cord knots. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 2006, 28, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, T. Ultrasound abnormalities of the amniotic fluid, membranes, umbilical cord, and placenta. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 31, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, W.; Wong, A.E.; Gomez, L.; Alcalde, J.L. Improving sonographic evaluation of the umbilical cord at the second-trimester anatomy scan. J. Ultrasound Med. 2009, 28, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.D.; Crawford, J.R. The short-form version of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-21): Construct validity and normative data in a large non-clinical sample. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 44 Pt 2, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.A.M.; Middleton, M.M.; Matthey, A.A.P.S.; Goldfeld, P.S.; Kemp, P.L.; Orsini, M.F. A comparison of two measures to screen for mental health symptoms in pregnancy and early postpartum: The Matthey Generic Mood Questionnaire and the Depression, Anxiety, Stress Scales short-form. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 281, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugon-Rodin, J.; Guilbert, J.-B.; Baron, X.; Camus, E. Notching of the umbilical artery waveform associated with cord entanglement in a monoamniotic twin pregnancy. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013, 26, 1559–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, N.; Angarita, A.M.; Casasbuenas, A.; Sarmiento, A. Three-dimensional high-definition flow imaging in prenatal diagnosis of a true umbilical cord knot. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 39, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurioles-Garibay, A.; Hernandez-Andrade, E.; Romero, R.; Garcia, M.; Qureshi, F.; Jacques, S.M.; Ahn, H.; Yeo, L.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Hassan, S.S. Presence of an umbilical artery notch in monochorionic/monoamniotic twins. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2014, 36, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polis, R.L.; Santolaya-Forgas, J.; Tong, C.; Onieal, G.; Canterino, J.C.; Matta, P.G.; Oyelese, Y. Personalized medicine in a patient with the antenatal diagnosis of an umbilical cord knot and a previous adverse outcome for this reason. J. Ultrasound Med. 2014, 33, 735–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikechebelu, J.; Eleje, G.; Ofojebe, C. True umbilical cord knot leading to fetal demise. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2014, 4 (Suppl. S2), S155–S158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilj, O.; Matijevic, R.; Blagaic, V.; Miskovic, B. Do we sometimes see too much? Prenatal diagnosis of a true umbilical cord knot. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2015, 187, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohîlțea, R.E.; Turcan, N.; Cîrstoiu, M. Prenatal ultrasound diagnosis and pregnancy outcome of umbilical cord knot—Debate regarding ethical aspects of a series of cases. J. Med. Life 2016, 9, 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Zbeidy, R.; Souki, F.G. One long umbilical cord, four nuchal cord loops and a true knot. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2017-223241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherer, D.M.; Dalloul, M.; Ward, K.; Nakagawa, J.; Joseph, I.; Grube, S.; Abulafia, O. Coexisting true umbilical cord knot and nuchal cord: Possible cumulative increased risk of adverse perinatal outcome. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 50, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arezzo, F.; Muzzupapa, G. Umbilical Cord Knot. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissmann-Brenner, A.; Meyer, R.; Domniz, N.; Levin, G.; Hendin, N.; Yoeli-Ullman, R.; Mazaki-Tovi, S.; Weissbach, T.; Kassif, E. The perils of true knot of the umbilical cord: Antepartum, intrapartum and postpartum complications and clinical implications. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissmann-Brenner, A.; Domniz, N.; Weissbach, T.; Mazaki-Tovi, S.; Achiron, R.; Weisz, B.; Kassif, E. Antenatal Detection of True Knot in the Umbilical Cord—How Accurate Can We Be? Ultraschall Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, E.; Pashaj, S. True or false umbilical cord knot? Differentiation via 3D/4D color Doppler ultrasound. Ultraschall Med. 2018, 39, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramón, Y.; Cajal, C.L.; Martínez, R.O. Prenatal diagnosis of true knot of the umbilical cord. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 23, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherer, D.M.; Amoabeng, O.; Dryer, A.M.; Dalloul, M. Current Perspectives of Prenatal Sonographic Diagnosis and Clinical Management Challenges of True Knot of the Umbilical Cord. Int. J. Womens Health 2020, 12, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousian, M.; Verwoerd-Dikkeboom, C.M.; Koning, A.H.J.; Hop, W.C.; van der Spek, P.J.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Exalto, N. First trimester umbilical cord and vitelline duct measurements using virtual reality. Early Hum. Dev. 2011, 87, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugurlucan, F.G.; Yuksel, A. Is complete umbilical cord scanning possible at the second-trimester ultrasound scan? J. Clin. Ultrasound JCU 2015, 43, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, W.; Shennan, A.H.; Bower, S.; Nicolaidis, P.; Fisk, N.M. True knot of the umbilical cord: A difficult prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 1995, 5, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gembruch, U.; Baschat, A.A. True knot of the umbilical cord: Transient constrictive effect to umbilical venous blood flow demonstrated by Doppler sonography. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 1996, 8, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasbun, J.; Alcalde, J.L.; Sepulveda, W. Three-dimensional power Doppler sonography in the prenatal diagnosis of a true knot of the umbilical cord: Value and limitations. J. Ultrasound Med. 2007, 26, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scioscia, M.; Fornalè, M.; Bruni, F.; Peretti, D.; Trivella, G. Four-dimensional and Doppler sonography in the diagnosis and surveillance of a true cord knot. J. Clin. Ultrasound JCU 2011, 39, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershkovitz, R.; Silberstein, T.; Sheiner, E.; Shoham-Vardi, I.; Holcberg, G.; Katz, M.; Mazor, M. Risk factors associated with true knots of the umbilical cord. Eur. J. Obs. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2001, 9, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
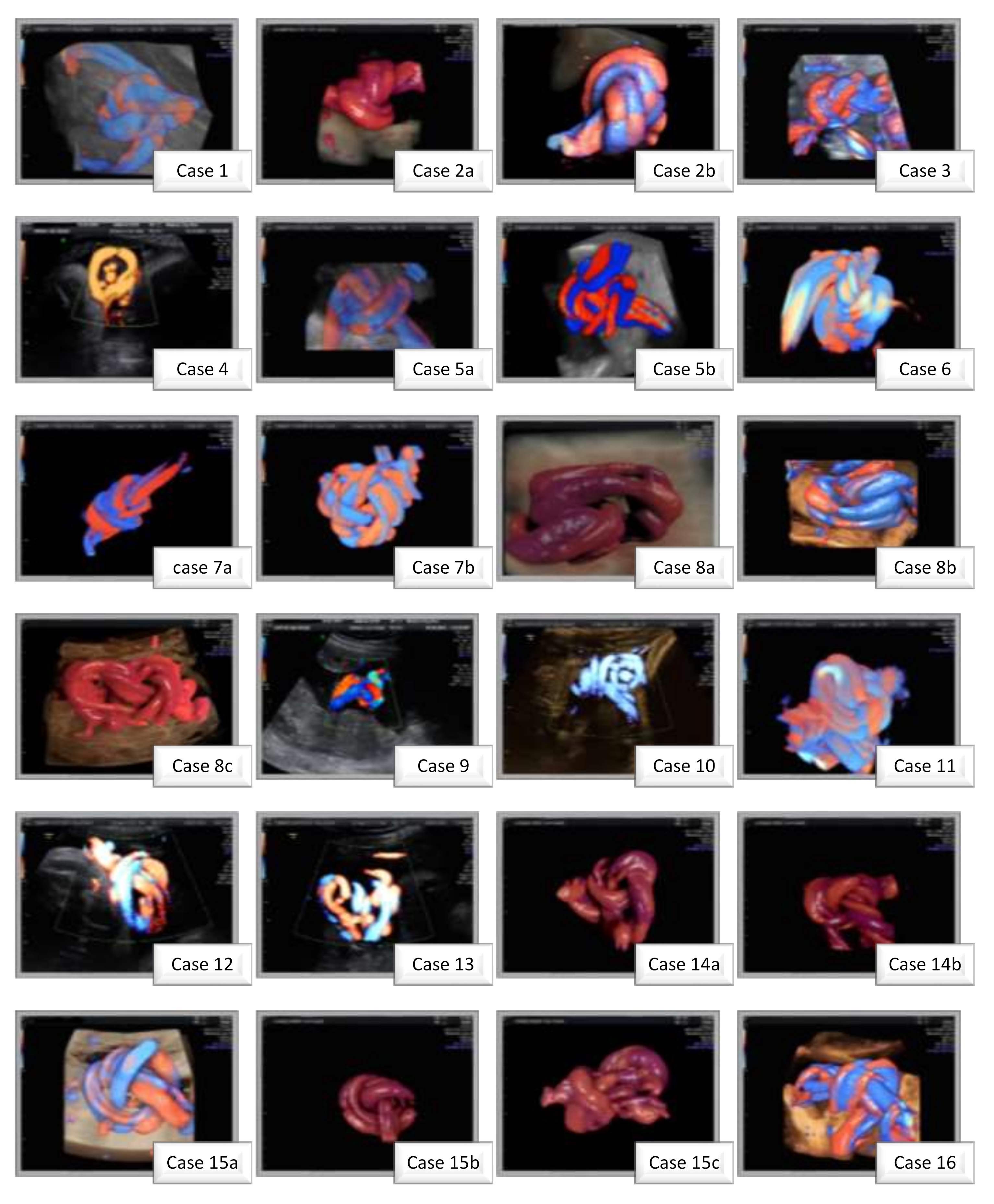
| Age, mean ± SD (years) | 33 ± 5.06 |
| Parity | |
| Primiparous | 9 |
| Secundiparous | 5 |
| Gestational age at diagnosis (weeks) | 25.5 ± 6.72 |
| Weight of newborns (grams) | 3332.85 ± 277 |
| Gestational age at birth | 38.42 ± 1.15 |
| Maternal anxiety | |
| Low | 6 |
| Moderate | 3 |
| High | 5 |
| Diabetic patients | 4 |
| Arterial hypertension | 1 |
| Fetal sex | |
| Male | 5 |
| Female | 9 |
| Amniotic fluid | |
| Normal | 11 |
| Polyhydramnios | 2 |
| Oligohydramnios | 1 |
| Nuchal cord | |
| No | 7 |
| One | 4 |
| Double | 3 |
| Study | Year | Cases | Gestational Age at Birth (Weeks + Days) | Ultrasonographic Findings | Postnatal Examination | Obstetrical and Neonatal Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hugon-Rodin [25] | 2013 | 1 (twin pregnancy) | 32 | A clear notch was described on the first twin’s umbilical artery flow in a free cord loop at 31 weeks; TK undiagnosed prenatal | Tight TK found | Iatrogenic prematurity |
| Rodriguez [26] | 2014 | 1 | 39 | TK at 35+5 weeks | TK was confirmed | Elective cesarean with a favorable neonatal outcome |
| Aurioles-Garibay [27] | 2014 | 2 (twin pregnancy) | 32+2 (case 1) 32+2 (case 2) | Case 1: Cord entanglement umbilical artery notch in 1 twin at 26 weeks Case 2: Cord entanglement umbilical artery notch in both twins at 28 weeks | Case 1: Cord entanglement, forked placental cord insertion, and cord knot were confirmed Case 2: Cord entanglement and cord knot were confirmed | Case 1: Respiratory distress syndrome Case 2: Respiratory distress syndrome and hyperbilirubinemia |
| Polis [28] | 2014 | 1 | 37 | TK at 32 weeks | TK confirmed | Elective cesarean; Anxiety due to a previous intrauterine demise of a 37 weeks fetus with a true knot diagnosed postpartum |
| Ikechebelu [29] | 2014 | 1 | 36 | NA | TK confirmed | Neonatal death due to intrapartum asphyxia |
| Vasilj [30] | 2015 | 1 | 39+2 | TK at 27 weeks | TK was confirmed | Vaginal delivery with a favorable neonatal outcome |
| Bohiltea [31] | 2016 | 133 | 36 (case 1) 36 (case 2) 36+5 (case 3) the rest at term | TK between 22–23 weeks in 16 cases (0.08% detection rate) | TK confirmed in all cases | Iatrogenic prematurity due to maternal anxiety (3 cases prenatally diagnosed) Prematurity of non-specified cause in 39 cases |
| da Cunha [17] | 2016 | 1 | 30 | IUGR at 25 weeks Placenta accreta TK at 29 weeks | TK confirmed | Emergency cesarean due to signs of brain sparing effect; Prematurity; IUGR |
| Zbeidy [32] | 2017 | 1 | 36 | IUGR at 36 weeks | TK and 4 NC confirmed | Iatrogenic prematurity for fetal distress; SGA |
| Sherer [33] | 2017 | 3 | 36+2 (case 1) 39 (case 2) 36 (case 3) | Case 1: NC and TK at 36 weeks Case 2: NC and TK at 37 weeks Case 3: NC and TK at 29 weeks | Case 1: TK and NC confirmed Case 2: TK and NC confirmed Case 3: Two separate TK and NC confirmed | Case 1: emergency cesarean due to fetal bradycardia; prematurity Case 2: emergency cesarean due to fetal bradycardia. Case 3: emergency cesarean due to fetal bradycardia; prematurity. |
| Singh [18] | 2020 | 1 | 37+5 | A single loop of nuchal cord and true knot at 35 weeks | TK confirmed | Cesarean delivery on the mother’s request (anxiety) |
| Arrezo [34] | 2020 | 1 (twin pregnancy) | 32 | NA | TK was diagnosed | Acute fetal distress |
| Weissmann-Brenner [35] | 2021 | 867 | <37 | NA | TK confirmed | 95 cases (10.95%) preterm deliveries |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bohiltea, R.E.; Varlas, V.-N.; Dima, V.; Iordache, A.-M.; Salmen, T.; Mihai, B.-M.; Bohiltea, A.T.; Vladareanu, E.M.; Ducu, I.; Grigoriu, C. The Strategy against Iatrogenic Prematurity Due to True Umbilical Knot: From Prenatal Diagnosis Challenges to the Favorable Fetal Outcome. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030818
Bohiltea RE, Varlas V-N, Dima V, Iordache A-M, Salmen T, Mihai B-M, Bohiltea AT, Vladareanu EM, Ducu I, Grigoriu C. The Strategy against Iatrogenic Prematurity Due to True Umbilical Knot: From Prenatal Diagnosis Challenges to the Favorable Fetal Outcome. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(3):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030818
Chicago/Turabian StyleBohiltea, Roxana Elena, Valentin-Nicolae Varlas, Vlad Dima, Ana-Maria Iordache, Teodor Salmen, Bianca-Margareta Mihai, Alexia Teodora Bohiltea, Emilia Maria Vladareanu, Ioniță Ducu, and Corina Grigoriu. 2022. "The Strategy against Iatrogenic Prematurity Due to True Umbilical Knot: From Prenatal Diagnosis Challenges to the Favorable Fetal Outcome" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 3: 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030818
APA StyleBohiltea, R. E., Varlas, V.-N., Dima, V., Iordache, A.-M., Salmen, T., Mihai, B.-M., Bohiltea, A. T., Vladareanu, E. M., Ducu, I., & Grigoriu, C. (2022). The Strategy against Iatrogenic Prematurity Due to True Umbilical Knot: From Prenatal Diagnosis Challenges to the Favorable Fetal Outcome. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(3), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030818








