Relationship between Multimorbidity and Quality of Life in a Primary Care Setting: The Mediating Role of Dyspnea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
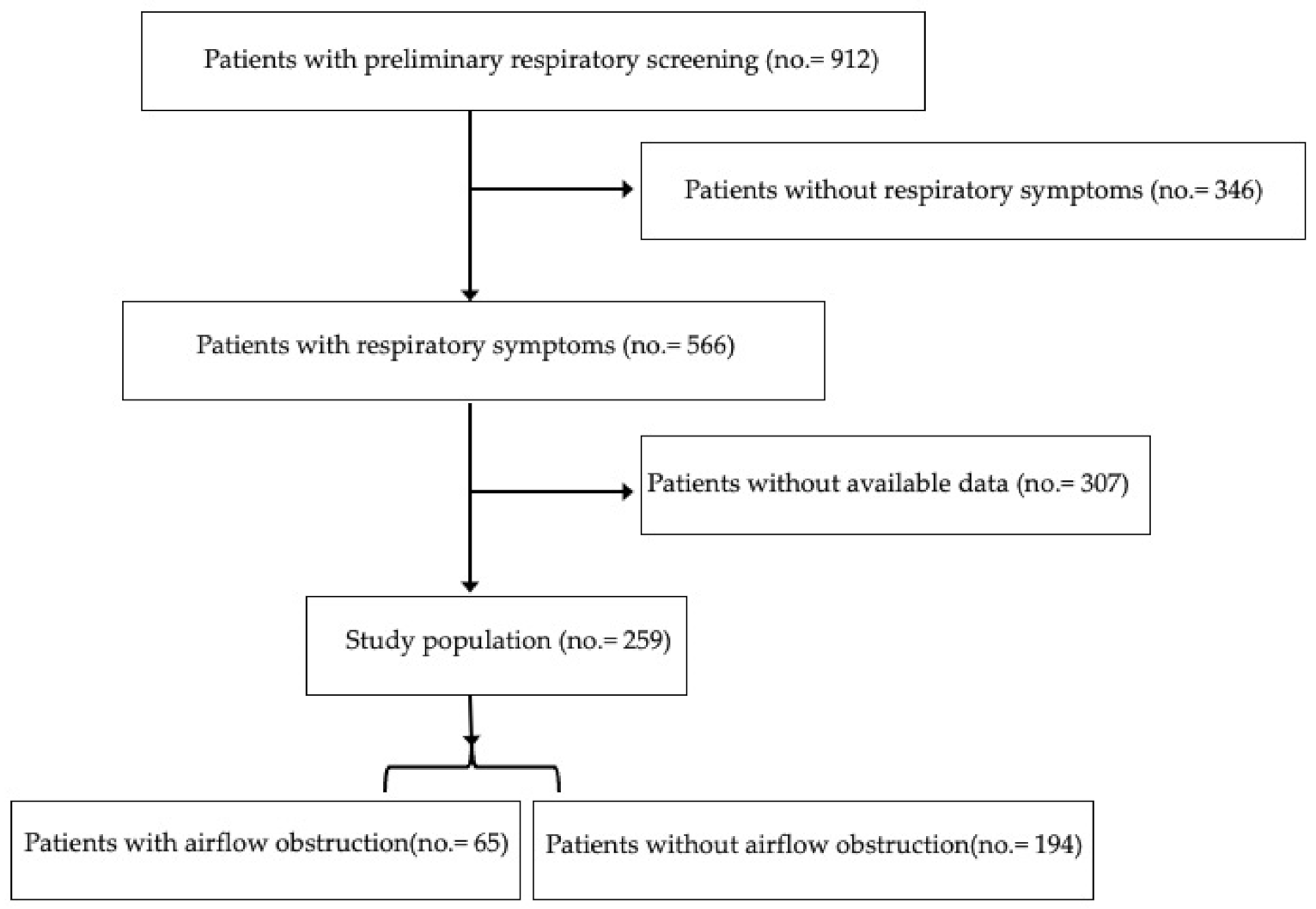
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Smoking History
2.4. Spirometry
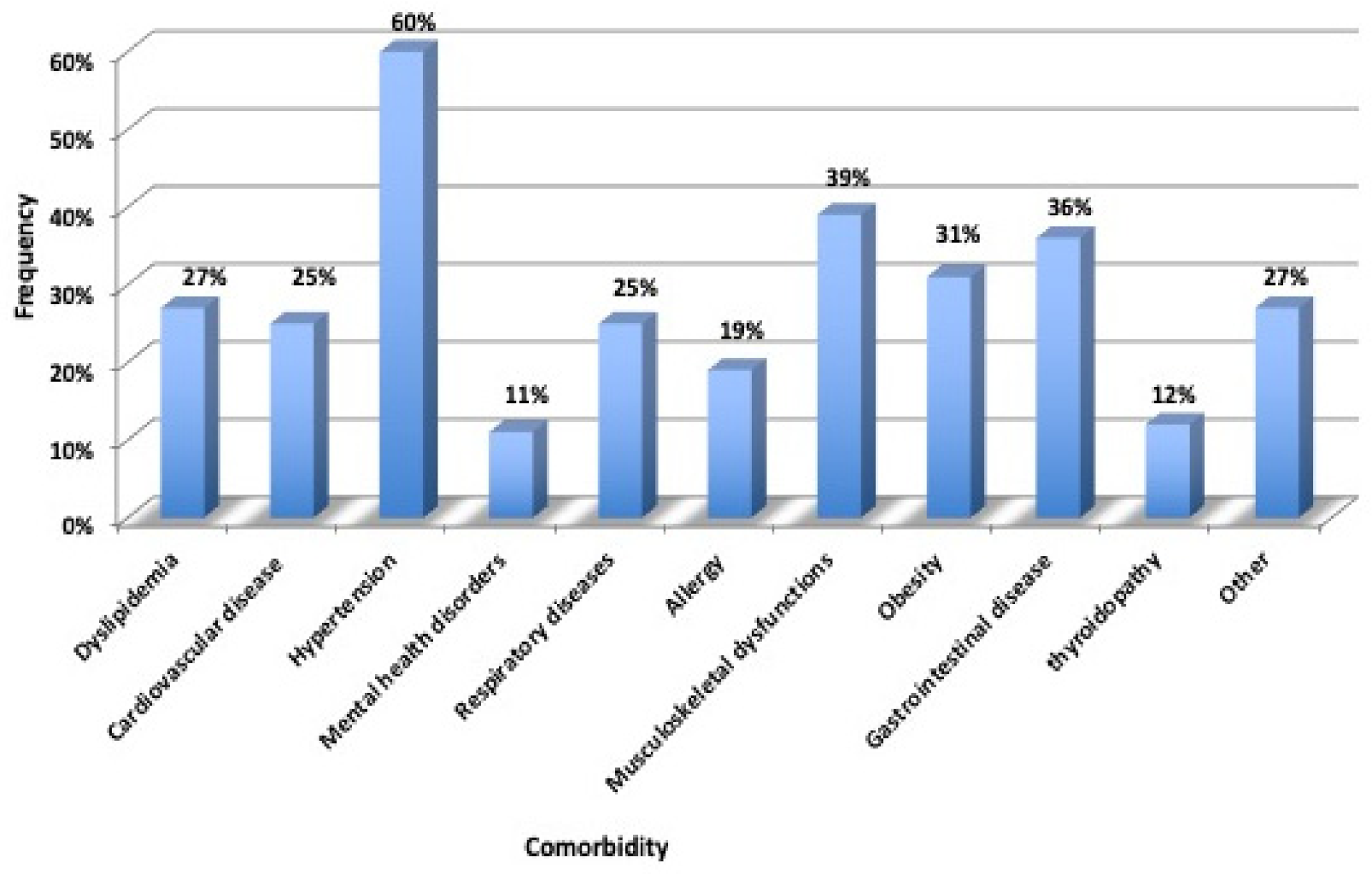
2.5. Hospitalization and Comorbidities
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
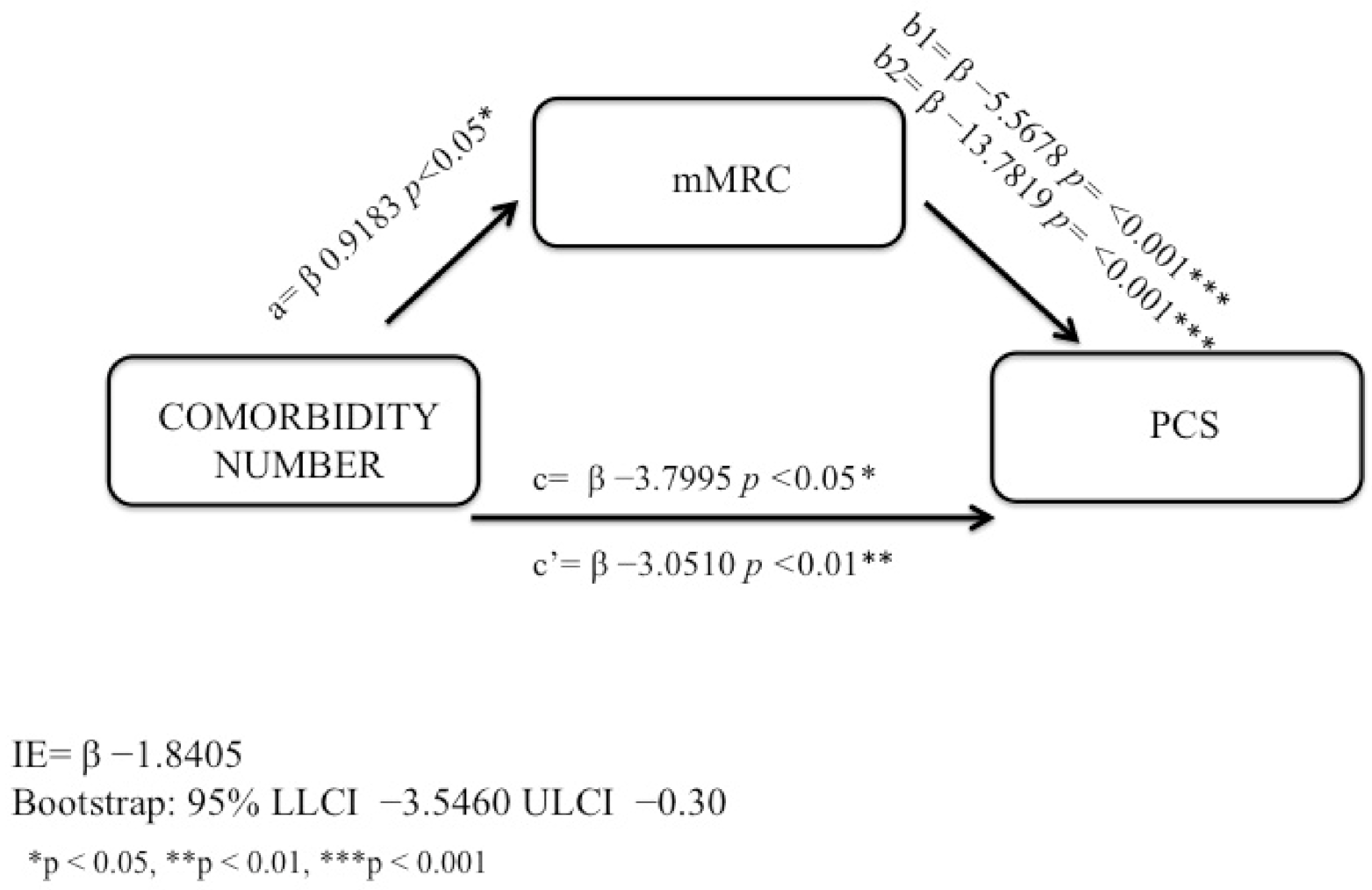
Model of Mediating Effects
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marengoni, A.; Angleman, S.; Melis, R.; Mangialasche, F.; Karp, A.; Garmen, A.; Meinow, B.; Fratiglioni, L. Aging with multimorbidity: A systematic review of the literature. Ageing Res. Rev. 2011, 10, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Pírez, J.; Poblador-Plou, B.; Ioakeim-Skoufa, I.; González-Rubio, F.; Gimeno-Feliú, L.A.; Díez-Manglano, J.; Laguna-Berna, C.; Marin, J.M.; Gimeno-Miguel, A.; Prados-Torres, A. Multimorbidity clusters in patients with chronic obstructive airway diseases in the EpiChron Cohort. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaas, D.; Wise, R.; Wiener, C. Airway Obstruction Is Common but Unsuspected in Patients Admitted to a General Medicine Service. Chest 2004, 125, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegi, G.; Maio, S.; Fasola, S.; Baldacci, S. Global Burden of Chronic Respiratory Diseases. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2020, 33, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegi, G.; Matteelli, G.; Angino, A.; Scognamiglio, A.; Baldacci, S.; Soriano, J.B.; Carrozzi, L. The proportional Venn diagram of obstructive lung disease in the Italian general population. Chest 2004, 126, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrik, C.S.; Løkke, A.; Dahl, R.; Dollerup, J.; Hansen, G.; Cording, P.H.; Andersen, K.K. Early detection of COPD in general practice. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2011, 6, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbiens, N.A.; Mueller-Rizner, N.; Connors, A.F.; Wenger, N.S. The relationship of nausea and dyspnea to pain in seriously ill patients. Pain 1997, 71, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currow, D.C.; Plummer, J.L.; Crockett, A.; Abernethy, A. A Community Population Survey of Prevalence and Severity of Dyspnea in Adults. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2009, 38, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshall, M.B.; Schwartzstein, R.M.; Adams, L.; Banzett, R.B.; Manning, H.L.; Bourbeau, J.; Calverley, P.M.; Gift, A.G.; Harver, A.; Lareau, S.C.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society Statement: Update on the Mechanisms, Assessment, and Management of Dyspnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansing, R.W.; Gracely, R.H.; Banzett, R.B. The multiple dimensions of dyspnea: Review and hypotheses. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2009, 167, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Vos, T.; Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Flaxman, A.D.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2197–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, C.; Marks, G.; Buist, S.; Gnatiuc, L.; Gislason, T.; McBurnie, M.A.; Nielsen, R.; Studnicka, M.; Toelle, B.; Benediktsdottir, B.; et al. The impact of COPD on health status: Findings from the BOLD study. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braido, F.; Baiardini, I.; Stagi, E.; Scichilone, N.; Rossi, O.; Lombardi, C.; Ridolo, E.; Gani, F.; Balestracci, S.; Girbino, G.; et al. RhinAsthma Patient Perspective: A short daily asthma and rhinitis QoL assessment. Allergy 2012, 67, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oga, T.; Tsukino, M.; Hajiro, T.; Ikeda, A.; Nishimura, K. Analysis of longitudinal changes in dyspnea of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: An observational study. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koroukian, S.M.; Warner, D.F.; Owusu, C.; Given, C.W. Peer Reviewed: Multimorbidity Redefined: Prospective Health Outcomes and the Cumulative Effect of Co-Occurring Conditions. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2015, 12, E55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.; Kim, S.; Rhee, Y.E.; Lee, J.; Yun, Y.H. Self-management strategies and comorbidities in chronic disease patients: Associations with quality of life and depression. Psychol. Health Med. 2020, 26, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, M.P.F.; Lacedonia, D.; Palladino, G.P.; Bergantino, L.; Ruggeri, C.; Martinelli, D.; Carpagnano, G.E. Dyspnea perception in asthma: Role of airways inflammation, age and emotional status. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.; Szefler, S.J.; Halpin, D.M.G. Impact of comorbid conditions on asthmatic adults and children. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2020, 30, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, Z.; Sandberg, J.; Honson, A.; Vandersman, Z.; Currow, D.C.; Ekström, M. Is chronic breathlessness less recognised and treated compared with chronic pain? A case-based randomised controlled trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioakeim-Skoufa, I.; Poblador-Plou, B.; Carmona-Pírez, J.; Díez-Manglano, J.; Navickas, R.; Gimeno-Feliu, L.A.; González-Rubio, F.; Jureviciene, E.; Dambrauskas, L.; Prados-Torres, A.; et al. Multimorbidity Patterns in the General Population: Results from the EpiChron Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikman, A.; Wardle, J.; Steptoe, A. Quality of Life and Affective Well-Being in Middle-Aged and Older People with Chronic Medical Illnesses: A Cross-Sectional Population Based Study. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Lynd, L.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Marra, C.A.; Rousseau, R.; Sadatsafavi, M. The added effect of comorbidity on health-related quality of life in patients with asthma. Qual. Life Res. 2015, 24, 2507–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.B.; Wacker, M.E.; Vogelmeier, C.F.; Leidl, R. Comorbid Influences on Generic Health-Related Quality of Life in COPD: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.G.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, B.H.; Park, M.S.; Kim, Y.S. Health behaviour and quality of life in Korean adults with respiratory disease: National Health Survey, 2005. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2010, 14, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wallace, E.; Salisbury, C.; Guthrie, B.; Lewis, C.; Fahey, T.; Smith, S. Managing patients with multimorbidity in primary care. BMJ 2015, 350, h176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, M.; Bravo, G.; Hudon, C.; Lapointe, L.; Almirall, J.; Dubois, M.-F.; Vanasse, A. Relationship Between Multimorbidity and Health-Related Quality of Life of Patients in Primary Care. Qual. Life Res. 2006, 15, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovski, T.T.; Schmitz, S.; Zeegers, M.P.; Stranges, S.; Akker, M.V.D. Multimorbidity and quality of life: Systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 53, 100903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Fukuhara, S.; Fujinuma, Y.; Yamamoto, Y. Effect of multimorbidity patterns on the decline in health-related quality of life: A nationwide prospective cohort study in Japan. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e047812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Rodríguez, A.; León-Muñoz, L.M.; Balboa-Castillo, T.; Banegas, J.R.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F.; Guallar-Castillón, P. Change in health-related quality of life as a predictor of mortality in the older adults. Qual. Life Res. 2010, 19, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, M.; Nakamura, H.; Sasaki, M.; Miyazaki, M.; Chubachi, S.; Takahashi, S.; Asano, K.; Jones, P.W.; Betsuyaku, T.; Keio COPD Comorbidity Research (K-CCR) Group. Determinants of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease severity in the late-elderly differ from those in younger patients. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchmanowicz, I.; Uchmanowicz, B.; Panaszek, B.; Rosińczuk, J. Sociodemographic factors affecting the quality of life of patients with asthma. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2016, 10, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, C.H.; Diaz, A.A.; Parulekar, A.D.; Rennard, S.I.; Kanner, R.E.; Hansel, N.N.; Couper, D.; Holm, K.E.; Hoth, K.F.; Curtis, J.L.; et al. Age-Related Differences in Health-Related Quality of Life in COPD. Chest 2016, 149, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayen, A.; Herigstad, M.; Pattinson, K.T. Understanding dyspnea as a complex individual experience. Maturitas 2013, 76, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Tauleria, E.; IMCA Working Group. Indicators for Monitoring COPD and Asthma in the EU; European Commission, Directorate for Public Health and Safety Work: Barcelona, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bestall, J.C.; Paul, E.A.; Garrod, R.; Garnham, R.; Jones, P.W.; Wedzicha, J.A. Usefulness of the Medical Research Council (MRC) dyspnoea scale as a measure of disability in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 1999, 54, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolone, G.; Mosconi, P. The Italian SF-36 Health Survey: Translation, Validation and Norming. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1998, 51, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; Van Der Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quanjer, P.H.; Stanojevic, S.; Cole, T.J.; Baur, X.; Hall, G.L.; Culver, B.H.; Enright, P.L.; Hankinson, J.L.; Ip, M.S.M.; Zheng, J.; et al. Multi-ethnic reference values for spirometry for the 3–95-year age range: The global lung function 2012 equations. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 1324–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegi, G.; Pedreschi, M.; Pistelli, F.; Di Pede, F.; Baldacci, S.; Carrozzi, L.; Giuntini, C. Prevalence of Airways Obstruction in a General Population: European Respiratory Society vs American Thoracic Society definition. Chest 2000, 117, 339S–345S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garin, N.; Olaya, B.; Moneta, M.V.; Miret, M.; Lobo, A.; Ayuso-Mateos, J.L.; Haro, J.M. Impact of Multimorbidity on Disability and Quality of Life in the Spanish Older Population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingley, D.; Yamamoto, T.; Hirose, K.; Keele, L.; Imai, K. Mediation: R Package for Causal Mediation Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 59, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 120–141. [Google Scholar]
- Shrout, P.E.; Bolger, N. Mediation in experimental and nonexperimental studies: New procedures and recommendations. Psychol. Methods 2002, 7, 422–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preacher, K.J.; Hayes, A.F. Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav. Res. Methods 2008, 40, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preacher, K.J.; Kelley, K. Effect size measures for mediation models: Quantitative strategies for communicating indirect effects. Psychol. Methods 2011, 16, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.L.; Tse, E.Y.; Gandek, B.; Fong, D.Y. The SF-36 summary scales were valid, reliable, and equivalent in a Chinese population. J. Clin. Epidemiology 2005, 58, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, I.; Van Riel, A.; Schuuring, M.; Duffels, M.; Vis, J.; Van Dijk, A.; Hoendermis, E.; Mulder, B.; Bouma, B. Decrease in quality of life predicts mortality in adult patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension due to congenital heart disease. Neth. Hear. J. 2015, 23, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.; Ferrer, M.; Gandek, B.; Ware, J.E., Jr.; Aaronson, N.K.; Mosconi, P.; Rasmussen, N.K.; Bullinger, M.; Fukuhara, S.; Kaasa, S.; et al. Health-related quality of life associated with chronic conditions in eight countries: Results from the International Quality of Life Assessment (IQOLA) Project. Qual. Life Res. 2004, 13, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiro, T.; Nishimura, K.; Tsukino, M.; Ikeda, A.; Oga, T.; Izumi, T. A Comparison of the Level of Dyspnea vs Disease Severity in Indicating the Health-Related Quality of Life of Patients With COPD. Chest 1999, 116, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damarell, R.A.; Morgan, D.; Tieman, J.J. General practitioner strategies for managing patients with multimorbidity: A systematic review and thematic synthesis of qualitative research. BMC Fam. Pract. 2020, 21, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviolette, L.; Laveneziana, P. Dyspnoea: A multidimensional and multidisciplinary approach. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 1750–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, K.E.; Bowler, R.P.; Make, B.J.; Wamboldt, F.S. Family Relationship Quality is Associated with Psychological Distress, Dyspnea, and Quality of Life in COPD. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2009, 6, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nowobilski, R.; Furgał, M.; Czyż, P.; De Barbaro, B.; Polczyk, R.; Bochenek, G.; Nizankowska-Mogilnicka, E.; Szczeklik, A. Psychopathology and Personality Factors Modify the Perception of Dyspnea in Asthmatics. J. Asthma 2007, 44, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuler, M.; Wittmann, M.; Faller, H.; Schultz, K. The interrelations among aspects of dyspnea and symptoms of depression in COPD patients—A network analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 240, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masror-Roudsary, D.; Aghdam, N.F.; Rafii, F.; Baha, R.; Khajeh, M.; Mardani, A. The Relationship between Experienced Respiratory Symptoms and Health-Related Quality of Life in the Elderly with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, 5564275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, C.H.; Reed, R.M.; Villalonga-Olives, E.; Slejko, J.F.; Eakin, M.N.; So, J.Y.; Zafari, Z. Quantifying heterogeneity of physical and mental health-related quality of life in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients in the United States. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2020, 14, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, A.; Pickering, A.; Williams, P.; Bland, J.M.; Johnson, M.J. Breathlessness and presentation to the emergency department: A survey and clinical record review. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spathis, A.; Booth, S.; Moffat, C.; Hurst, R.; Ryan, R.; Chin, C.; Burkin, J. The Breathing, Thinking, Functioning clinical model: A proposal to facilitate evidence-based breathlessness management in chronic respiratory disease. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2017, 27, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voll-Aanerud, M.; Eagan, T.M.L.; Plana, E.; Omenaas, E.R.; Bakke, P.S.; Svanes, C.; Siroux, V.; Pin, I.; Antó, J.M.; Leynaert, B. Respiratory symptoms in adults are related to impaired quality of life, regardless of asthma and COPD: Results from the European community respiratory health survey. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2010, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; LόpezSánchez, G.F.; Shin, J.I.; Soysal, P.; Veronese, N.; Kostev, K.; Jacob, L.; Oh, H.; Schuch, F.; Butler, L.; et al. Multimorbidity and Anxiety Symptoms among Adults Aged 50 Years and Over from Six Low- and Middle-Income Countries. J. Ageing Longev. 2021, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franssen, F.M.; Rochester, C.L. Comorbidities in patients with COPD and pulmonary rehabilitation: Do they matter? Eur. Respir. Rev. 2014, 23, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanfleteren, L.E.G.W.; Spruit, M.A.; Groenen, M.; Gaffron, S.; Van Empel, V.P.M.; Bruijnzeel, P.L.B.; Rutten, E.P.A.; Roodt, J.O.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Franssen, F.M.E. Clusters of Comorbidities Based on Validated Objective Measurements and Systemic Inflammation in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatila, W.M.; Thomashow, B.M.; Minai, O.A.; Criner, G.J.; Make, B.J. Comorbidities in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Jhun, B.W.; Cho, J.; Yoo, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, J.D.; Jung, K.-S.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.Y. Different impacts of respiratory symptoms and comorbidities on COPD-specific health-related quality of life by COPD severity. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 12, 3301–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ierodiakonou, D.; Kampouraki, M.; Poulonirakis, I.; Papadokostakis, P.; Lintovoi, E.; Karanassos, D.; Maltezis, K.; Chorti, M.; Petrovitsos, E.; Dimopoulou, S.; et al. Determinants of frailty in primary care patients with COPD: The Greek UNLOCK study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.; Agur, K.; Mercer, S.; Eiras, A.; González-Montalvo, J.I.; Gruffydd-Jones, K. Managing multimorbidity in primary care in patients with chronic respiratory conditions. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2016, 26, 16043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettschneider, C.; Leicht, H.; Bickel, H.; Dahlhaus, A.; Fuchs, A.; Gensichen, J.; Maier, W.; Heller, S.R.; Schafer, I.; Schon, G.; et al. Relative impact of multimorbid chronic conditions on health-related quality of life–results from the MultiCare Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Liang, Y.; Liu, S.; Cao, W.; Tu, H.; Guo, L.; Xu, Y. Health-Related Quality of Life as Measured with EQ-5D among Populations with and without Specific Chronic Conditions: A Population-Based Survey in Shaanxi Province, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmeier, C.F.; Criner, G.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Bourbeau, J.; Celli, B.R.; Chen, R.; Decramer, M.; Fabbri, L.M.; et al. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2017 Report. GOLD Executive Summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 557–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, N.; Dalmay, F.; Perez, T.; Kuntz, C.; Vergnenègre, A.; Neukirch, F.; Giordanella, J.-P.; Huchon, G. FEV1/FVC and FEV1 for the assessment of chronic airflow obstruction in prevalence studies: Do prediction equations need revision? Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sorino, C.; Battaglia, S.; Scichilone, N.; Pedone, C.; Antonelli-Incalzi, R.; Sherrill, D.; Bellia, V. Diagnosis of airway obstruction in the elderly: Contribution of the SARA study. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2012, 7, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOLD Executive Committee. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: 2019 Report; Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease: Fontana, WI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lamprecht, B.; Schirnhofer, L.; Kaiser, B.; Buist, S.A.; Mannino, D.; Studnicka, M. Subjects with Discordant Airways Obstruction: Lost between Spirometric Definitions of COPD. Pulm. Med. 2011, 2011, 780215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Rio, F.; Soriano, J.B.; Miravitlles, M.; Muñoz, L.; Duran-Tauleria, E.; Sánchez, G.; Sobradillo, V.; Ancochea, J. Overdiagnosing Subjects with COPD Using the 0.7 Fixed Ratio: Correlation with a Poor Health-Related Quality of Life. Chest 2011, 139, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.; Cusack, R.P.; Chaudhary, N.; Satia, I.; Kurmi, O.P. Under- and over-diagnosis of COPD: A global perspective. Breathe 2019, 15, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Huang, Q.; Shuai, T.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Assessment of comorbidities and prognosis in patients with COPD diagnosed with the fixed ratio and the lower limit of normal: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, B.R.; Halbert, R.J. Point: Should We Abandon FEV 1/FVC <0.70 to detect airway obstruction? No. Chest 2010, 138, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.F.; O’Mahony, M.S.; Steward, J.A.; Breay, P.; Buchalter, M.; Burr, M.L. Dyspnoea and quality of life in older people at home. Age Ageing 2001, 30, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, E. Some preliminerary findings on the physical complaints from a prospective study of 1,064,004 men and women. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1964, 54, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, K.; Arrington, M.; Mangelsdorff, A. The prevalence of symptoms in medical outpatients and the adequacy of therapy. Arch. Intern. Med. 1990, 150, 1685–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currow, D.C.; Chang, S.; Reddel, H.K.; Kochovska, S.; Ferreira, D.; Kinchin, I.; Johnson, M.; Ekström, M. Breathlessness, Anxiety, Depression, and Function–The BAD-F Study: A Cross-Sectional and Population Prevalence Study in Adults. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2020, 59, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekström, M.; Chang, S.; Johnson, M.J.; Fazekas, B.; Kochovska, S.; Huang, C.; Currow, D.C. Low agreement between mMRC rated by patients and clinicians when assessing eligibility in randomised controlled trials e implications for practice. Eur. Resp. J. 2019, 54, 1901517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| N (Valid %) or Mean (SD) or Median | |
|---|---|
| Male | 148 (57%) |
| Age | 65.65 (10.15) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 28.3 (4.8) |
| Current smokers | 81 (31%) |
| Former smokers | 119 (46%) |
| Airflow obstruction | 65 (25%) |
| Comorbidity number | 3 Mdn |
| Patients with history of Hospitalization (>1) | 148 (57%) |
| SF36 PCS | 46.9 (9.1) |
| SF36 MCS | 45.7 (9.5) |
| No. (Valid %) | |
|---|---|
| 0 | 70 (27%) |
| 1 | 143 (55%) |
| 2 | 42 (16%) |
| 3 | 4 (2%) |
| 4 | 0 (0) |
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||
| 0.399, p = 0.001 ** | 1 | ||
| −0.296, p = 0.017 * | −0.441, p < 0.001 ** | 1 | |
| −0.139 NS | −0.259 p < 0.05 * | −0.039 NS | 1 |
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||
| 0.246, p = 0.001 ** | 1 | ||
| −0.323, p = 0.000 *** | −0.517, p = 0.000 *** | 1 | |
| 0.082 NS | −0.076 NS | −0.114 NS | 1 |
| Independent Variable | Dependent Variable | β | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total effect | |||||
| comorbidity number | SF36 (PCS) | −3.737 | −7.489 | −0.17 | 0.036 * |
| Direct effect | |||||
| comorbidity number | SF36 (PCS) | −2.595 | −5.817 | 0.69 | 0.144 |
| Indirect effect | |||||
| comorbidity number | mMRC | −1.141 | −3.468 | −0.05 | 0.049 * |
| Independent Variable | Dependent Variable | β | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total effect | |||||
| comorbidity number | SF36 (PCS) | −4.8915 | −7.6929 | −2.27 | 0.000 *** |
| Direct effect | |||||
| comorbidity number | SF36 (PCS) | −3.0510 | −5.2455 | −0.79 | 0.001 ** |
| Indirect effect | |||||
| comorbidity number | mMRC | −1.8405 | −3.5460 | −0.30 | 0.02 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfano, P.; Cuttitta, G.; Audino, P.; Fazio, G.; La Grutta, S.; Marcantonio, S.; Snamid Palermo Cooperative Group; Bucchieri, S. Relationship between Multimorbidity and Quality of Life in a Primary Care Setting: The Mediating Role of Dyspnea. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030656
Alfano P, Cuttitta G, Audino P, Fazio G, La Grutta S, Marcantonio S, Snamid Palermo Cooperative Group, Bucchieri S. Relationship between Multimorbidity and Quality of Life in a Primary Care Setting: The Mediating Role of Dyspnea. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(3):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030656
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfano, Pietro, Giuseppina Cuttitta, Palma Audino, Giovanni Fazio, Sabina La Grutta, Salvatore Marcantonio, Snamid Palermo Cooperative Group, and Salvatore Bucchieri. 2022. "Relationship between Multimorbidity and Quality of Life in a Primary Care Setting: The Mediating Role of Dyspnea" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 3: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030656
APA StyleAlfano, P., Cuttitta, G., Audino, P., Fazio, G., La Grutta, S., Marcantonio, S., Snamid Palermo Cooperative Group, & Bucchieri, S. (2022). Relationship between Multimorbidity and Quality of Life in a Primary Care Setting: The Mediating Role of Dyspnea. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(3), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030656






