Syphilis Infections, Reinfections and Serological Response in a Large Italian Sexually Transmitted Disease Centre: A Monocentric Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Setting
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Clinical Management
2.4. Definitions
2.5. Ethical Aspects
2.6. Statistical Analysis
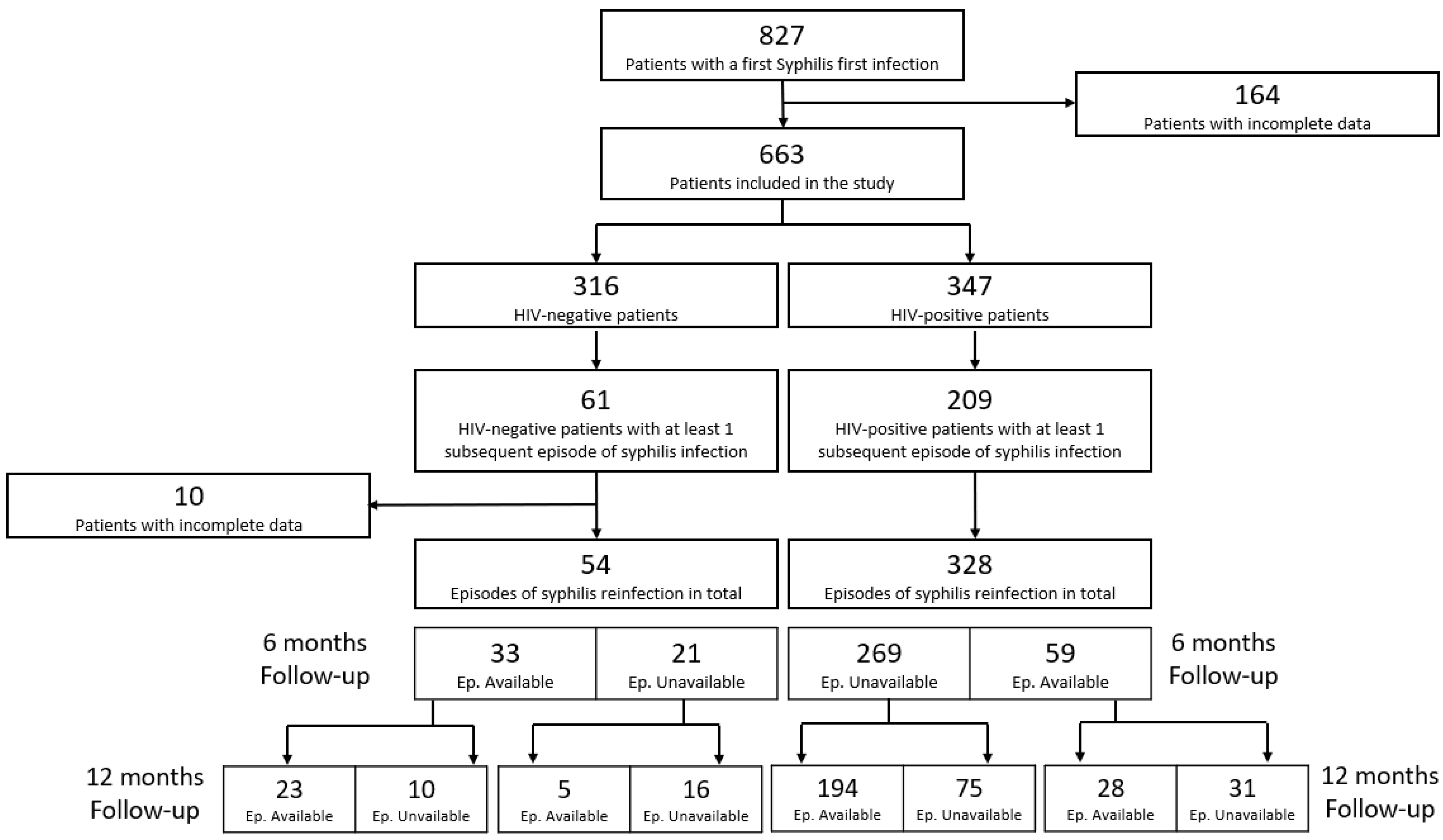
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of Syphilis Episodes in the Study Period
3.2. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Included Patients
3.3. Serological Response to Treatment in Syphilis Reinfection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiecco, G.; Degli Antoni, M.; Storti, S.; Marchese, V.; Focà, E.; Torti, C.; Castelli, F.; Quiros-Roldan, E. A 2021 Update on Syphilis: Taking Stock from Pathogenesis to Vaccines. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention Reported STDs Reach All-Time High for 6th Consecutive Year. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2021/p0413-stds.html (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità Sifilide—Aspetti Epidemiologici. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/sifilide/epidemiologia-italia (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Le Infezioni Sessualmente Trasmesse: Aggiornamento Dei Dati Due Sistemi Sorveglianza Sentinella in Italia al 31 Dicembre 2017. Not Ist Super Sanità, June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pagaoa, M.; Grey, J.; Torrone, E.; Kreisel, K.; Stenger, M.; Weinstock, H. Trends in Nationally Notifiable Sexually Transmitted Disease Case Reports During the US COVID-19 Pandemic, January to December 2020. Sex Transm. Dis. 2021, 48, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonato, F.; Ferreli, C.; Satta, R.; Rongioletti, F.; Atzori, L. Syphilis and the COVID-19 Pandemic: Did the Lockdown Stop Risky Sexual Behavior? Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 39, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Yu, A.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Ma, P. Consequences of HIV/Syphilis Co-Infection on HIV Viral Load and Immune Response to Antiretroviral Therapy. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 2851–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rompalo, A.M.; Joesoef, M.R.; O’Donnell, J.A.; Augenbraun, M.; Brady, W.; Radolf, J.D.; Johnson, R.; Rolfs, R.T. Clinical Manifestations of Early Syphilis by HIV Status and Gender. Sex Transm. Dis. 2001, 28, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetola, N.M.; Klausner, J.D. Syphilis and HIV Infection: An Update. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Dashwood, T.; Walmsley, S. The Intersection of HIV and Syphilis: Update on the Key Considerations in Testing and Management. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2021, 18, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, M.; Evans, J.; Davies, E.P.; Rowley, J.; Korenromp, E.L.; Clayton, T.; Taylor, M.M.; Mabey, D.; Chico, R.M. Prevalence of Syphilis among Men Who Have Sex with Men: A Global Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis from 2000–20. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e1110–e1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Statistics Division Methodology: Standard Country or Area Codes for Statistical Use (M49). Available online: https://unstats.un.org/unsd/methodology/m49/ (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Boog, G.H.P.; Lopes, J.V.Z.; Mahler, J.V.; Solti, M.; Kawahara, L.T.; Teng, A.K.; Munhoz, J.V.T.; Levin, A.S. Diagnostic Tools for Neurosyphilis: A Systematic Review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Gong, H.Z.; Hu, K.R.; Zheng, H.; Wan, X.; Li, J. Effect of Syphilis Infection on HIV Acquisition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sex Transm. Infect. 2021, 97, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmet, T.; Cotte, L.; Allavena, C.; Huleux, T.; Duvivier, C.; Laroche, H.; Cabie, A.; Pugliese, P.; Jovelin, T.; Maurel, M.; et al. High Syphilis Prevalence and Incidence in People Living with HIV and Preexposure Prophylaxis Users: A Retrospective Review in the French Dat’AIDS Cohort. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelou, K.; Rozani, S.; Pafiti, M.; Syrigos, N. Syphilis Transmission: Exacerbated Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic? Ethics Med. Public Health 2022, 22, 100782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiros-Roldan, E.; Magro, P.; Carriero, C.; Chiesa, A.; el Hamad, I.; Tratta, E.; Fazio, R.; Formenti, B.; Castelli, F. Consequences of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Continuum of Care in a Cohort of People Living with HIV Followed in a Single Center of Northern Italy. AIDS Res. Ther. 2020, 17, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiros-Roldan, E.; Izzo, I.; Carriero, C.; Antoni, M.D.; Storti, S.; Tiecco, G.; Gardini, G.; Focà, E.; Castelli, F. Decrease in New Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS in the Two Years Period 2019–2020: Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Public Health Res. 2022, 11, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità IST. Aggiornamento Dei Dati Dei Due Sistemi Di Sorveglianza Sentinella Attivi in Italia al 31 Dicembre 2020. Notiziario dell’Istituto Superiore di Sanità, June 2022; 6. [Google Scholar]
- Pastuszczak, M.; Bociąga-Jasik, M.; Sitko, M.; Wojas-Pelc, A. HIV Infection and Sex in Sex-on-Premises Venues Are Associated with a Higher Risk of Syphilis Reinfection among Men Who Have Sex with Men. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2018, 35, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doron, A.; Rahav, G.; Wieder-Feinsod, A.; Litchevski, V.; Olmer, L.; Amit, S.; Lubitz, I.; Levy, I. Syphilis Reinfection among People Living with HIV. Int. J. STD AIDS 2022, 33, 416–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Tullio, F.; Mandel, V.D.; Cuomo, G.; Coppini, M.; Guaraldi, G.; Mussini, C.; Pellacani, G.; Borghi, V. HIV and Syphilis: Incidence Rate of Coinfection and Syphilis Reinfection in a Cohort of Newly Diagnosed HIV Patients. Ital. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 157, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, J.; Santos, G.-M.; Scheer, S.; Gibson, S.; Crouch, P.-C.; Kohn, R.; Chang, W.; Carrico, A.W. Rates and Correlates of Syphilis Reinfection in Men Who Have Sex with Men. LGBT Health 2017, 4, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhu, L.; Ding, Y.; Yuan, J.; Li, W.; Wu, Q.; Tian, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, T.; et al. Factors Associated with Syphilis Treatment Failure and Reinfection: A Longitudinal Cohort Study in Shenzhen, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, V.C.; Donalisio, M.R.; Cordeiro, R. Factors Associated with Reinfection of Syphilis in Reference Centers for Sexually Transmitted Infections. Rev. Saude Publica 2017, 51, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.A.; Franzeck, F.C.; Balakrishna, S.; Lautenschlager, S.; Thurnheer, M.C.; Trellu, L.T.; Cavassini, M.; Vernazza, P.; Bernasconi, E.; Braun, D.; et al. Repeated Syphilis Episodes in HIV-Infected Men Who Have Sex with Men: A Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study on Risk Factors and the Potential Role of Syphilis Immunity. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henninger, M.L.; Bean, S.I.; Lin, J.S. Screening for Syphilis Infection in Nonpregnant Adults and Adolescents. JAMA 2022, 328, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangione, C.M.; Barry, M.J.; Nicholson, W.K.; Cabana, M.; Chelmow, D.; Coker, T.R.; Davis, E.M.; Donahue, K.E.; Jaén, C.R.; Kubik, M.; et al. Screening for Syphilis Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults. JAMA 2022, 328, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuddenham, S.; Ghanem, K.G. The Critical Need to Modernize Syphilis Screening. JAMA 2022, 328, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workowski, K.A.; Bachmann, L.H.; Chan, P.A.; Johnston, C.M.; Muzny, C.A.; Park, I.; Reno, H.; Zenilman, J.M.; Bolan, G.A. Sexually Transmitted Infections Treatment Guidelines, 2021. MMWR. Recomm. Rep. 2021, 70, 1–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-Y.; Yang, C.-J.; Sun, H.-Y.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Chang, L.-H.; Liu, W.-C.; Su, Y.-C.; Chang, S.-Y.; Hung, C.-C.; Chang, S.-C. Comparisons of Serologic Responses of Early Syphilis to Treatment with a Single-Dose Benzathine Penicillin G Between HIV-Positive and HIV-Negative Patients. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuddenham, S.; Ghanem, K.G. Management of Adult Syphilis: Key Questions to Inform the 2021 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Sexually Transmitted Infections Treatment Guidelines. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, S127–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-J.; Lee, N.-Y.; Chen, T.-C.; Lin, Y.-H.; Liang, S.-H.; Lu, P.-L.; Huang, W.-C.; Tang, H.-J.; Lee, C.-H.; Lin, H.-H.; et al. One Dose versus Three Weekly Doses of Benzathine Penicillin G for Patients Co-Infected with HIV and Early Syphilis: A Multicenter, Prospective Observational Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittes, J.; Aichelburg, M.C.; Antoniewicz, L.; Geusau, A. Enhanced Therapy for Primary and Secondary Syphilis: A Longitudinal Retrospective Analysis of Cure Rates and Associated Factors. Int. J. STD AIDS 2013, 24, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.-R.; Tsai, M.-S.; Yang, C.-J.; Sun, H.-Y.; Liu, W.-C.; Yang, S.-P.; Wu, P.-Y.; Su, Y.-C.; Chang, S.-Y.; Hung, C.-C. Spirochetemia Due to Treponema Pallidum Using Polymerase-Chain-Reaction Assays in Patients with Early Syphilis: Prevalence, Associated Factors and Treatment Response. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O524–O527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Szadkowski, L.; Walmsley, S.L. Deciphering the Serological Response to Syphilis Treatment in Men Living with HIV. AIDS 2020, 34, 2089–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwenburg, S.A.; Sprenger, R.J.; Schim van der Loeff, M.F.; de Vries, H.J.C. Clinical Outcomes of Syphilis in HIV-Negative and HIV-Positive MSM: Occurrence of Repeat Syphilis Episodes and Non-Treponemal Serology Responses. Sex Transm. Infect. 2022, 98, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, D.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Devlin, J.; Buss, Z.; Parkes, L.; Williams, D. Primary Syphilis Lesion Characteristics, Serological Response and Management in HIV-Positive and HIV-Negative Men Who Have Sex with Men. Int. J. STD AIDS 2020, 31, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.Z.; Li, J.; Zheng, H.Y. The Treatment Outcome and Predictors of Serological Response in Syphilis in a Sexually Transmitted Infections Center, China. Int. J. STD AIDS 2022, 33, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, G.; Wesselmann, J.; Adzic, D.; Malin, J.; Suarez, I.; Priesner, V.; Kümmerle, T.; Wyen, C.; Jung, N.; Bremen, K.; et al. Predictors of Serofast State after Treatment for Early Syphilis in HIV-infected Patients. HIV Med. 2021, 22, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-C.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lu, P.-L.; Shen, N.-J.; Yang, C.-J.; Lee, N.-Y.; Tang, H.-J.; Liu, Y.-M.; Huang, W.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; et al. Comparison of Serological Response to Doxycycline versus Benzathine Penicillin G in the Treatment of Early Syphilis in HIV-Infected Patients: A Multi-Center Observational Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jinno, S.; Anker, B.; Kaur, P.; Bristow, C.C.; Klausner, J.D. Predictors of Serological Failure after Treatment in HIV-Infected Patients with Early Syphilis in the Emerging Era of Universal Antiretroviral Therapy Use. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, K.G.; Moore, R.D.; Rompalo, A.M.; Erbelding, E.J.; Zenilman, J.M.; Gebo, K.A. Antiretroviral Therapy Is Associated with Reduced Serologic Failure Rates for Syphilis among HIV-Infected Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First Syphilis Infections | Syphilis Reinfections | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | HIV-Negative | HIV-Positive | HIV-Negative | HIV-Positive |
| Year, n (%) | ||||
| 2013 | 51 (12%) | 35 (8.4%) | 14 (9.9%) | 70 (7.9%) |
| 2014 | 48 (12%) | 43 (10%) | 27 (19%) | 107 (12%) |
| 2015 | 48 (12%) | 52 (12%) | 30 (21%) | 118 (13%) |
| 2016 | 54 (13%) | 68 (16%) | 16 (11%) | 123 (14%) |
| 2017 | 54 (13%) | 58 (14%) | 18 (13%) | 95 (11%) |
| 2018 | 60 (15%) | 40 (9.6%) | 9 (6.3%) | 89 (10%) |
| 2019 | 38 (9.2%) | 40 (9.6%) | 13 (9.2%) | 106 (12%) |
| 2020 | 24 (5.8%) | 38 (9.1%) | 7 (4.9%) | 115 (13%) |
| 2021 | 34 (8.3%) | 42 (10%) | 8 (5.6%) | 67 (7.5%) |
| HIV-Negative | HIV-Positive | Total | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients with syphilis infection (n, %) | 316 (48%) | 347 (52%) | 663 | |
| Gender | <0.001 | |||
| Males (n, %) | 176 (56%) | 332 (96%) | 508 (77%) | |
| Females (n, %) | 140 (44%) | 15 (4%) | 155 (23%) | |
| Age | 0.026 | |||
| Median (Minimum, Maximum) | 36 (12–83) | 40 (12–75) | 39 (12–83) | |
| Geographical origin | <0.001 | |||
| Europe (n, %) | 230 (73%) | 292 (84%) | 522 (79%) | |
| Other (n, %) | 86 (27%) | 55 (16%) | 141 (21%) | |
| Sexual orientation | <0.001 | |||
| Homosexual/Bisexual (n, %) | 39 (12%) | 260 (75%) | 299 (45%) | |
| Heterosexual (n, %) | 184 (58%) | 73 (21%) | 257 (39%) | |
| Prefer not to disclose (n, %) | 93 (30%) | 14 (4%) | 107 (16%) | |
| Syphilis stage during first infection | <0.001 | |||
| Late Latent (n, %) | 228 (78%) | 158 (51%) | 386 (64%) | |
| Other (n, %) | 63 (22%) | 150 (49%) | 213 (36%) | |
| Missing (n) | 25 | 39 | 64 | |
| Reasons for syphilis test | <0.001 | |||
| Screening/Follow-up (n, %) | 148 (47%) | 278 (80%) | 426 (64%) | |
| Symptom onset (n, %) | 168 (53%) | 69 (20%) | 237 (36%) | |
| Patients with syphilis reinfections | <0.001 | |||
| Yes (n, %) | 61 (19%) | 209 (60%) | 270 (41%) | |
| No (n, %) | 255 (81%) | 138 (40%) | 393 (59%) | |
| Number of syphilis episodes per person | <0.001 | |||
| Median (Minimum, Maximum) | 1 (1–3) | 1 (1–7) | 1 (1–7) |
| Characteristic | IRR 1 | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Female | — | — | |
| Male | 2.44 | 0.98, 8.13 | 0.090 |
| Age (years) | |||
| ≤30 | — | — | |
| 30–40 | 0.85 | 0.63, 1.15 | 0.3 |
| 40–50 | 0.65 | 0.47, 0.91 | 0.011 |
| >50 | 0.55 | 0.35, 0.86 | 0.009 |
| Geographical origin | |||
| Other | — | — | |
| Europe | 0.98 | 0.72, 1.34 | 0.9 |
| Sexual orientation | |||
| Heterosexual | — | — | |
| Homosexual/Bisexual | 1.52 | 1.09, 2.18 | 0.017 |
| Nadir CD4 | 0.98 | 0.91, 1.06 | 0.5 |
| HIV-Negative | HIV-Positive | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reinfection Episodes (n, %) | 54 (14%) | 328 (86%) | |
| Serological response at 6 months | 0.2 | ||
| Yes (n, %) | 13 (39%) | 139 (52%) | |
| No or SNR (n, %) | 20 (61%) | 130 (48%) | |
| Missing (n) | 21 | 59 | |
| Serological response at 12 months | 0.1 | ||
| Yes (n, %) | 14 (50%) | 147 (66%) | |
| No or SNR (n, %) | 14 (50%) | 75 (34%) | |
| Missing (n) | 26 | 106 | |
| Seroreversion rate at 6 months | 0.8 | ||
| Yes (n, %) | 6 (21%) | 62 (23%) | |
| No (n, %) | 26 (79%) | 207 (77%) | |
| Missing (n) | 21 | 59 | |
| Seroreversion rate at 12 months | 0.3 | ||
| Yes (n, %) | 7 (21%) | 70 (32%) | |
| No (n, %) | 22 (79%) | 152 (68%) | |
| Missing (n) | 26 | 106 | |
| Serofast status at 6 months | 0.2 | ||
| Yes (n, %) | 8 (24%) | 94 (35%) | |
| No (n, %) | 25 (76%) | 175 (65%) | |
| Missing (n) | 21 | 59 | |
| Serofast status at 12 months | 0.8 | ||
| Yes (n, %) | 10 (36%) | 86 (39%) | |
| No (n, %) | 18 (64%) | 138 (61%) | |
| Missing (n) | 26 | 106 |
| Serological Non-Response | Serofast Status | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | OR | 95% CI 1 | p-Value | OR | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
| Time | ||||||
| 6 months | — | — | — | — | ||
| 12 months | 0.38 | 0.22, 0.65 | <0.001 | 1.40 | 0.87, 2.25 | 0.2 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | — | — | — | — | ||
| Male | 2.67 | 0.25, 28.4 | 0.4 | 1.01 | 0.13, 8.06 | >0.9 |
| Age | ||||||
| ≤50 years | — | — | — | — | ||
| >50 years | 0.58 | 0.20, 1.67 | 0.3 | 1.17 | 0.47, 2.91 | 0.7 |
| Previous Episodes | 1.24 | 0.96, 1.60 | 0.11 | 0.92 | 0.72, 1.18 | 0.5 |
| CD4 at Diagnosis | ||||||
| >350 cells/mcL | — | — | — | — | ||
| ≤350 cells/mcL | 1.03 | 0.35, 3.00 | >0.9 | 1.24 | 0.47, 3.24 | 0.7 |
| HIV-RNA | ||||||
| Negative | — | — | — | — | ||
| Positive | 0.89 | 0.48, 1.63 | 0.7 | 0.97 | 0.56, 1.69 | >0.9 |
| RPR titre | ||||||
| ≤1:16 | — | — | — | — | ||
| >1:16 | 2.26 | 1.14, 4.51 | 0.020 | 0.69 | 0.37, 1.28 | 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marchese, V.; Tiecco, G.; Storti, S.; Degli Antoni, M.; Calza, S.; Gulletta, M.; Viola, F.; Focà, E.; Matteelli, A.; Castelli, F.; et al. Syphilis Infections, Reinfections and Serological Response in a Large Italian Sexually Transmitted Disease Centre: A Monocentric Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7499. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247499
Marchese V, Tiecco G, Storti S, Degli Antoni M, Calza S, Gulletta M, Viola F, Focà E, Matteelli A, Castelli F, et al. Syphilis Infections, Reinfections and Serological Response in a Large Italian Sexually Transmitted Disease Centre: A Monocentric Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(24):7499. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247499
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarchese, Valentina, Giorgio Tiecco, Samuele Storti, Melania Degli Antoni, Stefano Calza, Maurizio Gulletta, Francesca Viola, Emanuele Focà, Alberto Matteelli, Francesco Castelli, and et al. 2022. "Syphilis Infections, Reinfections and Serological Response in a Large Italian Sexually Transmitted Disease Centre: A Monocentric Retrospective Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 24: 7499. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247499
APA StyleMarchese, V., Tiecco, G., Storti, S., Degli Antoni, M., Calza, S., Gulletta, M., Viola, F., Focà, E., Matteelli, A., Castelli, F., & Quiros-Roldan, E. (2022). Syphilis Infections, Reinfections and Serological Response in a Large Italian Sexually Transmitted Disease Centre: A Monocentric Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(24), 7499. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247499









