Single-Stage Revision Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: Preoperative Planning, Surgical Technique, and Mixed Reality Execution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preoperative Planning for Revision Shoulder Arthroplasty
2.1. Patient Factors
2.2. Implants and Bony Anatomy
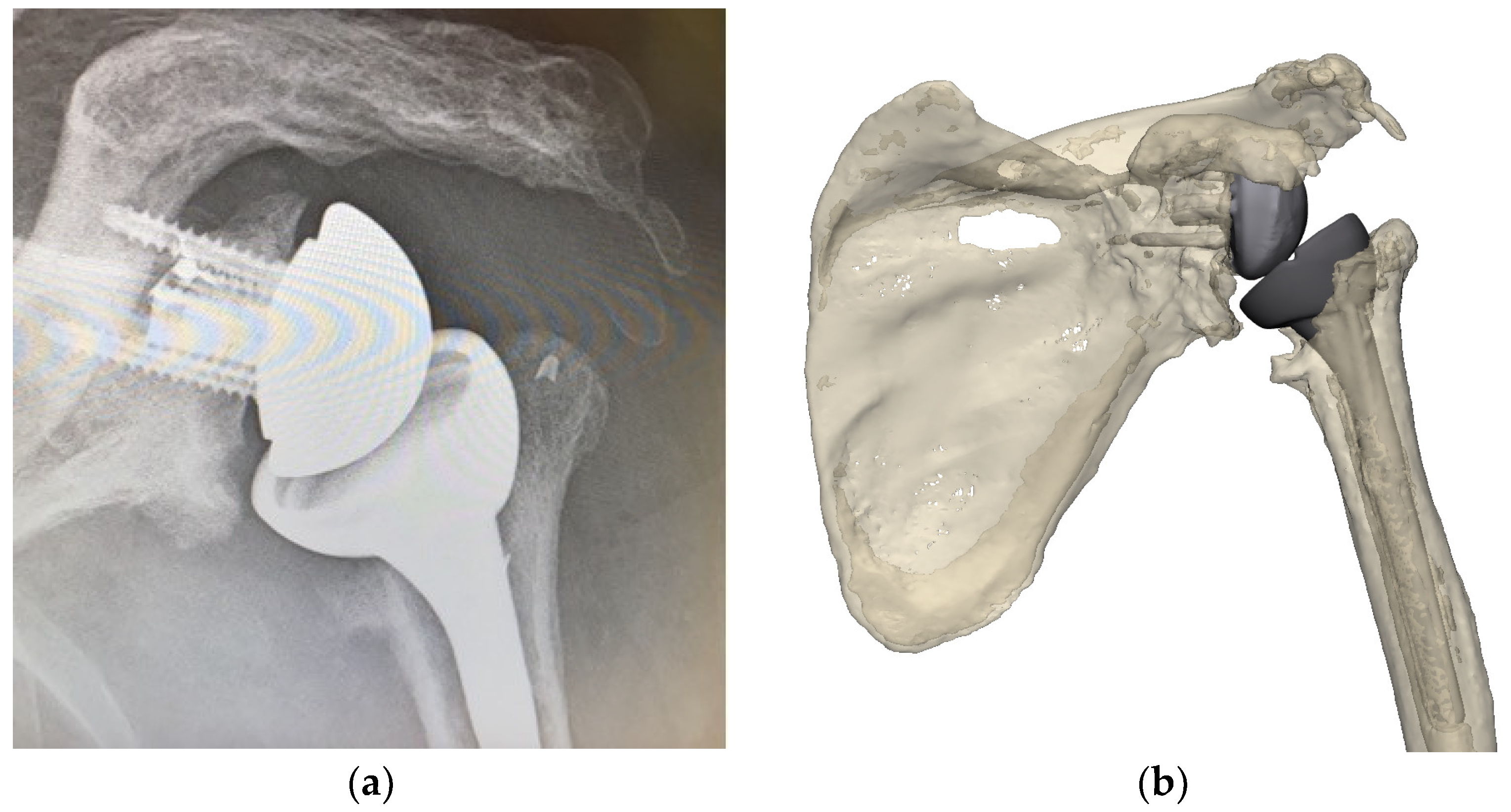
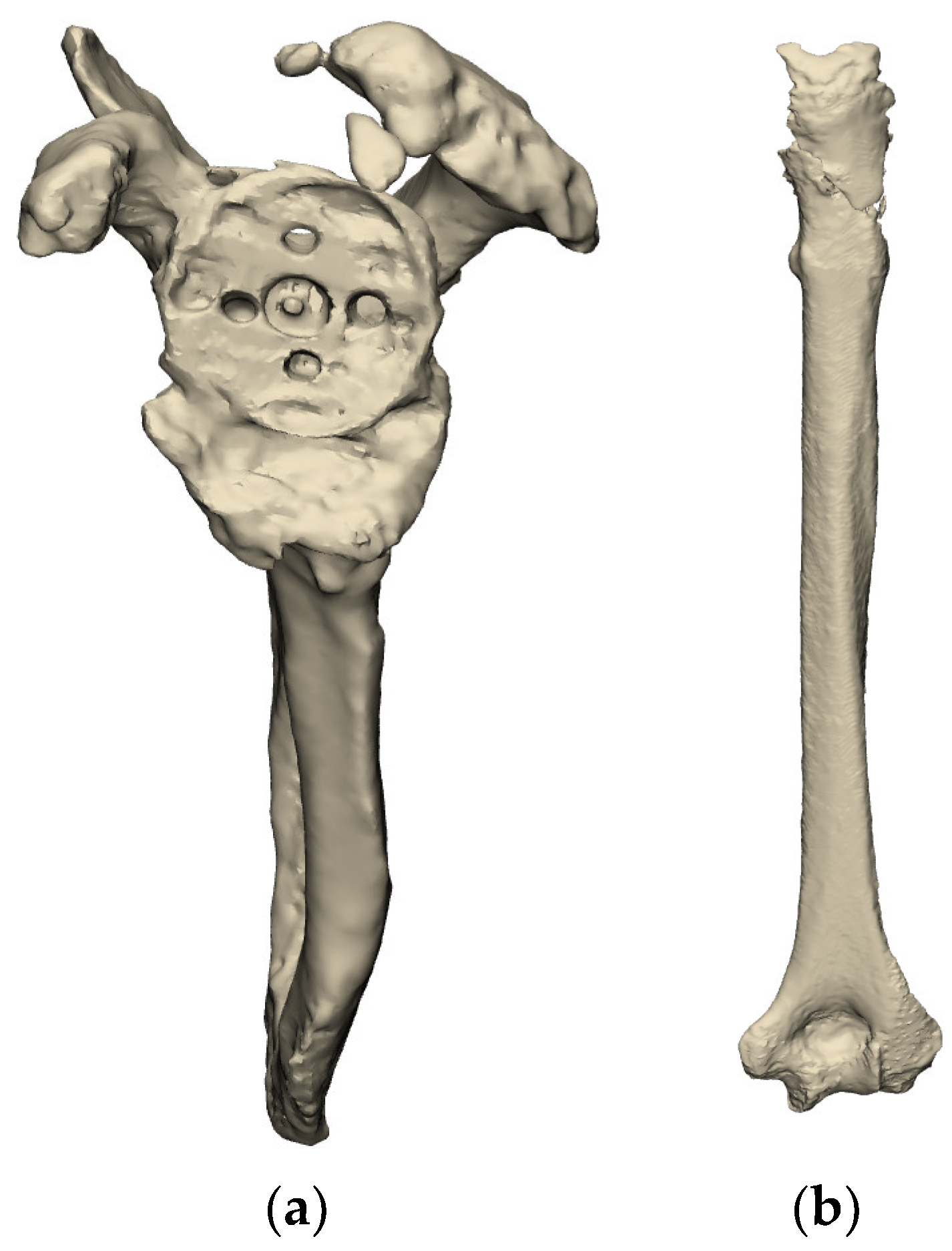
2.2.1. Existing Implants
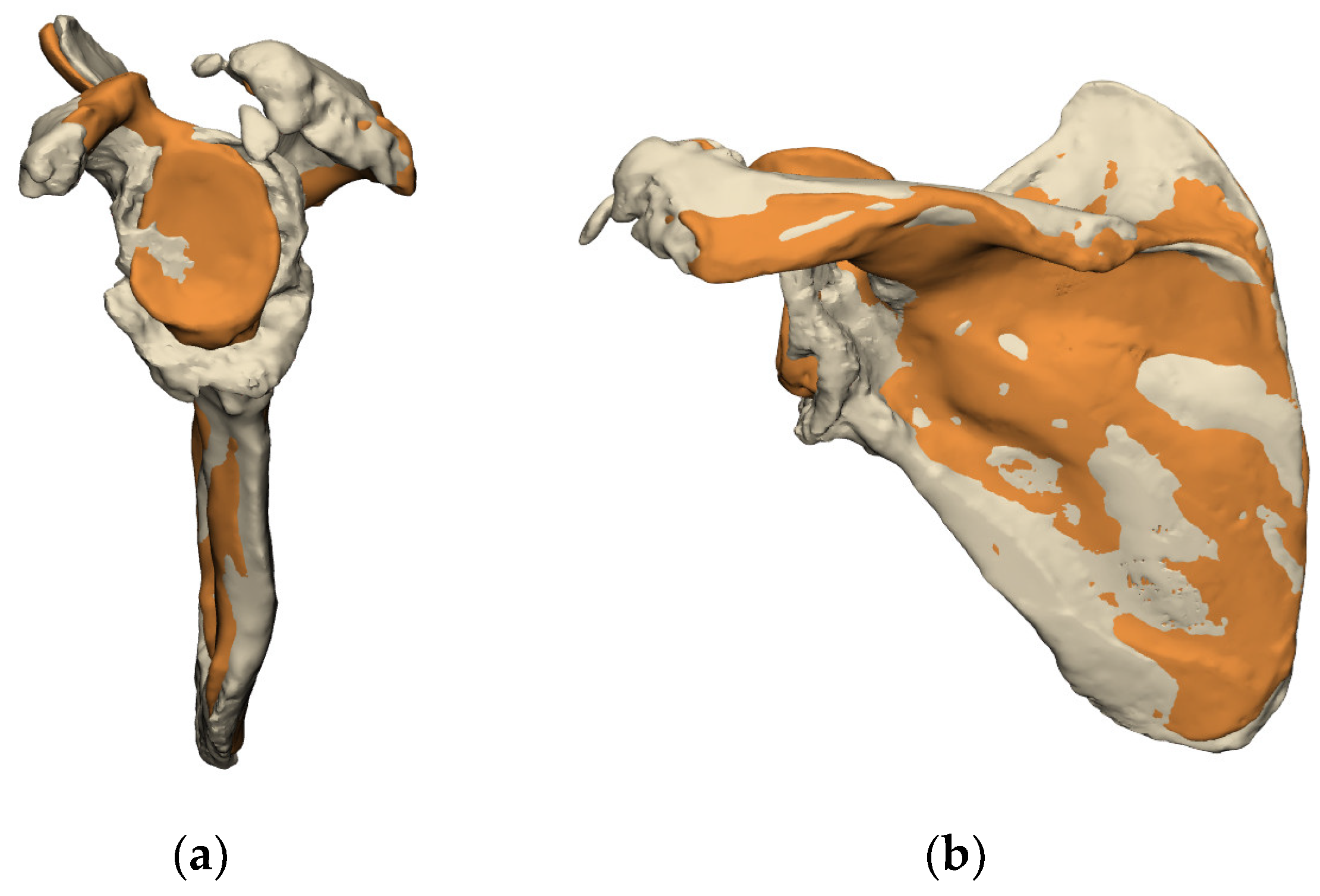
2.2.2. Bony Anatomy
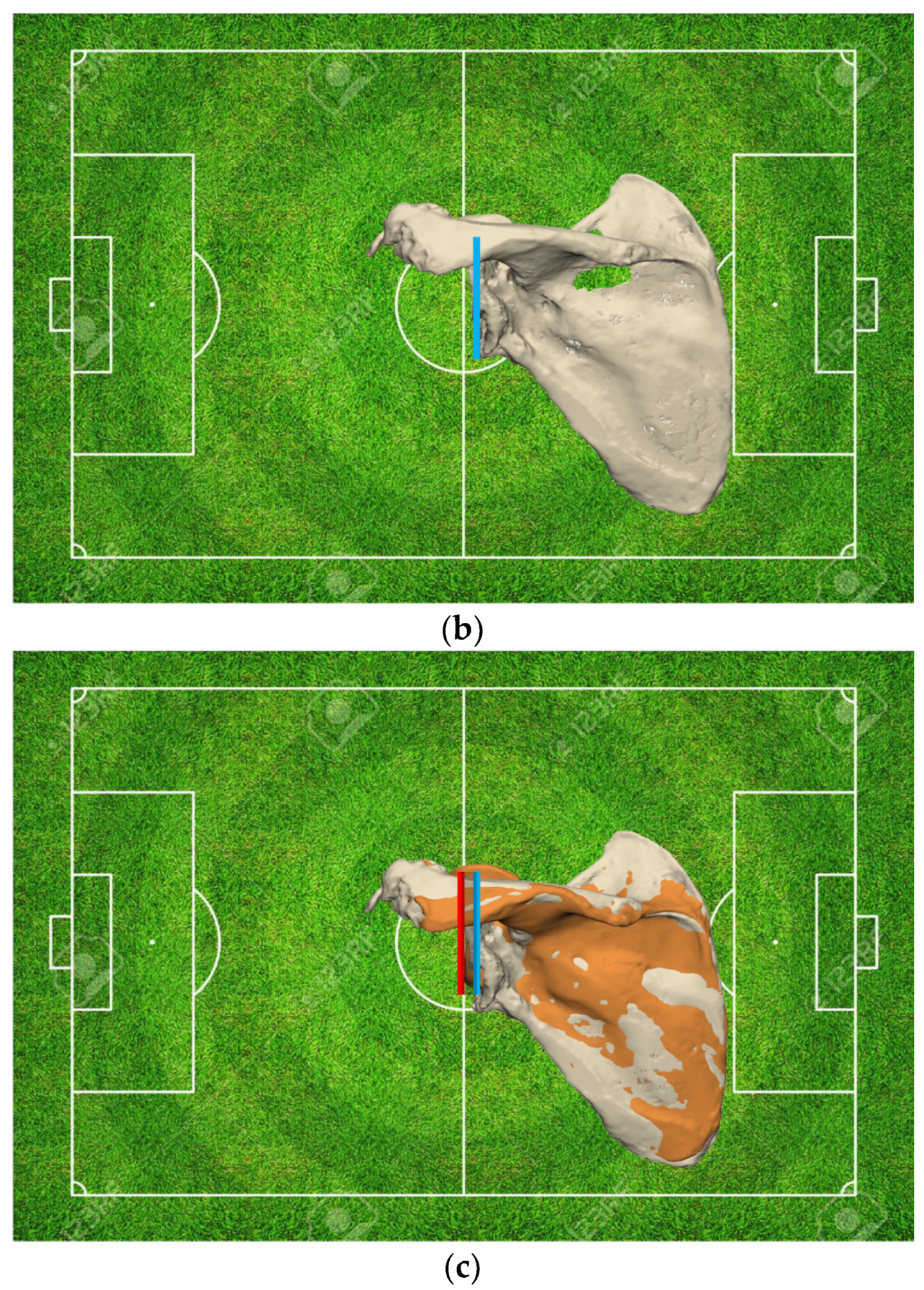
Glenoid
- Evaluation of the Glenoid Bone Loss
- Residual Bone Stock available for Reconstruction
- Evaluation of the volumetric bone loss in the glenoid,
- Development of a framework for reconstruction modalities: use of bone grafts, metal augments, or custom implants.
- Most critically, it enables the surgeon to restore the glenoid joint line.
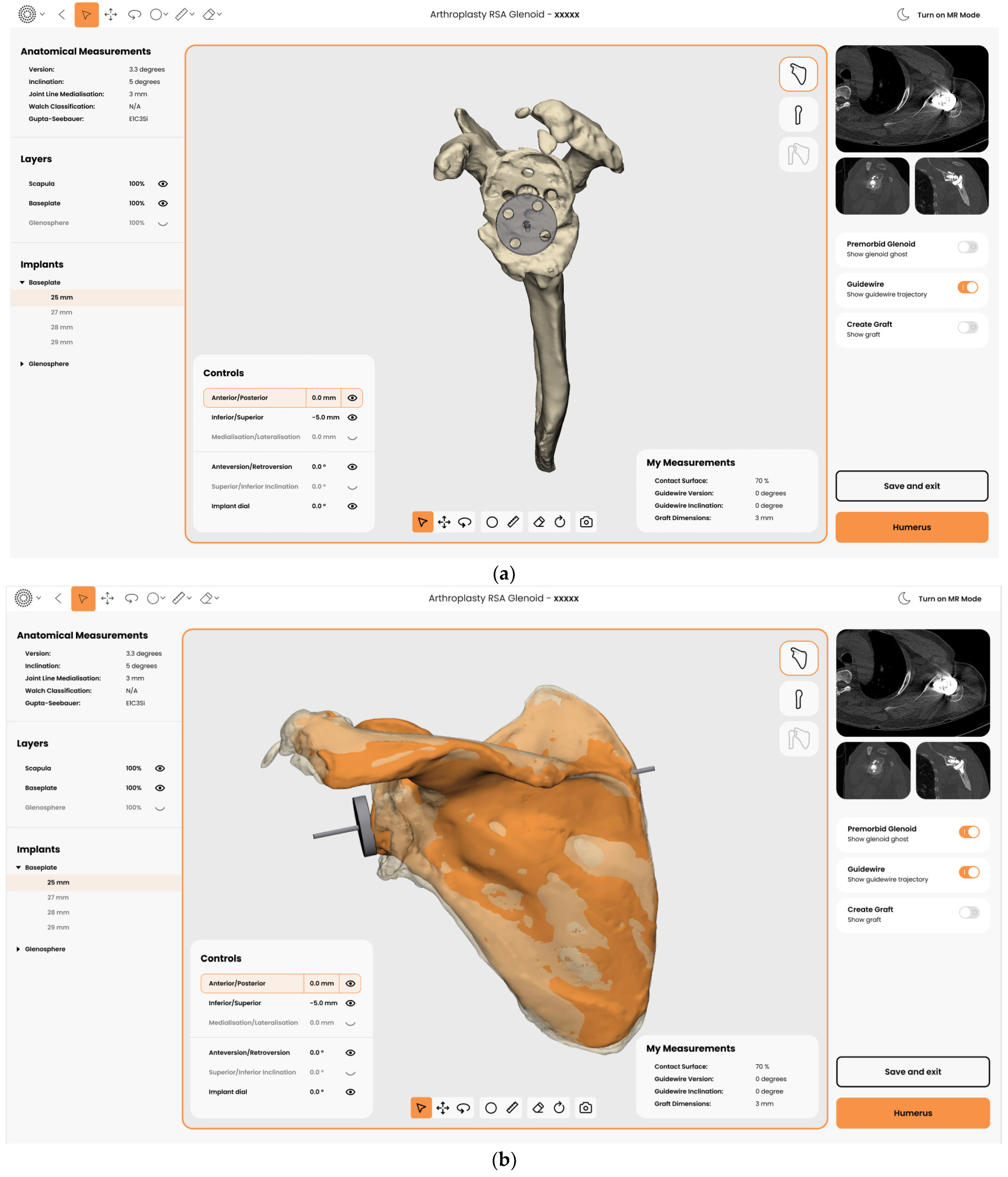
- Glenoid Joint Line Concept
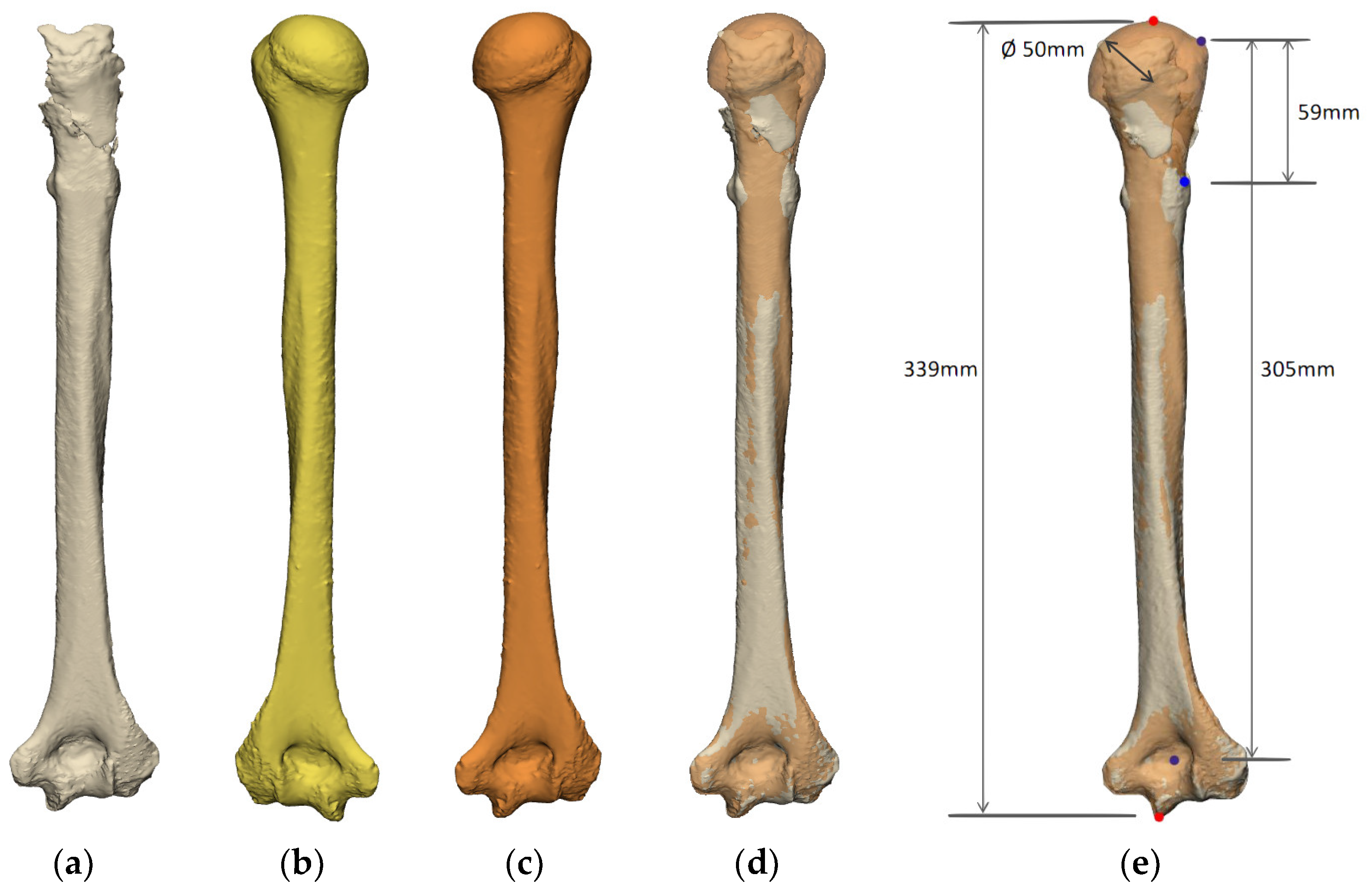
Humerus
2.2.3. Planning of Implants
Glenoid
Humerus
- Bone Deficiencies Proximal to the Pectoralis Major Tendon Insertion (<6 cm)
- Bone Deficiencies below the Pectoralis Major Origin but Proximal to Deltoid Insertion (6–14 cm)
- Bone Deficiencies Below the Deltoid Insertion (>14 cm)
2.3. Soft Tissue Condition
3. Surgical Technique
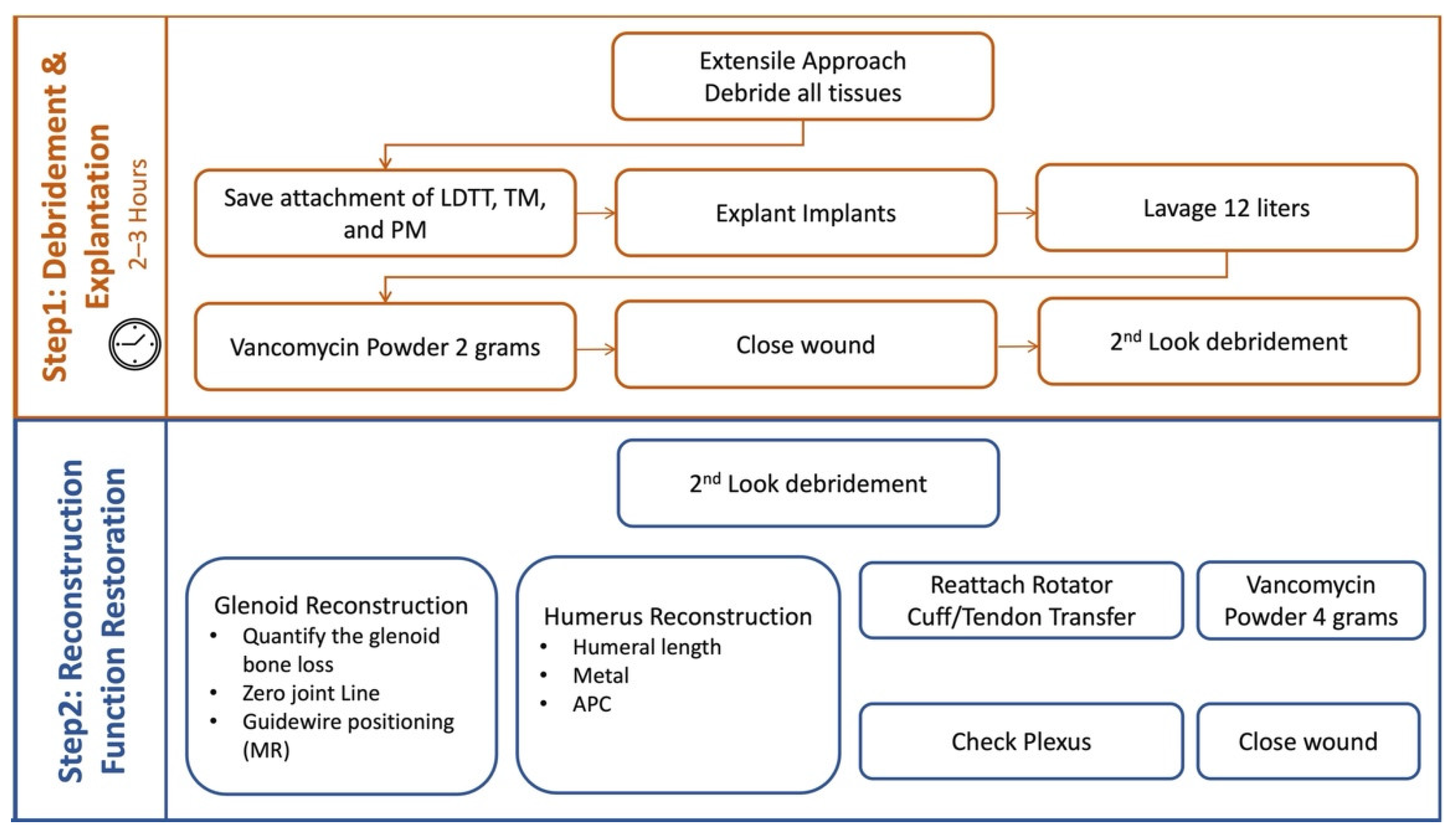
3.1. Two Step Single-Stage Procedure
- First Step
- Second Step
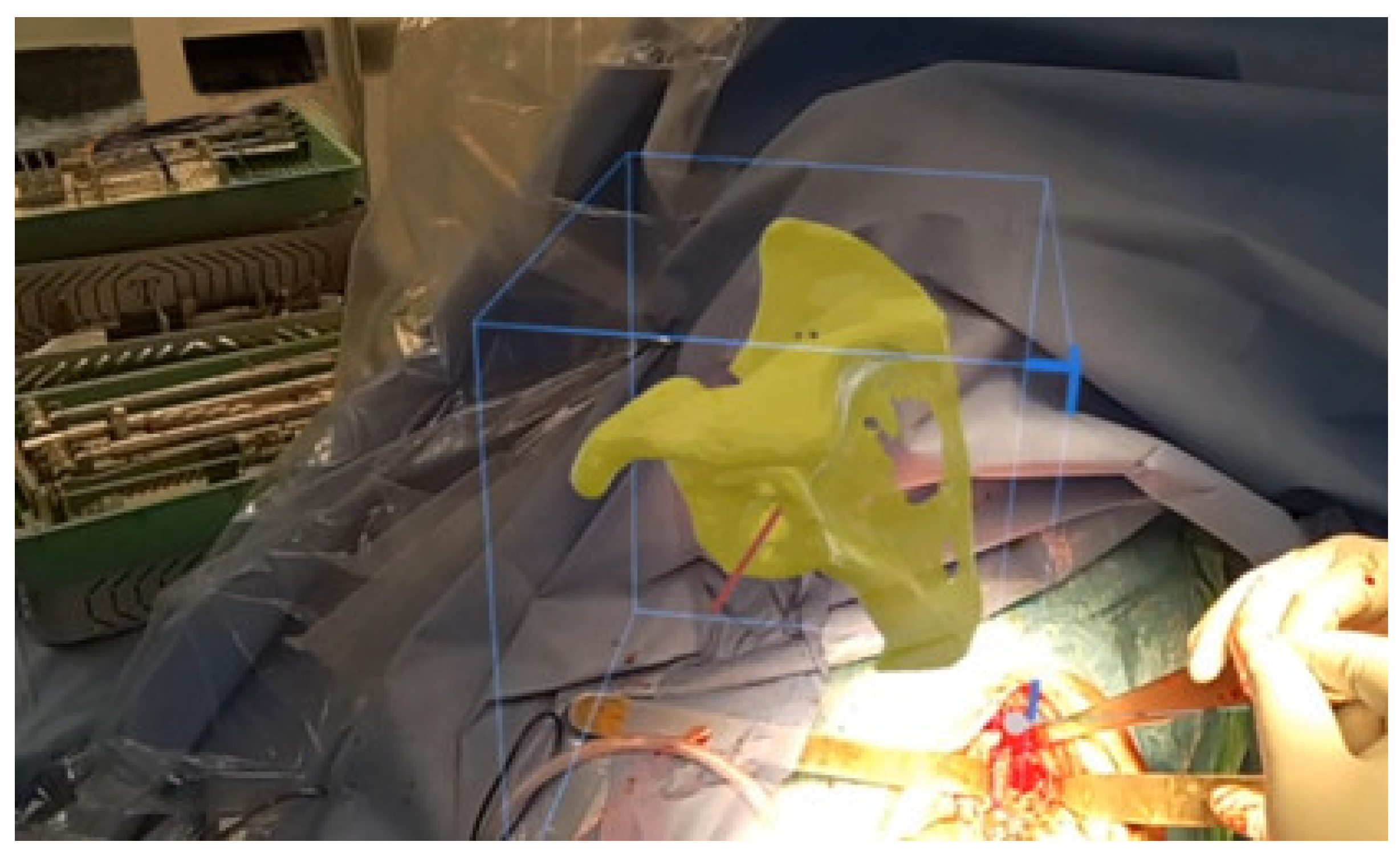
3.2. Execution with Mixed Reality (MR)
3.3. Soft Tissue Balancing and Reconstruction
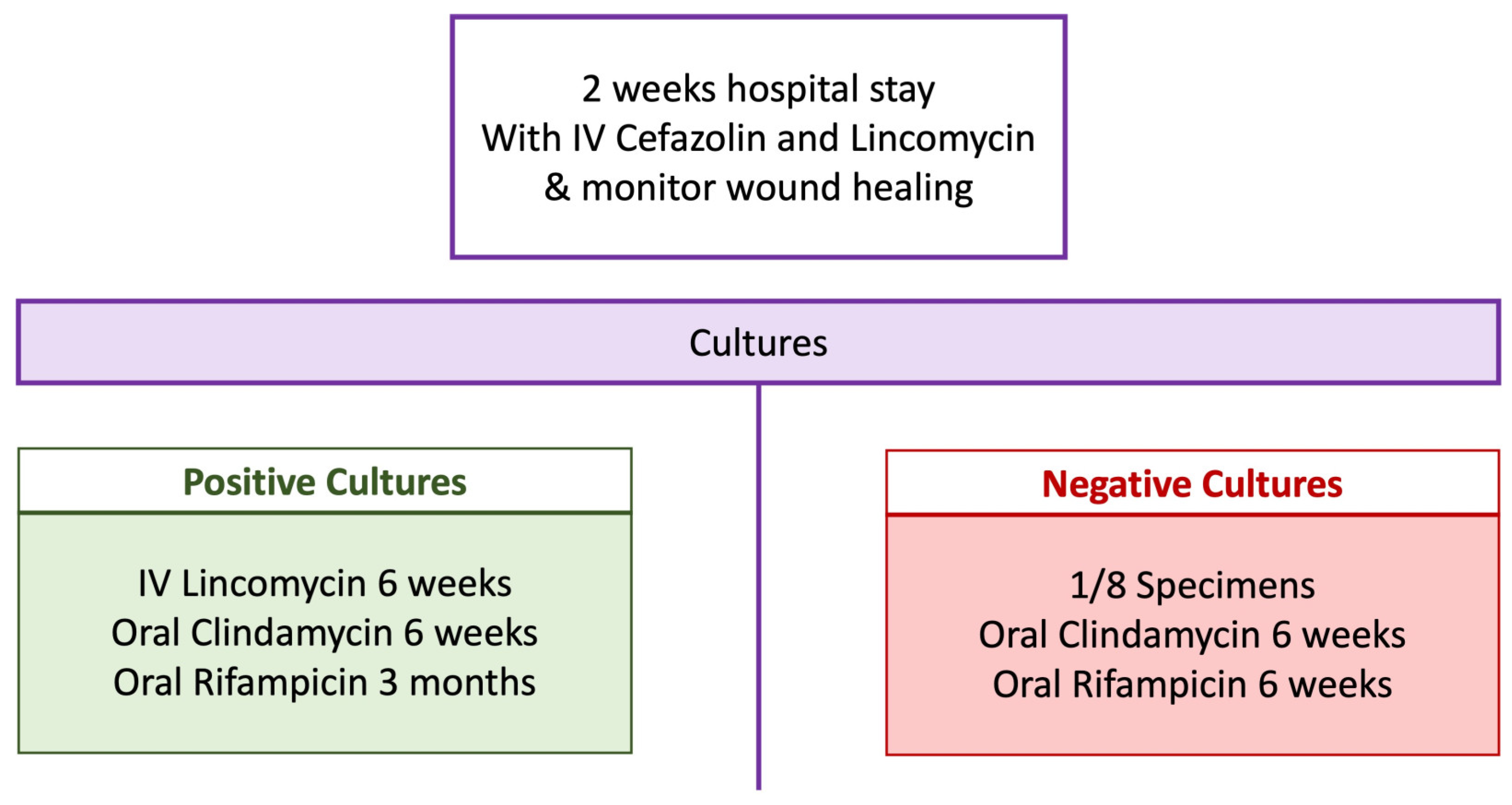
3.4. Postoperative Antibiotic Regimen
4. Preliminary Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry (AOANJRR). Hip, Knee & Shoulder Arthroplasty: 2022 Annual Report; AOA: Adelaide, Australia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, D.R.J.; Page, R.S.; Graves, S.E.; Rainbird, S.; Hatton, A. The Rate of 2nd Revision for Shoulder Arthroplasty as Analyzed by the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry (AOANJRR). Acta Orthop. 2021, 92, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, B.C.; Burrus, M.T.; Begho, I.; Gwathmey, F.W.; Brockmeier, S.F. Early Revision within 1 Year after Shoulder Arthroplasty: Patient Factors and Etiology. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2015, 24, e323–e330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melis, B.; Bonnevialle, N.; Neyton, L.; Lévigne, C.; Favard, L.; Walch, G.; Boileau, P. Glenoid Loosening and Failure in Anatomical Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Is Revision with a Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty a Reliable Option? J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2012, 21, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boileau, P. Complications and Revision of Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2016, 102, S33–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alentorn-Geli, E.; Samitier, G.; Torrens, C.; Wright, T.W. Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty. Part 2: Systematic Review of Reoperations, Revisions, Problems, and Complications. Int. J. Shoulder Surg. 2015, 9, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnetzke, M.; Preis, A.; Coda, S.; Raiss, P.; Loew, M. Anatomical and Reverse Shoulder Replacement with a Convertible, Uncemented Short-Stem Shoulder Prosthesis: First Clinical and Radiological Results. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2017, 137, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiari, A.; Hamoodi, Z.; Newton, A.; Nixon, M.; Webb, M.; Kenyon, P. The Incidence of Humeral Bone Resorption in Uncemented Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty and the Impact on Functional Outcomes. Semin. Arthroplast. JSES 2022, 32, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, P.; Melis, B.; Duperron, D.; Moineau, G.; Rumian, A.P.; Han, Y. Revision Surgery of Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2013, 22, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denard, P.J.; Haidamous, G.; Gobezie, R.; Romeo, A.A.; Lederman, E. Short-Term Evaluation of Humeral Stress Shielding Following Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Using Press-Fit Fixation Compared with Cemented Fixation. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2020, 29, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumstein, M.A.; Pinedo, M.; Old, J.; Boileau, P. Problems, Complications, Reoperations, and Revisions in Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2011, 20, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatte, T.O.; Kendoff, D.; Kamath, A.F.; Jonen, V.; Rueger, J.M.; Frommelt, L.; Gebauer, M.; Gehrke, T. Single-Stage Revision for Fungal Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Single-Centre Experience. Bone Jt. J. 2014, 96 B, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawi, N.; Kendoff, D.; Citak, M.; Gehrke, T.; Haasper, C. Septic Single-Stage Knee Arthrodesis after Failed Total Knee Arthroplasty Using a Cemented Coupled Nail. Bone Jt. J. 2015, 97-B, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Kieboom, J.; Tirumala, V.; Box, H.; Oganesyan, R.; Klemt, C.; Kwon, Y.M. One-Stage Revision Is as Effective as Twostage Revision for Chronic Culture-Negative Periprosthetic Joint Infection after Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty a Retrospective Cohort Study. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103-B, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liechti, E.F.; Neufeld, M.E.; Soto, F.; Linke, P.; Busch, S.M.; Gehrke, T.; Citak, M. Favourable Outcomes of Repeat One-Stage Exchange for Periprosthetic Joint Infection of the Hip. Bone Jt. J. 2022, 104, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuff, D.J.; Virani, N.A.; Levy, J.; Frankle, M.A.; Derasari, A.; Hines, B.; Pupello, D.R.; Cancio, M.; Mighell, M. The Treatment of Deep Shoulder Infection and Glenohumeral Instability with Debridement, Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty and Post-Operative Antibiotics. J. Bone Jt. Surg.-Ser. B 2008, 90, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, A.; Seemann, K.; Frommelt, L.; Katzer, A.; Loehr, J.F. One-Stage Exchange Shoulder Arthroplasty for Peri-Prosthetic Infection. J. Bone Jt. Surg.-Ser. B 2005, 87, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatte, T.O.; Junghans, K.; Al-Khateeb, H.; Rueger, J.M.; Gehrke, T.; Kendoff, D.; Neumann, J. Single-Stage Revision for Peri-Prosthetic Shoulder Infection. Bone Jt. J. 2013, 95-B, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, Z.C.; Holland, C.T.; Meehan, J.P. Systematic Review of Single Stage Revision for Prosthetic Joint Infection. World J. Orthop. 2020, 11, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, A.; Taylor, F. Classifications in Brief: The McPherson Classification of Periprosthetic Infection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, M.J.; Holleman, R.; Klamerus, M.L.; Bosworth, H.B.; Edelman, D.; Heisler, M. Factors Associated with Persistent Poorly Controlled Diabetes Mellitus: Clues to Improving Management in Patients with Resistant Poor Control. Chronic Illn. 2014, 10, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, B.; Chen, A.F. Reducing the Risk of Infection after Total Joint Arthroplasty: Preoperative Optimization. Arthroplasty 2019, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casp, A.J.; Montgomery, S.R.; Cancienne, J.M.; Brockmeier, S.F.; Werner, B.C. Osteoporosis and Implant-Related Complications After Anatomic and Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 28, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalmers, P.N.; Romeo, A.A.; Nicholson, G.P.; Boileau, P.; Keener, J.D.; Gregory, J.M.; Salazar, D.H.; Tashjian, R.Z. Humeral Bone Loss in Revision Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: The Proximal Humeral Arthroplasty Revision Osseous InSufficiency (PHAROS) Classification System. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2019, 477, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalise, J.J.; Iannotti, J.P. Bone Grafting Severe Glenoid Defects in Revision Shoulder Arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Thussbas, C.; Koch, M.; Seebauer, L. Management of Glenoid Bone Defects with Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty—Surgical Technique and Clinical Outcomes. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2018, 27, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salhi, A.; Burdin, V.; Boutillon, A.; Brochard, S.; Mutsvangwa, T.; Borotikar, B. Statistical Shape Modeling Approach to Predict Missing Scapular Bone. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 48, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italia, K.R.; Green, N.; Maharaj, J.; Launay, M.; Gupta, A. Computed Tomographic Evaluation of Glenoid Joint Line Restoration with Glenoid Bone Grafting and Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty in Patients with Significant Glenoid Bone Loss. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2021, 30, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, L.; Launay, M.; Green, N.; Maharaj, J.; Cutbush, K.; Gupta, A. A 3-Dimensional Method to Estimate Restoration of Native Joint Line Preoperatively. In Proceedings of the 2022 Shoulder and Elbow Society of Australia Biennial Conference, Sydney, Australia, 3 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, D.M.; Frank, T.; Whyne, C.M.; Henry, P.D. Glenoid Component Positioning and Guidance Techniques in Anatomic and Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Shoulder Elb. 2019, 11, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lädermann, A.; Edwards, T.B.; Walch, G. Arm Lengthening after Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Review. Int. Orthop. 2014, 38, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markes, A.R.; Cheung, E.; Ma, C.B. Failed Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty and Recommendations for Revision. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2020, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, S.; Greiwe, R.M.; Frankle, M.A.; Siegal, S.; Lee, W.E. Biomechanical Comparison of Component Position and Hardware Failure in the Reverse Shoulder Prosthesis. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2007, 16, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laver, L.; Garrigues, G.E. Avoiding Superior Tilt in Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Review of the Literature and Technical Recommendations. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2014, 23, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohlke, F.; Abdelkawi, A.A.; Eltair, H.; Aboalata, M.; Hussein, W.; Abdrabo, M.S.; Jasper, T. Revision of Failed Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty—A Point of No Return?: Analysis of a Series of 136 Consecutive Cases, Review of the Literature, and Recommendations. Obere Extrem. 2020, 15, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrier, A.; Ramondetti, S.; Merlini, F.; Pioletti, D.D.; Farron, A. Biomechanical Consequences of Humeral Component Malpositioning after Anatomical Total Shoulder Arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2010, 19, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, B.H.; Halpern, A.L.; Deal, M.J.; Richey, B.P.; Mason, E.M.; Gupta, H.O.; Callegari, J.; Bravo, C.J. Management of Revision Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Arthroplast. 2020, 4, 247154922090229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankle, M.A.; Teramoto, A.; Luo, Z.-P.; Levy, J.C.; Pupello, D. Glenoid Morphology in Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: Classification and Surgical Implications. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2009, 18, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, C.C.; Ekhtiari, S.; Oral, I.; Selznick, A.; Mundi, R.; Chaudhry, H.; Pincus, D.; Wolfstadt, J.; Kandel, C.E. The Use of Rifampin in Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A. Two-Stage vs Single-Stage Revision Arthroplasty—Clinical Outcomes. In Proceedings of the 2022 Shoulder and Elbow Society of Australia (SESA) Biennial Conference, Sydney, Australia, 2 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sheth, B.; Lavin, A.C.; Martinez, C.; Sabesan, V.J. The Use of Preoperative Planning to Decrease Costs and Increase Efficiency in the OR. JSES Int. 2022, 6, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Patient Factors | Bony Anatomy | Implants | Soft Tissue Balancing |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Etiology | |
|---|---|
| Infection | 17% |
| Pain | 21% |
| Implant loosening | 8% |
| Fracture | 8% |
| Other | 21% |
| Preop | Postop | |
|---|---|---|
| Total Hospital stay (days) | 16 ± 13 | |
| Forward Flexion (deg) | 65 ± 52 | 142 ± 29 |
| Lateral Elevation (deg) | 58 ± 43 | 128 ± 36 |
| External Rotation (deg) | 14 ± 23 | 38 ± 22 |
| Patient satisfaction (%) | 5 | 87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Italia, K.; Launay, M.; Gilliland, L.; Nielsen, J.; Pareyon, R.; Hollman, F.; Salhi, A.; Maharaj, J.; Jomaa, M.; Cutbush, K.; et al. Single-Stage Revision Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: Preoperative Planning, Surgical Technique, and Mixed Reality Execution. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7422. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247422
Italia K, Launay M, Gilliland L, Nielsen J, Pareyon R, Hollman F, Salhi A, Maharaj J, Jomaa M, Cutbush K, et al. Single-Stage Revision Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: Preoperative Planning, Surgical Technique, and Mixed Reality Execution. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(24):7422. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247422
Chicago/Turabian StyleItalia, Kristine, Marine Launay, Luke Gilliland, James Nielsen, Roberto Pareyon, Freek Hollman, Asma Salhi, Jashint Maharaj, Mohammad Jomaa, Kenneth Cutbush, and et al. 2022. "Single-Stage Revision Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: Preoperative Planning, Surgical Technique, and Mixed Reality Execution" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 24: 7422. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247422
APA StyleItalia, K., Launay, M., Gilliland, L., Nielsen, J., Pareyon, R., Hollman, F., Salhi, A., Maharaj, J., Jomaa, M., Cutbush, K., & Gupta, A. (2022). Single-Stage Revision Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: Preoperative Planning, Surgical Technique, and Mixed Reality Execution. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(24), 7422. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11247422








