Lung Cancer Clinical Trials with a Seamless Phase II/III Design: Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction
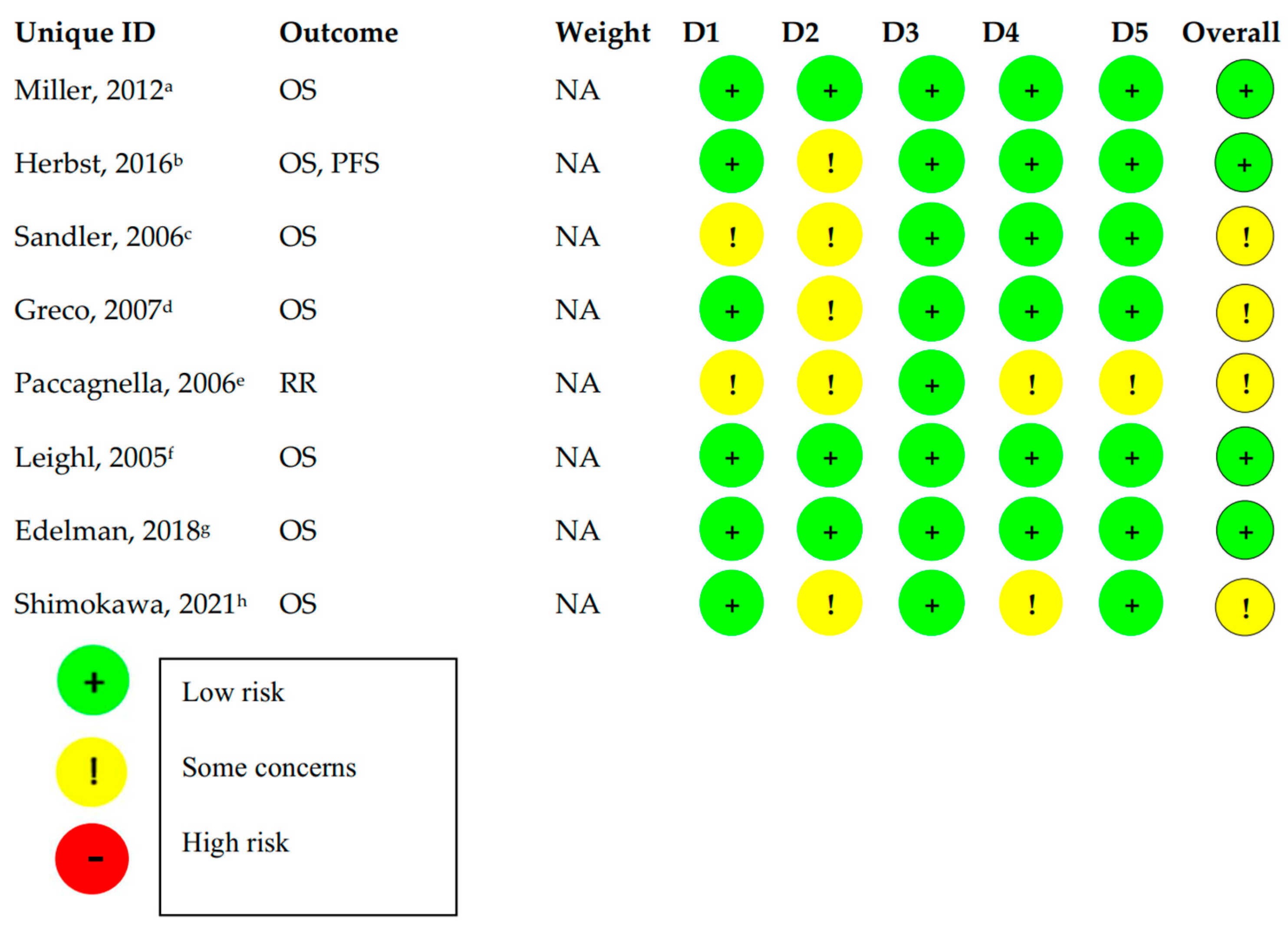
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
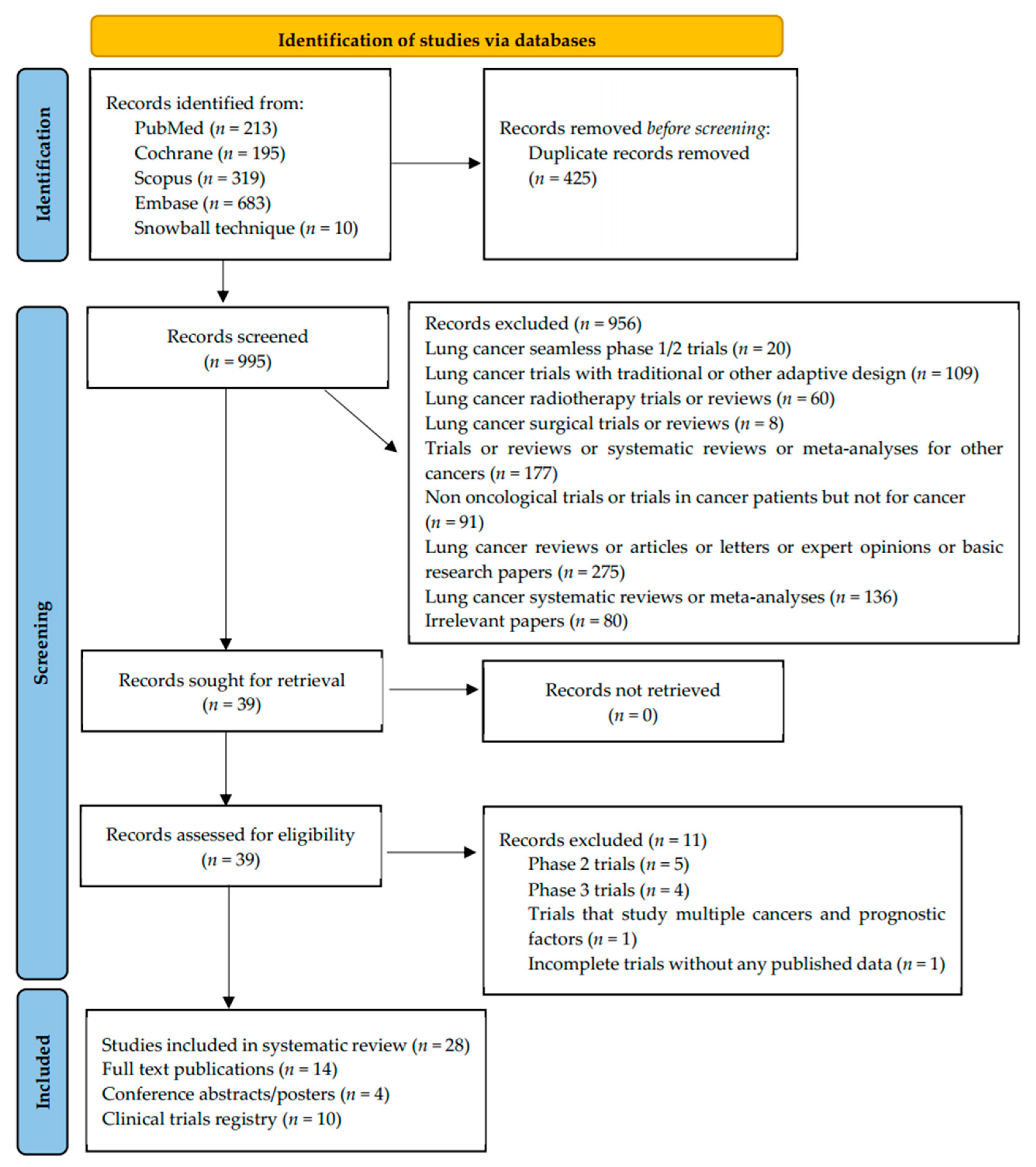
3. Results
3.1. Subtypes of Seamless Phase II/III Design
- (a)
- Phase II/III trials with inefficacy/futility analyses (Inferentially Seamless)
- (b)
- Dose escalation Phase II/III trials (Operationally Seamless)
- (c)
- Multi-Arm Multi Stage (MAMS) phase II/III trials
- (d)
- Trials with other design
3.2. Risk of Bias Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thai, A.A.; Solomon, B.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Gainor, J.F.; Heist, R.S. Lung cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, A.G.; Tsao, M.S.; Beasley, M.B.; Borczuk, A.C.; Brambilla, E.; Cooper, W.A.; Dacic, S.; Jain, D.; Kerr, K.M.; Lantuejoul, S.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Advances Since 2015. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 17, 362–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin, C.M.; Brambilla, E.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Sage, J. Small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imyanitov, E.N.; Iyevleva, A.G.; Levchenko, E.V. Molecular testing and targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: Current status and perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2021, 157, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallmann, P.; Bedding, A.W.; Choodari-Oskooei, B.; Dimairo, M.; Flight, L.; Hampson, L.V.; Holmes, J.; Mander, A.P.; Odondi, L.; Sydes, M.R.; et al. Adaptive designs in clinical trials: Why use them, and how to run and report them. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Herbst, R.S.; Boshoff, C. Toward personalized treatment approaches for non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, R.; Gupta, K. Adaptive design clinical trials: Methodology, challenges and prospect. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2010, 42, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuffe, R.L.; Lawrence, D.; Stone, A.; Vandemeulebroecke, M. When is a seamless study desirable? Case studies from different pharmaceutical sponsors. Pharm. Stat. 2014, 13, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, E.L.; Freidlin, B.; Abrams, J.S.; Halabi, S. Design Issues in Randomized Phase II/III Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, W.S.; Wilson, M.C.; Nishikawa, J.; Hayward, R.S. The well-built clinical question: A key to evidence-based decisions. ACP J. Club 1995, 123, A12–A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, V.A.; Hirsh, V.; Cadranel, J.; Chen, Y.-M.; Park, K.; Kim, S.-W.; Zhou, C.; Su, W.-C.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; et al. Afatinib versus placebo for patients with advanced, metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of erlotinib, gefitinib, or both, and one or two lines of chemotherapy (LUX-Lung 1): A phase 2b/3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, A.; Gray, R.; Perry, M.C.; Brahmer, J.; Schiller, J.H.; Dowlati, A.; Lilenbaum, R.; Johnson, D.H. Paclitaxel–Carboplatin Alone or with Bevacizumab for Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2542–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paccagnella, A.; Oniga, F.; Bearz, A.; Favaretto, A.; Clerici, M.; Barbieri, F.; Riccardi, A.; Chella, A.; Tirelli, U.; Ceresoli, G.; et al. Adding Gemcitabine to Paclitaxel/Carboplatin Combination Increases Survival in Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results of a Phase II-III Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eba, J.; Shimokawa, T.; Nakamura, K.; Shibata, T.; Misumi, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Yamamoto, N. A randomized phase II/III study comparing carboplatin and irinotecan with carboplatin and etoposide for the treatment of elderly patients with extensive-disease small cell lung cancer (JCOG1201/TORG1528). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. 15), 8571. [Google Scholar]
- Greco, F.A.; Spigel, D.R.; Kuzur, M.E.; Shipley, D.; Gray, J.R.; Thompson, D.S.; Burris, H.A.; Yardley, D.A.; Pati, A.; Webb, C.D.; et al. Paclitaxel/Carboplatin/Gemcitabine Versus Gemcitabine/Vinorelbine in Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase II/III Study of the Minnie Pearl Cancer Research Network. Clin. Lung Cancer 2007, 8, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, G.D.; Arnold, A.; Shepherd, F.A.; Dediu, M.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Fenton, D.; Zukin, M.; Walde, D.; Laberge, F.; Vincent, M.D.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blind Trial of Carboplatin and Paclitaxel with Either Daily Oral Cediranib or Placebo in Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: NCIC Clinical Trials Group BR24 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quoix, E.; Lena, H.; Losonczy, G.; Forget, F.; Chouaid, C.; Papai, Z.; Gervais, R.; Ottensmeier, C.; Szczesna, A.; Kazarnowicz, A.; et al. TG4010 immunotherapy and first-line chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (TIME): Results from the phase 2b part of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b/3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 17, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Wolf, J.; Litten, J.B.; Higashi, L.A.; Isaacson, J.D.; Mok, T. TIGER 1: A randomized, open-label, phase 2/3 study of rociletinib (CO-1686) or erlotinib as first-line treatment for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33 (Suppl. 15), TPS8108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, J.H.; Storer, B.; Dreicer, R.; Rosenquist, D.; Frontiera, M.; Carbone, P.P. Randomized Phase II-III Trial of Combination Beta and Gamma Interferons and Etoposide and Cisplatin in Inoperable Non-Small Cell Cancer of the Lung. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1989, 81, 1739–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leighl, N.B.; Paz-Ares, L.; Douillard, J.-Y.; Peschel, C.; Arnold, A.; Depierre, A.; Santoro, A.; Betticher, D.C.; Gatzemeier, U.; Jassem, J.; et al. Randomized Phase III Study of Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitor BMS-275291 in Combination With Paclitaxel and Carboplatin in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: National Cancer Institute of Canada-Clinical Trials Group Study BR.18. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 2831–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EEdelman, M.J.; Redman, M.W.; Albain, K.S.; McGary, E.C.; Rafique, N.M.; Petro, D.; Waqar, S.N.; Minichiello, K.; Miao, J.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; et al. SWOG S1400C (NCT02154490)—A Phase II Study of Palbociclib for Previously Treated Cell Cycle Gene Alteration–Positive Patients with Stage IV Squamous Cell Lung Cancer (Lung-MAP Substudy). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghaei, H.; Redman, M.W.; Kelly, K.; Waqar, S.N.; Robert, F.; Kiefer, G.J.; Stella, P.J.; Minichiello, K.; Gandara, D.R.; Herbst, R.S.; et al. SWOG S1400A (NCT02154490): A Phase II Study of Durvalumab for Patients with Previously Treated Stage IV or Recurrent Squamous Cell Lung Cancer (Lung-MAP Sub-study). Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 22, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCT03811002: Testing the Addition of a New Immunotherapy Drug, Atezolizumab (MPDL3280A), to the Usual Chemoradiation (CRT) Therapy Treatment for Limited Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (LS-SCLC). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03811002 (accessed on 29 July 2022).
- NCT04750083: HX008 Plus Chemotherapy VS Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy as the First-line Treatment in Participants with Advanced or Metastatic Nonsquamous Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04750083 (accessed on 29 July 2022).
- NCT04929041: Testing the Addition of Radiation Therapy to the Usual Treatment (Immunotherapy with or Without Chemotherapy) for Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Who Are PD-L1 Negative. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04929041 (accessed on 29 July 2022).
- NCT05255302: De-escalation Immunotherapy mAintenance Duration Trial for Stage IV Lung Cancer Patients with Disease Control After Chemo-Immunotherapy Induction (DIAL). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05255302 (accessed on 29 July 2022).
- NCT02926638: Lung-MAP: Rilotumumab and Erlotinib Hydrochloride or Erlotinib Hydrochloride Alone as Second-Line Therapy in Treating Patients with Recurrent Stage IV Squamous Cell Lung Cancer and Positive Biomarker Matches. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02926638 (accessed on 29 July 2022).
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.-W.; Felip, E.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.-Y.; Molina, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Arvis, C.D.; Ahn, M.-J.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, M.J.; Juan, O.; Navarro, A.; Golden, G.; Borg, E.; Saunders, A.V. A two-part, open-label, randomized, phase 2/3 study of dinutuximab and irinotecan versus irinotecan for second-line treatment of subjects with relapsed or refractory small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. 15), TPS8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Chen, Y.; Jove, M.; Juan-Vidal, O.; Rich, P.; Hayes, T.; Calderón, V.G.; Caro, R.B.; Navarro, A.; et al. RESILIENT part 1: A phase 2 dose-exploration and dose-expansion study of second-line liposomal irinotecan in adults with small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2022, 128, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCT04254471: This Phase II/III, Multicenter Study is Designed to Evaluate the Safety and Clinical Activity of AL3810 in Patients. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04254471 (accessed on July 29 2022).
- NCT05001724: KN046 Plus Lenvatinib in Subject with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Failure of Anti-PD-(L)1 Agent. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05001724 (accessed on 29 July 2022).
- Dziadziuszko, R.; Mok, T.; Peters, S.; Han, J.-Y.; Alatorre-Alexander, J.; Leighl, N.; Sriuranpong, V.; Pérol, M.; Junior, G.D.C.; Nadal, E.; et al. Blood First Assay Screening Trial (BFAST) in Treatment-Naive Advanced or Metastatic NSCLC: Initial Results of the Phase 2 ALK-Positive Cohort. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 2040–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wislez, M.; Barlesi, F.; Besse, B.; Mazières, J.; Merle, P.; Cadranel, J.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Gautier-Felizot, L.; Goupil, F.; et al. Customized Adjuvant Phase II Trial in Patients with Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: IFCT-0801 TASTE. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, B.; Mazières, J.; Ribassin-Majed, L.; Barlesi, F.; Bennouna, J.; Gervais, R.; Moreau, L.; Berard, H.; Debieuvre, D.; Molinier, O.; et al. Pazopanib or placebo in completely resected stage I NSCLC patients: Results of the phase II IFCT-0703 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindan, R.; Morris, J.C.; Rossi, G.R.; Vahanian, N.N.; Link, C.J. NLG-0301: An open-label, randomized phase 2B active control study of second-line tergenpumatucel-L immunotherapy versus docetaxel in patients with progressive or relapsed non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32 (Suppl. 15), TPS8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCT03653546: First Line Treatment in EGFR Mutation Positive Advanced NSCLC Patients with Central Nervous System (CNS) Metastases (BM). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03653546 (accessed on 29 July 2022).
- NCT04206072: D-0316 Versus Icotinib in Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic EGFRSensitising Mutation Positive, N.S.C.L.C. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04206072 (accessed on 29 July 2022).
- Wang, S.; Zimmermann, S.; Parikh, K.; Mansfield, A.S.; Adjei, A.A. Current Diagnosis and Management of Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 1599–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, M.W.; Goldman, B.H.; LeBlanc, M.; Schott, A.; Baker, L.H. Modeling the relationship between progression-free survival and overall survival: The phase II/III trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2646–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Prowell, T.M.; Theoret, M.R.; Pazdur, R. Seamless Oncology-Drug Development. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2001–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nass, S.J.; Rothenberg, M.L.; Pentz, R.; Hricak, H.; Abernethy, A.; Anderson, K.; Gee, A.W.; Harvey, R.D.; Piantadosi, S.; Bertagnolli, M.M.; et al. Accelerating anticancer drug development—Opportunities and trade-offs. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidlin, B.; Korn, E.L.; Abrams, J.S. Bias, Operational Bias, and Generalizability in Phase II/III Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1902–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaptive Designs for Clinical Trials of Drugs and Biologics Guidance for Industry. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/78495/download (accessed on 31 September 2022).
- Sharma, M.R.; Stadler, W.M.; Ratain, M.J. Randomized phase II trials: A long-term investment with promising returns. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Dignam, J.J.; Zhang, Q.E.; DeGroot, J.F.; Mehta, M.P.; Hunsberger, S. Integrated phase II/III clinical trials in oncology: A case study. Clin. Trials. 2012, 9, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maca, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Dragalin, V.; Gallo, P.; Krams, M. Adaptive Seamless Phase II/III Designs—Background, Operational Aspects, and Examples. Drug Inf. J. 2006, 40, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerpohl, J.J.; Herrle, F.; Reinders, S.; Antes, G.; von Elm, E. Scientific value of systematic reviews: Survey of editors of core clinical journals. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Category | Inclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Population | Lung cancer patients (NSCLC or SCLC) |
| Interventions | Administration of any systematic treatment (chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy) |
| Comparator | Administration of any systematic treatment (chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy) |
| Outcomes | No restrictions |
| Study design | Seamless Phase II/III trials were defined as having both a prespecified Phase II (exploratory) and Phase III (confirmatory) portion that were occurring seamlessly, i.e., without a pause. |
| Other | Peer-reviewed publications, conference abstracts or Clinical registry records in the English language |
| Reference | Status | Condition | Treatment | No Arms | Year Started | Enrollment (Projected/ Actual) | Phase 3 Randomisation | Blinding | Phase II/III Type | Primary Endpoints | Secondary Endpoints | No Interim Analyses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | Completed | NSCLC | TT a (TKI k) | 2 | 2008 | 560/585 | Yes | Triple f | Phase IIb analysis (ORR) before full phase III accrual | OS | PFS, ORR, DOR, safety, | 1 |
| [15] | Completed | NSCLC | Combination of IT b (VEGF l inhibitor) and CT c | 2 | 2002 | Originally: 640 In January 2004: 842/878 | Yes | Open label | Phase II with 2 interim analyses with stopping rules for efficacy and futility (OS, PFS) | OS | PFS, RR | 2 |
| [16] | Completed | NSCLC | CT | 2 | 1998 | 324/324 | Yes | NR | Phase II trial (RR)amended to further evaluate the impact of the two CT regimens on OS | OS, RR | Toxicity | NR |
| [17] | Completed | SCLC | CT | 2 | 2013 | 250/258 | Yes | Open label | Phase II (ORR) to assess adequate efficacy in elderly patients | Phase II:ORR Phase III: OS | PFS, toxicity | 2 |
| [18] | Completed | NSCLC | CT | 6 | 2004 | 330/337 | Yes | Open label | 4-arm prospective randomized phase II trial (RR) extended to a randomized 2-arm phase III | OS, RR | PFS, toxicity | 1 |
| [19] | Completed only phase II portion | NSCLC | Combination of TT (TKI) and CT | 2 | 2005 | 750/296 | Yes | Double-blind | Phase II (PFS, RR, toxicity) which would continue to full phase III (OS) accrual if the HR for PFS was 0.77 with no toxicity concerns | Phase II: PFS, RR, toxicity Phase III: OS | Health economics, tissue markers, QoL g | 1 |
| [20] | Completed only phase II portion | NSCLC | Combination of IT (vaccine) and CT | 2 | 2012 | NR/222 | Yes | Double-blind | Phase IIB (PFS) to validate the TrPAL biomarker; Phase III (OS) | PFS | OR, DoR h, OS, safety, time to OR | 1 |
| [21] | Terminated | NSCLC | TT (TKI) | 3 | 2014 | 100 for phase II, 500 for phase III/100 | Yes | Open Label | Data from the Phase II part will determine the sample size in the Phase III part | PFS | OS, ORR, DoR, QoL, safety, PK i | 1 every 3–6 months |
| [22] | Terminated | NSCLC | Combination of IT (interferons) and CT | 2 | 1980s | 46/37 | Yes | Open Label | Embedded phase II (RR) trial within the combination arm | ORR | Safety | 1 |
| [23] | Terminated | NSCLC | Combination of a MMPI d with CT | 2 | 2000 | 750/774 | Yes | Triple f | Phase II (RR, toxicity), phase III (OS) | OS | PFS, RR, DoR, QoL, toxicity | 1 |
| [24] | Amended to phase II | NSCLC | TT (TKI) vs. CT | 3 | 2014 | 400/98 | Yes | Open label | Phase II (PFS), Phase III (OS) | PFS, OS | DoR, toxicity | 1 |
| [25] | Amended to phase II | NSCLC | IT (PD-L1 inhibitor) vs. CT | 2 | 2014 | NR/53 | Yes | Open label | Phase II/III trial (OS, PFS) | OS, PFS | (IA-PFS), OS, toxicity | NR |
| [26] | Ongoing | SCLC | Combination of IT (PD-L1 inhibitor) and CRT e | 2 | 2019 | 506/N/A | Yes | Open label | Phase II (PFS), Phase III (OS) | Phase II: PFS Phase III: OS | PFS, ORR, DMFS m, QoL, TMB j | NR |
| [27] | Ongoing | NSCLC | IT (PD-1 inhibitor) and CT | 2 | 2020 | 700/NR | Yes | Phase II: Open label Phase III: Participant | Phase II(ORR, adverse events) to proceed to phase III (PFS) | Phase II: ORR, AEs Phase III: PFS | Phase II: PFS, DoR, OS Phase III: ORR, DoR, OS | NR |
| [28] | Ongoing | NSCLC | Combination of IT (PD-1 inhibitor) and CT | 2 | 2021 | 100/NR | Yes | Open label | Phase II (PFS), Phase III (OS) | Phase II: PFS; Phase III: OS | ORR, QoL, AEs | NR |
| [29] | Ongoing | NSCLC | Combination of IT (PD-1 inhibitor) and CT | 2 | 2022 | 286/NR | Yes | Open label | Only patients with disease control at 6 months (phase II) will be randomized 1:1 (phase III) | Phase II (OS), phase III (OS) | AEs, PFS, QoL | 0 |
| [30] | Terminated | NSCLC | Combination of IT (CD-20 inhibitor) and TT | 2 | 2014 | NR/9 | Yes | Open Label | Phase II: PFS Phase III: OS | PFS, OS | Safety | NR |
| Author_Year | Status | Condition | Treatment | No Arms | Year Started | Enrollment (Projected/Actual) | Phase 3 Randomisation | Blinding | Phase II/III Type | Primary Endpoints | Secondary Endpoints | No Interim Analyses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [31] | Completed | NSCLC | IT (PD-1 inhibitor) | 3 | 2013 | 920/1034 | Yes | Study: Blinded study statisticianPD-L1 positivity: double-blindedPFS: independent radiologist. | Multiple dose phase II (ORR,OS) to proceed to phase III (OS) | OS, PFS, Safety | ORR, DoR | 2 |
| [32] | Completed | SCLC | Combination of IT (glycolipid GD2 inhibitor)and CT | 3 | 2017 | 460/483 | Yes | Open label | Phase II: intra-subject dose escalation. Phase III: OS | OS | PFS, ORR, CBR a | 0 |
| [33] | Ongoing | SCLC | CT | 2 | 2018 | 480/NR | Yes | Open label | Phase II: Dose determination Phase III: Randomized, efficacy study | Phase II: Safety, Optimal dosePhase III: OS | PFS, ORR, QoL | 1 |
| [34] | Ongoing | SCLC | Combination of TT (TKI)and CT | 2 | 2019 | 313/NR | Yes | Double-blind | Phase II: Dose findingPhase III: PFS | Phase II: Adverse events Phase III: PFS | NR | NR |
| [35] | Ongoing | NSCLC | IT (PD-L1/CTLA-4 bispecific inhibitor) and TT (TKI) | 2 | 2021 | 522/NR | Yes | Open Label | Phase II: DLTs Phase III: OS, PFS | Phase II: DLTsPhase III: OS, PFS | ORR, DCR b, DoR, CBR, TTR c | NR |
| Status | Condition | Treatment | No Arms | Year Started | Enrollment (Projected/Actual) | Phase 3 Randomisation | Blinding | Phase II/III Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ongoing | NSCLC | Multiple TTs and ITs | 9 | 2017 | 700/NR | Yes | Open label | MAMS |
| Reference | Status | Condition | Treatment | Νο Arms | Year Started | Enrollment (Projected/ Actual) | Phase 3 Randomisation | Blinding | Phase II/III Type | Primary Endpoints | Secondary Endpoints | Nο of Interim Analyses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [37] | Completed only phase II portion | NSCLC | Combination of TT (TKI) and CT | 4 | 2009 | 164/150 | Yes | Open Label | Phase II adjuvant trial (feasibility) Phase III: DFS | Feasibility defined as 80% of patients being able to start adjuvant therapy within 2 months after surgery | tolerability, compliance biomarker distribution | 0 |
| [38] | Completed only phase II portion | NSCLC | TT (TKI) | 2 | 2008 | 112/142 | Yes | Quadruple b | Phase II (compliance/feasibility of regime), phase III (DFS) | Compliance based on both self-reporting and pill counts. Patients were classified as compliant if they received treatment of at least 12 weeks | OS, recurrence-free survival a, toxicity, QOL | 1 |
| [39] | Terminated | NSCLC | Combination ofIT (vaccine) and CT | 3 | 2013 | 240/135 | Yes | Open Label | Design with patients staying on trial after progression | OS | RR | NR |
| [40] | Ongoing | NSCLC | TT (TKI) | 2 | 300/492 | Yes | Open label | NR | PFS assessed by blinded independent radiologist | IA-PFS c IC-PFS, EC-PFS, ORR, DoR, OS, QoL, DCR | NR | |
| [41] | Ongoing | NSCLC | TT (TKI) | 2 | 2019 | 360/362 | Yes | Open label | NR | PFS | ORR, DCR, iORR d, IC-PFS OS, DoR, safety | NR |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palermos, D.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Malandrakis, P.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Terpos, E.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I. Lung Cancer Clinical Trials with a Seamless Phase II/III Design: Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237176
Palermos D, Sergentanis TN, Gavriatopoulou M, Malandrakis P, Psaltopoulou T, Terpos E, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I. Lung Cancer Clinical Trials with a Seamless Phase II/III Design: Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(23):7176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237176
Chicago/Turabian StylePalermos, Dionysios, Theodoros N. Sergentanis, Maria Gavriatopoulou, Panagiotis Malandrakis, Theodora Psaltopoulou, Evangelos Terpos, and Ioannis Ntanasis-Stathopoulos. 2022. "Lung Cancer Clinical Trials with a Seamless Phase II/III Design: Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 23: 7176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237176
APA StylePalermos, D., Sergentanis, T. N., Gavriatopoulou, M., Malandrakis, P., Psaltopoulou, T., Terpos, E., & Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I. (2022). Lung Cancer Clinical Trials with a Seamless Phase II/III Design: Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(23), 7176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237176









