Tear and Plasma Levels of Cytokines in Patients with Uveitis: Search for Active Disease Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Tear Sample Collection
2.3. Serum Sample Collection
2.4. Analysis of Tear and Serum Cytokines/Chemokines
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Data
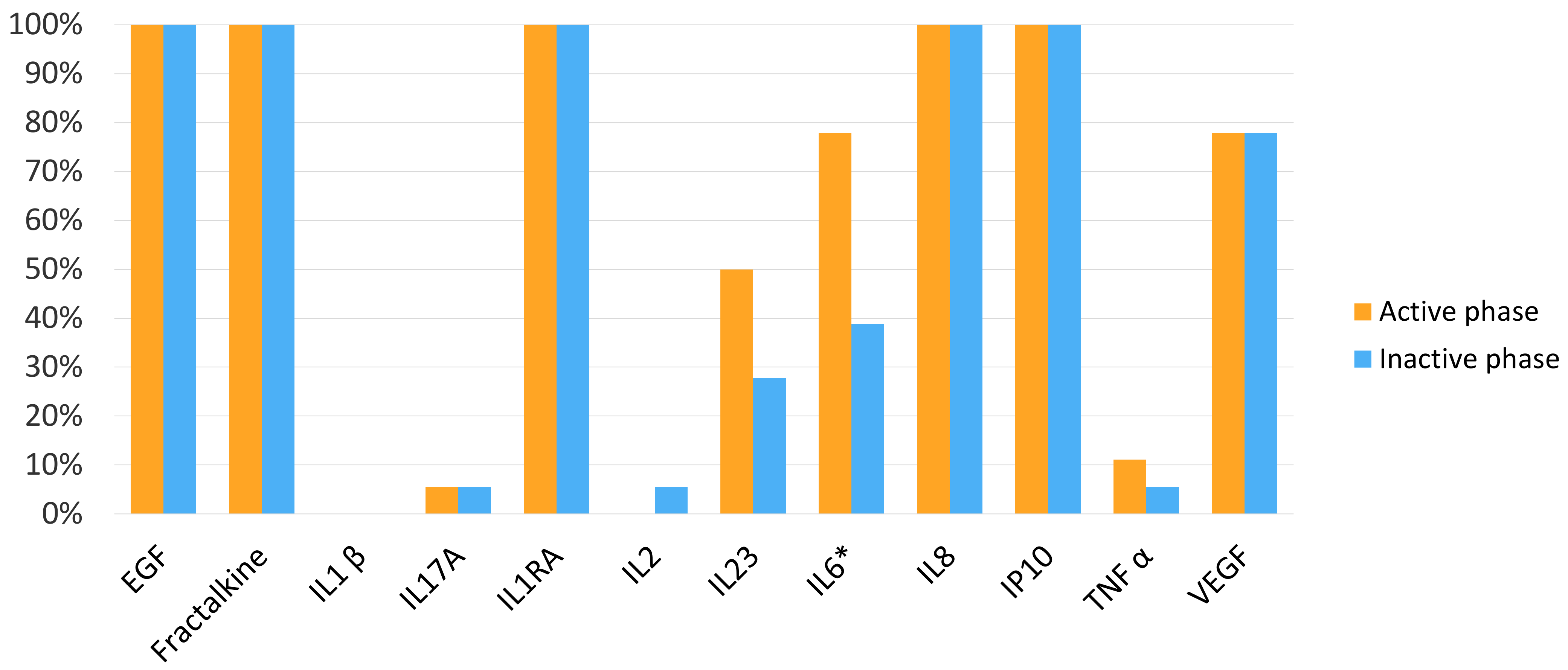
3.2. Cytokine and Chemokine Percentages of Detection in Tear Samples
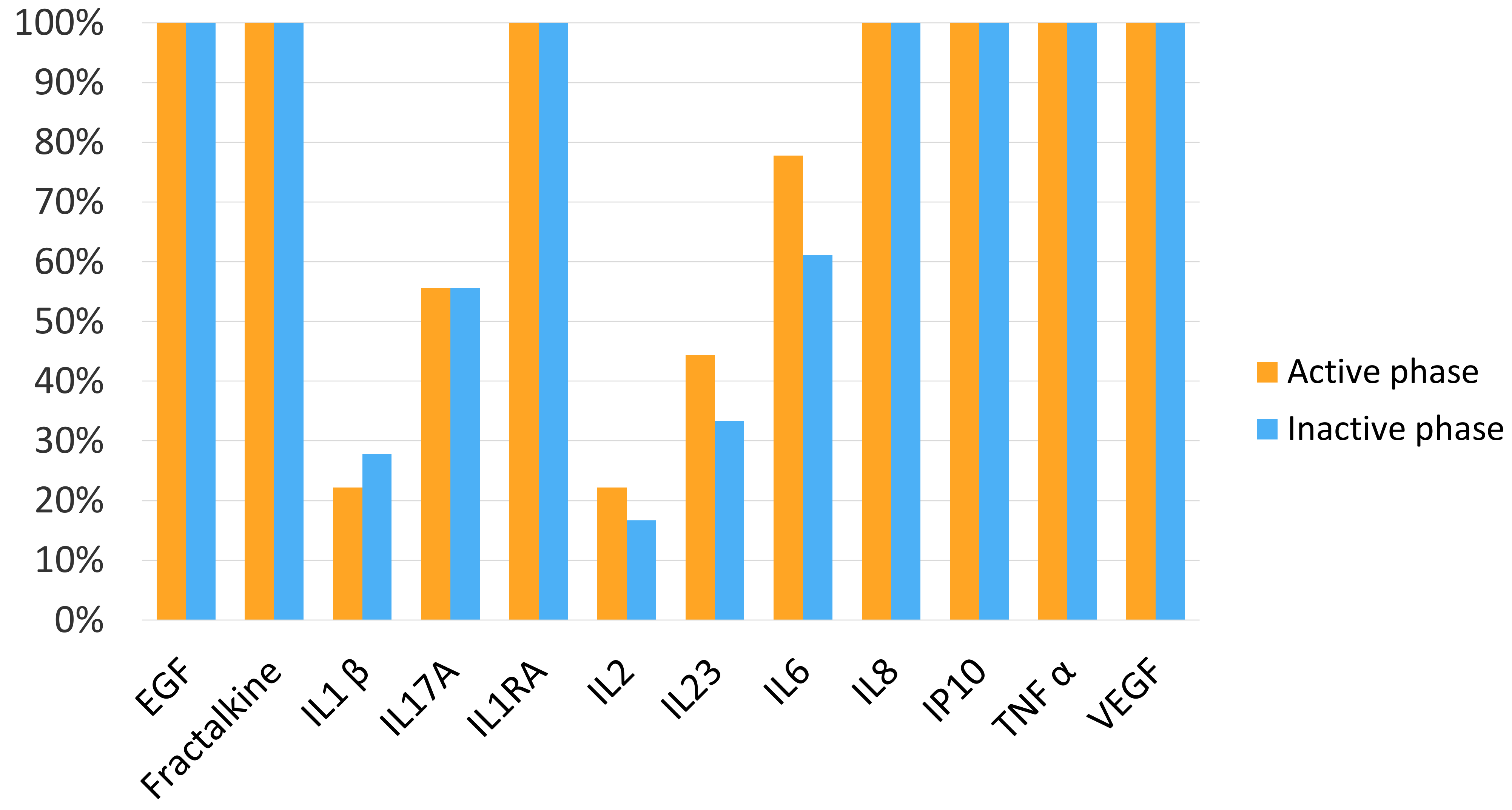
3.3. Cytokine and Chemokine Percentages of Detection in Plasma Samples
3.4. Cytokine and Chemokine Tear Levels According to Uveitis Activity
3.5. Cytokine and Chemokine Plasma Levels According to Uveitis Activity
3.6. Comparison of Cytokine and Chemokine Concentrations in Tears and Plasma Measured in the Active Phase
3.7. Comparison of Cytokine and Chemokine Concentration in Tears and Plasma in the Inactive Phase
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rothova, A.; Suttorp-van Schulten, M.S.A.; Frits Treffers, W.; Kijlstra, A. Causes and Frequency of Blindness in Patients with Intraocular Inflammatory Disease. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1996, 80, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adán-Civera, A.M.; Benítez-del-Castillo, J.M.; Blanco-Alonso, R.; Pato-Cour, E.; Sellas-Fernández, A.; Bañares-Cañizares, A. Burden and Direct Costs of Non Infectious Uveitis in Spain. Reumatol. Clínica 2016, 12, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, A.; Yin, K.; Coyle, L.; Harper, R.; Jones, N.P. Vision-Related Quality of Life and Employment Status in Patients with Uveitis of Working Age: A Prospective Study. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2012, 20, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirbach, S.; Hayes, O.; Rheum, M.C.-A. The economic burden of uveitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 788. [Google Scholar]
- Kobelt, G.; Bodaghi, B.; Richard, B.; Plesnilla, C.; Buchholz, P.; Brézin, A.P.; Heron, E.; Labetoulle, M.; Sahel, J. The cost of uveitis treatment in france: A one-year retrospective analysis. Value Health 2008, 11, A335–A659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriola-Villalobos, P.; Abásolo, L.; García-Feijoo, J.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, B.; Méndez-Fernández, R.; Pato, E.; Díaz-Valle, D.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, L. Vision-related Quality of Life in Patients with Non-infectious Uveitis: A Cross-sectional Study. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2018, 26, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, A.D.; Tundia, N.; Sorg, R.; Zhao, C.; Chao, J.; Joshi, A.; Skup, M. Risk of ocular complications in patients with noninfectious intermediate uveitis, posterior uveitis, or panuveitis. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritz, D.C.; Schwaber, E.J.; Wong, I.G. Complications of Uveitis: The Northern California Epidemiology of Uveitis Study. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2018, 26, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maini, R.; O’Sullivan, J.; Reddy, A.; Watson, S.; Edelsten, C. The risk of complications of uveitis in a district hospital cohort. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 88, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkins-Netzer, O.; Talat, L.; Bar, A.; Lula, A.; Taylor, S.R.J.; Joshi, L.; Lightman, S. Long-term clinical outcome and causes of vision loss in patients with uveitis. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 2387–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borish, L.C.; Steinke, J.W. 2. Cytokines and chemokines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, S460–S475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.D.; Nedjai, B.; Hurst, T.; Pennington, D.J. Cytokines and chemokines: At the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (Bba)-Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 2563–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curnow, S.J.; Murray, P.I. Inflammatory mediators of uveitis: Cytokines and chemokines. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2006, 17, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, K.G.J.; Galatowicz, G.; Calder, V.L.; Lightman, S.L. Cytokines and chemokines in uveitis—Is there a correlation with clinical phenotype? Clin. Med. Res. 2006, 4, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahmar, I.; Abou-Bacar, A.; Abdelrahman, T.; Guinard, M.; Babba, H.; Ben Yahia, S.; Kairallah, M.; Speeg-Schatz, C.; Bourcier, T.; Sauer, A.; et al. Cytokine Profiles in Toxoplasmic and Viral Uveitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu El-Asrar, A.M.; Al-Obeidan, S.S.; Kangave, D.; Geboes, K.; Opdenakker, G.; Van Damme, J.; Struyf, S. CXC chemokine expression profiles in aqueous humor of patients with different clinical entities of endogenous uveitis. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper, J.J.W.; Mutis, T.; De Jager, W.; De Groot-Mijnes, J.D.F.; Rothova, A. Intraocular interleukin-17 and proinflammatory cytokines in HLA-A-29-associated birdshot chorioretinopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 152, 177–182.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El-Asrar, A.M.; Struyf, S.; Kangave, D.; Al-Obeidan, S.A.; Opdenakker, G.; Geboes, K.; Van Damme, J. Cytokine and CXC chemokine expression patterns in aqueous humor of patients with presumed tuberculous uveitis. Cytokine 2012, 59, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, M.; Cheung, G.; Vania, M.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Chee, S.P. Aqueous cytokine and chemokine analysis in uveitis associated with tuberculosis. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 565–573. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.P.; Agarwal, A.; Gupta, V.; Katoch, D.; Sehgal, S.; Singh, N. Tear IL-6 and IL-10 levels in HLA-B27-Associated Uveitis and Its clinical Implications. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2020, 29, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño, E.; Portero, A.; Herreras, J.M.; García-Vázquez, C.; Whitcup, S.M.; Stern, M.E.; Calonge, M.; Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A. Cytokine and chemokine tear levels in patients with uveitis. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, e405–e414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeles-Han, S.T.; Yeh, S.; Patel, P.; Duong, D.; Jenkins, K.; Rouster-Stevens, K.A.; Altaye, M.; Fall, N.; Thornton, S.; Prahalad, S.; et al. Discovery of tear biomarkers in children with chronic non-infectious anterior uveitis: A pilot study. J. Ophthalmic. Inflamm. Infect. 2018, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabs, D.A.; Nussenblatt, R.B.; Rosenbaum, J.T.; Atmaca, L.S.; Becker, M.D.; Brezin, A.P.; Chee, S.P.; Davis, J.L.; Deschenes, J.; de Smet, M.; et al. Standardization of uveitis nomenclature for reporting clinical data. Results of the first international workshop. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 140, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A.; Castellanos, E.; Stern, M.E.; Fernández, I.; Carreño, E.; García-Vázquez, C.; Herreras, J.M.; Calonge, M. Tear cytokine and chemokine analysis and clinical correlations in evaporative-type dry eye disease. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 862–873. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto-Fraga, J.; Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A.; Calonge, M.; González-García, M.J.; López-Miguel, A.; López-de la Rosa, A.; García-Vázquez, C.; Calder, V.; Stern, M.E.; Fernández, I. Severity, therapeutic, and activity tear biomarkers in dry eye disease: An analysis from a phase III clinical trial. Ocul. Surf. 2018, 16, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buuren SVan Oudshoorn, K. Flexible Multivariate Imputation by MICE; TNO: Leiden, Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Takase, H.; Futagami, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Kamoi, K.; Sugita, S.; Imai, Y.; Mochizuki, M. Cytokine Profile in Aqueous Humor and Sera of Patients with Infectious or Noninfectious Uveitis. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; García-Medina, J.J.; Sanz-González, S.M.; O’connor, J.E.; Casaroli-Marano, R.P.; Valero-Velló, M.; López-Gálvez, M.; Peris-Martínez, C.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; Diaz-Llopis, M. Signature of Circulating Biomarkers in Recurrent Non-Infectious Anterior Uveitis. Immunomodulatory Effects of DHA-Triglyceride. A Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Asrar, A.M.A.; Berghmans, N.; Al-Obeidan, S.A.; Gikandi, P.W.; Opdenakker, G.; Van Damme, J.; Struyf, S. Differential CXC and CX3C chemokine expression profiles in aqueous humor of patients with specific endogenous uveitic entities. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 2222–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, S.; Das, D.; Hasanreisoglu, M.; Toy, B.C.; Akhter, M.; Anuradha, V.; Anthony, E.; Gurnani, B.; Kaur, K. Interleukins and cytokine biomarkers in uveitis. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 68, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirinsky, I.V.; Biryukova, A.A.; Kalinovskaya, N.Y.; Shirinsky, V.S. Tear cytokines as potential biomarkers in non-infectious uveitis: Post hoc analysis of a randomised clinical trial. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 258, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, E.; Sonoda, S.; Kinukawa, N.; Sakamoto, T. Alteration pattern of tear cytokines during the course of a day: Diurnal rhythm analyzed by multicytokine assay. Cytokine 2006, 33, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, M.J.; González-García, M.J.; Tesón, M.; García, N.; Fernández, I.; Calonge, M.; Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A. Intra- and inter-day variation of cytokines and chemokines in tears of healthy subjects. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 120, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Hong, X.; Ding, F.; Huang, S.; Lian, W.; Wang, H.; Zheng, W.; Ni, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, Q. High Level of Inflammatory Cytokines in the Tears: A Bridge of Patients with Concomitant Exotropia and Dry Eye. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 5662550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amil-Bangsa, N.H.; Mohd-Ali, B.; Ishak, B.; Abdul-Aziz, C.N.N.; Ngah, N.F.; Hashim, H.; Ghazali, A.R. Total Protein Concentration and Tumor Necrosis Factor α in Tears of Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2019, 96, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costagliola, C.; Romano, V.; de Tollis, M.; Aceto, F.; Dell’Omo, R.; Romano, M.R.; Pedicino, C.; Semeraro, F. TNF-alpha levels in tears: A novel biomarker to assess the degree of diabetic retinopathy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 629529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curnow, S.J.; Falciani, F.; Durrani, O.M.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Ross, E.J.; Wloka, K.; Rauz, S.; Wallace, G.R.; Salmon, M.; Murray, P.I. Multiplex bead immunoassay analysis of aqueous humour reveals distinct cytokine profiles in uveitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 4251–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkhur, S.; Hasanreisoglu, M.; Vigil, E.; Halim, M.S.; Hassan, M.; Plaza, C.; Nguyen, N.V.; Afridi, R.; Tran, A.T.; Do, D.V.; et al. Interleukin-6 inhibition in the management of non-infectious uveitis and beyond. J. Ophthalmic Inflamm. Infect. 2019, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.; Monselise, Y.; Bahar, I.; Cohen, Y.; Weinberger, D.; Goldenberg-Cohen, N. Serum cytokine levels in active uveitis and remission. Curr. Eye Res. 2007, 32, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, A.M.; Luyendijk, L.; Zaal, M.J.W.; Rothova, A.; Hack, C.E.; Kijlstra, A. Elevated serum IL-8 levels are associated with disease activity in idiopathic intermediate uveitis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1998, 82, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Lacomba, M.; Marcos Martín, C.; Gallardo Galera, J.M.; Gómez Vidal, M.A.; Collantes Estévez, E.; Ramírez Chamond, R.; Omar, M.M. Aqueous Humor and Serum Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Clinical Uveitis. Ophthalmic. Res. 2001, 33, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, W.; Zhu, X.; Yang, P.; Liu, X.; Lin, X.; Zhou, H.; Huang, X.; Kijlstra, A. Upregulated IL-23 and IL-17 in Behçet patients with active uveitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 3058–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yang, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Hou, S.; Kijlstra, A. Upregulation of Interleukin 21 and Promotion of Interleukin 17 Production in Chronic or Recurrent Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Disease. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2010, 128, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, X.; Luo, L.; Qu, B.; Huang, X.; Xu, L.; Lin, Y.; Ye, S.; Liu, Y. Elevated serum IL-23 correlates with intraocular inflammation after cataract surgery in patients with Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada disease. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 94, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türkçüoğlu, P.; Arat, Y.O.; Kan, E.; Kan, E.K.; Chaudhry, I.A.; Koca, S.; Çeliker, Ü.; İlhan, N. Association of Disease Activity with Serum and Tear IL-2 Levels in Behçet Disease. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2016, 24, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidet, J.R.; Akopian, M.; Olstad, O.K.; Jørstad, Ø.K.; Moe, M.C.; Petrovski, G.; Pepaj, M. The acute phase response protein SERPINA3 is increased in tear fluid from the unaffected eyes of patients with unilateral acute anterior uveitis. J. Ophthalmic. Inflamm. Infect. 2021, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidet, J.R.; Jørstad, Ø.K.; Fostad, I.G.; Olstad, O.K.; Sørland, R.; Moe, M.C.; Petrovski, G.; Pepaj, M. Unilateral acute anterior uveitis is associated with ipsilateral changes in the tear fluid proteome that involves the LXR/RXR pathway. J. Ophthalmic. Inflamm. Infect. 2020, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleja, S.; Cordero-Coma, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Llorente, M.; Franco, M.; Ruiz De Morales, J.G. Adalimumab specifically induces CD3+ CD4+ CD25high Foxp3+ CD127− T-regulatory cells and decreases vascular endothelial growth factor plasma levels in refractory immuno-mediated uveitis: A non-randomized pilot intervention study. Eye 2012, 26, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero-Coma, M.; Calleja, S.; Llorente, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Franco, M.; Ruiz De Morales, J.G. Serum cytokine profile in adalimumab-treated refractory uveitis patients: Decreased IL-22 correlates with clinical responses. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2013, 21, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, I.; Roszkowska, A.M.; Alessandrello, F.; Oliverio, G.W.; Tumminello, G.; Gallizzi, R.; Conti, G.; Aragona, P. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis-associated uveitis: A retrospective analysis from a centre of South Italy. Int. Ophthalmol. 2019, 40, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles-Han, S.T.; Miraldi Utz, V.; Thornton, S.; Schulert, G.; Rodriguez-Smith, J.; Kauffman, A.; Sproles, A.; Mwase, N.; Hennard, T.; Grom, A.; et al. S100 Proteins, Cytokines, and Chemokines as Tear Biomarkers in Children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis-associated Uveitis. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2020, 29, 1616–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles-Han, S.T.; Yeh, S.; Patel, P.; Duong, D.; Jenkins, K.; Prahalad, S.; Holland, G.N. Tear Proteomics in Pediatric Chronic Non-infectious Uveitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 2155. [Google Scholar]
- Tiffany, J.M. The Normal Tear Film. Dev. Ophthalmol. 2008, 41, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasza, M.; Balogh, Z.; Biro, L.; Ujhelyi, B.; Damjanovich, J.; Csutak, A.; Várdai, J.; Berta, A.; Nagy, V. Vascular endothelial growth factor levels in tears of patients with retinal vein occlusion. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 253, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, J.E.; Suhler, E.; Skup, M.; Tari, S.; Macaulay, D.; Chao, J.; Ganguli, A. Prevalence of noninfectious uveitis in the United States: A claims-based analysis. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016, 134, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionne, K.; Redfern, R.L.; Nichols, J.J.; Nichols, K.K. Analysis of tear inflammatory mediators: A comparison between the microarray and Luminex methods. Mol. Vis. 2016, 22, 177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, S.Z.; Koh, S.K.; Chen, L.; Vaz, C.; Tanavde, V.; Li, X.R.; Beuerman, R.W. In-depth analysis of the human tear proteome. J. Proteomics. 2012, 75, 3877–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age mean (± SD) | 52.5 (±12.2) |
| Gendern(%) | |
| Male | 8 (44.4) |
| Female | 10 (66.6) |
| Anatomical location of uveitisn(%) | |
| Anterior | 18 (100) |
| Distributionn(%) | |
| Unilateral | 15 (83.3) |
| Bilateral | 3(16.7) |
| Underlying diagnosisn(%) | |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | 3 (16.7) |
| Herpetic uveitis | 3 (16.7) |
| Psoriatic arthritis | 1 (5.5) |
| Fuchs Heterochromic Iridocyclitis | 1 (5.5) |
| Idiopathic | 10 (55.5) |
| Totaln(%) | 18 (100) |
| Active Uveitis Mean ± SD (pg/mL) | Inactive Uveitis Mean ± SD (pg/mL) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGF | 563.09 ± 22.70 | 625.90 ± 26.41 | 0.789 |
| Fractalkine | 1633.50 ± 145.51 | 912.69 ± 150.12 | 0.181 |
| IL-1RA | 5592 ± 120.50 | 4330.90 ± 134.80 | 0.653 |
| IL8 | 148.41 ± 34.90 | 187.40 ± 40.50 | 0.640 |
| IP10 | 8745.45 ± 100.98 | 10,102.50 ± 150.76 | 0.655 |
| VEGF | 97.12 ± 9.90 | 98.12 ± 8.98 | 0.316 |
| IL-6 | 34.68 ± 3.76 | 34.88 ± 1.70 | 0.396 † |
| Active Uveitis Mean ± SD (pg/mL) | Inactive Uveitis Mean ± SD (pg/mL) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGF | 167.93 ± 35.64 | 207.98 ± 25.68 | 0.572 |
| Fractalkine | 477.39 ± 46.51 | 426.57 ± 52.59 | 0.122 † |
| IL1-β | 2.02 ± 1.49 | 3.02 ± 1.92 | 0.335 † |
| IL-17A | 7.6 ± 4.35 | 8.02 ± 2.99 | 0.813 † |
| IL-1RA | 26.10 ± 12.43 | 29.28 ± 10.31 | 0.116 † |
| IL-2 | 2.09 ± 1.53 | 2.06 ± 1.94 | 0.260 † |
| IL-8 | 15.38 ± 10.41 | 16.30 ± 12.49 | 0.922 |
| IP-10 | 306.78 ± 102.01 | 268.32 ± 90.95 | 0.952 |
| TNF-α | 7.94 ± 4.60 | 8.94 ± 3.70 | 0.842 |
| VEGF | 159,75 ± 30.89 | 169.38 ± 40.70 | 0.849 † |
| IL-6 | 13.06 ± 6.03 | 207.98 ± 25.68 | 0.731 † |
| Tear Sample Mean ± SD (pg/mL) | Plasma Sample Mean ± SD (pg/mL) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGF | 563.09 ± 22.70 | 167.93 ± 35.64 | 0.000 |
| Fractalkine | 1633.50 ± 145.51 | 477.39 ± 46.51 | 0.000† |
| IL1-β | - | 2.02 ± 1.49 | - |
| IL-17α | - | 7.6 ± 4.35 | - |
| IL-1RA | 5592.02 ± 120.50 | 26.10 ± 12.43 | 0.000 |
| IL-2 | - | 2.09 ± 1.53 | - |
| IL8 | 148.41 ± 34.90 | 15.38 ± 10.41 | 0.000 |
| IP10 | 8745.45 ± 100.98 | 306.78 ± 102.01 | 0.000 |
| TNF-α | - | 7.94 ± 4.60 | - |
| VEGF | 97.12 ± 9.90 | 159,75 ± 30.89 | 0.815 † |
| IL-6 | 34.68 ± 3.76 | 13.06 ± 6.03 | 0.000† |
| Tear Sample Mean ± SD (pg/mL) | Plasma Sample Mean ± SD (pg/mL) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGF | 625.90 ± 26.41 | 207.98 ± 25.68 | 0.000 |
| Fractalkine | 912.69 ± 150.12 | 426.57 ± 52.59 | 0.000 |
| IL1-β | - | 3.02 ± 1.92 | - |
| IL-17A | - | 8.02 ± 2.99 | - |
| IL-1RA | 4330.90 ± 134.80 | 29.28 ± 10.31 | 0.000† |
| IL-2 | - | 2.06 ± 1.94 | - |
| IL-8 | 187,40 ± 40.50 | 16.30 ± 12.49 | 0.000 |
| IP-10 | 10,102.50 ± 150.76 | 268.32 ± 90.95 | 0.000 |
| TNF-α | - | 8.94 ± 3.70 | - |
| VEGF | 98.12 ± 8.98 | 169.38 ± 40.70 | 0.212 † |
| IL-6 | 34.88 ± 1.70 | 12.94 ± 5.18 | 0.000† |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Onrubia, L.; Mateos Olivares, M.; García-Vázquez, C.; Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A.; Cocho, L.; Herreras Cantalapiedra, J.M. Tear and Plasma Levels of Cytokines in Patients with Uveitis: Search for Active Disease Biomarkers. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237034
García-Onrubia L, Mateos Olivares M, García-Vázquez C, Enríquez-de-Salamanca A, Cocho L, Herreras Cantalapiedra JM. Tear and Plasma Levels of Cytokines in Patients with Uveitis: Search for Active Disease Biomarkers. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(23):7034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237034
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Onrubia, Luis, Milagros Mateos Olivares, Carmen García-Vázquez, Amalia Enríquez-de-Salamanca, Lidia Cocho, and José María Herreras Cantalapiedra. 2022. "Tear and Plasma Levels of Cytokines in Patients with Uveitis: Search for Active Disease Biomarkers" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 23: 7034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237034
APA StyleGarcía-Onrubia, L., Mateos Olivares, M., García-Vázquez, C., Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A., Cocho, L., & Herreras Cantalapiedra, J. M. (2022). Tear and Plasma Levels of Cytokines in Patients with Uveitis: Search for Active Disease Biomarkers. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(23), 7034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237034






