Abstract
The mutual exclusivity of myositis-specific antibodies (MSAs) has been reported before, but the coexistence of 2 or more MSAs was still found in a few case reports. This study aims to confirm the existence and prevalence of double MSAs in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) and to clarify the clinical features of these patients. One hundred fifty-one patients with IIM diagnosed from 1 July 2018 to 31 July 2022, at National Cheng Kung University Hospital, Taiwan, were enrolled and divided into two groups, patients with ≤1 MSA (n = 128, 84.8%) and those with ≥2 MSAs (n = 23, 15.2%) according to the initial serology results. After being re-examined by ANA-IIF assay, 8 out of 23 patients were confirmed to have ≥2 MSAs. The demographic data and clinical features were presented. The prevalence of double-positive MSAs among IIM was 5.3% in this cohort. The coexistence of two MSAs in an IIM patient does exist but is rare. Patients with two MSAs belonging to two distinct IIM subtypes presented clinical features skewed to one subtype instead of “mixed phenotypes”. No apparent difference in clinical severity was found between patients with ≥2 MSAs and ≤1 MSA. Longer follow-ups and more studies are required to characterize the patients of IIM with ≥2 MSAs.
1. Introduction
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs), collectively called myositis, are heterogeneous disorders characterized by muscle weakness, myalgia, elevated creatine kinase (CK) levels, and multiple extra-muscular manifestations, including variable degrees of skin, lung, or joint involvements. The revised classification of IIMs based on histopathology and myositis autoantibodies comprise dermatomyositis (DM), polymyositis (PM), inclusion body myositis (IBM), immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), and overlap myositis (OM) [1,2,3,4]. The subtyping of IIM was necessary because it was directly linked to the incidence of extra-muscular organ involvement, such as interstitial lung disease (ILD) [5,6] and concomitant malignancy [7].
Recent advances and the growing number of myositis autoantibodies have facilitated the diagnosis and classification of IIM [8,9,10,11,12]. Myositis autoantibodies can be divided into myositis-specific antibodies (MSAs) and myositis-associated antibodies (MAAs). MSAs are present only with specific subtype of IIM, whereas MAAs are not limited to IIM and are also found in other autoimmune diseases. The mutual exclusivity of MSAs has been reported before [13], which made the serology tests for MSAs more crucial for IIM subtyping. However, the coexistence of 2 or more MSAs was still found in a few case reports [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23].
This study aimed to confirm the existence and the prevalence of double MSAs in patients with IIM and to clarify the clinical features of these patients.
2. Materials
2.1. Ethical Approval
Clinical studies were conducted according to the principles of the Nuremberg Code and the Declaration of Helsinki. The Institutional Review Board (IRB) of National Cheng Kung University Hospital approved the protocol (Approval No. B-BR-109-254). Because of the retrospective nature of the study, the IRB waived the requirement for informed patient consent.
2.2. Study Design and Subjects
This retrospective case–control study was nested with a one-group pretest-posttest design. Patients with IIM diagnosed from 1 July 2018 to 31 July 2022, in National Cheng Kung University Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan, were enrolled and divided into two groups, patients with ≤1 MSA and those with ≥2 MSAs, according to the serology test results obtained from the line blot assay. The diagnosis of IIM was based on the EULAR/ACR Classification Criteria [24,25] and autoantibody serology. The one-group pretest-posttest design was nested in both groups of ≥2 MSAs and ≤1 MSA. To minimize the assay-related false positivities, samples with ≥2 MSAs shown by line blot tests were further tested by cell-based antinuclear antibody indirect immunofluorescence (ANA-IIF) assay [8,11]. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for antibodies against melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (anti-MDA5) was applied for samples with the anti-MDA5 antibody on the line blot test. In parallel, in the group of ≤1 MSA, 39 serum samples were randomly picked out for ANA-IIF to confirm the result of the line blot test (Figure 1).
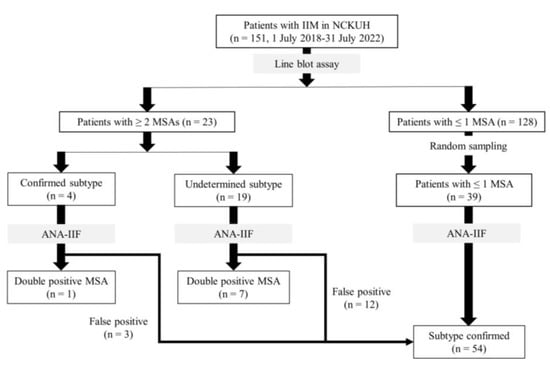
Figure 1.
Flowchart of patient selection. IIM: idiopathic inflammatory myopathy; NCKUH: National Cheng-Kung University Hospital; MSA: myositis specific antibody; ANA-IIF: antinuclear antibody indirect immunofluorescence.
2.3. Demographic Data Collection
Clinical data were collected retrospectively through a comprehensive chart review. Muscle power was scored by the attending physician based on the medical research council (MRC) scale. Skin manifestations, such as heliotrope, Gottron’s sign, Gottron’s papule, V-sign, and shawl sign, were recorded. The CK level was documented when the patient presented to the clinic due to muscle weakness or relevant extra-muscular symptoms. Clinical course, comorbidities, treatments, periods of hospital stay due to flare-up of myositis, respiratory failure or not, reasons and date of mortality were all recorded.
2.4. Tests for Myositis Autoantibodies
2.4.1. The Line Blot Assay
The line blot assay was carried out according to the instruction manual. In brief, fresh serum samples diluted in 100× were incubated with the pre-treated membrane-fixed immuno-blot for 30 min, in which the following MSAs are included, anti-Mi-2α, anti-Mi-2β, anti-TIF-1γ, anti-MDA5, anti-NXP-2, anti-SAE, anti-Jo-1, anti-SRP, anti-PL-7, anti-PL-12, anti-EJ, anti-OJ; and MAAs: anti-Ku, anti-PM-Scl100, anti-PM-Scl75, and anti-Ro52 (EUROIMMUN AG, Lübeck, Germany). After washing three times, the blot was incubated with enzyme conjugate for 30 min. Then, the blot was washed and incubated with a substrate for 5 min. The reaction was terminated by washing with distilled water. Afterward, dry the blot at room temperature. The intensity of bands was semi-quantified by the software EuroLineScan (Euroimmun AG, Lübeck, Germany) and graded as negative (−), equivocal (+/−), and the intensity of positivity was graded in tertile as +, ++, and +++ after comparing with positive and negative controls. In our cohort, graded as negative (−) or borderline (+/−) was considered a negative result.
2.4.2. Cell-Based ANA Indirect Immunofluorescence
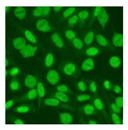
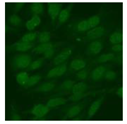
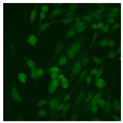
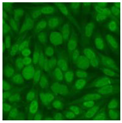
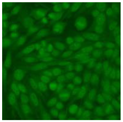
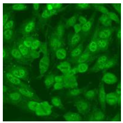
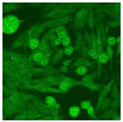
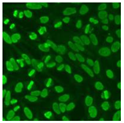
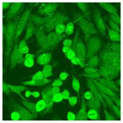
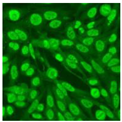
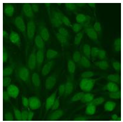
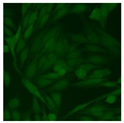
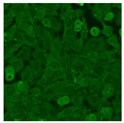
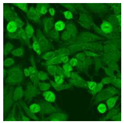
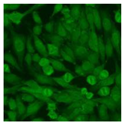
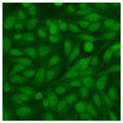
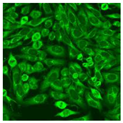
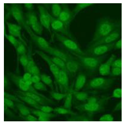
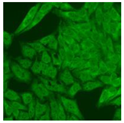
Residual serum thrown from −80 °C storage was tested with the Hep-2 cell-based IIF (EUROIMMUN AG, Lübeck, Germany), namely the ANA test. Diluted serum (40×) was incubated with fixed Hep-2 cells for 30 min, washed, and incubated with the fluorescent secondary antibody for another 30 min. Then, washed, mounted, visualized, and captured. The intensity of the images was quantified. The IIF pattern was confirmed by manual interpretation from 2 independent clinical laboratory technologists according to the international consensus on ANA patterns (ICAP) (Table 1) [8,10,26].

Table 1.
Summary of IIF pattern and main features of MSAs.
2.4.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Human interferon-induced helicase C domain-containing protein 1 ELISA Kit (FineTest, Wuhan, China) was used to quantify the level of anti-MDA5 antibody in human serum according to the instruction manual. In brief, the ELISA plate was washed twice, and then 100 μL standards and samples were added to each well. The plate was sealed with a cover and incubated for 90 min at 37 °C. After washing with wash buffer, a 100 μL biotin-labeled antibody working solution was added and incubated for 60 min at 37 °C. Then, 100 μL HPR-Streptavidin conjugate (SABC) working solution was added to each well and incubated for 30 min at 37 °C after washing. Finally, the wells were washed with wash buffer five times, keeping the buffer in the well for 2–3 min each time, then 90 μL TMB substrate was added to each well. The plate was incubated at 37 °C in the dark for 10–20 min. Afterward, 50 μL stop solution was added immediately and read at O.D. 450 nm.
3. Results
From July 2018 to July 2022, 151 patients with IIM (59.97 ± 14.33 years old, 66.2% female) at National Cheng Kung University Medical Center received a myositis autoantibody line blot test. Among them, 128 (84.8%) had ≤one MSA, and 23 (15.2%) had ≥two MSAs. When the ≥two coexisted MSAs belonged to the same subtype of IIM, the patient was allocated to the “confirmed subtype” undoubtedly. In contrast, while the ≥ two coexisted MSAs belonged to different subtypes of IIM, patients were assigned to the “subtype undetermined” group. Four of the 23 patients with ≥two MSAs had confirmed IIM subtypes, and 19 had undetermined IIM subtypes.
3.1. The Prevalence of Double-Positive MSAs in IIM
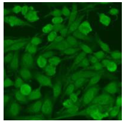
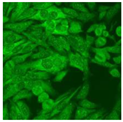
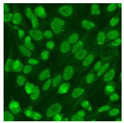
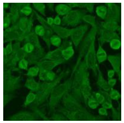
The serum samples of the 23 patients with ≥two MSAs in the first serology test were re-examined by cell-based ANA pattern assay. After reading through and reaching an agreement with two technologists, the concluded ANA pattern, the titer, and the representative immunofluorescence images were summarized in Table 2. Because MDA5 was not expressed well on Hep-2 cells, the ANA pattern of the anti-MDA5 antibody can be negative or cytoplasmic [10,27]. Thus, we used the ELISA assay to confirm the positivity of the anti-MDA5 antibody.

Table 2.
Summary of ANA pattern of 23 patients with double seropositivity in line blot test.
After comparing the ANA pattern with the line blot results, 3 out of 4 samples in the “confirmed subtype” group were finally proved that one of the coexisted MSA on line blot was a false positive. The true positive MSA was TIF-1γ in patient 1, MDA5 in patient 2, and patient 12 (Table 2). The false-positive antibodies were MDA5 in patient 1, SAE antibody in patients 2 and 12. Only one subject in the “confirmed subtype” group, patient 5, had truly double-positive MSAs: the coexistence of anti-MDA5 and anti-Mi-2β antibodies, Table 2).
In the “subtype undetermined” group (n = 19), six patients had coexistence of 2 MSAs suggested DM and IMNM, two patients had 2 MSAs suggested OM and IMNM, ten patients had 2 MSAs belonged to DM and OM, and one patient had 3 MSAs suggested DM, OM, and IMNM. Seven out of 19 patients in the “subtype undetermined” group were confirmed to have double-positive MSAs. The prevalence of double-positive MSAs among IIM was 5.3% (8/151). None had triple-positive MSAs.
3.2. The False-Positive Rate of Immunoassays
In the group with ≤1 positive MSA, the ANA patterns of the randomly picked up 39 samples were compared to the line blot assay results. Twenty-nine out of 39 patients have confirmed single positive MSAs: 6 had anti-Jo-1, 6 had anti-PL-7, 4 had anti-SRP, 3 had anti-MDA5, 2 had anti-EJ, 2 had anti-TIF-1γ, 2 had anti-PL-12, 1 had anti-SAE, 1 d had anti-NXP-2, 1 had anti-Mi-2β, and 1 had anti-Mi-2α antibody, while the rest were seronegative. Nearly all subjects (n = 38) had consistent results between the above two tests, except for one patient. This patient’s serum was tested positive for anti-OJ antibody via line blot assay at three different time points. However, his ANA-IIF suggested an unrecognizable antibody at the nuclear membrane with a titer of 1:640 and 1:1280. The clinical manifestations of this patient, including myalgia, arthritis, and fever, suggested a favorable diagnosis of antisynthetase syndrome or overlap myositis. Even though the MSA serology result from line blot was inconsistent with the ANA-IIF, the final diagnosis of this patient remained.
In the group with ≥2 MSAs, the false positive antibodies on line blot were summarized as follows: There were 2 false positive MDA5 (both graded as +), 3 SAE (all graded as +), 2 PL-7 (graded as +), 7 SRP (4 graded as +, 2 graded as ++, and 1 graded as +++), 1 Mi-2α (graded as +), 2 EJ (graded as ++ and +++, respectively), 3 Jo-1 (graded as +,+, and ++, respectively), 2 NXP-2 (graded as + and ++, respectively), 2 TIF-1γ (all graded as +), one OJ (graded as +) and one PL-12 (graded as +). Among all MSAs, the false positive rate was 100% (1/1) for PL-12, 70% (7/10) for SRP, 66.7% (2/3) for EJ, 66.7% (2/3) for NXP-2, 50% (3/6) for SAE, 50% (1/2) for Mi-2α, 50% (1/2) for OJ, 50% (2/4) for PL-7, 42.9% (3/7) for Jo-1, 33.3% (2/6) for MDA5, 28.6% (2/7) for TIF-1γ, and 0% (0/2) for Mi-2β.
3.3. The Clinical Features of IIM Patients with Double-Positive MSAs
The demographic and clinical data of the eight “true” double-MSA patients were summarized in Table 3. Female patients accounted for 75% (6/8). The average age of onset was 56.3 years old. The age and sex distribution were not different from the entire cohort of IIM. Two patients (Patient 5 and Patient 20 in Table 3) had two antibodies belonging to the same IIM subtype, DM, and also presented typical signs. The other five patients had two antibodies belonging to the distinct IIM subtypes. They showed typical signs predominant to one of the two IIM subtypes instead of mixed features of the two IIM subtypes. For instance, patients 19 and 23 had double positive anti-SRP and anti-SAE antibodies, but one developed typical clinical symptoms of DM, and the other presented as IMNM. Patients 17 and Patient 18 had coexisted anti-PL-7/anti-TIF-1γ and anti-Jo-1/anti-TIF-1γ antibodies, respectively. They were diagnosed as OM instead of DM according to their clinical manifestations and muscle pathology. The two patients had no malignancy found during the follow-up period, although the anti-TIF-1γ antibody was reported to be associated with a higher risk for cancer [28,29]. Patient 7, 17, and 18 had comorbidities of ILD. Patient 5 and patient 17 were found to have overlapping rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Overall, no respiratory failure or mortality happened during the follow-up period in all myositis patients with double MSA.

Table 3.
Summary of clinical features of 8 patients of IIM with double positive MSAs.
4. Discussion
This study demonstrated a 5.3% of double positive MSAs in patients with IIM after excluding false positivity by additional immunoassay. Their final diagnoses were DM (n = 5), OM (n = 2) and IMNM (n = 1). Patients with double MSAs had the following features: Firstly, the severity and extensiveness of clinical phenotypes in these double-MSA IIM patients were similar to IIM patients with single-positive MSAs. Secondly, while presenting two antibodies belonging to two distinct IIM subtypes, their phenotypes skewed to one of them. No “mixed phenotypes” from the two different IIM subtypes were found in our cohort. Thus, a muscle biopsy will be helpful when the clinical features and the coexisted MSAs belonging to the distinct IIM subtypes confuse the diagnosis [30]. Our results did not go against the notion that the presence of MSAs was essentially mutually exclusive in IIM [13]. The coexistence of two MSAs in an IIM patient is rare but does exist [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23].
With the double confirmation of additional immune assays, we found a high false-positive rate (around 33.3% (28/84)) of the line blot test, particularly in samples with ≥2 MSAs (48.1%, 25/52). The high false positive rate in multiple positive blots suggested possible systematic issues that alter the cutoff between positive and negative values, such as human error or the quality control of the assay kit. Or it reflected the varied specificity of each antigen or autoantibody.
The accuracy of serology test was of clinical significance because of the developing serology-based model for disease prognosis [31,32]. Thus, when the coexisted MSAs belonged to separate IIM subtypes, a careful confirmation by ANA-IIF, ELISA, or immunoprecipitation was recommended for the precise subtyping of IIM. The IIM subtyping was crucial because it was relevant to the frequency of tumors and the coexisted extra-muscular phenotypes, such as ILD. In this study, the second assay identified two-thirds of patients with false-positive results.
Compared with IIM patients with ≤1 MSA, the age of patients with double MSA showed no significant difference in this cohort (≤1 MSA and double MSA groups, aged 52.3 and 56.3 years, respectively; p = 0.54). Due to the fact that DM is the most prevalent IIM subtype, we also compared the age of DM patients with double MSAs (n = 5, aged 54.2 years) to DM patients with single or zero MSA (n = 14, aged 57 years), and the result revealed no statistical difference (p-value = 0.762). The sex distribution was also similar (≤1 MSA and double MSAs groups, 74.4 and 75% female, respectively; p = 0.71). Compared with previous studies, Bodoki L. reported a 1.8% prevalence double positive MSAs in IIM patients by using immunoblot (Orgentec Diagnostika) and radiolabelled immunoprecipitation (RIA) [22], Betteridge Z. reported a 0.2% prevalence by using RIA, and ELISA, particularly for anti-MDA5 and anti-NXP-2 antibodies [13] (Table 4), the prevalence of double seropositivity in our cohort was slightly higher. Like previous studies, DM was the most common clinical diagnosis in IIM patients with ≥2 MSAs [14,17,18,21].

Table 4.
Literature review.
Because of the low prevalence of double seropositive IIM, the frequency of various combinations of MSAs remained unknown. In our eight double seropositive cases, except for the coexistence of anti-SRP and anti-Mi-2β antibodies (Patient 4), the other combinations had not been reported before: anti-MDA5 plus anti-Mi-2β (Patient 5), anti-Jo-1 plus anti-NXP-2 (Patient 7), anti-PL-7 plus anti-TIF-1γ (Patient 17), anti-SRP plus anti-SAE (Patient 19 and 23), anti-MDA5 plus anti-TIF-1γ antibodies (Patient 20), anti-Jo-1 plus anti-TIF-1γ (Patient 18). Whether there is a common rule for the combination of MSAs needs further studies.
Regarding the clinical features, patients with double MSAs in this cohort presented predominant features skewed to either IIM subtypes instead of mixed features corresponding to the coexisted two MSAs. For instance, our Patient 19 presented both anti-SRP and anti-SAE antibodies manifested as amyotrophic DM, without typically profound muscle weakness as anti-SRP-related IMNM. However, a few reports showed mixed features of two IIM subtypes in the double-seropositive cases. Malkan A. reported a case with the coexistence of anti-SRP and anti-PL-12 antibodies, presenting with “mixed features” of both IMNM and antisynthetase syndrome [21].
In addition, there seems to be no hierarchy in coexisted MSAs when presenting relevant clinical features. For incidence, in patients with anti-SRP and anti-Mi-2β antibodies, our Patient 1 manifested as amyotrophic DM, more like the pertinent presentations to anti- Mi-2β antibody. In contrast, the case reported by Akintayo RO presented profound muscle weakness without skin rash, more like the presentation of anti-SRP IMNM [20]. In the case series from Hungarian IIM patients, one patient with anti-SRP and anti-Mi2 manifested polymyositis without skin rash [22].
Regarding the severity of clinical presentations, Sugie K. stated that the coexistence of 2 MSAs, as in his case with anti-Jo-1 and anti-SRP antibodies, may lead to more severe clinical symptoms [23]. However, we did not find a more severe clinical course in double seropositivity patients in this cohort. Our cases had no respiratory failure or mortality during follow-up. Besides, patients 4, 5, and 19 manifested amyotrophic DM without apparent muscle weakness.
About the comorbidities, 3 out of 8 patients (37.5%) had ILD in our cohort. High frequency of concomitant ILD was noted in previous studies (summarized in Table 4). In total, 14 out of 18 cases (77.8%) with double MSAs listed in Table 4 had ILD. A previous report addressed a higher frequency (2 out of 12 patients) of overlapped RA in IIM patients with double MSAs [33]. Two subjects (Patient 5 and Patient 17) in our cohort also had RA. Patient 5, with anti-MDA5 and anti-Mi-2β antibodies presented DM first, followed by RA. Patient 17, with anti-PL-7 and anti-TIF-1γ antibodies had RA first and was subsequently diagnosed with OM. However, the clinical relevance between arthritis and double-seropositive IIM requires more studies.
In conclusion, the coexistence of ≥2 MSAs does exist but is rare. Additional immune assays are recommended to confirm the double positive results in the line blot assay and exclude false positive cases. Applying the widely used cell-based ANA pattern in this study is convenient and efficient [34]. Most patients with ≥2 MSAs clinically resembled DM, which is also one of the most commonly seen IIM. No precise rule was noted in the combination of 2 MSAs. We did not find an MSA that is persistently superior to another MSA regarding its relevance to clinical presentations. No mixed phenotype or more severe course was found in this cohort. Finally, further accumulation of such cases is necessary for clarifying the features of the coexistence of 2 MSAs and whether differences in profile patterns translate into varying clinical phenotypes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.-T.S. and H.-L.H.; methodology, Y.-T.S. and H.-L.H.; software, W.-C.L.; validation, Y.-T.S.; formal analysis, W.-C.L.; investigation, W.-L.T.; resources, Y.-T.S., C.-T.W., M.-Y.W. and C.-H.W.; data curation, Y.-T.S. and H.-L.H.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-L.H.; writing—review and editing, Y.-T.S.; visualization, H.-L.H. and W.-L.T.; supervision, Y.-T.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors were supported by the grant from National Cheng Kung University Hospital (NCKUH-11008011, NCKUH-11002033).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of National Cheng Kung University Hospital (Approval No. B-BR-109-254).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Selva-O’Callaghan, A.; Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Trallero-Araguás, E.; Milisenda, J.C.; Grau-Junyent, J.M.; Mammen, A.L. Classification and management of adult inflammatory myopathies. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J. Current Classification and Management of Inflammatory Myopathies. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2018, 5, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariampillai, K.; Granger, B.; Amelin, D.; Guiguet, M.; Hachulla, E.; Maurier, F.; Meyer, A.; Tohmé, A.; Charuel, J.L.; Musset, L.; et al. Development of a New Classification System for Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Based on Clinical Manifestations and Myositis-Specific Autoantibodies. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclair, V.; Lundberg, I.E. New Myositis Classification Criteria-What We Have Learned Since Bohan and Peter. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.L.; Lin, W.C.; Lin, P.Y.; Weng, M.Y.; Sun, Y.T. The significance of myositis autoantibodies in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy concomitant with interstitial lung disease. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 2855–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.L.; Lin, W.C.; Yeh, C.C.; Sun, Y.T. Serological risk factors for concomitant interstitial lung disease in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 74, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selva-O’Callaghan, A.; Martinez-Gomez, X.; Trallero-Araguas, E.; Pinal-Fernandez, I. The diagnostic work-up of cancer-associated myositis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuhlmüller, B.; Schneider, U.; González-González, J.B.; Feist, E. Disease Specific Autoantibodies in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palterer, B.; Vitiello, G.; Carraresi, A.; Giudizi, M.G.; Cammelli, D.; Parronchi, P. Bench to bedside review of myositis autoantibodies. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2018, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, N.J.; Tansley, S.L. Autoantibodies in myositis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, A.; Lim, J.; de Visser, M.; van Engelen, B.; Pruijn, G.; Benveniste, O.; van der Kooi, A.; Saris, C. Autoantibody testing in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Pract. Neurol. 2019, 19, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, M.; Tanaka, S.; Ceribelli, A.; Calise, S.J.; Chan, E.K. A Comprehensive Overview on Myositis-Specific Antibodies: New and Old Biomarkers in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 52, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betteridge, Z.; Tansley, S.; Shaddick, G.; Chinoy, H.; Cooper, R.G.; New, R.P.; Lilleker, J.B.; Vencovsky, J.; Chazarain, L.; Danko, K.; et al. Frequency, mutual exclusivity and clinical associations of myositis autoantibodies in a combined European cohort of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy patients. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 101, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Gill, E.; Mo, F.; Reyes, C. Double anti-PL-7 and anti-MDA-5 positive Amyopathic Dermatomyositis with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease in a Hispanic patient. BMC Pulm Med. 2020, 20, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Moriya, C.; Matsuyama, K.; Shu, E.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Seishima, M. A Case of Dermatomyositis Coexisting with Both Anti-Mi-2 and Anti-NXP-2 Antibodies. Case Rep. Derm. 2020, 12, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melguizo Madrid, E.; Fernández Riejos, P.; Toyos Sáenz de Miera, F.J.; Fernández Pérez, B.; González Rodríguez, C. Coexistence of anti-Jo1 and anti-signal recognition particle antibodies in a polymyositis patient. Reum. Clin. 2019, 15, e111–e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakashima, R.; Tanaka, M.; Kuramoto, N.; Murakami, K.; Yoshifuji, H.; Ohmura, K.; Mimori, T. Anti-EJ, anti-MDA5 double-positive chronic clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis: A case report. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2018, 2, rky022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, M.; Xiao, Y.; Zuo, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Coexistence of anti-HMGCR and anti-MDA5 identified by an unlabeled immunoprecipitation assay in a chinese patient cohort with myositis. Medicine 2018, 97, e13236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naniwa, T.; Tamechika, S.; Okazaki, Y.; Maeda, S.; Kuwana, M. Coexistence of anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 and anti-aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetase antibodies in a patient with dermatomyositis and rapidly progressive and relapsing interstitial lung disease. Mod. Rheumatol. Case Rep. 2017, 1, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintayo, R.O.; Agbola, O.F.; Adeyemo, A.W.; Adelowo, O. Hyperacute muscle weakness in an unusual coexistence of antisignal recognition particle and anti-Mi-2 antibodies. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkan, A.; Cappelen-Smith, C.; Beran, R.; Griffith, N.; Toong, C.; Wang, M.X.; Cordato, D. Anti-synthetase syndrome associated with anti PL-12 and anti-Signal recognition particle antibodies and a necrotizing autoimmune myositis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 396–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodoki, L.; Nagy-Vincze, M.; Griger, Z.; Betteridge, Z.; Szöllősi, L.; Jobanputra, R.; Dankó, K. Rare myositis-specific autoantibody associations among Hungarian patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. Acta Reum. Port 2015, 40, 337–347. [Google Scholar]
- Sugie, K.; Tonomura, Y.; Ueno, S. Characterization of dermatomyositis with coexistence of anti-Jo-1 and anti-SRP antibodies. Intern. Med. 2012, 51, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, I.E.; Tjärnlund, A.; Bottai, M.; Werth, V.P.; Pilkington, C.; Visser, M.; Alfredsson, L.; Amato, A.A.; Barohn, R.J.; Liang, M.H.; et al. 2017 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and their major subgroups. Ann. Rheum Dis. 2017, 76, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottai, M.; Tjärnlund, A.; Santoni, G.; Werth, V.P.; Pilkington, C.; de Visser, M.; Alfredsson, L.; Amato, A.A.; Barohn, R.J.; Liang, M.H.; et al. EULAR/ACR classification criteria for adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and their major subgroups: A methodology report. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damoiseaux, J.; Andrade, L.E.C.; Carballo, O.G.; Conrad, K.; Francescantonio, P.L.C.; Fritzler, M.J.; Garcia de la Torre, I.; Herold, M.; Klotz, W.; Cruvinel, W.M.; et al. Clinical relevance of HEp-2 indirect immunofluorescent patterns: The International Consensus on ANA patterns (ICAP) perspective. Ann. Rheum Dis. 2019, 78, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nombel, A.; Fabien, N.; Coutant, F. Dermatomyositis With Anti-MDA5 Antibodies: Bioclinical Features, Pathogenesis and Emerging Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 773352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vooght, J.; Vulsteke, J.B.; De Haes, P.; Bossuyt, X.; Lories, R.; De Langhe, E. Anti-TIF1-γ autoantibodies: Warning lights of a tumour autoantigen. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, A.; Yamashita, T.; Hosono, Y.; Inoue, M.; Kaida, K.; Kadoya, M.; Miwa, Y.; Yajima, N.; Maezawa, R.; Arai, S.; et al. Anti-TIF1-γ antibody and cancer-associated myositis: A clinicohistopathologic study. Neurology 2016, 87, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.J.; Liao, W.A.; Lin, P.Y.; Sun, Y.T. Muscle Biopsy: A Requirement for Precision Medicine in Adult-Onset Myopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoloni, E.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Scire, C.; Castaneda, S.; Gerli, R.; Lopez-Longo, F.J.; Martinez-Barrio, J.; Govoni, M.; Furini, F.; Pina, T.; et al. Clinical follow-up predictors of disease pattern change in anti-Jo1 positive anti-synthetase syndrome: Results from a multicenter, international and retrospective study. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavagna, L.; Nuno, L.; Scire, C.A.; Govoni, M.; Longo, F.J.; Franceschini, F.; Neri, R.; Castaneda, S.; Sifuentes Giraldo, W.A.; Caporali, R.; et al. Serum Jo-1 Autoantibody and Isolated Arthritis in the Antisynthetase Syndrome: Review of the Literature and Report of the Experience of AENEAS Collaborative Group. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 52, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, A.; Yoshino, K.; Soejima, M.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Satoh, T.; Kuwana, M.; Yamanaka, H. High frequencies and co-existing of myositis-specific autoantibodies in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies overlapped to rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 2057–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infantino, M.; Tampoia, M.; Fabris, M.; Alessio, M.G.; Previtali, G.; Pesce, G.; Deleonardi, G.; Porcelli, B.; Musso, M.; Grossi, V.; et al. Combining immunofluorescence with immunoblot assay improves the specificity of autoantibody testing for myositis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).