Abstract
Although epidemiological studies suggest a lower prostate cancer incidence rate in patients with type 2 diabetes, cancer survival is markedly reduced. Underlying mechanisms that connect the two diseases are still unclear. Potential links between type 2 diabetes and prostate cancer are hallmarks of the metabolic syndrome, such as hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia. Therefore, we explored the systemic metabolism of 103 prostate cancer patients with newly diagnosed and yet untreated prostate cancer compared to 107 healthy controls, who were carefully matched for age and BMI. Here, we report that patients with prostate cancer display higher fasting blood glucose levels and insulin resistance, without changes in insulin secretion. With respect to lipid metabolism, serum triglyceride levels were lower in patients with prostate cancer. In addition, we report increased adrenal steroid biosynthesis in these patients. Our results indicate that higher fasting glucose levels in patients with prostate cancer may be explained at least in part by insulin resistance, due to the enhanced synthesis of adrenal steroids.
1. Introduction
Epidemiological studies suggest a lower prostate cancer (PCa) incidence in patients with type 2 diabetes [1,2]. However, the cancer survival in the case of coexisting diabetes is clearly reduced [3]. Both diabetes and PCa rank among the most frequent diseases in males worldwide with an enormous impact on morbidity and mortality. Although both diseases share several common risk factors, the precise causal links between them are not fully understood.
Important factors that may link PCa and diabetes are hallmarks of the metabolic syndrome, i.e., hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia [4]. In general, patients with higher blood glucose levels have more aggressive PCa [5]. Strong evidence exists for the impact of hyperglycemia on PCa recurrence after primary surgical or radiation therapy [6] and hyperglycemia-induced chemoresistance of PCa [7]. Vice versa, the commonly used first line androgen deprivation therapy for advanced PCa often causes metabolic disturbances, namely insulin resistance and hyperglycemia [8].
Recently, we could show a markedly higher prevalence of lymph node metastasis and more high-grade tumors in prostate cancer patients with coexistent diabetes [9]. One possible explanation for this phenomenon could be the elevated androgen receptor signaling in men with diabetes [10]. Besides these alterations in prostatic tissue, the systemic metabolism could contribute to it. Therefore, we investigated the metabolic profile of PCa patients in comparison to well-matched healthy controls.
2. Material and Methods
For this purpose, we phenotyped 103 patients with newly diagnosed and yet untreated PCa who were recruited in the Department of Urology, University of Tübingen prior to radical prostatectomy (for tumor characteristics, see Supplementary Tables S1 and S2), and 107 male controls without PCa from the Tübingen Family Study [11] who were carefully matched for age and BMI. Patients with a history of malignancy other than prostate were excluded. To avoid interference by glucose-lowering medication, we excluded patients with overt diabetes. The insulin sensitivity index was calculated as proposed by Matsuda and deFronzo based on a 5-point oral glucose tolerance test. Insulin secretion was calculated as the area under the curve (AUC) according to the trapezoid method as ½[½(C-Pep0′) + C-Pep30′ + C-Pep60′ + C-Pep90′ + ½(C-Pep120)]/½[½(Glc0′) + Glc30′ + Glc60′ + Glc90′ + ½(Glc120′)], with C-Pep = C-peptide. Insulin secretion was analyzed after adjustment for insulin sensitivity [12].
Liver fat was assessed by 1H-MR spectroscopy in a subset of 114 subjects. The Ethics Committee of the University of Tübingen approved the protocol and all participants provided written informed consent.
Plasma concentrations of glucose, wide range C-reactive protein, triglycerides (TGs) and total-, HDL- and low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol were measured using the ADVIA XPT clinical chemical analyzer (Siemens Healthineers, Eschborn, Germany). Plasma concentrations of total non-esterified fatty acid (NEFA) were measured with an enzymatic method (WAKO Chemicals, Neuss, Germany) on the latter instrument.
Plasma insulin, C-peptide, estradiol, cortisol and progesterone were determined using the ADVIA Centaur XP Immunoassay System, and DHEAS as well as androstenedione were measured using the Immulite 2000 XPi system (both Siemens Healthineers, Eschborn, Germany).
The matching of patients with PCa to similar participants without PCa was performed using a nearest match procedure with the package “MatchIt” in R (http://www.jstatsoft.org/v42/i08/, accessed on 12 January 2019). Statistical analyses were conducted using JMP 14.0 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Associations of PCa status with basal glucose and insulin sensitivity were tested in multivariate linear regression analyses of log-transformed data with adjustment for age and BMI, while associations with insulin secretion were tested after adjustment for age and insulin sensitivity. A p-value < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
3. Results
Compared to the controls, here we report that PCa patients displayed higher fasting blood glucose levels (5.65 ± 0.05 mmol/L and 5.44 ± 0.05 mmol/L, respectively, p = 0.002), independently of age and BMI. In parallel, this went along with reduced insulin sensitivity in the PCa group (9.1 ± 0.5 AU and 10.3 ± 0.5 AU, respectively, p = 0.016, Figure 1). By contrast, patients with PCa displayed no significant difference in insulin secretion compared to controls (p = 0.66, Table 1). The PSA-levels in patients with PCa were 9.27 ± 0.89 ng/mL with a median of 6.9 [0.47–59]. PSA levels in the control group were not available. Regarding lipid metabolism, serum triglyceride levels were lower in patients with PCa (95.4 ± 5.9 mg/dL and 130.6 ± 5.8 mg/dL, respectively, p < 0.0001), while no differences between the two groups were detectable in NEFA and cholesterol levels (p = 0.35 and p = 0.06, respectively, Table 1). Moreover, our results indicate increased steroid synthesis in PCa patients, as they displayed elevated serum cortisol (476.1 ± 14 nmol/L and 438 ± 13.9 nmol/L, respectively, p = 0.029), androstenedione (6.5 ± 0.3 nmol/L and 4.8 ± 0.3 nmol/L, respectively, p < 0.0001), progesterone (1.3 ± 0.04 nmol/L and 0.8 ± 0.04 nmol/L, respectively, p < 0.0001), DHEA-Sulfate (4.2 ± 0.2 µmol/L and 2.9 ± 0.2 µmol/L, respectively, p < 0.0001) and estradiol (126.4 ± 3.1 pmol/L and 115.5 ± 3.0 pmol/L, respectively, p = 0.009) levels (Figure 2).
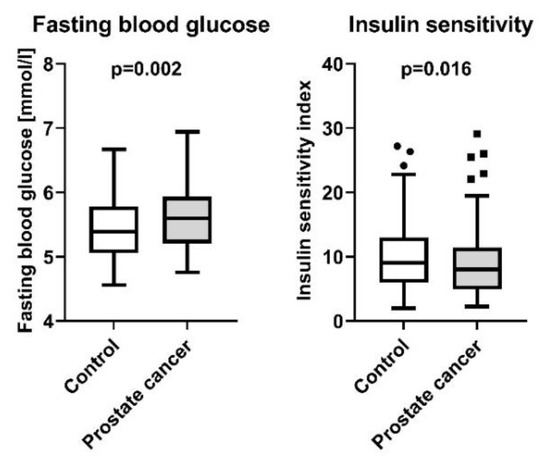
Figure 1.
Fasting blood glucose and insulin sensitivity index in 103 patients with newly diagnosed and yet untreated PCa, and 107 male controls without PCa from the Tübingen Family Study. Presented are box plots with whiskers indicating 1.5 interquartile range.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the study population. Included are 103 patients with newly diagnosed and yet untreated PCa, and 107 male controls without PCa from the Tübingen Family Study. Abbreviations: AUC, area under the curve; BMI, body mass index. Data are given as mean ± SEM for all parameters. p-values are given for unadjusted data, p*-values are for a model adjusting for age and BMI, except the associations with insulin secretion which are adjusted for age and insulin sensitivity.
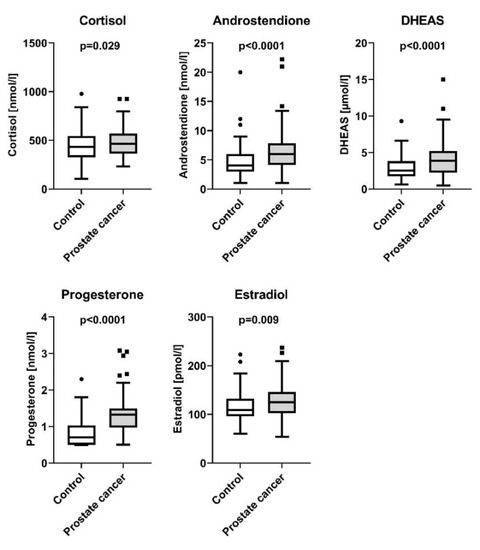
Figure 2.
Steroid hormones in controls and patients with prostate cancer. Presented are box plots with whiskers indicating 1.5 interquartile range.
4. Discussion
Although epidemiological studies indicated lower PCa risk in men with type 2 diabetes, the precise relationships between PCa and hyperglycemia are not well understood. In particular, it is unclear whether hyperglycemia may modulate PCa risk and vice versa. Moreover, antidiabetic medication may also impact on PCa risk through different mechanisms independently of lowering blood glucose levels [13]. In the Finnish Randomized Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer (FinRSPC) with a median follow-up of 14.7 years, increased fasting glucose was identified as a predictor of PCa development [13]. Although we excluded patients with diabetes, men with PCa in our study clearly displayed higher fasting glucose levels, compared to carefully matched controls. Thus, our results are in line with the aforementioned Finnish study.
In another study, Gerlini et al. could show that glucose intolerance and insulin resistance regulate adipocyte transcription in human obesity [14]. As we found hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in PCa, it is tempting to speculate that comparable transcriptional effects might exist in the prostate.
Interestingly, the metabolic pattern of hyperglycemia in the context of low circulating triglycerides was associated with poor prognosis and increased risk of PCa death in a previous study [4]. The role of triglycerides in PCa is not fully understood yet. However, lipid metabolism seems essential for prostate cancer cells, while they do not depend on increased aerobic glycolysis [15]. As we detected lower triglycerides in PCa patients, while liver fat content was comparable to healthy controls, triglyceride uptake might be higher in prostate cancer cells. This hypothesis needs to be addressed in future studies.
One known determinant of insulin sensitivity/insulin resistance, which might further support our findings, are steroid hormones. PCa was reported to release miRNA, which affect steroid biosynthesis mainly in the adrenal gland [16,17]. We therefore measured key steroid hormones in our patients.
PCa is a hormone-dependent cancer, and androgen signaling represents a key driver for cancer cell growth. However, in a collaborative analysis investigating direct correlations between risk of PCa and serum concentrations of circulating sex steroids, no associations were found [18]. In spite of this, complex interactions between diabetes and sex steroids exist [19]. We hypothesized that hyperglycemia in PCa patients may be linked to the elevated synthesis of sex steroids. Testosterone synthesis has been reported to be reduced in patients with diabetes [20], but continued androgen receptor (AR) activation in the presence of low circulating levels of testosterone have been proposed, indicating alternative AR ligands to bypass the testosterone/dihydrotestosterone-mediated AR activation [10]. Therefore, we assessed adrenal steroids as androgen precursors. Indeed, we found elevated levels of cortisol, androstenedione, DHEA-Sulfate, progesterone and estradiol in PCa. Of note, serum levels of gonadal steroid testosterone were comparable between the groups (Table 1). The adrenal hormones may, on the one hand, activate at least mutated AR, a frequent mechanism in PCa to provoke resistance to hormonal therapy [21], but on the other hand, also elevate fasting glucose levels in PCa patients by introducing insulin resistance. Unfortunately, unlike in our study, most previous studies did not perform the rigorous matching for anthropometric determinants of steroid hormones and may, therefore, have missed to detect differentially regulated hormones in cancer vs. control. Nevertheless, our results are supported by a previous report showing higher levels of estradiol in PCa [22]. Several reports exist suggesting a proliferative role of estradiol in PCa especially via activating the estrogen receptor α [23]. Androstenedione seems relevant for AR activation with regard to being largely unaffected by ADT or orchiectomy in spite of testosterone/dihydrotestosterone [24].
Among the limitations of our work is the cross-sectional study design that can never fully uncover changes over time. The prostate cancer cases were heterogeneous in grade and stage which might have impacted our findings (see Supplementary Tables S1 and S2). Due to the available sample size, we could not investigate potential differences due to cancer grade/stage in further subgroups in more detail. Clearly, additional experimental studies are needed to unravel the molecular links between steroid hormones, diabetes and PCa.
Our results suggest that higher fasting glucose levels in patients with PCa may be explained at least in part by insulin resistance, due to the enhanced synthesis of adrenal steroids. This may pave the way for new therapeutic approaches in coexisting diabetes and PCa.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm11226762/s1. Supplementary Table S1: Gleason-Scores of 103 patients with newly diagnosed and yet untreated PCa. Supplementary Table S2: Stages of PCa of 103 patients with newly diagnosed and yet untreated Pca.
Author Contributions
The study was designed by M.H., N.S., A.F. (Andreas Fritsche) and H.-U.H. Data acquisition was performed by J.H., C.D., L.F. and M.H. Data analysis and interpretation was performed by S.Z.L., R.W., A.F. (Andras Franko), H.-U.H., M.H. and S.Z.L. drafted the manuscript. K.K., R.W., A.P., N.S., A.F. (Andreas Fritsche), T.T., A.S., H.-U.H. and M.H. contributed to the discussion. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was supported in part by a grant from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), grant number 01GI0925 to the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD e.V.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of University of Tübingen (protocol code 360/2013BO2 and date of approval 10 October 2013).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data are not publicly available as they contain information that could compromise research participant privacy/consent.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all study participants for their cooperation. We gratefully acknowledge the excellent technical assistance of Dorothee Neuscheler and Elisabeth Metzinger.
Conflicts of Interest
Outside of the current work, M.H. reports research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim and Sanofi (to the University Hospital of Tübingen), advisory board for Boehringer Ingelheim, and lecture fees from Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, and Amryt. A.F. (Andras Franko) is an employee of JOTEC GmbH. However, the company had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
ADT: androgen-deprivation therapy; AU: arbitrary units; DHT: dihydrotestosterone; OGTT: oral glucose tolerance test; PCa: prostate cancer.
References
- Kasper, J.S.; Liu, Y.; Giovannucci, E. Diabetes mellitus and risk of prostate cancer in the health professionals follow-up study. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1398–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonovas, S.; Filioussi, K.; Tsantes, A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of prostate cancer: A meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, F.; Saito, E.; Lin, Y.; Song, M.; Luu, H.N.; Gupta, P.C.; Sawada, N.; Tamakoshi, A.; Shu, X.O.; et al. Association between type 2 diabetes and risk of cancer mortality: A pooled analysis of over 771,000 individuals in the Asia Cohort Consortium. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, R.; Moller, H.; Garmo, H.; Holmberg, L.; Stattin, P.; Malmstrom, H.; Lambe, M.; Hammar, N.; Walldius, G.; Robinson, D.; et al. Association between baseline serum glucose, triglycerides and total cholesterol, and prostate cancer risk categories. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Presti, J.C., Jr.; Aronson, W.J.; Terris, M.K.; Kane, C.J.; Amling, C.L.; Freedland, S.J. Glycemic control and prostate cancer progression: Results from the SEARCH database. Prostate 2010, 70, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.L.; Plymate, S.R.; Porter, M.P.; Gore, J.L.; Lin, D.W.; Hu, E.; Zeliadt, S.B. Hyperglycemia and prostate cancer recurrence in men treated for localized prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2013, 16, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacka, K.M.; Uzoh, C.C.; Zeng, L.; Persad, R.A.; Bahl, A.; Gillatt, D.; Perks, C.M.; Holly, J.M. Hyperglycaemia-induced chemoresistance of prostate cancer cells due to IGFBP2. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E.J.; Gianatti, E.; Strauss, B.J.; Wentworth, J.; Lim-Joon, D.; Bolton, D.; Zajac, J.D.; Grossmann, M. Increase in visceral and subcutaneous abdominal fat in men with prostate cancer treated with androgen deprivation therapy. Clin. Endocrinol. 2011, 74, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, S.Z.; Todenhofer, T.; Wagner, R.; Hennenlotter, J.; Ferchl, J.M.; Scharpf, M.O.; Martus, P.; Staiger, H.; Fritsche, A.; Stenzl, A.; et al. Higher prevalence of lymph node metastasis in prostate cancer in patients with diabetes. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, L19–L22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, S.Z.; Hennenlotter, J.; Scharpf, M.O.; Sailer, C.; Fritsche, L.; Schmid, V.; Kantartzis, K.; Wagner, R.; Lehmann, R.; Berti, L.; et al. Androgen receptor overexpression in prostate cancer in type 2 diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2018, 8, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Heni, M.; Tabák, A.G.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Randrianarisoa, E.; de Angelis, M.H.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Stefan, N.; Peter, A.; et al. Pathophysiology-based subphenotyping of individuals at elevated risk for type 2 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrén, B.; Pacini, G. Importance of quantifying insulin secretion in relation to insulin sensitivity to accurately assess beta cell function in clinical studies. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 150, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtola, T.J.; Vihervuori, V.J.; Lahtela, J.; Talala, K.; Taari, K.; Tammela, T.L.; Auvinen, A. Fasting blood glucose, glycaemic control and prostate cancer risk in the Finnish Randomized Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlini, R.; Berti, L.; Darr, J.; Lassi, M.; Brandmaier, S.; Fritsche, L.; Scheid, F.; Bohm, A.; Konigsrainer, A.; Grallert, H.; et al. Glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity define adipocyte transcriptional programs in human obesity. Mol. Metab. 2018, 18, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadra, G.; Photopoulos, C.; Loda, M. The fat side of prostate cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 1518–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.; MacKenzie, S.M.; Alvarez-Madrazo, S.; Diver, L.A.; Lin, J.; Stewart, P.M.; Fraser, R.; Connell, J.M.; Davies, E. MicroRNA-24 is a novel regulator of aldosterone and cortisol production in the human adrenal cortex. Hypertension 2013, 62, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.S.C.; Olkhov-Mitsel, E.; Jeyapala, R.; Zhao, F.; Commisso, K.; Klotz, L.; Loblaw, A.; Liu, S.K.; Vesprini, D.; Fleshner, N.E.; et al. Assessment of Serum microRNA Biomarkers to Predict Reclassification of Prostate Cancer in Patients on Active Surveillance. J. Urol. 2018, 199, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endogenous, H.; Prostate Cancer Collaborative Group. Endogenous sex hormones and prostate cancer: A collaborative analysis of 18 prospective studies. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, M.; Gianatti, E.J.; Zajac, J.D. Testosterone and type 2 diabetes. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2010, 17, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, E.L.; Song, Y.; Malik, V.S.; Liu, S. Sex differences of endogenous sex hormones and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2006, 295, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, J.; McEwan, I.J. Mutation of histidine 874 in the androgen receptor ligand-binding domain leads to promiscuous ligand activation and altered p160 coactivator interactions. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 2943–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosman, H.; Fabre, B.; Mesch, V.; Lopez, M.A.; Schreier, L.; Mazza, O.; Berg, G. Lipoproteins, sex hormones and inflammatory markers in association with prostate cancer. Aging Male 2010, 13, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.P.; Hofland, J.; Foster, P.A. In touch with your feminine side: How oestrogen metabolism impacts prostate cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R249–R266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaghel, E.A. Beyond T and DHT—Novel steroid derivatives capable of wild type androgen receptor activation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).