The Screening of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Virus Infection among HIV-Infected Inpatients and Evaluation of Correlated Characteristics in a General Hospital in Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
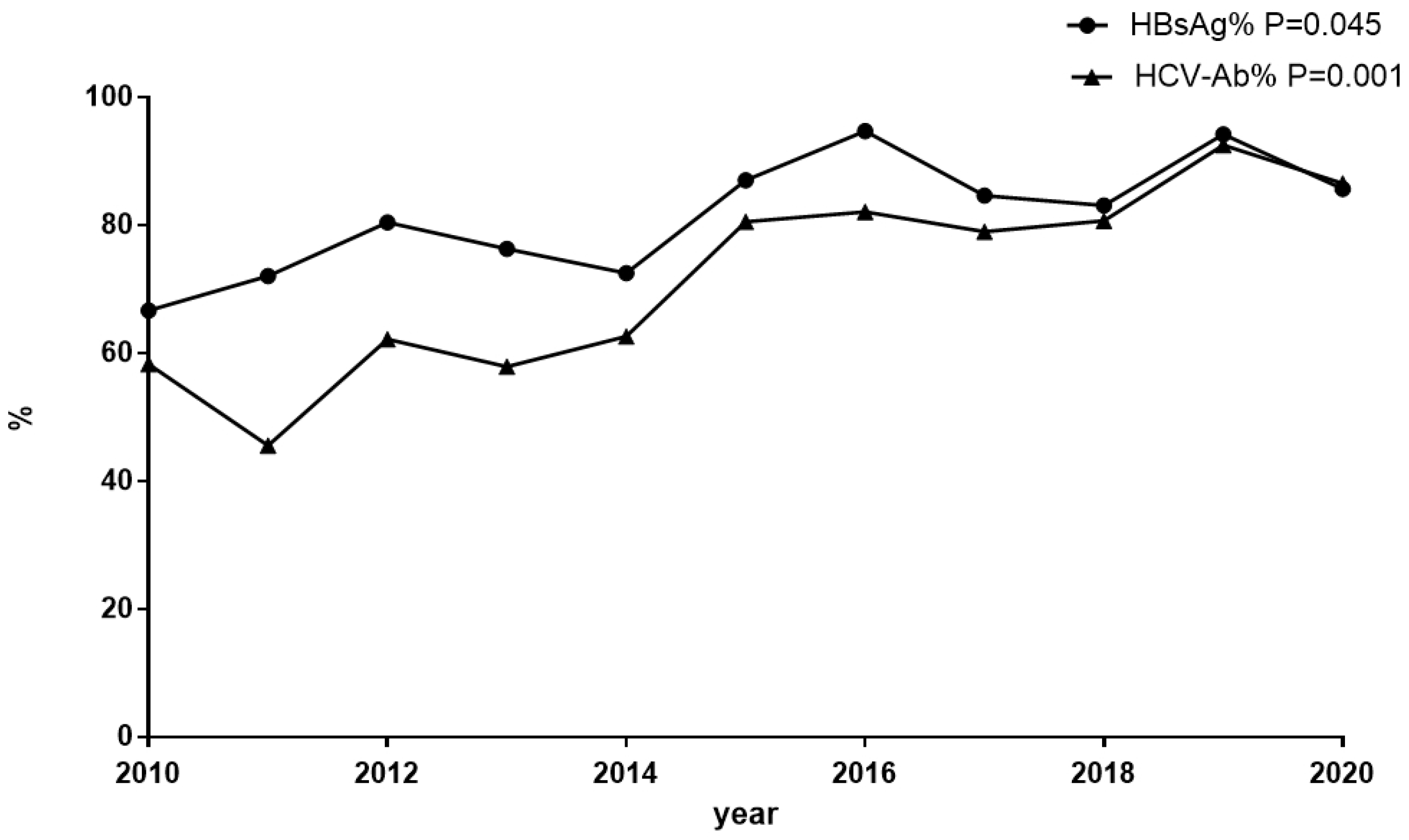
3.1. The Prevalence of Screening for HBsAg and Anti-HCV among Inpatients with HIV Infection
3.2. Distribution of HBV Serological Markers among Cases with Complete Serological Results
3.3. Clinical Characteristics at Baseline among HIV/HBV-Coinfected Patients
3.4. Clinical Characteristics at Baseline among HIV/HCV-Coinfected Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HBsAg | hepatitis B surface antigen |
| anti-HCV | hepatitis C virus antibody |
| HBV | hepatitis B virus |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| HCV | hepatitis C virus |
| IVDUs | intravenous drug user |
| MSM | men who have sex with men |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| ART | antiretroviral therapy |
| HBeAg | hepatitis B e-antigen |
| RAHC | recently acquired HCV infection |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| BMI | body mass index |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| HB | hemoglobin |
| PLT | platelet |
| ALT | glutamic alanine transaminase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| GGT, | gamma-glutamyltransferase |
| TBIL | total bilirubin |
| ALB | albumin |
| Scr | serum creatinine |
| PT | prothrombin time |
| HBsAb | hepatitis B surface antibody |
| HBeAb | hepatitis B e antibody |
| HBcAb | hepatitis B core antibody |
| CLIA | chemiluminescence immunoassay |
| OR | odds ratios |
| AOR | adjusted odds ratios |
| CI | confidence intervals |
| OBI | occult hepatitis B |
| OCI | occult hepatitis C |
| TDF | tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
| TAF | tenofovir alafenamide |
| DAAs | direct-acting antiviral therapies |
References
- Shahriar, S.; Araf, Y.; Ahmad, R.; Kattel, P.; Sah, G.S.; Rahaman, T.I.; Sadiea, R.Z.; Sultana, S.; Islam, M.S.; Zheng, C.; et al. Insights Into the Coinfections of Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Hepatitis B Virus, Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Hepatitis C Virus, and Hepatitis B Virus-Hepatitis C Virus: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 780887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodsworth, N.J.; Cooper, D.A.; Donovan, B. The influence of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection on the development of the hepatitis B virus carrier state. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 163, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clausen, L.N. Factors associated with resolution and progression of HIV/hepatitis C virus infection. Dan. Med. J. 2014, 61, B4838. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidbauer, C.; Chromy, D.; Schmidbauer, V.; Bauer, D.; Apata, M.; Nguyen, D.; Mandorfer, M.; Simbrunner, B.; Rieger, A.; Mayer, F.; et al. Epidemiological trends in HCV transmission and prevalence in the Viennese HIV+ population. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2020, 40, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lana, R.; Núñez, M.; Mendoza, J.L.; Soriano, V. Rate and risk factors of liver toxicity in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. Med. Clin. 2001, 117, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, A.; Riva, A.; Falvella, F.S.; Oreni, M.L.; Cattaneo, D.; Cheli, S.; Renisi, G.; Di Cristo, V.; Lupo, A.; Clementi, E.; et al. Clinical and genetic factors associated with increased risk of severe liver toxicity in a monocentric cohort of HIV positive patients receiving nevirapine-based antiretroviral therapy. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, E.; Roussillon, C.; Salmon-Céron, D.; Georget, A.; Hénard, S.; Huleux, T.; Gueit, I.; Mortier, E.; Costagliola, D.; Morlat, P.; et al. Liver-related deaths in HIV-infected patients between 1995 and 2010 in France: The Mortavic 2010 study in collaboration with the Agence Nationale de Recherche sur le SIDA (ANRS) EN 20 Mortalité 2010 survey. HIV Med. 2015, 16, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zhu, Q.; Deng, L.; Lan, G.; Johnson, A.; Chen, H.; Shen, Z.; Li, J.; Xing, H.; Ruan, Y.; et al. Treatment outcomes of HIV patients with hepatitis B and C virus co-infections in Southwest China: An observational cohort study. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, A.; Ochola, E.; Oreni, L.; Vassalini, P.; Rizzardini, G.; Galli, M. Hepatitis B and HIV coinfection in Northern Uganda: Is a decline in HBV prevalence on the horizon? PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafeero, H.M.; Ndagire, D.; Ocama, P.; Kudamba, A.; Walusansa, A.; Sendagire, H. Prevalence and predictors of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in east Africa: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies published from 2005 to 2020. Arch. Public Health 2021, 79, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, L.; Easterbrook, P.; Gower, E.; McDonald, B.; Sabin, K.; McGowan, C.; Yanny, I.; Razavi, H.; Vickerman, P. Prevalence and burden of HCV co-infection in people living with HIV: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayana, D.A.; Mulu, A.; Mihret, A.; Seyoum, B.; Aseffa, A.; Howe, R. Hepatitis B virus seromarkers among HIV infected adults on ART: An unmet need for HBV screening in eastern Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, M.H.; Zhai, X.J. Prevalence of HBV co-infection in HIV-positive population in China: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi 2021, 42, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Deng, M. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevalence among people living with HIV/AIDS in China: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Ou, W.; Li, D.; Feng, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Shao, Y. Changing Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus Coinfection in a Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Population in China: Results From the Third and Fourth Nationwide Molecular Epidemiologic Surveys. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2021, 73, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, K.C.; Poudel-Tandukar, K. High prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus in people living with HIV in Kathmandu, Nepal. Infect. Dis. 2021, 53, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, R.; Patel, N.; Fox, J.; Cosgrove, C.; Pett, S.L.; Burns, F.; Ustianowski, A.; Rosenvinge, M.; Bhagani, S.; Dusheiko, G.; et al. Prevalence of HIV/hepatitis B and HIV/hepatitis C coinfection among people of East, South, Central and West African ancestry in the United Kingdom. AIDS 2021, 35, 1701–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffie, P.A.; Egger, M.; Vinikoor, M.J.; Zannou, M.; Diero, L.; Patassi, A.; Kuniholm, M.H.; Seydi, M.; Bado, G.; Ocama, P.; et al. Trends in hepatitis B virus testing practices and management in HIV clinics across sub-Saharan Africa. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.K.; Vigil, K.J.; Parisot, P.; Go, G.; Vu, T.; Li, X.; Hansen, L.; Taylor, B.S. Incidence and Predictors of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Clearance in HIV Patients: A Retrospective Multisite Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, A.L.; Corrêa, M.C. Evolution of hepatitis B serological markers in HIV coinfected patients: A case study. Rev. Saude Publica 2017, 51, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloquel, B.; Jeulin, H.; Burty, C.; Letranchant, L.; Rabaud, C.; Venard, V. Occult hepatitis B infection in patients infected with HIV: Report of two cases of hepatitis B reactivation and prevalence in a hospital cohort. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Msomi, N.; Naidoo, K.; Yende-Zuma, N.; Padayatchi, N.; Govender, K.; Singh, J.A.; Abdool-Karim, S.; Abdool-Karim, Q.; Mlisana, K. High incidence and persistence of hepatitis B virus infection in individuals receiving HIV care in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Serna, A.; Macias, J.; Palacios, R.; Gómez-Ayerbe, C.; Tellez, F.; Rivero-Juárez, A.; Fernandez, M.; Santos, J.; Real, L.M.; Gonzalez-Domenech, C.M.; et al. Incidence of recently acquired hepatitis C virus infection among HIV-infected patients in southern Spain. HIV Med. 2021, 22, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, L.J.; Cooke, G.S.; Smith, C.; Stingone, C.; Ghosh, I.; Dakshina, S.; Jain, L.; Waters, L.J.; Mahungu, T.; Ferro, F.; et al. Decline in Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Incidence in Men Who Have Sex with Men Living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus: Progress to HCV Microelimination in the United Kingdom? Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2021, 72, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xu, H.; Hu, Y.; Shang, J.; Jiang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; et al. Hepatitis C screening in hospitals: Find the missing patients. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Draft Global Health Sector Strategies Viral Hepatitis 2016–2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/hepatitis/strategy2016-2021/ghss-hep/en/ (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- Su, S.; Wong, W.C.; Zou, Z.; Cheng, D.D.; Ong, J.J.; Chan, P.; Ji, F.; Yuen, M.F.; Zhuang, G.; Seto, W.K.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of universal screening for chronic hepatitis B virus infection in China: An economic evaluation. Lancet. Glob. Health 2022, 10, e278–e287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Xu, H.; Sui, D.; Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Niu, J. A retrospective serological survey of hepatitis B virus infection in Northeast China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qi, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qin, S.; Zhao, P.; Guo, H.; Jiao, J.; Zhou, C.; et al. Epidemiology of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Infections and Benefits of Programs for Hepatitis Prevention in Northeastern China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2016, 62, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Chen, Q.; Li, D.; Wang, T.; Gou, Y.; Wei, B.; Tao, C. High prevalence of syphilis, HBV, and HCV co-infection, and low rate of effective vaccination against hepatitis B in HIV-infected patients in West China hospital. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Shen, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, D.; Liu, M. Seroepidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection in 2 million men aged 21–49 years in rural China: A population-based, cross-sectional study. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.H.; Meier-Stephenson, V.; Genetu, M.; Damtie, D.; Abate, E.; Alemu, S.; Aleka, Y.; Van Marle, G.; Fonseca, K.; Coffin, C.S.; et al. Prevalence and genetic variability of occult hepatitis B virus in a human immunodeficiency virus positive patient cohort in Gondar, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, R.R.; Mathur, A.; Mathur, D.; Udawat, H.P.; Nepalia, S.; Nijhawan, S.; Mathur, A. Prevalence of occult hepatitis B & C in HIV patients infected through sexual transmission. Trop. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Dig. Dis. Found. 2007, 28, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Demosthenes, J.P.; Sachithanandham, J.; Fletcher, G.J.; Zachariah, U.G.; Varghese, G.M.; John Daniel, H.D.; Jeyaseelan, L.; Abraham, P.; Kannangai, R. Characteristics of treatment-naïve HBV-infected individuals with HIV-1 coinfection: A cross-sectional study from South India. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 37, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lô, G.; Sow-Sall, A.; Diop-Ndiaye, H.; Mandiouba, N.C.; Thiam, M.; Diop, F.; Ndiaye, O.; Gueye, S.B.; Seck, S.M.; Dioura, A.A.; et al. Prevalence of hepatitis B markers in Senegalese HIV-1-infected patients. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Wahed, A.S.; King, W.C.; Kleiner, D.E.; Khalili, M.; Sulkowski, M.; Chung, R.T.; Jain, M.K.; Lisker-Melman, M.; Wong, D.K.; et al. Spectrum of Liver Disease in Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Patients Co-infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV): Results of the HBV-HIV Cohort Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thio, C.L.; Smeaton, L.; Saulynas, M.; Hwang, H.; Saravanan, S.; Kulkarni, S.; Hakim, J.; Nyirenda, M.; Iqbal, H.S.; Lalloo, U.G.; et al. Characterization of HIV-HBV coinfection in a multinational HIV-infected cohort. AIDS 2013, 27, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thio, C.L.; Seaberg, E.C.; Skolasky, R., Jr.; Phair, J.; Visscher, B.; Muñoz, A.; Thomas, D.L. HIV-1, hepatitis B virus, and risk of liver-related mortality in the Multicenter Cohort Study (MACS). Lancet 2002, 360, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donyavi, T.; Bokharaei-Salim, F.; Khanaliha, K.; Sheikh, M.; Bastani, M.N.; Moradi, N.; Babaei, R.; Habib, Z.; Fakhim, A.; Esghaei, M. High prevalence of occult hepatitis C virus infection in injection drug users with HIV infection. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggorowati, N.; Yano, Y.; Heriyanto, D.S.; Rinonce, H.T.; Utsumi, T.; Mulya, D.P.; Subronto, Y.W.; Hayashi, Y. Clinical and virological characteristics of hepatitis B or C virus co-infection with HIV in Indonesian patients. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavini, M.; Angeli, E.; Mainini, A.; Zerbi, P.; Duca, P.G.; Gubertini, G.; Vago, L.; Fociani, P.; Giorgi, R.; Cargnel, A. Risk factors for fibrosis progression in HIV/HCV coinfected patients from a retrospective analysis of liver biopsies in 1985–2002. HIV Med. 2006, 7, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, F.H.; Ferreira, L.E.; Silva, A.E.; Ferraz, M.L. Liver fibrosis progression in HIV/hepatitis C virus coinfected patients with normal aminotransferases levels. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2012, 45, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissmann, L.; Picone, C.M.; Gouvêa, M.S.G.; Ferreira, P.R.A.; Viana, M.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Cassenote, A.J.F.; Segurado, A.C. Hepatitis B viremia in HIV-coinfected individuals under antiretroviral therapy. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Braz. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2019, 23, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Hong, S.; Im, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Baek, J.H.; Kwon, H.Y. Systematic review and meta-analysis of immune response of double dose of hepatitis B vaccination in HIV-infected patients. Vaccine 2020, 38, 3995–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretto, F.; Catherine, F.X.; Esteve, C.; Blot, M.; Piroth, L. Isolated Anti-HBc: Significance and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piroth, L.; Launay, O.; Michel, M.L.; Bourredjem, A.; Miailhes, P.; Ajana, F.; Chirouze, C.; Zucman, D.; Wendling, M.J.; Nazzal, D.; et al. Vaccination Against Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) in HIV-1-Infected Patients with Isolated Anti-HBV Core Antibody: The ANRS HB EP03 CISOVAC Prospective Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsachouridou, O.; Georgiou, A.; Naoum, S.; Vasdeki, D.; Papagianni, M.; Kotoreni, G.; Forozidou, E.; Tsoukra, P.; Gogou, C.; Chatzidimitriou, D.; et al. Factors associated with poor adherence to vaccination against hepatitis viruses, streptococcus pneumoniae and seasonal influenza in HIV-infected adults. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cui, F. Expanded screening for chronic hepatitis B virus infection in China. Lancet. Glob. Health 2022, 10, e171–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Modes | Group | n | HBsAg+ HBeAg+ HBcAb+ [n (%)] | HBsAg+ HBeAg− HBcAb+ [n (%)] | HBsAg− HBSAb− HBcAb+ [n (%)] | HBsAg− HBSAb+ HBcAb+ [n (%)] | HBsAg− HBSAb+ HBcAb− [n (%)] | HBsAg− HBSAb− HBcAb− [n (%)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <30 | 106 | 6(1.2) | 4(0.8) | 8(1.6) | 3(0.6) | 43(8.8) | 42(8.6) |
| 30–50 | 233 | 8(1.6) | 11(2.3) | 51(10.5) | 51(10.5) | 62(12.7) | 50(10.3) | |
| >50 | 148 | 9(1.9) | 9(1.9) | 33(6.8) | 47(9.7) | 24(4.9) | 26(5.3) | |
| Sex | male | 443 | 22(4.5) | 18(3.7) | 88(18.1) | 88(18.1) | 124(25.5) | 103(21.2) |
| female | 44 | 1(0.2) | 6(1.2) | 4(0.8) | 13(2.7) | 5(1.0) | 15(3.1) | |
| total | 487 | 23(4.7) | 24(4.9) | 92(18.9) | 101(20.7) | 129(26.5) | 118(24.2) |
| Characteristics | HBSAg+ (n, %) | HBsAg− (n, %) | P1 | HCV-RNA+ (n, %) | HCVAb− (n, %) | P2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 89(100.0) | 731(100.0) | 18(100.0) | 710(100.0) | ||
| Age < 30 30–50 >50 | 20(22.5) | 152(20.8) | 0(0.0) | 158(22.3) | ||
| 52(58.4) | 363(49.7) | 10(55.6) | 363(51.1) | |||
| 17(19.1) | 216(29.5) | 0.113 | 8(44.4) | 190(26.8) | 0.047 * | |
| College education | 27(30.3) | 213(29.1) | 0.814 | 4(22.2) | 216(30.4) | 0.606 |
| Sex (male) | 82(92.1) | 662(90.6) | 0.161 | 16(88.9) | 650(91.5) | 0.690 |
| Local residents | 45(50.6) | 341(46.7) | 0.485 | 11(61.1) | 332(46.8) | 0.228 |
| WHO clinical stage III–IV | 60(67.4) | 492(67.3) | 0.983 | 9(50) | 493(69.4) | 0.078 |
| Alcohol consumption history | 9(10.1) | 45(6.2) | 0.161 | 1(5.6) | 48(6.8) | 0.587 |
| Fatty liver | 7(7.9) | 55(7.5) | 0.921 | 1(5.6) | 56(7.9) | 0.989 |
| Underlying medical conditions | 21(23.6) | 185(25.3) | 0.703 | 2(11.1) | 176(24.8) | 0.743 |
| ART prior to admission | 32(36.0) | 224(30.6) | 0.311 | 7(38.9) | 232(32.7) | 0.582 |
| HB < 9 g/dL | 12(13.5) | 68(9.3) | 0.209 | 2(11.1) | 73(10.3) | 0.909 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 16(18.0) | 45(6.2) | 0.001 * | 3(16.7) | 53(7.5) | 0.148 |
| ALT > 50 U/L | 31(34.8) | 180(24.6) | 0.038 * | 9(50) | 180(25.4) | 0.018 * |
| AST > 40 U/L | 43(48.3) | 208(28.5) | 0.001 * | 10(55.5) | 215(30.3) | 0.022 * |
| ALP > 100 U/L | 38(42.7) | 196(26.8) | 0.002 * | 10(55.5) | 204(28.7) | 0.014 * |
| GGT > 60 U/L | 49(55.1) | 362(49.5) | 0.324 | 12(66.7) | 356(50.1) | 0.166 |
| TBIL > 17.1 µmol/L | 1(1.1) | 17(2.3) | 0.728 | 0(0.0) | 18(2.5) | 1.000 |
| Serum ALB < 30 g/L | 46(51.7) | 266(36.4) | 0.036 * | 3(16.7) | 278(39.2) | 0.053 |
| PT > 13.7 S | 51(57.3) | 298(40.8) | 0.003 * | 7(38.9) | 303(42.7) | 0.748 |
| Serum Na < 135 µmol/L | 29(32.6) | 222(30.4) | 0.669 | 6(33.3) | 225(31.7) | 0.882 |
| Scr > 104 μmol/L | 4(4.5) | 13(1.8) | 0.090 | 1(5.6) | 17(2.4) | 0.394 |
| CD4 < 200 /µL | 74(83.1) | 557(76.2) | 0.219 | 8(44.4) | 556(78.3) | 0.001 * |
| BMI < 18 | 9(10.1) | 118(16.1) | 0.106 | 2(11.1) | 110(15.5) | 0.751 |
| Death | 4(4.5) | 36(4.9) | 0.859 | 1(5.6) | 33(4.6) | 0.857 |
| HIV/HBV-Coinfected | HIV/HCV-Coinfected | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | OR(95%CI) | P1 Value | Adjust OR(95%CI) | P2 Value | OR(95%CI) | P3 Value | Adjust OR(95%CI) | P4 Value |
| ALT > 50 U/L | ||||||||
| No | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||||||
| Yes | 1.636(1.198–3.029) | 0.039 | 2.944(1.151–7.532) | 0.024 | ||||
| AST > 40 U/L | ||||||||
| No | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |||||
| Yes | 2.350(1.505–3.670) | 0.043 | 1.959(1.235–3.109) | 0.004 | 2.878(1.120–7.392) | 0.028 | 3.380(1.292–8.841) | 0.013 |
| ALP > 100 U/L | ||||||||
| No | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||||||
| Yes | 2.034(1.296–3.192) | 0.002 | 3.100(1.207–7.967) | 0.019 | ||||
| Thrombocytopenia | ||||||||
| No | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||||||
| Yes | 3.341(1.798–6.208) | 0.001 | 3.061(1.621–5.780) | 0.001 | ||||
| ALB < 30 g/L | ||||||||
| No | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |||||
| Yes | 1.870(1.202–2.910) | 0.006 | 1.698(1.074–2.685) | 0.024 | 0.311(0.089–1.083) | 0.067 | ||
| PT > 13.7 S | ||||||||
| No | 1.000 | |||||||
| Yes | 1.950(1.249–3.044) | 0.003 | ||||||
| Scr > 104 μmol/L | ||||||||
| No | 1.000 | |||||||
| Yes | 1.383(0.388–4.933) | 0.090 | ||||||
| WHO clinical stage III–IV | ||||||||
| No | 1.000 | |||||||
| Yes | 0.440(0.172–1.124) | 0.078 | ||||||
| CD4 < 200/µL | ||||||||
| No | 1.000 | |||||||
| Yes | 0.222(0.086–0.571) | 0.002 | 0.195(0.075–0.510) | 0.001 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Lu, X.; Sun, C.; Liu, P.; Wen, Y. The Screening of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Virus Infection among HIV-Infected Inpatients and Evaluation of Correlated Characteristics in a General Hospital in Shenyang, Liaoning, China. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6620. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226620
Li C, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Liu S, Wang W, Lu X, Sun C, Liu P, Wen Y. The Screening of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Virus Infection among HIV-Infected Inpatients and Evaluation of Correlated Characteristics in a General Hospital in Shenyang, Liaoning, China. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(22):6620. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226620
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chengbo, Ying Zhou, Yu Wang, Sheng Liu, Wen Wang, Xu Lu, Cuiming Sun, Pei Liu, and Ying Wen. 2022. "The Screening of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Virus Infection among HIV-Infected Inpatients and Evaluation of Correlated Characteristics in a General Hospital in Shenyang, Liaoning, China" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 22: 6620. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226620
APA StyleLi, C., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, S., Wang, W., Lu, X., Sun, C., Liu, P., & Wen, Y. (2022). The Screening of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Virus Infection among HIV-Infected Inpatients and Evaluation of Correlated Characteristics in a General Hospital in Shenyang, Liaoning, China. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(22), 6620. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226620





