Mechanical Thrombectomy in Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: Reports of a Retrospective Single-Center Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Retrieval
- 0: No obvious thrombosis/anatomical variability such as absence or hypoplasia of a sinus;
- 1: Thrombosis without impaired blood flow;
- 2: Thrombosis with impaired blood flow;
- 3: Thrombosis with complete vascular occlusion.
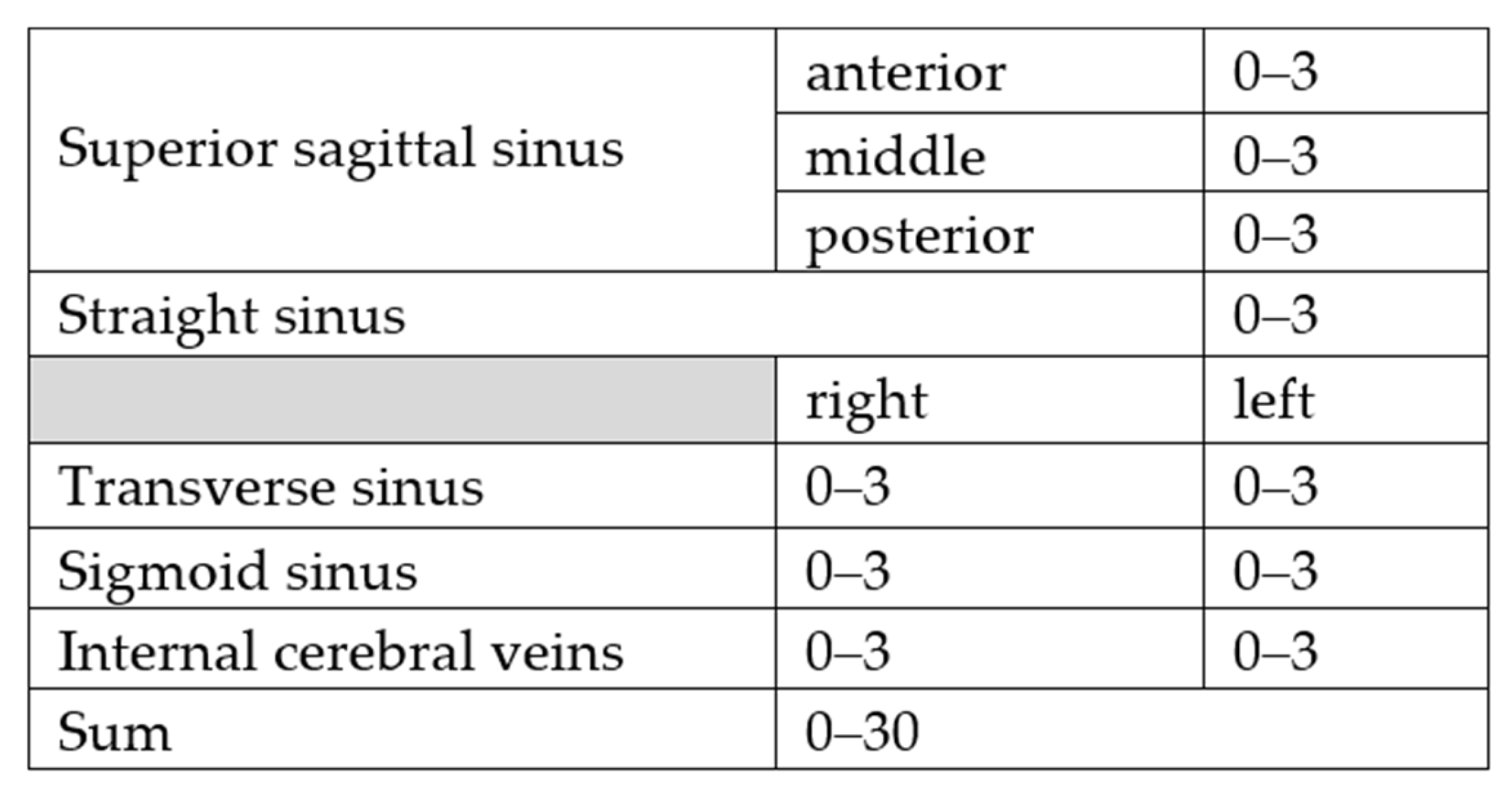
2.2. Statistical Evaluation
2.3. Venous Mechanical Thrombectomy
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coutinho, J.M.; Zuurbier, S.M.; Aramideh, M.; Stam, J. The incidence of cerebral venous thrombosis: A cross-sectional study. Stroke 2012, 43, 3375–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devasagayam, S.; Wyatt, B.; Leyden, J.; Kleinig, T. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis incidence is higher than previously thought: A retrospective population-based study. Stroke 2016, 47, 2180–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, J.M.; Canhão, P.; Stam, J.; Bousser, M.-G.; Barinagarrementeria, F. Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: Results of the international study on cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis (ISCVT). Stroke 2004, 35, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, F.M.; Dandapat, S.; Banerjee, C.; Zuurbier, S.M.; Johnson, M.; Stam, J.; Coutinho, J.M. Mechanical thrombectomy in cerebral venous thrombosis: Systematic review of 185 cases. Stroke 2015, 46, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konakondla, S.; Schirmer, C.M.; Li, F.; Geng, X.; Ding, Y. New developments in the pathophysiology, workup, and diagnosis of dural venous sinus thrombosis (DVST) and a systematic review of endovascular treatments. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salottolo, K.; Wagner, J.; Frei, D.F.; Loy, D.; Bellon, R.J.; McCarthy, K.; Jensen, J.; Fanale, C.; Bar-Or, D. Epidemiology, Endovascular Treatment, and Prognosis of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: US Center Study of 152 Patients. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2017, 6, e005480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arauz, A.; Vargas-González, J.-C.; Arguelles-Morales, N.; A Barboza, M.; Calleja, J.; Martínez-Jurado, E.; Ruiz-Franco, A.; Quiroz-Compean, A.; Merino, J.G. Time to recanalisation in patients with cerebral venous thrombosis under anticoagulation therapy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 87, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, J.M.; Zuurbier, S.M.; Stam, J. Declining mortality in cerebral venous thrombosis: A systematic review. Stroke 2014, 45, 1338–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canhão, P.; Ferro, J.M.; Lindgren, A.G.; Bousser, M.-G.; Stam, J.; Barinagarrementeria, F. Causes and predictors of death in cerebral venous thrombosis. Stroke 2005, 36, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnell, C.; Saposnik, G. Evaluation and management of cerebral venous thrombosis. Continuum 2014, 20, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putaala, J.; Hiltunen, S.; Salonen, O.; Kaste, M.; Tatlisumak, T. Recanalization and its correlation to outcome after cerebral venous thrombosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 292, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einhäupl, K.; Stam, J.; Bousser, M.G.; De Bruijn SF, T.M.; Ferro, J.M.; Martinelli, I.; Masuhr, F. EFNS guideline on the treatment of cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis in adult patients. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, J.M.; Bousser, M.G.; Canhão, P.; Coutinho, J.M.; Crassard, I.; Dentali, F.; di Minno, M.; Maino, A.; Martinelli, I.; Masuhr, F.; et al. European stroke organization guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of cerebral venous thrombosis - endorsed by the European Academy of Neurology. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Mokin, M.; Hetts, S.W.; Fifi, J.T.; Bousser, M.-G.; Fraser, J.F. Current endovascular strategies for cerebral venous thrombosis: Report of the SNIS Standards and Guidelines Committee. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2018, 10, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saposnik, G.; Barinagarrementeria, F.; Brown Jr, R.D.; Bushnell, C.D.; Cucchiara, B.; Cushman, M.; Deveber, G.; Ferro, J.M.; Tsai, F.Y. Diagnosis and management of cerebral venous thrombosis: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2011, 42, 1158–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zeng, X.; Hussain, M.; Meng, R.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, K.; Sikharam, C.; Ding, Y.; Ling, F.; Ji, X. Safety and Validity of Mechanical Thrombectomy and Thrombolysis on Severe Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Neurosurgery 2013, 72, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnaq, S.A.; Qeadan, F.; Thacker, T.; Abbas, M.; Carlson, A.P. High-Risk Features of Delayed Clinical Progression in Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: A Proposed Prediction Score for Early Intervention. Interv. Neurol. 2018, 7, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, J.M.; Zuurbier, S.M.; Bousser, M.G.; Ji, X.; Canhão, P.; Roos, Y.B.; Crassard, I.; Nunes, A.P.; Uyttenboogaart, M.; Chen, J.; et al. Effect of endovascular treatment with medical management vs standard care on severe cerebral venous thrombosis: The TO-ACT Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, A.B.; Mahmoodi, M.; Edgell, R.C.; Cruz-Flores, S.; Ghanaati, H.; Jamshidi, M.; Zaidat, O.O. Mechanical thrombectomy for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: A comprehensive literature review. Clin. Appl. ThrombHemost. 2014, 20, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, F.M.; Banerjee, C.; Zuurbier, S.M.; Hao, Q.; Ahn, C.; Pride, G.L.; Wasay, M.; Majoie, C.B.; Liebeskind, D.; Johnson, M.; et al. Mechanical thrombectomy versus intrasinus thrombolysis for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: A non-randomized comparison. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2014, 20, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Sang, H.; Dai, Q.; Xu, G. Endovascular treatments for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis. 2015, 40, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokin, M.; Lopes, D.K.; Binning, M.J.; Veznedaroglu, E.; Liebman, K.M.; Arthur, A.; Doss, V.T.; Levy, E.I.; Siddiqui, A.H. Endovascular treatment of cerebral venous thrombosis: Contemporary multicenter experience. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2015, 21, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, A.; Chen, C.-J.; Raper, D.M.; Ding, D.; Buell, T.; Mastorakos, P.; Liu, K.C. Endovascular mechanical thrombectomy for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: A systematic review. J. NeuroInterventional Surg. 2017, 9, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, F.M.; Weber, M.W.; Dandapat, S.; Scaife, S.; Buhnerkempe, M.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; Aksan, N.; Elias, A.; Coutinho, J.M. Endovascular Thrombolysis or Thrombectomy for Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: Study of Nationwide Inpatient Sample 2004-2014. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleau, S.W.; Schmidt, R.; Stevens, S.; Osborn, A.; MacDonald, J.D. Extensive Experience with Dural Sinus Thrombosis. Neurosurgery 2003, 52, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashti, S.R.; Hu, Y.C.; Yao, T.; Fiorella, D.; Mitha, A.P.; Albuquerque, F.C.; McDougall, C.G. Mechanical thrombectomy as first-line treatment for venous sinus thrombosis: Technical considerations and preliminary results using the AngioJet device. J. Neurointerventional Surg. 2013, 5, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shui, S.-F.; Li, T.-F.; Han, X.-W.; Ma, J.; Guo, D. Balloon dilatation and thrombus extraction for the treatment of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Neurol. India 2014, 62, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Shui, S.-F.; Han, X.-W.; Guo, D.; Li, T.-F.; Yan, L. Mechanical thrombectomy with Solitaire AB stents for the treatment of intracranial venous sinus thrombosis. Acta Radiol. 2016, 57, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styczen, H.; Tsogkas, I.; Liman, J.; Maus, V.; Psychogios, M.N. Endovascular Mechanical Thrombectomy for Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: A Single-Center Experience. World Neurosurg. 2019, 127, e1097–e1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungersböck, K.; Heimann, A.; Kempski, O. Cerebral blood flow alterations in a rat model of cerebral sinus thrombosis. Stroke 1993, 24, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Patient | Age | Sex | Presenting Symptoms | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 38 | F | Altered mental status | Unknown |
| 2 | 22 | F | Coma | Trauma |
| 3 | 79 | M | Coma | Trauma |
| 4 | 20 | F | Headache, focal neurological deficits, Seizure | Oral contraceptives |
| 5 | 29 | F | Headache, focal neurological deficits | Factor V Leiden |
| 6 | 21 | M | Coma | Trauma |
| 7 | 9 | M | altered mental status | Urinary tract infection |
| 8 | 49 | M | Headache, focal neurological deficits | Multiple sclerosis |
| 9 | 58 | F | Altered mental status, focal neurological deficits, Seizure | Thrombophilia of unclear cause |
| 10 | 41 | F | Headache, altered mental status, focal neurological deficits | Thrombophilia of unclear cause |
| 11 | 52 | M | Headache, focal neurological deficits | Malignancy |
| 12 | 21 | M | Headache, altered mental status, focal neurological deficits | Malignancy |
| 13 | 50 | M | Headache, focal neurological deficits | Unknown |
| 14 | 14 | M | Headache, altered mental status, focal neurological deficits | Unknown |
| 15 | 22 | F | Headache, altered mental status | Pregnancy |
| 16 | 57 | F | Headache, focal neurological deficits | Factor V Leiden |
| 17 | 55 | F | Headache, altered mental status, focal neurological deficits | Unknown |
| 18 | 33 | F | Headache, focal neurological deficits | Ulcerative colitis, 3 weeks postpartum |
| 19 | 22 | F | Headache * | Oral contraceptives, Prothrombin G20210A |
| 20 | 34 | F | Headache, altered mental status, Seizure | Pregnancy, mutation of Methylene |
| Tetrahydrofolate Reductase |
| Patient | IPH | SDH | SAH | VI | EVD | ICPMD | DHC | Location of CVST | Findings in Follow-Up Imaging after MT till Discharge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | + | + | + | + | - | + | before MT | SigS, SS, TS | no rebleeding, infarction constant |
| 2 | + | + | + | - | - | + | before MT | SigS, TS | increasing epidural bleeding after Craniotomy |
| 3 | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | SigS, TS | increasing IPH and edema |
| 4 | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | SSS, SigS, TS | decreasing edema, no bleeding |
| 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SSS, SigS, SS, TS | no bleeding, no infarction |
| 6 | + | + | + | - | - | + | before MT | SigS, TS | no rebleeding, no infarction |
| 7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SSS, TS | no bleeding, no infarction |
| 8 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | SSS, SigS, TS | no bleeding, no infarction |
| 9 | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | SSS, SigS, SS, TS | no rebleeding, infarction constant |
| 10 | - | - | - | * | + | + | after MT | SSS, SigS, TS | malignant media infarct with bleeding |
| 11 | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | SSS, SigS, TS | no rebleeding, infarct constant |
| 12 | + | - | - | + | - | + | after MT | SSS, SigS, TS | severe rebleeding, increasing edema |
| 13 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SSS, SigS, SS, TS | no bleeding, no infarction |
| 14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SigS, TS | no bleeding, no infarction |
| 15 | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | SSS, SigS, TS | no rebleeding, infarction constant |
| 16 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | SSS, SigS, TS | no rebleeding, no infarction |
| 17 | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | SigS, TS | no rebleeding, infarction constant |
| 18 | + | - | + | + | - | + | - | SSS, SigS, SS, TS, ICV | no rebleeding, infarction constant |
| 19 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | SSS, SigS, SS, TS, ICV | no bleeding, no infarction, |
| 20 | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | SSS, SigS, SS, TS, ICV | no rebleeding, infarction constant |
| Patient | Interval from Clinical Onset | Admission to MT | MT Device | Complication | B *-** | A *-** | Q | mRS at Admission | mRS at Discharge | mRS at 6m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4d | 4d | Penumbra, Solitaire | None | 7-9 | 5-5 | 0.63 | 5 | 4 | 1 |
| 2 | 4d | 4d | Solitaire, Balloon-PTA | increasing epidural bleeding after Craniotomy | 4-4 | 4-4 | 1 | 5 | 6 | died |
| 3 | 1d | 1d | Solitaire | increasing IPH | 5-5 | 4-4 | 0.80 | 5 | 6 | died |
| 4 | 3d | 3d | Solitaire, Balloon-PTA | None | 12-13 | 7-7 | 0.56 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
| 5 | 10d | 1d | Solitaire, Balloon-PTA | None | 16-17 | 10-10 | 0.61 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 6 | 1d | 1d | Solitaire, Balloon-PTA | None | 6-4 | 2-1 | 0.29 | 5 | 1 | 2 |
| 7 | 2d | 2d | Solitaire | access site bleeding in groin area | 13-13 | 7-8 | 0.58 | 3 | 2 | NA |
| 8 | 21d | 7d | Solitaire | None | 16-15 | 0.84 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 9 | 0d | 0d | Solitaire | None | 13-11 | 0.58 | 5 | 1 | 0 | |
| 10 | 2d | 2d | Solitaire | malignant media infarction with bleeding | 9-11 | 7-8 | 0.75 | 5 | 6 | died |
| 11 | 1d | 1d | Catch Maxi | None | 10-9 | 6-5 | 0.58 | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| 12 | 11d | 1d | Catch Maxi | None | 12-11 | 12-11 | 1 | 5 | 6 | died |
| 13 | 0d | 0d | Fargo + Catch Maxi | None | 20-15 | 11-11 | 0.64 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
| 14 | 0d | 0d | Solitaire | None | 6-6 | 6-6 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| 15 | 0d | 0d | Catch Maxi, Sofia Plus | None | 18-18 | 9-9 | 0.50 | 4 | 1 | NA |
| 16 | 6d | 1d | Catch Maxi, Sofia Plus | None | 15-16 | 9-8 | 0.55 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| 17 | 2d | 1d | Solitaire, Sofia Plus | None | 6-6 | 4-3 | 0.58 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| 18a | 1d | 0d | Catch Maxi, Sofia Plus | None | 24-23 | 12-18 | 0.83 | 3 | 5 | see 18b |
| 18b | 7d | 6d | Catch Maxi, Sofia Plus | None | 17-16 | 14-12 | 0.79 | 5 | 4 | 2 |
| 19 | 2d | 0d | Sofia Plus | None | 16-16 | 10-11 | 0.66 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 20 | 6d | 0d | Catch Maxi, Sofia Plus | None | 26-26 | 22-22 | 0.85 | 5 | 1 | NA |
| Study | N (Follow-Up)/Interventions | MT Method | At Least Partial Recanalization | Good Outcome (mRS 0–2) | Complications | Mortality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soleau et al. [25] | 8/8 | B | 6 (75%) | 4 (50%) | 2 | 1 |
| Dashti et al. [26] | 13 (9)/13 | AngioJet | 13 (100%) | 7 (53.8%) | NA | 2 |
| Shui et al. [27] | 26/26 | B | 26 (100%) | 26 * (100%) | 0 | 0 |
| Ma et al. [28] | 23/23 | S | 23 (100%) | 22 (95.6%) | 0 | 0 |
| Styczen et al. [29] | 13/14 | A/A+S | 13 (92%) | 12 (85.7%) | 3 | 1 |
| this study | 20/21 | BP+S/A/S/A+S | 18 (85.7%) | 17 (80.9%) | 1 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jedi, F.; Dethlefs, G.; Hauser, T.-K.; Hennersdorf, F.; Mengel, A.; Ernemann, U.; Bender, B. Mechanical Thrombectomy in Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: Reports of a Retrospective Single-Center Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216381
Jedi F, Dethlefs G, Hauser T-K, Hennersdorf F, Mengel A, Ernemann U, Bender B. Mechanical Thrombectomy in Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: Reports of a Retrospective Single-Center Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(21):6381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216381
Chicago/Turabian StyleJedi, Farzaneh, Gero Dethlefs, Till-Karsten Hauser, Florian Hennersdorf, Annerose Mengel, Ulrike Ernemann, and Benjamin Bender. 2022. "Mechanical Thrombectomy in Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: Reports of a Retrospective Single-Center Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 21: 6381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216381
APA StyleJedi, F., Dethlefs, G., Hauser, T.-K., Hennersdorf, F., Mengel, A., Ernemann, U., & Bender, B. (2022). Mechanical Thrombectomy in Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: Reports of a Retrospective Single-Center Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(21), 6381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216381






