Polymorphic Variants of the PDGFRB Gene Influence Efficacy of PRP Therapy in Treating Tennis Elbow: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
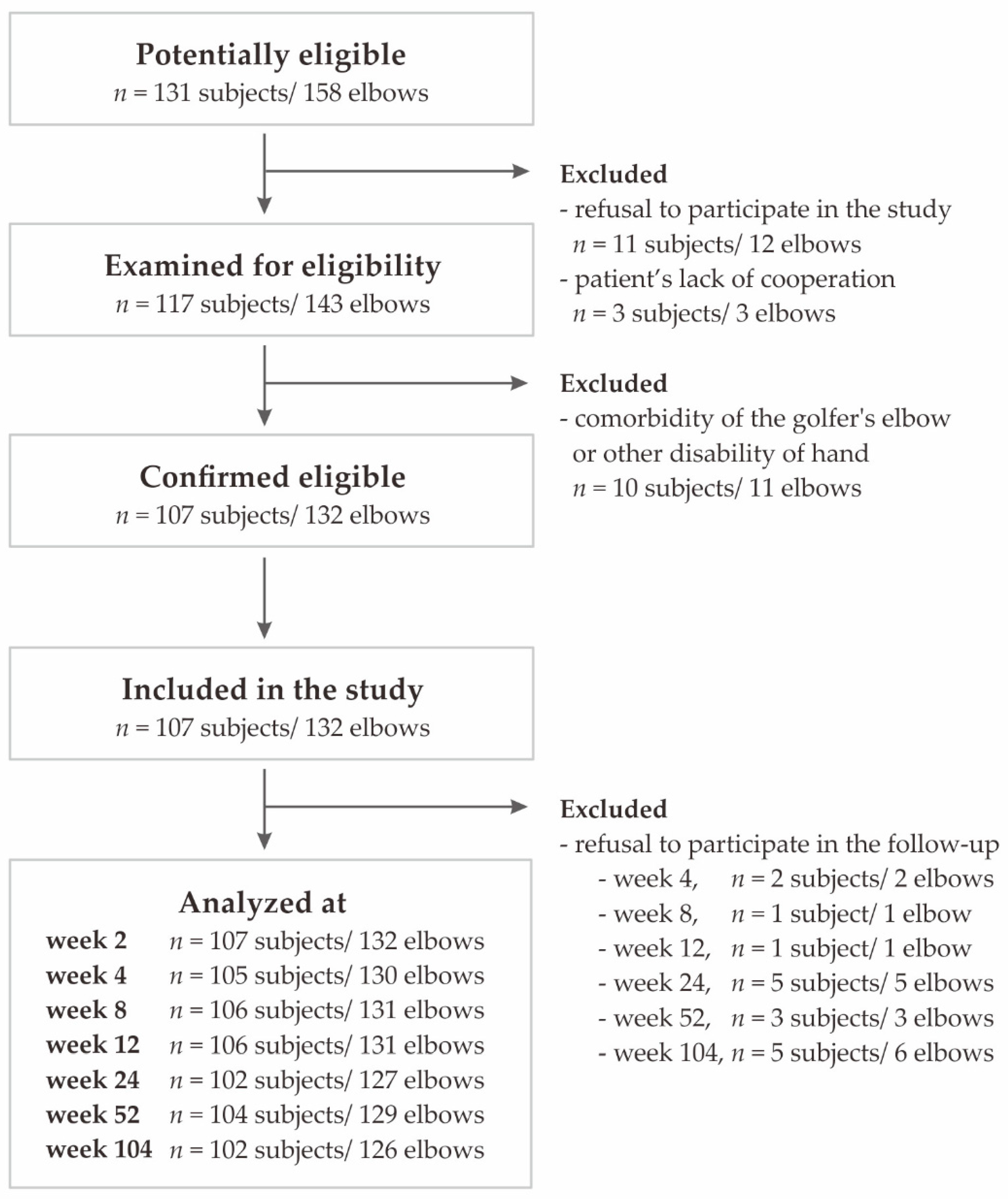
2.1. Patients
2.2. PRP Separation, Injection Procedure, Whole Blood, and PRP Parameters
2.3. Follow-Up, Outcomes, Measures of Effectiveness
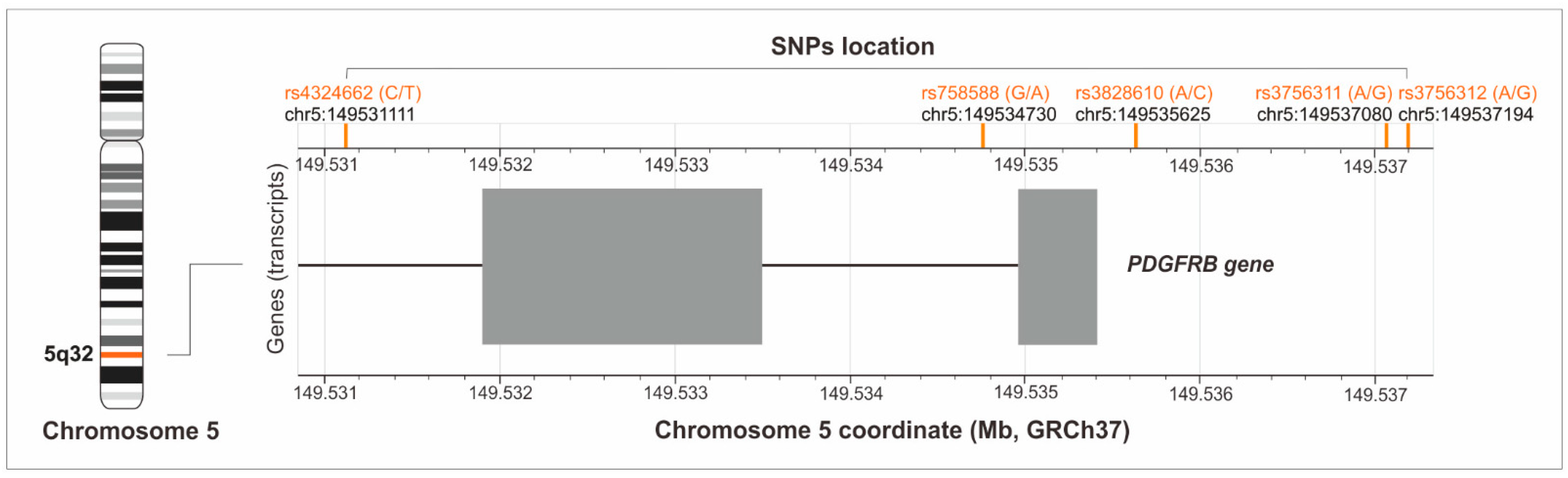
2.4. Genetic Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Study Group
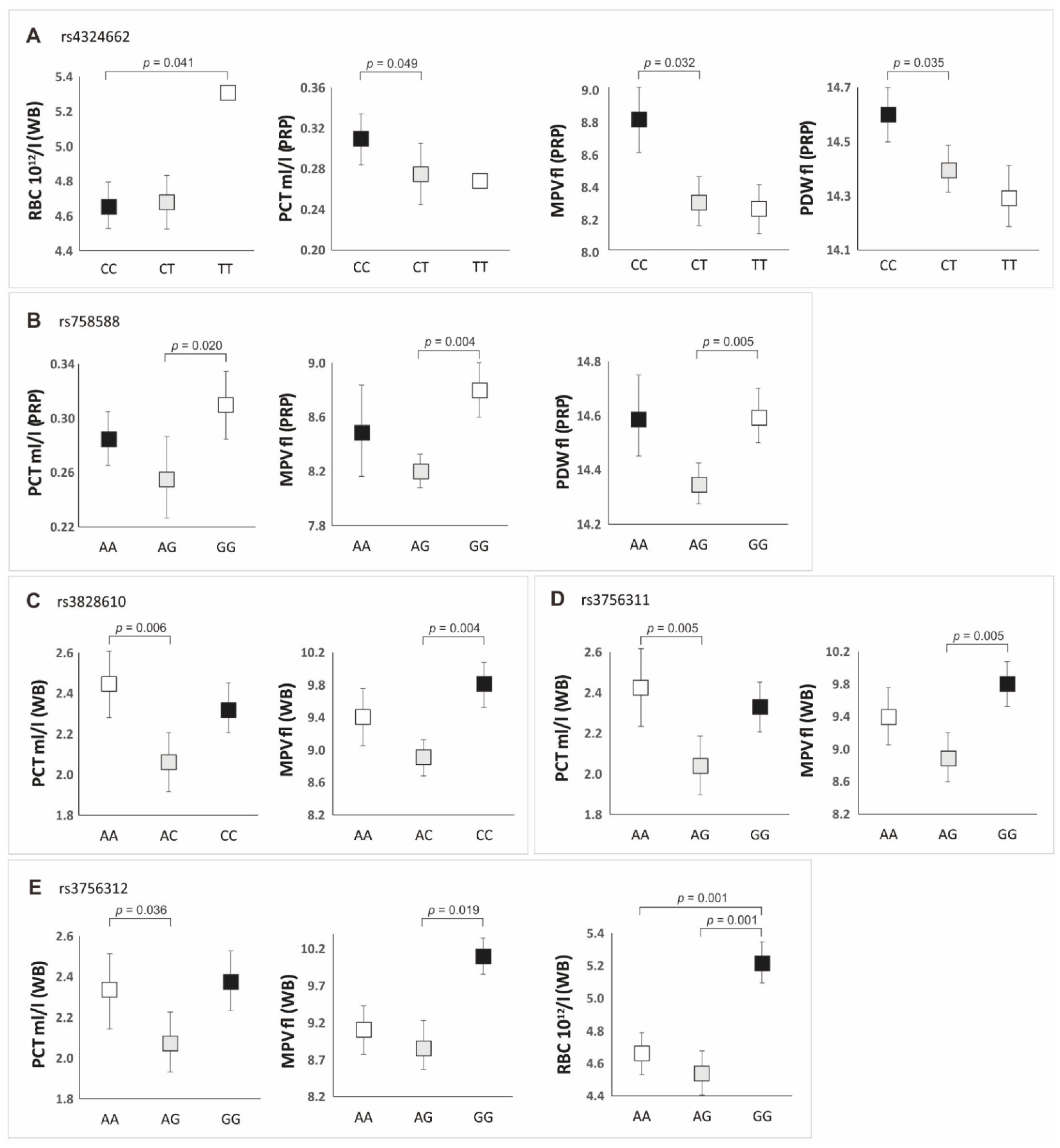
3.2. Analysis of the PDGFRB Gene Polymorphisms
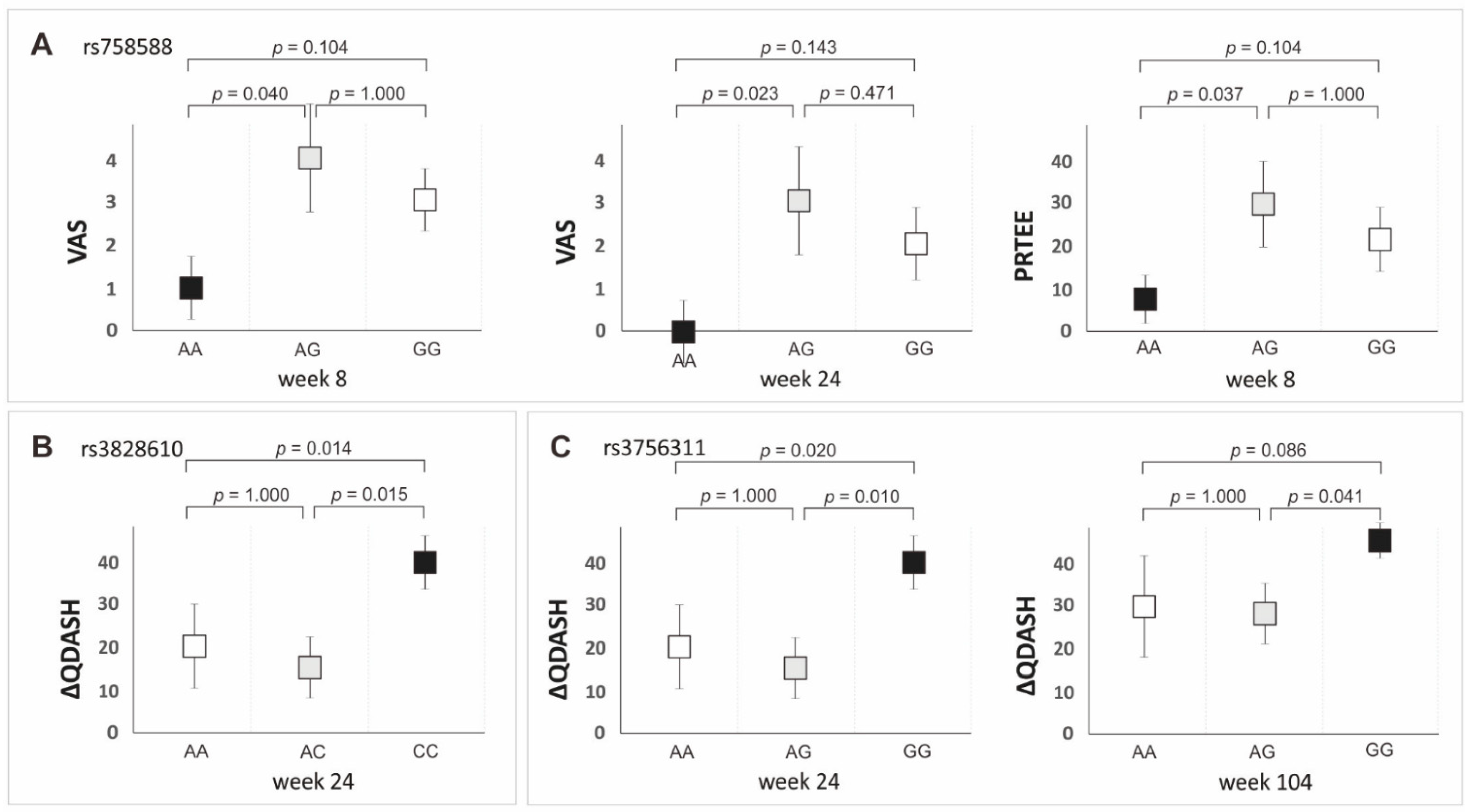
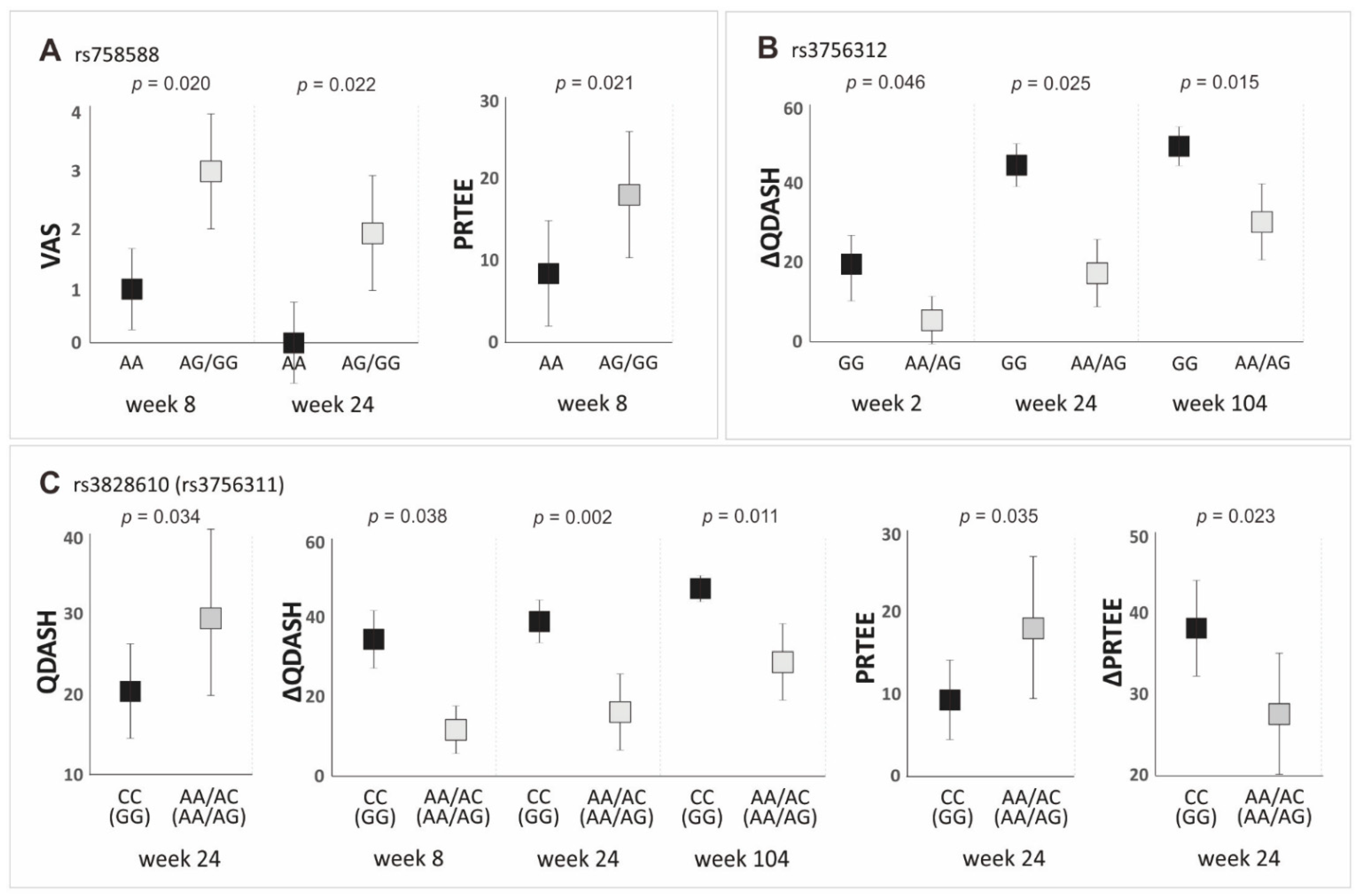
3.3. Polymorphisms of the PDGFRB Gene and Clinical Phenotype
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johns, N.; Shridhar, V. Lateral epicondylitis: Current concepts. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2020, 49, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Jones, I.A.; Park, C.; Vangsness, C.T., Jr. The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Tendon and Ligament Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis With Bias Assessment. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 2020–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemiec, P.; Szyluk, K.; Jarosz, A.; Iwanicki, T.; Balcerzyk, A. Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Lateral Epicondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Based on Achievement of Minimal Clinically Important Difference. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2022, 10, 23259671221086920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, P.; Wu, P.; Yang, J.; Du, Z.; Liu, S.; Wei, F. Platelet-Rich Plasma Vs Autologous Blood Vs Corticosteroid Injections in the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis: A Systematic Review, Pairwise and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PM R 2020, 12, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houck, D.A.; Kraeutler, M.J.; Thornton, L.B.; McCarty, E.C.; Bravman, J.T. Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis With Autologous Blood, Platelet-Rich Plasma, or Corticosteroid Injections: A Systematic Review of Overlapping Meta-analyses. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2019, 7, 2325967119831052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, J.; Cheng, L. Comparison of platelet-rich plasma and corticosteroids in the management of lateral epicondylitis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Surg. 2019, 67, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, T.; Richards, B.; Buchbinder, R. Platelet-rich plasma injection for tennis elbow: Did it ever work? BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2022, 8, e001258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, S.; Patel, S.; Gobbur, A.; Patil, S.C.; Ks, K.H.; Yadav, V.; Jeyaraman, M. Platelet-rich plasma therapy ensures pain reduction in the management of lateral epicondylitis—A PRISMA-compliant network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2022, 22, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruna, R.; Til, L.; Artells, R. Could single nucleotide polymorphisms influence on the efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of sports injuries? Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014, 4, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz, A.; Szyluk, K.; Iwanicka, J.; Balcerzyk, A.; Nowak, T.; Iwanicki, T.; Negru, M.; Kalita, M.; Francuz, T.; Garczorz, W.; et al. What Role Does PDGFA Gene Polymorphisms Play in Treating Tennis Elbow with PRP? A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiec, P.; Szyluk, K.; Balcerzyk, A.; Kalita, M.; Jarosz, A.; Iwanicka, J.; Iwanicki, T.; Nowak, T.; Negru, M.; Francuz, T.; et al. Why PRP works only on certain patients with tennis elbow? Is the PDGFB gene a key for PRP therapy effectiveness? A prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldin, C.; Lennartsson, J. Structural and Functional Properties of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor and Stem Cell Factor Receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a009100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Library of Medicine (US): National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/ (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Machiela, M.J.; Chanock, S.J. LDlink: A web-based application for exploring population-specific haplotype structure and linking correlated alleles of possible functional variants. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3555–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, S.B.; Schaffner, S.F.; Nguyen, H.; Moore, J.M.; Roy, J.; Blumenstiel, B.; Higgins, J.; DeFelice, M.; Lochner, A.; Faggart, M.; et al. The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science 2002, 296, 2225–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keeffe, A.G.; Ambler, G.; Barber, J.A. Sample size calculations based on a difference in medians for positively skewed outcomes in health care studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2017, 17, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salini, V.; Vanni, D.; Pantalone, A.; Abate, M. Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy in Non-insertional Achilles Tendinopathy: The Efficacy is Reduced in 60-years Old People Compared to Young and Middle-Age Individuals. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Lingampalli, N.; Koltsov, J.C.B.; Leung, L.L.; Bhutani, N.; Robinson, W.H.; Chu, C.R. Men and Women Differ in the Biochemical Composition of Platelet-Rich Plasma. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, A.M.; Dirckx, N.; Tower, R.J.; Peredo, N.; Vanuytven, S.; Theunis, K.; Nefyodova, E.; Cardoen, R.; Lindner, V.; Voet, T.; et al. Activation of Skeletal Stem and Progenitor Cells for bone regeneration is driven by PDGFRβ signaling. Dev. Cell 2019, 51, 236–254.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Choe, B.; Kim, J.W.; Park, J.K.; Cho, A.; Bae, H.; Shin, D.; Yim, S.V.; Kwack, K.; et al. Ge-netic association between 5′-upstream single-nucleotide polymorphisms of PDGFRB and schizophrenia in a Korean population. Schizophr. Res. 2008, 103, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparyan, A.Y.; Ayvazyan, L.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Kitas, G.D. Mean platelet volume: A link between thrombosis and inflammation? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparyan, A.Y.; Samdoo, A.; Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou, A.; Kitas, G.D. Mean platelet volume in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: The effect of anti-TNF-alpha therapy. Rheumatol. Int. 2010, 30, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korniluk, A.; Koper-Lenkiewicz, O.M.; Kamińska, J.; Kemona, H.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V. Mean Platelet Volume (MPV): New Perspectives for an Old Marker in the Course and Prognosis of Inflammatory Conditions. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 9213074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braekkan, S.K.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Njølstad, I.; Wilsgaard, T.; Størmer, J.; Hansen, J.B. Mean platelet volume is a risk factor for venous thromboembolism: The Tromsø study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 8, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Human Protein Atlas. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000113721-PDGFRB/tissue/ (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Zhao, G.Z.; Zhang, L.Q.; Liu, Y.; Fang, J.; Li, H.Z.; Gao, K.H.; Chen, Y.Z. Effects of platelet-derived growth factor on chondrocyte proliferation, migration and apoptosis via regulation of GIT1 expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| General | number of subjects, N | 107 | - |
| number of elbows, n (%) | 132 | (100.0) | |
| tennis elbow in the dominant hand, n (%) | 86 | (65.2) | |
| tennis elbow in the non-dominant hand, n (%) | 46 | (34.8) | |
| females, n (%) | 77 | (58.3) | |
| age, median ± QD | 46.00 | 5.50 | |
| BMI, median ± QD | 25.65 | 2.00 | |
| overweight/obesity, BMI ≥ 25, n (%) | 86 | (65.2) | |
| current smokers, n (%) | 22 | (16.6) | |
| former smokers, n (%) | 48 | (36.4) | |
| Comorbidities | diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 4 | (3.0) |
| gout, n (%) | 8 | (6.1) | |
| thyroid diseases, n (%) | 15 | (11.4) | |
| hypercholesterolemia, n (%) | 7 | (5.3) | |
| hypertension, n (%) | 18 | (13.6) | |
| heart failure, n (%) | 4 | (3.0) | |
| Whole Blood | PLT 109/L, median ± QD | 240.00 | 40.50 |
| parameters | PCT mL/L, median ± QD | 2.31 | 0.36 |
| MPV fl, median ± QD | 9.10 | 0.73 | |
| PDW fl, median ± QD | 16.10 | 0.15 | |
| WBC 109/L, median ± QD | 6.26 | 1.16 | |
| RBC 1012/L, median ± QD | 4.66 | 0.29 | |
| PRP parameters | PLT 109/L, median ± QD | 343.00 | 65.00 |
| PCT ml/L, median ± QD | 0.30 | 0.06 | |
| MPV fl, median ± QD | 8.60 | 0.40 | |
| PDW fl, median ± QD | 14.60 | 0.25 |
| SNP | Genotypes | n (%) | Alleles | n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs4324662 | CC | 88 (66.7) | C | 216 (81.8) |
| CT | 40 (30.3) | T | 48 (18.2) | |
| TT | 4 (3.0) | |||
| CC + CT | 128 (96.9) | |||
| TT + CT | 44 (33.3) | |||
| rs758588 | AA | 11 (8.3) | A | 56 (21.2) |
| AG | 34 (25.8) | G | 208 (78.8) | |
| GG | 87 (65.9) | |||
| AA + AG | 45 (34.1) | |||
| AG + GG | 121 (91.7) | |||
| rs3828610 | AA | 56 (42.4) | A | 163 (61.7) |
| AC | 51 (38.6) | C | 101 (38.3) | |
| CC | 25 (18.9) | |||
| AA + AC | 107 (81.1) | |||
| CC + AC | 76 (57.6) | |||
| rs3756311 | AA | 55 (41.7) | A | 162 (61.4) |
| AG | 52 (39.4) | G | 102 (38.6) | |
| GG | 25 (18.9) | |||
| AA + AG | 107 (81.1) | |||
| GG + AG | 77 (58.3) | |||
| rs3756312 | AA | 64 (48.5) | A | 180 (68.2) |
| AG | 52 (39.4) | G | 84 (31.8) | |
| GG | 16 (12.1) | |||
| AA + AG | 116 (87.9) | |||
| GG + AG | 68 (51.5) |
| Rs Number | Parameter (Source) | Median | ±QD | Median | ±QD | p Mann–Whitney U Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs4324662 | CC | CT/CT | ||||
| PLT 109/L (PRP) | 353.00 | 70.50 | 327.00 | 59.75 | 0.024 | |
| PCT mL/L (PRP) | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 0.009 | |
| MPV fl (PRP) | 8.80 | 0.40 | 8.30 | 0.32 | 0.006 | |
| PDW fl (PRP) | 14.60 | 0.20 | 14.40 | 0.18 | 0.005 | |
| rs3828610 | CC | AA/AC | ||||
| MPV fl (WB) | 9.80 | 0.55 | 9.00 | 0.70 | 0.003 | |
| RBC 1012/L (WB) | 4.96 | 0.33 | 4.66 | 0.25 | 0.024 | |
| rs3756311 | GG | AA/AG | ||||
| MPV fl (WB) | 9.80 | 0.55 | 9.00 | 0.70 | 0.003 | |
| RBC 1012/L (WB) | 4.96 | 0.33 | 4.66 | 0.25 | 0.024 | |
| rs3756312 | GG | AA/AG | ||||
| MPV fl (WB) | 10.10 | 0.50 | 9.00 | 0.70 | 0.005 | |
| RBC 1012/L (WB) | 5.22 | 0.26 | 4.65 | 0.26 | 0.000 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szyluk, K.; Jarosz, A.; Balcerzyk-Matić, A.; Iwanicka, J.; Iwanicki, T.; Nowak, T.; Gierek, M.; Negru, M.; Kalita, M.; Górczyńska-Kosiorz, S.; et al. Polymorphic Variants of the PDGFRB Gene Influence Efficacy of PRP Therapy in Treating Tennis Elbow: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6362. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216362
Szyluk K, Jarosz A, Balcerzyk-Matić A, Iwanicka J, Iwanicki T, Nowak T, Gierek M, Negru M, Kalita M, Górczyńska-Kosiorz S, et al. Polymorphic Variants of the PDGFRB Gene Influence Efficacy of PRP Therapy in Treating Tennis Elbow: A Prospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(21):6362. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216362
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzyluk, Karol, Alicja Jarosz, Anna Balcerzyk-Matić, Joanna Iwanicka, Tomasz Iwanicki, Tomasz Nowak, Marcin Gierek, Marius Negru, Marcin Kalita, Sylwia Górczyńska-Kosiorz, and et al. 2022. "Polymorphic Variants of the PDGFRB Gene Influence Efficacy of PRP Therapy in Treating Tennis Elbow: A Prospective Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 21: 6362. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216362
APA StyleSzyluk, K., Jarosz, A., Balcerzyk-Matić, A., Iwanicka, J., Iwanicki, T., Nowak, T., Gierek, M., Negru, M., Kalita, M., Górczyńska-Kosiorz, S., Kania, W., & Niemiec, P. (2022). Polymorphic Variants of the PDGFRB Gene Influence Efficacy of PRP Therapy in Treating Tennis Elbow: A Prospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(21), 6362. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216362









