Clinical Implication of Serum Adiponectin Levels in Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Enrollment of Study Subjects
2.2. Clinical and Laboratory Data Collection
2.3. Treatment of Severe AD Patients
2.4. Measurement of Serum Adiponectin Levels
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Study Subjects
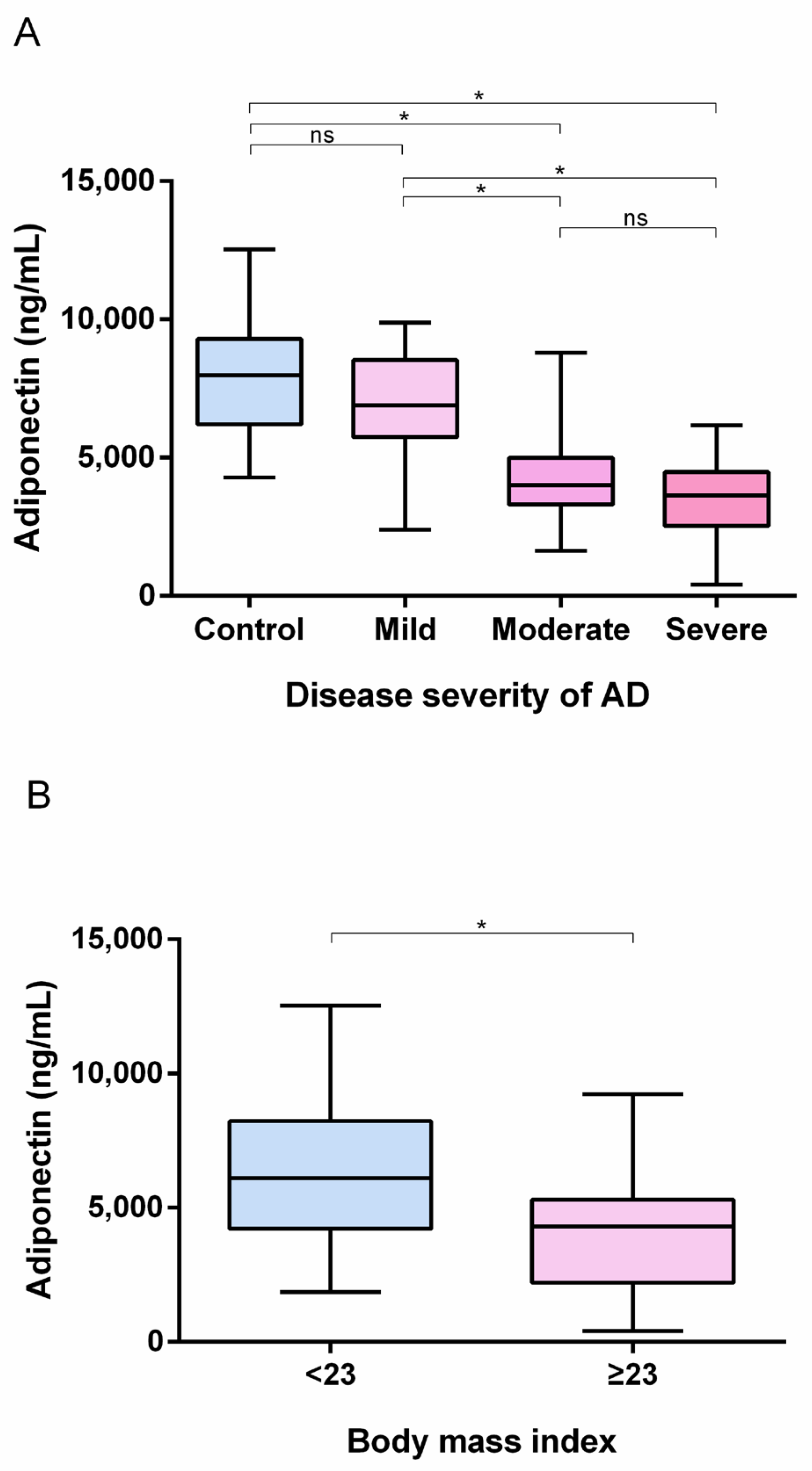
3.2. Serum Adiponectin Levels Were Lower in the AD and High BMI Groups
3.3. Association of Serum Adiponectin Levels with Various AD Patient Data
3.4. Changes in Serum Adiponectin Levels According to AD Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahn, J.; Choi, Y.; Simpson, E.L. Therapeutic new era for atopic dermatitis: Part 1. Biologics. Ann. Dermatol. 2021, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miniotti, M.; Lazzarin, G.; Ortoncelli, M.; Mastorino, L.; Ribero, S.; Leombruni, P. Impact on health-related quality of life and symptoms of anxiety and depression after 32 weeks of Dupilumab treatment for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, A.J.; Kaulback, K.; Chamlin, S.L. The socioeconomic impact of atopic dermatitis in the United States: A systematic review. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2008, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edslev, S.M.; Agner, T.; Andersen, P.S. Skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chang, C.; Lu, Q. The genetics and epigenetics of atopic dermatitis-filaggrin and other polymorphisms. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 51, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.E.; Park, G.H.; Bae, J.M.; Byun, J.Y.; Shin, M.K.; Han, T.Y.; Hong, S.P.; Jang, Y.H.; Kim, H.O.; et al. Consensus update for systemic treatment of atopic dermatitis. Ann. Dermatol. 2021, 33, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastorino, L.; Viola, R.; Panzone, M.; Avallone, G.; Gallo, G.; Ortoncelli, M.; Cavaliere, G.; Quaglino, P.; Ribero, S. Dupilumab induces a rapid decrease of pruritus in adolescents: A pilot real-life study. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastorino, L.; Rosset, F.; Gelato, F.; Ortoncelli, M.; Cavaliere, G.; Quaglino, P.; Ribero, S. Chronic Pruritus in Atopic Patients Treated with Dupilumab: Real Life Response and Related Parameters in 354 Patients. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renert-Yuval, Y.; Thyssen, J.P.; Bissonnette, R.; Bieber, T.; Kabashima, K.; Hijnen, D.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Biomarkers in atopic dermatitis-a review on behalf of the International Eczema Council. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1174–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, A.; Jaworski, J.C.; Simpson, E.L.; Boguniewicz, M.; Russell, J.J.; Block, J.K.; Tofte, S.; Dunn, J.D.; Feldman, S.R.; Clark, A.R.; et al. Major comorbidities of atopic dermatitis: Beyond allergic disorders. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Ulrik, C.S.; Agner, T.; Thomsen, S.F. Association between atopic dermatitis and the metabolic syndrome: A systematic review. Dermatology 2018, 234, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Cortegana, C.; Ortiz-García, G.; Serrano, A.; Moreno-Ramírez, D.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Possible role of leptin in atopic dermatitis: A literature review. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, D.; Fazekas, F.; Oláh, A.; Törőcsik, D. Adipokines in the skin and in dermatological diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, J.M.; Rajka, G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1980, 92, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, M.H.; Lee, W.Y.; Kim, S.S.; Kang, J.H.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, B.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, E.M.; et al. 2018 Korean society for the study of obesity guideline for the management of obesity in Korea. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 28, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Shin, M.K.; Park, G.H.; Lee, U.H.; Lee, J.H.; Han, T.Y.; Koh, H.C.; Jang, Y.H.; Kim, H.O.; Na, C.H.; et al. 2019 Consensus Korean diagnostic guidelines to define severity classification and treatment refractoriness for atopic dermatitis: Objective and subjective assessment of severity. Ann. Dermatol. 2019, 31, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnowicki, T.; He, H.; Krueger, J.G.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Atopic dermatitis endotypes and implications for targeted therapeutics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T. Atopic dermatitis: An expanding therapeutic pipeline for a complex disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 21, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, H.A.; Azeem, M.; Jwayed, S.A.; Al-Shehhi, A.; Tabassum, A.; Ayoub, M.A.; Hetta, H.F.; Waheed, Y.; Iratni, R.; Al-Dhaheri, A.; et al. Current insights into immunology and novel therapeutics of atopic dermatitis. Cells 2021, 10, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, M.; Yüksel, M.; Gökbel, H.; Okudan, N.; Mevlitoğlu, I. Serum leptin, adiponectin, resistin and ghrelin levels in psoriatic patients treated with cyclosporin. J. Dermatol. 2012, 39, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.J.; Lim, H.K.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, N.I. Serum leptin and adiponectin levels in Korean patients with psoriasis. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, A.; Flisiak, I.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Świderska, M. Serum adiponectin and leptin levels in psoriatic patients according to topical treatment. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2015, 26, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.J.; Kim, H.R.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, H.O.; Chung, B.Y.; Park, C.W. Effect of weight reduction on treatment outcomes for patients with atopic dermatitis. Ann. Dermatol. 2020, 32, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, S.; Pinter, A.; Biermann, M.; Papavassilis, C.; Reinhardt, M. Adiponectin levels in a large pooled plaque psoriasis study population. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2020, 31, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworek, A.K.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Szafraniec, K.; Jaworek, M.; Hałubiec, P.; Wojas-Pelc, A.; Pokorski, M. Adipokines as biomarkers of atopic dermatitis in adults. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorena, K.; Jachimowicz-Duda, O.; Ślęzak, D.; Robakowska, M.; Mrugacz, M. Adipokines and obesity. Potential link to metabolic disorders and chronic complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unamuno, X.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V. Adipokine dysregulation and adipose tissue inflammation in human obesity. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Judd, R.L. Adiponectin regulation and function. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1031–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.S.; Seong, K.H.; Kim, C.D.; Seo, S.J.; Park, B.C.; Kim, M.H.; Hong, S.P. Adiponectin attenuates the inflammation in atopic dermatitis-like reconstructed human epidermis. Ann. Dermatol. 2019, 31, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wu, W.H.; Bae, J.M.; Son, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Han, T.Y. Serum leptin and adiponectin levels in atopic dermatitis (AD) and their relation to disease severity. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 75, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peters, M.J.; Watt, P.; Cherry, L.; Welsh, P.; Henninger, E.; Dijkmans, B.A.; McInnes, I.B.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Sattar, N. Lack of effect of TNFalpha blockade therapy on circulating adiponectin levels in patients with autoimmune disease: Results from two independent prospective studies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1687–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, S.; Oliveira, H.; Reis, F.; Belo, L.; Rocha, S.; Quintanilha, A.; Figueiredo, A.; Teixeira, F.; Castro, E.; Rocha-Pereira, P.; et al. Circulating adipokine levels in Portuguese patients with psoriasis vulgaris according to body mass index, severity and therapy. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Cerdeira, C.; Cordeiro-Rodríguez, M.; Carnero-Gregorio, M.; López-Barcenas, A.; Martínez-Herrera, E.; Fabbrocini, G.; Sinani, A.; Arenas-Guzmán, R.; González-Cespón, J.L. Biomarkers of Inflammation in Obesity-Psoriatic Patients. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 7353420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendar, J.; Frohberger, S.J.; Karunakaran, I.; Schmitt, V.; Stamminger, W.; Neumann, A.L.; Wilhelm, C.; Hoerauf, A.; Hübner, M.P. Adiponectin Limits IFN-γ and IL-17 Producing CD4 T Cells in Obesity by Restraining Cell Intrinsic Glycolysis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Folco, E.J.; Shimizu, K.; Libby, P. Adiponectin induces pro-inflammatory programs in human macrophages and CD4+ T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36896–36904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekaria, A.S.; Brunner, P.M.; Aleisa, A.I.; Bonomo, L.; Lebwohl, M.G.; Israel, A.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis patients show increases in serum C-reactive protein levels, correlating with skin disease activity. F1000Research 2017, 6, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kägi, M.K.; Joller-Jemelka, H.; Wüthrich, B. Correlation of eosinophils, eosinophil cationic protein and soluble interleukin-2 receptor with the clinical activity of atopic dermatitis. Dermatology 1992, 185, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishima, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Takekuma, K.; Hoshika, A. Changes in serum lactate dehydrogenase activity in children with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Int. Off. J. Jpn. Pediatr. Soc. 2010, 52, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.; Lee, K.S.; Ha, E.G.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, M.A.; Lee, S.W.; Jee, H.M.; Sheen, Y.H.; Jung, Y.H.; Han, M.Y. An association of periostin levels with the severity and chronicity of atopic dermatitis in children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 28, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Park, K.Y.; Seo, S.J. Adiponectin upregulates filaggrin expression via SIRT1-mediated signaling in human normal keratinocytes. Ann. Dermatol. 2017, 29, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Characteristic | Control (n = 28) | Atopic Dermatitis | p Value * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild (n = 25) | Moderate (n = 22) | Severe (n = 28) | |||
| Age | 28.93 ± 5.40 | 27.77 ± 6.45 | 24.45 ± 7.23 | 25.66 ± 6.58 | NS |
| Male | 15 (53.5) | 14 (56.0) | 12 (54.5) | 15 (53.5) | NS |
| Disease duration (year) | - | 11.39 ± 4.51 | 15.08 ± 5.87 | 14.85 ± 6.42 | NS |
| Allergic disorders | |||||
| Rhinitis | 0 | 16 (64) | 15 (68.2) | 20 (71.4) | <0.001 |
| Conjunctivitis | 0 | 6 (24) | 8 (36.4) | 17 (60.7) | <0.001 |
| Asthma | 0 | 1 (4) | 3 (13.6) | 6 (21.4) | <0.001 |
| Total IgE (IU/mL) | 69.2 ± 124.4 | 420.7 ± 279.8 | 825.5 ± 624.1 | 1140.1 ± 950.6 | <0.001 |
| Blood eosinophils count (%) | 2.45 ± 1.79 | 5.81 ± 2.09 | 7.55 ± 2.72 | 7.40 ± 2.21 | NS |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 173.5 ± 37.75 | 169.45 ± 29.87 | 179.26 ± 36.74 | 183.74 ± 39.88 | NS |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 121.53 ± 25.64 | 122.02 ± 21.55 | 130.57 ± 28.63 | 133.24 ± 30.26 | NS |
| Body mass index | 21.53 ± 1.80 | 21.68 ± 2.12 | 21.82 ± 1.91 | 22.19 ± 2.13 | NS |
| <23 | 24 (85.7) | 20 (80) | 17 (77.3) | 16 (57.1) | |
| ≥23, <25 | 3 (10.7) | 4 (16) | 4 (18.2) | 10 (35.7) | |
| ≥25 | 1 (3.5) | 1 (4) | 1 (4.5) | 2 (7.1) | |
| EASI score | - | 7.23 ± 2.82 | 18.15 ± 1.87 | 28.96 ± 4.88 | <0.001 |
| IGA scale | - | 1.24 ± 0.44 | 3.23 ± 0.43 | 4.21 ± 0.42 | <0.001 |
| Pruritus NRS | - | 2.68 ± 1.11 | 5.23 ± 1.11 | 6.68 ± 1.36 | <0.001 |
| Value | EASI | IGA | Pruritus_NRS | BMI | Total IgE | EOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EASI | ||||||
| Coefficient of correlation | 1 | 0.944 ** | 0.698 ** | 0.077 | 0.455 ** | 0.263 * |
| p value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.512 | 0.000 | 0.023 | |
| N | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| IGA | ||||||
| Coefficient of correlation | 0.944 ** | 1 | 0.770 ** | 0.054 | 0.459 ** | 0.295 * |
| p value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.644 | 0.000 | 0.010 | |
| N | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| Pruritus NRS | ||||||
| Coefficient of correlation | 0.698 ** | 0.770 ** | 1 | −0.024 | 0.233 * | 0.286 * |
| p value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.840 | 0.044 | 0.013 | |
| N | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| BMI | ||||||
| Coefficient of correlation | 0.077 | 0.054 | −0.024 | 1 | 0.048 | −0.036 |
| p value | 0.512 | 0.644 | 0.840 | 0.684 | 0.757 | |
| N | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| Total IgE | ||||||
| Coefficient of correlation | 0.455 ** | 0.459 ** | 0.233 * | 0.048 | 1 | 0.210 |
| p value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.044 | 0.684 | 0.070 | |
| N | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| EOS | ||||||
| Coefficient of correlation | 0.263 * | 0.295 * | 0.286 * | −0.036 | 0.210 | 1 |
| p value | 0.023 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.757 | 0.070 | |
| N | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| Value | Baseline | Week 16 | Week 52 | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EASI score | 28.96 ± 4.88 | 4.01 ± 1.83 | 2.63 ±1.72 | <0.001 |
| IGA scale | 4.21 ± 0.42 | 1.43 ± 0.50 | 1.07 ± 0.60 | <0.001 |
| Pruritus NRS | 6.68 ± 1.36 | 3.45 ± 1.02 | 2.01 ± 1.12 | <0.001 |
| Body mass index | 22.19 ± 2.13 | 22.43 ± 2.12 | 21.58 ± 2.11 | NS |
| Adiponectin (ng/mL) | 3524 ± 1370 | 3382 ± 1355 | 3778 ± 1600 | NS |
| Total IgE (IU/mL) | 1140.1 ± 950.6 | 1084 ± 937.6 | 1010 ± 895.8 | <0.05 |
| Blood eosinophils count (%) | 7.40 ± 2.21 | 7.29 ± 2.18 | 7.35 ± 2.54 | NS |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 183.74 ± 39.88 | 188.45 ± 41.69 | 179.22 ± 36.41 | NS |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 133.24 ± 30.26 | 137.15 ± 30.85 | 127.49 ± 29.22 | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-H.; Bae, Y.; Park, Y.-L. Clinical Implication of Serum Adiponectin Levels in Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6255. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216255
Lee S-H, Bae Y, Park Y-L. Clinical Implication of Serum Adiponectin Levels in Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(21):6255. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216255
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sul-Hee, Youin Bae, and Young-Lip Park. 2022. "Clinical Implication of Serum Adiponectin Levels in Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 21: 6255. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216255
APA StyleLee, S.-H., Bae, Y., & Park, Y.-L. (2022). Clinical Implication of Serum Adiponectin Levels in Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(21), 6255. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216255





