Impact of Dexamethasone and Inhaled Nitric Oxide on Severe Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19
Abstract
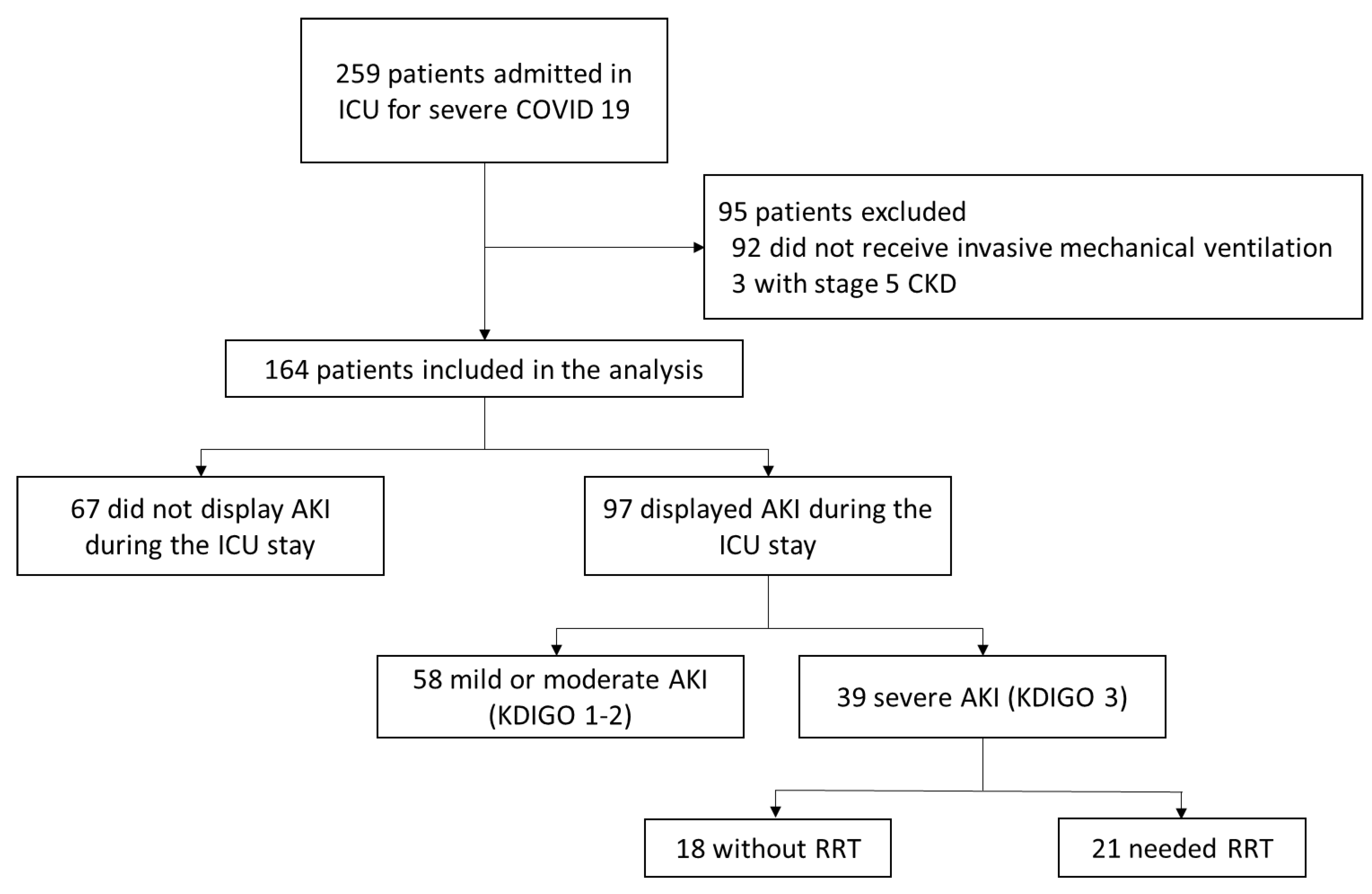
1. Background
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| ACEI | Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors |
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| ARB | Angiotensin Receptor Blockers |
| ARDS | Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
| iNO | Inhaled Nitric Oxide |
| MV | Mechanical Ventilation |
| NSAID | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs |
| PEEP | Positive End-Expiratory Pressure |
| RRT | Renal Replacement Therapy |
| VV-ECMO | Extra-Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation |
References
- Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Shu, H.; Xia, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Fang, M.; et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarre, P.; Dumas, G.; Dupont, T.; Darmon, M.; Azoulay, E.; Zafrani, L. Acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Yu, C.; Ma, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; Yao, Y.; et al. Renal Involvement and Early Prognosis in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burtey, S.; Sallée, M. Kidney damage in COVID-19. Nephrol. Ther. 2021, 17, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlicot, S.; Jamme, M.; Gaillard, F.; Oniszczuk, J.; Couturier, A.; May, O.; Grünenwald, A.; Sannier, A.; Moktefi, A.; Le Monnier, O.; et al. The spectrum of kidney biopsies in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, acute kidney injury, and/or proteinuria. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2021, 36, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.; Marsh, S. Steroid use in critical care. BJA Educ. 2018, 18, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Recovery Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volff, M.; Tonon, D.; Bommel, Y.; Peres, N.; Lagier, D.; Agard, G.; Jacquier, A.; Bartoli, A.; Carvelli, J.; Max, H.; et al. Factors Associated with 90-Day Mortality in Invasively Ventilated Patients with COVID-19 in Marseille, France. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ARDS Definition Task Force; Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar]
- Kdigo Aki Working Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Husain-Syed, F.; Slutsky, A.S.; Ronco, C. Lung-Kidney Cross-Talk in the Critically Ill Patient. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostermann, M.; Chang, R. Riyadh ICU Program Users Group Correlation between the AKI classification and outcome. Crit. Care Lond. Engl. 2008, 12, R144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, S.-Y.; Huang, T.-M.; Wu, H.-Y.; Wu, H.-D.; Yu, C.-J.; Lai, M.-S. Inhaled nitric oxide therapy and risk of renal dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebistorf, F.; Karam, O.; Wetterslev, J.; Afshari, A. Inhaled nitric oxide for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in children and adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD002787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehberg, S.; Maybauer, M.O.; Maybauer, D.M.; Traber, L.D.; Enkhbaatar, P.; Traber, D.L. The role of nitric oxide and reactive nitrogen species in experimental ARDS. Front. Biosci. Sch. Ed. 2010, 2, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Orieux, A.; Khan, P.; Prevel, R.; Gruson, D.; Rubin, S.; Boyer, A. Impact of dexamethasone use to prevent from severe COVID-19-induced acute kidney injury. Crit. Care Lond. Engl. 2021, 25, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total Population (n = 164) | KDIGO < 3 (n = 125) | KDIGO 3 AKI (n = 39) | p Univariate | OR (CI 95%) | p Multivariate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 62.9 ± 11.2 | 62.1 ± 11.0 | 65.5 ± 11.8 | 0.097 | - | ns |
| Male, n (%) | 126 (76.8) | 95 (76.0) | 31 (79.5) | 0.652 | - | - |
| BMI > 25 cm·Kg2 | 108 (65.9) | 82 (65.6) | 26 (66.7) | 0.902 | - | - |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 93 (56.7) | 65 (52.0) | 28 (71.8) | 0.029 | - | ns |
| Coronary arterial disease, n (%) | 21 (12.8) | 13 (10.4) | 8 (20.5) | 0.099 | - | ns |
| Chronic heart failure, n (%) | 4 (2.4) | 3 (2.4) | 1 (2.6) | 1.000 | - | - |
| Severe cardiovascular disease, n (%) | 34 (20.7) | 23 (18.4) | 11 (28.2) | 0.187 | - | ns |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 62 (37.8) | 43 (34.4) | 19 (48.7) | 0.107 | - | ns |
| Chronic respiratory disease, n (%) | 28 (17.1) | 18 (14.4) | 10 (25.6) | 0.103 | - | ns |
| Chronic kidney disease, n (%) | 11 (6.7) | 4 (3.2) | 7 (17.9) | 0.004 | - | ns |
| - Stage 1 | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.8) | 0 (0.0) | >0.999 | ||
| - Stage 2 | 3 (1.8) | 2 (1.6) | 1 (2.6) | 0.560 | ||
| - Stage 3 | 5 (3.0) | 1 (0.8) | 4 (10.3) | 0.012 | ||
| - Stage 4 | 2 (1.2) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.1) | 0.055 | ||
| NSAID, n (%) | 4 (2.4) | 3 (2.4) | 1 (2.6) | 1.000 | - | - |
| ACEI, n (%) | 26 (15.9) | 15 (12.0) | 11 (28.2) | 0.016 | 4.238 (1.307–13.736) | 0.016 |
| ARB, n (%) | 28 (17.1) | 19 (15.2) | 9 (23.1) | 0.254 | - | - |
| APACHE II, mean ± SD | 13.0 ± 6.1 | 11.9 ± 5.2 | 16.3 ± 7.8 | 0.004 | ||
| APACHE II without age points, mean ± SD | 9.2 ± 5.8 | 8.3 ± 5.1 | 12.1 ± 7.0 | 0.006 | 1.138 (1.044–1.241) | 0.003 |
| Septic shock, n (%) | 70 (42.7) | 52 (41.6) | 18 (46.2) | 0.616 | - | - |
| PEEP, cmH2O | 12.7 ± 3.1 | 12.7 ± 3.1 | 12.6 ± 3.3 | 0.896 | - | ns |
| Plateau pressure, cmH2O | 25.1 ± 4.8 | 25.0 ± 5.1 | 25.3 ± 3.9 | 0.729 | - | - |
| Compliance RS, mL/cm H2O | 36.9 ± 12.2 | 37.0 ± 12.7 | 36.7 ± 10.3 | 0.918 | - | - |
| Driving pressure, cmH2O | 12.1 ± 4.2 | 12.0 4.3 | 12.5 ± 3.9 | 0.613 | - | - |
| PaO2/FIO2 ratio | 141.8 ± 59.1 | 142.3 ± 61.2 | 140.3 ± 53.0 | 0.859 | - | - |
| Prone positioning (intubated), n (%) | 137 (83.6) | 108 (86.4) | 29 (74.4) | 0.077 | 0.234 (0.057–0.967) | 0.045 |
| Awake prone positioning, n (%) | 22 (13.4) | 19 (15.2) | 3 (7.7) | 0.230 | - | - |
| Inhaled Nitric Oxide, n (%) | 53 (32.3) | 36 (28.8) | 17 (43.6) | 0.085 | 5.694 (1.953–16.606) | 0.001 |
| Duration of iNO, days | 6.4 ± 4.6 | 6.4 ± 4.5 | 6.3 ± 5.0 | 0.943 | - | - |
| Maximum dose, ppm | 13.9 ± 5.5 | 12.1 ± 3.4 | 14.8 ± 6.2 | 0.080 | - | - |
| iNO for right ventricular dysfunction | 12 (23.5) | 7 (19.4) | 5 (33.3) | 0.287 | ||
| VV-ECMO, n (%) | 27 (16.5) | 18 (14.4) | 9 (23.1) | 0.202 | - | ns |
| Neuromuscular blockage, n (%) | 156 (95.1) | 119 (95.2) | 37 (94.9) | 1.000 | - | - |
| Dexamethasone, n (%) | 47 (28.7) | 40 (32.0) | 7 (17.9) | 0.090 | 0.194 (0.053–0.713) | 0.014 |
| Hydroxychloroquine, n (%) | 106 (64.6) | 82 (65.6) | 22 (61.5) | 0.643 | - | - |
| Azithromycin, n (%) | 33 (67.3) | 26 (65.0) | 7 (77.8) | 0.460 | - | - |
| Lopinavir/ritonavir, n (%) | 18 (11.0) | 13 (10.4) | 5 (12.8) | 0.673 | - | - |
| Tocilizumab, n (%) | 3 (1.8) | 2 (1.6) | 1 (2.6) | 0.695 | - | - |
| Ruloxitinib, n (%) | 19 (11.6) | 13 (10.4) | 6 (15.4) | 0.396 | - | - |
| Anakinra, n (%) | 18 (11.0) | 13 (10.4) | 5 (12.8) | 0.673 | - | - |
| Aminoglycosides, n (%) | 57 (35.0) | 43 (34.4) | 14 (36.8) | 0.782 | - | - |
| Vancomycin, n (%) | 17 (10.4) | 12 (9.6) | 5 (13.2) | 0.530 | - | - |
| Iodinated contrast media, n (%) | 112 (70.4) | 89 (71.8) | 23 (65.7) | 0.488 | - | - |
| Higher serum urea level mmol/L | 19.8 ± 12.4 | 15.0 ± 7.2 | 36.6 ± 12.1 | <0.001 | - | - |
| Higher serum creatinine level, µmol/L | 163.8 ± 139.3 | 106.3 ± 48.2 | 363.4 ± 166.5 | <0.001 | - | - |
| Outcome | ||||||
| D28 mortality, n (%) | 31 (18.9) | 18 (14.4) | 13 (33.3) | 0.008 | - | - |
| D60 mortality, n (%) | 45 (27.6) | 24 (19.2) | 21 (53.8) | <0.001 | - | - |
| D90 mortality, n (%) | 46 (28.2) | 24 (19.2) | 22 (56.4) | <0.001 | - | - |
| RRT, n (%) | 21 (12.8) | 0 (0.0) | 21 (53.8) | <0.001 | - | - |
| Length of stay in ICU, days | 24 (15–43) | 23 (15–41) | 29 (17–46) | 0.479 | - | - |
| Length of stay in hospital, days | 34 (21–49) | 32.5 (21–47) | 37 (17–49) | 0.827 | - | - |
| Length of MV, days | 16.5 (8–32) | 16 (8–31) | 18 (9–37) | 0.578 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bobot, M.; Tonon, D.; Peres, N.; Guervilly, C.; Lefèvre, F.; Max, H.; Bommel, Y.; Volff, M.; Leone, M.; Lopez, A.; et al. Impact of Dexamethasone and Inhaled Nitric Oxide on Severe Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206130
Bobot M, Tonon D, Peres N, Guervilly C, Lefèvre F, Max H, Bommel Y, Volff M, Leone M, Lopez A, et al. Impact of Dexamethasone and Inhaled Nitric Oxide on Severe Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(20):6130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206130
Chicago/Turabian StyleBobot, Mickaël, David Tonon, Noémie Peres, Christophe Guervilly, Flora Lefèvre, Howard Max, Youri Bommel, Maxime Volff, Marc Leone, Alexandre Lopez, and et al. 2022. "Impact of Dexamethasone and Inhaled Nitric Oxide on Severe Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 20: 6130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206130
APA StyleBobot, M., Tonon, D., Peres, N., Guervilly, C., Lefèvre, F., Max, H., Bommel, Y., Volff, M., Leone, M., Lopez, A., Simeone, P., Carvelli, J., Chopinet, S., Hraiech, S., Papazian, L., Velly, L., Bourenne, J., & Forel, J.-M., on behalf of the GRAM+ (Groupe de Recherche en Réanimation et Anesthésie deMarseille). (2022). Impact of Dexamethasone and Inhaled Nitric Oxide on Severe Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(20), 6130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206130







