Pneumatosis Intestinalis Induced by Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
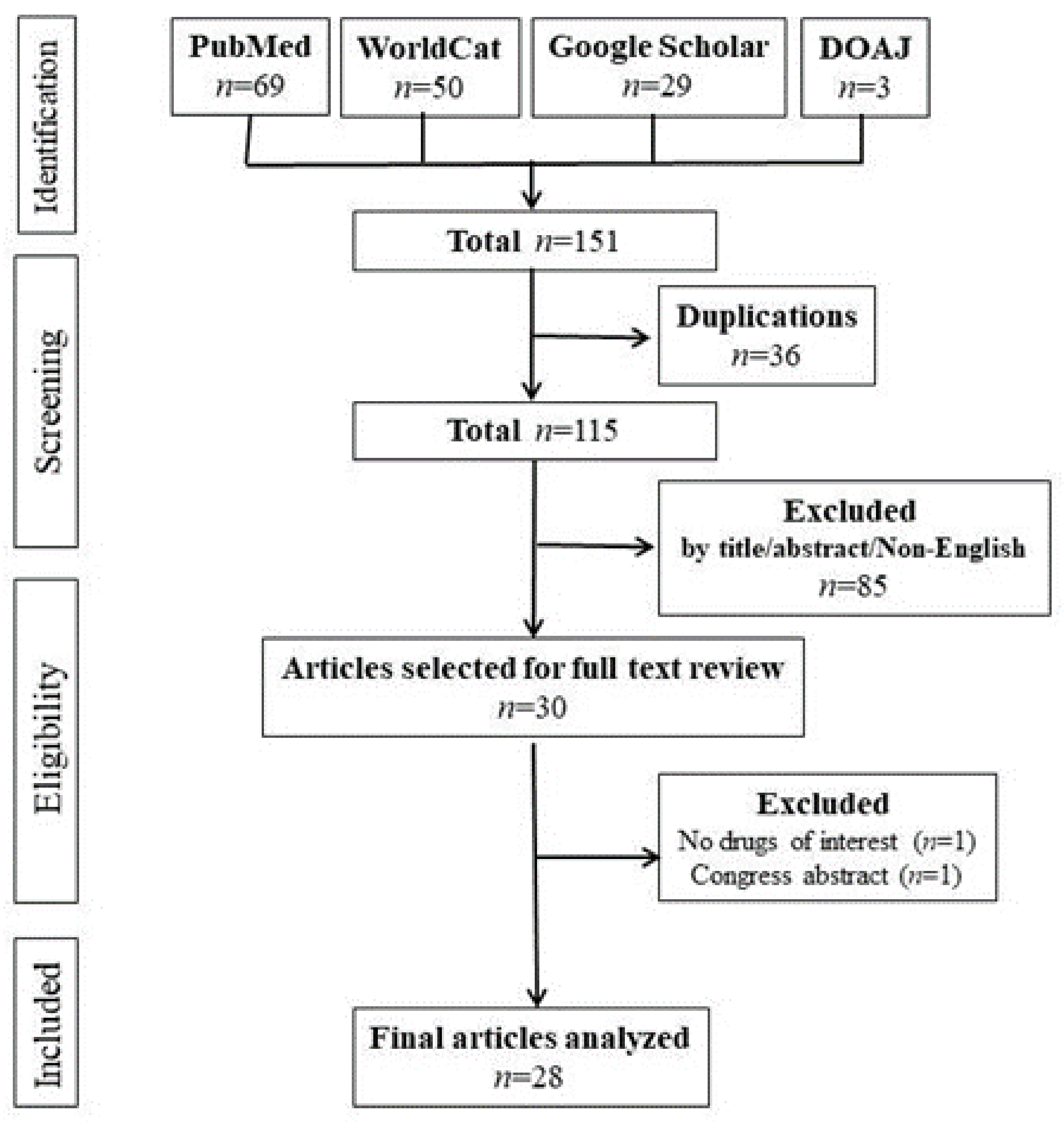
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Articles Included
3.2. Clinical Characteristics of PI
3.3. Type of αGIs
3.4. Concomitant Use of Other Drugs
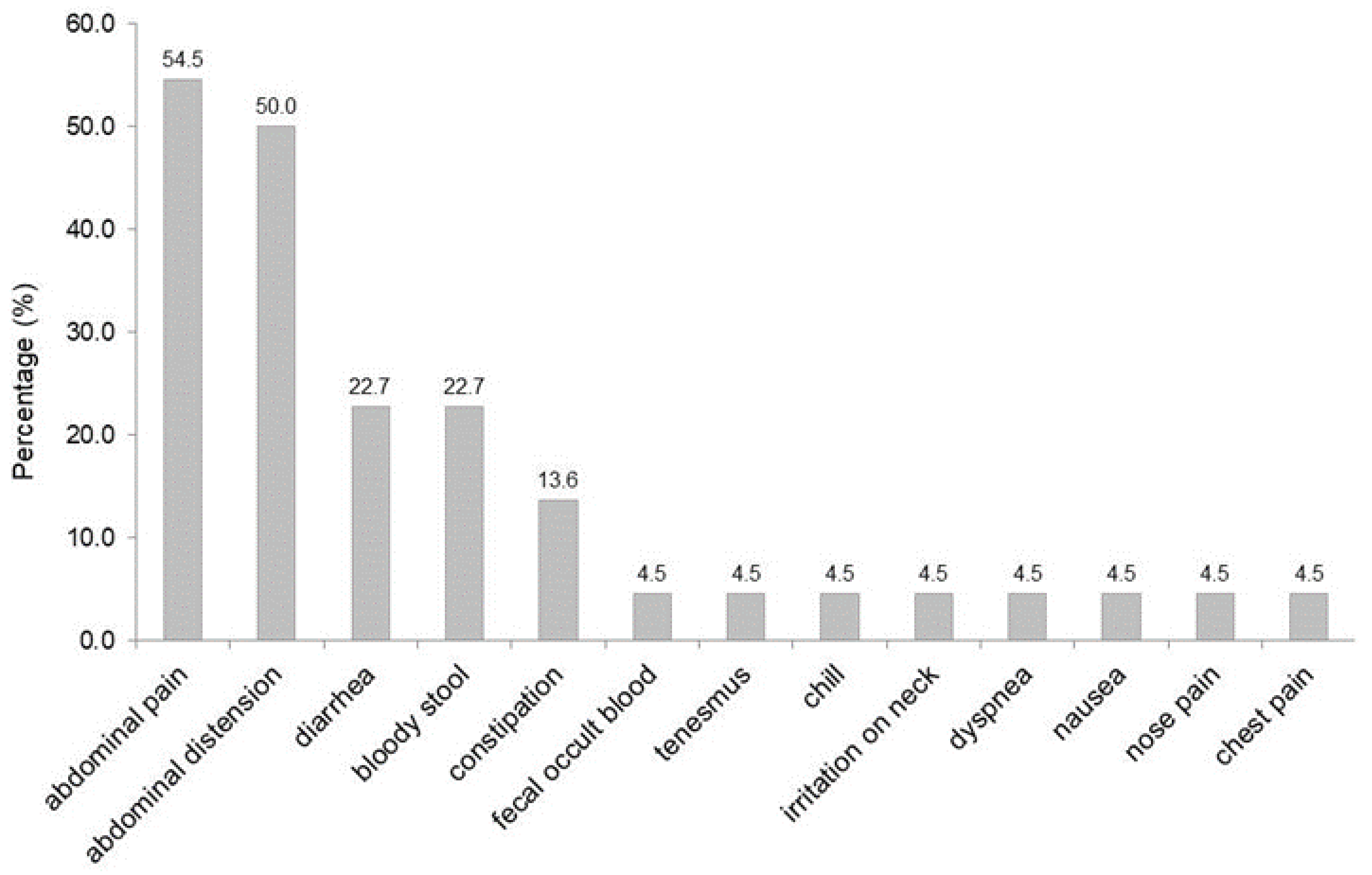
3.5. Symptoms
3.6. Segment of Bowel Involved
3.7. Free Air in the Portal Vein and Intraabdominal Cavities and Extraintestinal Involvement
3.8. Comparison between Patients Treated with Acarbose and Patients Treated with Voglibose
3.9. Diagnosis
3.10. Treatment and Complications
3.11. Outcome or Duration of PI
4. Discussion
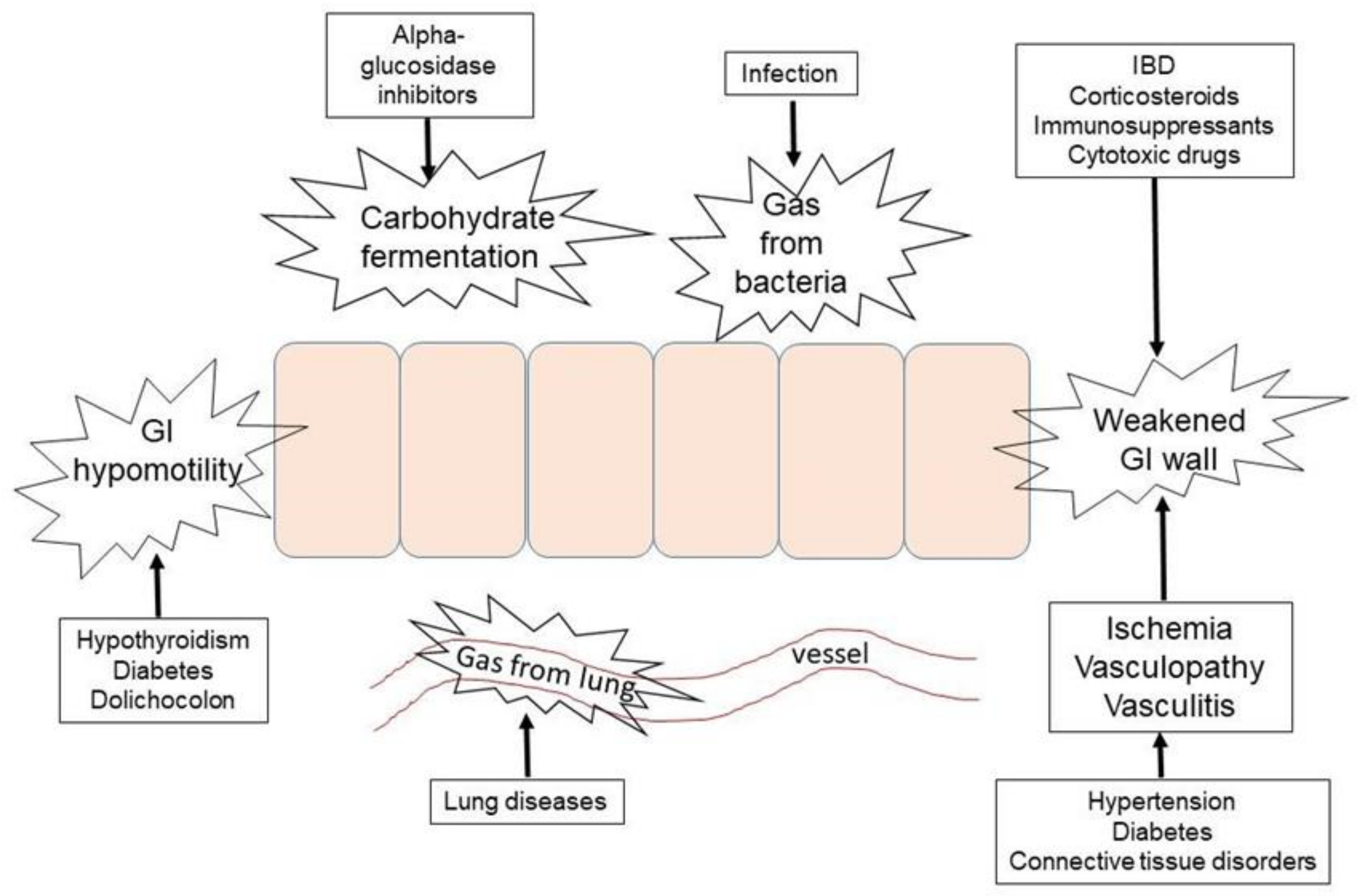
4.1. Mechanisms of αGIs-Induced PI
4.2. Comparison of Three αGIs
4.3. Symptoms and Treatments
4.4. Strength and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Im, J.; Anjum, F. Pneumatosis Intestinalis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564381/ (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Gazzaniga, G.; Villa, F.; Tosi, F.; Pizzutilo, E.G.; Colla, S.; D’Onghia, S.; Sanza, G.D.; Fornasier, G.; Gringeri, M.; Lucatelli, M.V.; et al. Pneumatosis Intestinalis Induced by Anticancer Treatment: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, Y.; Schuffler, M.D.; Haggitt, R.C.; Rohrmann, C.A. Pneumatosis intestinalis: A review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1995, 90, 1747–1758. [Google Scholar]
- Ksiadzyna, D.; Peña, A.S. Segmental pneumatosis cystoides coli: Computed tomography-facilitated diagnosis. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2016, 108, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alpuim Costa, D.; Modas Daniel, P.; Vieira Branco, J. The Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis-A Scoping Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 601872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.H.H.; Tellambura, S. Pneumatosis intestinalis: Not always bowel ischemia. Radiol. Case Rep. 2022, 17, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Ohbe, H.; Fujita, M.; Kushimoto, S. Clinical characteristics and prediction of the asymptomatic phenotype of pneumatosis intestinalis in critically ill patients: A retrospective observational study. Acute Med. Surg. 2020, 7, e556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.M.; Paulson, E.K.; Thompson, W.M. Pneumatosis intestinalis in the adult: Benign to life-threatening causes. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 1604–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Uffenheimer, M.; Ashamallah, M.; Grimaldi, G.; Swaminath, A.; Sultan, K. Presentation and outcomes among inflammatory bowel disease patients with concurrent pneumatosis intestinalis: A case series and systematic review. Intest. Res. 2020, 18, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGettigan, M.J.; Menias, C.O.; Gao, Z.J.; Mellnick, V.M.; Hara, A.K. Imaging of Drug-induced Complications in the Gastrointestinal System. RadioGraphics 2016, 36, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmiya, N.; Hirata, I.; Sakamoto, H.; Morishita, T.; Saito, E.; Matsuoka, K.; Nagaya, T.; Nagata, S.; Mukae, M.; Sano, K.; et al. Multicenter epidemiological survey of pneumatosis intestinalis in Japan. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, K.; Tsujimoto, T.; Fujii, H.; Morimoto, T.; Yoshioka, S.; Kato, S.; Yasuhara, Y.; Aizawa, S.; Sawai, M.; Makutani, S.; et al. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis induced by the α-glucosidase inhibitor miglitol. Intern. Med. 2010, 49, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, T.; Yoneshima, M.; Abe, T.; Nomura, G. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis after treatment with an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 366–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanaru, R.; Hizawa, K.; Nakamura, S.; Yoshimura, R.; Watanabe, K.; Nakamura, U.; Yoshinari, M.; Matsumoto, T. Regression of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis after discontinuing of alpha-glucosidase inhibitor administration. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2002, 35, 204–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furio, L.; Vergura, M.; Russo, A.; Bisceglia, N.; Talarico, S.; Gatta, R.; Tomaiuolo, M.; Tomaiuolo, P. Pneumatosis coli induced by acarbose administration for diabetes mellitus. Case report and literature review. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2006, 52, 339–346. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Bao, Z. Population-Based Study of the Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors of Ischemic Colitis. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 32, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.J.; Yen, C.S.; Ming-Jenn Chen, M.J. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Formos. J. Surg. 2011, 44, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takase, A.; Akuzawa, N.; Naitoh, H.; Aoki, J. Pneumatosis intestinalis with a benign clinical course: A report of two cases. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.H.; Lo, Y.P.; Liao, Y.K.; Lin, C.H. Pneumatosis Cystoides Coli Related to Acarbose Treatment. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.M.; Zheng, Y.M.; Jiang, H.Q.; Zhang, J. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: Six case reports and a review of the literature. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018, 18, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.C.; Wang, K.C. Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis Secondary to Use of an α-Glucosidase Inhibitor. Radiology 2019, 290, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azami, Y. Paralytic ileus accompanied by pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis after acarbose treatment in an elderly diabetic patient with a history of heavy intake of maltitol. Intern. Med. 2000, 39, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisamoto, A.; Mizushima, T.; Sato, K.; Haruta, Y.; Tanimoto, Y.; Tanimoto, M.; Matsuo, K. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis after alpha-glucosidase inhibitor treatment in a patient with interstitial pneumonitis. Intern. Med. 2006, 45, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, Y.; Inaba, N.; Aoyagi, M.; Kanda, E.; Shiigai, T. Fulminant pneumatosis intestinalis in a patient with diabetes mellitus and minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Intern. Med. 2007, 46, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Tanikawa, A.; Nakasute, K.; Tanaka, M.; Nishikawa, T. Additive contribution of multiple factors in the development of pneumatosis intestinalis: A case report and review of the literature. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimoto, T.; Shioyama, E.; Moriya, K.; Kawaratani, H.; Shirai, Y.; Toyohara, M.; Mitoro, A.; Yamao, J.; Fujii, H.; Fukui, H. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis following alpha-glucosidase inhibitor treatment: A case report and review of the literature. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 6087–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, Y.; Buchner, N.J.; Szpakowski, M.; Tannapfel, A.; Henning, B.F. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis of the ascending colon related to acarbose treatment: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2009, 3, 9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimojima, Y.; Ishii, W.; Matsuda, M.; Tojo, K.; Watanabe, R.; Ikeda, S. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus with diabetes mellitus: Case report and literature review. Mod. Rheumatol. 2011, 21, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Doi, Y.; Takata, N.; Yoshinaka, I.; Harada, K. Successful conservative treatment of pneumatosis intestinalis associated with intraperitoneal free air: Report of a case. Surg. Today. 2012, 42, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Shirakawa, Y.; Takehara, Y.; Maeda, N.; Katsube, R.; Ohara, T.; Sakurama, K.; Noma, K.; Fujiwara, T. Successfully treated pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis with pneumoperitoneum onset in a patient administered α-glucosidase inhibitor. Acta Med. Okayama 2013, 67, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makiyama, H.; Kataoka, R.; Tauchi, M.; Sumitomo, H.; Fuita, R. Do alpha-glucosidase inhibitors have the potential to induce portal venous gas? -Two clinical case reports. Intern. Med. 2014, 53, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogo, A.; Hasuzawa, N.; Sakaki, Y.; Sakamoto, R.; Matoba, Y. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis related to α-glucosidase inhibitor treatment in a polymyalgia rheumatica patient with diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Int. 2014, 5, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottenstreich, A.; Agmon, Y.; Elazary, R. A Rare Case of Benign Pneumatosis Intestinalis with Portal Venous Gas and Pneumoperitoneum Induced by Acarbose. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 1733–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, E.; Kanno, T.; Hazama, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Watanabe, H.; Ohira, H. Four Cases of Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis Complicated by Connective Tissue Diseases. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Guo, D.; Zhu, L. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: A case report and literature review. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Police, A.; Charre, L.; Volpin, E.; Antonopulos, C.; Braham, H.; El Arbi, N. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis induced by the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor complicated from sigmoid volvulus in a diabetic patient. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2020, 35, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, Y.; Ishioka, K.; Moriya, H.; Taguchi, S.; Oki, R.; Matsui, K.; Mochida, Y.; Hidaka, S.; Ohtake, T.; Kobayashi, S. Peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis complicated with nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia. CEN Case Rep. 2021, 10, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, S.; Ujiie, H.; Kato, T.; Shiiya, H.; Fujiwara-Kuroda, A.; Hida, Y.; Kaga, K.; Wakasa, S.; Inoue, R.; Iimura, Y. Pneumatosis Intestinalis After Living Donor Lung Transplantation Associated With Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitor Treatment: A Case Report. Transplant. Proc. 2021, 53, 1379–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillon, J.; Tadesse, K.; Logan, R.F.; Holt, S.; Sircus, W. Breath hydrogen in pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Gut 1979, 20, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagara, A.; Kitagawa, K.; Furuichi, K.; Kitajima, S.; Toyama, T.; Okumura, T.; Hara, A.; Sakai, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Wada, T. Three cases of pneumatosis intestinalis presenting in autoimmune diseases. Mod. Rheumatol. 2012, 22, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannes, G.P.; de Boer, W.J.; van der Jagt, E.J.; Meinesz, A.F.; Meuzelaar, J.J.; van der Bij, W. Pneumatosis intestinalis and active cytomegaloviral infection after lung transplantation. Groningen Lung Transplant Group. Chest 1994, 105, 929–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernagis, L.Y.; Levine, M.S.; Jacobs, J.E. Pneumatosis intestinalis in patients with ischemia: Correlation of CT findings with viability of the bowel. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 180, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, E.; Ough, M.; Wu, A.; Liao, J.; Andresen, K.J.; Kuehn, D.; Wilkinson, N. Management algorithm for pneumatosis intestinalis and portal venous gas: Treatment and outcome of 88 consecutive cases. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2010, 14, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, H. Pharmacology of α-Glycosidase Inhibitors Drugs in Development α-Glycosidase Inhibition Potential Use in Diabetes; Neva: Branford, CT, USA, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Standl, E.; Schernthaner, G.; Rybka, J.; Hanefeld, M.; Raptis, S.A.; Naditch, L. Improved glycaemic control with miglitol in inadequately-controlled type 2 diabetics. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2001, 51, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabhi, A.S.; Bhatt, N.R.; Shah, M.J. Voglibose: An alpha glucosidase inhibitor. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 3023–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, M.; Yamashita, S.; Tashiro, J.; Tanaka, M.; Takenaka, Y.; Yamasaki, K.; Masaki, Y. Clinical characteristics of patients with pneumatosis intestinalis. ANZ J. Surg. 2021, 91, 1826–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Li, Y. Predictors and risk factors for intestinal necrosis in patients with mesenteric ischemia. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | n | (% of Cases) |
|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 29 | |
| Men/women/undefined sex | 11/17/1 | |
| Age in years (mean ± SD) (median) | 68.1 ± 10.3 (67) | |
| Age range | 48–87 | |
| Diabetes’ duration (mean ± SD) (median) | 6.0 ± 6.1 (4) | |
| Range | 2 days to 20 years | |
| Comorbidities and/or past medical history | ||
| Number of patients | 19 | (65.5) |
| Connective tissue disorders/autoimmune diseases | 7 | (24.1) |
| Hypertension | 2 | (6.9) |
| Hypertension + post cerebral infarction | 1 | (3.4) |
| Hypertension + diabetic nephropathy + ischemic heart disease | 1 | (3.4) |
| Hypertension + diabetic nephropathy + peritonitis + nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia (NOMI) + ischemic disease + post cerebral infarction | 1 | (3.4) |
| Minimal change disease—nephrotic syndrome + E. coli sepsis | 1 | (3.4) |
| Chronic inflammatory colitis | 2 | (6.9) |
| Post lung transplantation + pneumonia 1 month prior | 1 | (3.4) |
| Sigmoid volvulus/dolichocolon | 1 | (3.4) |
| Non-specific interstitial pneumonitis (NSIP) | 1 | (3.4) |
| Acute cholecystitis | 1 | (3.4) |
| Medications | ||
| Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors | ||
| Acarbose | 12 | (41.4) |
| Median of duration (year) (Range) | 5 (1–12) | |
| Voglibose | 13 | (44.8) |
| Median of duration (year) (Range) | 0.6 (0.005–10) | |
| Miglitol | 2 | (6.9) |
| Median of duration (year) (Range) | 3.8 (0.7–7) | |
| Undefined | 2 | (6.9) |
| Concomitant drugs/supplements | ||
| Prednisone/prednisolone | 6 | (20.7) |
| Prednisolone + tacrolimus | 1 | (3.4) |
| Prednisolone + mizoribine | 1 | (3.4) |
| Prednisolone + methotrexate | 1 | (3.4) |
| Insulin | 7 | (24.1) |
| Sulfonylurea | 4 | (13.8) |
| Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors | 2 | (6.9) |
| Metformin | 1 | (3.4) |
| Maltitol | 1 | (3.4) |
| Characteristics | n | (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | ||
| Asymptomatic | 7 | (24.1) |
| Symptomatic | 22 | (75.9) |
| Imaging | ||
| Abdominal X-ray | 29 | (100) |
| Abdominal CT | 29 | (100) |
| Colonoscopy | 11 | (37.9) |
| Segments involved | ||
| Large bowel only | ||
| Ascending colon only | 5 | (17.2) |
| Sigmoid only | 5 | (17.2) |
| Ascending + sigmoid | 1 | (3.4) |
| Ascending + transverse colon | 2 | (6.9) |
| Ascending + descending colon | 2 | (6.9) |
| Cecum + splenic flexure colon | 1 | (3.4) |
| Cecum + ascending + transverse + sigmoid colon | 1 | (3.4) |
| All colon | 2 | (6.9) |
| Small intestine only | ||
| Ileum only | 1 | (3.4) |
| Whole small intestine | 6 | (20.7) |
| Combined | ||
| Ileum + ascending colon | 2 | (6.9) |
| Ileum + ascending + transverse colon | 1 | (3.4) |
| Free gas in cavities or other tissue | ||
| Pneumoperitoneum | 7 | (24.1) |
| Pneumoretroperitoneum | 2 | (6.9) |
| Portal venous gas | 2 | (6.9) |
| Portal venous gas + pneumoperitoneum | 1 | (3.4) |
| Subcutaneous air in the cervical region + pneumomediastinum + pneumoretroperitoneum + pneumoperitoneum | 1 | (3.4) |
| Pneumomediastinum + pneumopericardium + pneumoretroperitoneum | 1 | (3.4) |
| Treatment | ||
| Termination of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors | 29 | (100) |
| Conservative | 25 | (86.2) |
| Fasting | 12 | (41.4) |
| Fluid supplementation | 8 | (27.6) |
| Antibiotics | 7 | (24.1) |
| Oxygen therapy | ||
| Conventional | 5 | (17.2) |
| Mechanical | 1 | (3.4) |
| Endoscopy (colonoscopy) therapy | ||
| Needle puncture + electro-resection of gas cysts | 1 | (3.4) |
| Hemofiltration | 2 | (6.9) |
| Exploratory laparotomy but with conservative therapy | 2 | (6.9) |
| Laparoscopic sigmoidectomy | 1 | (3.4) |
| Laparotomy and hemicolectomy | 1 | (3.4) |
| Outcome | ||
| Survival | 29 | (100) |
| Free air disappearance was confirmed radiologically | 22 | (75.9) |
| Median of duration in days (range) | 18 (2-180) |
| Patient without Comorbidities (n = 10) | Patients with Comorbidities (n = 19) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) (mean±SD) (median) | 65.5 ± 8.4 (64.5) | 69.6 ± 11.0 (70) |
| Pneumoperitoneum or pneumoretroperitoneum | 1 | 9 * |
| Pneumomediastinum or pneumopericardium or subcutaneous air | 0 | 2 |
| Portal venous gas | 0 | 3 |
| Small intestine involvement | 2 | 8 * |
| Combination of small and large intestines | 1 | 2 |
| Exploratory laparotomy | 1 | 2 |
| Surgery | 1 | 1 |
| PI disappearance (days) (median) (range) | 21.5 (4–180) | 21 (4–90) |
| Acarbose | Voglibose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Comorbidities | With Comorbidities | Without Comorbidities | With Comorbidities | |
| Number of patients | 5 | 7 | 3 | 10 |
| Age (years) (mean±SD) (median) | 63.6 ± 8.2 (65) | 72.6 ± 9.3 (72) | 67.7 ± 9.1 (64) | 64.8 ± 10.1 (69.5) |
| Diabetes’ duration (years) (mean ± SD) (median) | Unknown | 9.8 ± 3.5 (10) | 11.5 ± 12 (11.5) | 1.1 ± 1.6 (0.08) |
| αGIs duration range (years) (median) | 1–10 (3) | 2–12 (8) | 0.05–5 (0.17) | 0.005–10 (1.7) |
| Concomitant prednisone/prednisolone ± immunosuppressants (case) (%) | 1 (14.3%) | 8 (80%) ** | ||
| Portal venous gas | 1 (14.3%) | 2 (20%) | ||
| Pneumoperitoneum +/− Pneumoretroperitoneum | 3 (42.9%) | 5 (50%) | ||
| Pneumomediastinum, Pneumopericardium, Pneumoretroperitoneum | 1(10%) | |||
| Subcutaneous air in the cervical region, pneumomediastinum, pneumoperitoneum, pneumoretroperitoneum | 1(10%) | |||
| Exploratory laparotomy | 1 (14.3%) | 1(10%) | ||
| Laparoscopic sigmoidectomy | 1 (14.3%) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McKinley, B.J.; Santiago, M.; Pak, C.; Nguyen, N.; Zhong, Q. Pneumatosis Intestinalis Induced by Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5918. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195918
McKinley BJ, Santiago M, Pak C, Nguyen N, Zhong Q. Pneumatosis Intestinalis Induced by Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5918. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195918
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcKinley, Blake J., Mariangela Santiago, Christi Pak, Nataly Nguyen, and Qing Zhong. 2022. "Pneumatosis Intestinalis Induced by Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5918. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195918
APA StyleMcKinley, B. J., Santiago, M., Pak, C., Nguyen, N., & Zhong, Q. (2022). Pneumatosis Intestinalis Induced by Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5918. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195918






