Efficacy of Classic Ear Molding for Neonatal Ear Deformity: Case Series and Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Series
2.1.1. Patient Selection
2.1.2. Treatment and Evaluation
2.1.3. Statistical Analysis
2.2. Systematic Literature Review
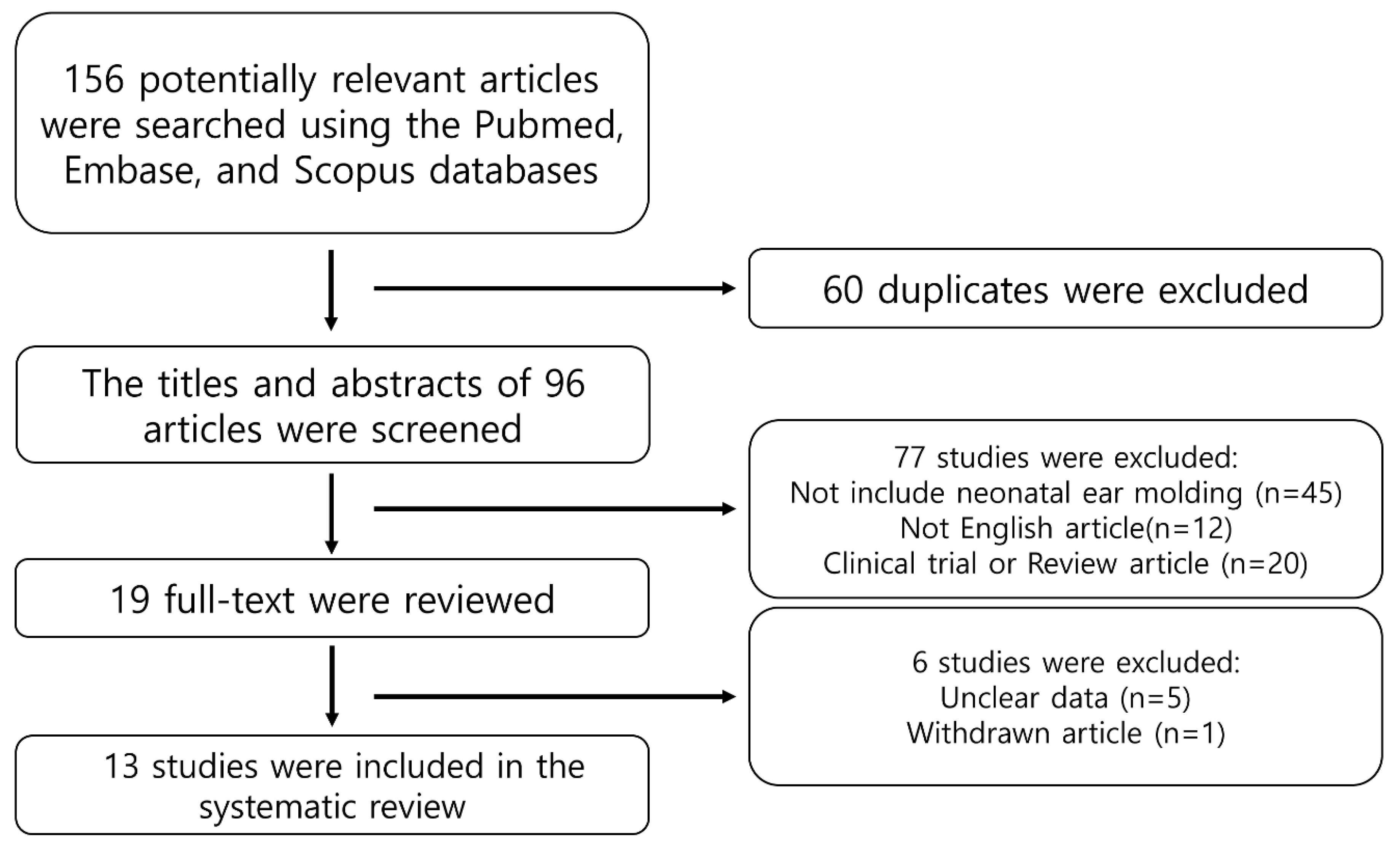
2.2.1. Search Protocol
2.2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Case Series
3.1.1. Types of Anomalies and Outcomes
3.1.2. Patient Age and Duration of Application
3.2. Systematic Review
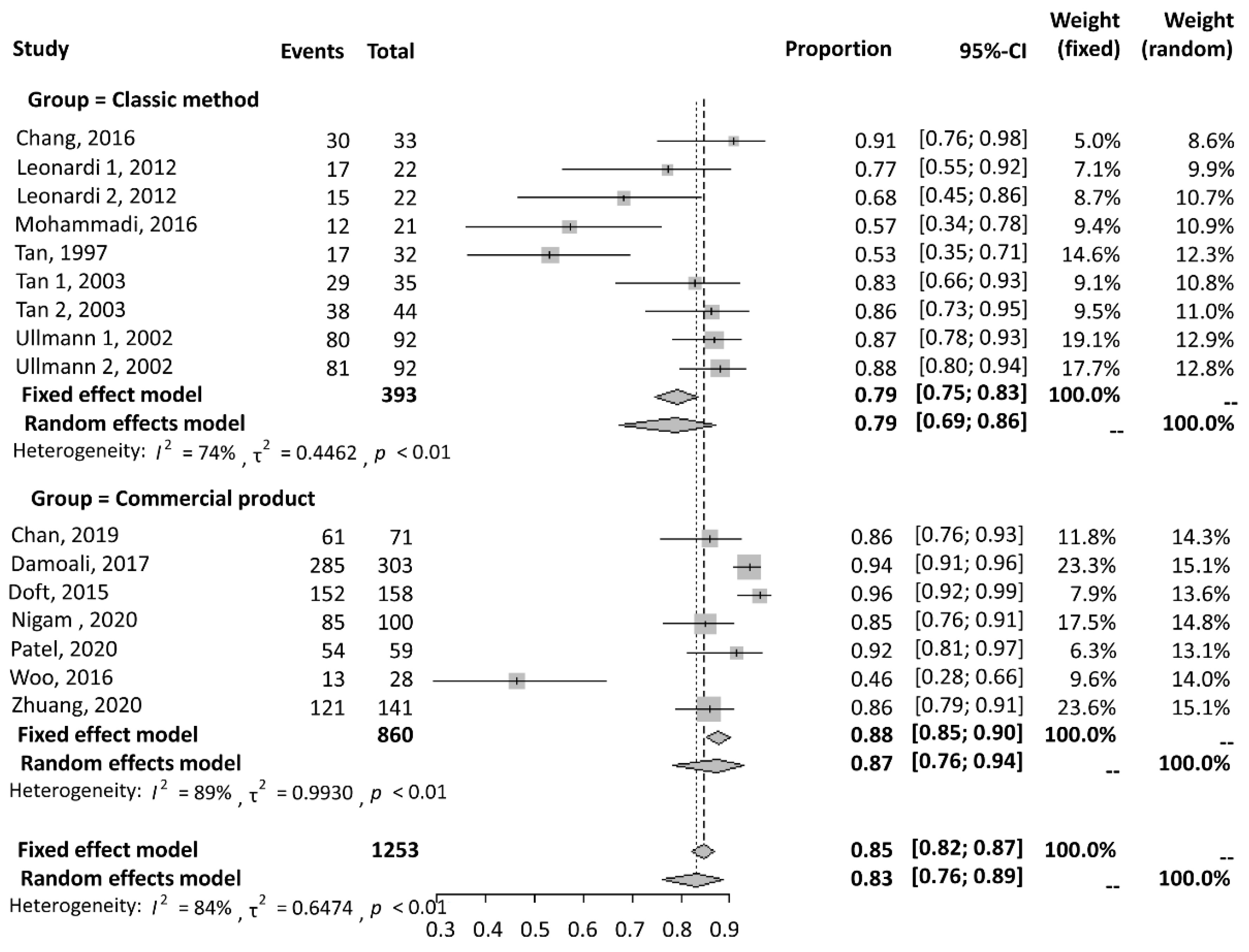
3.2.1. Success Rate
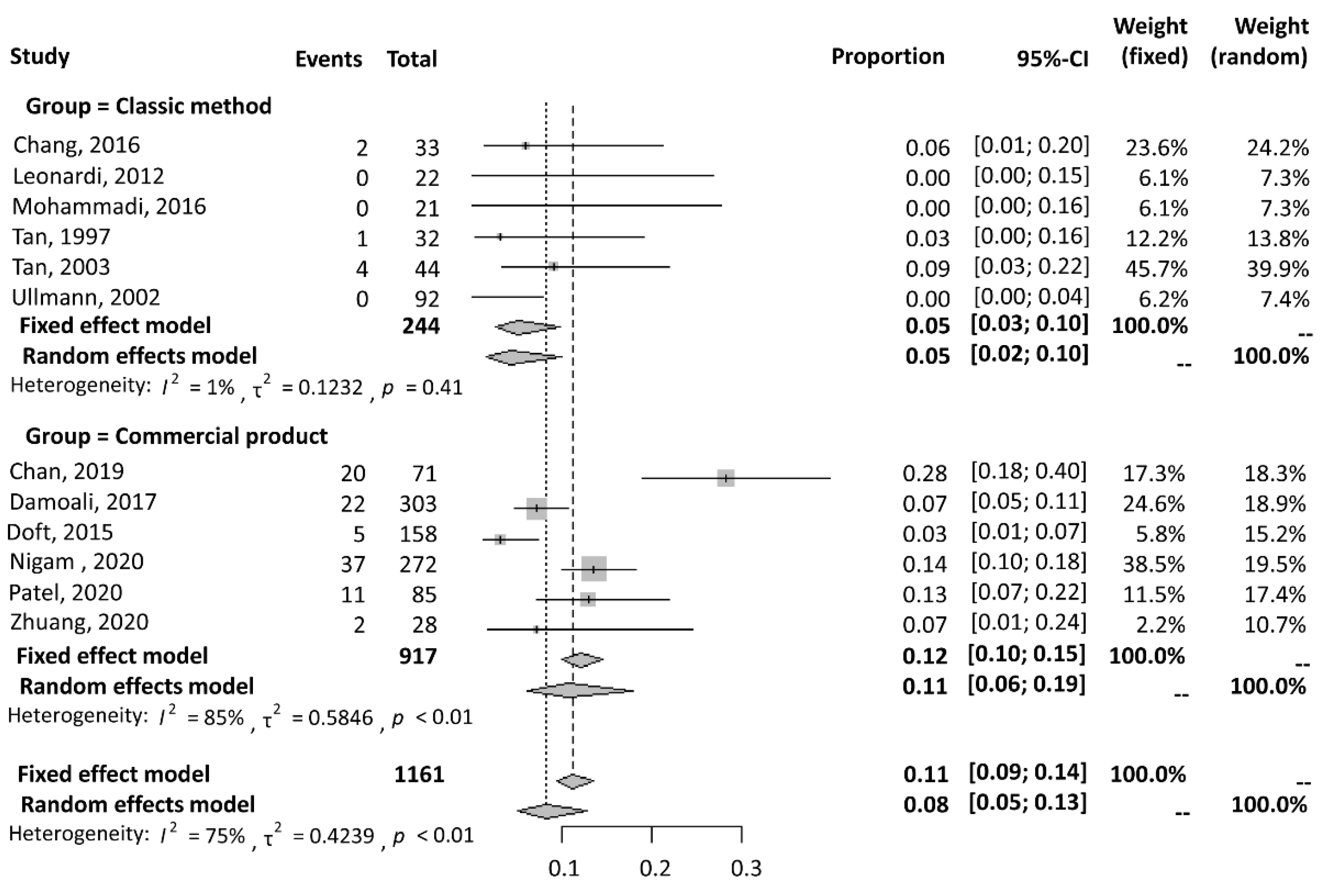
3.2.2. Complication Rate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, S.L.S.; Lim, G.J.S.; Por, Y.C.; Chiang, M.F.; Ho, S.; Saffari, S.E.; Chia, H.L. Efficacy of ear molding in infants using the earwell infant correction system and factors affecting outcome. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 648e–658e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Arias, J.P.; Gutiérrez Venturini, A.; Pampín Martínez, M.M.; Gómez García, E.; Muñoz Caro, J.M.; San Basilio, M.; Martín Pérez, M.; Cebrián Carretero, J.L. Microtia ear reconstruction with patient-specific 3D models—A segmentation protocol. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, C.; Chinnadurai, S. Nonsurgical management of congenital auricular anomalies. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.T.; Abramson, D.L.; MacDonald, D.M.; Mulliken, J.B. Molding therapy for infants with deformational auricular anomalies. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1997, 38, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, Y.S.; Roh, T.S.; Yun, I.S. Cryptotia recurrence lowering technique with additional acellular dermal matrix graft. Arch. Craniofacial Surg. 2019, 20, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Xu, J.; Zhai, J.; Chen, S.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, H. Comparison of 2 ear molding systems for nonsurgical management of newborn auricular deformities. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100, 652S–656S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.S.; Bartlett, S.P. A simplified nonsurgical method for the correction of neonatal deformational auricular anomalies. Clin. Pediatr. 2017, 56, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, A.; Bianca, C.; Basile, E.; Ungari, C.; Arangio, P.; Filiaci, F.; Papoff, P.; Vellone, V.; Moretti, C.; Cascone, P. Neonatal molding in deformational auricolar anomalies. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 1554–1558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, A.A.; Imani, M.T.; Kardeh, S.; Karami, M.M.; Kherad, M. Non-surgical management of congenital auricular deformities. World J. Plast. Surg. 2016, 5, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.; Wright, A.; Hemphill, A.; Ashton, K.; Evans, J. Correction of deformational auricular anomalies by moulding—Results of a fast-track service. N. Z. Med. J. 2003, 116, U584. [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann, Y.; Blazer, S.; Ramon, Y.; Blumenfeld, I.; Peled, I.J. Early nonsurgical correction of congenital auricular deformities. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2002, 109, 907–913; discussion 914–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniali, L.N.; Rezzadeh, K.; Shell, C.; Trovato, M.; Ha, R.; Byrd, H.S. Classification of newborn ear malformations and their treatment with the earwell infant ear correction system. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doft, M.A.; Goodkind, A.B.; Diamond, S.; DiPace, J.I.; Kacker, A.; LaBruna, A.N. The newborn butterfly project: A shortened treatment protocol for ear molding. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 577e–583e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigam, M.; Kotha, V.S.; Barra, C.; Baker, S.B. Nonoperative molding of congenital ear deformities: The impact of birth-initiation delay on correction outcome. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2020, 31, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Mazzaferro, D.M.; Swanson, J.W.; Taylor, J.A.; Bartlett, S.P. Public perception of helical rim deformities and their correction with ear molding. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2020, 31, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, T.; Kim, Y.S.; Roh, T.S.; Lew, D.H.; Yun, I.S. Correction of congenital auricular deformities using the ear-molding technique. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2016, 43, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Q.; Wei, N.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yu, D.; Wang, P.; Shi, H. Efficacy and timing of neonatal ear correction molding. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2020, 44, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, K.Y.; Yang, J.D.; Chung, H.Y.; Cho, B.C. Correction of microtia with constriction features using a superficial temporal fascial flap combined with a rib cartilage graft. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2020, 47, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, H.S.; Langevin, C.J.; Ghidoni, L.A. Ear molding in newborn infants with auricular deformities. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Li, C.L.; Fu, Y.Y.; Zhang, T.Y. Newborn ear defomities and their treatment efficiency with earwell infant ear correction system in china. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 124, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joukhadar, N.; McKee, D.; Caouette-Laberge, L.; Bezuhly, M. Management of congenital auricular anomalies. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 146, 205e–216e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Long-term effectiveness of ear molding in infants using the earwell infant correction system in china. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 148, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.U.; Lazarou, M.; Kyle, A.; Jones, N.W. Neonatal ear splinting for congenital ear deformities. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2020, 73, 2239–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, K.; Guillen, D.; Maricevich, R.S. Newborn ear deformities: Early recognition and novel nonoperative techniques. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2017, 31, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

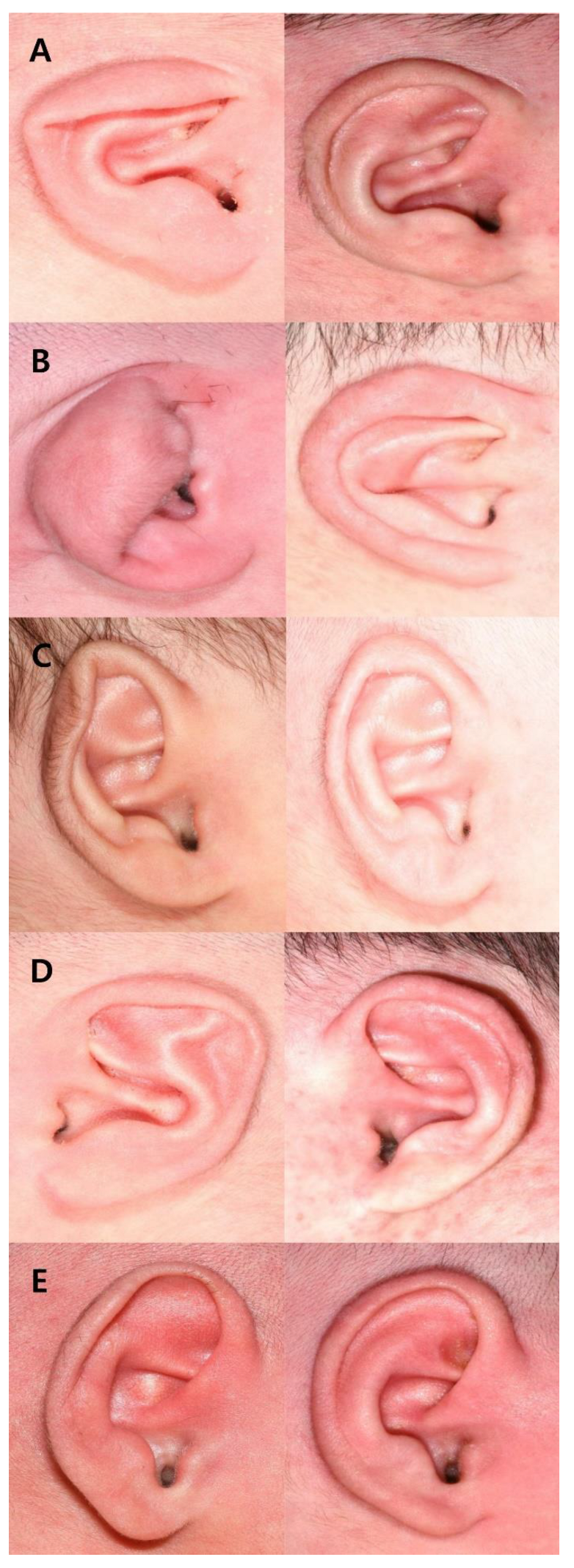
| Grade | Shape | Deformation/Malformation |
|---|---|---|
| Excellent | Normal ear shape | No appearance of original deformation/malformation |
| Good | Nearly normal ear shape | Mild yet nondistracting retention of original deformation/malformation |
| Moderate | Improved but not a normal ear shape | Noticeable, distracting retention of original deformation/malformation |
| Poor | No improvement | Abnormal ear shape with retention of original deformation/malformation |
| Classic Method | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study No. | Study | Device | Cases (n) | Type of Anomaly (%) | Initiation (Mean Weeks ± SD; Range) | Duration (Mean Weeks ± SD; Range) | Responder | Success * (n) | Complication † (n) |
| 1 | Chang 2017 [7] | Conformer, Velcro tape, and gel sealing | 33 | Helical (30.3); Lop (18.2); Prom. (21.2); Stahl’s (24.2); mixed (6.1) | 4.5; 0.86 to 15.1 | 3.9; 1.7 to 6.6 | Physician | 30 | 2 |
| 2 | Leonardi 1 2012 [8] | Splinting and taping | 22 | Const. (36.4); Lop (9.1); Prom. (18.2); Stahl’s (18.2) | N/A; 0.29 to 6 | N/A; 5–8 | Parents | 17 | 0 |
| Leonardi 2 2012 [8] | Physician | 15 | |||||||
| 3 | Mohammadi 2016 [9] | Splinting and taping | 21 | Const. (38.1); Lop (23.8); Prom. (20.7) | 7.52 ± 5.6; 2 to 24 | 13.33 ± 2; 11 to 18 | Physician | 12 | 0 |
| 4 | Tan 1997 [4] | Splinting and taping | 32 | Concha (3.1); Lop (65.6); Prom. (18.8); Stahl’s (6.3); mixed (6.3) | 2.4 ± 3.5; 0.14 to 10 | 10.9 ± 9; 5 to 38.5 | Physician and parents | 17 | 1 |
| 5 | Tan 1 2003 [10] | Splinting and taping | 44 | Cup (18.2); Lop (38.6); Helical (11.4) Prom. (31.8) | 3.4; 0.14 to 15 | 7; 1 to 14 | Parents | 29 (total n: 35) | 4 |
| Tan 2 2003 [10] | Physician | 38 | |||||||
| 6 | Ullmann 1 2002 [11] | Splinting and taping | 92 | Costricted (21.7); Lop (30.4); Prom. (26.1); Stahl’s (21.7) | N/A; 0.14 to 1.43 | 6.8; 6 to 12 | Parents | 80 | 0 |
| Ullmann 2 2002 [11] | Physician | 81 | |||||||
| Commercial Product | |||||||||
| 7 | Chan 2019 [1] | Earwell® | 71 | Concha (0.95); Constricted (32.4); Cryptotia (0.95); Helical (9.5); Lidding (28.6); Lop (4.8); Prom.(4.8); Stahl’s (18.1) | 2.24; 0 to 13.9 | 4.1; 1.5 to 6 | Physician | 61 | 20 |
| 8 | Daniali 2017 [12] | Earwell® | 303 | Concha (36.4); Helical (24.8); Lidding (19.1); Prom. (8.9); Stahl’s (20.8) | 1.79; N/A | 5.29; 1.7 to 15.6 | Physician | 285 | 22 |
| 9 | Doft 2015 [13] | Earwell® | 158 | Constricted (18); Cryptotia (0.5); Helical (38); Prom. (18.5); Stahl’s (25) | N/A; N/A | 2; 1 to 6 | Parents | 152 | 5 |
| 10 | Nigam 2020 [14] | Earwell® /InfantEar® | 272 | Concha (2.2); Cup (7.7); Helical (14.3); Lidding/Lop (8.8); Prom. (23.2); Stahl’s (8.4) | 2.9; N/A | N/A | Parents | 85 (total n: 100) | 37 |
| 11 | Patel 2020 [15] | InfantEar® | 85 | Helical (100) | 4.9; 8.6 to 10.9 | 4.4; 1 to 10.3 | Survey | 54 (total n: 59) | 11 |
| 12 | Woo 2016 [16] | Earwell® | 28 | Constricted (62.4); Cryptotia (7.1); Prom. (7.1); Stahl’s (21.4) | 3.2; 0.7 to 7.4 | 4.7; 3.4 to 7.6 | Parents | 13 | N/A |
| 13 | Zhuang 2020 [17] | Earlimn® | 141 | Concha (7.8); Constricted (17.7); Cryptotia (9.2); Cup (9.2); Helical (18.4); Lop (16.3); Prom. (10.6); Stahl’s (10.6) | 5 ± 3.3; N/A | 2.5 ± 1.86; N/A | Physician | 121 | 2 |
| n | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | M | 41 | 43.6 |
| F | 53 | 56.4 | |
| type | Lop ear | 65 | 69.1 |
| Constricted ear | 12 | 12.8 | |
| Helical rim deformity | 7 | 7.4 | |
| Stahl’s ear | 7 | 7.4 | |
| Prominent ear | 3 | 3.2 | |
| Grade | Excellent | 48 | 51.1 |
| Good | 39 | 41.5 | |
| Moderate | 7 | 7.4 | |
| Poor | 0 | 0 | |
| Age at application(days) | 5.81 ± 6.09 | 6.09 | |
| Duration of application(days) | 32.13 ± 7.90 | 7.9 | |
| Grade | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excellent | Good | Moderate | Poor | Total | ||
| Lop ear | 35(54) | 26(40) | 4(6) | 0(0) | 65(100) | 0.210 |
| Constricted ear | 3(25) | 7(58) | 2(17) | 0(0) | 12(100) | |
| Helical rim deformity | 2(29) | 4(57) | 1(14) | 0(0) | 7(100) | |
| Stahl’s ear | 6(86) | 1(14) | 0(0.0) | 0(0) | 7(100) | |
| Prominent ear | 2(67) | 1(33) | 0(0.0) | 0(0) | 3(100) | |
| Total | 48 | 39 | 7 | 0(0) | 94 | |
| Excellent | Good (n = 39) | Moderate (n = 7) | Total (n = 94) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 48) | |||||
| Age at application (days) | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 4.58 ± 4.74 | 7.72 ± 7.28 | 3.71 ± 4.64 | 5.82 ± 6.09 | 0.035 a |
| Median(range) | 4 (1–22) | 4 (1–22) | 2 (1–22) | 4 (1–22) | 0.007 b |
| Duration of application (days) | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 30.27 ± 8.58 | 33.64 ± 7.07 | 36.43 ± 2.94 | 32.13 ± 7.90 | 0.044 a |
| Median(range) | 35 (15–47) | 35 (15–47) | 35 (15–47) | 35 (15–47) | 0.159 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Jo, T.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.; Jeong, W. Efficacy of Classic Ear Molding for Neonatal Ear Deformity: Case Series and Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195751
Kim J, Jo T, Choi J, Kim J, Jeong W. Efficacy of Classic Ear Molding for Neonatal Ear Deformity: Case Series and Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195751
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jeonghoon, Taehee Jo, Jaehoon Choi, Junhyung Kim, and Woonhyeok Jeong. 2022. "Efficacy of Classic Ear Molding for Neonatal Ear Deformity: Case Series and Literature Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195751
APA StyleKim, J., Jo, T., Choi, J., Kim, J., & Jeong, W. (2022). Efficacy of Classic Ear Molding for Neonatal Ear Deformity: Case Series and Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195751





