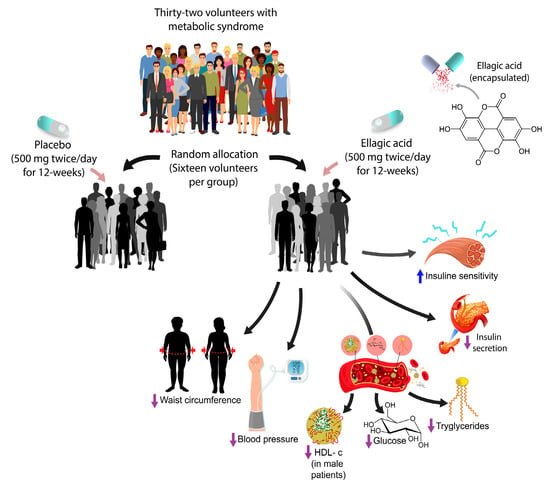
Ellagic Acid Effect on the Components of Metabolic Syndrome, Insulin Sensitivity and Insulin Secretion: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Study Variables
2.4. Randomization
2.5. Pharmacological Intervention
2.6. Blinding
2.7. Procedures
2.7.1. Clinical Determinations
2.7.2. Laboratory Determinations
2.7.3. Calculations
2.8. Follow-Up for Treatment Adherence
2.9. Ethical Considerations
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
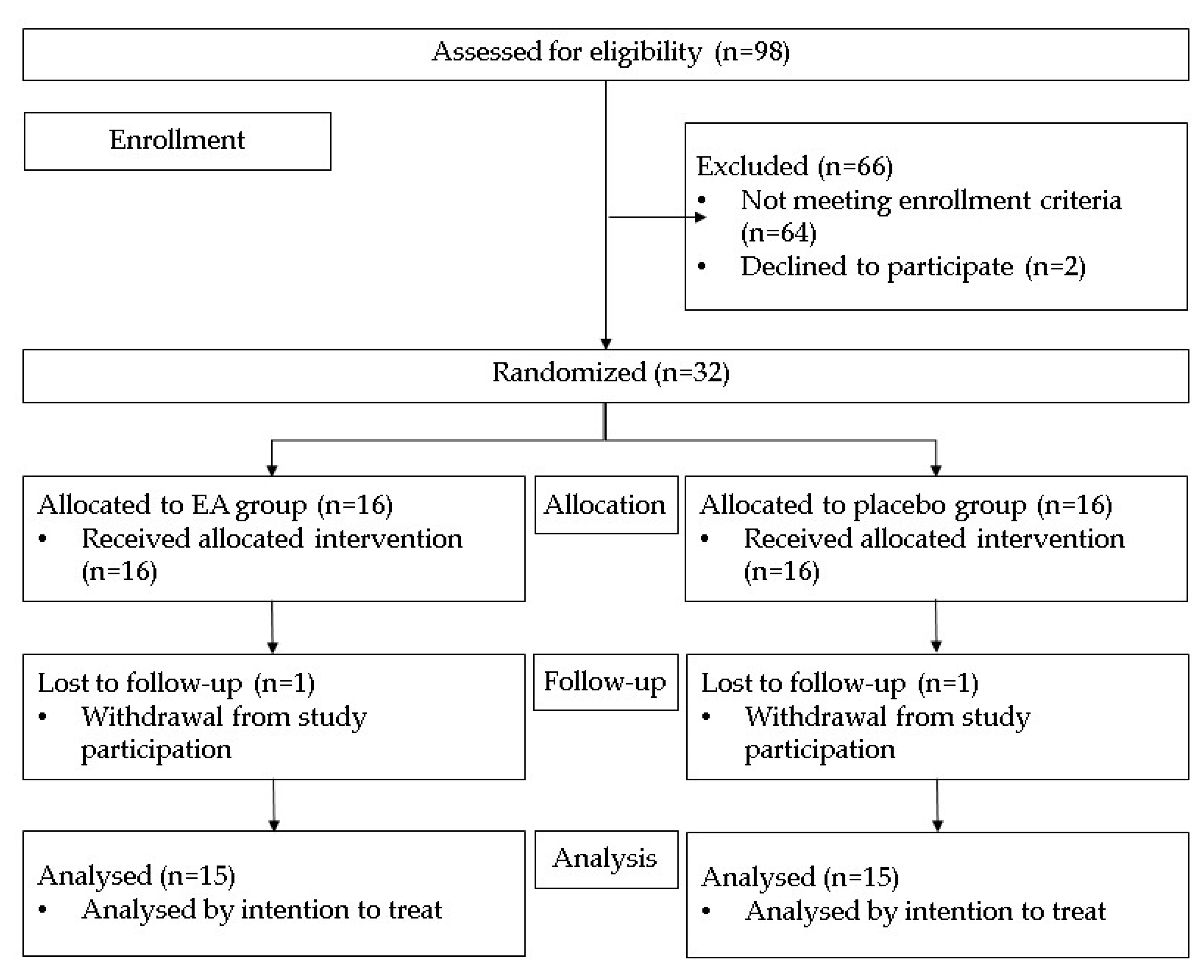
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Clinical Results
3.2.1. Primary Outcomes
3.2.2. Secondary Outcomes
3.3. Laboratory Results
3.3.1. Primary Outcomes
3.3.2. Secondary Outcomes
3.4. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Abdominal Obesity
4.2. Arterial Hypertension
4.3. Plasma Glucose
4.4. Insulin Sensitivity and Secretion
4.5. Triglicerides
4.6. HDL-c
4.7. Uric Acid
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Zerdan, M.B.; Allam, S.; Zerdan, M.B.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic syndrome: Updates on pathophysiology and management in 2021. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, P.; Sato, W.; Reungjui, S.; Heinig, M.; Gersch, M.; Sautin, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Johnson, R.J. Uric acid, the metabolic syndrome, and renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, S165–S168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podkowińska, A.; Formanowicz, D. Chronic kidney disease as oxidative stress- and inflammatory-mediated cardiovascular disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M. Drug therapy of the metabolic syndrome: Minimizing the emerging crisis in polypharmacy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubiak, G.K.; Osadnik, K.; Lejawa, M.; Osadnik, T.; Goławski, M.; Lewandowski, P.; Pawlas, N. “Obesity and insulin resistance” Is the component of the metabolic syndrome most strongly associated with oxidative stress. Antioxidants 2021, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzak, M.; Stanek, A.; Jakubiak, G.K.; Cholewka, A.; Cieślar, G. Arterial stiffness assessment by pulse wave velocity in patients with metabolic syndrome and its components: Is it a useful tool in clinical practice? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, M.; Zatterale, F.; Naderi, J.; Parrillo, L.; Formisano, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Adipose tissue dysfunction as determinant of obesity-associated metabolic complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, J.L.; Giner, R.M.; Marín, M.; Recio, C. A pharmacological update of ellagic acid. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 1068–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, M.; Foroughi, F.; Hashemipour, S.; Nooshabadi, M.R.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Nezhad, B.A.; Haghighian, H.K. Randomized double-blind clinical trial examining the Ellagic acid effects on glycemic status, insulin resistance, antioxidant, and inflammatory factors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Lalooha, F.; Nooshabadi, M.R.; Dashti, F.; Kavianpour, M.; Haghighian, H.K. Randomized double blind clinical trial evaluating the Ellagic acid effects on insulin resistance, oxidative stress and sex hormones levels in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome. J. Ovarian Res. 2021, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino-Wakagi, Y.; Yoshimura, Y.; Uzawa, Y.; Zaima, N.; Moriyama, T.; Kawamura, Y. Ellagic acid in pomegranate suppresses resistin secretion by a novel regulatory mechanism involving the degradation of intracellular resistin protein in adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulose, N.; Prasad, V.; Haridas, P.A.N.; Gopalakrishnapillai, A. Ellagic acid stimulates glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and C2C12 myotubes by AMP activated protein kinase mediated pathway. J. Diabetes Metab. 2011, 25, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, S.K.; Ward, L.; Brown, L. Ellagic acid attenuates high-carbohydrate, high-fat diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, L.; Ran, X.; Long, M.; Zhang, M.; Tao, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Halmurati, U.; et al. Ellagic acid reduces adipogenesis through inhibition of differentiation-prevention of the induction of Rb phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 287534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ieda, A.; Wada, M.; Moriyasu, Y.; Okuno, Y.; Zaima, N.; Moriyama, T. Ellagic acid suppresses ApoB secretion and enhances ApoA-1 secretion from human hepatoma cells, HepG2. Molecules 2021, 26, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Nagaoka, S. Ellagic acid affects mRNA expression levels of genes that regulate cholesterol metabolism in HepG2 cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkban, T.; Boonprom, P.; Bunbupha, S.; Welbat, J.U.; Kukongviriyapan, U.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Pakdeechote, P.; Prachaney, P. Ellagic acid prevents L-NAME-induced hypertension via restoration of eNOS and p47phox expression in rats. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5265–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyr, A.R.; Huckaby, L.V.; Shiva, S.S.; Zuckerbraun, B.S. Nitric oxide and endothelial dysfunction. Crit. Care Clin. 2020, 36, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaki, M.; Umemura, T.; Maeda, M.; Ishii, Y.; Okamura, T.; Inoue, T.; Kuroiwa, Y.; Hirose, M.; Nishikawa, A. Safety assessment of ellagic acid, a food additive, in a subchronic toxicity study using F344 rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, F.; Yu, H.; Li, X.; Dong, W.; Lin, R.; Liu, Q. Chronic administration of ellagic acid improved the cognition in middle-aged overweight men. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 43, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiojima, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Akanuma, M. Effect of ellagic acid on body fat and triglyceride reduction in healthy overweight volunteers: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel group study. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2020, 10, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J.; Grundy, S.M. The IDF consensus worldwide definition of the metabolic syndrome. Int. Diabetes Fed. 2006. Available online: https://www.idf.org/component/attachments/attachments.html?id=705&task=download (accessed on 20 July 2018).
- Unger, T.; Borghi, C.; Charchar, F.; Khan, N.A.; Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Ramirez, A.; Schlaich, M.; Stergiou, G.S.; Tomaszewski, M.; et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1334–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumvoll, M.; Van-Haeften, T.; Fritsche, A.; Gerich, J. Oral glucose tolerance test indexes for insulin sensitivity and secretion based on various availabilities of sampling times. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 796–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlTamimi, J.Z.; Alshammari, G.M.; AlFaris, N.A.; Alagal, R.I.; Aljabryn, D.H.; Albekairi, N.A.; Alkhateeb, M.A.; Yahya, M.A. Ellagic acid protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in streptozotocin-diabetic rats by activating AMPK. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; De Fronzo, R.A. Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: Comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonvecchio-Arenas, A.; Fernández-Gaxiola, A.C.; Plazas-Belausteguigoitia, M.; Kaufer-Horwitz, M.; Pérez-Lizaur, A.B.; Rivera-Dommarco, J.A. Guías Alimentarias y de Actividad Física en Contexto de Sobrepeso y Obesidad en la Población Mexicana; Academia Nacional de Medicina de México: Mexico City, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- World Medical Association. Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 27, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Rodríguez, A.M.; González-Ortiz, M.; Martínez-Abundis, E.; Acuña-Ortega, N. Effect of ursolic acid on metabolic syndrome, insulin sensitivity, and inflammation. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, A.; Cash, K.C.; Champagne, C.M.; Gupta, A.K.; Boston, R.; Beyl, R.A.; Johnson, W.D.; Cefalu, W.T. Blueberries improve endothelial function, but not blood pressure, in adults with metabolic syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutrients 2015, 7, 4107–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudish, L.I.; Reusch, J.E.; Sussel, L. β Cell dysfunction during progression of metabolic syndrome to type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4001–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasanta, D.; Htun, K.T.; Pan, J.; Montree Tungjai, M.; Kaewjaeng, S.; Chancharunee, S.; Tima, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kæwkhao, J.; Kothan, S. Waist circumference and BMI are strongly correlated with MRI-derived fat compartments in young adults. Life 2021, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMarco, V.G.; Aroor, A.R.; Sowers, J.R. The pathophysiology of hypertension in patients with obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flack, J.; Adekola, B. Blood pressure and the new ACC/AHA hypertension guidelines. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 30, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivasi, G.; Rafanelli, M.; Mossello, E.; Brignole, M.; Ungar, A. Drug-related orthostatic hypotension: Beyond anti-hypertensive medications. Drugs Aging 2020, 37, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.F.; Carpentier, A.C.; Pereira, S.; Hahn, M.; Giacca, A. Direct and indirect control of hepatic glucose production by insulin. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgerton, D.S.; Kraft, G.; Smith, M.; Farmer, B.; Williams, P.E.; Coate, K.C.; Printz, R.L.; O’Brien, R.M.; Cherrington, A.D. Insulin’s direct hepatic effect explains the inhibition of glucose production caused by insulin secretion. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e91863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakis, E.; Stravodimos, G.A.; Kantsadi, A.L.; Chatzileontiadou, D.S.M.; Skamnaki, V.T.; Leonidas, D.D. Natural flavonoids as antidiabetic agents. The binding of gallic and ellagic acids to glycogen phosphorylase b. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudak, S.; Huber, P.; Lamprinou, A.; Fritsche, L.; Stefan, N.; Peter, A.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Fritsche, A.; Heni, M.; Wagner, R. Reproducibility and discrimination of different indices of insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Liu, H.; Yu, J.; He, S.; Li, P.; Ma, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Ping, F.; Li, W.; et al. Triglyceride is independently correlated with insulin resistance and islet beta cell function: A study in population with different glucose and lipid metabolism states. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormazabal, V.; Nair, S.; Elfeky, O.; Aguayo, C.; Salomon, C.; Zuñiga, F.A. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, D.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Albert, M.A.; Buroker, A.B.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Hahn, E.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; Khera, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; McEvoy, J.W.; et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: Executive summary: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 140, e563–e595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Guo, Y.; Wu, R.; Shao, T.; Long, J.; Yu, B.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. New insight into metformin-induced cholesterol-lowering effect crosstalk between glucose and cholesterol homeostasis via ChREBP (Carbohydrate-Responsive Element-Binding Protein)-mediated PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9) regulation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, e208–e223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Miranda, J.A.; Almeida, G.G.; Martins, R.I.L.; Cunha, M.B.; Belo, V.A.; dos Santos, J.E.T.; Mourão-Júnior, C.A.; Lanna, C.M.M. O papel do ácido úrico na resistência insulínica em crianças e adolescentes com obesidade [The role of uric acid in the insulin resistance in children and adolescents with obesity]. Rev. Paul Pediatr. 2015, 33, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Cheng, J.D. Uric acid and cardiovascular disease: An update from molecular mechanism to clinical perspective. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 582680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.R.; Liu, H.R.; Hu, D.; Fan, M.S.; Wang, M.Y.; An, M.F.; Zhao, Y.L.; Xiang, Z.M.; Sheng, J. Ellagic acid exerts beneficial effects on hyperuricemia by inhibiting xanthine oxidase and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 12741–12752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdis, A.; Masi, S.; Casiglia, E.; Tikhonoff, V.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Ungar, A.; Rivasi, G.; Salvetti, M.; Barbagallo, C.M.; Bombelli, M.; et al. Identification of the Uric Acid Thresholds Predicting an Increased Total and Cardiovascular Mortality Over 20 Years. Hypertension 2020, 75, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.-C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
| Selection Criteria |
|---|
| Inclusion criteria Male and female 30 to 59 years old Diagnosis of MetS according to the International Diabetes Federation criteria [22] Signed informed consent |
| Exclusion criteria Prior diagnosis of liver, kidney, pancreas, heart, or thyroid disease T2DM or arterial hypertension History of alcoholism, drug abuse or tobacco use SBP ≥1 40 mmHg and/or DBP ≥90 mmHg Body mass index ≥35.0 kg/m2 Triglycerides ≥ 5.7 mmol/L FPG ≥ 7.0 mmol/L LDL-c > 4.9 mmol/L Body weight variability ≥ 5% throughout the prior last three months Suspected or confirmed pregnancy Lactation Known allergy to any of the interventions Impossibility to swallow capsules Hormonal contraceptive or replacement therapy Physical activity < 3 or >5 metabolic equivalents Pharmacological, dietary, or herbal therapy in the last three months before the trial. |
| Elimination criteria Withdrawal of informed consent Intolerance to EA or placebo Loss of follow-up Adherence to treatment < 80% |
| Placebo | Ellagic Acid | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | n = 16 | Week 12 | n = 15 | Baseline, | n = 16 | Week 12 | n = 15 | p *** | |
| Mean | (SD) | Mean | (SD) | Mean | (SD) | Mean | (SD) | ||
| MetS diagnosis criteria | |||||||||
| WC, cm | ♂101.4 | (1.1) | ♂ 101.8 | (1.2) | ♂102.2 | (4.2) | ♂99.5 | (3.2) * | 0.010 |
| ♀ 95.5 | (10.1) | ♀ 96.70 | (10.7) | ♀ 99.8 | (6.7) | ♀ 96.0 | (4.7) ** | 0.011 | |
| SBP, mmHg | 112.0 | (10.0) | 112.5 | (6.8) | 118.1 | (10.5) | 113.7 | (7.8) ** | 0.011 |
| DBP, mmHg | 74.0 | (5.6) | 74.3 | (5.5) | 77.8 | (7.8) | 75.2 | (5.8) ** | 0.013 |
| FPG, mmol/L | 6.2 | (0.6) | 6.4 | (0.6) | 6.5 | (0.5) | 5.7 | (0.6) ** | 0.001 |
| TG, mmol/L | 2.7 | (0.8) | 3.1 | (1.1) * | 2.8 | (1.1) | 2.1 | (0.7) ** | 0.001 |
| HDL-c, mmol/L | ♂ 0.7 | (0.1) | ♂ 0.7 | (0.1) | ♂ 0.7 | (0.2) | ♂ 0.8 | (0.2) * | 0.019 |
| ♀ 0.8 | (0.2) | ♀ 0.8 | (0.2) | ♀ 0.8 | (0.2) | ♀ 0.9 | (0.2) | 0.175 | |
| Insulin sensitivity | |||||||||
| Matsuda index | 1.8 | (0.4) | 1.6 | (0.5) | 1.7 | (0.8) | 3.1 | (1.7) ** | 0.001 |
| Insulin secretion | |||||||||
| 1p Stumvoll index | 1494 | (679) | 1568 | (831) | 1573 | (714) | 1191 | (614) * | 0.011 |
| Ratio AUC | 72 | (31) | 73 | (31) | 69 | (31) | 58 | (32) * | 0.091 |
| Placebo | Ellagic Acid | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | n = 16 | 12-w | n = 15 | Baseline | n = 16 | 12-w | n = 15 | ||
| Mean | (SD) | Mean | (SD) | Mean | (SD) | Mean | (SD) | p *** | |
| Clinical outcomes | |||||||||
| BW, kg | 77.6 | (3.4) | 78.5 | (3.8) | 79.9 | (7.1) | 78.6 | (6.6) * | 0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 30.8 | (1.6) | 31.2 | (2.0) | 30.6 | (2.6) | 30.1 | (2.8) * | 0.001 |
| Laboratory outcomes | |||||||||
| 2h-PG, mmol/L | 8.8 | (1.8) | 9.7 | (1.8) | 9.4 | (1.6) | 7.9 | (1.6) ** | 0.001 |
| Glucose AUC, mmol/L/min | 1150 | (198) | 1278 | (176) * | 1219 | (195) | 1089 | (159) ** | 0.001 |
| FPI, pmol/L | 133.4 | (38.4) | 142.7 | (50.8) | 153.1 | (66.7) | 93.3 | (43.0) ** | 0.001 |
| Insulin AUC pmol/L/min | 80593 | (32748) | 83871 | (41430) * | 92678 | (38379) | 63447 | (37072) ** | 0.001 |
| TC, mmol/L | 5.0 | (0.9) | 5.1 | (0.9) | 5.1 | (1.0) | 4.7 | (1.0) | 0.073 |
| Uric acid, µmol/L | 336.1 | (66.3) | 348.9 | (63.7) | 357.3 | (68.4) | 344.2 | (53.1) * | 0.002 |
| Placebo Group | EA Group | Mean Difference | 95% CI | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| MetS diagnosis criteria | ||||||
| WC, cm | 0.200 | −2.533 | 2.733 | 1.537 | 3.930 | 0.010 |
| SBP, mmHg | −0.067 | −4.933 | 4.867 | 1.256 | 8.478 | 0.011 |
| DBP, mmHg | −0.400 | −3.133 | 2.733 | 0.611 | 4.855 | 0.013 |
| FPG, mmol/L | 0.212 | −0.792 | 1.004 | 0.615 | 1.393 | 0.001 |
| TG, mmol/L | 0.480 | −0.733 | 1.213 | 0.608 | 1.818 | 0.001 |
| HDL-c, mmol/L | −0.066 | 0.054 | −0.120 | −0.190 | −0.049 | 0.015 |
| Insulin sensitivity | ||||||
| Matsuda index | −0.213 | 1.354 | −1.566 | −2.201 | −0.932 | 0.001 |
| Insulin secretion | ||||||
| 1p Stumvoll index | 66.005 | −375.195 | 441.200 | 107.327 | 775.072 | 0.011 |
| Ratio AUC | −1.094 | −11.539 | 10.444 | −1.798 | 22.687 | 0.091 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hidalgo-Lozada, G.M.; Villarruel-López, A.; Martínez-Abundis, E.; Vázquez-Paulino, O.; González-Ortiz, M.; Pérez-Rubio, K.G. Ellagic Acid Effect on the Components of Metabolic Syndrome, Insulin Sensitivity and Insulin Secretion: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195741
Hidalgo-Lozada GM, Villarruel-López A, Martínez-Abundis E, Vázquez-Paulino O, González-Ortiz M, Pérez-Rubio KG. Ellagic Acid Effect on the Components of Metabolic Syndrome, Insulin Sensitivity and Insulin Secretion: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195741
Chicago/Turabian StyleHidalgo-Lozada, Gladys Maribel, Angélica Villarruel-López, Esperanza Martínez-Abundis, Olga Vázquez-Paulino, Manuel González-Ortiz, and Karina Griselda Pérez-Rubio. 2022. "Ellagic Acid Effect on the Components of Metabolic Syndrome, Insulin Sensitivity and Insulin Secretion: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195741
APA StyleHidalgo-Lozada, G. M., Villarruel-López, A., Martínez-Abundis, E., Vázquez-Paulino, O., González-Ortiz, M., & Pérez-Rubio, K. G. (2022). Ellagic Acid Effect on the Components of Metabolic Syndrome, Insulin Sensitivity and Insulin Secretion: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195741