The Distribution Pattern of First-Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drug Concentrations between the Blood and the Vertebral Focus of Spinal Tuberculosis Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.1.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Measures and Statistics
2.2.1. Sample Collection and Processing
2.2.2. Apparatus
2.2.3. HPLC–MS/MS Condition
2.2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. The Results of Anti-Tuberculosis Drug Concentrations in Each Group
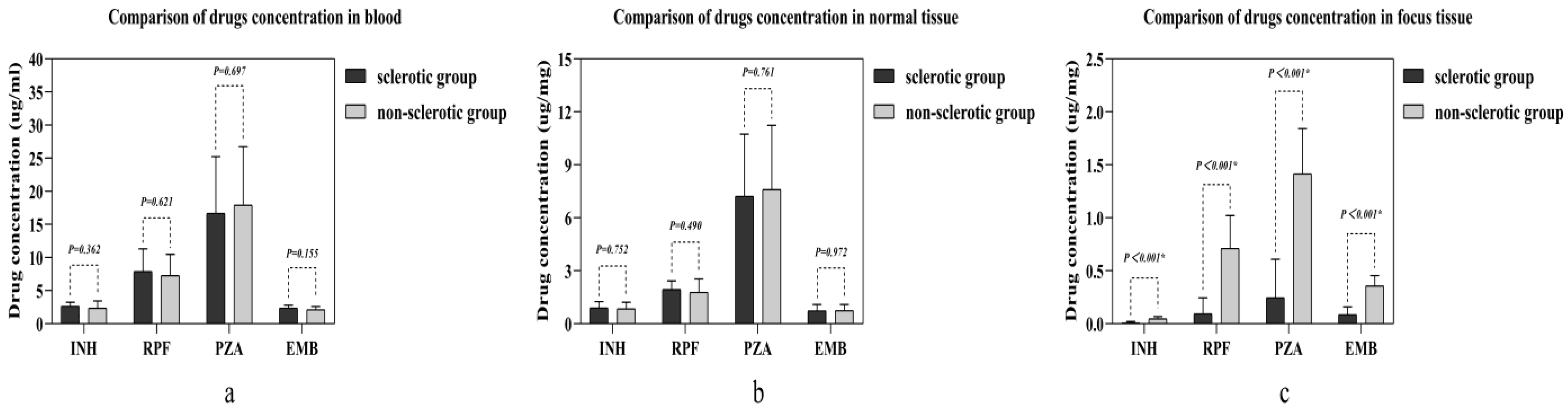
3.3. Comparison of Drug Concentrations in Different Samples between the Two Groups
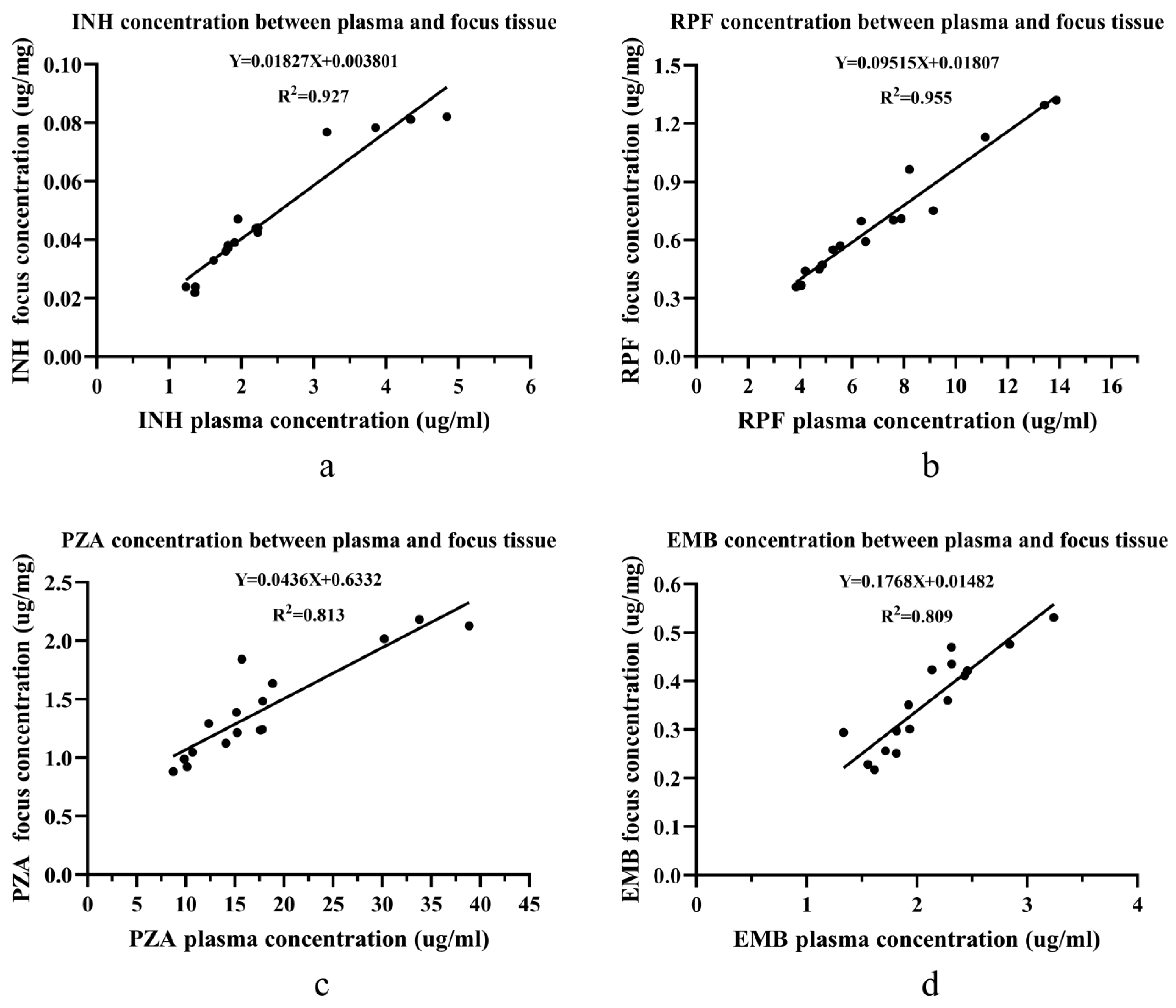
The Linear Relationship of Drug Concentrations in the Non-sclerotic Bone Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daniel, T.M. The history of tuberculosis. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, R.N.; Ben, H.M. Spinal tuberculosis: Review of current management. Bone Jt. J. 2018, 100, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Hao, D. Current Study of Medicinal Chemistry for Treating Spinal Tuberculosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 5201–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boachie, A.O.; Papadopoulos, E.C.; Pellisé, F.; Cunningham, M.E.; Perez-Grueso, F.S.; Gupta, M.; Lonner, B.; Paonessa, K.; King, A.; Sacramento, C.; et al. Late treatment of tuberculosis-associated kyphosis: Literature review and experience from a SRS-GOP site. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassman, P.M.; Muzykantov, V.R. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Properties of Drug Delivery Systems. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, Y. Research and progress of PK/PD for anti-tuberculosis drugs. Chin. J. Antituberc. 2019, 41, 700–704. [Google Scholar]
- Du, B.; Yan, B.; Xu, M.; Chen, D. Studies on the method of Microbioassay and Inactivation Type of Isoniazid in Serum. Chin. J. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 1981, 4, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J. Clinical Pharmacology; People’s Health Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 692–700. [Google Scholar]
- Hashida, M. Role of pharmacokinetic consideration for the development of drug delivery systems: A historical overview. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 157, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Zhang, T.; Yu, X.; Dong, W.; Lan, T.; Fan, J.; Xue, Y.; Wang, F.; Dong, L.; Qin, S.; et al. Bone penetration of linezolid in osteoarticular tuberculosis patients of China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 103, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ge, Z.; Jin, W.; Qiao, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhao, H.; Lin, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, W. Treatment of spinal tuberculosis with ultrashort-course chemotherapy in conjunction with partial excision of pathologic vertebrae. Spine J. 2007, 7, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, M. Measurement of the concentration of three antituberculosis drugs in the focus of spinal tuberculosis. Eur. Spine J. 2008, 17, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhu, Q.; Jiang, J. Distribution of three antituberculous drugs and their metabolites in different parts of pathological vertebrae with spinal tuberculosis. Spine 2011, 36, E1290–E1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; An, J.; Shu, W.; Huo, F.; Chu, N.; Gao, M.; Qin, S.; Huang, H.; Chen, X.; Xu, S. Epidemiology of Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis among Inpatients, China, 2008–2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, S.; Khandelwal, G. Drug therapy in spinal tuberculosis. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Kong, L.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hao, D. Recurrent complex spinal tuberculosis accompanied by sinus tract formation: Causes of recurrence and clinical treatments. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Ou, Y.-S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Luo, W.; He, B.; Peng, Q.-Q.; Hu, J.-Y. One stage posterior debridement, non-structural bone graft in the surgical treatment of single segment thoracic tuberculosis: A retrospective single-center cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2019, 65, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ouyang, D. Opportunities and challenges of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling in drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 2100–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Dong, W.; Lan, T.; Fan, J.; Wen, S.; Zhang, T.; Qin, S.; Guo, A. Penetration of linezolid into bone tissue 24 h after administration in patients with multidrug-resistant spinal tuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Neradi, D.; Sherry, B.; Gaurav, A.; Dhatt, S.S. Tuberculosis of the spine and drug resistance: A review article. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 45, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Yang, G.T.; Lin, S.Z.; Wang, X.F.; Xiao, C.Z. Modern Tuberculosis; People’s Health Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 510–527. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Musbahi, O.; White, V.L.C.; Montgomery, A.S. Spinal Tuberculosis: A Literature Review. JBJS Rev. 2019, 7, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K. Tuberculosis of the spine: A fresh look at an old disease. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2010, 92, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotgiu, G.; Centis, R.; Migliori, G.B. Tuberculosis management and determinants of recurrence. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2016, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Ge, Q.P.; Tian, X.Z.; Gao, W.; Jia, Z. Treatment and recurrence on re-treatment tuberculosis patients: A randomized clinical trial and 7-year perspective cohort study in China. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIvor, A.; Koornhof, H.; Kana, B.D. Relapse, re-infection and mixed infections in tuberculosis disease. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75, ftx020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Characteristics | Sclerotic Group (n = 15) | Non-Sclerotic Group (n = 16) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 45.87 ± 19.48 | 50.75 ± 17.09 | 0.463 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.37 ± 2.81 | 20.70 ± 3.09 | 0.630 |
| Sex (n, %) | 0.870 | ||
| Female | 7 (46.7%) | 7 (43.8%) | |
| Male | 8 (53.3%) | 9 (56.2%) | |
| Site of infectious focus (n) | 0.886 | ||
| Thoracic | 9 | 10 | |
| Lumbar | 6 | 6 | |
| Operation time (min) | 191.20 ± 29.98 | 185.19 ± 27.64 | 0.566 |
| Operation blood loss (mL) | 343.93 ± 174.62 | 330.50 ± 208.43 | 0.859 |
| Course of disease (month) | 5.57 ± 4.15 | 6.13 ± 3.14 | 0.730 |
| Administration time (day) | 25.80 ± 3.97 | 27.19 ± 4.22 | 0.354 |
| Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs | Plasma (μg/mL) | Healthy Bone Tissue (μg/mg) | Focus Tissue (μg/mg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-S Group | S Group | p-Value | Non-S group | S Group | p-Value | Non-S Group | S Group | p-Value | |
| Isoniazid | 2.356 ± 1.101 | 2.656 ± 0.609 | 0.362 | 0.849 ± 0.371 | 0.891 ± 0.361 | 0.752 | 0.047 ± 0.021 | 0.010 ± 0.011 | <0.001 * |
| Rifampin | 7.287 ± 3.197 | 7.884 ± 3.449 | 0.621 | 1.776 ± 0.772 | 1.940 ± 0.487 | 0.490 | 0.711 ± 0.311 | 0.094 ± 0.150 | <0.001 * |
| Pyrazinamide | 17.928 ± 8.838 | 16.699 ± 8.536 | 0.697 | 7.611 ± 3.638 | 7.215 ± 3.531 | 0.761 | 1.415 ± 0.427 | 0.245 ± 0.364 | <0.001 * |
| Ethambutol | 2.107 ± 0.496 | 2.358 ± 0.457 | 0.155 | 0.738 ± 0.352 | 0.734 ± 0.361 | 0.972 | 0.358 ± 0.098 | 0.086 ± 0.074 | <0.001 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, G.; Qin, W.; Du, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xiong, T.; Zhao, D.; Ou, Y. The Distribution Pattern of First-Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drug Concentrations between the Blood and the Vertebral Focus of Spinal Tuberculosis Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5409. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185409
Jiang G, Qin W, Du X, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Xiong T, Zhao D, Ou Y. The Distribution Pattern of First-Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drug Concentrations between the Blood and the Vertebral Focus of Spinal Tuberculosis Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(18):5409. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185409
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Guanyin, Wanyuan Qin, Xing Du, Ye Zhang, Muzi Zhang, Tuotuo Xiong, Dezhang Zhao, and Yunsheng Ou. 2022. "The Distribution Pattern of First-Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drug Concentrations between the Blood and the Vertebral Focus of Spinal Tuberculosis Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 18: 5409. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185409
APA StyleJiang, G., Qin, W., Du, X., Zhang, Y., Zhang, M., Xiong, T., Zhao, D., & Ou, Y. (2022). The Distribution Pattern of First-Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drug Concentrations between the Blood and the Vertebral Focus of Spinal Tuberculosis Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(18), 5409. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185409




