Plasma Levels of Interleukins 36α, 36β, and 37 in Patients with Psoriasis and Their Correlation with Disease Activity Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Assessment of IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-37 Concentrations in the Plasma of Patients with Psoriasis and Control Subjects
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
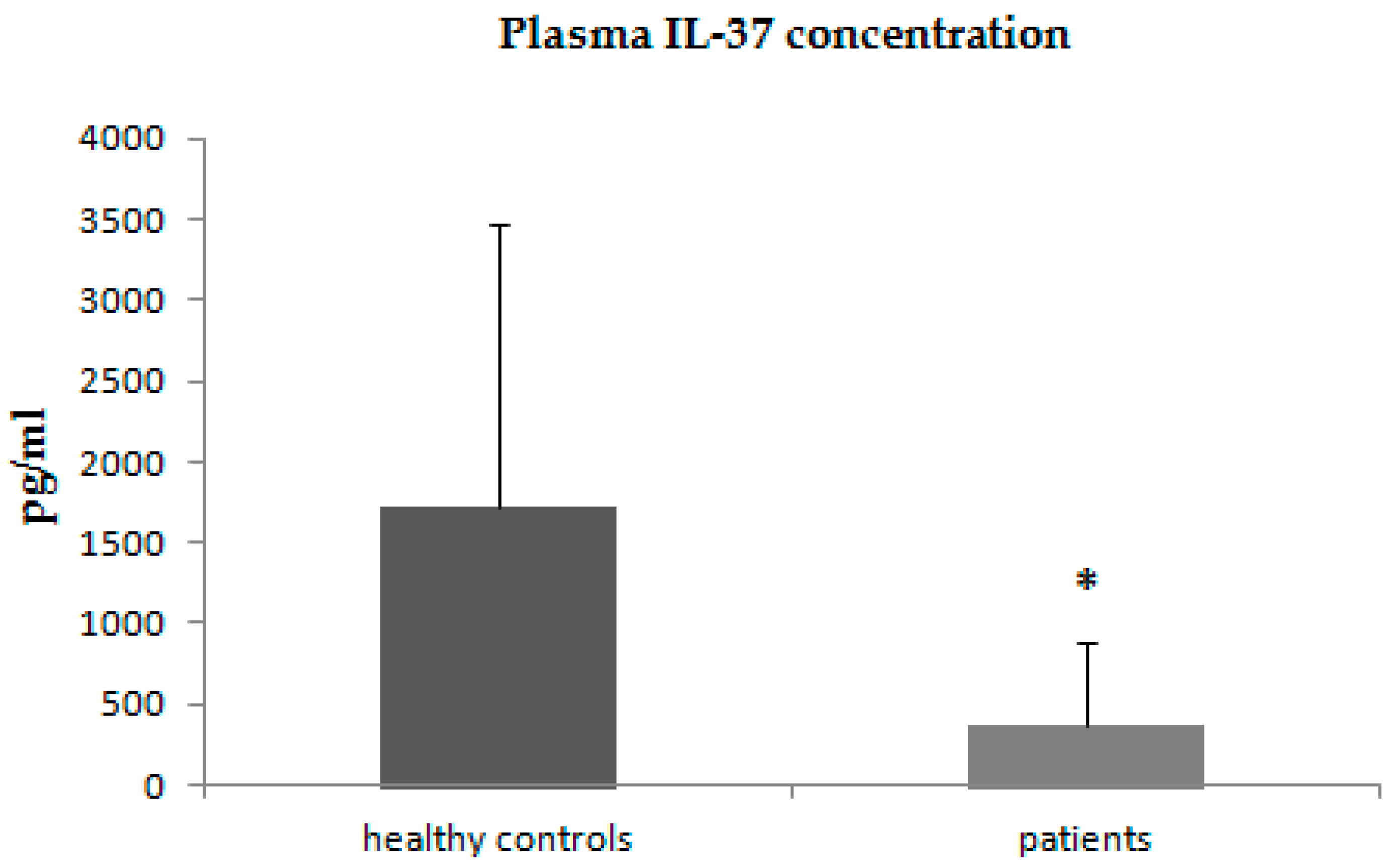
3.1. Analysis of IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-37 Concentrations in the Plasma of Patients with Psoriasis and Control Subjects
3.2. Correlations between Plasma Concentrations of IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-37 and Clinical Parameters in Patients with Psoriasis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Springate, D.; Parisi, R.; Kontopantelis, E.; Reeves, D.; Griffiths, C.; Ashcroft, D. Incidence, prevalence and mortality of patients with psoriasis: A U.K. population-based cohort study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapp, S.R.; Feldman, S.R.; Exum, M.L.; Fleischer, A.B., Jr.; Reboussin, D.M. Psoriasis causes as much disability as other major medical diseases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1999, 41 Pt 1, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauchli, Y.; Jick, S.; Miret, M.; Meier, C. Psoriasis and risk of incident myocardial infarction, stroke or transient ischaemic attack: An inception cohort study with a nested case-control analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 160, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakkee, M.; Herings, R.M.; Nijsten, T. Psoriasis may not be an independent risk factor for acute ischemic heart disease hospitalizations: Results of a large population-based Dutch cohort. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowlatshahi, E.A.; Kavousi, M.; Nijsten, T.; Ikram, M.A.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.H.; Wakkee, M. Psoriasis is not associated with atherosclerosis and incident cardiovascular events: The Rotterdam Study. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2347–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Harskamp, C.T.; Armstrong, E.J. Psoriasis and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexis, A.F.; Blackcloud, P. Psoriasis in skin of color: Epidemiology, genetics, clinical presentation, and treatment nuances. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2014, 7, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, N.; Quaranta, M.; Prescott, N.; Allen, M.; Smith, R.; Burden, A.D.; Worthington, J.; Griffiths, C.; Mathew, C.; Barker, J.; et al. Psoriasis is associated with pleiotropic susceptibility loci identified in type II diabetes and Crohn disease. J. Med. Genet. 2008, 45, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachakonda, T.D.; Schupp, C.W.; Armstrong, A.W. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Wang, T.; Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C.; Tian, S.; Liu, Y.; Peng, G.; Zhou, J.; Xue, S.; et al. Prevalence of psoriasis in China: A population-based study in six cities. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2012, 22, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, A.L.; Picciani, B.L.S.; Azulay-Abulafia, L.; Fausto-Silva, A.K.; Almeida, P.N.; Cunha, K.S.G.; Dias, E.P.; Carneiro, S. Evaluation of ICAM-1 expression and vascular changes in the skin of patients with plaque, pustular, and erythrodermic psoriasis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, C.E.; Barker, J.N.W.N. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet 2007, 370, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, L.; Lv, P.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qian, X.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. The role of Th17 cells in psoriasis. Immunol. Res. 2020, 68, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachen, K.L.; Greving, C.N.A.; Towne, J.E. Role of IL-36 cytokines in psoriasis and other inflammatory skin conditions. Cytokine 2022, 156, 155897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iznardo, H.; Puig, L. Exploring the Role of IL-36 Cytokines as a New Target in Psoriatic Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F. IL-36 in chronic inflammation and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 55, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, G.; Dinarello, C.A. Suppression of inflammation and acquired immunity by IL-37. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wen, X.; Hao, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; He, G.; Jiang, X. The role of IL-37 in skin and connective tissue diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 122, 109705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Tan, S.; Wu, D. IL-37 As a Potential Biotherapeutics of Inflammatory Diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2020, 21, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminara, N.; Abuabara, K.; Shin, D.; Langan, S.; Kimmel, S.; Margolis, D.; Troxel, A.; Gelfand, J. Validity of The Health Improvement Network (THIN) for the study of psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 164, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayran, Y.; Allı, N.; Yücel, Ç.; Akdoğan, N.; Turhan, T. Serum IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ levels in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: Association with disease characteristics, smoking, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020, 312, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alcantara, C.C.; Reiche, E.M.V.; Simão, A.N.C. Cytokines in psoriasis. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2021, 100, 171–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.H.; Hua, K.F.; Lin, Y.C.; Chu, C.L.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Hsu, Y.J.; Ka, S.M.; Tsai, Y.L.; Liu, F.C.; Chen, A.; et al. IL-36 Signaling Facilitates Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome and IL-23/IL-17 Axis in Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2022–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, T.; Li, M. Serum IL-36 cytokines levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with obesity, insulin resistance, and inflammation. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, M.; Zhao, S.; Le, H.T.; Wang, J.; Neurath, M.F.; Neufert, C.; Fiocchi, C.; Rieder, F. IL-36 in chronic inflammation and fibrosis-bridging the gap? J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e144336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, L.; Ferhat, M.; Salamé, E.; Robin, A.; Herbelin, A.; Gombert, J.-M.; Silvain, C.; Barbarin, A. Interleukin-1 Family Cytokines: Keystones in Liver Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oji, V.; Luger, T.A. The skin in psoriasis: Assessment and challenges. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33 (Suppl. 93), S14–S19. [Google Scholar]
- Boutet, M.A.; Bart, G.; Penhoat, M.; Amiaud, J.; Brulin, B.; Charrier, C.; Morel, F.; Lecron, J.C.; Rolli-Derkinderen, M.; Bourreille, A. Distinct expression of interleukin (IL)-36α lpha, beta and gamma, their antagonist IL-36Ra and IL-38 in psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 184, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, Y.; Ma, H.-L.; Ramon, H.E.; Napierata, L.; Small, C.; O’Toole, M.; Young, D.A.; Fouser, L.A.; Nickerson-Nutter, C.; Collins, M.; et al. Inter-Regulation of Th17 Cytokines and the IL-36 Cytokines In Vitro and In Vivo: Implications in Psoriasis Pathogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2428–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehat, M.; Talaei, R.; Dadgostar, E.; Nikoueinejad, H.; Akbari, H. Evaluating Serum Levels of IL-33, IL-36, IL-37 and Gene Expression of IL-37 in Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 17, 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Madonna, S.; Girolomoni, G.; Dinarello, C.A.; Albanesi, C. The Significance of IL-36 Hyperactivation and IL-36R Targeting in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yu, X.; Wu, C.; Jin, H. IL-36γ inhibits differentiation and induces inflammation of keratinocyte via Wnt signaling pathway in psoriasis. Int. J. Med Sci. 2017, 14, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaff, C.M.; Marquardt, Y.; Fietkau, K.; Baron, J.M.; Lüscher, B. The psoriasis-associated IL-17A induces and cooperates with IL-36 cytokines to control keratinocyte differentiation and function. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohko, K.; Nakajima, K.; Kataoka, S.; Takaishi, M.; Sano, S. IL-36 Signaling Is Essential for Psoriatic Inflammation through the Augmentation of Innate Immune Responses. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigne, S.; Palmer, G.; Lamacchia, C.; Martin, P.; Talabot-Ayer, D.; Rodriguez, E.; Ronchi, F.; Sallusto, F.; Dinh, H.; Sims, J.; et al. IL-36R ligands are potent regulators of dendritic and T cells. Blood 2011, 118, 5813–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgewood, C.; Stacey, M.; Alase, A.; Lagos, D.; Graham, A.; Wittmann, M. IL-36γ has proinflammatory effects on human endothelial cells. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigne, S.; Palmer, G.; Martin, P.; Lamacchia, C.; Strebel, D.; Rodriguez, E.; Olleros, M.L.; Vesin, D.; Garcia, I.; Ronchi, F.; et al. IL-36 signaling amplifies Th1 responses by enhancing proliferation and Th1 polarization of naive CD4+ T cells. Blood 2012, 120, 3478–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Iwata, Y.; Fukushima, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Saito, K.; Ito, H.; Sugiura, M.; Akiyama, M.; Sugiura, K. Neutrophil extracellular traps are involved in enhanced contact hypersensitivity response in IL-36 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germán, B.; Wei, R.; Hener, P.; Martins, C.; Ye, T.; Gottwick, C.; Yang, J.; Seneschal, J.; Boniface, K.; Li MGermán, B.; et al. Disrupting the IL-36 and IL-23/IL-17 loop underlies the efficacy of calcipotriol and corticosteroid therapy for psoriasis. JCI Insight. 2019, 4, e123390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Pregliasco, F.; Bellomo, R.; Gallenga, C.; Caraffa, A.; Kritas, S.; Lauritano, D.; Ronconi, G. Mast Cell Cytokines IL-1, IL-33, and IL-36 Mediate Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis: A Novel Therapeutic Approach with the Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines IL-37, IL-38, and IL-1Ra. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magne, D.; Palmer, G.; Barton, J.L.; Mézin, F.; Talabot-Ayer, D.; Bas, S.; Duffy, T.; Noger, M.; Guerne, P.-A.; Nicklin, M.J.H.; et al. The new IL-1 family member IL-1F8 stimulates production of inflammatory mediators by synovial fibroblasts and articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twelves, S.; Mostafa, A.; Dand, N.; Burri, E.; Farkas, K.; Wilson, R.; Cooper, H.L.; Irvine, A.D.; Oon, H.H.; Kingo, K.; et al. Clinical and genetic differences between pustular psoriasis subtypes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, A.; Vollmer, S.; Besgen, P.; Galinski, A.; Summer, B.; Kawakami, Y.; Wollenberg, A.; Dornmair, K.; Spannagl, M.; Ruzicka, T.; et al. Unopposed IL-36 Activity Promotes Clonal CD4+ T-Cell Responses with IL-17A Production in Generalized Pustular Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ganesan, R.; Raymond, E.L.; Mennerich, D.; Woska, J.R.; Caviness, G.; Grimaldi, C.; Ahlberg, J.; Perez, R.; Roberts, S.; Yang, D.; et al. Generation and functional characterization of anti-human and anti-mouse IL-36R antagonist monoclonal antibodies. mAbs 2017, 9, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Paulsboe, S.; Wetter, J.; Salte, K.; Kannan, A.; Mathew, S.; Horowitz, A.; Gerstein, C.; Namovic, M.; Todorović, V.; et al. IL-36 receptor antagonistic antibodies inhibit inflammatory responses in preclinical models of psoriasiform dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelez, H.; Choon, S.-E.; Marrakchi, S.; Burden, A.D.; Tsai, T.-F.; Morita, A.; Turki, H.; Hall, D.B.; Shear, M.; Baum, P.; et al. Inhibition of the Interleukin-36 Pathway for the Treatment of Generalized Pustular Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahil, S.K.; Catapano, M.; Di Meglio, P.; Dand, N.; Ahlfors, H.; Carr, I.M.; Smith, C.H.; Trembath, R.C.; Peakman, M.; Wright, J.; et al. An analysis of IL-36 signature genes and individuals with IL1RL2 knockout mutations validates IL-36 as a psoriasis therapeutic target. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maçães, C.O.; Lé, A.M.; Torres, T. Generalized pustular psoriasis: The new era of treatment with IL-36 receptor inhibitors. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudloff, I.; Cho, S.X.; Lao, J.C.; Ngo, D.; McKenzie, M.; Nold-Petry, C.A.; Nold, M.F. Monocytes and dendritic cells are the primary sources of interleukin 37 in human immune cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, X.; Hu, Z.; Wei, X.; Wang, Z.; Guan, T.; Liu, N.; Liu, X.; Ye, N.; Deng, G.; Luo, C.; et al. IL-37 Ameliorates the Inflammatory Process in Psoriasis by Suppressing Proinflammatory Cytokine Production. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønholt, K.; Nielsen, A.L.-L.; Johansen, C.; Vestergaard, C.; Fauerbye, A.; López-Vales, R.; Dinarello, C.A.; Iversen, L. IL-37 Expression Is Downregulated in Lesional Psoriasis Skin. ImmunoHorizons 2020, 4, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keermann, M.; Koks, S.; Reimann, E.; Abram, K.; Erm, T.; Silm, H.; Kingo, K. Expression of IL-36 family cytokines and IL-37 but not IL-38 is altered in psoriatic skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 80, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolino, G.; Buratta, S.; Mercuri, S.R.; Pellegrino, R.M.; Urbanelli, L.; Emiliani, C.; Bertuccini, L.; Iosi, F.; Huber, V.; Brianti, P.; et al. Lipidic Profile Changes in Exosomes and Microvesicles Derived from Plasma of Monoclonal Antibody-Treated Psoriatic Patients. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 923769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameters | Patients with Psoriasis n-53 | Control Group n-31 |
|---|---|---|
| Gender M/F | 29/24 | 17/14 |
| Age [years] | 49.7 ± 17.6 | 48.5 ± 14.2 |
| Age of disease onset [years] | 34.03 ± 20.08 | - |
| Smoking | 19 | 12 |
| DLQI | 11.7 ± 8.19 | - |
| PASI | 11.28 ± 10.87 | - |
| BSA | 21.33 ± 21.18 | - |
| IL-36α | IL-36β | IL-37 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Rs | p | Rs | p | Rs | p |
| Age | −0.0195 | 0.88 | −0.1922 | 0.16 | −0.0999 | 0.47 |
| Age of disease onset | −0.1078 | 0.44 | −0.1384 | 0.32 | −0.1462 | 0.3 |
| DLQI | 0.2849 | 0.04 | 0.5389 | <0.001 | 0.1767 | 0.21 |
| PASI | 0.4268 | 0.001 | 0.4852 | <0.001 | 0.1647 | 0.23 |
| BSA | 0.3606 | 0.007 | 0.4829 | <0.001 | 0.1772 | 0.2 |
| Erythrocytes | 0.1987 | 0.36 | 0.2243 | 0.3 | 0.1399 | 0.52 |
| Hemoglobin | 0.439 | 0.03 | 0.3959 | 0.06 | 0.1483 | 0.49 |
| Leukocytes | −0.3419 | 0.11 | −0.4394 | 0.03 | 0.1126 | 0.6 |
| ESR | −0.1616 | 0.46 | −0.068 | 0.75 | 0.0373 | 0.86 |
| CRP | −0.1302 | 0.55 | −0.186 | 0.39 | −0.0908 | 0.68 |
| AST | 0.4114 | 0.05 | 0.7832 | <0.001 | 0.3213 | 0.13 |
| ALT | 0.4519 | 0.03 | 0.4003 | 0.05 | 0.1287 | 0.55 |
| Creatinin | 0.4584 | 0.03 | 0.2678 | 0.22 | 0.3122 | 0.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Słucznowska-Głabowska, S.; Jaworska, W.; Staniszewska, M.; Tkacz, M.; Safranow, K.; Łuczkowska, K.; Zagrodnik, E.; Stecewicz, I.; Machaliński, B.; Pawlik, A. Plasma Levels of Interleukins 36α, 36β, and 37 in Patients with Psoriasis and Their Correlation with Disease Activity Parameters. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5254. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185254
Słucznowska-Głabowska S, Jaworska W, Staniszewska M, Tkacz M, Safranow K, Łuczkowska K, Zagrodnik E, Stecewicz I, Machaliński B, Pawlik A. Plasma Levels of Interleukins 36α, 36β, and 37 in Patients with Psoriasis and Their Correlation with Disease Activity Parameters. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(18):5254. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185254
Chicago/Turabian StyleSłucznowska-Głabowska, Sylwia, Weronika Jaworska, Marzena Staniszewska, Marta Tkacz, Krzysztof Safranow, Karolina Łuczkowska, Edyta Zagrodnik, Iwona Stecewicz, Bogusław Machaliński, and Andrzej Pawlik. 2022. "Plasma Levels of Interleukins 36α, 36β, and 37 in Patients with Psoriasis and Their Correlation with Disease Activity Parameters" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 18: 5254. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185254
APA StyleSłucznowska-Głabowska, S., Jaworska, W., Staniszewska, M., Tkacz, M., Safranow, K., Łuczkowska, K., Zagrodnik, E., Stecewicz, I., Machaliński, B., & Pawlik, A. (2022). Plasma Levels of Interleukins 36α, 36β, and 37 in Patients with Psoriasis and Their Correlation with Disease Activity Parameters. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(18), 5254. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185254





