Architectural Ultrasound Pennation Angle Measurement of Lumbar Multifidus Muscles: A Reliability Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
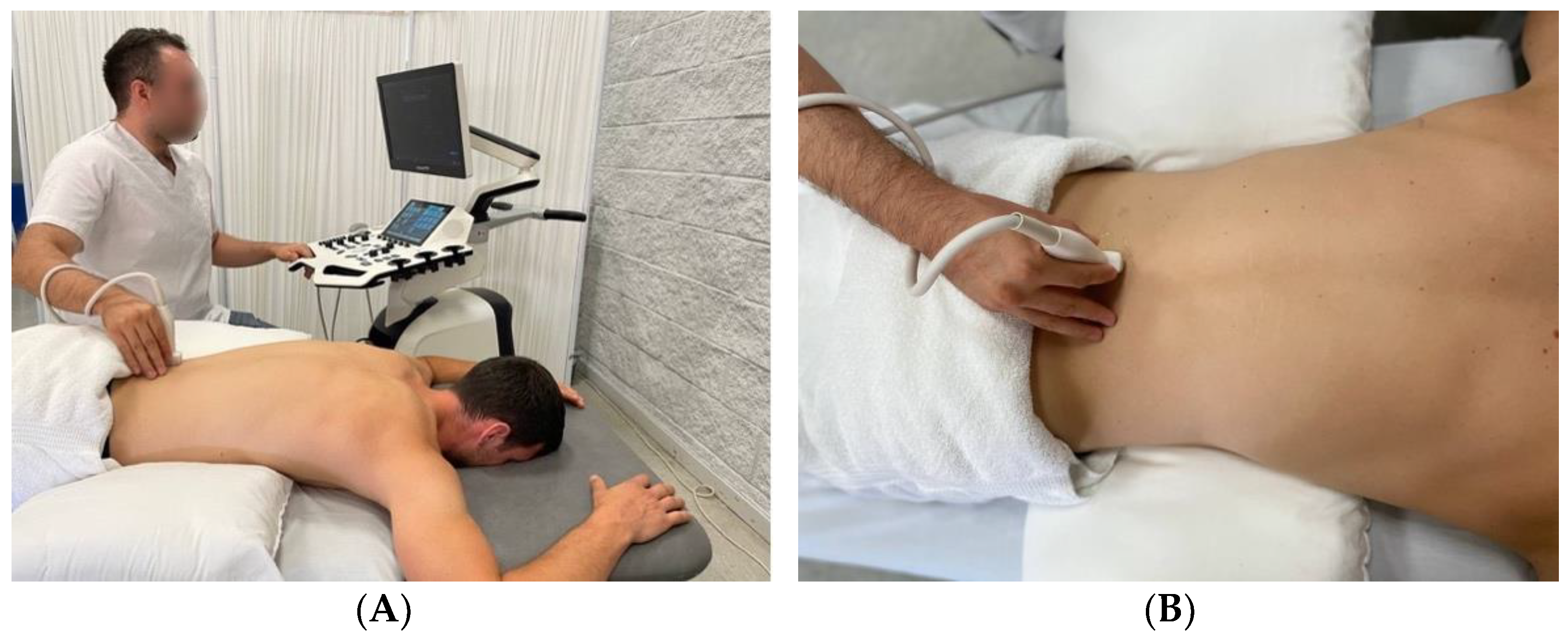
Procedure
3. Results
Reliability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perkisas, S.; Baudry, S.; Bauer, J.; Beckwée, D.; De Cock, A.-M.; Hobbelen, H.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Kasiukiewicz, A.; Landi, F.; Marco, E.; et al. Application of ultrasound for muscle assessment in sarcopenia: Towards standardized measurements. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 9, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, R.L.; Fridén, J. Functional and clinical significance of skeletal muscle architecture. Muscle Nerve 2000, 23, 1647–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hullfish, T.J.; O’Connor, K.M.; Baxter, J.R. Gastrocnemius fascicles are shorter and more pennate throughout the first month following acute Achilles tendon rupture. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchi, M.V.; Reeves, N.; Narici, M.V. Skeletal Muscle Remodeling in Response to Eccentric vs. Concentric Loading: Morphological, Molecular, and Metabolic Adaptations. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaz, M.; Kireşi, D.; Oğuz, H.; Emlik, D.; Levendoğlu, F. CT measurement of trunk muscle areas in patients with chronic low back pain. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 13, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fortin, M.; Macedo, L. Multifidus and Paraspinal Muscle Group Cross-Sectional Areas of Patients with Low Back Pain and Control Patients: A Systematic Review with a Focus on Blinding. Phys. Ther. 2013, 93, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhiar, N.; Al-Sayeagh, H.; Chan, O.; King, J.; Maffulli, N. Pennation angle of the soleus in patients with unilateral Achilles tendinopathy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2008, 30, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta-Vargas, A.I.; González-Sánchez, M. Original article: Ability to Discriminate between Healthy and Low Back Pain Sufferers Using Ultrasound During Maximum Lumbar Extension. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, M.V.; Raiteri, B.J.; Longo, S.; Sinha, S.; Narici, M.V.; Csapo, R. Muscle Architecture Assessment: Strengths, Shortcomings and New Frontiers of in Vivo Imaging Techniques. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2492–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narici, M.; Franchi, M.; Maganaris, C. Muscle structural assembly and functional consequences. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219 Pt 2, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narici, M. Human skeletal muscle architecture studied in vivo by non-invasive imaging techniques: Functional significance and applications. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Electrophysiol. Kinesiol. 1999, 9, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimstra, M.; Dowling, J.; Durkin, J.L.; MacDonald, M. The effect of ultrasound probe orientation on muscle architecture measurement. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Electrophysiol. Kinesiol. 2007, 17, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, M.; Hides, J.; Elliott, J.; Kiesel, K.; Hodges, P. Rehabilitative ultrasound imaging of the posterior paraspinal muscles. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2007, 37, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airaksinen, O.; Brox, J.I.; Cedraschi, C.; Hildebrandt, J.; Klaber-Moffett, J.; Kovacs, F.; Mannion, A.F.; Reis, S.; Staal, J.B.; Ursin, H.; et al. Chapter 4 European guidelines for the management of chronic nonspecific low back pain. Eur. Spine J. 2006, 15 (Suppl. 2), S192–S300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teyhen, D.S.; Childs, J.D.; Stokes, M.J.; Wright, A.C.; Dugan, J.L.; George, S.Z. Abdominal and lumbar multifidus muscle size and symmetry at rest and during contracted states. J. Ultrasound Med. Off. J. Am. Inst. Ultrasound Med. 2012, 31, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.D.; Woodham, M.A.; Woodham, A.W. The role of the lumbar multifidus in chronic low back pain: A review. PM&R 2010, 2, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, N.; O’Sullivan, C.; Kelly, G. Multifidus muscle size and percentage thickness changes among patients with unilateral chronic low back pain (CLBP) and healthy controls in prone and standing. Man. Ther. 2014, 19, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticinesi, A.; Narici, M.V.; Lauretani, F.; Nouvenne, A.; Colizzi, E.; Mantovani, M.; Corsonello, A.; Landi, F.; Meschi, T.; Maggio, M. Assessing sarcopenia with vastus lateralis muscle ultrasound: An operative protocol. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 30, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottner, J.; Audigé, L.; Brorson, S.; Donner, A.; Gajewski, B.J.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Roberts, C.; Shoukri, M.; Streiner, D.L. Guidelines for reporting reliability and agreement studies (GRRAS) were proposed. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzini, J.L. Declaración de helsinki: Principios éticos para la investigación médica sobre sujetos humanos. Acta Bioethica 2000, 6, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, G.Y. Sample size formulas for estimating intraclass correlation coefficients with precision and assurance. Stat. Med. 2012, 31, 3972–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiesel, K.B.; Uhl, T.; Underwood, F.B.; Rodd, D.W.; Nitz, A.J. Measurement of lumbar multifidus muscle contraction with rehabilitative ultrasound imaging. Man. Ther. 2007, 12, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppenhaver, S.L.; Parent, E.C.; Teyhen, D.S.; Hebert, J.J.; Fritz, J.M. The effect of averaging multiple trials on measurement error during ultrasound imaging of transversus abdominis and lumbar multifidus muscles in individuals with low back pain. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2009, 39, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, R.L. Gray. Anatomía para Estudiantes, 4th ed.; Bar. Elsevier España: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, E.D.; Rosenberg, J.G.; Scharville, M.J.; Sobolewski, E.J.; Tweedell, A.J.; Kleinberg, C.R. Pennation angle does not influence the age-related differences in echo intensity of the medial gastrocnemius. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liljequist, D.; Elfving, B.; Roaldsen, K.S. Intraclass correlation—A discussion and demonstration of basic features. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Batterham, A.M. Spreadsheets for Analysis of Validity and Reliability. Sportscience 2015, 19, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wallwork, T.L.; Hides, J.A.; Stanton, W.R. Intrarater and interrater reliability of assessment of lumbar multifidus muscle thickness using rehabilitative ultrasound imaging. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2007, 37, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Brechue, W.F.; Fujita, S.; Brown, J.B. Gender differences in FFM accumulation and architectural characteristics of muscle. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1998, 30, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brechue, W.F.; Abe, T. The role of FFM accumulation and skeletal muscle architecture in powerlifting performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 86, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, H.; Muraoka, Y.; Kawakami, Y.; Fukunaga, T. Fascicle arrangements of vastus lateralis and gastrocnemius muscles in highly trained soccer players and swimmers of both genders. Int. J. Sports Med. 2003, 24, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazevich, A.; Gill, N.D.; Zhou, S. Intra- and intermuscular variation in human quadriceps femoris architecture assessed in vivo. J. Anat. 2006, 209, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirmaci, Z.I.K.; Firat, T.; Özkur, H.A.; Neyal, A.M.; Neyal, A.; Ergun, N. Muscle architecture and its relationship with lower extremity muscle strength in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2021, 121, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, M.; Rankin, G.; Newham, D. Ultrasound imaging of lumbar multifidus muscle: Normal reference ranges for measurements and practical guidance on the technique. Man. Ther. 2005, 10, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, K.; Kanehisa, H.; Azuma, K.; Ishizu, M.; Kuno, S.-Y.; Okada, M.; Fukunaga, T. Muscle Architectural characteristics in young and elderly men and women. Int. J. Sports Med. 2003, 24, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, T.D.; Reeves, N.D.; Baltzopoulos, V.; Jones, D.A.; Maganaris, C.N. In vivo measurements of muscle specific tension in adults and children. Exp. Physiol. 2009, 95, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| n | 27 | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender, n (%) | Female | 15 (55.6) |
| Male | 12 (44.4) | |
| Age | 23.37 ± 3.35 | |
| Height (cm) | 173.81 ± 11.00 | |
| Weight (kg) | 68.13 ± 12.25 | |
| Body Mass Index | 22.48 ± 2.99 | |
| Dominant, n (%) | Left | 2 (7.4) |
| Right | 25 (92.6) | |
| Regular physical activity yes/no, n (%) | No | 6 (22.2) |
| Yes | 21 (77.8) | |
| Times per week | 2.81 ± 1.88 |
| Observer 1 | Observer 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | Female | Male | |
| n | 15 | 12 | 15 | 12 |
| Thickness superficial left | 0.63 ± 0.11 | 0.79 ± 0.14 | 0.71 ± 0.17 | 0.87 ± 0.17 |
| Thickness superficial right | 0.67 ± 0.16 | 0.76 ± 0.12 | 0.77 ± 0.23 | 0.92 ± 0.20 |
| Thickness deep left | 1.44 ± 0.29 | 1.59 ± 0.23 | 1.63 ± 0.32 | 1.94 ± 0.22 |
| Thickness deep right | 1.36 ± 0.29 | 1.75 ± 0.28 | 1.61 ± 0.31 | 1.81 ± 0.22 |
| Pennation angle superficial left | 7.31 ± 3.26 | 9.78 ± 3.48 | 9.51 ± 3.16 | 11.29 ± 3.34 |
| Pennation angle superficial right | 8.14 ± 2.63 | 11.33 ± 4.64 | 10.12 ± 3.91 | 13.38 ± 5.17 |
| Pennation angle deep left | 13.47 ± 3.56 | 13.42 ± 4.00 | 15.71 ± 4.89 | 14.43 ± 2.82 |
| Pennation angle deep right | 12.42 ± 4.12 | 15.13 ± 5.05 | 15.17 ± 4.92 | 17.02 ± 5.60 |
| Thickness | Pennation Angle | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC (95% CI) | ICC Categorical | ap Value | SEM (95% CI) | ICC (95% CI) | ICC Categorical | ap Value | SEM (95% CI) | ||||
| Superficial | Left | Intraobserver | Observer 1 | 0.851 (0.74, 0.923) | Good | <0.001 | 0.059 (0.047, 0.071) | 0.801 (0.665, 0.896) | Good | <0.001 | 1.714 (1.354, 2.074) |
| Left | Observer 2 | 0.842 (0.728, 0.918) | Good | <0.001 | 0.076 (0.059, 0.094) | 0.669 (0.478, 0.817) | Moderate | <0.001 | 2.187 (1.707, 2.667) | ||
| Right | Observer 1 | 0.776 (0.627, 0.881) | Good | <0.001 | 0.076 (0.059, 0.093) | 0.667 (0.476, 0.816) | Moderate | <0.001 | 2.591 (1.916, 3.266) | ||
| Right | Observer 2 | 0.711 (0.535, 0.843) | Moderate | <0.001 | 0.138 (0.096, 0.181) | 0.838 (0.721, 0.916) | Good | <0.001 | 1.979 (1.574, 2.385) | ||
| Left | Interobserver | 0.392 (0.046, 0.661) | Poor | 0.012 | 0.127 (0.088, 0.166) | 0.304 (−0.038, 0.595) | Poor | 0.037 | 2.767 (1.962, 3.571) | ||
| Right | 0.458 (0.052, 0.724) | Poor | 0.001 | 0.128 (0.087, 0.169) | 0.514 (0.171, 0.745) | Moderate | 0.001 | 2.877 (2.044, 3.711) | |||
| Deep | Left | Intraobserver | Observer 1 | 0.764 (0.61, 0.874) | Good | <0.001 | 0.144 (0.113, 0.174) | 0.556 (0.337, 0.744) | Moderate | <0.001 | 2.943 (2.175, 3.711) |
| Left | Observer 2 | 0.886 (0.798, 0.942) | Good | <0.001 | 0.112 (0.085, 0.14) | 0.702 (0.522, 0.837) | Moderate | <0.001 | 2.474 (1.842, 3.106) | ||
| Right | Observer 1 | 0.794 (0.653, 0.891) | Good | <0.001 | 0.171 (0.131, 0.211) | 0.709 (0.532, 0.842) | Moderate | <0.001 | 2.817 (2.172, 3.462) | ||
| Right | Observer 2 | 0.708 (0.531, 0.841) | Moderate | <0.001 | 0.172 (0.124, 0.22) | 0.738 (0.57, 0.86) | Moderate | <0.001 | 2.836 (2.101, 3.572) | ||
| Left | Interobserver | 0.389 (−0.041, 0.687) | Poor | 0.002 | 0.202 (0.143, 0.262) | 0.4 (0.055, 0.667) | Poor | 0.011 | 2.936 (2.166, 3.706) | ||
| Right | 0.494 (0.137, 0.735) | Poor | 0.001 | 0.212 (0.153, 0.271) | 0.519 (0.171, 0.749) | Moderate | 0.001 | 3.246 (2.329, 4.163) | |||
| Thickness vs. Pennation Angle | ||
|---|---|---|
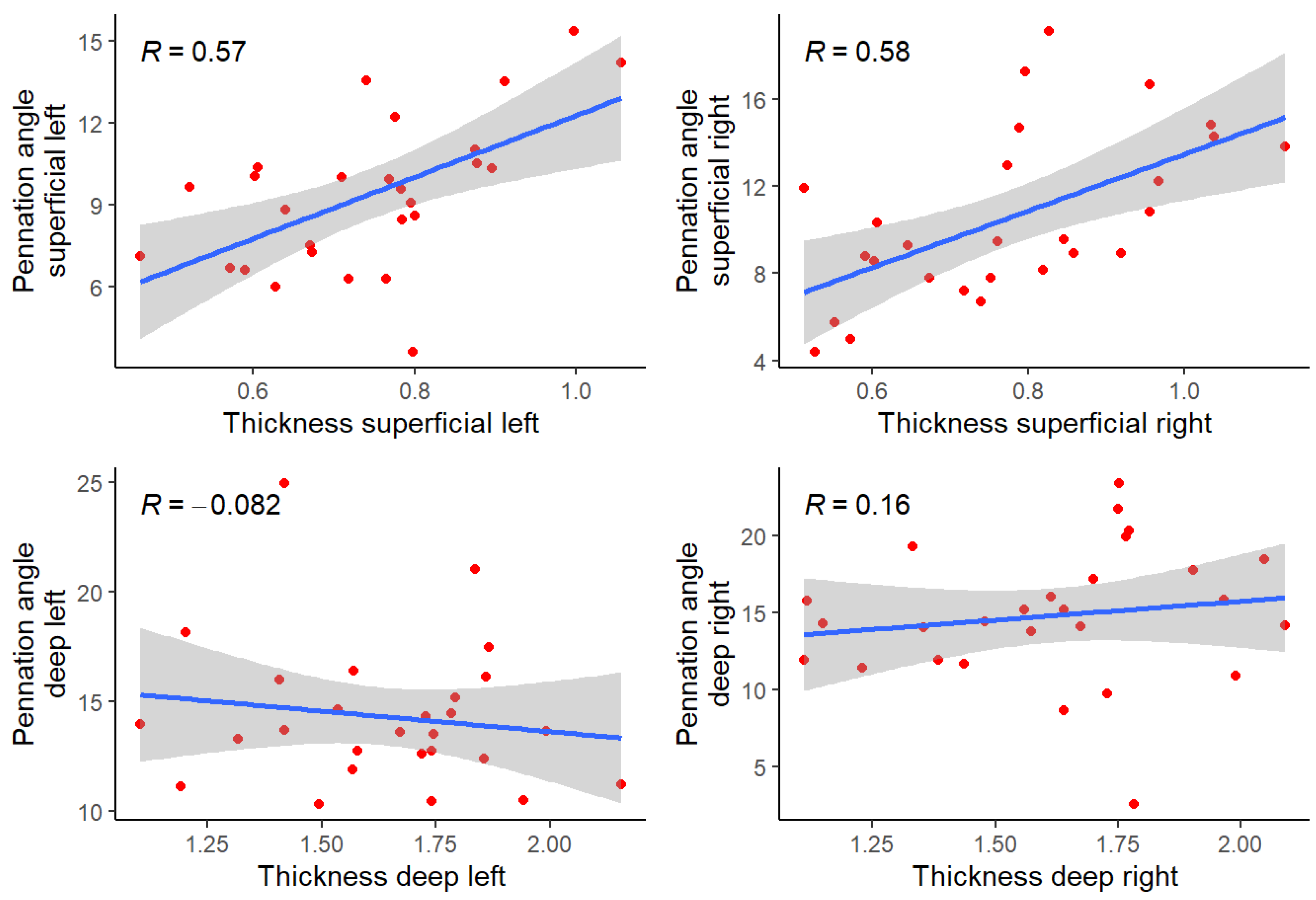
| Thickness superficial left vs. Pennation angle superficial left | 0.573 | High |
| Thickness superficial right vs. Pennation angle superficial right | 0.576 | High |
| Pennation angle and thickness vs. Baseline variables | ||
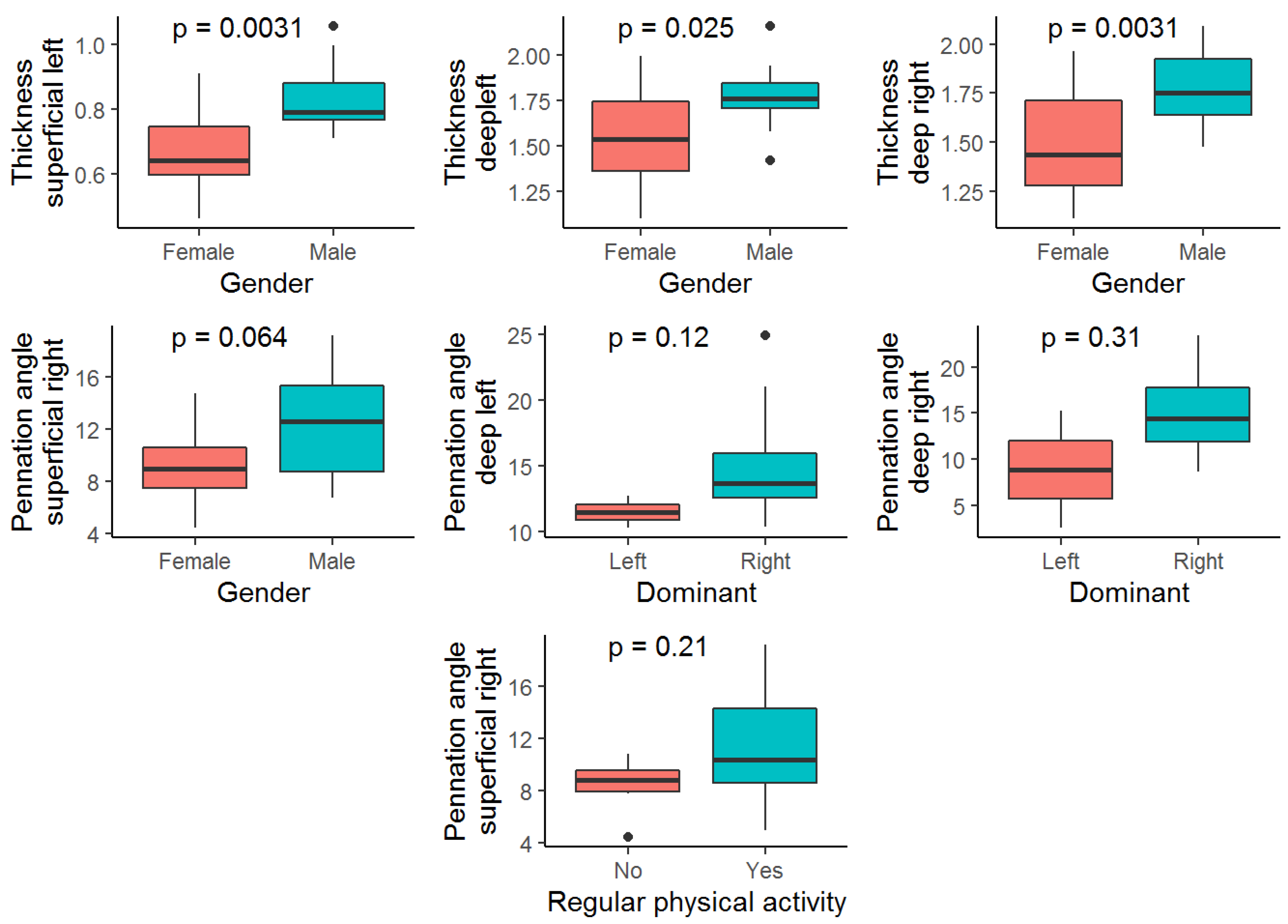
| Thickness superficial left vs. Gender | 0.730 | High |
| Thickness deep left vs. Gender | 0.594 | High |
| Thickness deep right vs. Gender | 0.677 | High |
| Pennation angle superficial right vs. Gender | 0.530 | High |
| Thickness deep left vs. Weight (kg) | 0.684 | High |
| Thickness deep right vs. Weight (kg) | 0.621 | High |
| Pennation angle deep left vs. Dominant | 0.708 | High |
| Pennation angle deep right vs. Dominant | 0.576 | High |
| Pennation angle superficial right vs. Regular physical activity (yes/no) | 0.517 | High |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monsalve-Vicente, C.; Muñoz-Zamarro, D.; Cuenca-Zaldívar, N.; Fernández-Carnero, S.; Selva-Sarzo, F.; Nunez-Nagy, S.; Naranjo-Cinto, F.; Gallego-Izquierdo, T. Architectural Ultrasound Pennation Angle Measurement of Lumbar Multifidus Muscles: A Reliability Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5174. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175174
Monsalve-Vicente C, Muñoz-Zamarro D, Cuenca-Zaldívar N, Fernández-Carnero S, Selva-Sarzo F, Nunez-Nagy S, Naranjo-Cinto F, Gallego-Izquierdo T. Architectural Ultrasound Pennation Angle Measurement of Lumbar Multifidus Muscles: A Reliability Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(17):5174. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175174
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonsalve-Vicente, Cristina, Daniel Muñoz-Zamarro, Nicolás Cuenca-Zaldívar, Samuel Fernández-Carnero, Francisco Selva-Sarzo, Susana Nunez-Nagy, Fermin Naranjo-Cinto, and Tomás Gallego-Izquierdo. 2022. "Architectural Ultrasound Pennation Angle Measurement of Lumbar Multifidus Muscles: A Reliability Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 17: 5174. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175174
APA StyleMonsalve-Vicente, C., Muñoz-Zamarro, D., Cuenca-Zaldívar, N., Fernández-Carnero, S., Selva-Sarzo, F., Nunez-Nagy, S., Naranjo-Cinto, F., & Gallego-Izquierdo, T. (2022). Architectural Ultrasound Pennation Angle Measurement of Lumbar Multifidus Muscles: A Reliability Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(17), 5174. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175174







