Otological Manifestations in Adults with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: A Controlled Radio-Clinical Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Clinical Examination
3.3. Hearing Evaluation
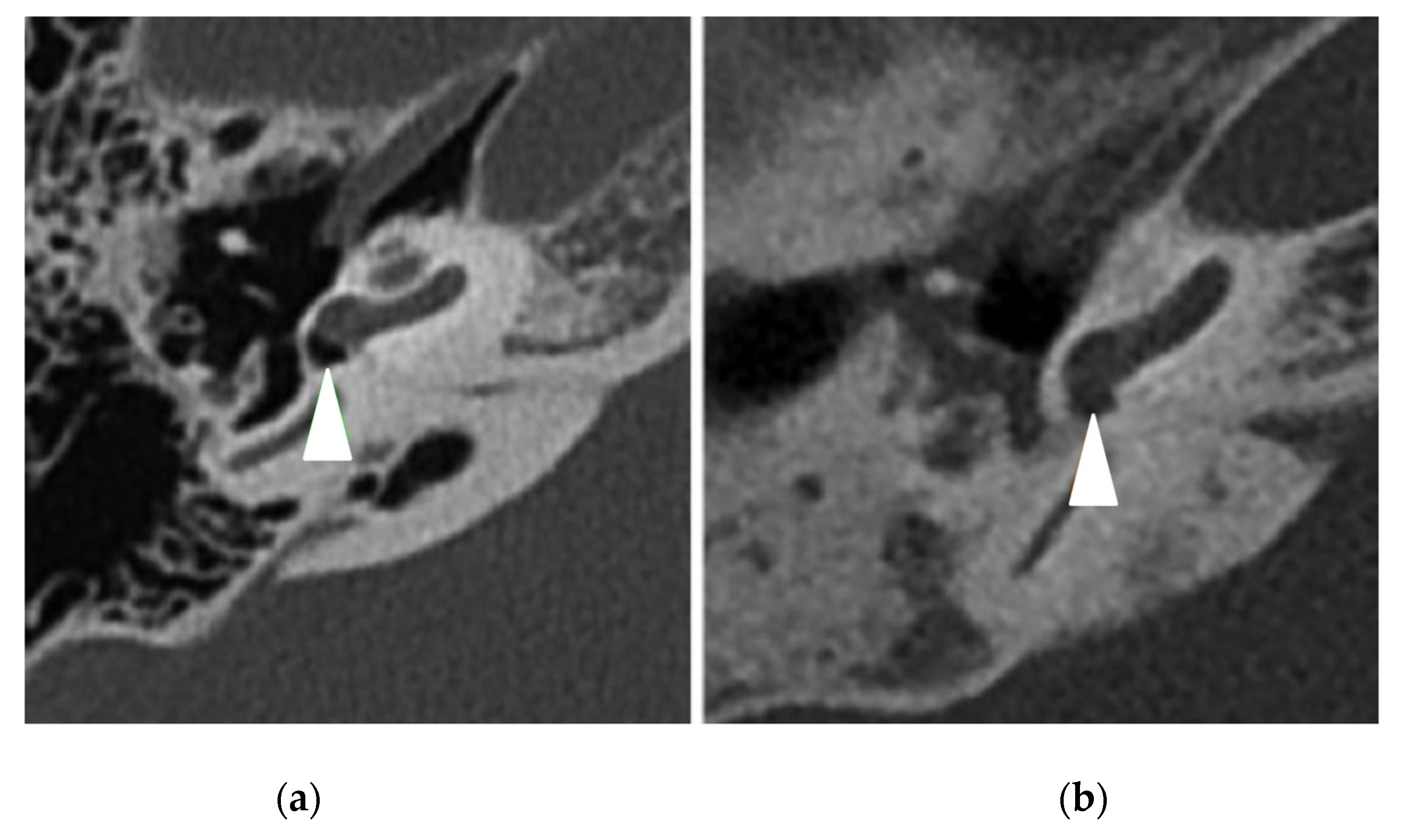
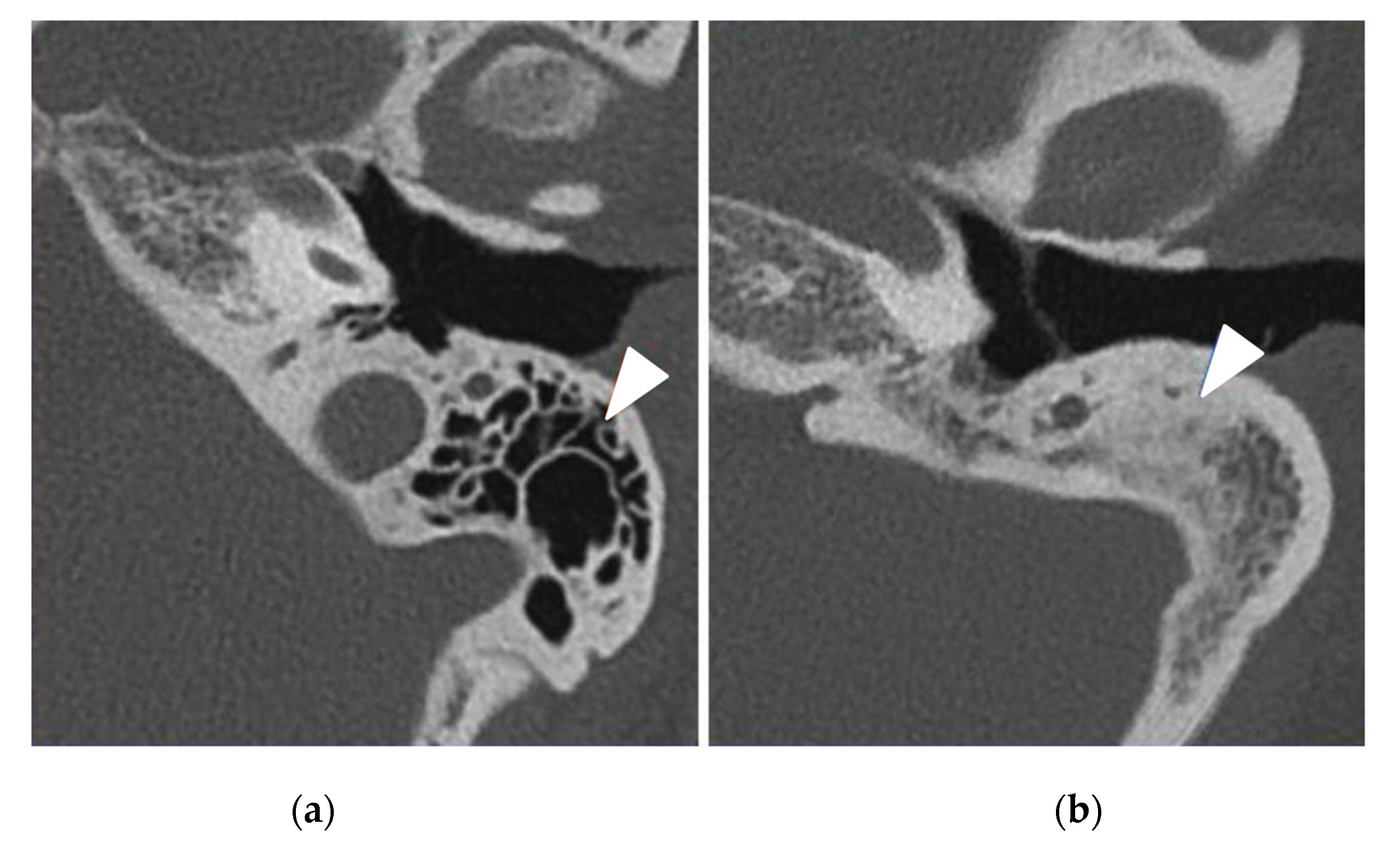
3.4. Temporal Bone CT-Scan Exploration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bush, A.; Chodhari, R.; Collins, N.; Copeland, F.; Hall, P.; Harcourt, J.; Hariri, M.; Hogg, C.; Lucas, J.; Mitchison, H.M.; et al. Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Current State of the Art. Arch. Dis. Child. 2007, 92, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fretzayas, A.; Moustaki, M. Clinical Spectrum of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in Childhood. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2016, 5, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccaldi, P.-F.; Carré-Pigeon, F.; Youinou, Y.; Delépine, B.; Bryckaert, P.-E.; Harika, G.; Quéreux, C.; Gaillard, D. Kartagener’s syndrome and infertility: Observation, diagnosis and treatment. J. Gynecol. Obstet. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 33, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, C.; Chilvers, M.; Hogg, C.; Bush, A.; Lucas, J. Diagnosing Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Thorax 2007, 62, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehni, C.E.; Frischer, T.; Strippoli, M.-P.F.; Maurer, E.; Bush, A.; Nielsen, K.G.; Escribano, A.; Lucas, J.S.A.; Yiallouros, P.; Omran, H.; et al. Factors Influencing Age at Diagnosis of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in European Children. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifferi, M.; Bush, A.; Caramella, D.; Di Cicco, M.; Zangani, M.; Chinellato, I.; Macchia, P.; Boner, A.L. Agenesis of Paranasal Sinuses and Nasal Nitric Oxide in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majithia, A.; Fong, J.; Hariri, M.; Harcourt, J. Hearing Outcomes in Children with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia--a Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2005, 69, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prulière-Escabasse, V.; Coste, A.; Chauvin, P.; Fauroux, B.; Tamalet, A.; Garabedian, E.-N.; Escudier, E.; Roger, G. Otologic Features in Children with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 136, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, J.U.; Schäfer, K.; Omran, H.; Olbrich, H.; Wallmeier, J.; Blum, A.; Hörmann, K.; Stuck, B.A. ENT Manifestations in Patients with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Prevalence and Significance of Otorhinolaryngologic Co-Morbidities. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2011, 268, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bequignon, E.; Dupuy, L.; Zerah-Lancner, F.; Bassinet, L.; Honoré, I.; Legendre, M.; Devars du Mayne, M.; Escabasse, V.; Crestani, B.; Maître, B.; et al. Critical Evaluation of Sinonasal Disease in 64 Adults with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucas, J.S.; Barbato, A.; Collins, S.A.; Goutaki, M.; Behan, L.; Caudri, D.; Dell, S.; Eber, E.; Escudier, E.; Hirst, R.A.; et al. European Respiratory Society Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, C.; Gillett, S.; Slack, R.; Lund, V.J.; Browne, J.P. Psychometric Validity of the 22-Item Sinonasal Outcome Test. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2009, 34, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeConde, A.S.; Bodner, T.E.; Mace, J.C.; Smith, T.L. Response Shift in Quality of Life after Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for Chronic Rhinosinusitis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 140, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J. Executive Summary of EPOS 2020 Including Integrated Care Pathways. Rhinology 2020, 58, 82–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, C.; Browne, J.P.; Slack, R.; Lund, V.; Brown, P. The Lund-Mackay Staging System for Chronic Rhinosinusitis: How Is It Used and What Does It Predict? Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 137, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium. Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium Guidelines for the Evaluation of Results of Treatment of Conductive Hearing Loss. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1995, 113, 186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreicher, K.L.; Schopper, H.K.; Naik, A.N.; Hatch, J.L.; Meyer, T.A. Hearing Loss in Children with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 104, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.J.; Zariwala, M.A.; Ferkol, T.; Davis, S.D.; Sagel, S.D.; Dell, S.D.; Rosenfeld, M.; Olivier, K.N.; Milla, C.; Daniel, S.J.; et al. Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Treatment of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: PCD Foundation Consensus Recommendations Based on State of the Art Review. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2016, 51, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.S.; Davis, S.D.; Omran, H.; Shoemark, A. Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in the Genomics Age. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Kitano, M.; Sakaida, H.; Usui, S.; Masuda, S.; Ogawa, S.; Ikejiri, M.; Nagao, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakatani, K. Analysis of Otologic Features of Patients With Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, e451–e456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayal, N.R.; Boyd, S.; Zach White, G.; Farrugia, M. Incidental Mastoid Effusion Diagnosed on Imaging: Are We Doing Right by Our Patients? Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, G.A.; Mills, J.H. Presbycusis. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2005, 366, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutaki, M.; Lam, Y.T.; Alexandru, M.; Anagiotos, A.; Armengot, M.; Bequignon, E.; Boon, M.; Burgess, A.; Coste, A.; Emiralioglu, N.; et al. Study Protocol: The Ear-Nose-Throat (ENT) Prospective International Cohort of Patients with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia (EPIC-PCD). BMJ Open 2021, 11, e051433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PCD 1 Group N = 17 | Control Group N = 17 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (Q1–Q3) | 39 (33–54) | 39 (33–54) | 0.89 |
| Gender male, n (%) | 8 (47%) | 6 (35%) | 0.49 |
| Ciliary ultrastructure defect, n (%) | |||
| nEM 2 | 5 (29%) | 17 (100%) | - |
| IDA + MTD 3 | 3 (18%) | 0 | - |
| ODA 4 | 6 (35%) | 0 | - |
| IDA + ODA | 3 (18%) | 0 | - |
| CC 5 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Kartagener syndrome, n (%) | 3 (18%) | 0 | 0.22 |
| Consanguinities, n (%) | 8 (47%) | 3 (18%) | 0.07 |
| Otitis media history, n (%) | 10 (59%) | 3 (18%) | 0.01 |
| Rhinosinusitis history, n (%) | 17 (100%) | 13 (76%) | 0.1 |
| CRSwNP 6, n(%) | 7 (41%) | 2 (12%) | 0.1 |
| SNOT-22 7 score, median (Q1–Q3) | 58 (46.5–69) | 33.5 (14.2–46) | 0.01 |
| Sinus hypo or aplasia, n (%) | 15 (88%) | 3 (18%) | 0.0001 |
| Modified Lund–Mackay score, median (Q1–Q3) | 13.5 (10–19.2) | 6 (2.7–10.2) | 0.01 |
| More Affected Ear | PCD 1 Group N = 17 | Control Group N = 17 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abnormal otoscopy, n (%) | 13 (76%) | 4 (24%) | 0.002 |
| 7 | 3 | |
| 4 | 1 | 0.04 |
| 2 | 0 | |
| Hearing loss, median (Q1–Q3) (dB) | 18.75 (13.75–42.5) | 12.5 (11.25–18.75) | 0.03 |
| Hearing loss, n(%) | |||
| None | 6 (35%) | 12 (71%) | |
| Sensorineural | 3 (18%) | 2 (12%) | 0.51 |
| Conductive | 4 (24%) | 2 (12%) | |
| Mixed | 4 (24%) | 1 (6%) | |
| Air-bone gap 250–500 Hz, median (Q1–Q3) (dB) | 5 (5–17.5) | 2.5 (0–10) | 0.02 |
| Air-bone gap 1000–2000–4000 Hz, Median (Q1–Q3) (dB) | 10 (2.5–12.5) | 0 (0–5) | 0.01 |
| SRT 5, median (Q1–Q3) | 25 (22.5–48.5) | 23.5 (17–26) | 0.06 |
| Intelligibility 100%, median (Q1–Q3) | 40 (35–65) | 30 (25–40) | 0.01 |
| Hearing threshold: | |||
| 500 Hz, median (Q1–Q3) | 20 (15–35) | 15 (10–20) | 0.04 |
| 1000 Hz, median (Q1–Q3) | 20 (10–40) | 10 (10–20) | 0.07 |
| 2000 Hz, median (Q1–Q3) | 15 (10–35) | 10 (10–15) | 0.08 |
| 4000 Hz, median (Q1–Q3) | 35 (15–45) | 20 (15–20) | 0.04 |
| Less Affected Ear | PCD 1 Group N = 17 | Control Group N = 17 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abnormal otoscopy, n (%) | 12 (71%) | 4 (24%) | 0.006 |
| 6 | 0 | |
| 5 | 2 | 0.01 |
| 1 | 2 | |
| Hearing loss, median (Q1–Q3) (dB) | 17.5 (10–33.75) | 8.75 (6.25–13.75) | 0.03 |
| Type of hearing loss, n (%) | |||
| None | 8 (47%) | 12 (71%) | |
| Sensorineural | 3 (18%) | 3 (18%) | |
| Conductive | 4 (24%) | 2 (12%) | 0.49 |
| Mixed | 2 (12%) | 0 | |
| Air-bone gap 250–500 Hz, median (Q1–Q3) | 5 (0–17.5) | 0 (0–2.5) | 0.04 |
| Air-bone gap 1000–2000–4000 Hz, Median (Q1–Q3) | 5 (0–10) | 0 (0–0) | 0.002 |
| SRT 5, median (Q1–Q3) (dB) | 25 (20–40) | 22 (20–26) | 0.10 |
| Intelligibility 100%, median (Q1–Q3) | 40 (30–55) | 30 (25–40) | 0.02 |
| Hearing thresholds: | |||
| 500 Hz, median (Q1–Q3) | 15 (10–25) | 10 (10–15) | 0.50 |
| 1000 Hz, median (Q1–Q3) | 15 (10–20) | 5 (5–10) | 0.03 |
| 2000 Hz, median (Q1–Q3) | 10 (10–30) | 5 (5–10) | 0.03 |
| 4000 Hz, median (Q1–Q3) | 20 (15–35) | 15 (10–15) | 0.01 |
| PCD 1 Group N = 34 N (%) | Control Group N = 34 N (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abnormal CT scan, | 32 (94%) | 11 (32%) | <0.0001 |
| Mastoid opacification | 13 (38%) | 8 (24%) | 0.19 |
| Mastoid condensation | 21 (62%) | 8 (24%) | 0.01 |
| Middle ear inflammation | 22 (65%) | 7 (21%) | 0.0002 |
| Ossicular anomaly | 12 (35%) | 3 (9%) | 0.01 |
| Other: | |||
| No other anomaly | 28 (85%) | 27 (79%) | |
| Gusher syndrome | 0 | 2 (6%) | 0.76 |
| SCC 2 dehiscence | 3 (9%) | 3 (9%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alexandru, M.; de Boissieu, P.; Benoudiba, F.; Moustarhfir, M.; Kim, S.; Bequignon, É.; Honoré, I.; Garcia, G.; Mitri-Frangieh, R.; Legendre, M.; et al. Otological Manifestations in Adults with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: A Controlled Radio-Clinical Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5163. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175163
Alexandru M, de Boissieu P, Benoudiba F, Moustarhfir M, Kim S, Bequignon É, Honoré I, Garcia G, Mitri-Frangieh R, Legendre M, et al. Otological Manifestations in Adults with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: A Controlled Radio-Clinical Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(17):5163. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175163
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlexandru, Mihaela, Paul de Boissieu, Farida Benoudiba, Malik Moustarhfir, Sookyung Kim, Émilie Bequignon, Isabelle Honoré, Gilles Garcia, Rana Mitri-Frangieh, Marie Legendre, and et al. 2022. "Otological Manifestations in Adults with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: A Controlled Radio-Clinical Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 17: 5163. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175163
APA StyleAlexandru, M., de Boissieu, P., Benoudiba, F., Moustarhfir, M., Kim, S., Bequignon, É., Honoré, I., Garcia, G., Mitri-Frangieh, R., Legendre, M., Crestani, B., Taillé, C., Escudier, E., Maitre, B., Papon, J.-F., & Nevoux, J. (2022). Otological Manifestations in Adults with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: A Controlled Radio-Clinical Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(17), 5163. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175163






