Primary Epstein–Barr Virus-Positive Mucocutaneous Ulcer of Esophagus: A Rare Case Report
Abstract
:1. Introduction
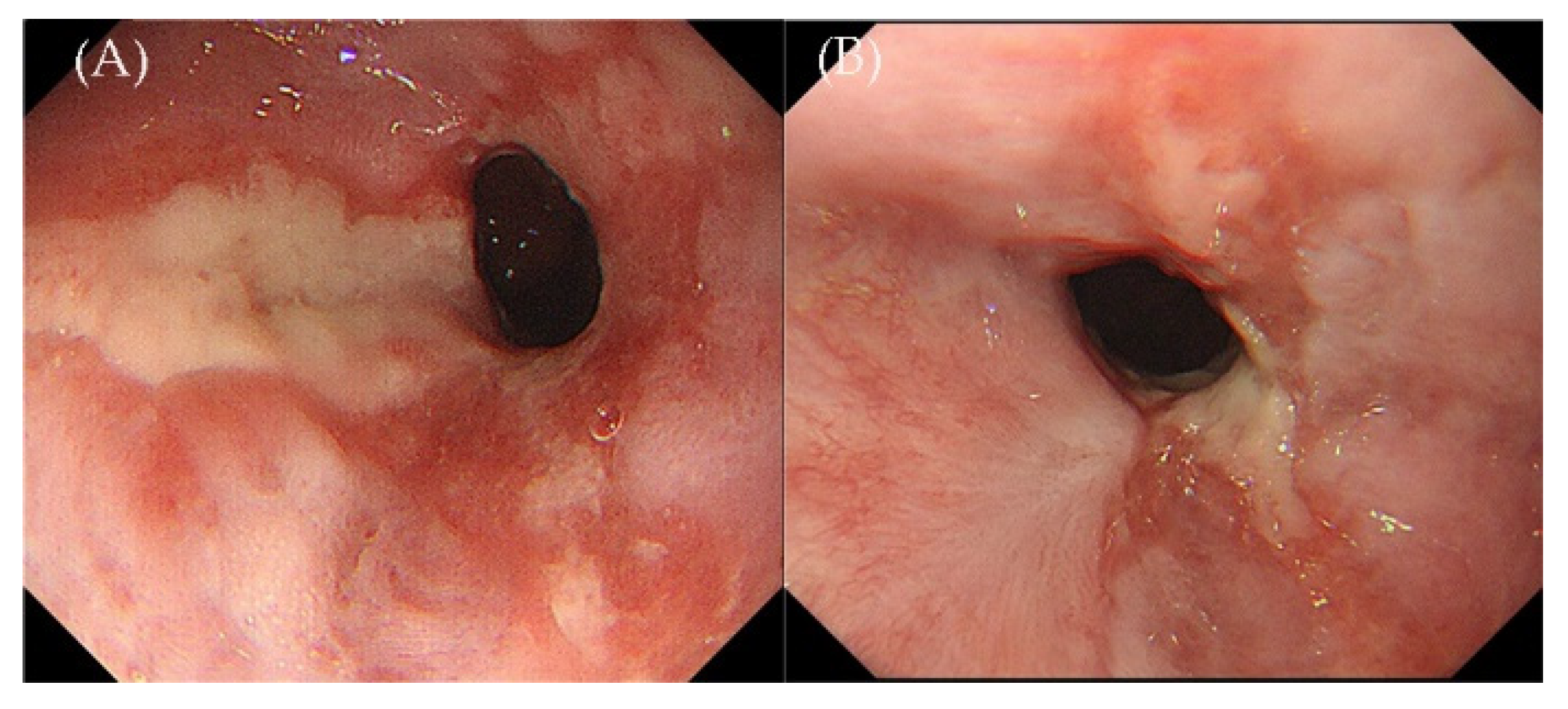
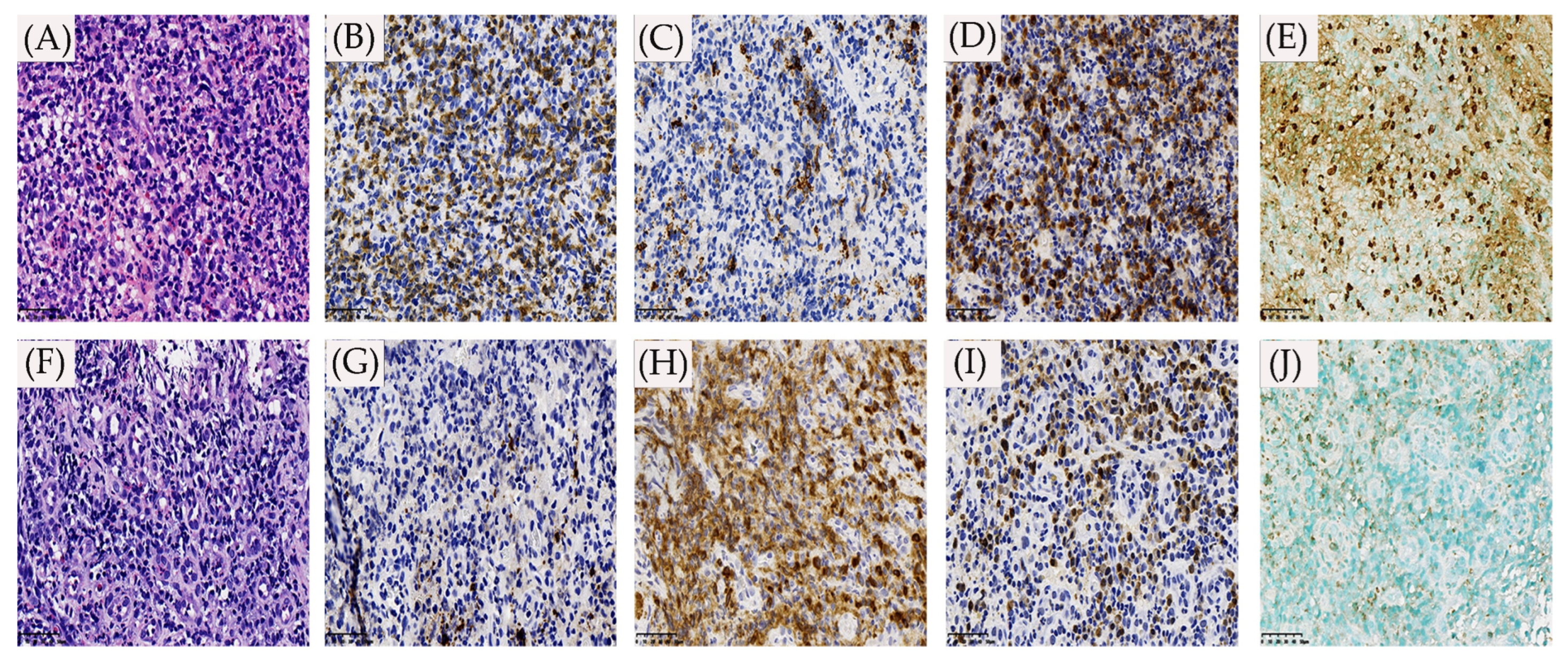
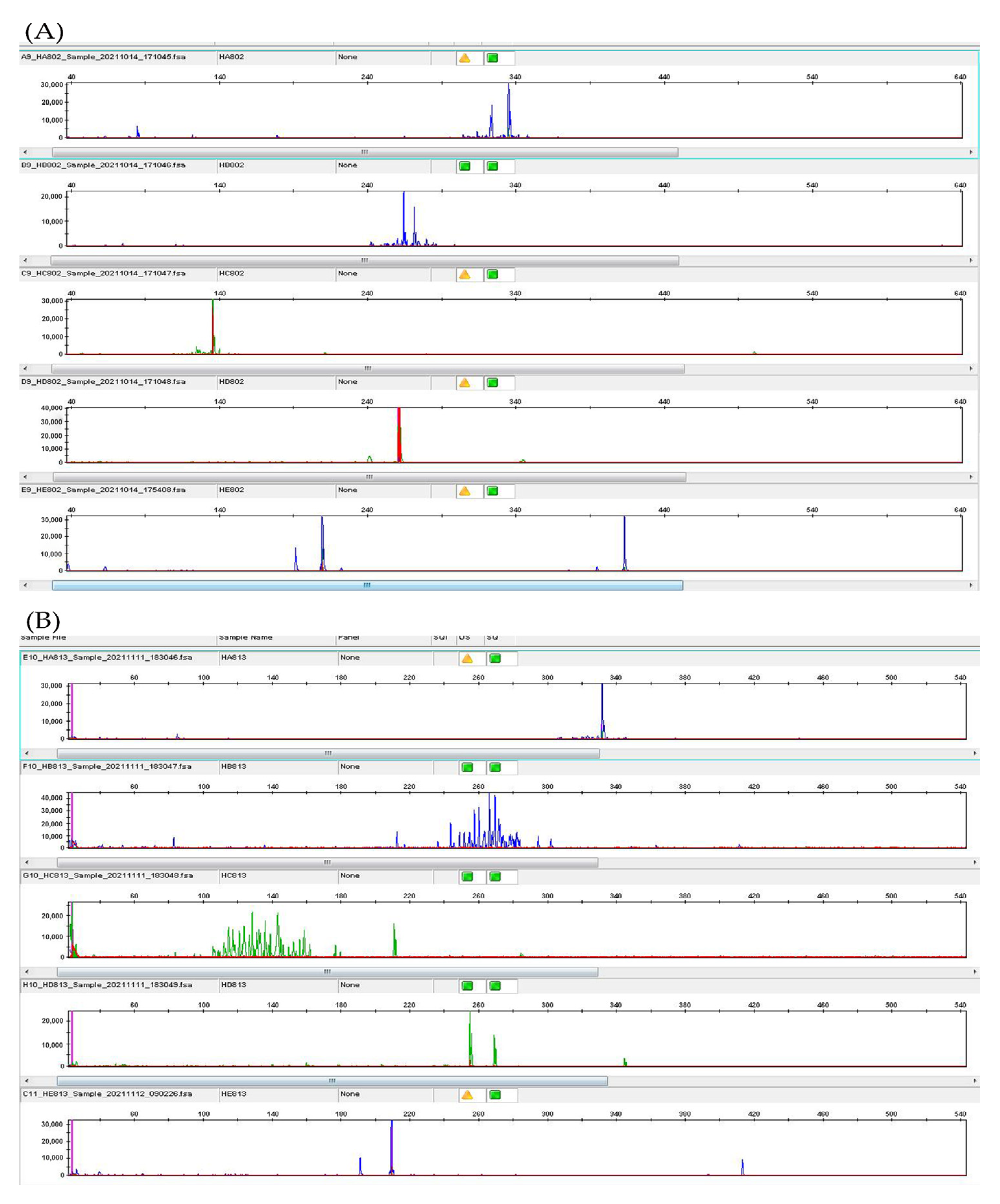
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| EBVMCU | Epstein–Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcer |
| EBV-LPDs | Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative diseases |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| PET-CT | Positron emission tomography–computer tomography |
| EBER | In situ hybridization with Epstein–Barr virus-encoded small RNA |
| ISH | In situ hybridization |
| PD-L1 | Programmed cell death-ligand 1 |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| HSV | Herpes simplex virus |
| HHV-8 | Human herpesvirus 8 |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| EBV-B-LPDs | Epstein–Barr virus B-cell lymphoproliferative diseases |
| EBV+ DLBCL | EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| NOS | Not otherwise specified |
| DLBCL-CI | DLBCL-associated chronic inflammation |
| LyG | Lymphomatoid granulomatosis |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal tract |
| RS | Reed–Sternberg |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| VZV | Varicella-zoster virus |
| HRS | Hodgkin’s lymphoma Reed–Sternberg |
References
- Ikeda, T.; Gion, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Tachibana, T.; Nishikori, A.; Nishimura, M.F.; Yoshino, T.; Sato, Y. Clinicopathological analysis of 34 Japanese patients with EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narimatsu, H.; Ota, Y.; Kami, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Suzuki, R.; Matsuo, K.; Matsumura, T.; Yuji, K.; Kishi, Y.; Hamaki, T.; et al. Clinicopathological features of pyothorax-associated lymphoma; a retrospective survey involving 98 patients. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isnard, P.; Bruneau, J.; Sberro-Soussan, R.; Wendum, D.; Legendre, C.; Molina, T.; Chatenoud, L.; Hermine, O.; Rossignol, J. Dissociation of humoral and cellular immune responses in kidney transplant recipients with EBV mucocutaneous ulcer. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2021, 23, e13552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, S.; Jhaveri, D.; Caimi, P.; Cameron, R.; Lemonovich, T.; Meyerson, H.; Hostoffer, R.; Tcheurekdjian, H. A rare presentation of EBV+ mucocut-aneous ulcer that led to a diagnosis of hypogammaglobulinemia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2014, 2, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dojcinov, S.D.; Venkataraman, G.; Raffeld, M.; Pittaluga, S.; Jaffe, E.S. EBV Positive Mucocutaneous Ulcer-A Study of 26 Ca-ses Associated with Various Sources of Immunosuppression. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.S.; Long, H.M.; Brooks, J.M.; Rickinson, A.B.; Hislop, A.D. The immunology of Epstein-Barr virus induced disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 787–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; Gross, A. Mechanisms of disease—Persistence of the Epstein-Barr virus and the origins of associated lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dojcinov, S.D.; Fend, F.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L. EBV-Positive Lymphoproliferations of B-T-and NK-Cell Derivation in Non-Immunocompromised Hosts. Pathogens 2018, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, M.; Thakral, B.; Yohe, S.; Balfour, H.H.; Singh, C.; Spears, M.; McKenna, R.W. EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer in organ transplant recipients: A localized indolent posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matnani, R.; Peker, D. Azathioprine induced Epstein Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcer arising in perianal fistula and abscess associated with Crohn’s disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2014, 8, 1747–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moran, N.R.; Webster, B.; Lee, K.; Trotman, J.; Kwan, Y.-L.; Napoli, J.L.; Leong, R. Epstein Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcer of the colon associated Hodgkin lymphoma in Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 6072–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, A.; Lobaton, T.; Tapja, G.; Manosa, M.; Cabrè, E.; Domènech, E. Epstein-Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcer in Cr-ohn’s disease. A condition to consider in immunosuppressed IBD patients. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanelli, M.; Mengoli, M.C.; Valli, R.; Froio, E.; Bisagni, A.; Zizzo, M.; De Marco, L.; Ascani, S. Primary classic Hodgkin lymphoma of the ileum and Epstein-Barr virus mucocutaneous ulcer of the colon: Two entities compared. Virchows Archiv. 2019, 474, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, M.; Al Salihi, M.; Abu Sitta, E.; Al Hadidi, S. A rare case of Epstein-Barr virus mucocutaneous ulcer of the colon. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr2017220717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, M.; Zizzo, M.; Foroni, M.; De Marco, L.; Martino, G.; Ascani, S. EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer within colonic diverticulitis mimicking diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 1795–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Torres, L.; Eraña, I.; Gil-Redondo, R.; De La Riva, I.G.; Manso, R.; Pajares, R.; Córdoba, R.; Machan, S.; Ara, M.; Requena, L.; et al. The spectrum of EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer: A study of 9 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetgebuer, R.L.; van der Woude, C.J.; de Ridder, L.; Doukas, M.; de Vries, A.C. Clinical and endoscopic complications of Epstein-Barr virus in inflammatory bowel disease: An illustrative case series. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2019, 34, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pugh, M.R.; Leopold, G.D.; Morgan, M.; Christian, A.D.; Hewett, R.; Durai, D.; Wagstaff, J.; Harris, D.; Dojcinov, S.D. Epstein Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcers complicate colitis caused by immune checkpoint regulator therapy and associate with colon perforation. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1785–1795.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daroontum, T.; Kohno, K.; Eladl, A.E.; Satou, A.; Sakakibara, A.; Matsukage, S.; Yakushiji, N.; Ya-In, C.; Nakamura, S.; Asano, N.; et al. Comparison of Epstein-Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcer associated with treated lymphoma or methotrexate in Japan. Histopathology 2018, 72, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, N.; Okuse, C.; Suetani, K.; Nakano, H.; Hiraishi, T.; Ishigooka, S.; Mori, S.; Shimamura, T.; Asakura, T.; Koike, J.; et al. A rare case of Epstein-Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcer that developed into an intestinal obstruction: A case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Napoli, A.; Giubettini, M.; Duranti, E.; Ferrari, A.; Guglielmi, C.; Uccini, S.; Ruco, L. Iatrogenic EBV-positive lymphoprolifeartive disorder with features of EBV plus mucocutaneous ulcer: Evidence for concomitant TCR gamma/IGH rearrangements in the Hodgkin-like neoplastic cells. Virchows Archiv. 2011, 458, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karube, K.; Takatori, M.; Kohno, K.; Tomoyose, T.; Ohshiro, K.; Nakazato, I. Co-occurrence of EBV-positive classic Hodgkin lymphoma and B-cell lymphomas of different clonal origins: A case report and literature review. Pathol. Int. 2020, 70, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, M.; Sumya, R.; Ono, H.; Nagai, T.; Kumazawa, K.; Shimizu, A.; Endo, D.; Aoyanagi, N. Cessation of methotrexate and a small intestine resection provide a good clinical course for a patient with a jejunum perforation induced by a methotrexateassociated lymphoproliferative disorder: A case report. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Chapman, J.R.; Vega, F. A case of EBV-associated blastic lymphoplasmacytic proliferation in an oesophageal ulcer with a self-limiting course: Overlapping lesion between EBV mucocutaneous ulcer and polymorphic lymphoplasmocytic disorder. Histopathology 2019, 74, 964–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, E.; Satou, A.; Nakamura, M.; Nakamura, S.; Fujishiro, M. Epstein-Barr virus positive B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. Cancers 2021, 13, 3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinit, R.B.; Horan, K.L.; Dorer, R.K.; Aboulafia, D.M. Epstein-Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcer: Case report and review of the first 100 published cases. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, e81–e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilbe, K.S.; Lloyd, D.A. A case of viral esophagitis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1986, 8, 494–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, M.; Mandraveli, K.; Sidiropoulos, I.; Koliouskas, D.; Alexiou-Daniel, S.; Frantzidouet, F. Unusual Epstein-Barr esophageal infection in an immunocompetent patient: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2009, 3, 7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annaházi, A.; Terhes, G.; Deák, J.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Rosztóczy, A.; Wittmann, T.; Róka, R. Fulminant Epstein- Barr virus esophagitis in an immunocompetent patient. Endoscopy 2011, 43 (Suppl. 2), E348–E349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorentsen, R.D.; Klarskov, L.L.; Steenholdt, C. Severe ulcerative oesophagitis caused by primary Epstein-Barr virus infection in an immunocompetent individual. BMJ Open Gastrol. 2021, 8, e000586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Gion, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Sato, Y. A review of EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcers focusing on clinical and pathological aspects. J. Clin. Exp. Hematopathol. 2019, 59, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, T.; Gion, Y.; Nishimura, M.F.; Yoshino, T.; Sato, Y. Epstein-Barr Virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcer: A unique and curious disease entity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeshima, A.M.; Taniguchi, H.; Ito, Y.; Hatta, S.; Suzuki, T.; Yuda, S.; Makita, S.; Fukuhara, S.; Munakata, W.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma involving small and large intestines: An analysis of 126 patients. Int. J. Hematol. 2019, 110, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, A.M.; Rocha, R.; Santana, G.O. Crohn’s disease of esophagus, stomach and duodenum. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 10, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumors Editorial Board (Ed.). WHO Classification of Tumors Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Daroontum, T.; Kohno, K.; Inaguma, Y.; Okamoto, A.; Okamoto, M.; Kimura, Y.; Nagahama, M.; Sakakibara, A.; Satou, A.; Nakamura, S. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arising in patient with a history of EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer and EBV-positive nodal polymorphous B-lymphoproliferative disorder. Pathol. Int. 2019, 69, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satou, A.; Banno, S.; Hanamura, I.; Takahashi, E.; Takahara, T.; Nobata, H.; Katsuno, T.; Takami, A.; Ito, Y.; Ueda, R.; et al. EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer arising in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with methotrexate: Single center series of nine cases. Pathol. Int. 2019, 69, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Age/Sex | Main Symptoms | Endoscopic Results | Diagnosis | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23/M [27] | Fever Diaphoresis Lethargy Weight loss Odynophagia Hematemesis | Multiple ulcerations | Positive Monospot and Paul Bunnell tests | Symptomatic |
| 27/F [28] | Dysphagia Odynophagia | Multiple well-circumscribed Ulcerations differing depths | PCR on biopsy materials | Aciclovir for 5 days |
| 48/M [29] | Fever Nausea Dysphagia | Denuded extensive ulcerations | PCR on biopsy samples | Aciclovir for 14 days |
| 18/M [30] | Fever Muscle pain heartburn Epigastric pain dysphagia Odynophagia | Multiple, centimeter long, linear and circular ulcerations of various depth | EBV serology Positive EBV-specific ISH PCR analysis of biopsy specimens | Symptomatic |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.; Wang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Nong, L.; Cai, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, X. Primary Epstein–Barr Virus-Positive Mucocutaneous Ulcer of Esophagus: A Rare Case Report. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4915. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164915
Sun C, Wang Q, Dong Y, Nong L, Cai Y, Wang L, Sun Y, Wang W, Liu X. Primary Epstein–Barr Virus-Positive Mucocutaneous Ulcer of Esophagus: A Rare Case Report. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(16):4915. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164915
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Chunping, Qingya Wang, Yujun Dong, Lin Nong, Yunlong Cai, Lihong Wang, Yuhua Sun, Wensheng Wang, and Xinmin Liu. 2022. "Primary Epstein–Barr Virus-Positive Mucocutaneous Ulcer of Esophagus: A Rare Case Report" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 16: 4915. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164915
APA StyleSun, C., Wang, Q., Dong, Y., Nong, L., Cai, Y., Wang, L., Sun, Y., Wang, W., & Liu, X. (2022). Primary Epstein–Barr Virus-Positive Mucocutaneous Ulcer of Esophagus: A Rare Case Report. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(16), 4915. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164915






