Clinical Implication of the Acumen Hypotension Prediction Index for Reducing Intraoperative Haemorrhage in Patients Undergoing Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Prospective Randomised Controlled Single-Blinded Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Randomisation
2.4. Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion and General Anaesthesia
2.5. Induced Hypotensive Anaesthesia and HPI Monitoring
2.6. Outcome Measurements
2.7. Clinical Variables
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pre- and Intraoperative Clinical Findings
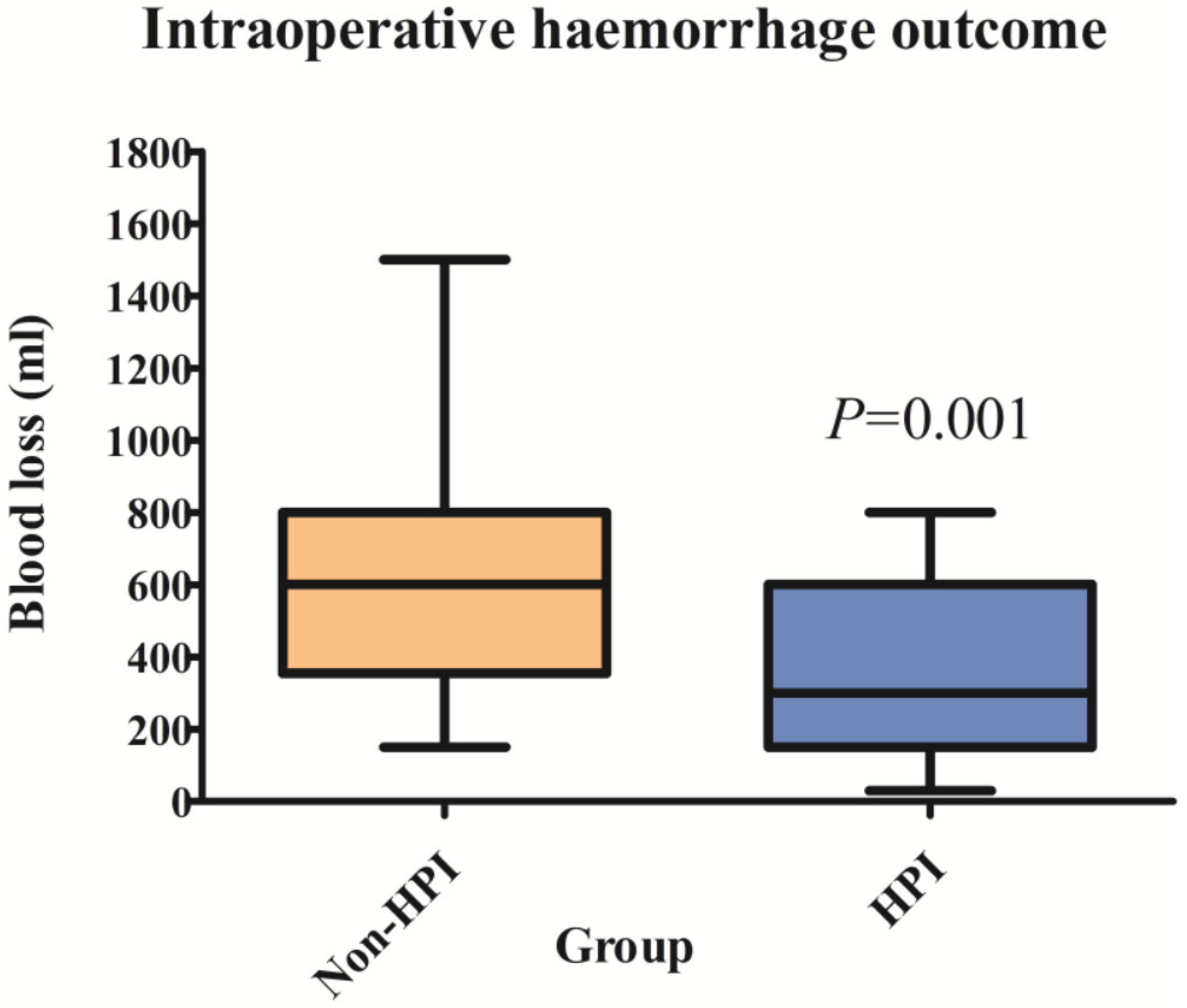
3.2. Intraoperative Haemorrhage Outcomes
3.3. Perioperative Haemoglobin and Blood Transfusion Outcomes
3.4. Postoperative Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dutton, R.P. Controlled hypotension for spinal surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2004, 13 (Suppl. S1), S66–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehman, L.W.; Saeed, M.; Moody, G.; Mark, R. Hypotension as a Risk Factor for Acute Kidney Injury in ICU Patients. Comput. Cardiol. 2010, 37, 1095–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Degoute, C.S. Controlled hypotension: A guide to drug choice. Drugs 2007, 67, 1053–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatib, F.; Jian, Z.; Buddi, S.; Lee, C.; Settels, J.; Sibert, K.; Rinehart, J.; Cannesson, M. Machine-learning Algorithm to Predict Hypotension Based on High-fidelity Arterial Pressure Waveform Analysis. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, K.; Buddi, S.; Jian, Z.; Settels, J.; Shimada, T.; Cohen, B.; Sessler, D.I.; Hatib, F. Performance of the Hypotension Prediction Index with non-invasive arterial pressure waveforms in non-cardiac surgical patients. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2021, 35, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneck, E.; Schulte, D.; Habig, L.; Ruhrmann, S.; Edinger, F.; Markmann, M.; Habicher, M.; Rickert, M.; Koch, C.; Sander, M. Hypotension Prediction Index based protocolized haemodynamic management reduces the incidence and duration of intraoperative hypotension in primary total hip arthroplasty: A single centre feasibility randomised blinded prospective interventional trial. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2020, 34, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.; Maler, S.A.; Reddy, K.; Fleming, N.W. Use of the Hypotension Prediction Index During Cardiac Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2021, 35, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.J.; Vistisen, S.T.; Jian, Z.; Hatib, F.; Scheeren, T.W.L. Ability of an Arterial Waveform Analysis-Derived Hypotension Prediction Index to Predict Future Hypotensive Events in Surgical Patients. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 130, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, J.; Wijnberge, M.; Maaskant, J.M.; Hollmann, M.W.; Hol, L.; Immink, R.V.; Vlaar, A.P.; van der Ster, B.J.P.; Geerts, B.F.; Veelo, D.P. Effect of Hypotension Prediction Index-guided intraoperative haemodynamic care on depth and duration of postoperative hypotension: A sub-study of the Hypotension Prediction trial. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 127, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmel, R. Anemia and aging: An overview of clinical, diagnostic and biological issues. Blood Rev. 2001, 15, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, E.; Calhoun, D.A. Apparent and true resistant hypertension: Definition, prevalence and outcomes. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2014, 28, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.H.; Ha, K.Y.; Rhyu, K.W.; Park, H.Y.; Cho, C.H.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.I. Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Techniques, Pearls and Pitfalls. Asian Spine J. 2020, 14, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Practice guidelines for perioperative blood management: An updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Perioperative Blood Management. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 241–275. [CrossRef]
- Ali Algadiem, E.; Aleisa, A.A.; Alsubaie, H.I.; Buhlaiqah, N.R.; Algadeeb, J.B.; Alsneini, H.A. Blood Loss Estimation Using Gauze Visual Analogue. Trauma Mon. 2016, 21, e34131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clavien, P.A.; Barkun, J.; de Oliveira, M.L.; Vauthey, J.N.; Dindo, D.; Schulick, R.D.; de Santibañes, E.; Pekolj, J.; Slankamenac, K.; Bassi, C.; et al. The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: Five-year experience. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.S. Blood loss in adult spinal surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2004, 13 (Suppl. S1), S3–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; He, Q.J.; Han, L.; Cheng, Y.L.; Bai, L.P.; Mo, X.Y.; Tang, H.Y.; Zheng, A. Risk Factors Associated with Intraoperative Blood Loss in Patients with Early Cervical Cancer. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2019, 50, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Halmin, M.; Chiesa, F.; Vasan, S.K.; Wikman, A.; Norda, R.; Rostgaard, K.; Vesterager Pedersen, O.B.; Erikstrup, C.; Nielsen, K.R.; Titlestad, K.; et al. Epidemiology of Massive Transfusion: A Binational Study from Sweden and Denmark. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basques, B.A.; Anandasivam, N.S.; Webb, M.L.; Samuel, A.M.; Lukasiewicz, A.M.; Bohl, D.D.; Grauer, J.N. Risk Factors for Blood Transfusion with Primary Posterior Lumbar Fusion. Spine 2015, 40, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bible, J.E.; Mirza, M.; Knaub, M.A. Blood-loss Management in Spine Surgery. JAAOS J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2018, 26, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.; Chung, H.; Hwang, W. Comparison of the Effects of Milrinone, Sodium Nitroprusside, and Nitroglycerine for Induced Hypotension in Elderly Patients Undergoing Spine Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Spine Surg. 2019, 32, E366–E371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, J.M.; Pinaud, M.; François, T.; Babin, M.; Macquin-Mavier, I.; Letenneur, J. Deliberate hypotension with nicardipine or nitroprusside during total hip arthroplasty. Anesth. Analg. 1991, 73, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, J.M.; Passuti, N.; Pinaud, M. Long-term hypotensive technique with nicardipine and nitroprusside during isoflurane anesthesia for spinal surgery. Anesth. Analg. 1992, 75, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.Y. Nicardipine infusion for hypotensive anesthesia during orthognathic surgery has protective effect on renal function. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, J.D.; Hersey, S.; Mencio, G.A.; Green, N.E. Nicardipine for controlled hypotension during spinal surgery. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1996, 16, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, J.C. Blood Pressure and the Brain: How Low Can You Go? Anesth. Analg. 2019, 128, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnberge, M.; Geerts, B.F.; Hol, L.; Lemmers, N.; Mulder, M.P.; Berge, P.; Schenk, J.; Terwindt, L.E.; Hollmann, M.W.; Vlaar, A.P.; et al. Effect of a Machine Learning-Derived Early Warning System for Intraoperative Hypotension vs Standard Care on Depth and Duration of Intraoperative Hypotension During Elective Noncardiac Surgery: The HYPE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 323, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadallah, D.; Thomas, G.; Saklayen, S.; Dalton, R.; Awad, H. Pro: Routine Use of the Hypotension Prediction Index (HPI) in Cardiac, Thoracic, and Vascular Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2021, 35, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, K.; Shimada, T.; Yang, D.; Khanna, S.; Cywinski, J.B.; Irefin, S.A.; Ayad, S.; Turan, A.; Ruetzler, K.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Hypotension Prediction Index for Prevention of Hypotension during Moderate- to High-risk Noncardiac Surgery. Anesthesiology 2020, 133, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Non-HPI | HPI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 33 | 35 | |
| Sex (Female) | 17 (51.5%) | 24 (68.6%) | 0.16 |
| Age (years) | 63 ± 8.7 | 64 ± 7.3 | 0.56 |
| BMI (kg m−1) | 26.1 ± 2.8 | 24.3 ± 3.2 | >0.89 |
| Preoperative vital signs | |||
| SBP (mmHg) | 134 ± 23 | 132 ± 20 | 0.71 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 79 ± 12 | 76 ± 9 | 0.42 |
| MBP (mmHg) | 97 ± 14 | 95 ± 12 | 0.52 |
| HR (beats/min) | 71 ± 10 | 73 ± 13 | 0.38 |
| ASA classifications | |||
| ASA I | 2 (6.1%) | 9 (22%) | 0.1 |
| ASA II | 31 (93.9%) | 26 (74.3%) | 0.08 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 6 (17.9%) | 8 (22.9%) | 0.63 |
| Hypertension | 19 (54.1%) | 19 (54.3%) | 0.79 |
| Preoperative lab findings | |||
| WBC count (109 L−1) | 6.3 ± 1.9 | 6.7 ± 2.5 | 0.45 |
| Neutrophil (%) | 57.9 ± 9.1 | 57.2 ± 9.6 | 0.58 |
| Lymphocyte (%) | 30.8 ± 9.0 | 33.2 ± 9.0 | 0.23 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 13.1 ± 1.8 | 13.0 ± 1.3 | 0.74 |
| Platelet count (109 L−1) | 235.7 ± 43.9 | 250.1 ± 60.6 | 0.24 |
| INR | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 0.7 |
| aPTT (s) | 25.7 ± 2.0 | 25.7 ± 2.5 | 0.6 |
| Glucose (mg dL−1) | 108.6 ± 23.2 | 108.7 ± 26.7 | 0.7 |
| Creatinine (mg dL−1) | 0.73 ± 0.2 | 0.66 ± 0.2 | 0.12 |
| Albumin (g dL−1) | 4.2 ± 0.5 | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 0.06 |
| AST (U L−1) | 24.9 ± 9.5 | 23.8 ± 8.5 | 0.59 |
| ALT (U L−1) | 23.6 ± 13.3 | 23.6 ± 17.5 | >0.999 |
| Calcium (mg dL−1) | 9.2 ± 0.5 | 9.3 ± 0.42 | 0.45 |
| Sodium (mmol L−1) | 139.3 ± 3.0 | 140.5 ± 2.4 | 0.55 |
| Potassium (mmol L−1) | 4.3 ± 0.3 | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Chloride (mmol L−1) | 103.5 ± 2.5 | 100.7 ± 15.8 | 0.3 |
| Group | Non-HPI | HPI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 33 | 35 | |
| Operation time (min) | 208 ± 59.3 | 207.9 ± 71.3 | 0.73 |
| Operation site | |||
| Involved level | |||
| Levels 1–2 | 25 (75.8%) | 27 (77.1%) | 0.28 |
| Levels 3–4 | 8 (24.2%) | 8 (22.9%) | |
| Infusion drug dose | |||
| Nicardipine (mg) | 11.3 ± 7.2 | 12.9 ± 8.6 | 0.68 |
| Ephedrine (mg) | 10.7 ± 6.2 | 11.2 ± 11.6 | 0.43 |
| Remifentanil (µg) | 664.0 ± 686.4 | 492.4 ± 533.5 | 0.21 |
| Fluid and blood management | |||
| Hourly crystalloid infusion (mL kg−1 h−1) | 7.3 ± 3.4 | 8.7 ± 4.2 | 0.1 |
| Colloid requirement (%) | 13 (39%) | 13 (37.1%) | 0.19 |
| Hourly urine output (mL kg −1 h−1) | 1.4 ± 1.5 | 1.3 ± 1.0 | 0.41 |
| Group | Non-HPI | HPI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 33 | 35 | |
| By surgical level (mL) | |||
| Levels 1–2 | 513.6 ± 216 | 319.6 ± 226.1 | 0.003 |
| Levels 3–4 | 930.0 ± 312.2 | 456.3 ± 255.6 | 0.005 |
| Group | Non-HPI | HPI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 33 | 35 | |
| Haemoglobin level (g dL−1) | |||
| T0 | 12.7 ± 1.6 | 12.4 ± 1.2 | 0.4 |
| T1 | 11.3 ± 1.7 †† | 11.5 ± 1.5 †† | 0.63 |
| POD 1 | 10.1 ± 1.7 †† | 11.2 ± 1.5 †† | 0.005 |
| POD 2 | 10.3 ± 1.6 †† | 10.9 ± 1.7 †† | 0.13 |
| POD 3 | 10.9 ± 1.6 †† | 11.6 ± 1.4 † | 0.07 |
| Haemoglobin level difference (g dL−1) | |||
| change in Hb (T0–T1) | 1.3 ± 1.0 | 0.9 ± 0.8 | 0.023 |
| change in Hb (T0–POD 1) | 2.6 ± 1.5 †† | 1.2 ± 1.8 | 0.001 |
| change in Hb (T0–POD 2) | 2.4 ± 1.3 †† | 1.4 ± 2.0 | 0.029 |
| change in Hb (T0–POD 3) | 1.7 ± 1.8 | 0.8 ± 1.7 | 0.026 |
| Group | Non-HPI | HPI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 33 | 35 | |
| Intraoperative transfusion | |||
| Requirement of PRBC (%) | 8 (24.2%) | 6 (17.1%) | 0.82 |
| Requirement of FFP (%) | 1 (3.0%) | 1 (2.8%) | >0.999 |
| Postoperative transfusion (between PODs 1 and 3) | |||
| Requirement of PRBC (%) | 9 (27.3%) | 1 (2.9%) | 0.021 |
| Requirement of FFP (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koo, J.M.; Choi, H.; Hwang, W.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, S.-I.; Kim, Y.-H.; Choi, S.; Kim, C.J.; Chae, M.S. Clinical Implication of the Acumen Hypotension Prediction Index for Reducing Intraoperative Haemorrhage in Patients Undergoing Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Prospective Randomised Controlled Single-Blinded Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4646. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164646
Koo JM, Choi H, Hwang W, Hong SH, Kim S-I, Kim Y-H, Choi S, Kim CJ, Chae MS. Clinical Implication of the Acumen Hypotension Prediction Index for Reducing Intraoperative Haemorrhage in Patients Undergoing Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Prospective Randomised Controlled Single-Blinded Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(16):4646. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164646
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoo, Jung Min, Hoon Choi, Wonjung Hwang, Sang Hyun Hong, Sang-Il Kim, Young-Hoon Kim, Seungtae Choi, Chang Jae Kim, and Min Suk Chae. 2022. "Clinical Implication of the Acumen Hypotension Prediction Index for Reducing Intraoperative Haemorrhage in Patients Undergoing Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Prospective Randomised Controlled Single-Blinded Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 16: 4646. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164646
APA StyleKoo, J. M., Choi, H., Hwang, W., Hong, S. H., Kim, S.-I., Kim, Y.-H., Choi, S., Kim, C. J., & Chae, M. S. (2022). Clinical Implication of the Acumen Hypotension Prediction Index for Reducing Intraoperative Haemorrhage in Patients Undergoing Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Prospective Randomised Controlled Single-Blinded Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(16), 4646. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164646







