The Impact of Air Pollution on Frequent Exacerbations among COPD Patients: An Observational Study on the Population of Western Romania
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Settings
2.2. Participants
2.3. Variables
2.4. Data Sources/Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Relationship between Air Quality and COPD Frequent Exacerbation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lamichhane, D.K.; Leem, J.H.; Kim, H.C. Associations between Ambient Particulate Matter and Nitrogen Dioxide and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases in Adults and Effect Modification by Demographic and Lifestyle Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hart, J.E.; Grady, S.T.; Laden, F.; Coull, A.; Koutrakis, P.; Schwartz, J.D.; Moy, M.L.; Garshick, E. Effects of Indoor and Ambient Black Carbon and PM2.5 on Pulmonary Function among Individuals with COPD. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 127008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulmeanu, R.; Fildan, A.P.; Rajnoveanu, R.M.; Fira-Mladinescu, O.; Toma, C.; Nemes, R.M.; Tudorache, E.; Oancea, C.; Mihaltan, F. Romanian clinical guideline for diagnosis and treatment of COPD. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520946907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, S.; Benzo, R. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Phenotypes: Implications for Care. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, C.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y.; Ma, L.; Hu, Y.; Yang, W.; Qi, H.; Zhou, Y. Effects of Atmospheric Fine Particulate Matter and Its Carrier Microbes on Pulmonary Microecology in Patients with COPD. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2021, 16, 2049–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bălă, G.P.; Râjnoveanu, R.M.; Tudorache, E.; Motișan, R.; Oancea, C. Air pollution exposure-the (in)visible risk factor for respiratory diseases. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 19615–19628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.C.; Guo, S.E.; Hwang, S.L.; Chou, C.T.; Lin, C.M.; Lin, Y.C. Exposure to Indoor Particulate Matter Worsens the Symptoms and Acute Exacerbations in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients of Southwestern Taiwan: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Fan, L.C.; Mao, B.; Yang, J.W.; Choi, A.M.K.; Cao, W.J.; Xu, J.F. Short-term Exposure to Ambient Fine Particulate Matter Increases Hospitalizations and Mortality in COPD: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Chest 2016, 149, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallius, M.J.; Ruuskanen, J.; Mirme, A.; Pekkanen, J. Concentrations and Estimated Soot Content of PM 1, PM 2.5, and PM 10 in a Subarctic Urban Atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1919–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, M.C.; Breysse, P.N.; Hansel, N.N.; Matsui, E.C.; Tonorezos, E.S.; Curtin-Brosnan, J.; Williams, D.L.; Buckley, T.J.; Eggleston, P.A.; Diette, G.B.; et al. Common household activities are associated with elevated particulate matter concentrations in bedrooms of inner-city Baltimore pre-school children. Environ. Res. 2008, 106, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCormack, M.C.; Belli, A.J.; Kaji, D.A.; Matsui, E.C.; Brigham, E.P.; Peng, R.D.; Sellers, C.; Williams, D.L.; Diette, G.B.; Breysse, P.N.; et al. Obesity as a susceptibility factor to indoor particulate matter health effects in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osman, L.M.; Douglas, J.G.; Garden, C.; Reglitz, K.; Lyon, J.; Gordon, S.; Ayres, J.G. Indoor air quality in homes of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Li, C.; Ji, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Tian, X.; Xu, K.F. Short-term effects of ambient air pollution on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease admissions in Beijing, China (2013–2017). Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2019, 14, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, F.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Chao, L.; Guan, J.; Li, R.; Yu, F.; Yan, X. The hospitalization attributable burden of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease due to ambient air pollution in Shijiazhuang, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 30866–30875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Sun, J.; Kan, H.; Cao, J.; Bai, H. Association of fine particulate matter on acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Yancheng, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, J.; Schikowski, T. COPD Patients as Vulnerable Subpopulation for Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, H.; Riahi, A.; Borsi, S.H.; Masoumi, K.; Khanjani, N.; AhmadiAngali, K.; Goudarzi, G.; Dastoorpoor, M. Acute Effects of Air Pollution on Hospital Admissions for Asthma, COPD, and Bronchiectasis in Ahvaz, Iran. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2020, 15, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morantes-Caballero, J.A.; Fajardo Rodriguez, H.A. Effects of air pollution on acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A descriptive retrospective study (pol-AECOPD). Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2019, 14, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, L.; Cai, Y.; Barratt, B.; Lyu, B.; Chan, Q.; Hansell, A.L.; Xie, W.; Zhang, D.; Kelly, F.J.; Tong, Z. Associations between daily air quality and hospitalisations for acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Beijing, 2013–2017: An ecological analysis. Lancet Planet. Health 2019, 3, e270–e279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Hartog, J.J.; Ayres, J.G.; Karakatsani, A.; Analitis, A.; Brink, H.T.; Hameri, K.; Harrison, R.; Katsouyanni, K.; Kotronarou, A.; Kavouras, I.; et al. Lung function and indicators of exposure to indoor and outdoor particulate matter among asthma and COPD patients. Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 67, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, N.; Xu, W.; Ji, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.-T.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Meng, S.; Tian, X.; Xu, K.-F. Lung function and systemic inflammation associated with short-term air pollution exposure in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients in Beijing, China. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pothirat, C.; Chaiwong, W.; Liwsrisakun, C.; Bumroongkit, C.; Deesomchok, A.; Theerakittikul, T.; Limsukon, A.; Tajaroenmuang, P.; Phetsuk, N. Influence of Particulate Matter during Seasonal Smog on Quality of Life and Lung Function in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.C.; Cheng, Y.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Louie, P.K.-K.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G. PM 1.0 and PM 2.5 Characteristics in the Roadside Environment of Hong Kong. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Total | Frequent Exacerbation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | p Value | ||
| Age | 65.49 ± 9.56 | 67.36 ± 9.21 | 63.47 ± 9.64 | 0.07 |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 18/22.8% | 10/24.4% | 8/21.1% | 0.79 |
| Male | 61/77.2% | 31/75.6% | 30/78.9% | |
| Residence | ||||
| Urban | 61/77.2% | 34/82.9% | 27/71.1% | 0.28 |
| Rural | 18/22.8% | 7/17.1% | 11/28.9% | |
| House Surface | 59 (43) | 64.0 (41.0) | 56.5 (37.5) | 0.82 |
| Type of cooking source | ||||
| Gas | 75/94.9% | 39/95.1% | 36/94.7% | 0.94 |
| Electric | 2/2.5% | 1/2.4% | 1/2.6% | |
| Biomass | 2/2.5% | 1/2.4% | 1/2.6% | |
| Type of heating | ||||
| Gas | 59/74.7% | 36/87.8% | 23/60.5% | 0.01 |
| Electric | 4/5.1% | 0/0.0% | 4/10.5% | |
| Biomass | 16/20.3% | 5/12.2% | 11/29.8% | |
| Smoke status | ||||
| Never | 1/1.3% | 1/2.4% | 0/0.0% | - |
| Former | 50/63.3% | 29/70.7% | 21/55.3% | 0.16 |
| Current | 25/31.6% | 10/24.4% | 15/39.5% | 0.22 |
| Secondhand smoke | 37/46.8% | 14/34.1% | 23/60.5% | 0.02 |
| Home Oxygen | 49/62.0% | 22/53.7% | 27/71.1% | 0.08 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Asthma | 11/13.9% | 6/14.6% | 5/13.2% | 0.55 |
| Bronchiectasis | 10/12.7% | 3/7.3% | 7/18.4% | 0.12 |
| Tuberculosis | 21/26.6% | 8/19.5% | 13/34.2% | 0.20 |
| Hypertension | 67/84.8% | 38/92.7% | 29/76.3% | 0.06 |
| Heart diseases | 51/64.6% | 29/70.7% | 22/57.9% | 0.25 |
| Diabetes | 10/12.7% | 7/17.1% | 3/7.9% | 0.31 |
| Spirometry | ||||
| FEV1 (%) | 33 (15.5) | 37.3 (14) | 29.0 (13.75) | 0.01 |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 51 (14.25) | 52.44 (10.49) | 45.55 (11.12) | 0.006 |
| FEF 25–75% | 13 (8.7) | 16.7 (8.9) | 11.5 (3.0) | <0.001 |
| COPD Stages | ||||
| GOLD 3 | 47/59.5% | 29/70.7% | 18/47.4% | 0.04 |
| GOLD 4 | 32/40.5% | 12/29.3% | 20/52.6% | |
| Variable | Total (Median [IQR]) | No Exacerbation (Median [IQR]) | Frequent Exacerbation (Median [IQR]) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
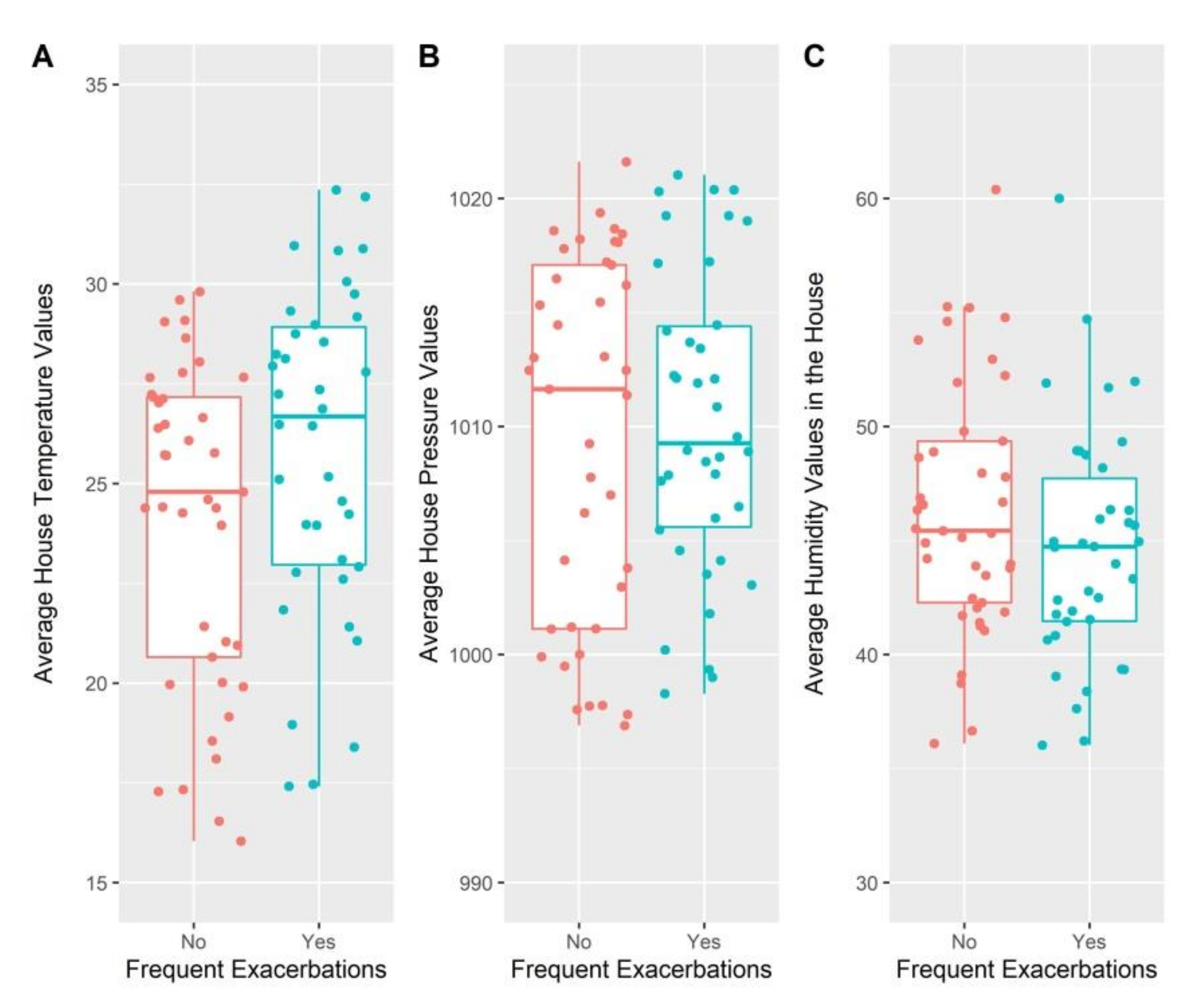
| House Temperature (°C) | ||||
| Minimum values | 20.23 (8.21) | 18.87 (7.02) | 21.96 (7.88) | 0.37 |
| Maximum values | 28.54 (4.81) | 27.92 [(7.65) | 28.99 (5.91) | 0.31 |
| Average | 25.72 (6.37) | 24.78 (6.91) | 26.67 (5.95) | 0.43 |
| House Humidity | ||||
| Minimum values | 39.00 (6.5) | 39.00 (6.50) | 38.25 (6.83) | 0.49 |
| Maximum values | 55.37 (9.50) | 55.50 (13.0) | 55.20 (8.60) | 0.82 |
| Average | 44.95 (7.01) | 45.42 (7.08) | 44.72 (6.26) | 0.26 |
| House pressure | ||||
| Minimum values | 1004.61 (12.91) | 1007.05 (14.62) | 1003.99 (11.76) | 0.50 |
| Maximum values | 1015.6 (9.94) | 1015.86 (16.85) | 1015.53 (8.20) | 0.82 |
| Average | 1010.86 (13.13) | 1011.64 (15.96) | 1009.25 (8.79) | 0.50 |
| Variables | B | S.E. | p Value | OR | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
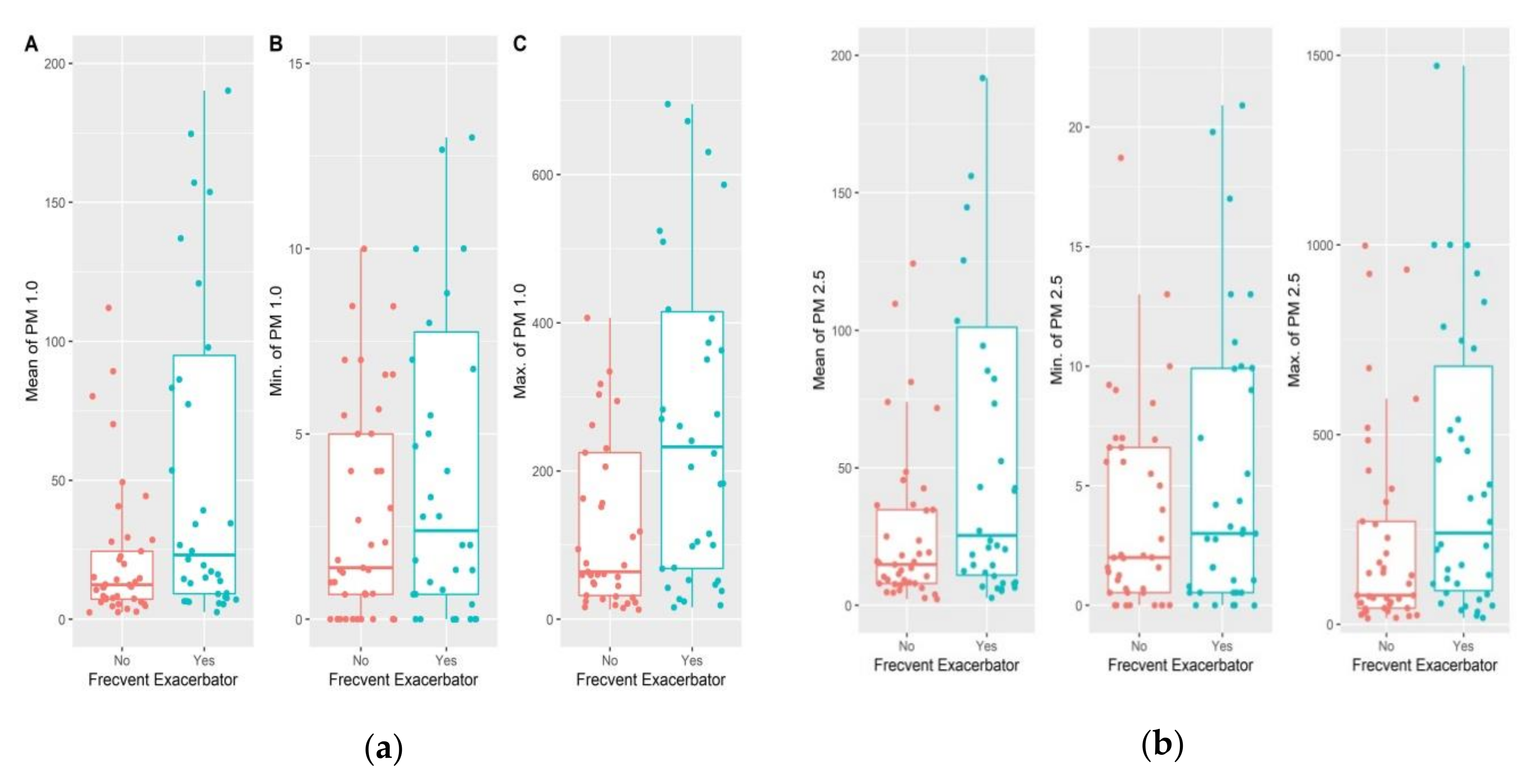
| PM 1.0 (µg/m3) | 0.017 | 0.007 | 0.01 | 1.017 | 1.004 | 1.030 |
| PM 2.5 (µg/m3) | 0.014 | 0.006 | 0.01 | 1.014 | 1.003 | 1.026 |
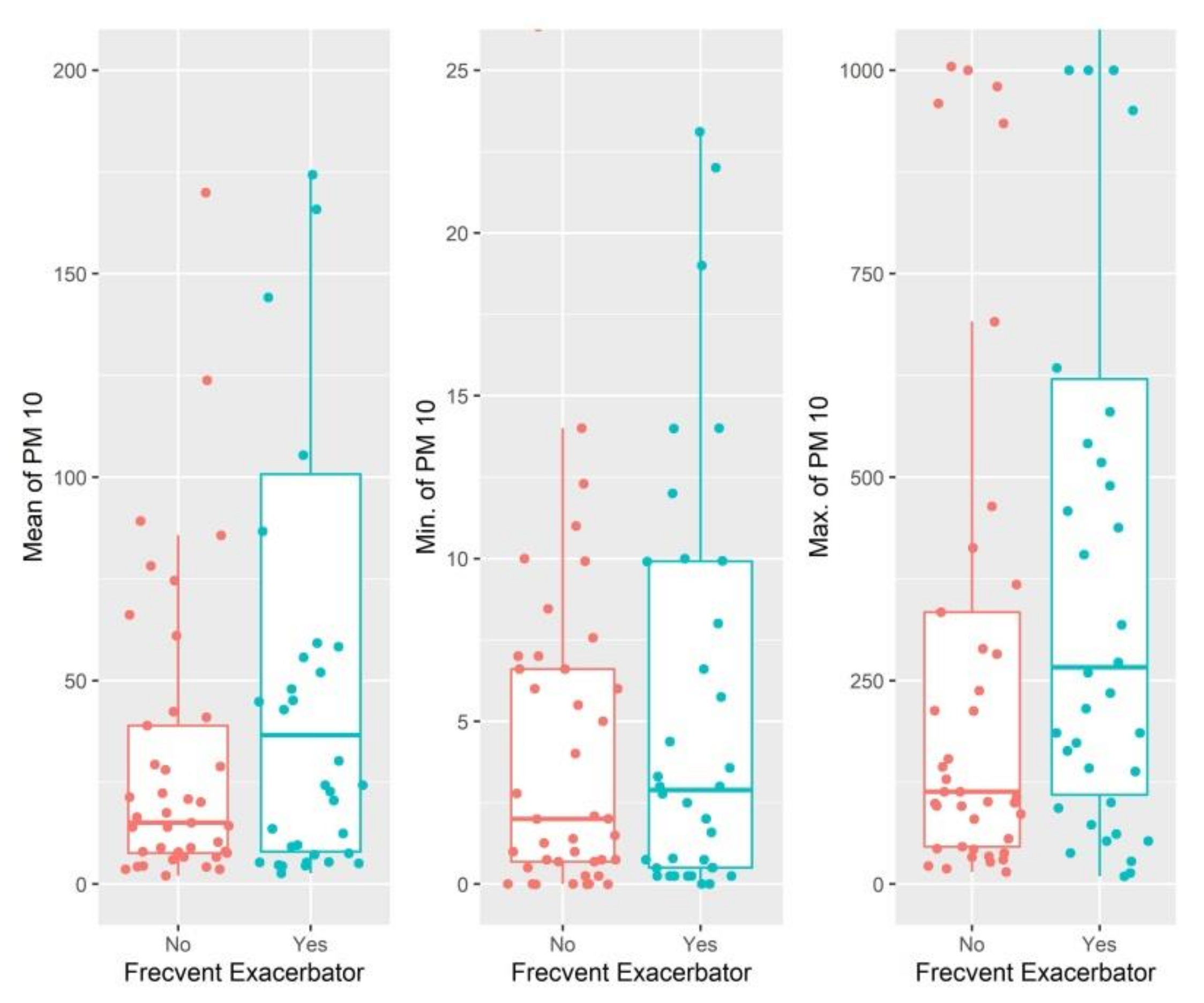
| PM 10.0 (µg/m3) | 0.009 | 0.004 | 0.03 | 1.010 | 1.001 | 1.018 |
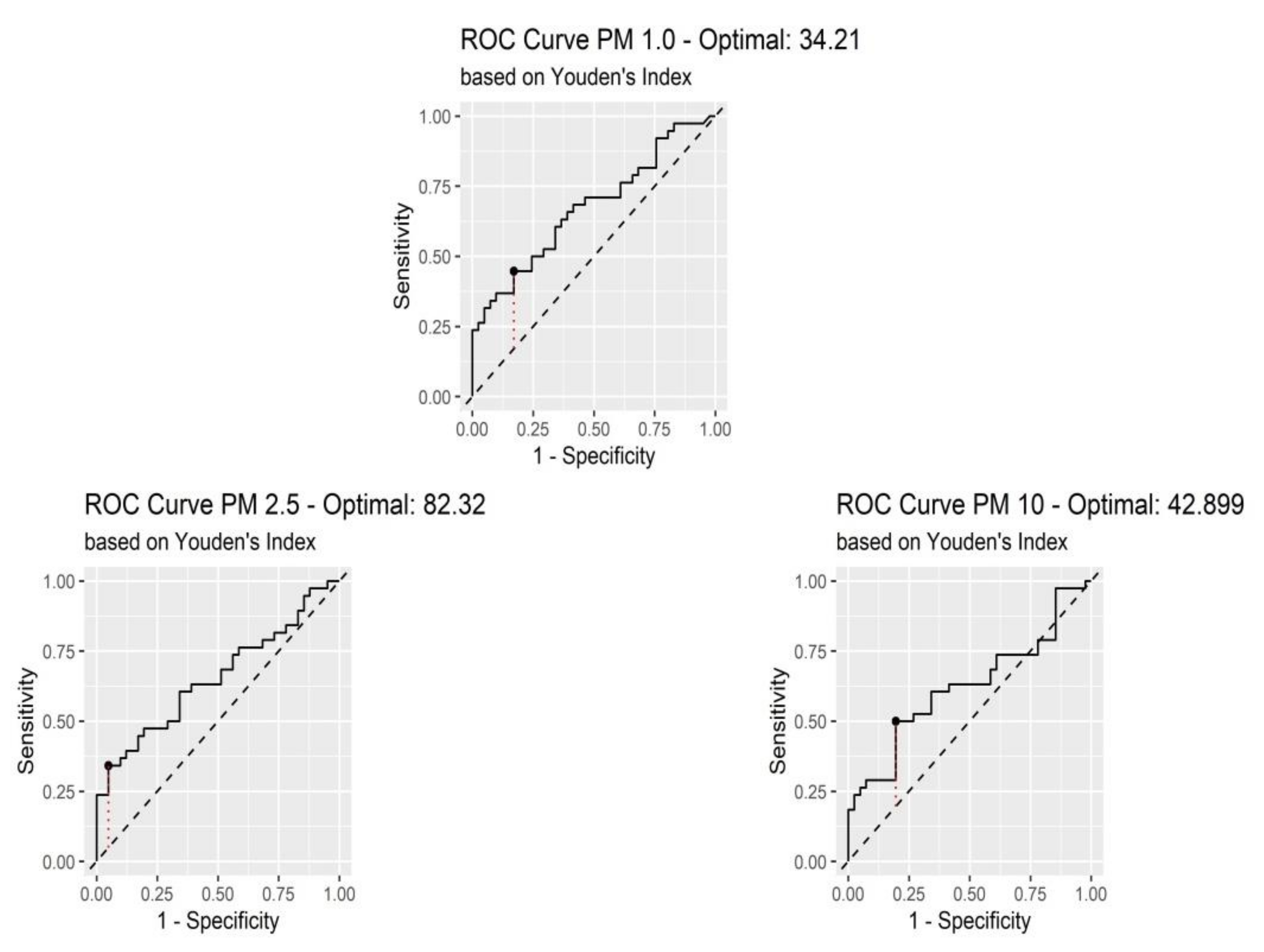
| Variables | AUC | Youden | Optimal Cut-Off | Sensitivity | Sensibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM 1.0 | 0.673 | 0.276 | 34.21 µg/m3 | 44% | 82% |
| PM 2.5 | 0.654 | 0.293 | 82.32 µg/m3 | 34% | 95% |
| PM 10.0 | 0.622 | 0.304 | 42.89 µg/m3 | 50% | 80% |
| Variables | B | S.E. | p Value | OR | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| PM 1.0 > 32.21 µg/m3 | 1.36 | 0.528 | 0.010 | 3.93 | 1.39 | 11.06 |
| PM 2.5 > 82.32 µg/m3 | 2.31 | 0.802 | 0.004 | 10.14 | 2.10 | 48.79 |
| PM 10 > 42.89 µg/m3 | 1.41 | 0.510 | 0.006 | 4.12 | 1.51 | 11.21 |
| Variables | B | S.E. | p Value | aOR * | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| PM 1.0 > 32.21 µg/m3 | 1.64 | 0.904 | 0.069 | 5.16 | 0.87 | 30.38 |
| PM 2.5 > 82.32 µg/m3 | 3.43 | 1.384 | 0.013 | 31.03 | 2.05 | 468.09 |
| PM 10 > 42.89 µg/m3 | 2.56 | 0.970 | 0.008 | 12.99 | 1.94 | 87.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bălă, G.-P.; Timar, B.; Gorun, F.; Motisan, R.; Pescaru, C.; Tudorache, E.; Marc, M.; Manolescu, D.; Citu, C.; Oancea, C. The Impact of Air Pollution on Frequent Exacerbations among COPD Patients: An Observational Study on the Population of Western Romania. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4352. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154352
Bălă G-P, Timar B, Gorun F, Motisan R, Pescaru C, Tudorache E, Marc M, Manolescu D, Citu C, Oancea C. The Impact of Air Pollution on Frequent Exacerbations among COPD Patients: An Observational Study on the Population of Western Romania. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(15):4352. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154352
Chicago/Turabian StyleBălă, Gabriel-Petrică, Bogdan Timar, Florin Gorun, Radu Motisan, Camelia Pescaru, Emanuela Tudorache, Monica Marc, Diana Manolescu, Cosmin Citu, and Cristian Oancea. 2022. "The Impact of Air Pollution on Frequent Exacerbations among COPD Patients: An Observational Study on the Population of Western Romania" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 15: 4352. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154352
APA StyleBălă, G.-P., Timar, B., Gorun, F., Motisan, R., Pescaru, C., Tudorache, E., Marc, M., Manolescu, D., Citu, C., & Oancea, C. (2022). The Impact of Air Pollution on Frequent Exacerbations among COPD Patients: An Observational Study on the Population of Western Romania. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(15), 4352. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154352







