The Prognostic Role of Mitral Valve Regurgitation Severity and Left Ventricle Function in Acute Heart Failure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
Statistical Analysis
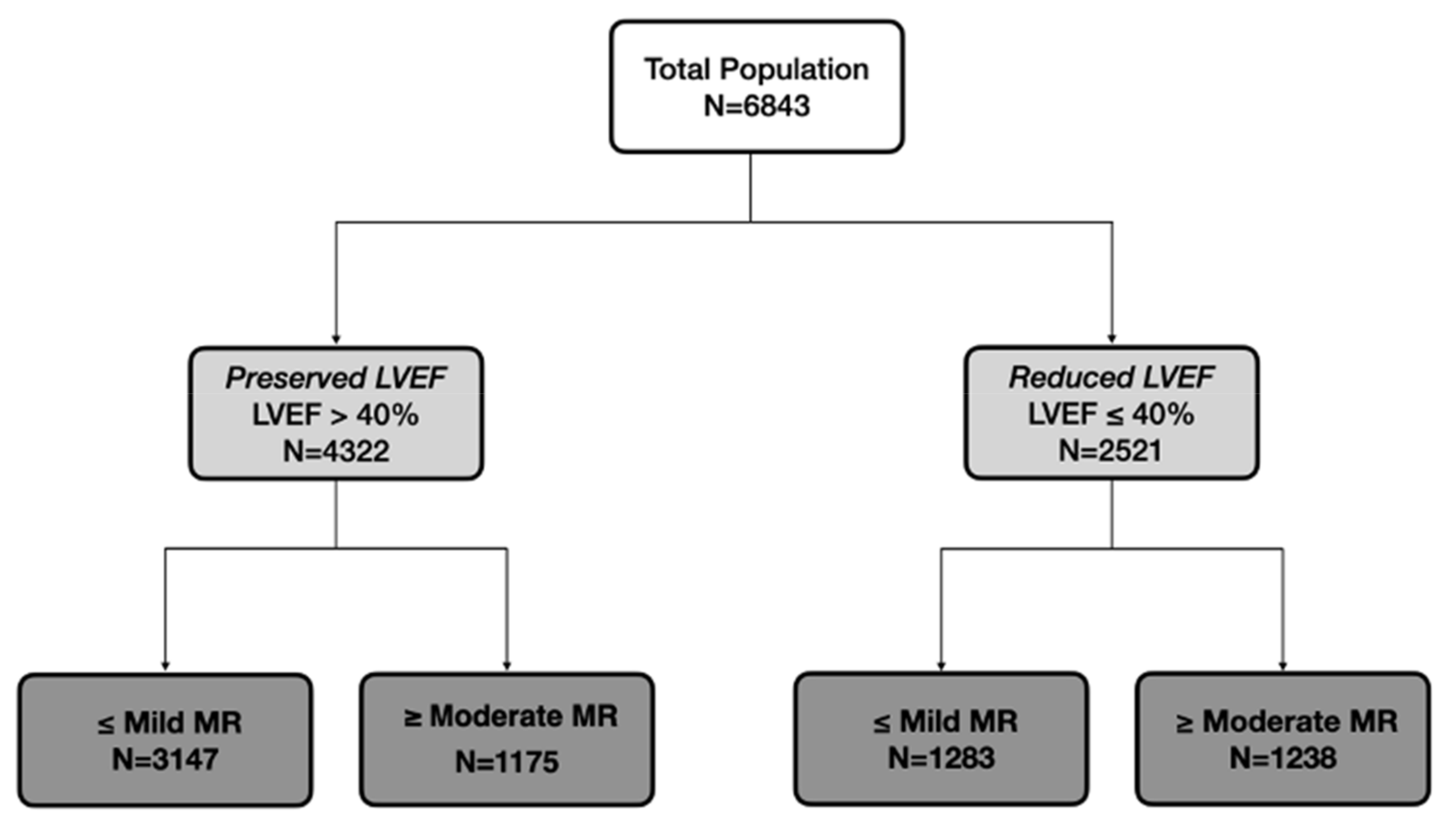
3. Results
3.1. Preserved LVEF (LVEF > 40%)
3.2. Reduced LVEF (LVEF ≤ 40%)
3.3. All-Cause Mortality
3.4. Rehospitalization Due to Heart Failure
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MR | Mitral regurgitation |
| LVEF | Left ventricular ejection fraction |
| AHF | Acute heart failure |
| LV | Left ventricle |
| SPAP | Systemic pulmonary artery pressure |
| MVR | Mitral valve replacement |
| LVEDD | LV end-diastolic dimension |
| LVEDV | LV end-diastolic volume |
| re-HFH | Recurrent heart failure hospitalizations |
References
- Robbins, J.D.; Maniar, P.B.; Cotts, W.; Parker, M.A.; Bonow, R.O.; Gheorghiade, M. Prevalence and severity of mitral regurgitation in chronic systolic heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.G.; Whitlow, P.L.; Raymond, R.E.; Schneider, J.P. Impact of mitral regurgitation on long-term survival after percutaneous coronary intervention. Am. J. Cardiol. 2002, 89, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigioni, F.; Enriquez-Sarano, M.; Zehr, K.; Bailey, K.; Tajik, A. Ischemic mitral regurgitation. Long-term outcome and prognostic implications with quantitative Doppler assessment. ACC Curr. J. Rev. 2001, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Dini, F.L.; Faggiano, P.; Agricola, E.; Cicoira, M.; Frattini, S.; Simioniuc, A.; Gullace, M.; Ghio, S.; Enriquez-Sarano, M.; et al. Independent prognostic value of functional mitral regurgitation in patients with heart failure. A quantitative analysis of 1256 patients with ischaemic and non-ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Heart 2011, 97, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichon, B.H.; Felker, G.; Shaw, L.K.; Cabell, C.H.; O’Connor, C.M. Relation of frequency and severity of mitral regurgitation to survival among patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction and heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obadia, J.-F.; Messika-Zeitoun, D.; Leurent, G.; Iung, B.; Bonnet, G.; Piriou, N.; Lefèvre, T.; Piot, C.; Rouleau, F.; Carrié, D.; et al. Percutaneous Repair or Medical Treatment for Secondary Mitral Regurgitation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2297–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, G.W.; Lindenfeld, J.; Abraham, W.T.; Kar, S.; Lim, D.S.; Mishell, J.M.; Whisenant, B.; Grayburn, P.A.; Rinaldi, M.; Kapadia, S.R.; et al. Transcatheter Mitral-Valve Repair in Patients with Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2307–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goliasch, G.; Bartko, P.E.; Pavo, N.; Neuhold, S.; Wurm, R.; Mascherbauer, J.; Lang, I.M.; Strunk, G.; Hülsmann, M. Refining the prognostic impact of functional mitral regurgitation in chronic heart failure. Eur. Hear. J. 2017, 39, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannino, A.; Smith, R.L.; Schiattarella, G.G.; Trimarco, B.; Esposito, G.; Grayburn, P.A. Survival and cardiovascular outcomes of patients with secondary mitral regurgitation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimoto, K.; Sato, N.; Takano, T. Functional mitral regurgitation at discharge and outcomes in patients hospitalized for acute decompensated heart failure with a preserved or reduced ejection fraction. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2016, 18, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mowakeaa, S.; Dwivedi, A.; Grossman, J.R.; Parikh, G.; Curillova, Z.; Aragam, K.G.; Elmariah, S.; Kinlay, S.; Aragam, J. Prognosis of patients with secondary mitral regurgitation and reduced ejection fraction. Open Hear. 2018, 5, e000745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, S.; Kawase, Y.; Hata, R.; Maruo, T.; Tada, T.; Kadota, K. Dynamic severe mitral regurgitation on hospital arrival as prognostic predictor in patients hospitalized for acute decompensated heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 273, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 16, 233–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 46, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar]
- Asch, F.M.; Bruce, C.J.; Gillam, L.D.; Grayburn, P.A.; Hahn, R.T.; Inglessis, I.; Islam, A.M.; Lerakis, S.; Little, S.H.; Siegel, R.J.; et al. Guidelines for the Evaluation of Valvular Regurgitation After Percutaneous Valve Repair or Replacement: A Report from the American Society of Echocardiography Developed in Collaboration with the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Ja. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2019, 32, 431–475. [Google Scholar]
- Lancellotti, P.; Tribouilloy, C.; Hagendorff, A.; Popescu, B.A.; Edvardsen, T.; Pierard, L.A.; Badano, L.; Zamorano, J.L. Recommendations for the echocardiographic assessment of native valvular regurgitation: An executive summary from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Hear. J.-Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 14, 611–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senni, M.; Adamo, M.; Metra, M.; Alfieri, O.; Vahanian, A. Treatment of functional mitral regurgitation in chronic heart failure: Can we get a ‘proof of concept’ from the MITRA-FR and COAPT trials? Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sabbagh, A.; Reddy, Y.N.V.; Nishimura, R.A. Mitral Valve Regurgitation in the Contemporary Era: Insights Into Diagnosis, Management, and Future Directions. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, 628–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoen, V.; Calle, S.; De Buyzere, M.; Timmermans, F. Proportionate or disproportionate secondary mitral regurgitation: How to untangle the Gordian knot? Heart 2020, 106, 1719–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartko, P.E.; Heitzinger, G.; Arfsten, H.; Pavo, N.; Spinka, G.; Andreas, M.; Mascherbauer, J.; Hengstenberg, C.; Hülsmann, M.; Goliasch, G. Disproportionate Functional Mitral Regurgitation: Advancing a Conceptual Framework to Clinical Practice. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 2088–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.B.; Borgeson, D.D.; Barnes, M.E.; Rihal, C.S.; Daly, R.C.; Redfield, M.M. Mitral regurgitation in patients with advanced systolic heart failure. J. Card. Fail. 2004, 10, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursi, F.; Barbieri, A.; Grigioni, F.; Reggianini, L.; Zanasi, V.; Leuzzi, C.; Ricci, C.; Piovaccari, G.; Branzi, A.; Modena, M.G. Prognostic implications of functional mitral regurgitation according to the severity of the underlying chronic heart failure: A long-term outcome study. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2010, 12, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cork, D.P.; McCullough, P.A.; Mehta, H.S.; Barker, C.M.; Gunnarsson, C.; Ryan, M.P.; Baker, E.R.; Van Houten, J.; Mollenkopf, S.; Verta, P. Impact of mitral regurgitation on cardiovascular hospitalization and death in newly diagnosed heart failure patients. ESC Hear. Fail. 2020, 7, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Espriella, R.; Santas, E.; Miñana, G.; Bodí, V.; Valero, E.; Payá, R.; Núñez, E.; Payá, A.; Chorro, F.J.; Bayés-Genis, A.; et al. Functional Mitral Regurgitation Predicts Short-Term Adverse Events in Patients with Acute Heart Failure and Reduced Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Ohara, T.; Funada, A.; Hasegawa, T.; Sugano, Y.; Kanzaki, H.; Yokoyama, H.; Yasuda, S.; Ogawa, H.; Anzai, T. Prognostic Impact of Functional Mitral Regurgitation in Patients Admitted with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. Circ. J. 2016, 80, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pecini, R.; Thune, J.J.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Hassager, C.; Køber, L. The relationship between mitral regurgitation and ejection fraction as predictors for the prognosis of patients with heart failure. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2011, 13, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Sivaraj, K.; Hendrickson, M.; Chang, P.P.; Weickert, T.; Qamar, A.; Vaduganathan, M.; Caughey, M.C.; Pandey, A.; Cavender, M.A.; et al. Prevalence and Prognostic Significance of Mitral Regurgitation in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: The ARIC Study. JACC Heart Fail. 2020, 9, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biner, S.; Rafique, A.; Rafii, F.; Tolstrup, K.; Noorani, O.; Shiota, T.; Gurudevan, S.; Siegel, R.J. Reproducibility of Proximal Isovelocity Surface Area, Vena Contracta, and Regurgitant Jet Area for Assessment of Mitral Regurgitation Severity. JACC: Cardiovasc. Imaging 2010, 3, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnesi, M.; Adamo, M.; Sama, I.E.; Anker, S.D.; Cleland, J.G.; Dickstein, K.; Filippatos, G.S.; Lang, C.C.; Ng, L.L.; Ponikowski, P.; et al. Impact of mitral regurgitation in patients with worsening heart failure: Insights from BIOSTAT-CHF. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2021, 23, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Cleland, J.G.; Dickstein, K.; Filippatos, G.; van der Harst, P.; Hillege, H.L.; Lang, C.C.; ter Maaten, J.M.; Ng, L.; et al. A systems BIOlogy Study to TAilored Treatment in Chronic Heart Failure: Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of BIOSTAT-CHF. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2016, 18, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grayburn, P.A.; Sannino, A.; Packer, M. Proportionate and Disproportionate Functional Mitral Regurgitation: A New Conceptual Framework That Reconciles the Results of the MITRA-FR and COAPT Trials. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asch, F.M.; Grayburn, P.A.; Siegel, R.J.; Kar, S.; Lim, D.S.; Zaroff, J.G.; Mishell, J.M.; Whisenant, B.; Mack, M.J.; Lindenfeld, J.; et al. Echocardiographic Outcomes After Transcatheter Leaflet Approximation in Patients with Secondary Mitral Regurgitation: The COAPT Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 2969–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| ≤Mild MR (n = 4430) | ≥Moderate MR (n = 2413) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Years) | 76.1 ± 12.5 | 76.5 ± 12.7 | 0.18 |
| Gender (Female) | 44.0% | 46.0% | 0.10 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.6 ± 5.8 | 27.2 ± 5.1 | <0.001 |
| BSA (m2) | 1.86 ± 0.47 | 1.81 ± 0.23 | <0.001 |
| LVEF (mean% ± SD) | 49.74 ± 14.70 | 41.70 ± 16.63 | <0.001 |
| LVEF > 40% (% of total) | 71.0% | 48.7% | <0.001 |
| LVEDD (cm ± SD) | 4.93 ±1.19 | 5.39 ± 1.98 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 40.2% | 33.8% | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 66.9% | 58.5% | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 42.5% | 40.1% | 0.03 |
| COPD | 16.7% | 10.6% | <0.001 |
| Anemia | 28.5% | 27.5% | 0.37 |
| Chronic renal failure | 34.2% | 35.2% | 0.4 |
| CVA/TIA | 17.1% | 14.3% | 0.01 |
| Atrial fib/flutter | 35.4% | 43.1% | <0.001 |
| Current smoker | 18.3% | 14.6% | 0.001 |
| PVD | 8.0% | 8.0% | 0.98 |
| Prior IHD | 52.7% | 54.5% | 0.147 |
| Prior MI | 26.1% | 24.9% | 0.52 |
| Prior cardiomyopathy | 6.9% | 10.4% | <0.001 |
| Reduced LVEF (n = 2521) | Preserved LVEF (n = 4322) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤Mild MR (n= 1283) | ≥Moderate MR (n = 1238) | p-Value | ≤Mild MR (n = 3147) | ≥Moderate MR (n = 1175) | p-Value | |
| Age (Years) | 72 ± 13 | 73 ± 13 | 0.05 | 78 ± 12 | 80 ± 11 | <0.001 |
| Gender (Female) | 23.5% | 29.9% | <0.001 | 52.4% | 63.1% | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.3 ± 5.1 | 26.6 ± 4.8 | 0.01 | 29.1 ± 6.1 | 27.9 ± 5.5 | <0.001 |
| BSA (m2) | 1.89 ± 0.63 | 1.84 ± 0.22 | <0.001 | 1.85 ± 0.39 | 1.78 ± 0.23 | <0.001 |
| LVEF (%) | 29 ± 8 | 27 ± 8 | <0.001 | 58 ± 6 | 57 ± 7 | <0.001 |
| LVEDD (cm) | 5.50 ± 0.81 | 5.81 ± 0.88 | <0.001 | 4.66 ±0.58 | 4.79 ± 0.64 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 42.2% | 37.5% | 0.05 | 39.4% | 30.0% | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 58.8% | 51.4% | <0.001 | 70.2% | 66.0% | 0.006 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 43.9% | 39.7% | 0.095 | 41.9% | 40.5% | 0.182 |
| COPD | 12.9% | 9.2% | <0.001 | 18.3% | 12.1% | <0.001 |
| Anemia | 22.2% | 22.6% | 0.89 | 31.3% | 32.7% | 0.45 |
| Chronic renal failure | 34.8% | 37.8% | 0.004 | 49.7% | 50.8% | 0.66 |
| CVA/TIA | 15.0% | 12.2% | 0.08 | 18.0% | 16.6% | 0.50 |
| Atrial fib/flutter | 31.1% | 34.1% | 0.015 | 37.1% | 52.5% | <0.001 |
| Current smoker | 24.9% | 18.6% | <0.001 | 15.6% | 10.4% | <0.001 |
| PVD | 9.7% | 10.7% | 0.645 | 7.3% | 5.1% | 0.013 |
| Prior IHD | 69.4% | 64.9% | 0.017 | 45.9% | 43.6% | 0.207 |
| Prior MI | 40.9% | 33.2% | p < 0.001 | 20.1% | 16.3% | 0.008 |
| Prior cardiomyopathy | 16.9% | 16.5% | 0.115 | 2.9% | 4.0% | 0.202 |
| Laboratory at Presentation | ||||||
| Creatinine | 1.56 ± 1.1 | 1.64 ± 1.0 | 0.36 | 1.51 ± 1.2 | 1.49 ± 1.1 | 0.96 |
| eGFR (MDRD) | 54.7 ± 46.6 | 51.7 ± 42.6 | 0.32 | 53.2 ± 36.6 | 53.0 ± 39.7 | 0.8 |
| Hemoglobin | 12.1 ± 2.2 | 11.8 ± 2.1 | 0.02 | 11.4 ± 2.1 | 11.2 ± 1.9 | 0.013 |
| Drugs at Presentation | ||||||
| Aldosterone blockers | 18.9% | 19.5% | 0.74 | 12.1% | 12.2% | 0.93 |
| ACE/ARB | 47.1% | 42.3% | 0.016 | 47.6% | 42.8% | 0.005 |
| Beta-blockers | 25.7% | 21.5% | 0.012 | 39.5% | 34.1% | 0.001 |
| Loop diuretics | 58.4% | 57.8% | 0.75 | 40.1% | 40.2% | 0.97 |
| Oral anticoagulants | 18.7% | 18.6% | 0.93 | 21.6% | 28.3% | <0.001 |
| 1-Year Mortality | HF Rehospitalization | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | HR 1 | 95% CI 1 | p-Value | HR 1 | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
| Preserved LVEF and ≤Mild MR | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Preserved LVEF and ≥moderate MR | 1.01 | 0.86, 1.17 | >0.9 | 1.34 | 1.17, 1.52 | <0.001 |
| Reduced LVEF and ≤mild MR | 1.31 | 1.12, 1.53 | <0.001 | 1.31 | 1.15, 1.51 | <0.001 |
| Reduced LVEF and ≥moderate MR | 1.44 | 1.25, 1.67 | <0.001 | 1.65 | 1.45, 1.88 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazin, I.; Arad, M.; Freimark, D.; Goldenberg, I.; Kuperstein, R. The Prognostic Role of Mitral Valve Regurgitation Severity and Left Ventricle Function in Acute Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4267. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154267
Mazin I, Arad M, Freimark D, Goldenberg I, Kuperstein R. The Prognostic Role of Mitral Valve Regurgitation Severity and Left Ventricle Function in Acute Heart Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(15):4267. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154267
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazin, Israel, Michael Arad, Dov Freimark, Ilan Goldenberg, and Rafael Kuperstein. 2022. "The Prognostic Role of Mitral Valve Regurgitation Severity and Left Ventricle Function in Acute Heart Failure" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 15: 4267. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154267
APA StyleMazin, I., Arad, M., Freimark, D., Goldenberg, I., & Kuperstein, R. (2022). The Prognostic Role of Mitral Valve Regurgitation Severity and Left Ventricle Function in Acute Heart Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(15), 4267. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154267






