Free versus Pedicled Flaps for Lower Limb Reconstruction: A Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
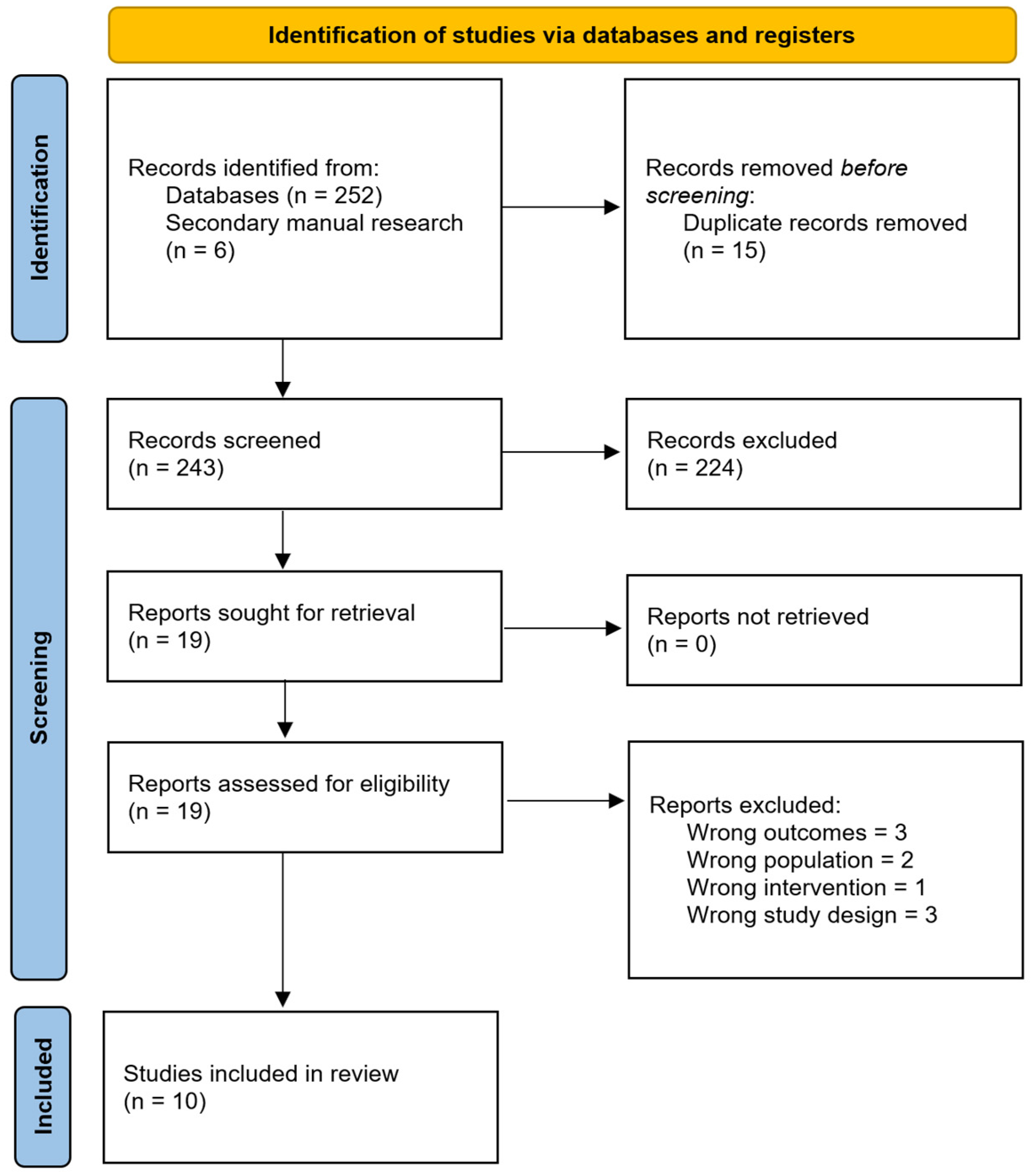
2. Materials and Methods
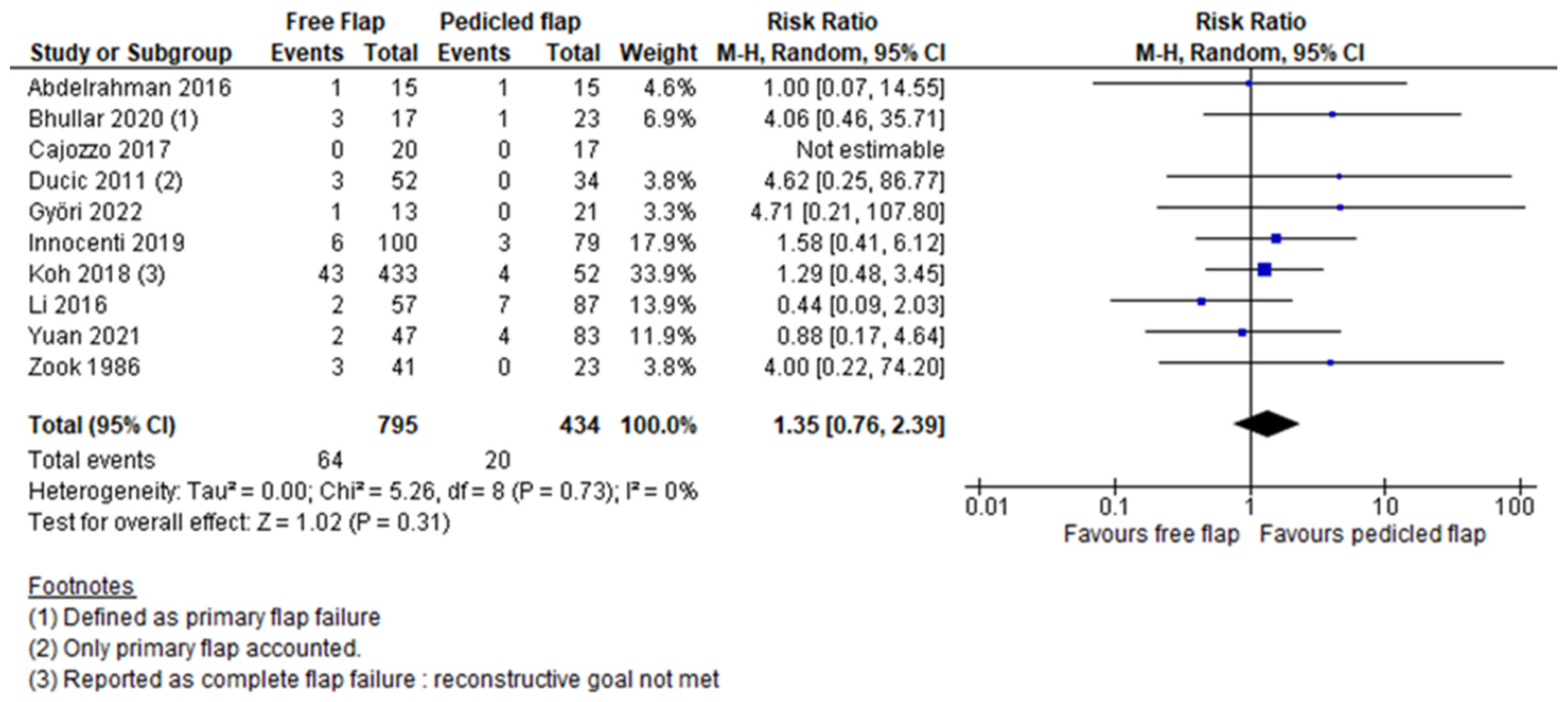
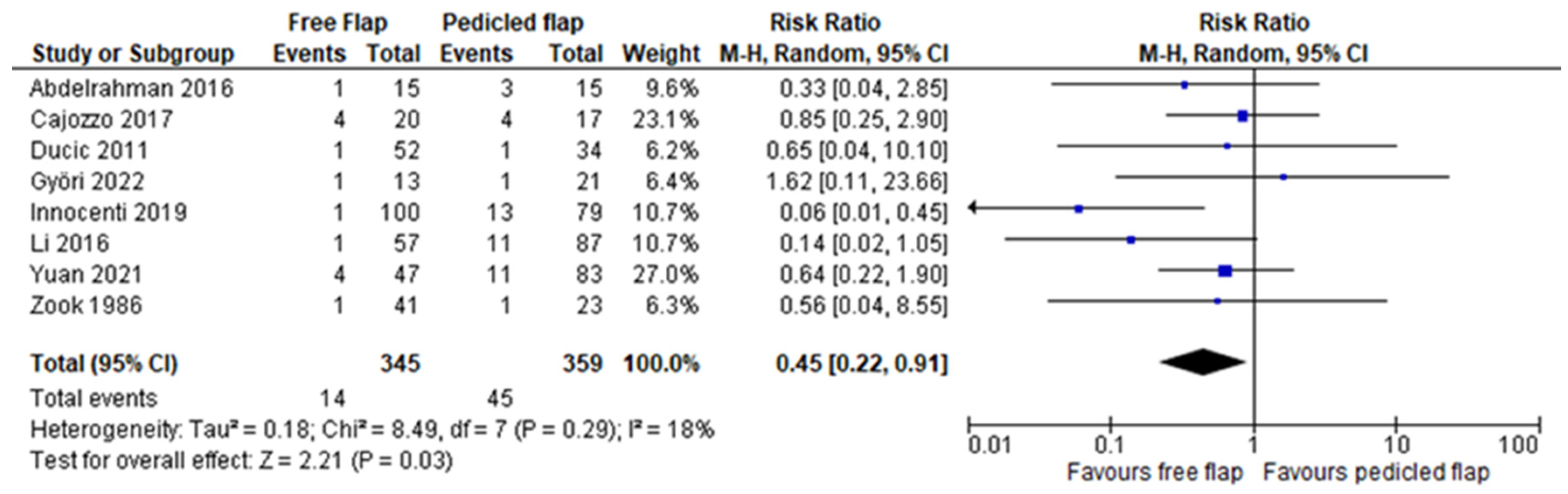
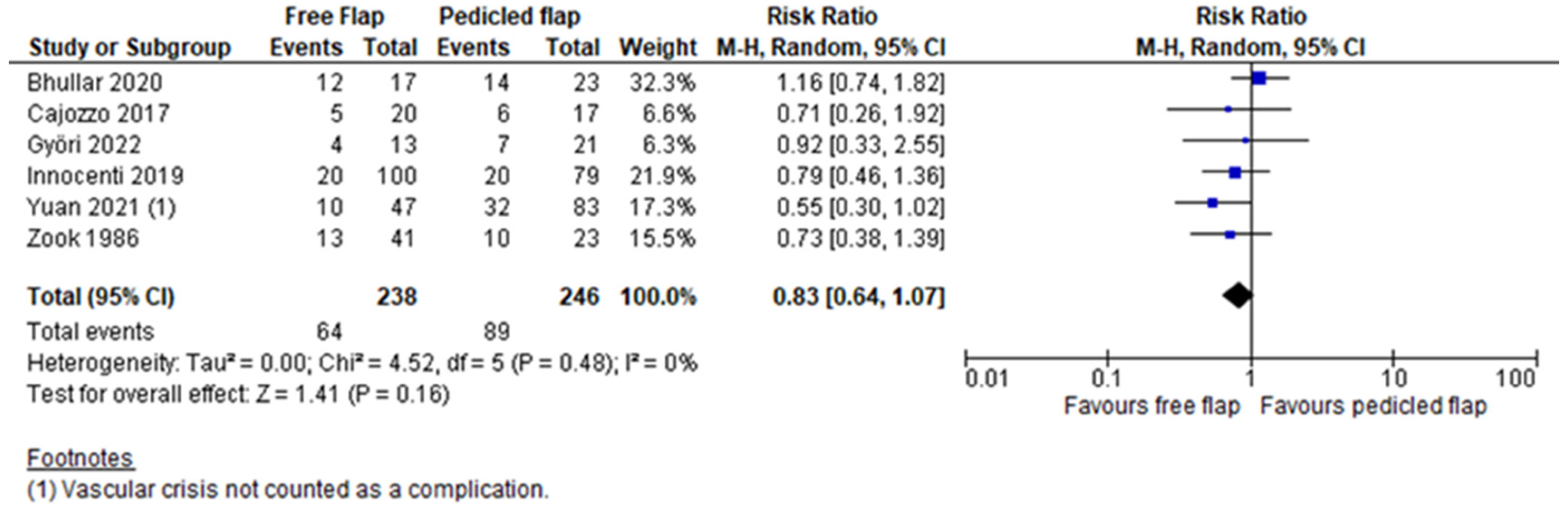
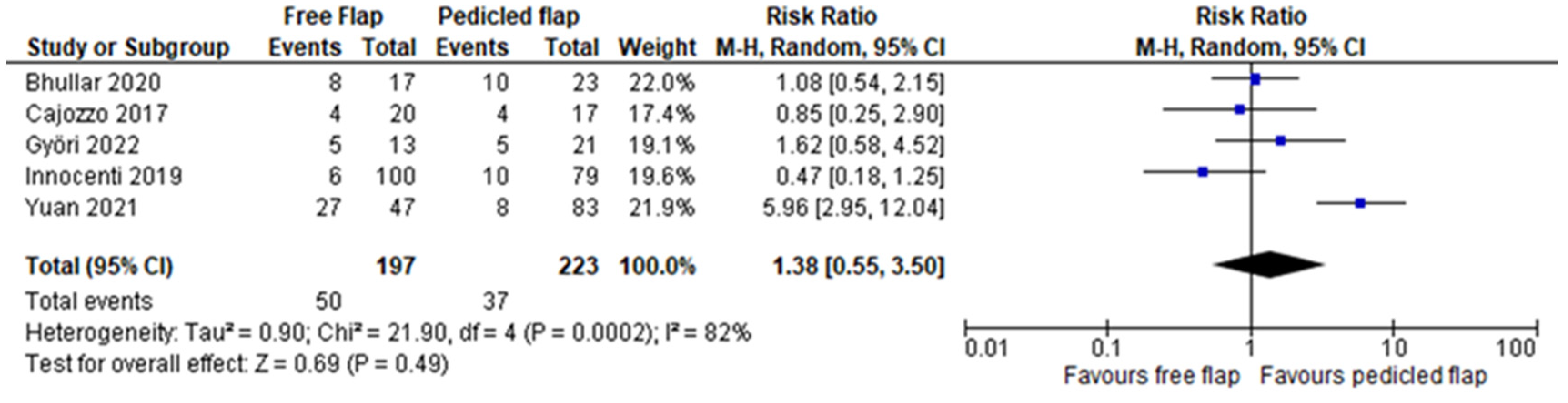
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steinberger, Z.; Therattil, P.J.; Levin, L.S. Orthoplastic Approach to Lower Extremity Reconstruction. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2021, 48, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoury, S.C.; Stranix, J.T.; Kovach, S.J.; Levin, L.S. Principles of Orthoplastic Surgery for Lower Extremity Reconstruction: Why Is This Important? J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2021, 37, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boriani, F.; Ul Haq, A.; Baldini, T.; Urso, R.; Granchi, D.; Baldini, N.; Tigani, D.; Tarar, M.; Khan, U. Orthoplastic Surgical Collaboration Is Required to Optimise the Treatment of Severe Limb Injuries: A Multi-Centre, Prospective Cohort Study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2017, 70, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajantri, B.; Bharathi, R.R.; Sabapathy, S.R. Wound Coverage Considerations for Defects of the Lower Third of the Leg. Indian J. Plast. Surg. Off. Publ. Assoc. Plast. Surg. India 2012, 45, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, S.X.; Morzycki, A.; Nickel, K.J.; Campbell, S.; Guilfoyle, R. One or Two Venous Pedicles by Anastomoses for Free Flaps in Reconstruction of the Lower Extremity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microsurgery 2021, 41, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.M.; Beem, H.M.; Wiper, J.; Rozen, W.M.; Wagels, M.; Leong, J.C. Muscle versus Fasciocutaneous Free Flaps in Heel Reconstruction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2015, 31, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basheer, M.H.; Wilson, S.M.; Lewis, H.; Herbert, K. Microvascular Free Tissue Transfer in Reconstruction of the Lower Limb. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2008, 61, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozusko, S.D.; Liu, X.; Riccio, C.A.; Chang, J.; Boyd, L.C.; Kokkalis, Z.; Konofaos, P. Selecting a Free Flap for Soft Tissue Coverage in Lower Extremity Reconstruction. Injury 2019, 50, S32–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying Heterogeneity in a Meta-Analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, I.; Moghazy, A.; Abbas, A.; Elmasry, M.; Adly, O.; Elbadawy, M.; Steinvall, I.; Sjoberg, F. A Prospective Randomized Cost Billing Comparison of Local Fasciocutaneous Perforator versus Free Gracilis Flap Reconstruction for Lower Limb in a Developing Economy. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. JPRAS 2016, 69, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajozzo, M.; Toia, F.; Innocenti, A.; Tripoli, M.; Zabbia, G.; D’Arpa, S.; Cordova, A. Retrospective Analysis in Lower Limb Reconstruction: Propeller Perforator Flaps versus Free Flaps. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2017, 33, S34–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducic, I.; Attinger, C.E. Foot and Ankle Reconstruction: Pedicled Muscle Flaps versus Free Flaps and the Role of Diabetes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Györi, E.; Fast, A.; Resch, A.; Rath, T.; Radtke, C. Reconstruction of Traumatic and Non-Traumatic Lower Extremity Defects with Local or Free Flaps. Eur. Surg. 2022, 54, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenti, M.; Dell’Acqua, I.; Famiglietti, M.; Vignini, L.; Menichini, G.; Ghezzi, S. Free Perforator Flaps vs Propeller Flaps in Lower Limb Reconstruction: A Cost/Effectiveness Analysis on a Series of 179 Cases. Injury 2019, 50 (Suppl. 5), S11–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.; Goh, T.L.H.; Song, C.T.; Suh, H.S.; Rovito, P.V.; Hong, J.-P.; Hallock, G.G. Free versus Pedicled Perforator Flaps for Lower Extremity Reconstruction: A Multicenter Comparison of Institutional Practices and Outcomes. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2018, 34, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, J.; Maharjan, S.; Lu, L.; Gong, X. Reconstruction of the Foot and Ankle Using Pedicled or Free Flaps: Perioperative Flap Survival Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Zhang, F.; Lineaweaver, W.C.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. The Coverage of Soft-Tissue Defects Around the Foot and Ankle Using Free or Local Flaps: A Comparative Cohort Study. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2021, 86, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zook, E.G.; Russell, R.C.; Asaadi, M. A Comparative Study of Free and Pedicle Flaps for Lower Extremity Wounds. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1986, 17, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhullar, D.S.; Karuppiah, S.V.; Aljawadi, A.; Gillham, T.; Fakih, O.; Khamdan, K.; Pillai, A. Local Flaps vs. Free Flaps for Complex Lower Limb Fractures: Effect of Flap Choice on Patient-Reported Outcomes. J. Orthop. 2019, 17, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, C.; Mayr, M.; Höfter, E.; Becker, A.; Pfeiffer, U.J.; Mühlbauer, W. Intraoperative Evaluation of Skin-Flap Viability Using Laser-Induced Fluorescence of Indocyanine Green. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 2002, 55, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui-Chou, H.G.; Sulek, J.; Bluebond-Langner, R.; Rodriguez, E.D. Secondary Refinements of Free Perforator Flaps for Lower Extremity Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyidova, N.; Anderson, K.; Abood, A. Comparison of Patients Satisfaction with Aesthetic Outcomes Following Lower Extremity Reconstruction: Muscle vs. Fasciocutaneous Free Flaps. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. JPRAS 2021, 74, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsougiani, D.; Platte, J.; Bigdeli, A.K.; Hoener, B.; Kremer, T.; Kneser, U.; Harhaus, L. Evaluation of 389 Patients Following Free-Flap Lower Extremity Reconstruction with Respect to Secondary Refinement Procedures. Microsurgery 2018, 38, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otchwemah, R.; Grams, V.; Tjardes, T.; Shafizadeh, S.; Bäthis, H.; Maegele, M.; Messler, S.; Bouillon, B.; Probst, C. Bacterial Contamination of Open Fractures—Pathogens, Antibiotic Resistances and Therapeutic Regimes in Four Hospitals of the Trauma Network Cologne, Germany. Injury 2015, 46 (Suppl. 4), S104–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekara, F.; Herlin, C.; Somda, S.; de Runz, A.; Grolleau, J.L.; Chaput, B. Free versus Perforator-Pedicled Propeller Flaps in Lower Extremity Reconstruction: What Is the Safest Coverage? A Meta-Analysis. Microsurgery 2018, 38, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mégevand, V.; Suva, D.; Mohamad, M.; Hannouche, D.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Muscle vs. Fasciocutaneous Microvascular Free Flaps for Lower Limb Reconstruction: A Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavien, P.A.; Barkun, J.; de Oliveira, M.L.; Vauthey, J.N.; Dindo, D.; Schulick, R.D.; de Santibañes, E.; Pekolj, J.; Slankamenac, K.; Bassi, C.; et al. The Clavien-Dindo Classification of Surgical Complications: Five-Year Experience. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelfattah, U.; Power, H.A.; Song, S.; Min, K.; Suh, H.P.; Hong, J.P. Algorithm for Free Perforator Flap Selection in Lower Extremity Reconstruction Based on 563 Cases. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, H.; Lin, C.-H.; Wei, F.-C. Role of Microsurgery in Lower Extremity Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 228S–238S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.J.; Campbell, K.A.; Mercuri, J.J.; Tejwani, N.C. Updates in the Management of Orthopedic Soft-Tissue Injuries Associated with Lower Extremity Trauma. Am. J. Orthop. 2012, 41, E27–E35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Struckmann, V.; Hirche, C.; Struckmann, F.; Kolios, L.; Lehnhardt, M.; Kneser, U.; Daigeler, A. Free and Pedicled Flaps for Reconstruction of the Weightbearing Sole of the Foot: A Comparative Analysis of Functional Results. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2014, 53, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serletti, J.M.; Carras, A.J.; O’Keefe, R.J.; Rosier, R.N. Functional Outcome after Soft-Tissue Reconstruction for Limb Salvage after Sarcoma Surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1998, 102, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Jakubietz, M.G.; Gilbert, F.; Hausknecht, F.; Meffert, R.H.; Jakubietz, R.G. Quality of Life after Flap Reconstruction of the Distal Lower Extremity: Is There a Difference Between a Pedicled Suralis Flap and a Free Anterior Lateral Thigh Flap? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeler, S.A.; de Jong, T.; Luijsterburg, A.J.M.; Mureau, M.A.M. Long-Term Patient-Reported Outcomes Following Free Flap Lower Extremity Reconstruction for Traumatic Injuries. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Database | Search Strategy | N° of Articles |
|---|---|---|
| Pubmed | (free flap[MeSH Terms/Title/Abstract]) AND (pedicled flap[MeSH Terms/Title/Abstract]) AND ((lower limb[MeSH Terms/Title/Abstract]) OR (lower extremity[MeSH Terms/Title/Abstract])) AND ((comparative study[MeSH Terms/Title/Abstract]) OR (comparison[Title/Abstract]) OR (versus[Title/Abstract]) OR (vs[Title/Abstract])) | 214 |
| Embase/Medline/Preprints | (‘free tissue graft’:kw,ti,ab OR ‘free flap reconstruction’:kw,ab,ti) AND (‘pedicled skin flap’:ab,kw,ti OR ‘flap’:ab,kw,ti) AND ‘lower limb’:ab,kw,ti AND ‘comparative study’:ab,kw,ti | 1 |
| Cochrane library | ID Search Hits #1 MeSH descriptor: [Surgical Flaps] explode all trees #2 MeSH descriptor: [Free Tissue Flaps] explode all trees #3 MeSH descriptor: [Lower Extremity] explode all trees #4 (“pedicle flap”):ti,ab,kw OR (pedicled flap):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #5 (free flap):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #6 (“lower-limb”):ti,ab,kw OR (“lower extremity”):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #7 #2 OR #5 #8 #1 OR #4 #9 #3 OR #6 #10 #7 AND #8 AND #9 | 13 |
| Web of science | (((ALL = (free flap OR free tissue transfer)) AND ALL = (pedicled flap)) AND ALL = (lower limb OR lower extremity)) AND ALL = (comparative study OR comparison OR versus OR vs) | 24 |
| PICOS | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Population | Adults and children who undergo lower limb reconstruction. | Cadaveric, animal studies. Upper extremity |
| Intervention | Free flap | |
| Comparator | Pedicled flaps (local, perforator, muscular, fascio-cutaneous) | |
| Outcomes | Main outcome flap necrosis, complications, patient satisfaction. | Studies that do not report main outcome |
| Study design | Comparative studies. | Reviews, meta-analysis, case reports, case series. Unpublished studies. |
| Author | Year | Study Period | N° Patients | Mean Age FF (SD or Range) | Mean Age PF (SD or Range) | N° FF | N° PF | Type of Flaps (FF/PF) | Mean Follow-Up (SD or Range) | Mean Defect Surface FF cm2 | Mean Defect Surface PF cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdelrahman [12] | 2016 | 2012–2015 | 30 | 27.9 (9.7) | 33.5 (10.6) | 15 | 15 | Muscle (FF)/FC flaps (PF) | *** | 35 | 28 |
| Bhullar [21] | 2020 | 2 years | 40 | 36.7 (14.9) | 48 (21.3) | 17 | 23 | Muscle flaps, FC flaps (FF)/Muscle flaps, FC flaps (PF) | 33.8 m (20.6–49.5) | *** | *** |
| Cajozzo [13] | 2017 | 2010–2015 | 37 | 61 (41–77) | 74 (64–82) | 20 | 17 | Muscle flaps, FC flaps (FF)/FC flaps (PF) | *** | *** | *** |
| Ducic [14] | 2011 | 1990–2000 | 80 | 51 (32–75) | 56 (44–77) | 52 | 34 | Muscle flaps, FC flaps (FF)/Muscle flaps (PF) | 97.2 m (37.2) | *** | *** |
| Györi [15] | 2022 | *** | 34 | 54.9 (11.9) | 62.4 (14.8) | 13 | 21 | Muscle flaps (FF)/Muscle flaps, FC flaps (PF) | Min 12 m | *** | *** |
| Innocenti [16] | 2019 | 2009–2015 | 179 | 49 (5–89) | 53 (11–92) | 100 | 79 | FC flaps (FF), FC flaps (PF) | 12 m (***) | 136 | 68 |
| Koh [17] | 2018 | 2011–2015 | *** | 50.6 (17.4) | 54.3 (19.2) | 433 | 52 | FC flaps (FF)/FC flaps (PF) | Min 12 m | *** | *** |
| Li [18] | 2016 | 2007–2014 | 144 | § | § | 57 | 87 | FC flaps (FF), FC flaps, Muscle flaps (PF) | *** | *** | *** |
| Yuan [19] | 2021 | 2010–2018 | 130 | 45.47 (***) | 44.72 (***) | 47 | 83 | *** | Min 6 m | 81 | 49 |
| Zook [20] | 1986 | 1976–1982 | 58 | *** | *** | 41 | 23 | Muscle flaps, FC flaps (FF)/Muscle flaps, FC flaps (PF) | *** | *** | *** |
| Pooled Risk Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Removed Study | Estimate (95%CI) | p | I2 (%) |
| Total flap necrosis/flap loss | Abdelrahman [12] | 1.37 (0.76–2.46) | 0.30 | 0 |
| Bhullar [21] | 1.24 (0.69–2.25) | 0.47 | 0 | |
| Cajozzo [13] | 1.35 (0.76–2.39) | 0.31 | 0 | |
| Ducic [14] | 1.28 (0.72–2.30) | 0.40 | 0 | |
| Györi [15] | 1.29 (0.72–2.31) | 0.39 | 0 | |
| Innocenti [16] | 1.30 (0.69–2.45) | 0.41 | 0 | |
| Koh [17] | 1.38 (0.68–2.79) | 0.37 | 0 | |
| Li [18] | 1.62 (0.87–3.00) | 0.13 | 0 | |
| Yuan [19] | 1.43 (0.78–2.63) | 0.25 | 0 | |
| Zook [20] | 1.29 (0.72–2.31) | 0.39 | 0 | |
| Partial flap necrosis | Abdelrahman [12] | 0.45 (0.20–1.02) | 0.06 | 29 |
| Cajozzo [13] | 0.37 (0.16–0.83) | 0.02 | 14 | |
| Ducic [14] | 0.42 (0.19–0.94) | 0.04 | 29 | |
| Györi [15] | 0.41 (0.19–0.86) | 0.02 | 21 | |
| Innocenti [16] | 0.59 (0.31–1.12) | 0.11 | 0 | |
| Li [18] | 0.52 (0.26–1.06) | 0.07 | 11 | |
| Yuan [19] | 0.38 (0.15–0.95) | 0.04 | 26 | |
| Zook [20] | 0.43 (0.19–0.96) | 0.04 | 29 | |
| Overall complication rate | Bhullar [21] | 0.71 (0.52–0.97) | 0.03 | 0 |
| Cajozzo [13] | 0.83 (0.63–1.11) | 0.21 | 10 | |
| Györi [15] | 0.82 (0.61–1.09) | 0.16 | 12 | |
| Innocenti [16] | 0.83 (0.60–1.14) | 0.25 | 13 | |
| Yuan [19] | 0.91 (0.69–1.20) | 0.50 | 0 | |
| Zook [20] | 0.84 (0.63–1.14) | 0.26 | 9 | |
| Revision surgery rate | Bhullar [21] | 1.46 (0.43–5.00) | 0.55 | 85 |
| Cajozzo [13] | 1.53 (0.52–4.53) | 0.44 | 86 | |
| Györi [15] | 1.32 (0.41–4.21) | 0.64 | 86 | |
| Innocenti [16] | 1.81 (0.68–4.78) | 0.23 | 80 | |
| Yuan [19] | 0.94 (0.58–1.52) | 0.80 | 8 | |
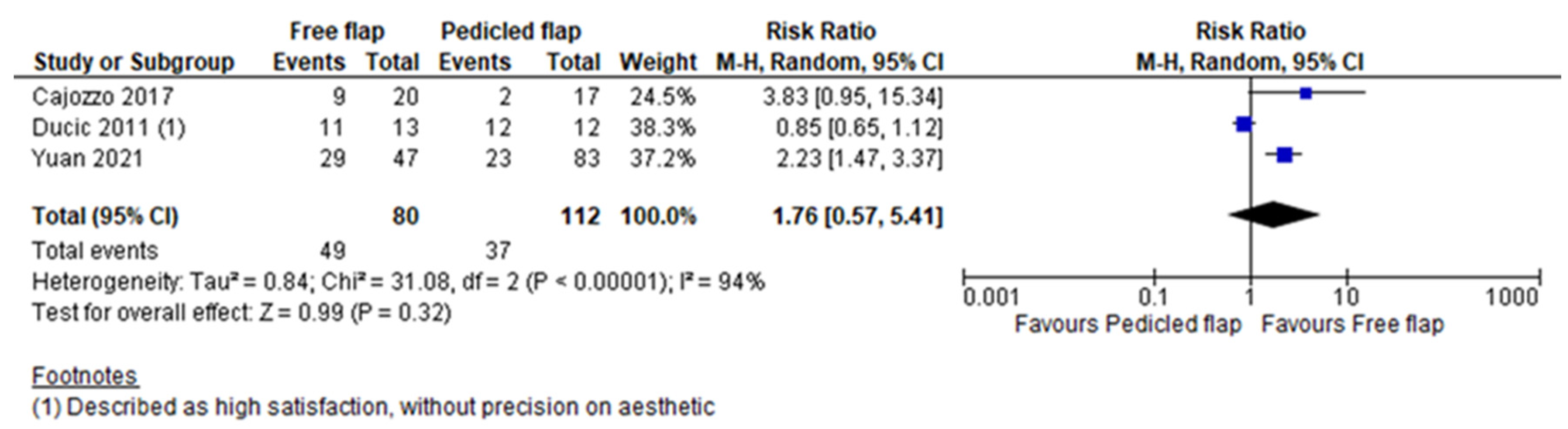
| High aesthetic satisfaction rate | Cajozzo [13] | 1.37 (0.4–4.63) | 0.61 | 96 |
| Ducic [14] | 2.33 (1.56–3.46) | <0.05 | 0 | |
| Yuan [19] | 1.70 (0.16–17.85) | 0.66 | 91 | |
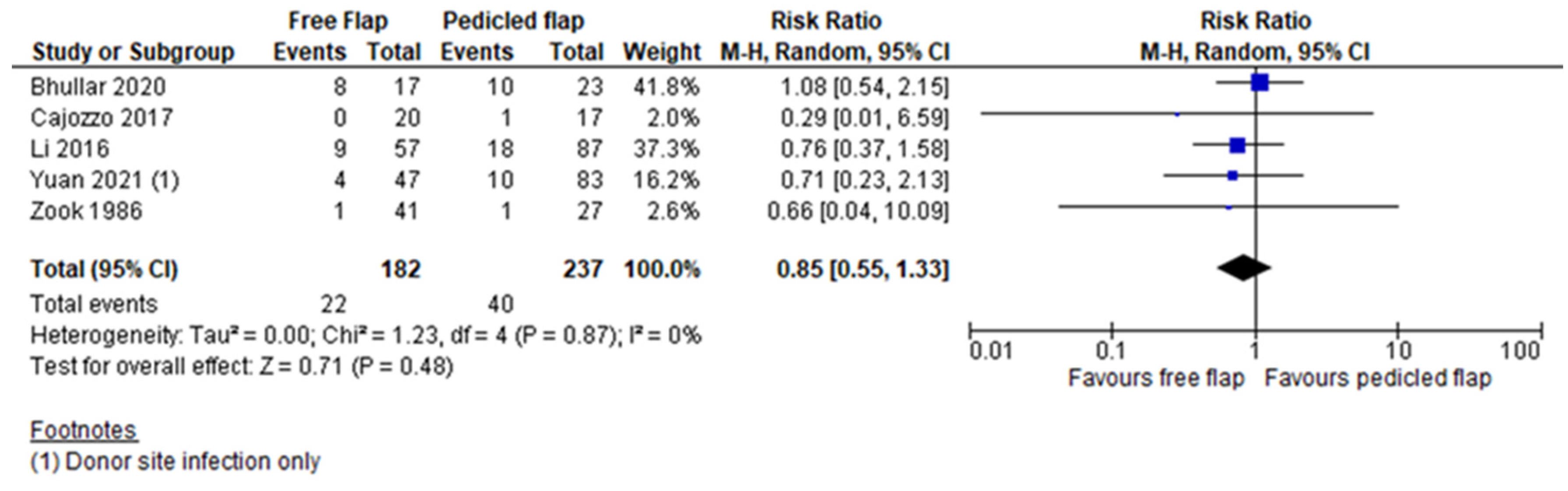
| Post-operative wound infection rate | Bhullar [21] | 0.72 (0.40–1.28) | 0.26 | 0 |
| Cajozzo [13] | 0.87 (0.56–1.36) | 0.55 | 0 | |
| Li [18] | 0.91 (0.52–1.59) | 0.74 | 0 | |
| Yuan [19] | 0.88 (0.54–1.44) | 0.62 | 0 | |
| Zook [20] | 0.86 (0.55–1.35) | 0.50 | 0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scampa, M.; Mégevand, V.; Suva, D.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Free versus Pedicled Flaps for Lower Limb Reconstruction: A Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3672. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133672
Scampa M, Mégevand V, Suva D, Kalbermatten DF, Oranges CM. Free versus Pedicled Flaps for Lower Limb Reconstruction: A Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(13):3672. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133672
Chicago/Turabian StyleScampa, Matteo, Vladimir Mégevand, Domizio Suva, Daniel F. Kalbermatten, and Carlo M. Oranges. 2022. "Free versus Pedicled Flaps for Lower Limb Reconstruction: A Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 13: 3672. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133672
APA StyleScampa, M., Mégevand, V., Suva, D., Kalbermatten, D. F., & Oranges, C. M. (2022). Free versus Pedicled Flaps for Lower Limb Reconstruction: A Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(13), 3672. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133672