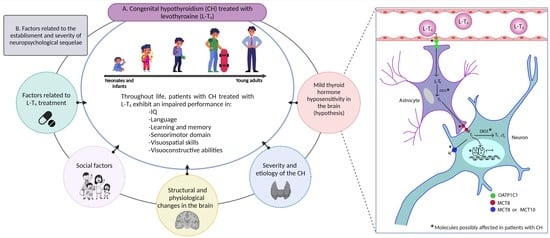
Neuropsychological Alterations in Patients with Congenital Hypothyroidism Treated with Levothyroxine: Linked Factors and Thyroid Hormone Hyposensitivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Neuropsychological Alterations in CH-Tx
3.1. IQ
3.2. Language
3.3. Learning
3.4. Memory
3.5. Sensorimotor Domain
3.6. Visuospatial and Visuoconstructive Skills
3.7. Optimum Neuropsychological Domains in Patients with CH-Tx
3.8. Summary of Neuropsychological Alterations in Patients with CH-Tx by Age Group
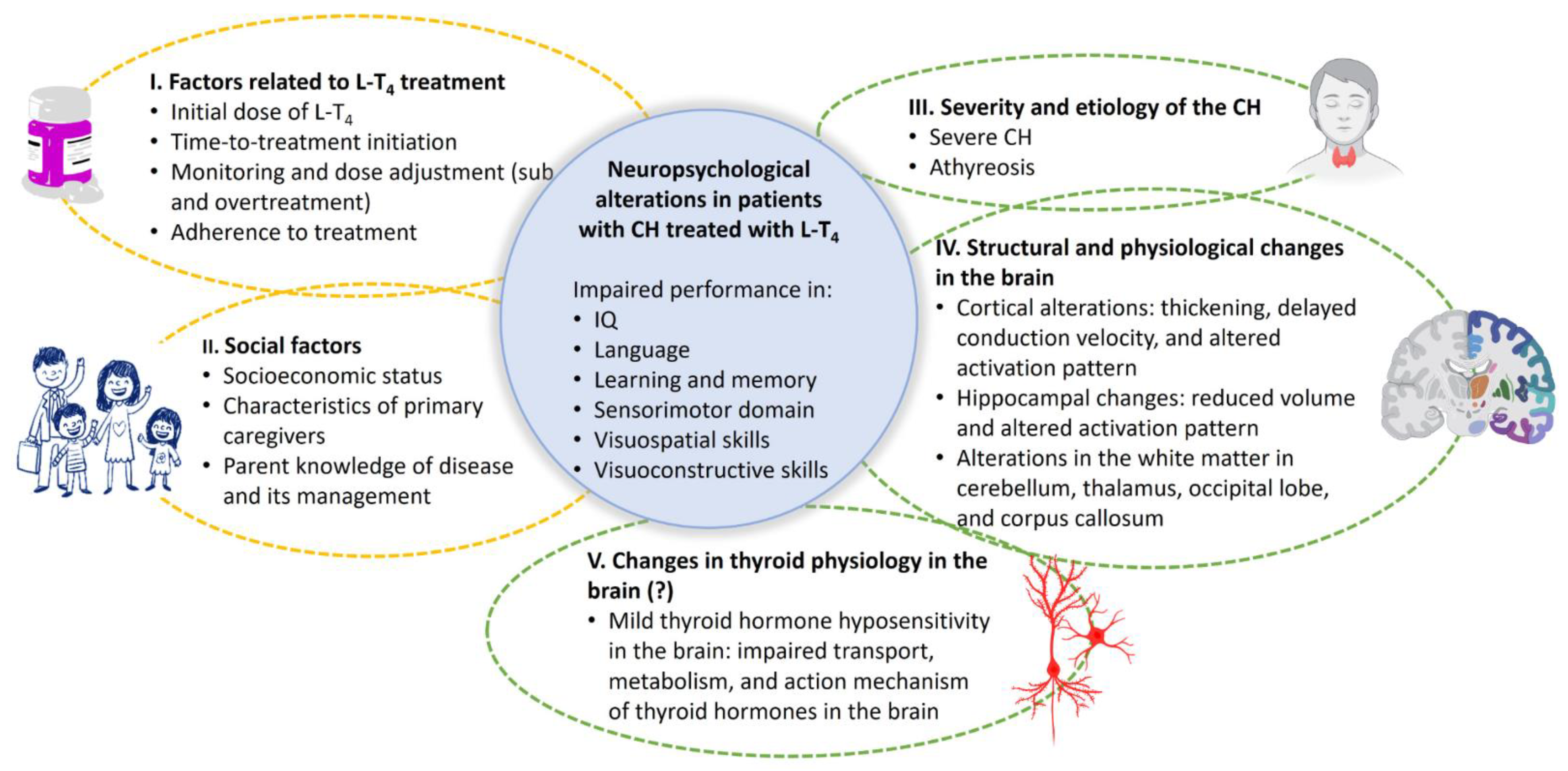
4. Factors Contributing to the Establishment of Neuropsychological Sequelae in Patients with CH
4.1. Factors Linked to Treatment with L-T4
4.2. Social Factors
4.3. Severity and Etiology of CH
4.4. Anatomical and Physiological Brain Changes in Patients with CH-Tx
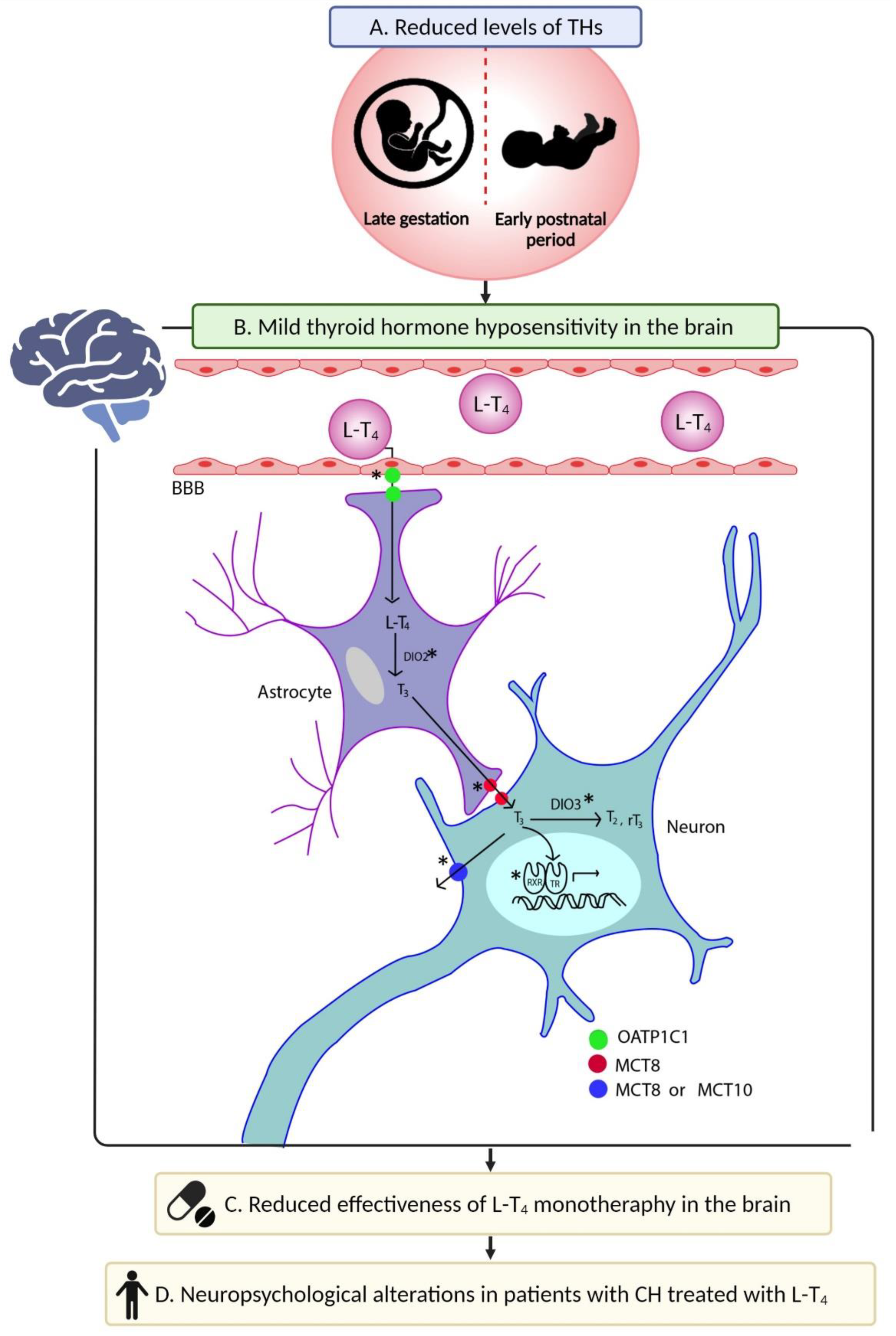
4.5. Changes in Brain Thyroid Physiology: Thyroid Hormone Hyposensitivity
- Daily dose of L-T4. Although there is still controversy [113], most reports have shown that pediatric CH patients require a higher daily dose of L-T4 than do patients with acquired or central hypothyroidism [111,114]. This has also been reported in young adults with this condition [110]. The increase in L-T4 dose suggests that tissues have a lower sensitivity to THs and there is a change in the set point of the hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis, since higher doses are prescribed to counteract the clinical symptoms of hypothyroidism and maintain TSH levels within the reference range.
- Serum TSH levels. When FT4 levels are within the reference range, 43% of patients with CH have hyperthyrotropinemia [111]. TSH is synthesized in the anterior pituitary gland, and its secretion is stimulated by a decrease in local T3 levels [115]. Therefore, the hyperthyrotropinemia observed in CH patients suggests a state of cerebral hypothyroidism that prevails despite peripheral euthyroidism.
- FT3/FT4 ratio. Patients with CH exhibit a lower Free T3 (FT3)/FT4 ratio than those with acquired hypothyroidism [110]. This suggests a reduction in the efficiency of triiodothyronine (T3) synthesis from T4 at tissue level.
- TSH vs. FT4 curve. Pediatric patients with CH show a rightward shift of the TSH/FT4 curve with respect to healthy individuals [112]. A similar change is observed in pediatric patients and young adults with CH when compared with patients with acquired hypothyroidism [110,111]. This indicates that a higher concentration of FT4 is required to maintain TSH within reference values, which supports the presence of a state of THH at the level of the central nervous system (CNS).
5. Research Agenda
- Study of CH-Tx patients with optimum neuropsychological profile and the factors linked to this satisfactory performance.
- Evaluation of the neuropsychological profile of adult and old-age patients with CH-Tx.
- Implementation of neuropsychological intervention therapies for patients with CH-Tx and evaluation of their therapeutic efficacy
- Search for structural and functional alterations in brain regions linked to language and sensorimotor, visuospatial and visuoconstructive abilities of patients with CH-Tx.
- Study of THH in patients with CH-Tx and its involvement in neuropsychological sequelae.
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CH | Congenital hypothyroidism |
| CH-Tx- | Congenital hypothyroidism treated with L-T4 |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| DIO2 | Type 2 deiodinase |
| DIO3 | Type 3 deiodinase |
| DUOX2 | Dual oxidase 2 |
| ERPs | Event related potentials |
| fMRI | Functional magnetic resonance imaging |
| FOXE1 | Forkhead Box E1 |
| FT3 | Free T3 |
| FT4 | Free T4 |
| IQ | Intellectual quotient |
| IYD | Iodotyrosine deiodinase |
| LL-SEP | Long latency somatosensory evoked potential |
| L-T3 | Liothyronine |
| L-T4 | Levothyroxine |
| MCT10 | Monocarboxylate transporter 10 |
| MCT8 | Monocarboxylate transporter 8 |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| msdMRI | Multi-Shell diffusion MRI |
| NKX2-1 | NK2 homeobox 1 |
| NKX2-5 | NK2 homeobox 5 |
| OATP1C1 | Organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1c1 |
| PAX8 | Paired box 8 |
| RXR | Retinoid X receptor |
| Scielo | Scientific Electronic Library Online |
| SLC26A4 | Solute carrier family 26 member 4 |
| SLC5A5 | Solute carrier family 5 member 5 |
| T3 | Triiodothyronine |
| T4 | Thyroxine |
| TG | Thyroglobulin |
| THH | Thyroid hormone hyposensitivity |
| THs | Thyroid hormones |
| TPO | Thyroid peroxidase |
| TRα1 | Thyroid hormone receptor-α1 |
| TRβ1 | Thyroid hormone receptor β1 |
| TRβ2 | Thyroid hormone receptor β2 |
| TSH | Thyrotropin |
| TSHR | Thyroid stimulating hormone receptor |
References
- Rastogi, M.V.; LaFranchi, S.H. Congenital Hypothyroidism. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2010, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Trotsenburg, P.; Stoupa, A.; Léger, J.; Rohrer, T.; Peters, C.; Fugazzola, L.; Cassio, A.; Heinrichs, C.; Beauloye, V.; Pohlenz, J.; et al. Congenital Hypothyroidism: A 2020–2021 Consensus Guidelines Update—An ENDO-European Reference Network Initiative Endorsed by the European Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and the European Society for Endocrinology. Thyroid 2021, 31, 387–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Hernández, A.; Huerta-Martínez, H.; Centeno-Navarrete, Y.; Flores-Escamilla, R.; Zurita-Cruz, J.N. Actualización En Hipotiroidismo Congénito: Definición, Epidemiología, Embriología y Fisiología. Primera Parte. Rev. Mex. Pediatría 2017, 84, 204–209. [Google Scholar]
- Vela-Amieva, M.; Gamboa-Cardiel, S.; Pérez-Andrade, M.E.; Ortiz-Cortés, J.; González-Contreras, C.R.; Ortega-Velázquez, V. Epidemiología Del Hipotiroidismo Congénito En México. Salud Pública México 2004, 46, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mitchell, M.L.; Hsu, H.-W.; Sahai, I. The Increased Incidence of Congenital Hypothyroidism: Fact or Fancy? Clin. Endocrinol. 2011, 75, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, C.F.; Harris, K.B.; Borgfeld, L.; Drummond-Borg, M.; Eaton, R.; Lorey, F.; Therrell, B.L.; Wallace, J.; Pass, K.A. Trends in Incidence Rates of Congenital Hypothyroidism Related to Select Demographic Factors: Data from the United States, California, Massachusetts, New York, and Texas. Pediatrics 2010, 125 (Suppl. S2), S37–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa-Trejo, M.A.; Vela-Amieva, M.; Ibarra-González, I.; de Cosío-Farias, A.P.; del Alba Herrera-Pérez, L.; Caamal-Parra, G.; Bolaños-Córdova, L.E.; García-Flores, E.P. Prevalencia Al Nacimiento de Hipotiroidismo Congénito. Acta Pediátrica México 2019, 39, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, R.; Sisi, A. A Simple Phenylalanine Method for Detecting Phenylketonuria in Large Populations of Newborn Infants. Pediatrics 1963, 32, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.J.; Wassner, A.J. Thyroid Hormone Therapy in Congenital Hypothyroidism and Pediatric Hypothyroidism. Endocrine 2019, 66, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrell, B.L.; Padilla, C.D.; Loeber, J.G.; Kneisser, I.; Saadallah, A.; Borrajo, G.J.C.; Adams, J. Current Status of Newborn Screening Worldwide: 2015. Semin. Perinatol. 2015, 39, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, J.; Olivieri, A.; Donaldson, M.; Torresani, T.; Krude, H.; van Vliet, G.; Polak, M.; Butler, G. European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology Consensus Guidelines on Screening, Diagnosis, and Management of Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Escobar, G.M.; Obregon, M.J.; del Rey, F.E. Maternal Thyroid Hormones Early in Pregnancy and Fetal Brain Development. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 18, 225–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalili, S.; Rezvani, S.M.; Dalili, H.; Mohtasham Amiri, Z.; Mohammadi, H.; Abrisham Kesh, S.; Novin, M.H.; Medghalchi, A.; Gholamnezhad, H. Congenital Hypothyroidism: Etiology and Growth-Development Outcome. Acta Med. Iran. 2014, 52, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salerno, M.; Di Maio, S.; Militerni, R.; Argenziano, A.; Valerio, G.; Tenore, A. Prognostic Factors in the Intellectual Development at 7 Years of Age in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 1995, 18, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreóla-Ramírez, G.; Barrera-Reyes, R.H.; Jiménez-Quiroz, R.; Ramírez Torres, M.A.; Segura-Cervantes, E.; Granados-Cepeda, M.L.; Ramírez-Vargas, M.N.; Meza-Rodríguez, M.D.P. Neurodesarrollo En Infantes Con Antecedente de Hipotiroidismo Congénito. Perinatología Reproducción Humana 2005, 19, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, S.M.; McAndrews, M.P.; Sheard, E.D.; Rovet, J. Visuospatial Associative Memory and Hippocampal Functioning in Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2012, 18, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepworth, S.L.; Pang, E.W.; Rovet, J.F. Word and Face Recognition in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism: An Event-Related Potential Study. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2006, 28, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellerbroek, V.L.; Bonfig, W.; Dörr, H.-G.; Bettendorf, M.; Hauffa, B.; Fricke-Otto, S.; Rohrer, T.; Reschke, F.; Schönau, E.; Schwab, K.O.; et al. Long-Term Surveillance of Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism: Data from the German Registry for Congenital Hypothyroidism (AQUAPE “Hypo Dok”). Klinische Pädiatrie 2015, 227, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.B.; Palacios, G.C.; Gómez, N.; Silva, A.; Fabela, J.H. Intelligence quotient related with congenital hypotyroidism etiology. Rev. Médica Inst. Mex. Seguro Soc. 2011, 49, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, M.K.; Yoon, J.S.; So, C.H.; Lee, H.S.; Hwang, J.S. Intellectual Development in Preschool Children with Early Treated Congenital Hypothyroidism. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 22, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soliman, A.T.; Azzam, S.; Elawwa, A.; Saleem, W.; Sabt, A. Linear Growth and Neurodevelopmental Outcome of Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism Detected by Neonatal Screening: A Controlled Study. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New England Congenital Hypothyroidism Collaborative. Elementary School Performance of Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Pediatr. 1990, 116, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovet, J.F. Congenital Hypothyroidism: An Analysis of Persisting Deficits and Associated Factors. Child Neuropsychol. 2002, 8, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez, A.; Bedregal, P.; Becerra, C.; Grob, F. Alteraciones Del Neurodesarrollo En Pacientes Con Hipotiroidismo Congénito: Recomendaciones Para El Seguimiento. Rev. Médica Chile 2017, 145, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Berenbaum, S.A. Neuropsychological Follow-Up in Neonatal Screening: Issues, Methods and Findings. Acta Paediatr. 1999, 88, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northam, E.A. Neuropsychological and Psychosocial Correlates of Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders—A Review. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 17, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovet, J.; Daneman, D. Congenital Hypothyroidism: A Review of Current Diagnostic and Treatment Practices in Relation to Neuropsychologic Outcome. Paediatr. Drugs 2003, 5, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovet, J.F. The Role of Thyroid Hormones for Brain Development and Cognitive Function. Endocr. Dev. 2014, 26, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers-Schokking, J.J.; de Muinck Keizer-Schrama, S.M.P.F. Influence of Timing and Dose of Thyroid Hormone Replacement on Mental, Psychomotor, and Behavioral Development in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Pediatr. 2005, 147, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitropoulos, A.; Molinari, L.; Etter, K.; Torresani, T.; Lang-Muritano, M.; Jenni, O.G.; Largo, R.H.; Latal, B. Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism: Long-Term Intellectual Outcome after Early High-Dose Treatment. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 65, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Morales, L.; Rodríguez Arnao, M.D.; Rodríguez Sánchez, A.; Dulín Íñiguez, E.; Álvarez González, M.A. Sustained Attention in School-Age Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism: Influence of Episodes of Overtreatment in the First Three Years of Life. Neurologia 2020, 35, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, S.; Alvarez, M.; Simoneau-Roy, J.; Leroux, S.; Van Vliet, G.; Robaey, P. Effects of Early High-Dose Levothyroxine Treatment on Auditory Brain Event-Related Potentials at School Entry in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism. Horm. Res. 2006, 66, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovet, J.F.; Ehrlich, R.M. Long-Term Effects of L-Thyroxine Therapy for Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Pediatr. 1995, 126, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, K.A.; Harper, A.; Downs, A.; Blasco, P.A.; Lafranchi, S.H. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Congenital Hypothyroidism: Comparison of Initial T4 Dose and Time to Reach Target T4 and TSH. J. Pediatr. 2005, 147, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simic, N.; Khan, S.; Rovet, J. Visuospatial, Visuoperceptual, and Visuoconstructive Abilities in Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2013, 19, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, S.M.; Willoughby, K.A.; McAndrews, M.P.; Rovet, J.F. Hippocampal Size and Memory Functioning in Children and Adolescents with Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1427–E1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufo-Campos, M. La Neuropsicología: Historia, Conceptos Básicos y Aplicaciones. Rev. Neurol. 2006, 43, S57–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portellano, J.A. Introducción a La Neuropsicología; McGrawHill: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 8448198212. [Google Scholar]
- Rovet, J.F.; Ehrlich, R.M.; Sorbara, D.L. Neurodevelopment in Infants and Preschool Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism: Etiological and Treatment Factors Affecting Outcome. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 1992, 17, 187–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopwood, N.J. Treatment of the Infant with Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Pediatr. 2002, 141, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmi, S.B.; Hashemipour, M.; Maracy, M.R.; Hovsepian, S.; Ghasemi, M. Intelligence Quotient in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism: The Effect of Diagnostic and Treatment Variables. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2013, 18, 395–399. [Google Scholar]
- Ordooei, M.; Mottaghipisheh, H.; Fallah, R.; Rabiee, A. Cognitive Outcomes for Congenital Hypothyroid and Healthy Children: A Comparative Study. Iran. J. Child Neurol. 2014, 8, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heyerdahl, S.; Kase, B.F.; Lie, S.O. Intellectual Development in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism in Relation to Recommended Thyroxine Treatment. J. Pediatr. 1991, 118, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooistra, L.; Laane, C.; Vulsma, T.; Schellekens, J.M.; van der Meere, J.J.; Kalverboer, A.F. Motor and Cognitive Development in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism: A Long-Term Evaluation of the Effects of Neonatal Treatment. J. Pediatr. 1994, 124, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, K.; Yarahmadi, S.; Etemad, K.; Mehrabi, Y.; Aghang, N.; Koosha, A.; Soori, H. Intelligence Quotient at the Age of Six Years of Iranian Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism. Indian Pediatr. 2018, 55, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovet, J.F. Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism and Their Siblings: Do They Really Differ? Pediatrics 2005, 115, e52–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulungan, A.B.; Oldenkamp, M.E.; van Trotsenburg, A.S.P.; Windarti, W.; Gunardi, H. Effect of Delayed Diagnosis and Treatment of Congenital Hypothyroidism on Intelligence and Quality of Life: An Observational Study. Med. J. Indones. 2019, 28, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clairman, H.; Skocic, J.; Lischinsky, J.E.; Rovet, J. Do Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism Exhibit Abnormal Cortical Morphology? Pediatr. Res. 2015, 78, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempers, M.J.E.; van der Sluijs Veer, L.; Nijhuis-van der Sanden, M.W.G.; Kooistra, L.; Wiedijk, B.M.; Faber, I.; Last, B.F.; de Vijlder, J.J.M.; Grootenhuis, M.A.; Vulsma, T. Intellectual and Motor Development of Young Adults with Congenital Hypothyroidism Diagnosed by Neonatal Screening. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.H.; Meltzer, S.; Kenny, F.M. Improved Prognosis in Congenital Hypothyroidism Treated before Age Three Months. J. Pediatr. 1972, 81, 912–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, M.A.; Güell, R.; Daniel, L.; Reyes-Berazaín, A.; Machado, C.; Pascual, A. Estado Neurocognitivo En Niños de 8 Años Con Hipotiroidismo Congénito Tratado Precozmentetle. Rev. Neurol. 1999, 28, 701–706. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, H.E.; Kaden, E.; Halliday, L.F.; Bamiou, D.-E.; Mankad, K.; Peters, C.; Clark, C.A. White Matter Microstructural Abnormalities in Children with Severe Congenital Hypothyroidism. NeuroImage. Clin. 2019, 24, 101980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, G.; Siragusa, V.; Rondanini, G.F.; Prina Cerai, L.M.; Mora, S.; Colombini, J.; Medaglini, S.; Lia, C.; Locatelli, T.; Comi, G. Neurophysiologic Studies and Cognitive Function in Congenital Hypothyroid Children. Pediatr. Res. 1995, 37, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rovet, J.F. Long-Term Neuropsychological Sequelae of Early-Treated Congenital Hypothyroidism: Effects in Adolescence. Acta Paediatr. 1999, 88, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempers, M.J.E.; van der Sluijs Veer, L.; Nijhuis-van der Sanden, R.W.G.; Lanting, C.I.; Kooistra, L.; Wiedijk, B.M.; Last, B.F.; de Vijlder, J.J.M.; Grootenhuis, M.A.; Vulsma, T. Neonatal Screening for Congenital Hypothyroidism in The Netherlands: Cognitive and Motor Outcome at 10 Years of Age. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Pérez, E.J.; Sánchez Pérez, M.D.C.; Moreno Macías, H.; Echeverría Arjonilla, J.C.; Rivera González, I.R.; Calzada León, R.; de la Luz Ruíz-Reyes, M.; Ontiveros Mendoza, E.; Nelly, B.-A.; Antonio, M.V.M. Hipotiroidismo Congénito Primario y Neurodesarrollo: Un Enfoque Terapéutico Integral. Acta Pediátrica México 2018, 39, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, M.; Militerni, R.; Di Maio, S.; Bravaccio, C.; Gasparini, N.; Tenore, A. Intellectual Outcome at 12 Years of Age in Congenital Hypothyroidism. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 141, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo Campos, M.L.; Musso, M.; Keselman, A.; Gruñeiro, L.; Bergadá, I.; Chiesa, A. Cognitive Profiles of Patients with Early Detected and Treated Congenital Hypothyroidism. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2017, 115, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, V.; Longaretti, R.; Giovanettoni, C.; Baldoli, C.; Pontesilli, S.; Vigone, C.; Saccuman, C.; Nigro, F.; Chiumello, G.; Scotti, G.; et al. Decreased Parietal Cortex Activity during Mental Rotation in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism. Neuroendocrinology 2009, 89, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, G.; Mora, S.; Prina Cerai, L.M.; Siragusa, V.; Colombini, J.; Medaglini, S.; Fornara, C.; Locatelli, T.; Comi, G.; Chiumello, G. Cognitive Function and Neurophysiological Evaluation in Early-Treated Hypothyroid Children. Neurol. Sci. 2000, 21, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, S.M.; McLelland, V.C.; Sheard, E.; McAndrews, M.P.; Rovet, J.F. Hippocampal Functioning and Verbal Associative Memory in Adolescents with Congenital Hypothyroidism. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleisner, A.; Torres, C.; Wilhelm, V.; Asenjo, S.; Adriazola, A.; Cafati, I.; Valenzuela, E.; Lillo, R. Congenital hypothyroidism: Neurological and psychometric evaluation. Rev. Chil. Pediatr. 1986, 57, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Chinchay, L.; Silva-Ocas, I.; Castro-Silva, N.; Del Águila Villar, C. Social, cognitive and psychomotor development in peruvian children with congenital hypothyroidism. Andes Pediatrica Rev. Chil. Pediatr. 2021, 92, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargagna, S.; Canepa, G.; Costagli, C.; Dinetti, D.; Marcheschi, M.; Millepiedi, S.; Montanelli, L.; Pinchera, A.; Chiovato, L. Neuropsychological Follow-Up in Early-Treated Congenital Hypothyroidism: A Problem-Oriented Approach. Thyroid 2000, 10, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, M.; Militerni, R.; Bravaccio, C.; Micillo, M.; Capalbo, D.; Di, M.S.; Tenore, A. Effect of Different Starting Doses of Levothyroxine on Growth and Intellectual Outcome at Four Years of Age in Congenital Hypothyroidism. Thyroid 2002, 12, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers-Schokking, J.J.; Resing, W.C.M.; de Rijke, Y.B.; de Ridder, M.A.J.; de Muinck Keizer-Schrama, S.M.P.F. Cognitive Development in Congenital Hypothyroidism: Is Overtreatment a Greater Threat than Undertreatment? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4499–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers-Schokking, J.J.; Resing, W.C.M.; Oostdijk, W.; de Rijke, Y.B.; de Muinck Keizer-Schrama, S.M.P.F. Individualized Treatment to Optimize Eventual Cognitive Outcome in Congenital Hypothyroidism. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 80, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamônica, D.A.C.; Anastácio-Pessan, F.D.L.; Ferraz, P.M.D.P.; Ribeiro, C.D.C. Performance in motor, communicative and cognitive skills of girls with congenital hypothyroidism treated from the neonatal period. CoDAS 2020, 32, e20190017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassie-Leite, A.P.; Behlau, M.; Nesi-França, S.; Lima, M.N.; Lacerda, L.D. Phonological Acquisition in Children with Early-Treated Congenital Hypothyroidism: Association with Clinical and Laboratory Parameters. CoDAS 2018, 30, e20180013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komur, M.; Ozen, S.; Okuyaz, C.; Makharoblidze, K.; Erdogan, S. Neurodevelopment Evaluation in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism by Bayley-III. Brain Dev. 2013, 35, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, C. Risk Factors for Neurodevelopmental Deficits in Congenital Hypothyroidism after Early Substitution Treatment. Endocr. J. 2011, 58, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.M.; Zaki, E.; Abdall, A.A.B.; Gomaa, M.A.; Wahab, M.M.A. Language Disorders in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism. Egypt. J. Otolaryngol. 2017, 33, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, H.; Abdel Hady, A.F.; Abdel Hamid, A.; Mahmoud, H. Language Profile in Congenital Hypothyroid Children Receiving Replacement Therapy. Folia Phoniatrica Logopaedica Off. Organ Int. Assoc. Logop. Phoniatr. 2016, 68, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gejão, M.G.; Ferreira, A.T.; Silva, G.K.; Anastácio-Pessan, F.D.L.; Lamônica, D.A.C. Communicative and Psycholinguistic Abilities in Children with Phenylketonuria and Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2009, 17, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Frezzato, R.C.; Santos, D.C.C.; Goto, M.M.F.; Ouro, M.P.C.D.; Santos, C.T.M.D.; Dutra, V.; Lima, M.C.M.P. Fine motor skills and expressive language: A study with children with congenital hypotyreoidism. CoDAS 2017, 29, e20160064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verche, E.; Hernández, S.; Quintero, I.; Acosta, V. Alteraciones de La Memoria En El Trastorno Específico Del Lenguaje: Una Perspectiva Neuropsicológica. Rev. Logop. Foniatría Audiol. 2013, 33, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa, B.E.C.; Saquipay, Á.D.C.; Matute, J.A.H.; Castro, J.E.C.; Brito, M.C.P. Neurodesarrollo En El Hipotiroidismo Congénito y Sus Particularidades Electroencefalográficas. Rev. Fac. Cienc. Médicas Univ. Cuenca 2016, 34, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, Y.; Marchena, H. Características Neuropsicológicas Del Niño Preescolar Con Hipotiroidismo Congénito En La Provincia de Cienfuegos. Rev. Chil. Neuropsicol. 2009, 4, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Olivares Torres, A.; Carlos Pías, N.; Mar Rodríguez, C.; Pérez Gesen, C.; Carvajal Martínez, F.; Rojas, E.; Acosta, C.; Fernández Yero, J.L.; Álvarez González, M.Á. Atención Sostenida En Niños En Edad Escolar Con Hipotiroidismo Congénito. Rev. Cuba. Endocrinol. 2004, 15, n.2. [Google Scholar]
- Rochiccioli, P.; Roge, B.; Alexandre, F.; Tauber, M.T. School Achievement in Children with Hypothyroidism Detected at Birth and Search for Predictive Factors. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 1992, 38, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerbeck, B.; Sundet, K.; Kase, B.F.; Heyerdahl, S. Congenital Hypothyroidism: Influence of Disease Severity and L-Thyroxine Treatment on Intellectual, Motor, and School-Associated Outcomes in Young Adults. Pediatrics 2003, 112, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagna, S.; Dinetti, D.; Pinchera, A.; Marcheschi, M.; Montanelli, L.; Presciuttini, S.; Chiovato, L. School Attainments in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism Detected by Neonatal Screening and Treated Early in Life. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 140, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Koromilas, C.; Liapi, C.; Schulpis, K.H.; Kalafatakis, K.; Zarros, A.; Tsakiris, S. Structural and Functional Alterations in the Hippocampus Due to Hypothyroidism. Metab. Brain Dis. 2010, 25, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, W.F.; Fuggle, P.W.; Grant, D.B.; Smith, I. Educational Progress, Behaviour, and Motor Skills at 10 Years in Early Treated Congenital Hypothyroidism. Arch. Dis. Child. 1997, 77, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.I.; Daneman, D.; Rovet, J. The Influence of Etiology and Treatment Factors on Intellectual Outcome in Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2001, 22, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willoughby, K.A.; McAndrews, M.P.; Rovet, J.F. Accuracy of Episodic Autobiographical Memory in Children with Early Thyroid Hormone Deficiency Using a Staged Event. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2014, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Oerbeck, B.; Sundet, K.; Kase, B.F.; Heyerdahl, S. Congenital Hypothyroidism: No Adverse Effects of High Dose Thyroxine Treatment on Adult Memory, Attention, and Behaviour. Arch. Dis. Child. 2005, 90, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, D.B.; Fuggle, P.W.; Smith, I. Increased Plasma Thyroid Stimulating Hormone in Treated Congenital Hypothyroidism: Relation to Severity of Hypothyroidism, Plasma Thyroid Hormone Status, and Daily Dose of Thyroxine. Arch. Dis. Child. 1993, 69, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral-Guillé, I.; Rivera-González, R.; Ontiveros-Mendoza, E. Psychomotricity and Its Relationship with the Intelligence Quotient in Preschoolers with Congenital Hypothyroidism. Int. Phys. Med. Rehab. J. 2019, 4, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Leneman, M.; Buchanan, L.; Rovet, J. Where and What Visuospatial Processing in Adolescents with Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2001, 7, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishkin, M.; Ungerleider, L.G.; Macko, K.A. Object Vision and Spatial Vision: Two Cortical Pathways. Trends Neurosci. 1983, 6, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Hernández, A.; Huerta-Martínez, H.; Centeno-Navarrete, Y.; Zurita-Cruz, J.N. Actualización En Hipotiroidismo Congénito: Etiología, Cuadro Clínico, Diagnóstico y Tratamiento. Segunda Parte. Rev. Mex. Pediatría 2018, 85, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Leung, A.A.C. Evaluation and Management of the Child with Hypothyroidism. World J. Pediatr. 2019, 15, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyttendaele, M.; Lambert, S.; Tenoutasse, S.; Boros, E.; Ziereisen, F.; Van Vliet, G.; Heinrichs, C.; Brachet, C. Congenital Hypothyroidism: Long-Term Experience with Early and High Levothyroxine Dosage. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2016, 85, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez Sánchez, A.; Chueca Guindulain, M.J.; Alija Merillas, M.; Ares Segura, S.; Moreno Navarro, J.C.; Rodríguez Arnao, M.D. Diagnosis and follow-Up of patients with congenital hypothyroidism detected by neonatal screening. Anales Pediatría 2019, 90, 250.e1–250.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers-Schokking, J.J.; Resing, W.C.M.; Oostdijk, W.; de Rijke, Y.B.; de Muinck Keizer-Schrama, S.M.P.F. Relation between Early Over- and Undertreatment and Behavioural Problems in Preadolescent Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2018, 90, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, A.R.; Grosse, S.D.; Baker, M.; Pollock, A.J.; Hinton, C.F.; Shapira, S.K. Treatment Discontinuation within 3 Years of Levothyroxine Initiation among Children Diagnosed with Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Pediatr. 2020, 223, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassner, A.J. Unraveling the Genetics of Congenital Hypothyroidism: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e3464–e3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makretskaya, N.; Bezlepkina, O.; Kolodkina, A.; Kiyaev, A.; Vasilyev, E.V.; Petrov, V.; Kalinenkova, S.; Malievsky, O.; Dedov, I.I.; Tiulpakov, A. High Frequency of Mutations in “dyshormonogenesis Genes” in Severe Congenital Hypothyroidism. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paone, L.; Fleisch, A.F.; Feldman, H.A.; Brown, R.S.; Wassner, A.J. Liothyronine Improves Biochemical Control of Congenital Hypothyroidism in Patients with Central Resistance to Thyroid Hormone. J. Pediatr. 2016, 175, 167–172.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brito, L.N.S.; Andrade, C.L.O.D.; Alves, C.D.A.D. Adhesion to Treatment by Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism: Knowledge of Caregivers in Bahia State, Brazil. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2021, 39, e2020074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera González, R.; Figueroa Olea, M.; Soto Romas, C.; Soto Villaseñor, F.; Sánchez, C. Interacción Madre-Hijo Durante La Alimentación En Niños Con Hipotiroidismo Congénito. Rev. Enfermería Neurológica 2014, 13, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuggle, P.W.; Grant, D.B.; Smith, I.; Murphy, G. Intelligence, Motor Skills and Behaviour at 5 Years in Early-Treated Congenital Hypothyroidism. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1991, 150, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.; Carvajal, F.; Renón, A.; Pérez, C.; Olivares, A.; Rodríguez, G.; Alvarez, V. Differential Effect of Fetal, Neonatal and Treatment Variables on Neurodevelopment in Infants with Congenital Hypothyroidism. Horm. Res. 2004, 61, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachmiel, M.; Blaser, S.; Widjaja, E.; Rovet, J. Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism Have Similar Neuroradiological Abnormal Findings as Healthy Ones. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 194918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norcross-Nechay, K.; Richards, G.E.; Cavallo, A. Evoked Potentials Show Early and Delayed Abnormalities in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism. Neuropediatrics 1989, 20, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.; Eidson, M.; Engle, H.; Sheldon, J.; Cleveland, W.W. Changes in Brain Maturation Detected by Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Pediatr. 1989, 115, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ArıYuca, S.; Yılmaz, C.; Kaya, A.; Üstyol, L.; Sal, E.; Cesur, Y.; Caksen, H. A Case of Congenital Hypothyroidism Presented with Dysmyelinization Findings. J. Acute Dis. 2014, 3, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rurale, G.; Di Cicco, E.; Dentice, M.; Salvatore, D.; Persani, L.; Marelli, F.; Luongo, C. Thyroid Hormone Hyposensitivity: From Genotype to Phenotype and Back. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagattini, B.; Cosmo, C.D.; Montanelli, L.; Piaggi, P.; Ciampi, M.; Agretti, P.; Marco, G.D.; Vitti, P.; Tonacchera, M. The Different Requirement of L-T4 Therapy in Congenital Athyreosis Compared with Adult-Acquired Hypothyroidism Suggests a Persisting Thyroid Hormone Resistance at the Hypothalamic-Pituitary Level. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 171, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempers, M.J.E.; van Trotsenburg, A.S.P.; van Tijn, D.A.; Bakker, E.; Wiedijk, B.M.; Endert, E.; de Vijlder, J.J.M.; Vulsma, T. Disturbance of the Fetal Thyroid Hormone State Has Long-Term Consequences for Treatment of Thyroidal and Central Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 4094–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.A.; Schoen, E.J.; La Franchi, S.; Mandel, S.H.; Nelson, J.C.; Carlton, E.I.; Goshi, J.H. The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid Negative Feedback Control Axis in Children with Treated Congenital Hypothyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 2722–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlsteyn, M.; Deladoëy, J.; Van Vliet, G. Similar Age-Dependent Levothyroxine Requirements of Schoolchildren with Congenital or Acquired Hypothyroidism. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2016, 175, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellerbroek, V.; Warncke, K.; Köhle, J.; Bonfig, W. A Levothyroxine Dose Recommendation for the Treatment of Children and Adolescents with Autoimmune Thyroiditis Induced Hypothyroidism. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 26, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoermann, R.; Midgley, J.E.M.; Larisch, R.; Dietrich, J.W. Homeostatic Control of the Thyroid-Pituitary Axis: Perspectives for Diagnosis and Treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitrescu, A.M.; Refetoff, S. The Syndromes of Reduced Sensitivity to Thyroid Hormone. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3987–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesema, E.C.H.; Kuiper, G.G.J.M.; Jansen, J.; Visser, T.J.; Kester, M.H.A. Thyroid Hormone Transport by the Human Monocarboxylate Transporter 8 and Its Rate-Limiting Role in Intracellular Metabolism. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 2761–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkemade, A.; Friesema, E.C.H.; Kalsbeek, A.; Swaab, D.F.; Visser, T.J.; Fliers, E. Expression of Thyroid Hormone Transporters in the Human Hypothalamus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E967–E971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkemade, A.; Friesema, E.C.; Unmehopa, U.A.; Fabriek, B.O.; Kuiper, G.G.; Leonard, J.L.; Wiersinga, W.M.; Swaab, D.F.; Visser, T.J.; Fliers, E. Neuroanatomical Pathways for Thyroid Hormone Feedback in the Human Hypothalamus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 4322–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkemade, A.; Vuijst, C.L.; Unmehopa, U.A.; Bakker, O.; Vennström, B.; Wiersinga, W.M.; Swaab, D.F.; Fliers, E. Thyroid Hormone Receptor Expression in the Human Hypothalamus and Anterior Pituitary. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M.A. Thyroid Hormone Action: A Binding Contract. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morte, B.; Bernal, J. Thyroid Hormone Action: Astrocyte-Neuron Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmo, J.; Chaves, C.M. Physiologic Significance of Epigenetic Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Target Gene Expression. Eur. Thyroid J. 2020, 9, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmo, J.; Scherberg, N.H.; Dumitrescu, A.M.; Refetoff, S. Reduced Sensitivity to Thyroid Hormone as a Transgenerational Epigenetic Marker Transmitted Along the Human Male Line. Thyroid 2019, 29, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichomkwun, P.; Anselmo, J.; Liao, X.-H.; Hönes, G.S.; Moeller, L.C.; Alonso-Sampedro, M.; Weiss, R.E.; Dumitrescu, A.M.; Refetoff, S. Fetal Exposure to High Maternal Thyroid Hormone Levels Causes Central Resistance to Thyroid Hormone in Adult Humans and Mice. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 3234–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.; Sinha, R.A.; Mohan, V.; Rao, G.; Pal, A.; Pathak, A.; Singh, M.; Godbole, M.M. Effect of Hypothyroxinemia on Thyroid Hormone Responsiveness and Action during Rat Postnatal Neocortical Development. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 228, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, M.; Goodwin, C.; Liao, X.; Page, D.; Refetoff, S.; Weiss, R.E. Effects of Maternal Levels of Thyroid Hormone (TH) on the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Set Point: Studies in TH Receptor β Knockout Mice. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5305–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcoxon, J.S.; Redei, E.E. Prenatal Programming of Adult Thyroid Function by Alcohol and Thyroid Hormones. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 287, E318–E326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Razón-Hernández, K.C.; Osnaya-Brizuela, N.; Valenzuela-Peraza, A.; Ontiveros-Mendoza, E.; Rodríguez-Serrano, L.M.; Pacheco-Rosado, J.; Barragán-Mejía, G.; Sánchez-Huerta, K. Neuropsychological Alterations in Patients with Congenital Hypothyroidism Treated with Levothyroxine: Linked Factors and Thyroid Hormone Hyposensitivity. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123427
Razón-Hernández KC, Osnaya-Brizuela N, Valenzuela-Peraza A, Ontiveros-Mendoza E, Rodríguez-Serrano LM, Pacheco-Rosado J, Barragán-Mejía G, Sánchez-Huerta K. Neuropsychological Alterations in Patients with Congenital Hypothyroidism Treated with Levothyroxine: Linked Factors and Thyroid Hormone Hyposensitivity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(12):3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123427
Chicago/Turabian StyleRazón-Hernández, Karla Cristina, Norma Osnaya-Brizuela, Armando Valenzuela-Peraza, Esperanza Ontiveros-Mendoza, Luis Miguel Rodríguez-Serrano, Jorge Pacheco-Rosado, Gerardo Barragán-Mejía, and Karla Sánchez-Huerta. 2022. "Neuropsychological Alterations in Patients with Congenital Hypothyroidism Treated with Levothyroxine: Linked Factors and Thyroid Hormone Hyposensitivity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 12: 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123427
APA StyleRazón-Hernández, K. C., Osnaya-Brizuela, N., Valenzuela-Peraza, A., Ontiveros-Mendoza, E., Rodríguez-Serrano, L. M., Pacheco-Rosado, J., Barragán-Mejía, G., & Sánchez-Huerta, K. (2022). Neuropsychological Alterations in Patients with Congenital Hypothyroidism Treated with Levothyroxine: Linked Factors and Thyroid Hormone Hyposensitivity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(12), 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123427