A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
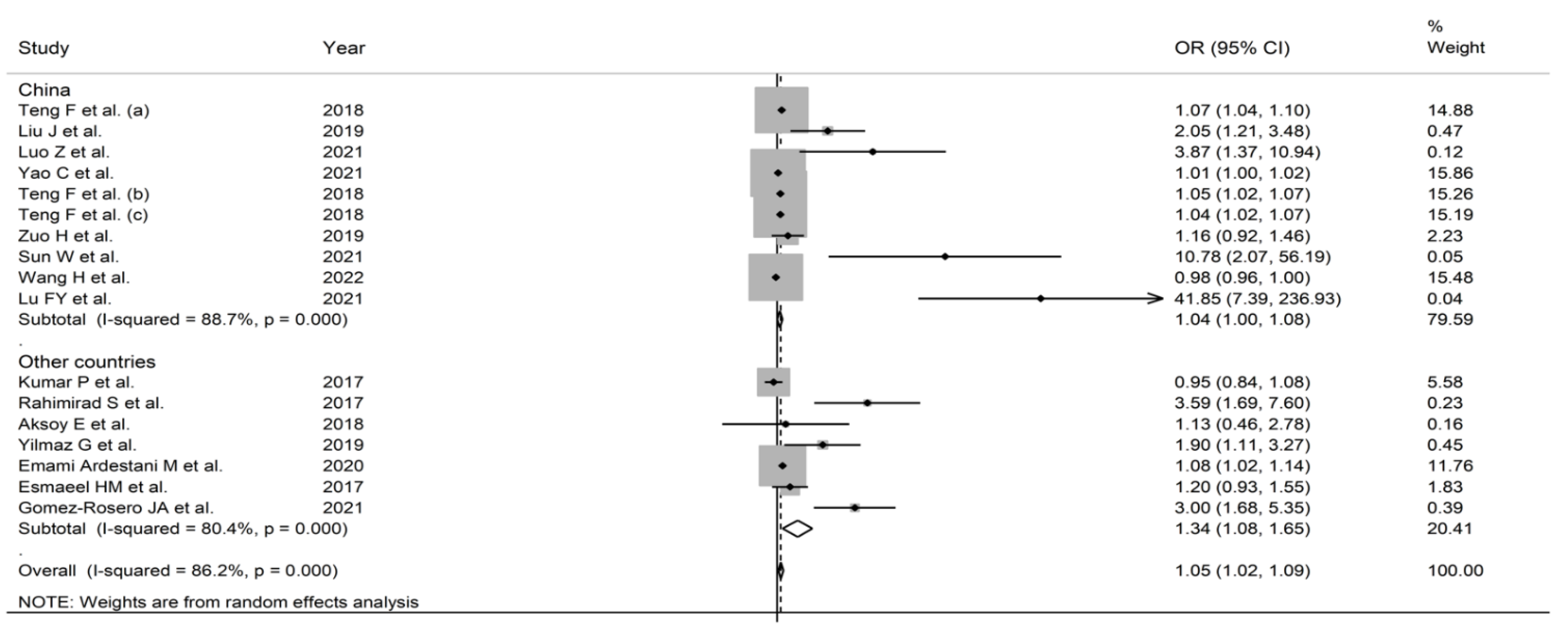
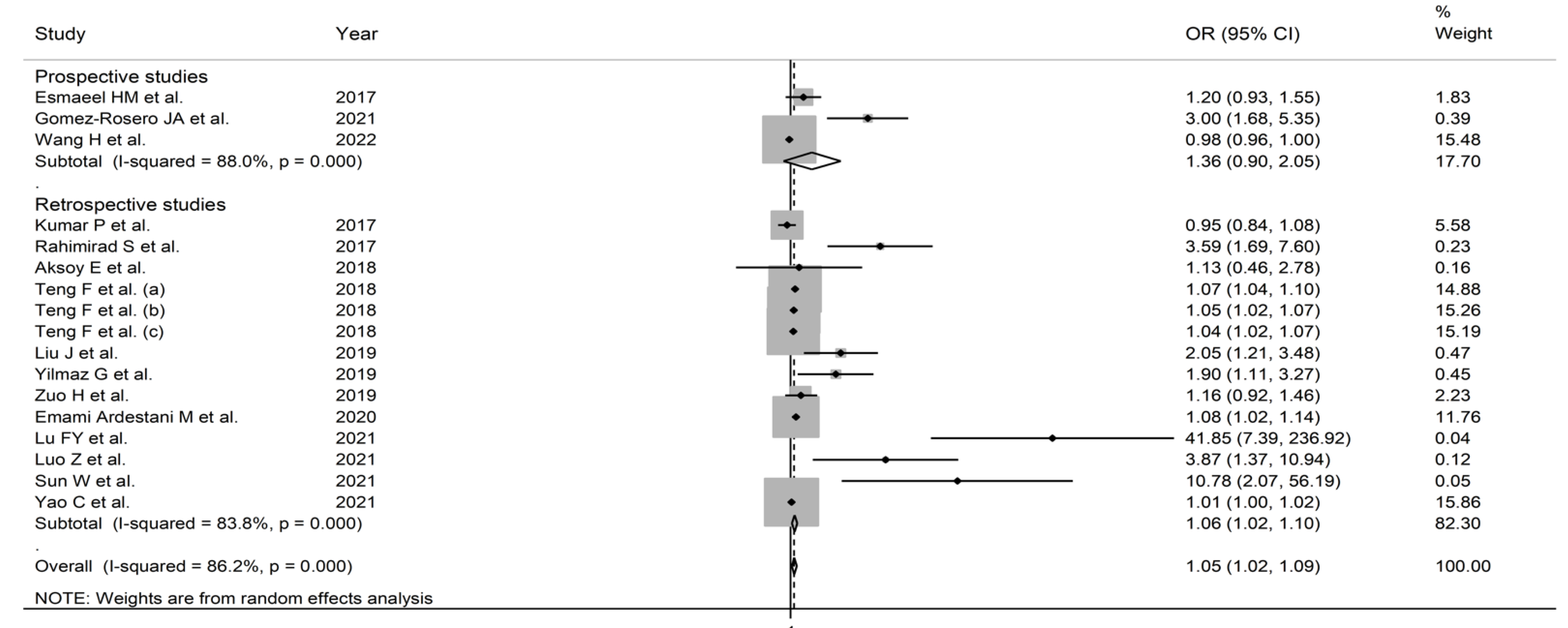
3.2. Pooled Odds Ratios
3.2.1. Study Characteristics
3.2.2. Risk of Bias
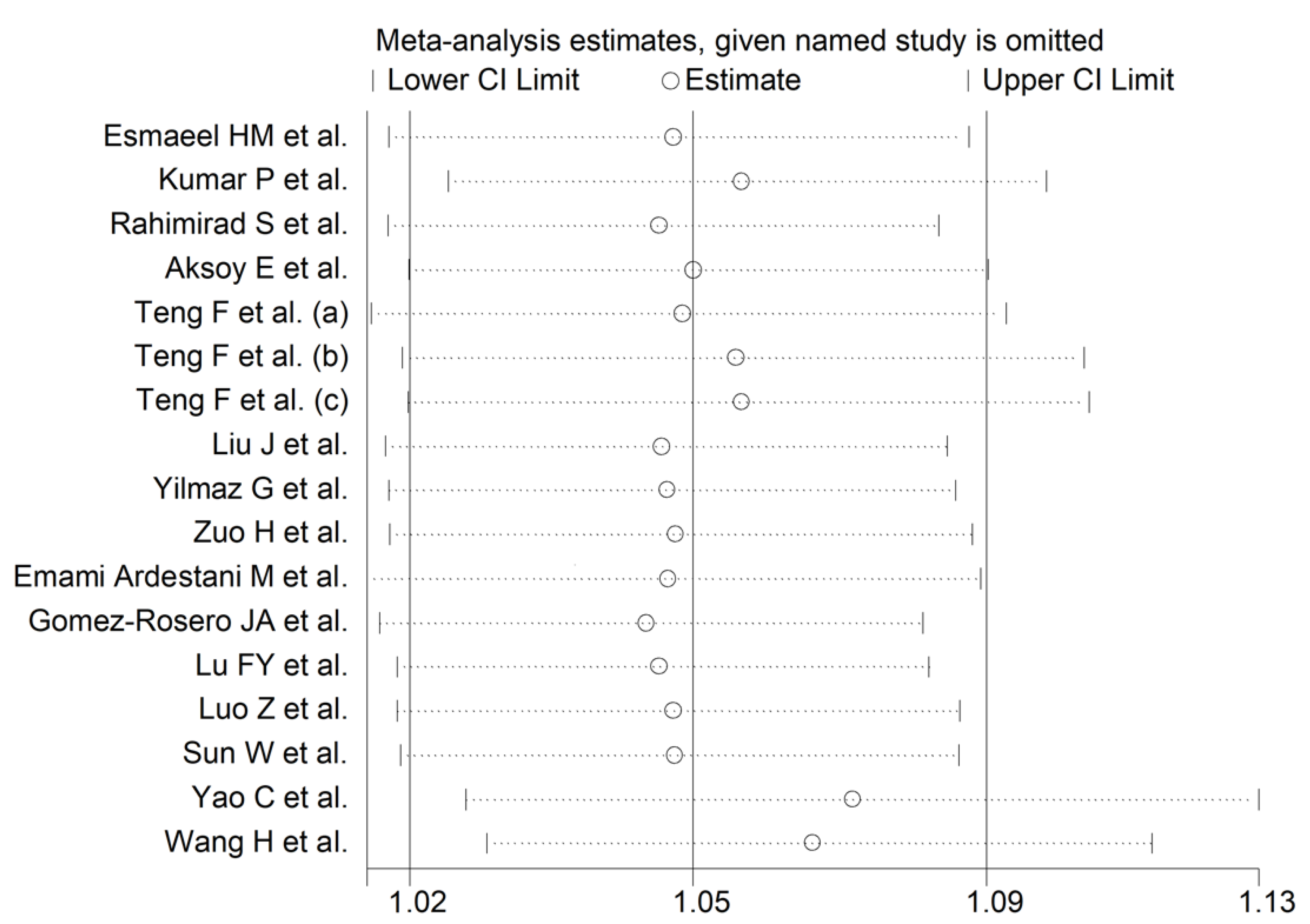
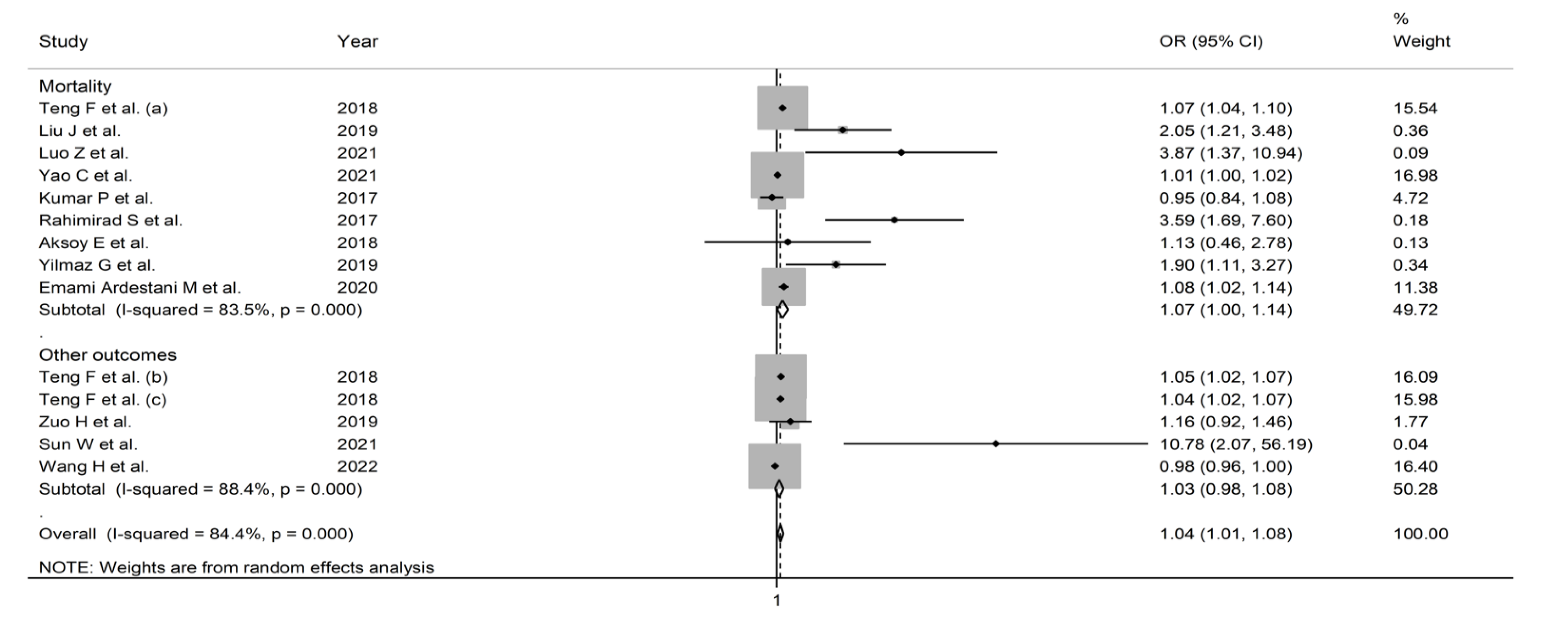
3.2.3. Results of Individual Studies and Syntheses
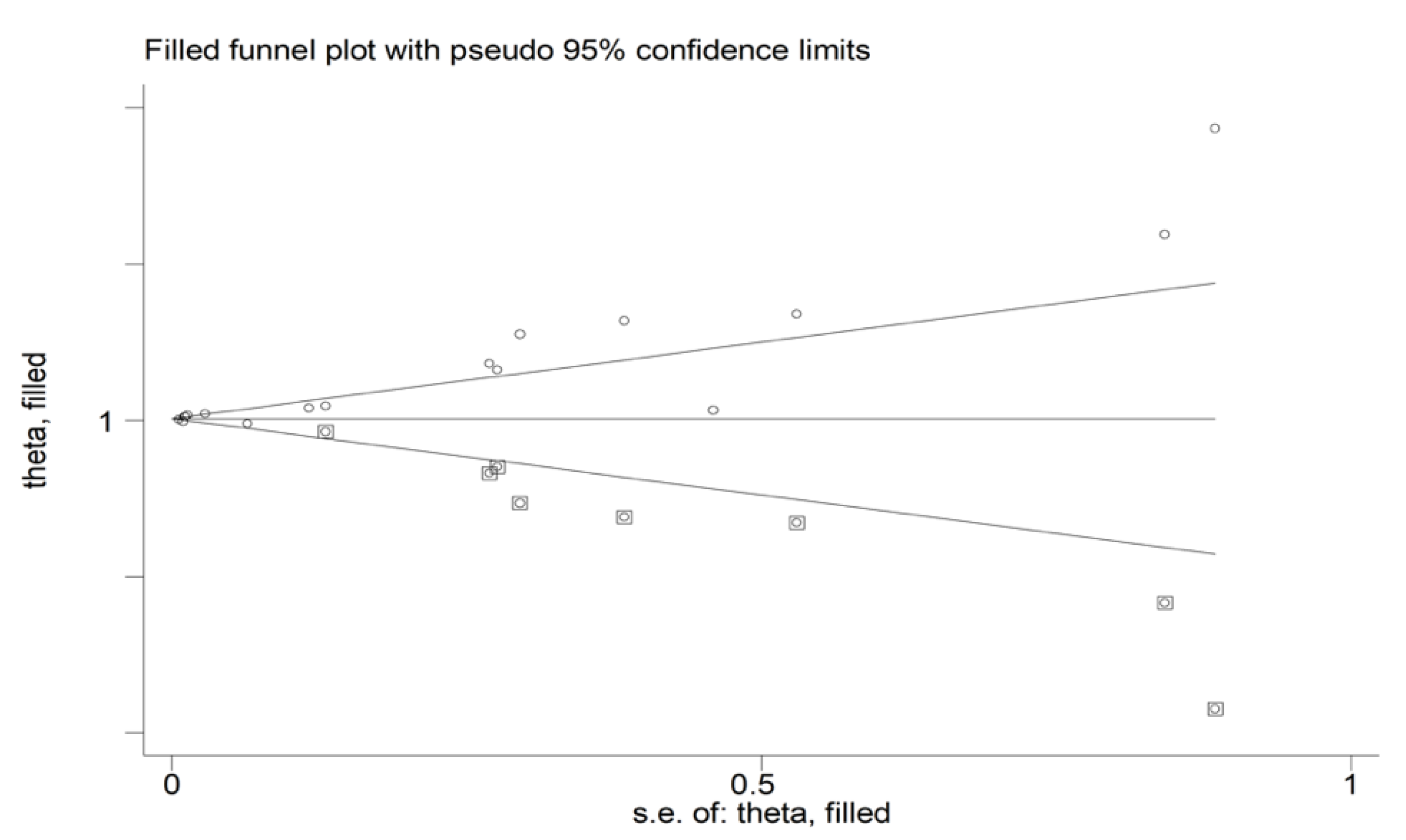
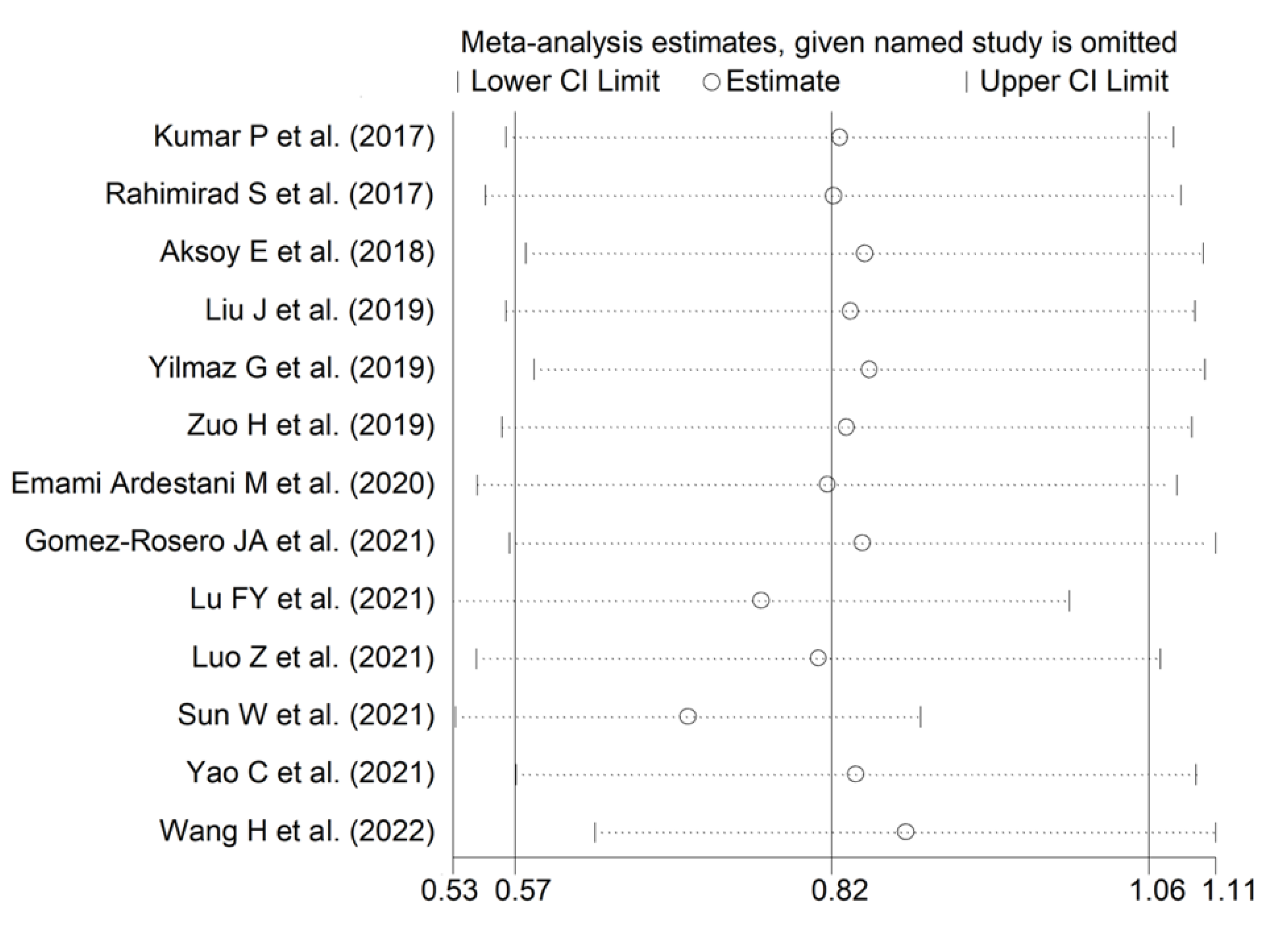
3.2.4. Publication Bias
3.2.5. Subgroup and Meta-Regression Analysis
3.2.6. Certainty of Evidence
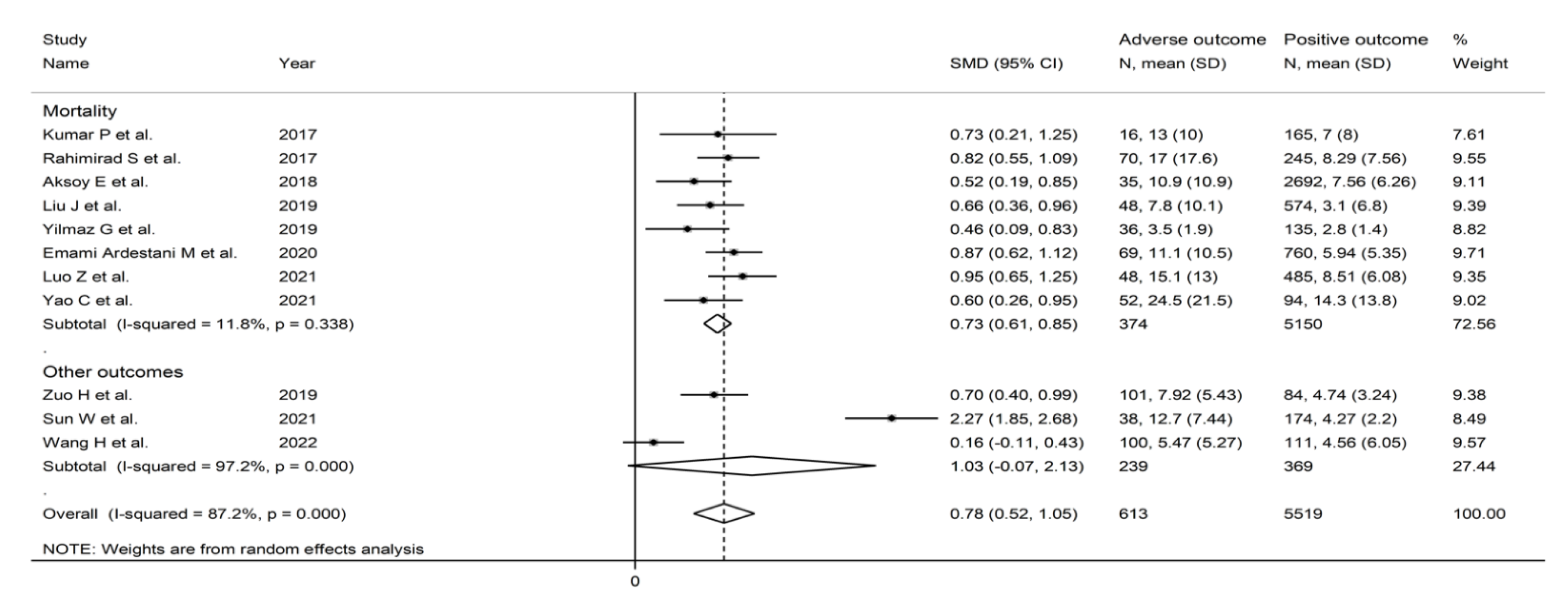
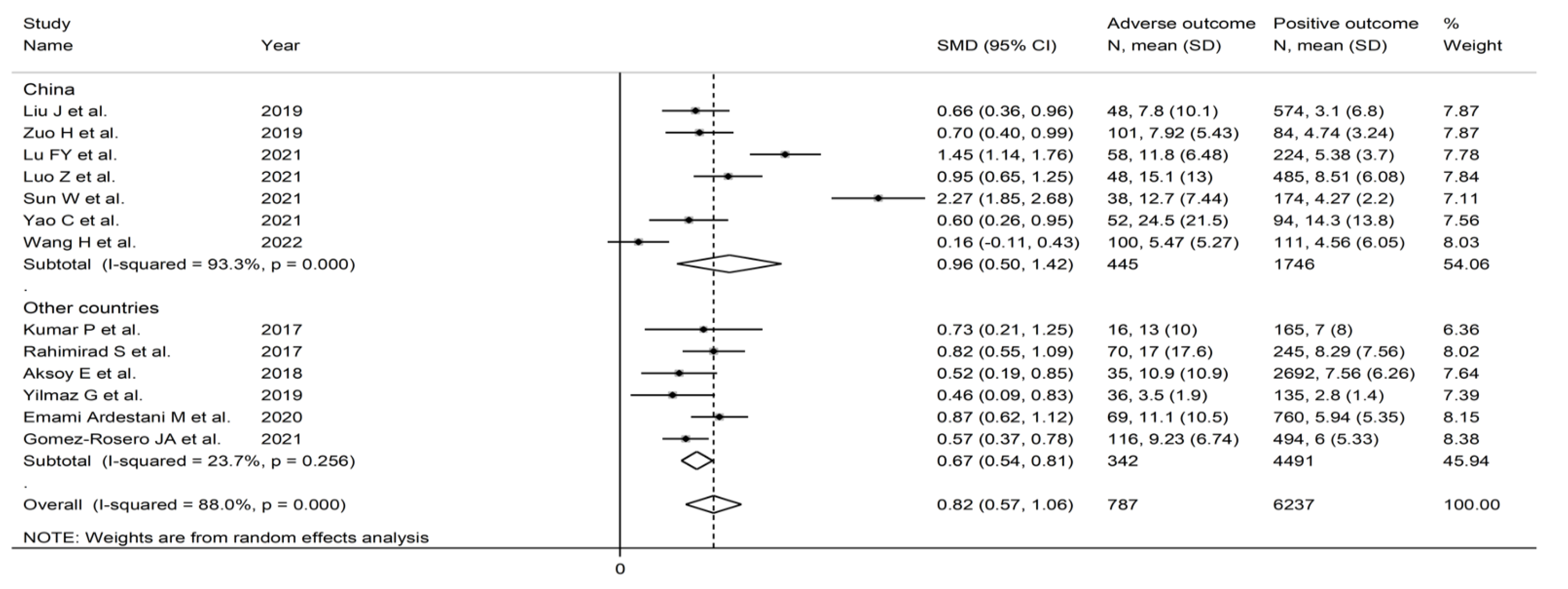
3.3. Pooled Standard Mean Differences
3.3.1. Study Characteristics
3.3.2. Risk of Bias
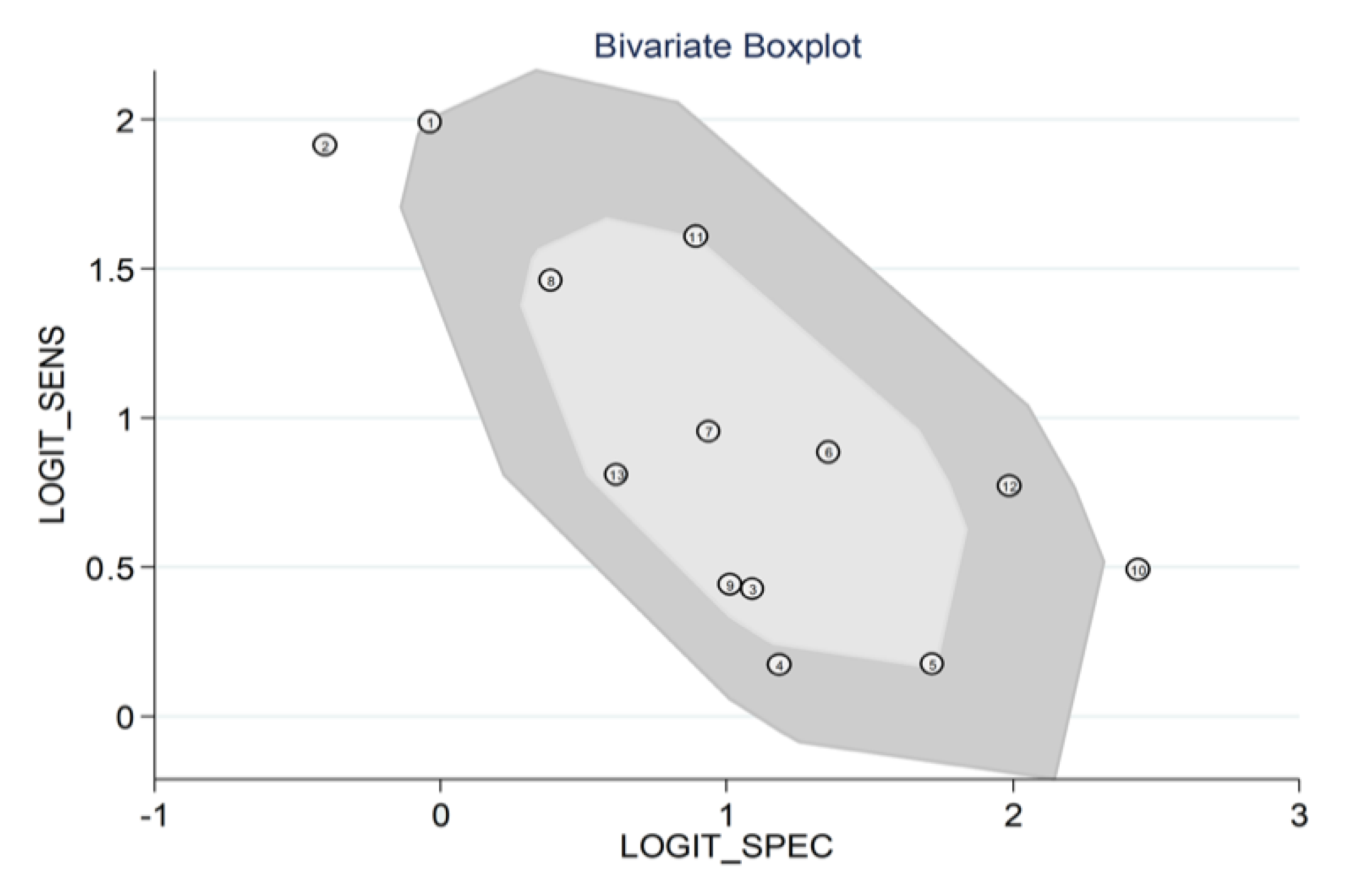
3.3.3. Results of Individual Studies and Syntheses
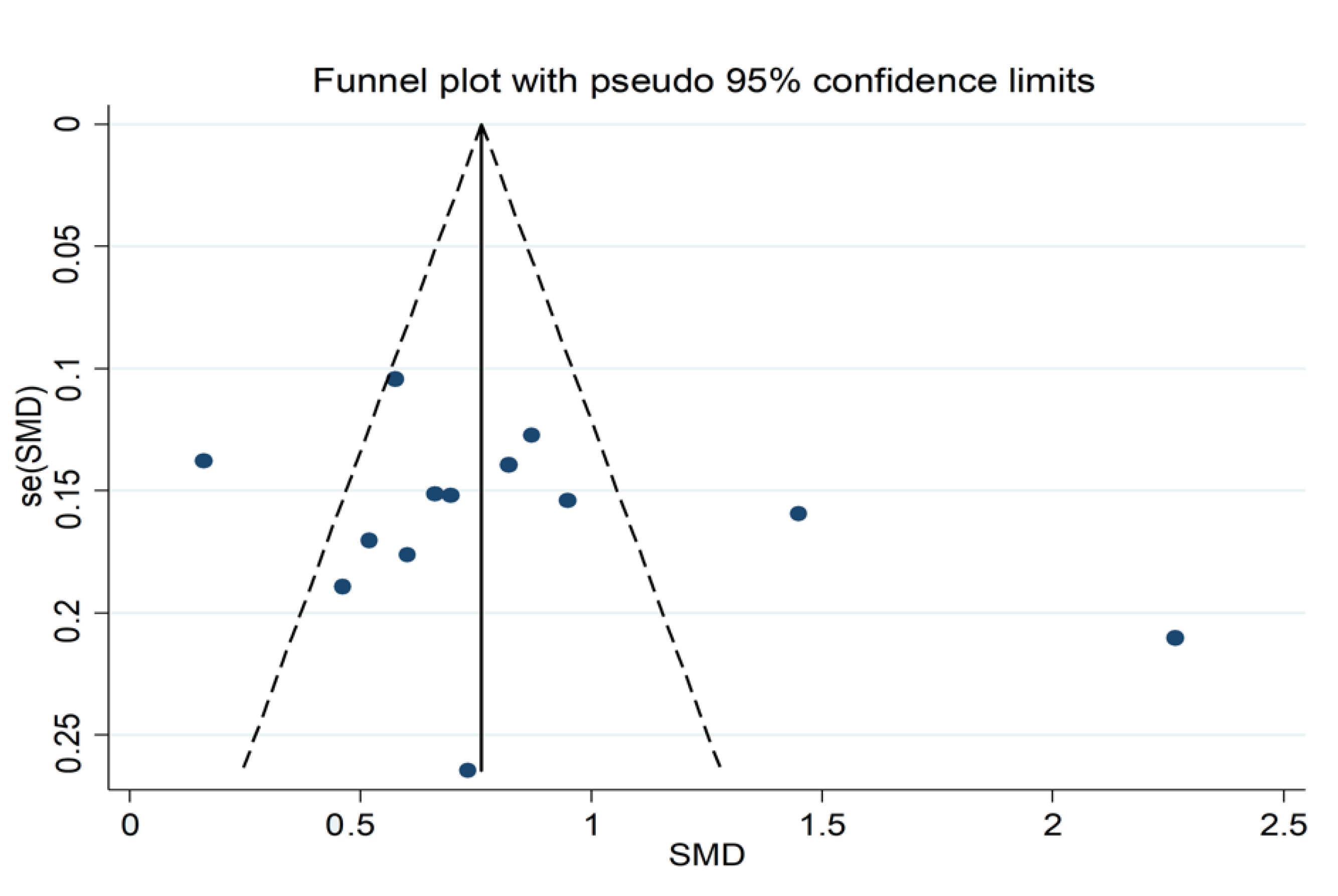
3.3.4. Publication Bias
3.3.5. Subgroup and Meta-Regression Analysis
3.3.6. Certainty of Evidence
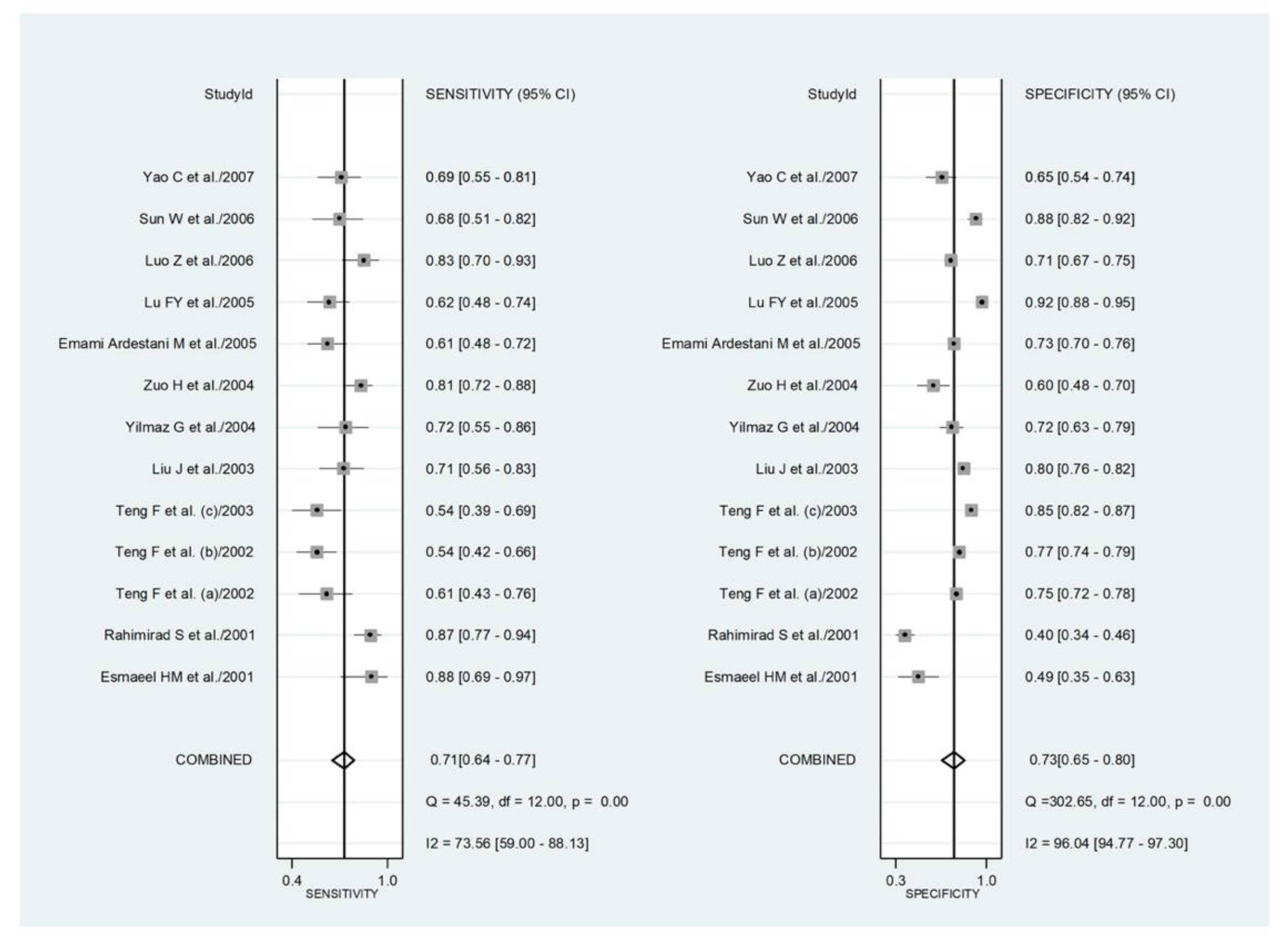
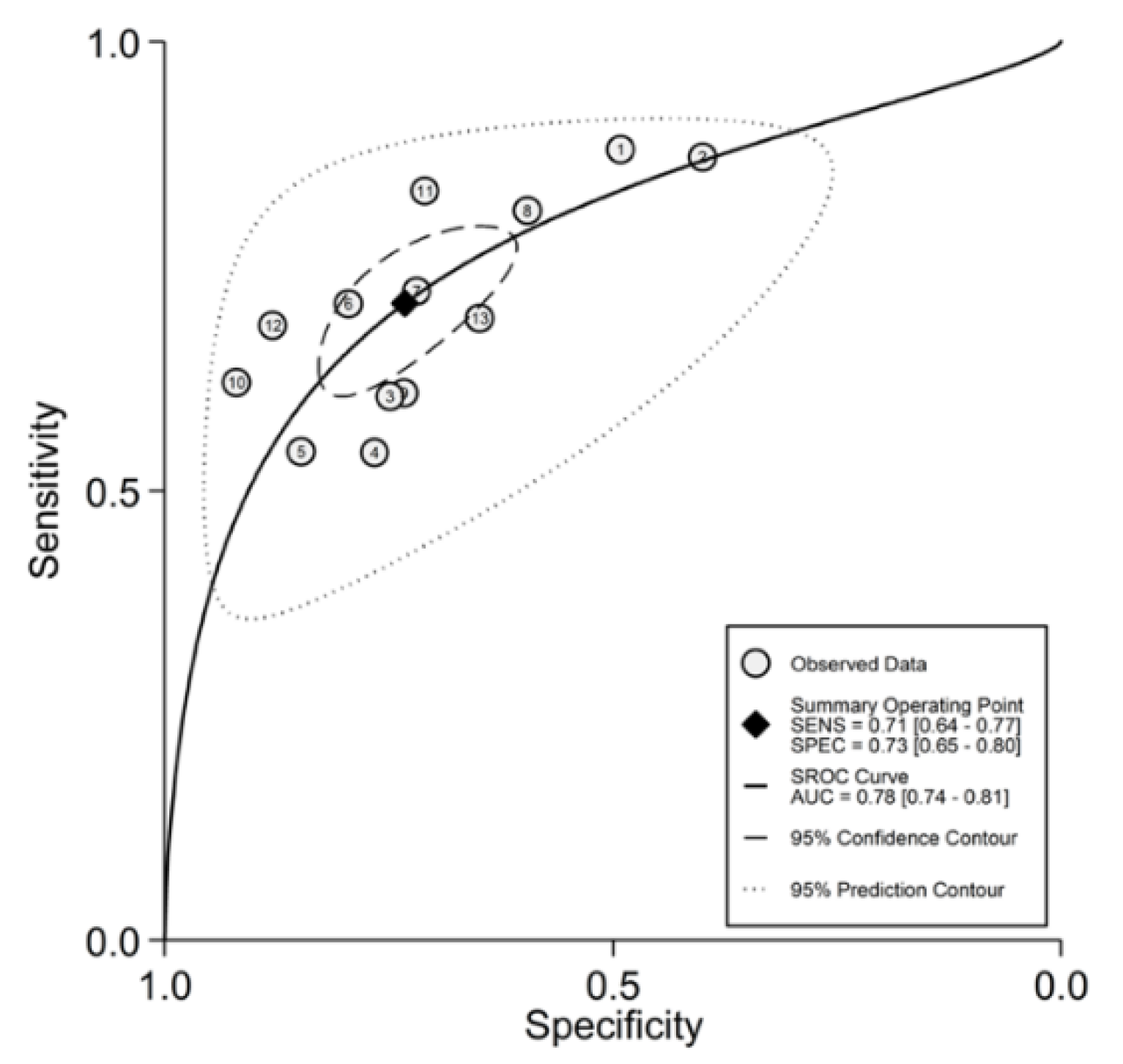
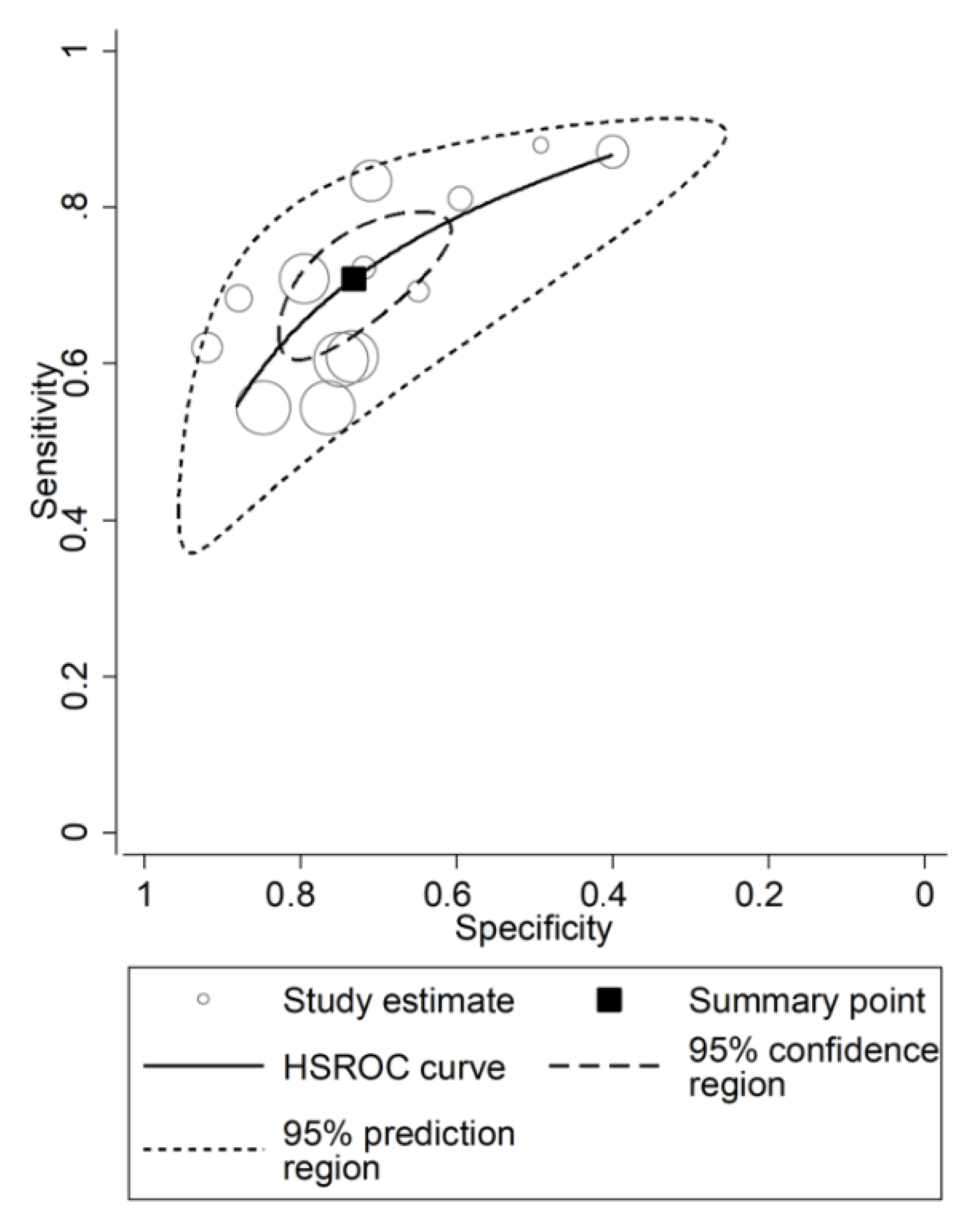
3.4. Prognostic Accuracy of the NLR
3.4.1. Study Characteristics
3.4.2. Risk of Bias
3.4.3. Results of Individual Studies and Syntheses
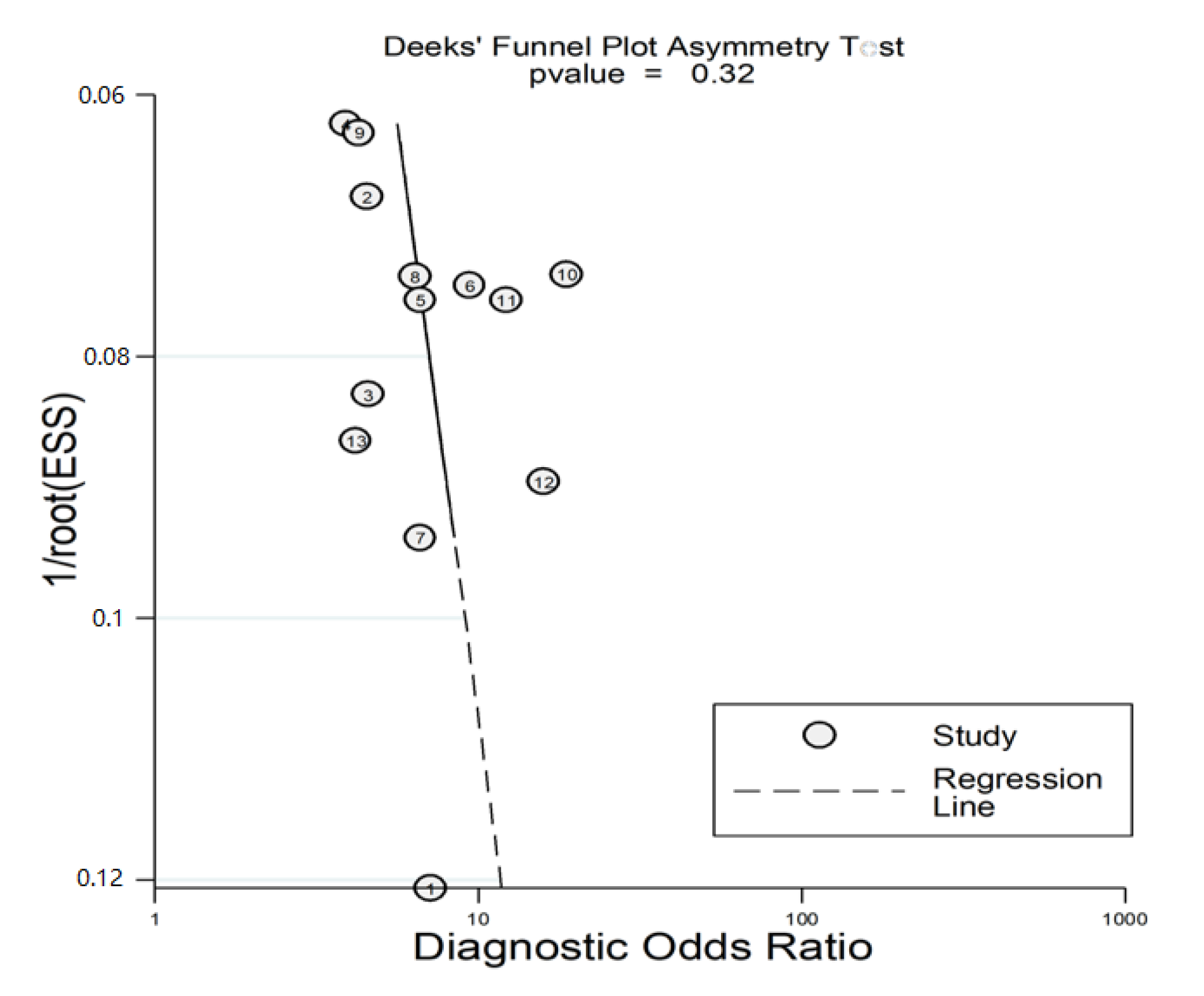
3.4.4. Publication Bias
3.4.5. Heterogeneity, Subgroup and Meta-Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blanco, I.; Diego, I.; Bueno, P.; Casas-Maldonado, F.; Miravitlles, M. Geographic distribution of COPD prevalence in the world displayed by Geographic Information System maps. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaderi, S.A.; Hurst, J.R. The unmet global burden of COPD. Glob. Health Epidemiol. Genom. 2018, 3, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleeman, K.E.; de Brito, M.F.; Etkind, S.N.; Nkhoma, K.; Guo, P.; Higginson, I.J.; Gomes, B.; Harding, R. The escalating global burden of serious health-related suffering: Projections to 2060 by world regions, age groups, and health conditions. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e883–e892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, A.L.; Adcock, I.M. The relationship between COPD and lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, A.D.; Zakeri, R.; Quint, J.K. Defining the relationship between COPD and CVD: What are the implications for clinical practice? Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2018, 12, 1753465817750524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, E.; Trajanoska, K.; LaHousse, L.; Schoufour, J.D.; Terzikhan, N.; De Roos, E.; De Jonge, G.B.; Williams, R.; Franco, O.H.; Brusselle, G.; et al. Sarcopenia in COPD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 190049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohannes, A.M.; Alexopoulos, G.S. Depression and anxiety in patients with COPD. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2014, 23, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzini, L.; Schiavi, M.; Pierobon, A.; Granata, N.; Giardini, A. From Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) to Dementia in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Implications for Clinical Practice and Disease Management: A Mini-Review. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestbo, J.; Hurd, S.S.; Agustí, A.G.; Jones, P.W.; Vogelmeier, C.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Fabbri, L.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Nishimura, M.; et al. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease GOLD Executive Summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogendoorn, M.; Hoogenveen, R.T.; Molken, M.P.R.-V.; Vestbo, J.; Feenstra, T.L. Case fatality of COPD exacerbations: A meta-analysis and statistical modelling approach. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 37, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, F.W.; Chan, K.P.; Hui, D.; Goddard, J.R.; Shaw, J.; Reid, D.; Yang, I. Acute exacerbation of COPD. Respirology 2016, 21, 1152–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singanayagam, A.; Schembri, S.; Chalmers, J.D. Predictors of Mortality in Hospitalized Adults with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2013, 10, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agusti, A.; Bel, E.; Thomas, M.; Vogelmeier, C.; Brusselle, G.; Holgate, S.; Humbert, M.; Jones, P.; Gibson, P.G.; Vestbo, J.; et al. Treatable traits: Toward precision medicine of chronic airway diseases. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, K.; Yasuo, M.; Urushibata, K.; Hanaoka, M.; Koizumi, T.; Kubo, K. Airway inflammation during stable and acutely exacerbated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 25, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brightling, C.; Greening, N. Airway inflammation in COPD: Progress to precision medicine. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliogiannis, P.; Fois, A.G.; Sotgia, S.; Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, E.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C.; Zinellu, A. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a marker of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its exacerbations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliogiannis, P.; Fois, A.G.; Sotgia, S.; Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, E.; Pirina, P.; Negri, S.; Carru, C.; Zinellu, A. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and clinical outcomes in COPD: Recent evidence and future perspectives. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 170113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; Aromataris, E.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; Lisy, K.; et al. Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer’s Manual; Aromataris, E., Munn, Z., Eds.; Johanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- GRADE Working Group. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2004, 328, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, J.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tobias, A. Assessing the influence of a single study in the meta-analysis estimate. Stata Tech. Bull. 1999, 47, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating Characteristics of a Rank Correlation Test for Publication Bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.; Egger, M. Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: Guidelines on choice of axis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and Fill: A Simple Funnel-Plot-Based Method of Testing and Adjusting for Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutter, C.M.; Gatsonis, C.A. A hierarchical regression approach to meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy evaluations. Stat. Med. 2001, 20, 2865–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaskill, P. Empirical Bayes estimates generated in a hierarchical summary ROC analysis agreed closely with those of a full Bayesian analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2004, 57, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitsma, J.B.; Glas, A.S.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Scholten, R.J.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Zwinderman, A.H. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2005, 58, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbord, R.M.; Whiting, P. Metandi: Meta-analysis of Diagnostic Accuracy Using Hierarchical Logistic Regression. Stata J. 2009, 9, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, J.J.; Macaskill, P.; Irwig, L. The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2005, 58, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, T.J. Nomogram for Bayes’s Theorem. N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 293, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeel, H.M.; Ahmed, H.A. The refined ABCD assessment and non-costly laboratory parameters are outcome predictors in acute exacerbation of COPD. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc. 2017, 66, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Law, S.; Sriram, K.B. Evaluation of platelet lymphocyte ratio and 90-day mortality in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimirad, S.; Ghaffary, M.R.; Rahimirad, M.H.; Rashidi, F. Association between admission neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and outcomes in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Tuberk. Toraks 2017, 64, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, E.; Gungor, S.; Agca, M.C.; Ozmen, I.; Duman, D.; Kocak, N.D.; Akturk, U.A.; Tuncay, E.; Salturk, C.; Yalcinsoy, M.; et al. A Revised Treatment Approach for Hospitalized Patients with Eosinophilic and Neutrophilic Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Turk. Thorac. J. 2018, 19, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Ye, H.; Xue, T. Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Zou, Y. Relationship between neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and short-term prognosis in the chronic obstructive pulmonary patients with acute exacerbation. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, G.; Salihoglu, Z. Does Mean Platelet Volume/Platelet Count Ratio and Red Rlood Cell Distribution Width Predict In-hospital Mortality in Patients Admitted for Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease? J. Immunol. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, H.; Xie, X.; Peng, J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, R. Predictive Value of Novel Inflammation-Based Biomarkers for Pulmonary Hypertension in the Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019, 2019, 5189165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami Ardestani, M.; Alavi-Naeini, N. Evaluation of the relationship of neutrophil-to lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio with in-hospital mortality in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin. Respir. J. 2020, 15, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Rosero, J.A.; Caceres-Galvis, C.; Ascuntar, J.; Atencia, C.; Vallejo, C.E.; Jaimes, F. Biomarkers as a Prognostic Factor in COPD Exacerbation: A Cohort Study. COPD 2021, 18, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.-Y.; Chen, R.; Li, N.; Sun, X.-W.; Zhou, M.; Li, Q.-Y.; Guo, Y. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Clinical Outcome of Severe Acute Exacerbation of COPD in Frequent Exacerbators. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2021, 16, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Xu, N. Prognostic Value of Neutrophil:Lymphocyte and Platelet:Lymphocyte Ratios for 28-Day Mortality of Patients with AECOPD. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 2839–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Luo, Z.; Jin, J.; Cao, Z.; Ma, Y. The Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio Could Predict Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation Failure in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Retrospective Observational Study. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2021, 16, 2267–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Wang, L.; Shi, F.; Chen, R.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Feng, M.; Li, S. Optimized combination of circulating biomarkers as predictors of prognosis in AECOPD patients complicated with Heart Failure. Int. J. Med Sci. 2021, 18, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, T.; Yu, X.; Chen, Z.; Ran, Y.; Wang, J.; Dai, G.; Deng, H.; Li, X.; Zhu, T. Risk Factors for Length of Hospital Stay in Acute Exacerbation Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 3447–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cohen, P.; Chen, S. How Big is a Big Odds Ratio? Interpreting the Magnitudes of Odds Ratios in Epidemiological Studies. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 2010, 39, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yao, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Gao, C. A step-by-step guide to the systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic and prognostic test accuracy evaluations. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 2299–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve in Diagnostic Test Assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettori, P.; Paliogiannis, P.; Pascale, R.M.; Zinellu, A.; Mangoni, A.A.; Pintus, G. Blood Cell Count Indexes of Systemic Inflammation in Carotid Artery Disease: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; Paliogiannis, P.; Sotgiu, E.; Mellino, S.; Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, E.; Negri, S.; Collu, C.; Pintus, G.; Serra, A.; et al. Blood Cell Count Derived Inflammation Indexes in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Lung 2020, 198, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliogiannis, P.; Zinellu, A.; Scano, V.; Mulas, G.; De Riu, G.; Pascale, R.M.; Arru, L.B.; Carru, C.; Pirina, P.; Mangoni, A.A.; et al. Laboratory test alterations in patients with COVID-19 and non COVID-19 interstitial pneumonia: A preliminary report. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2020, 14, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliogiannis, P.; Satta, R.; Deligia, G.; Farina, G.; Bassu, S.; Mangoni, A.A.; Carru, C.; Zinellu, A. Associations between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios and the presence and severity of psoriasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 19, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erre, G.L.; Paliogiannis, P.; Castagna, F.; Mangoni, A.A.; Carru, C.; Passiu, G.; Zinellu, A. Meta-analysis of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 49, e13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putzu, C.; Cortinovis, D.L.; Colonese, F.; Canova, S.; Carru, C.; Zinellu, A.; Paliogiannis, P. Blood cell count indexes as predictors of outcomes in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with Nivolumab. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cupp, M.A.; Cariolou, M.; Tzoulaki, I.; Aune, D.; Evangelou, E.; Berlanga-Taylor, A.J. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and cancer prognosis: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Huang, W.; Huang, K. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in sepsis: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, J.R.; Vestbo, J.; Anzueto, A.; Locantore, N.; Müllerova, H.; Tal-Singer, R.; Miller, B.; Lomas, D.A.; Agusti, A.; MacNee, W.; et al. Susceptibility to Exacerbation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, J.D.; Jacobson, S.; Kechris, K.; Kinney, G.L.; Foreman, M.G.; Doerschuk, C.M.; Make, B.J.; Curtis, J.L.; Rennard, S.I.; Barr, R.G.; et al. Biomarkers Predictive of Exacerbations in the SPIROMICS and COPDGene Cohorts. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noell, G.; Cosío, B.G.; Faner, R.; Monsó, E.; Peces-Barba, G.; De Diego, A.; Esteban, C.; Gea, J.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R.; Garcia-Nuñez, M.; et al. Multi-level differential network analysis of COPD exacerbations. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, R.; Scheiner, A.; Kanetsky, P.A.; Egan, K.M. Sociodemographic and lifestyle factors associated with the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. Ann. Epidemiol. 2019, 38, 11–21.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

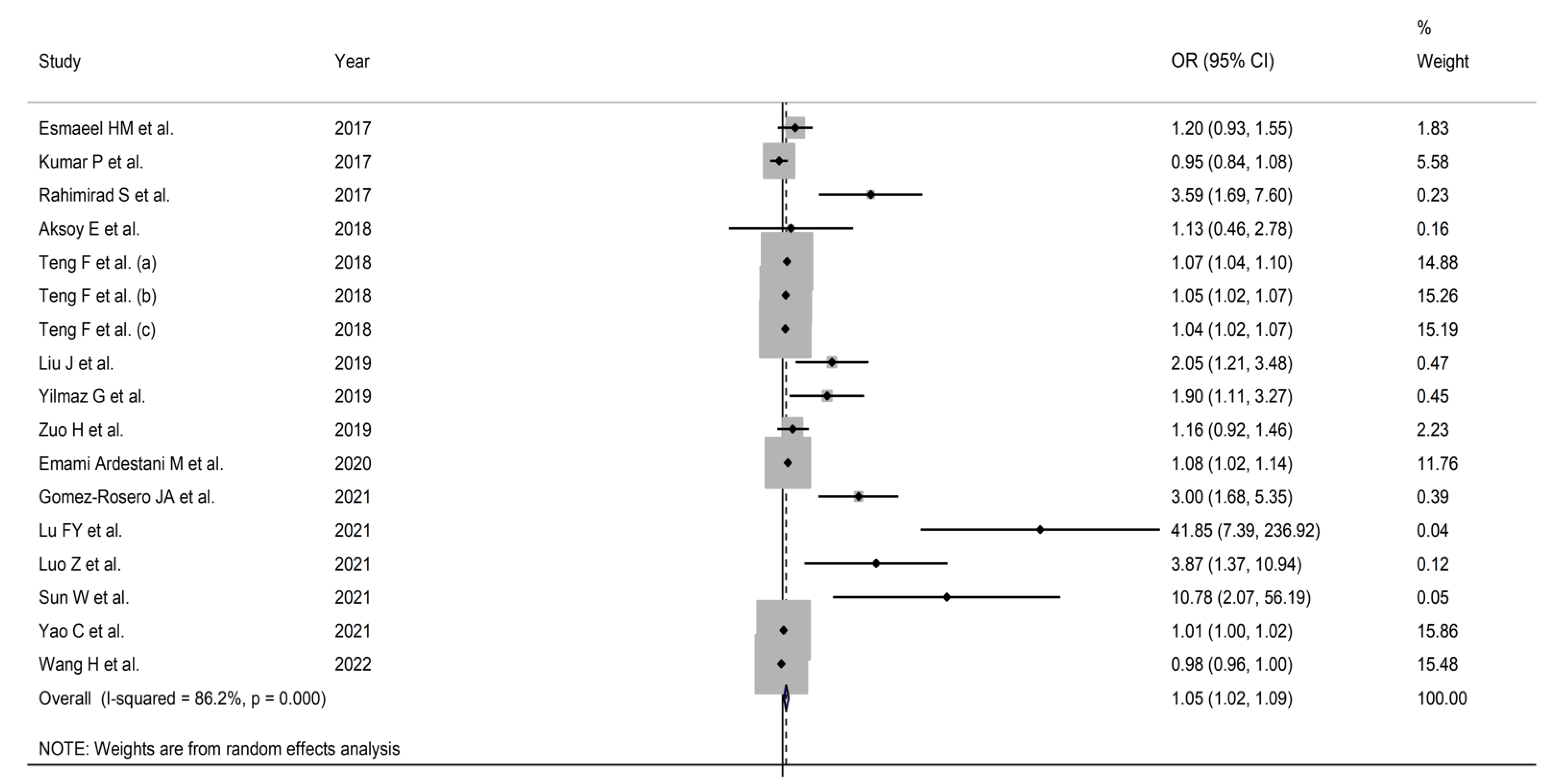




| First Author, Year, Country [Ref] | Study Design | Sample Size | OR (95% CI) | AUC (95% CI) | Cut-Off | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Clinical Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esmaeel H.M., 2017, Egypt [32] | P | 80 | 1.2 (0.9–1.5) | 0.642 (0.526–0.746) | 3.4 | 0.89 | 0.49 | In-hospital mortality or ICU transfer |
| Kumar P., 2017, Australia [33] | R | 181 | 0.95 (0.84–1.08) | NR | NR | NR | NR | 90-day mortality |
| Rahimirad S., 2017, Iran [34] | R | 174 | 3.586 (1.69–7.60) | 0.717 (0.623–0.811) | 4 | 0.87 | 0.4 | In-hospital mortality |
| Aksoy E., 2018, Turkey [35] | R | 2727 | 1.13 (0.46–2.78) | NR | NR | NR | NR | In-hospital mortality |
| Teng F. (a), 2018, China [36] | R | 904 | 1.067 (1.039–1.095) | 0.737 (0.661–0.814) | 8.13 | 0.61 | 0.75 | 28-day mortality |
| Teng F. (b), 2018, China [36] | R | 906 | 1.046 (1.023–1.068) | 0.676 (0.607–0.744) | 8.13 | 0.54 | 0.77 | ICU transfer |
| Teng F. (c), 2018, China [36] | R | 906 | 1.042 (1.019–1.066) | 0.732 (0.656–0.807) | 10.345 | 0.54 | 0.85 | IMV |
| Liu J., 2019, China [37] | R | 622 | 2.05 (1.21–3.48) | 0.742 (0.554–0.881) | 4.19 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 90-day mortality |
| Yilmaz G., 2019, Turkey [38] | R | 171 | 1.902 (1.108–3.266) | NR | 3.18 | 0.71 | 0.72 | In-hospital mortality |
| Zuo H., 2019, China [39] | R | 185 | 1.161 (0.924–1.458) | 0.701 (0.629–0.766) | 4.659 | 0.81 | 0.6 | In-hospital PH |
| Emami Ardestani M., 2020, Iran [40] | R | 829 | 1.08 (1.02–1.14) | 0.7 (0.67–0.73) | 6.9 | 0.61 | 0.73 | In-hospital mortality |
| Gomez-Rosero J.A., 2021, Colombia [41] | P | 610 | 3.0 (1.7–5.4) | NR | NR | NR | NR | In-hospital mortality or ICU transfer |
| Lu F.Y., 2021, China [42] | R | 282 | 41.85 (9.57–306.74) | 0.883 (0.771–0.894) | 10.23 | 0.62 | 0.92 | In-hospital mortality, ICU transfer, or IMV |
| Luo Z., 2021, China [43] | R | 533 | 3.87 (1.29–10.3) | 0.801 (NR) | 6.74 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 28-day mortality |
| Sun W., 2021, China [44] | R | 212 | 10.783 (2.069–56.194) | 0.858 (0.785–0.931) | 8.9 | 0.69 | 0.88 | NIMVF |
| Yao C., 2021, China [45] | R | 146 | 1.01 (0.999–1.022) | 0.83 (0.761–0.899) | 16.83 | 0.69 | 0.65 | 28-day mortality |
| Wang H., 2022, China [46] | P | 598 | 0.98118 (0.96271–0.999) | NR | NR | NR | NR | LHS |
| Study | Were the Groups Comparable Other than the NLR? | Were Cases and Controls Matched Appropriately? | Were the Same Criteria Used to Identify Cases and Controls? | Was Exposure Measured in a Standard, Valid, and Reliable Way? | Was Exposure Measured in the Same Way for Cases and Controls? | Were Confounding Factors Identified? | Were Strategies to Deal with Confounding Factors Stated? | Were Outcomes Assessed in a Standard, Valid, and Reliable Way for Cases and Controls? | Was the Exposure Period Long Enough to Be Meaningful? | Was Appropriate Statistical Analysis Used? | Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esmaeel H.M. [32] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Kumar P. [33] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Rahimirad S. [34] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Aksoy E. [35] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Teng F. [36] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Liu J. [37] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Yilmaz G. [38] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Zuo H. [39] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Emami Ardestani M. [40] | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Gomez-Rosero J.A. [41] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Lu F.Y. [42] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Luo Z. [43] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Sun W. [44] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Yao C. [45] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Wang H. [46] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Without Adverse Outcome | With Adverse Outcome | Outcome | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Author, Year, Country [Ref] | n | Age (Years) | Gender (M/F) | NLR (Mean ± SD) | n | Age (Years) | Gender (M/F) | NLR (Mean ± SD) | |
| Kumar P., 2017, Australia [33] | 165 | 70 | 81/84 | 7 ± 8 | 16 | 78 | 12/4 | 13 ± 10 | 90-day mortality |
| Rahimirad S., 2017, Iran [34] | 245 | 69 | 127/118 | 8.29 ± 7.56 | 70 | 74 | 47/23 | 17 ± 17.56 | In-hospital mortality |
| Aksoy E., 2018, Turkey [35] | 2,692 | NR | 1144/1548 | 7.56 ± 6.26 | 35 | NR | 23/12 | 10.85 ± 10.92 | In-hospital mortality |
| Liu J., 2019, China [37] | 574 | 74 | 281/293 | 3.1 ± 6.8 | 48 | 75 | 26/22 | 7.8 ± 10.1 | 90-day mortality |
| Yilmaz G., 2019, Turkey [38] | 135 | 71 | 73/62 | 2.8 ± 1.4 | 36 | 69 | 23/13 | 3.5 ± 1.9 | In-hospital mortality |
| Zuo H., 2019, China [39] | 84 | 70 | 64/20 | 4.74 ± 3.24 | 101 | 72 | 77/34 | 7.92 ± 5.43 | In-hospital PH |
| Emami Ardestani M., 2020, Iran [40] | 760 | 68 | 502/258 | 5.94 ± 5.35 | 69 | 72 | 53/16 | 11.12 ± 10.51 | In-hospital mortality |
| Gomez-Rosero J.A., 2021, Colombia [41] | 494 | 75 | 233/261 | 6 ± 5.33 | 116 | 71 | 58/58 | 9.23 ± 6.74 | In-hospital mortality or ICU transfer |
| Lu F.Y., 2021, China [42] | 224 | NR | NR | 5.38 ± 3.7 | 58 | NR | NR | 11.77 ± 6.48 | In-hospital mortality, ICU transfer, or IMV |
| Luo Z., 2021, China [43] | 485 | 75 | 325/160 | 8.51 ± 6.08 | 48 | 81 | 30/18 | 15.12 ± 12.99 | 28-day mortality |
| Sun W., 2021, China [44] | 174 | 73 | 123/51 | 4.27 ± 2.2 | 38 | 77 | 30/8 | 12.67 ± 7.44 | NIMVF |
| Yao C., 2021, China [45] | 94 | 78 | 67/27 | 14.3 ± 13.78 | 52 | 81 | 42/10 | 24.47 ± 21.48 | 28-day mortality |
| Wang H., 2021, China [46] | 111 | 70 | NR | 4.56 ± 6.05 | 100 | 78 | NR | 5.47 ± 5.27 | LHS |
| First Author, Year, Country [Ref] | n | Age (Years) | Gender (M/F) | AUC | 95% CI | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cut-Off | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esmaeel H.M., 2017, Egypt [32] | 80 | 61 | NR | 0.642 | 0.526–0.746 | 0.8889 | 0.4906 | 3.4 | ICU transfer or in-hospital mortality |
| Rahimirad S., 2017, Iran [34] | 315 | 70 | 245/70 | 0.717 | 0.623–0.811 | 0.87 | 0.4 | 4 | In-hospital mortality |
| Teng F. (a), 2018, China [36] | 904 | 82 | 525/379 | 0.737 | 0.661–0.814 | 0.605 | 0.748 | 8.13 | 28-day mortality |
| Teng F. (b), 2018, China [36] | 906 | 82 | 525/381 | 0.676 | 0.607–0.744 | 0.543 | 0.766 | 8.13 | ICU transfer |
| Teng F. (c), 2019, China [36] | 906 | 82 | 525/381 | 0.732 | 0.656–0.807 | 0.543 | 0.848 | 10.345 | IMV |
| Liu J., 2019, China [37] | 622 | 74 | 307/315 | 0.742 | 0.554–0.881 | 0.714 | 0.742 | 4.19 | 90-day mortality |
| Yilmaz G., 2019, Turkey [38] | 171 | 71 | 96/75 | NR | NR | 0.71 | 0.72 | 3.18 | In-hospital mortality |
| Zuo H., 2019, China [39] | 185 | 71 | 141/54 | 0.701 | 0.629–0.766 | 0.812 | 0.595 | 4.659 | In-hospital PH |
| Emami Ardestani M., 2020, Iran [40] | 829 | 68 | 555/274 | 0.70 | 0.67–0.73 | 0.6087 | 0.7329 | 6.9 | In-hospital mortality |
| Lu F.Y., 2021, China [42] | 282 | 78 | 247/35 | 0.883 | 0.771–0.894 | 0.62 | 0.92 | 10.23 | IMV, ICU transfer, or in-hospital mortality |
| Luo Z., 2021, China [43] | 533 | 76 | 355/178 | 0.801 | NR | 0.83 | 0.71 | 6.74 | 28-day mortality |
| Sun W., 2021, China [44] | 212 | 74 | 153/59 | 0.858 | 0.785–0.931 | 0.69 | 0.88 | 8.9 | NIMVF |
| Yao C., 2021, China [45] | 146 | 79 | 109/37 | 0.83 | 0.761–0.899 | 0.69 | 0.65 | 16.83 | 28-day mortality |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zinellu, A.; Zinellu, E.; Pau, M.C.; Carru, C.; Pirina, P.; Fois, A.G.; Mangoni, A.A. A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123365
Zinellu A, Zinellu E, Pau MC, Carru C, Pirina P, Fois AG, Mangoni AA. A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(12):3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123365
Chicago/Turabian StyleZinellu, Angelo, Elisabetta Zinellu, Maria Carmina Pau, Ciriaco Carru, Pietro Pirina, Alessandro G. Fois, and Arduino A. Mangoni. 2022. "A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 12: 3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123365
APA StyleZinellu, A., Zinellu, E., Pau, M. C., Carru, C., Pirina, P., Fois, A. G., & Mangoni, A. A. (2022). A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(12), 3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123365









