Impact of Smoking Status in Combination Treatment with EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Anti-Angiogenic Agents in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Susceptible EGFR Mutations: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.3. Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search
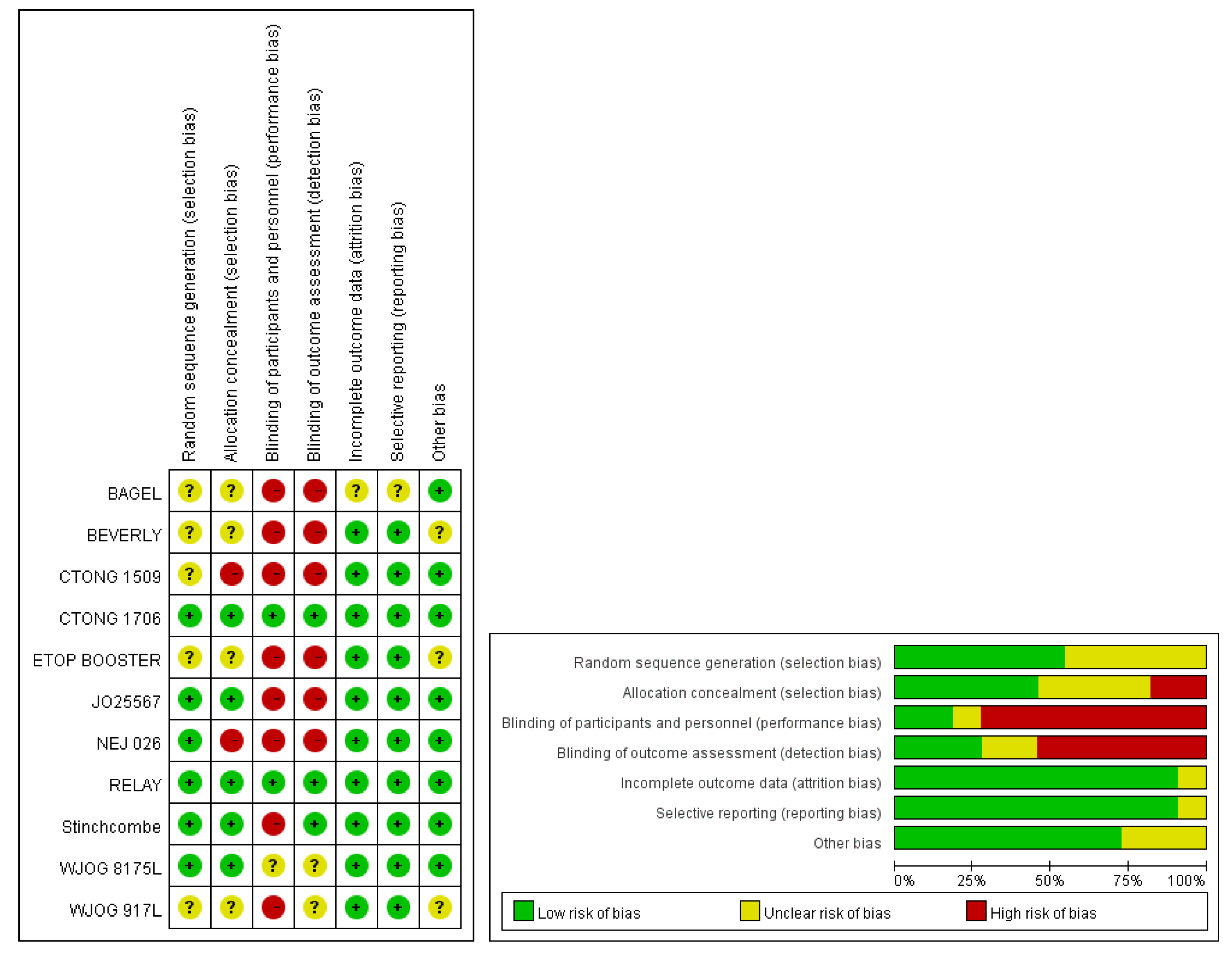
3.2. Study Characteristics and Quality Evaluation
3.3. Efficacy Comparisons between Combination Treatment with an EGFR-TKI plus an Anti-Angiogenic Agent and Treatment with an EGFR-TKI Alone
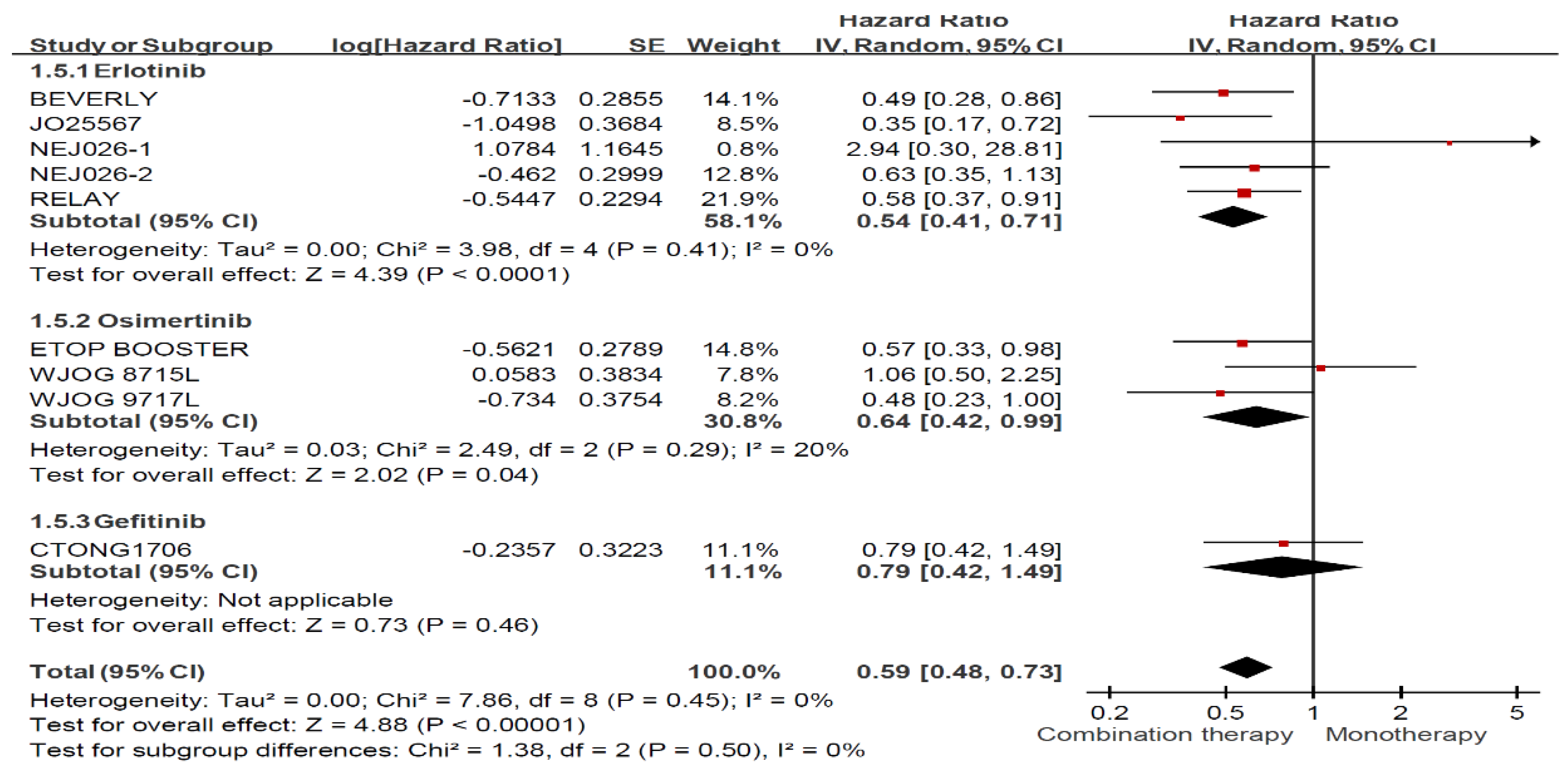
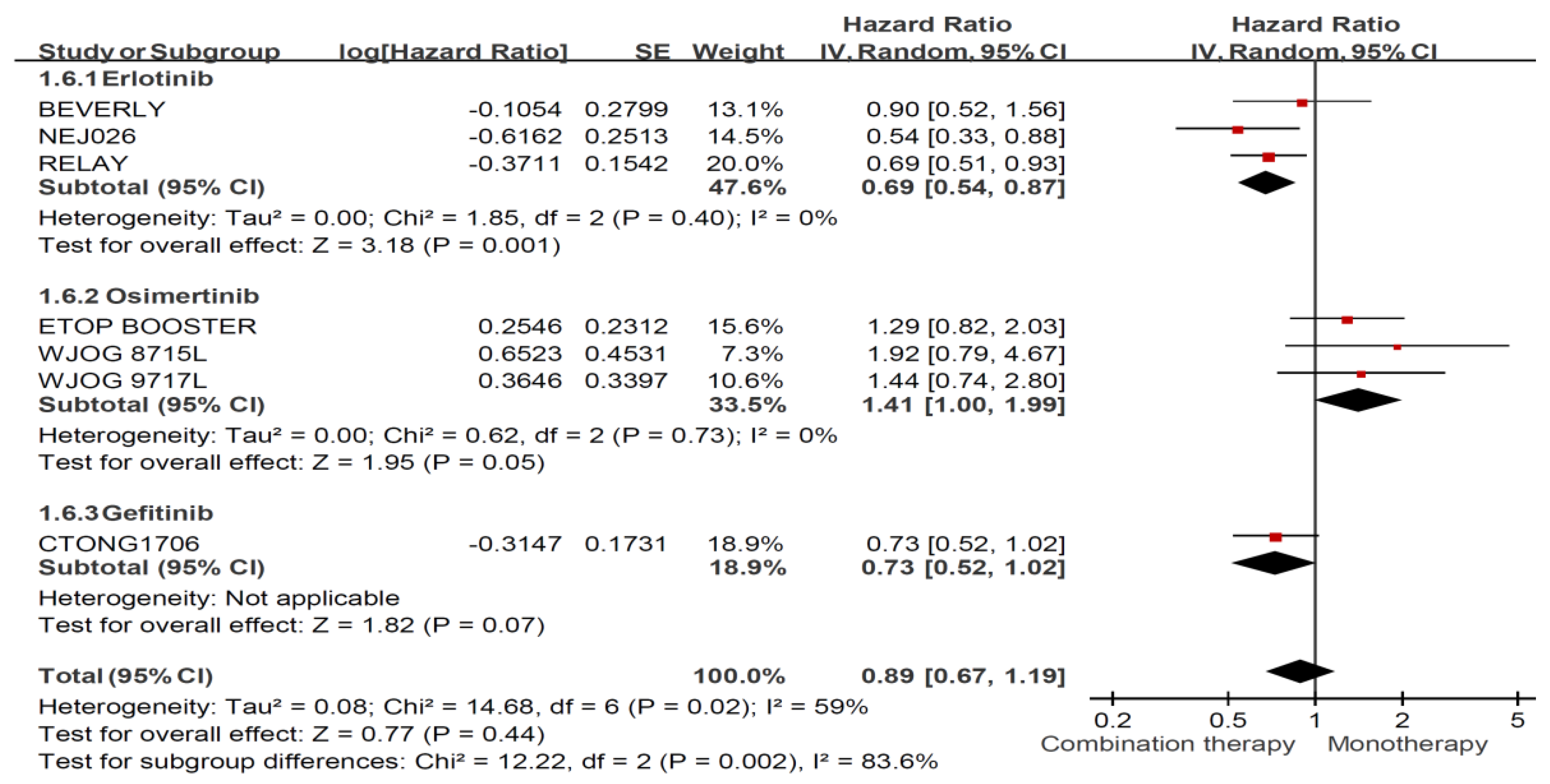
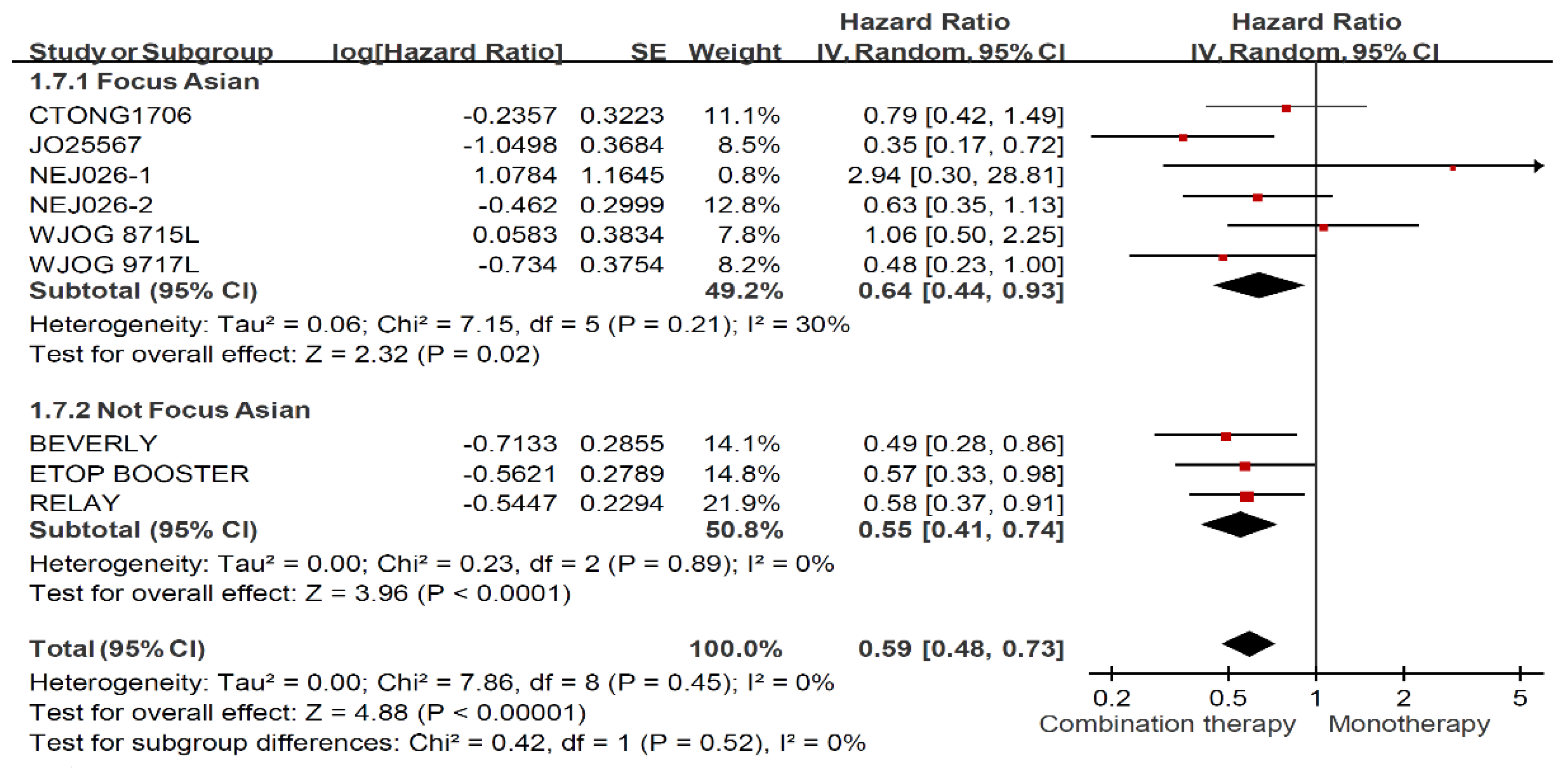
3.4. Treatment Effects among Ever Smokers and Never Smokers
3.5. Treatment Effects among Ever Smokers and Never Smokers Stratified by Treatment Regimen
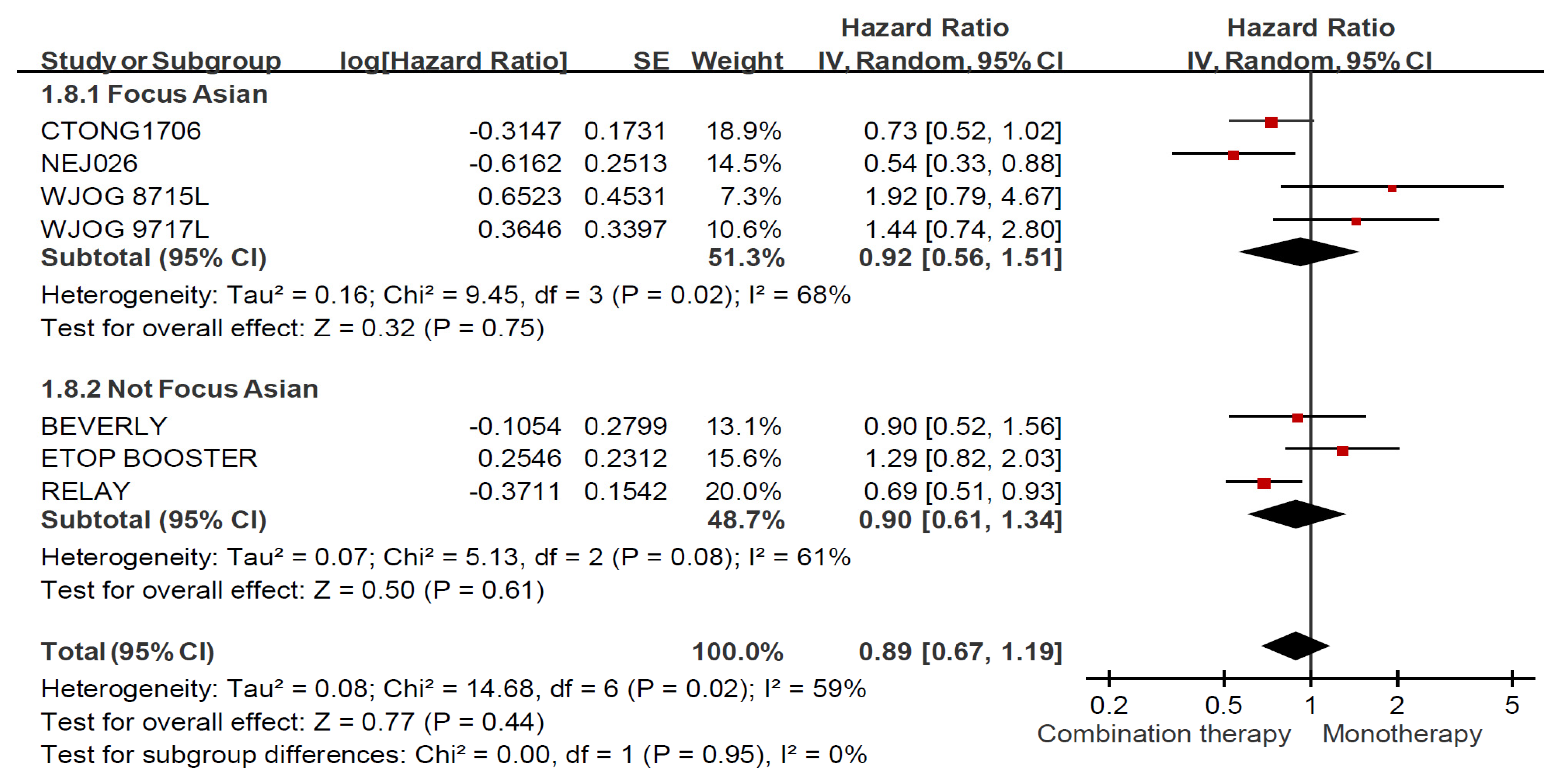
3.6. Treatment Effects among Ever Smokers and Never Smokers Stratified by Ethnicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- The Embase database: Contains biomedical literature from 1974 to present.
- The MEDLINE and PubMed database: Covers journals from 1966 to present.
- Embase Classic: The Embase back file covering almost 2 million biomedical and pharmacological citations drawn from over 3000 international titles from between 1947 and 1973.
| Search | Query | Results |
| #1 | ‘non-small cell lung cancer’/exp OR ‘bronchial non-small cell cancer’ OR ‘bronchial non-small cell carcinoma’ OR ‘lung non-small cell cancer’ OR ‘lung non-small cell carcinoma’ OR ‘microcellular lung carcinoma’ OR ‘pulmonary non-small cell cancer’ OR ‘pulmonary non-small cell carcinoma’ OR ‘non-small cell bronchial cancer’ OR ‘non-small cell bronchial carcinoma’ OR ‘non-small cell cancer, lung’ OR ‘non-small cell lung cancer’ OR ‘non-small cell lung carcinoma’ OR ‘non-small cell pulmonary cancer’ OR ‘non-small cell pulmonary carcinoma’ | 189,050 |
| #2 | ‘NSCLC’:ab,ti OR ‘nsclc’:ab,ti OR ((non NEAR/3 ‘small cell ‘ NEAR/3 lung NEAR/3 cancer):ab,ti) OR ((non NEAR/3 ‘small cell’ NEAR/3 lung NEAR/3 carcinoma):ab,ti) OR ((non NEAR/3 ‘small cell ‘ NEAR/3 lung NEAR/3 neoplasm):ab,ti) | 127,551 |
| #3 | ((‘ large cell ‘ NEAR/3 lung NEAR/3 cancer):ab,ti) OR ((‘ large cell ‘ NEAR/3 lung NEAR/3 carcinoma):ab,ti) OR ((‘ large cell ‘ NEAR/3 lung NEAR/3 neoplasm):ab,ti) OR ((squamous NEAR/3 lung NEAR/3 cancer):ab,ti) OR ((squamous NEAR/3 lung NEAR/3 carcinoma):ab,ti) OR ((squamous NEAR/3 lung NEAR/3 neoplasm):ab,ti) OR ((adenocarcinoma NEAR/3 lung NEAR/3 cancer):ab,ti) OR ((adenocarcinoma NEAR/3 lung NEAR/3 carcinoma):ab,ti) OR ((adenocarcinoma NEAR/3 lung NEAR/3 neoplasm):ab,ti) | 12,030 |
| #3 | #1 OR #2 OR #3 | 136,324 |
| #4 | (((‘tyrosine kinase’ NEAR/3 inhibit*):ab,ti) OR ((‘tyrosine kinase’ NEAR/3 antagonist*):ab,ti) OR ((‘tk’ NEAR/3 inhibit*):ab,ti) OR ((tk NEAR/3 antagonist*):ab,ti) OR ‘tki’:ab,ti OR ‘tkis’) AND ‘protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor’/exp | 54,909 |
| #5 | ‘epidermal growth factor receptor’/exp OR ‘egf receptor’:ab,ti OR ‘epidermal growth factor receptor’:ab,ti OR ‘egf near/3receptor’:ab,ti | 116,249 |
| #6 | #4 AND #5 | 15,561 |
| #7 | crizotinib:ab,ti OR ‘pf 02341066’:ab,ti OR ‘pf 1066’:ab,ti OR ‘pf 2341066’:ab,ti OR pf02341066:ab,ti OR pf1066:ab,ti OR pf2341066:ab,ti OR xalkori:ab,ti OR gefitinib:ab,ti OR ‘zd1839’:ab,ti OR ‘zd 1839’:ab,ti OR iressa:ab,ti OR erlotinib:ab,ti OR ‘erlotinib’/exp OR ‘cp 358774’:ab,ti OR ‘cp 35877401’:ab,ti OR ‘cp358774’:ab,ti OR ‘cp358774 01’:ab,ti OR ‘cp35877401’:ab,ti OR ‘nsc 718781’:ab,ti OR ‘nsc718781’:ab,ti OR ‘tarceva’:ab,ti OR ‘icotinib’/exp OR ‘bpi 2009’:ab,ti OR ‘bpi 2009h’:ab,ti OR ‘bpi2009’:ab,ti OR ‘bpi2009h’:ab,ti OR ‘conmana’:ab,ti OR ‘icotinib’:ab,ti OR ‘afatinib’/exp OR ‘afatinib’:ab,ti OR ‘bibw 2992’:ab,ti OR ‘bibw2992’:ab,ti OR ‘giotrif’:ab,ti OR ‘osimertinib’/exp OR ‘azd 9291’:ab,ti OR ‘azd9291’:ab,ti OR ‘osimertinib’:ab,ti OR ‘tagrisso’:ab,ti | 46,891 |
| #8 | #6 OR #7 | 51,874 |
| #9 | ((‘vascular endothelial cell growth factor’ NEAR/3 inhibit*):ab,ti) OR ((‘vascular endothelial cell growth factor’ NEAR/3 antagonist*):ab,ti) OR ((‘vegf’ NEAR/3 inhibit*):ab,ti) OR ((‘vegf’ NEAR/3 antagonist*):ab,ti) OR ‘vegfi’:ab,ti OR ‘vegfis’:ab,ti OR ‘vasculotropin’/exp OR ((vasculotropin NEAR/3 inhibit*):ab,ti) OR ((vasculotropin NEAR/3 antagonist*):ab,ti) OR ((‘vas’ NEAR/3 inhibit*):ab,ti) OR ((‘vas’ NEAR/3 antagonist*):ab,ti) OR vasis:ab,ti | 123,195 |
| #10 | ramucirumab:ab,ti OR ‘ly3009806’:ab,ti OR ‘ly 3009806’:ab,ti OR ‘imc1121b’:ab,ti OR ‘imc 1121b’:ab,ti OR cyramza:ab,ti OR bevacizumab:ab,ti OR ‘nsc 704865’:ab,ti OR ‘nsc704865’:ab,ti OR avastin:ab,ti OR ‘nintedanib’/exp OR ‘bibf 1120’:ab,ti OR ‘bibf1120’:ab,ti OR ‘intedanib’:ab,ti OR ‘nintedanib’:ab,ti OR ‘ofev’:ab,ti OR ‘vargatef’:ab,ti OR ‘sorafenib’/exp OR ‘bay 439006’:ab,ti OR ‘bay439006’:ab,ti OR ‘nexavar’:ab,ti OR ‘sorafenib’ OR ‘sunitinib’/exp OR ‘su 011248’:ab,ti OR ‘su 11248’:ab,ti OR ‘sunitinib’:ab,ti OR ‘sutent’:ab,ti OR ‘vandetanib’:ab,ti OR ‘caprelsa’:ab,ti | 83,453 |
| #11 | #9 OR #10 | 195,516 |
| #12 | #3 AND #8 AND #11 | 612 |
| #13 | ‘clinical trial’/de OR ‘randomized controlled trial’/de OR ‘randomization’/de OR ‘single blind procedure’/de OR ‘double blind procedure’/de OR ‘crossover procedure’/de OR (‘randomized controlled’ NEXT/1 trial*) OR rct OR ‘randomly allocated’ OR ‘allocated randomly’ OR ‘random allocation’ OR (allocated NEAR/2 random) OR (single NEXT/1 blind*) OR (double NEXT/1 blind*) OR ((treble OR triple) NEAR/1 blind*) | 1,865,092 |
| #14 | #12 AND #13 | 240 |
Appendix B. Forest Plot and Pooled Result among All Enrolled Patients
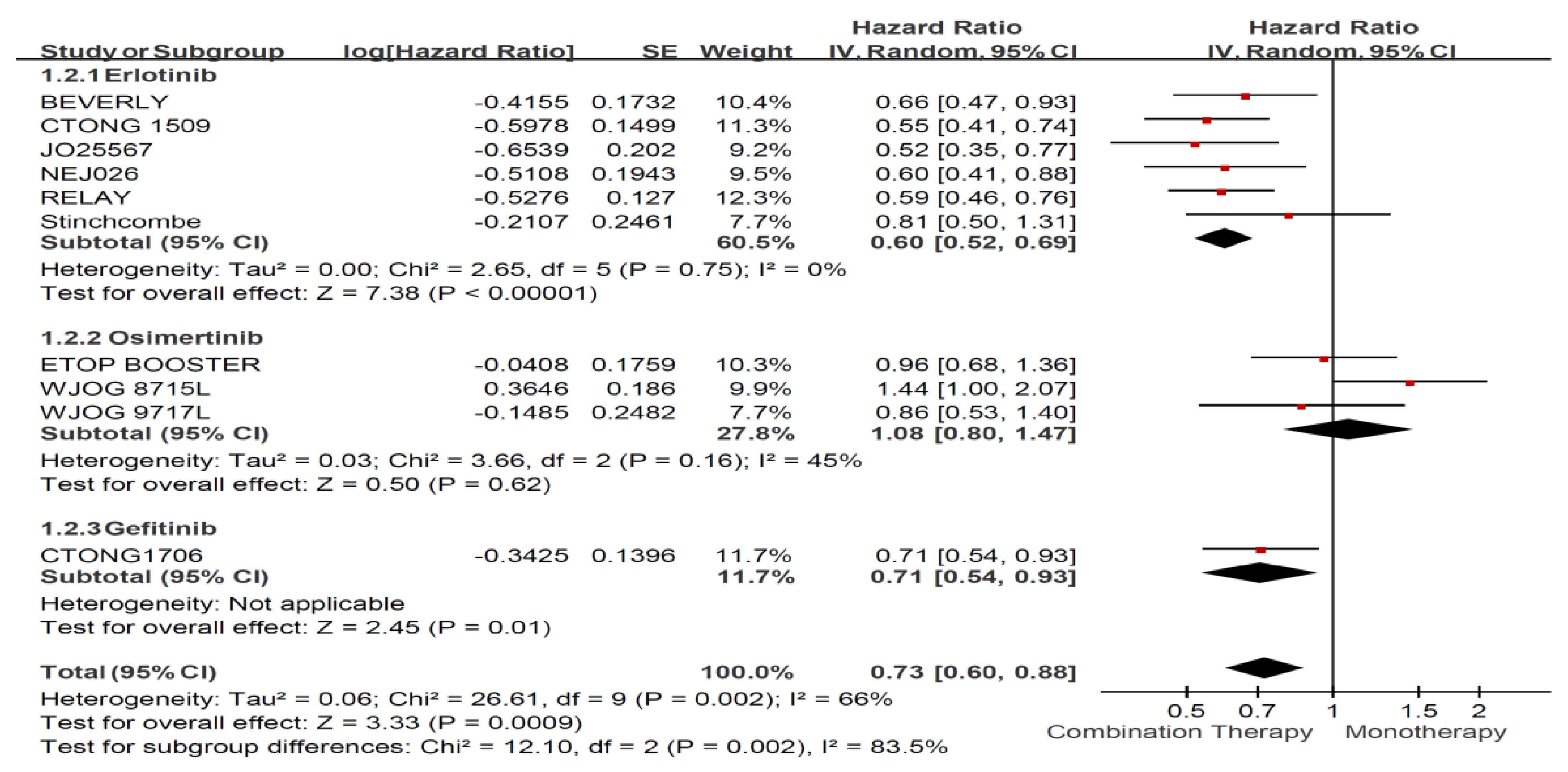
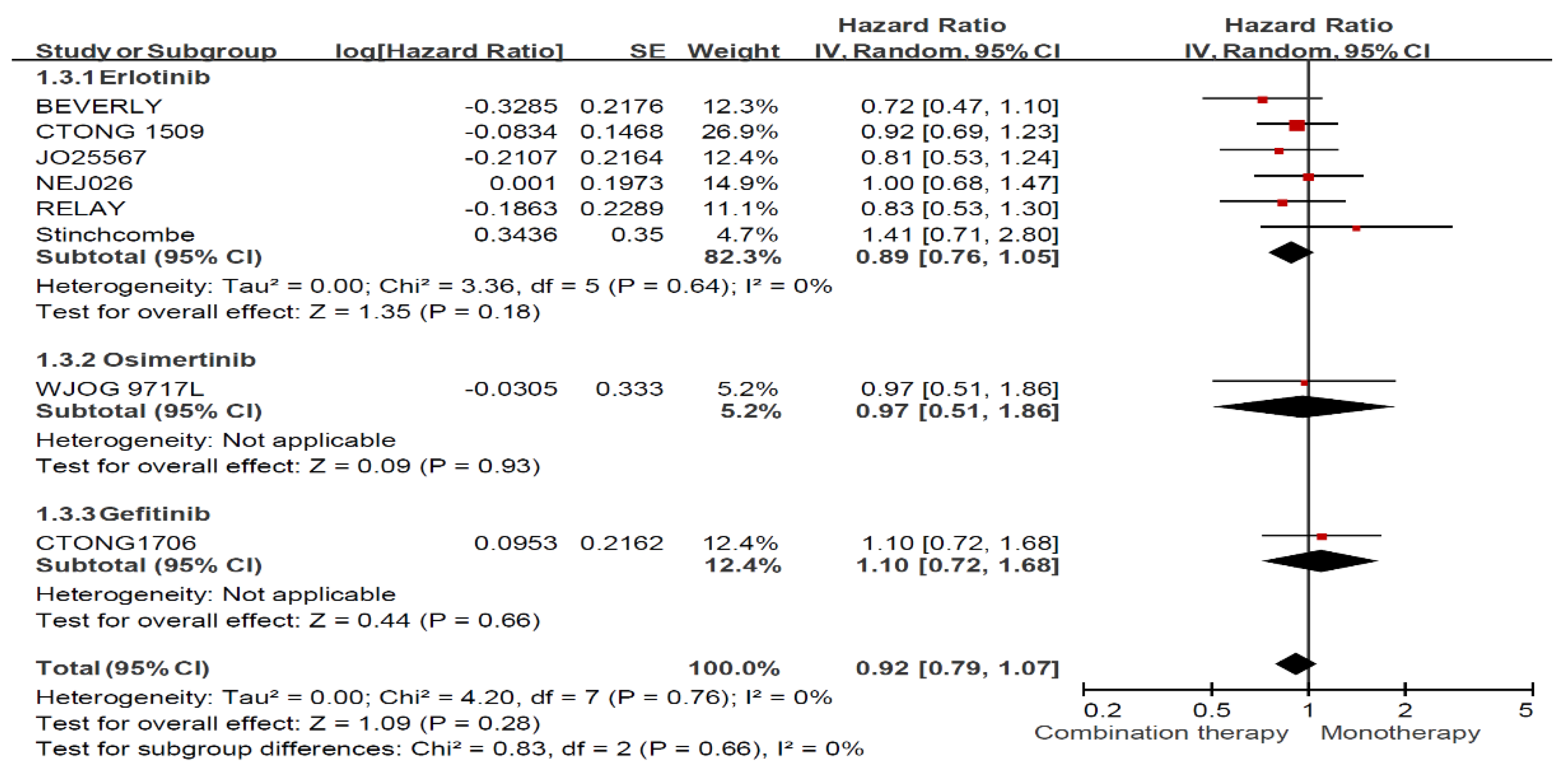
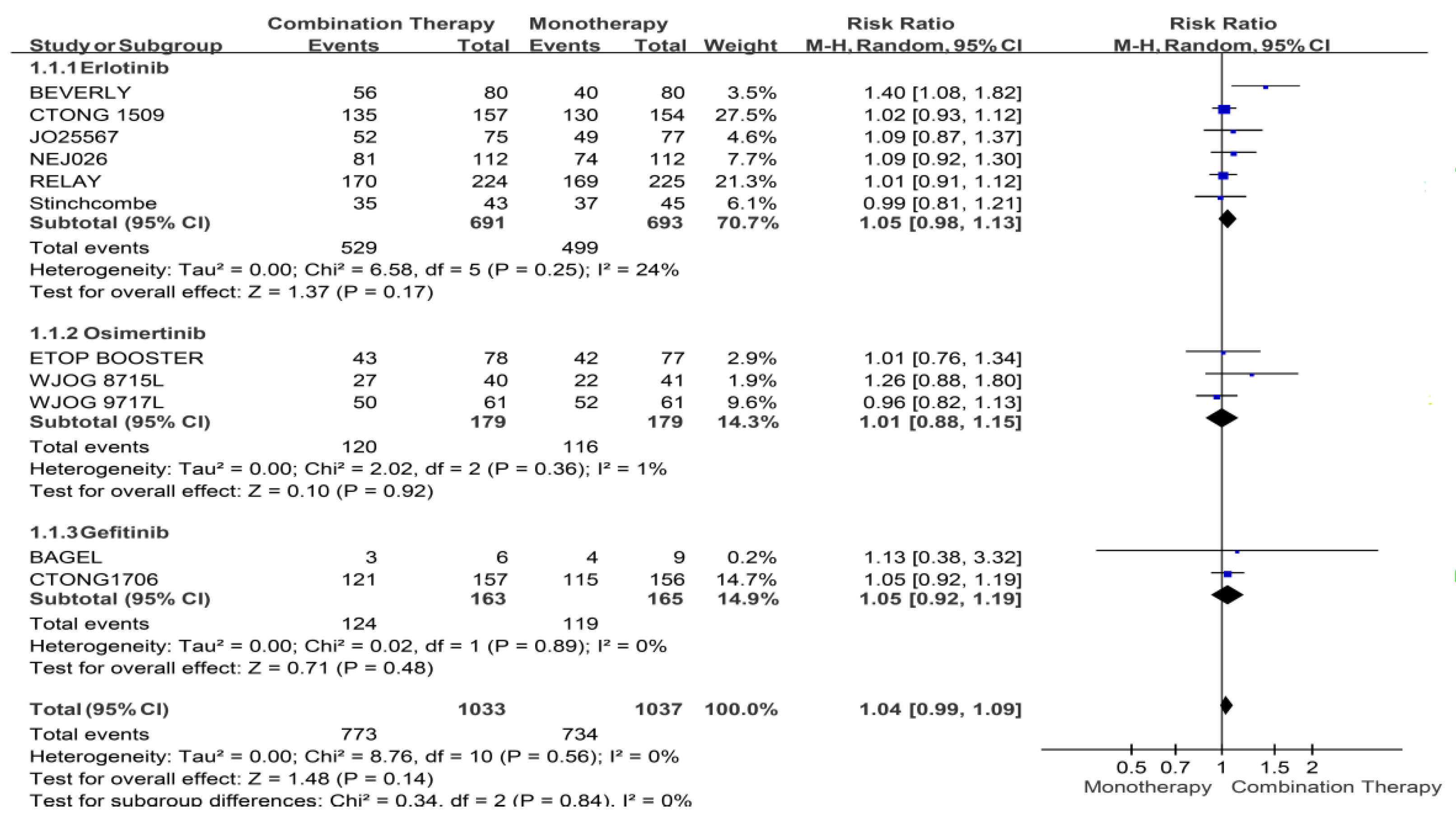
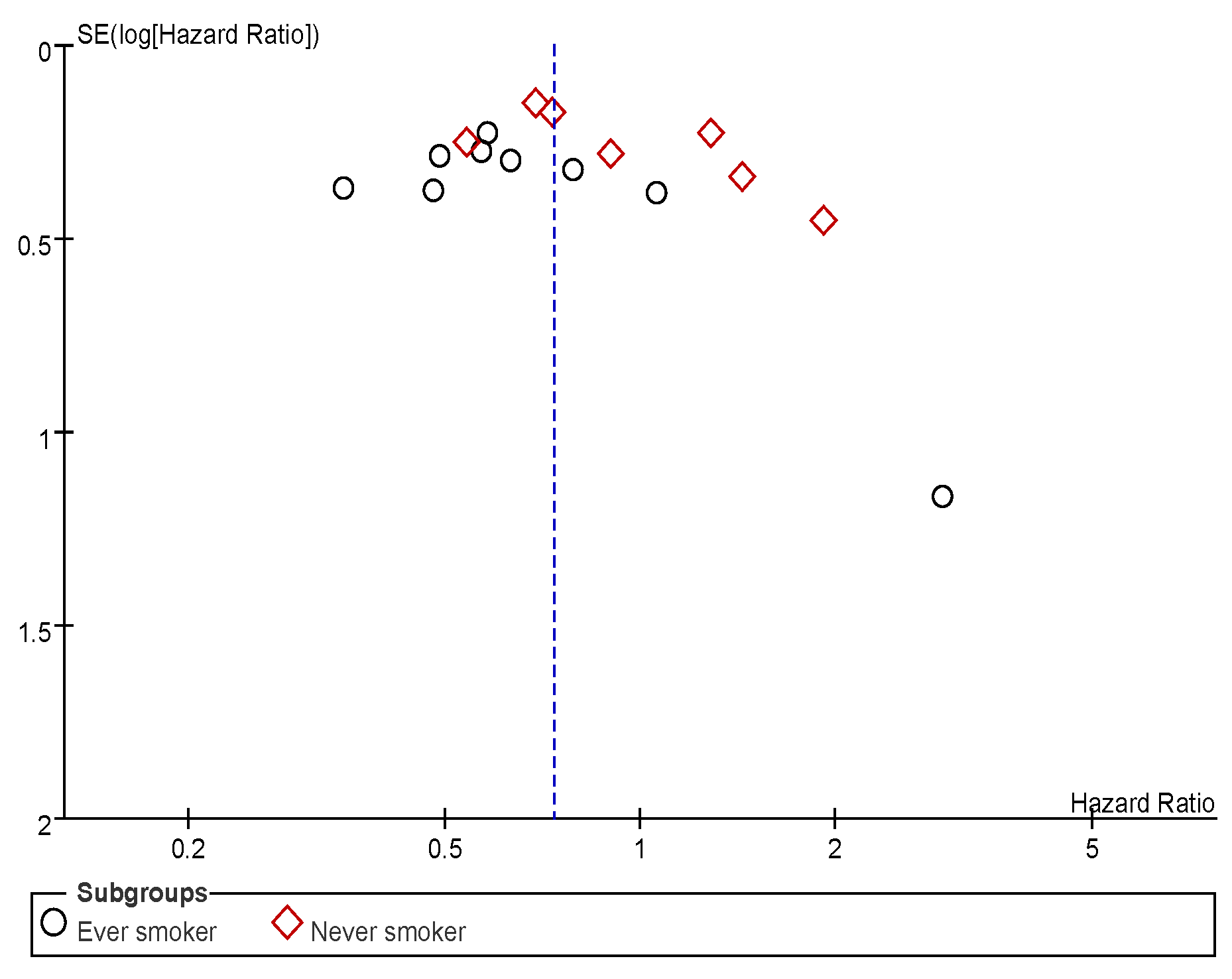
Appendix C. Funnel Plots
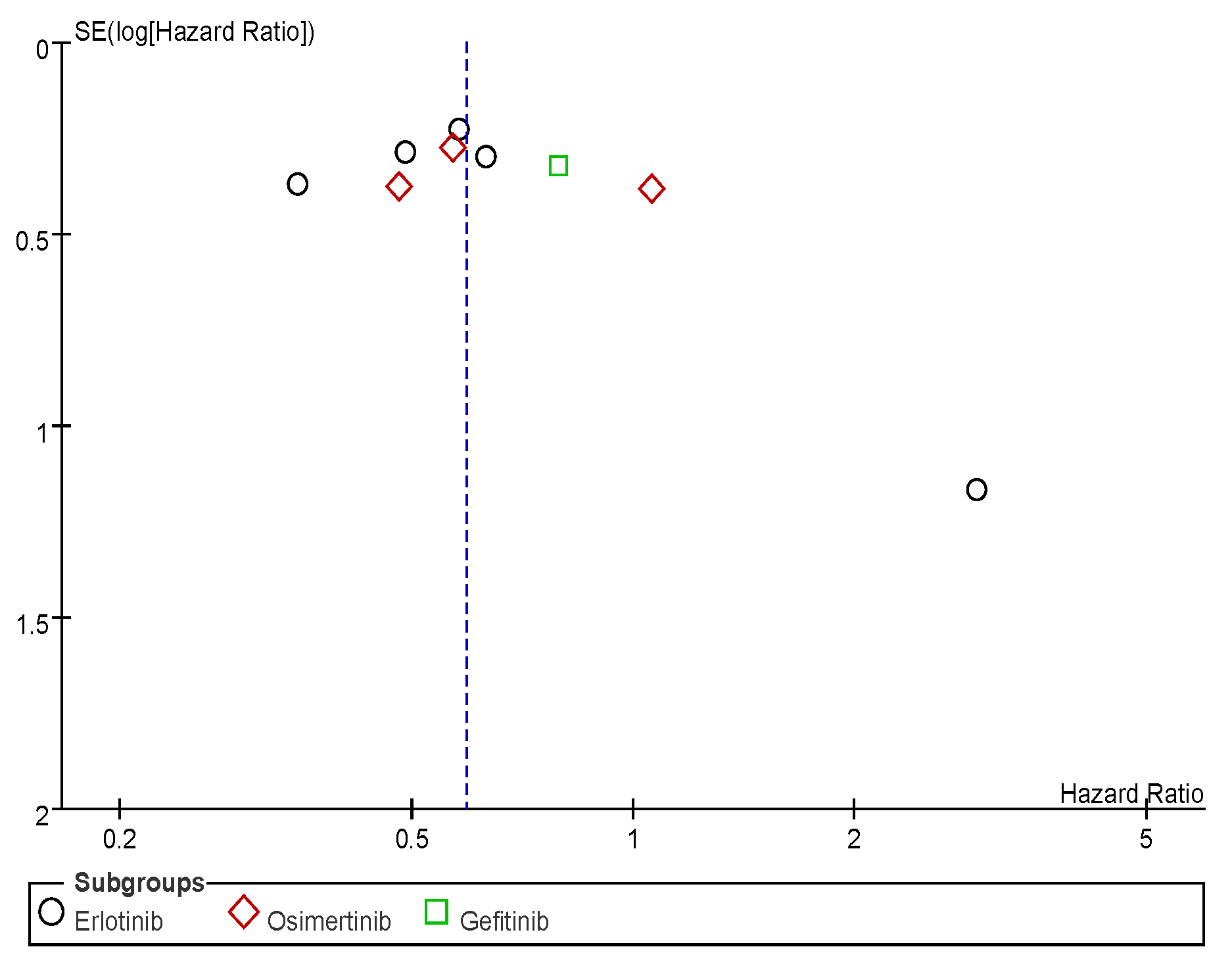
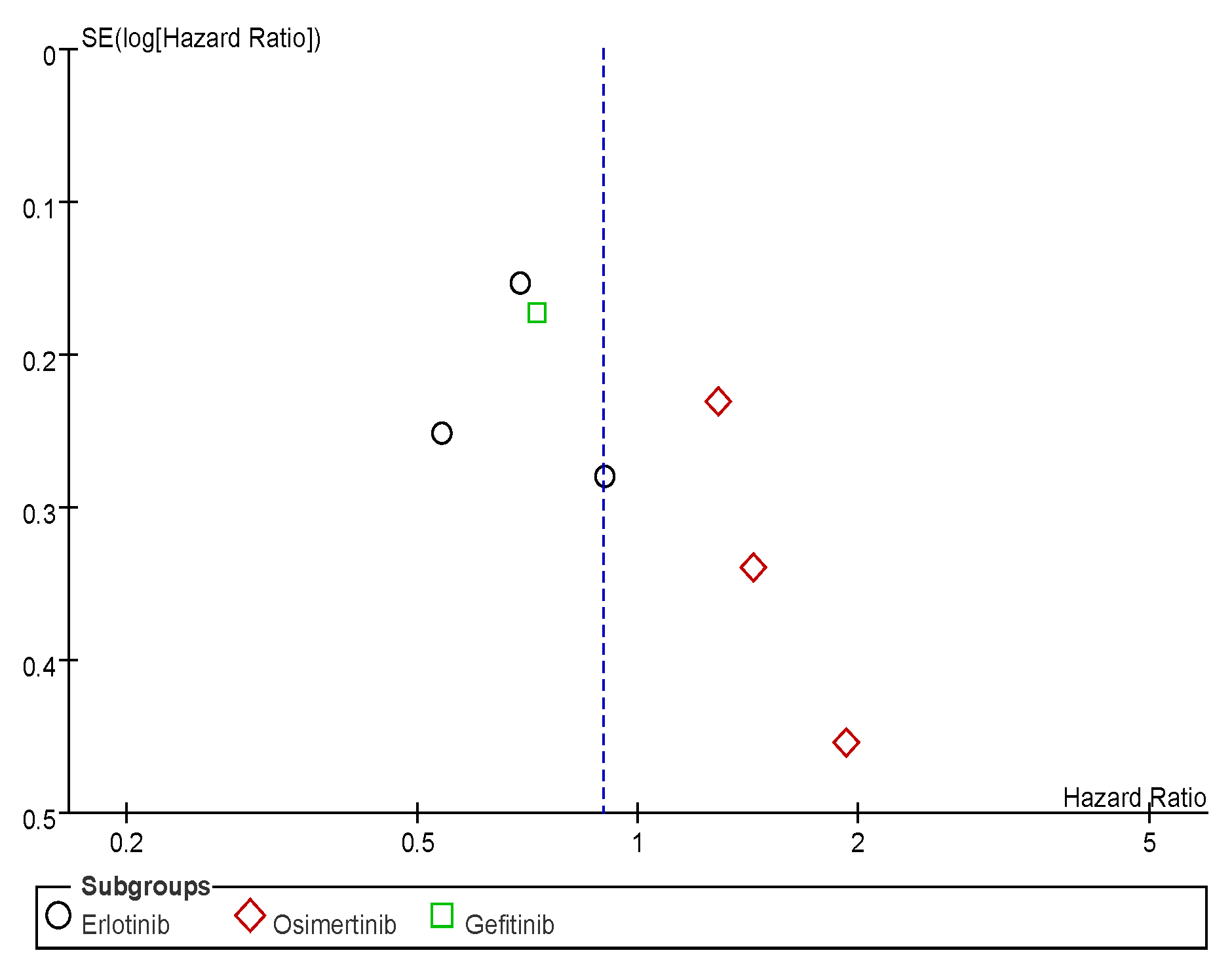
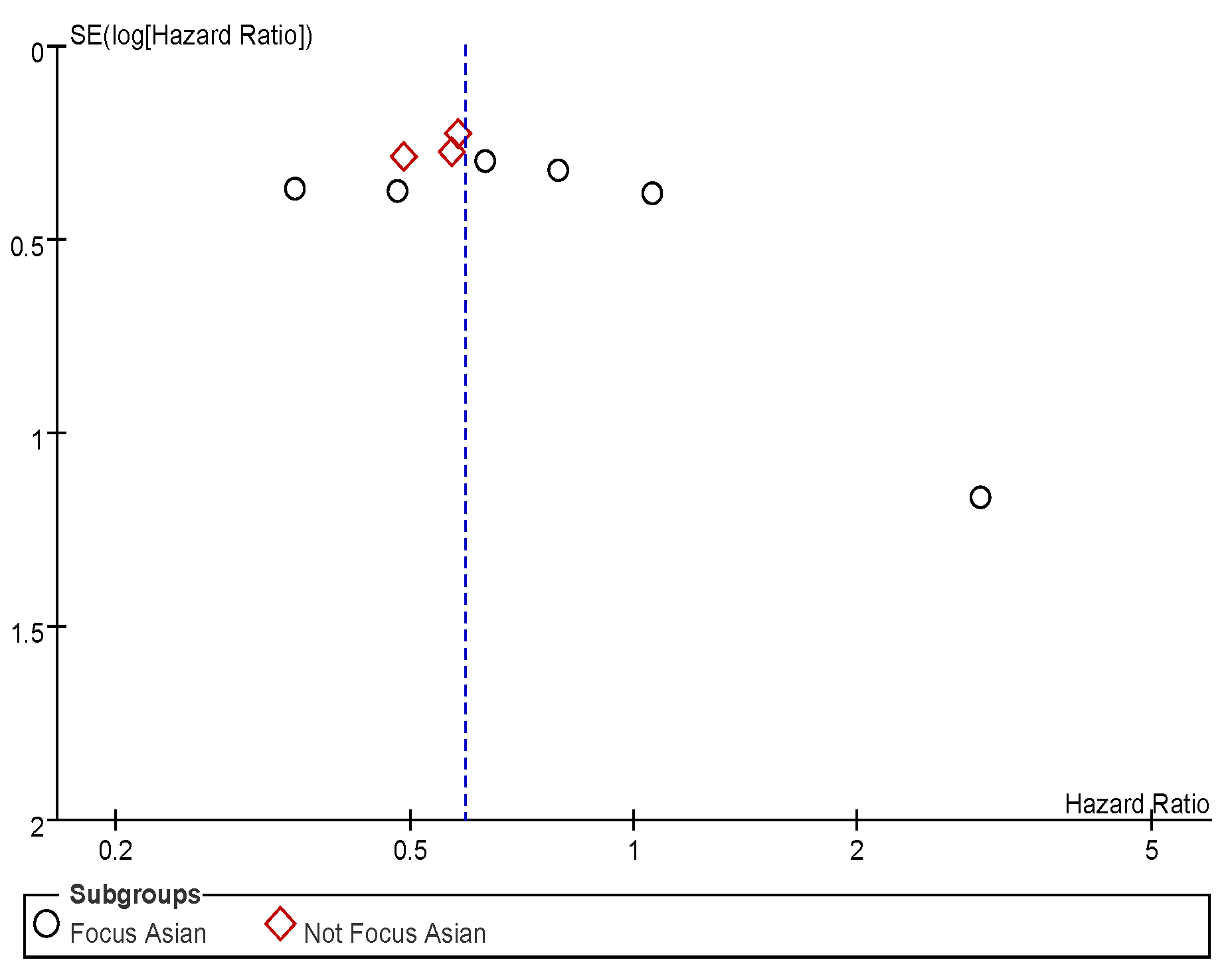

References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Burke, A.P.; Marx, A.; Nicholson, A.G. Introduction to The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus, and Heart. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar, J.; Urban, D.; Amit, U.; Appel, S.; Onn, A.; Margalit, O.; Beller, T.; Kuznetsov, T.; Lawrence, Y. Long-Term Survival of Patients with Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer over Five Decades. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 7836264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Au, J.; Thongprasert, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Tasi, C.M.; Khoa, M.; Heeroma, K.; Itoh, Y.; Cornelio, G.; Yang, P.C. A Prospective, Molecular Epidemiology Study of EGFR Mutations in Asian Patients with Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer of Adenocarcinoma Histology (PIONEER). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Koh, Y.; Ando, M.; Ito, N.; Takeo, S.; Adachi, H.; Tagawa, T.; Kakegawa, S.; Yamashita, M.; Kataoka, K.; et al. Prospective Analysis of Oncogenic Driver Mutations and Environmental Factors: Japan Molecular Epidemiology for Lung Cancer Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Yuan, J.Q.; Wang, K.F.; Fu, X.H.; Han, X.R.; Threapleton, D.; Yang, Z.Y.; Mao, C.; Tang, J.L. The prevalence of EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78985–78993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, R.; Carcereny, E.; Gervais, R.; Vergnenegre, A.; Massuti, B.; Felip, E.; Palmero, R.; Garcia-Gomez, R.; Pallares, C.; Sanchez, J.M.; et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Morita, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Negoro, S.; Okamoto, I.; Tsurutani, J.; Seto, T.; Satouchi, M.; Tada, H.; Hirashima, T.; et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.; Yamamoto, N.; O’Byrne, K.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.P.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, M.; Shi, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogure, Y.; Ando, M.; Saka, H.; Chiba, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Asami, K.; Hirashima, T.; Seto, T.; Nagase, S.; Otsuka, K.; et al. Histology and smoking status predict survival of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Results of West Japan Oncology Group (WJOG) Study 3906L. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.N.; O’Brien, M.E.; Petty, W.J.; Chick, J.B.; Rankin, E.; Woll, P.J.; Dunlop, D.; Nicolson, M.; Boinpally, R.; Wolf, J.; et al. Overcoming CYP1A1/1A2 mediated induction of metabolism by escalating erlotinib dose in current smokers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Kiang, A.; Lopez, J.P.; Kuo, S.Z.; Yu, M.A.; Abhold, E.L.; Chen, J.S.; Wang-Rodriguez, J.; Ongkeko, W.M. Cigarette smoke promotes drug resistance and expansion of cancer stem cell-like side population. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filosto, S.; Becker, C.R.; Goldkorn, T. Cigarette smoke induces aberrant EGF receptor activation that mediates lung cancer development and resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Nie, X.; Bie, Z.; Li, L. Impact of heavy smoking on the benefits from first-line EGFR-TKI therapy in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Medicine 2018, 97, e0006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, R.; Hong, D.S.; Warneke, C.L.; Lee, J.J.; Wheler, J.J.; Janku, F.; Naing, A.; Falchook, G.S.; Fu, S.; Piha-Paul, S.; et al. P53 mutations in advanced cancers: Clinical characteristics, outcomes, and correlation between progression-free survival and bevacizumab-containing therapy. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhang Ghahremani, M.; Goossens, S.; Nittner, D.; Bisteau, X.; Bartunkova, S.; Zwolinska, A.; Hulpiau, P.; Haigh, K.; Haenebalcke, L.; Drogat, B.; et al. p53 promotes VEGF expression and angiogenesis in the absence of an intact p21-Rb pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, H.; Lee, H.; Choi, C.M.; Sung, Y.H.; Lee, J.C.; Rho, J.K. Contribution of p53 in sensitivity to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Fang, W.; Hong, S.; Liang, W.; Yan, Y.; Qin, T.; Tang, Y.; Sheng, J.; Zhang, L. Impact of smoking status on EGFR-TKI efficacy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in EGFR mutants: A meta-analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2015, 16, 144–151.e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Huang, C.; Xie, X.; Wu, Z.; Tian, X.; Wu, Y.; Du, X.; Shi, L. The impact of smoking status on the progression-free survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving molecularly target therapy or immunotherapy versus chemotherapy: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2021, 46, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.F.; Lee, Y.L.; Chang, H.L.; Wei, P.J.; Shen, Y.T.; Lin, C.M.; Li, C.Y.; Chong, I.W.; Yang, C.J. Clinical efficacy of concurrent bevacizumab for malignant ascites in nonsquamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 15, e126–e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, A.; Gray, R.; Perry, M.C.; Brahmer, J.; Schiller, J.H.; Dowlati, A.; Lilenbaum, R.; Johnson, D.H. Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2542–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumov, G.N.; Nilsson, M.B.; Cascone, T.; Briggs, A.; Straume, O.; Akslen, L.A.; Lifshits, E.; Byers, L.A.; Xu, L.; Wu, H.K.; et al. Combined vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) blockade inhibits tumor growth in xenograft models of EGFR inhibitor resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3484–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Takayama, K.; Wang, S.; Shiraishi, Y.; Gotanda, K.; Harada, T.; Furuyama, K.; Iwama, E.; Ieiri, I.; Okamoto, I.; et al. Addition of bevacizumab enhances antitumor activity of erlotinib against non-small cell lung cancer xenografts depending on VEGF expression. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 74, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, C.; Yanagisawa, M.; Yorozu, K.; Kurasawa, M.; Furugaki, K.; Ishikura, N.; Iwai, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Yamamoto, K. Bevacizumab counteracts VEGF-dependent resistance to erlotinib in an EGFR-mutated NSCLC xenograft model. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Garon, E.B.; Seto, T.; Nishio, M.; Ponce Aix, S.; Paz-Ares, L.; Chiu, C.-H.; Park, K.; Novello, S.; Nadal, E.; et al. Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenmotsu, H.; Wakuda, K.; Mori, K.; Kato, T.; Sugawara, S.; Kirita, K.; Okamoto, I.; Azuma, K.; Nishino, K.; Teraoka, S.; et al. Primary results of a randomized phase II study of osimertinib plus bevacizumab versus osimertinib monotherapy for untreated patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations: WJOG9717L study. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32 (Suppl. 5), S1283–S1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, R.; Han, J.Y.; Dimopoulou, G.; Cho, B.C.; Yeo, C.M.; Nadal, E.; Carcereny, E.; de Castro, J.; Sala, M.A.; Bernabe, R.; et al. VP3-2021: A randomized phase II study of second-line osimertinib (Osi) and bevacizumab (Bev) versus Osi in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and T790M mutations (mt): Results from the ETOP BOOSTER trial. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 942–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirillo, M.C.; Bonanno, L.; Garassino, M.C.C.; Dazzi, C.; Cavanna, L.; Esposito, G.; Burgio, M.A.; Rosetti, F.; Rizzato, S.; Arenare, L.; et al. Bevacizumab + erlotinib vs erlotinib alone as firstline treatment of pts with EGFR mutated advanced non squamous NSCLC: Final analysis of the multicenter, randomized, phase III BEVERLY trial. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32 (Suppl. 5), S949–S1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Xu, C.R.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Chen, G.Y.; Cui, J.W.; Yang, N.; Song, Y.; Li, X.L.; Lu, S.; et al. Bevacizumab plus erlotinib in Chinese patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced NSCLC (ARTEMIS-CTONG1509): A multicenter phase 3 study. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1279–1291.e1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, T.; Kato, T.; Nishio, M.; Goto, K.; Atagi, S.; Hosomi, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Hida, T.; Maemondo, M.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Erlotinib alone or with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (JO25567): An open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Fukuhara, T.; Furuya, N.; Watanabe, K.; Sugawara, S.; Iwasawa, S.; Tsunezuka, Y.; Yamaguchi, O.; Okada, M.; Yoshimori, K.; et al. Erlotinib plus bevacizumab versus erlotinib alone in patients with EGFR-positive advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NEJ026): Interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinchcombe, T.E.; Janne, P.A.; Wang, X.; Bertino, E.M.; Weiss, J.; Bazhenova, L.; Gu, L.; Lau, C.; Paweletz, C.; Jaslowski, A.; et al. Effect of Erlotinib Plus Bevacizumab vs Erlotinib Alone on Progression-Free Survival in Patients With Advanced EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toi, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Fujimoto, D.; Tachihara, M.; Furuya, N.; Otani, S.; Shimizu, J.; Katakami, N.; Azuma, K.; Miura, N.; et al. A randomized phase II study of osimertinib with or without bevacizumab in advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients with EGFR T790M mutation (West Japan Oncology Group 8715L). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31 (Suppl. 4), S754–S840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, C.; Mori, M.; Ichiki, M.; Sukoh, N.; Kada, A.; Saito, A.M.; Ichinose, Y. Gefitinib Plus Bevacizumab vs. Gefitinib Alone for EGFR Mutant Non-squamous Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. In Vivo 2019, 33, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Yao, W.; Min, X.; Gu, K.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, J.; Miao, L.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; et al. Apatinib Plus Gefitinib as First-Line Treatment in Advanced EGFR-Mutant NSCLC: The Phase III ACTIVE Study (CTONG1706). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, E.R.; Summy, J.; Bauer, T.W.; Liu, W.; Gallick, G.E.; Ellis, L.M. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to Therapies Targeting the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Ansari, R.; Bustin, F.; Flynn, P.; Hart, L.; Otterson, G.A.; Vlahovic, G.; Soh, C.-H.; O’Connor, P.; Hainsworth, J. Efficacy of bevacizumab plus erlotinib versus erlotinib alone in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of standard first-line chemotherapy (BeTa): A double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.L.; Hsu, J.F.; Yang, C.J. Tracheoesophageal Fistula in a Patient with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Who Received Chemoradiotherapy and Ramucirumab. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e17–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
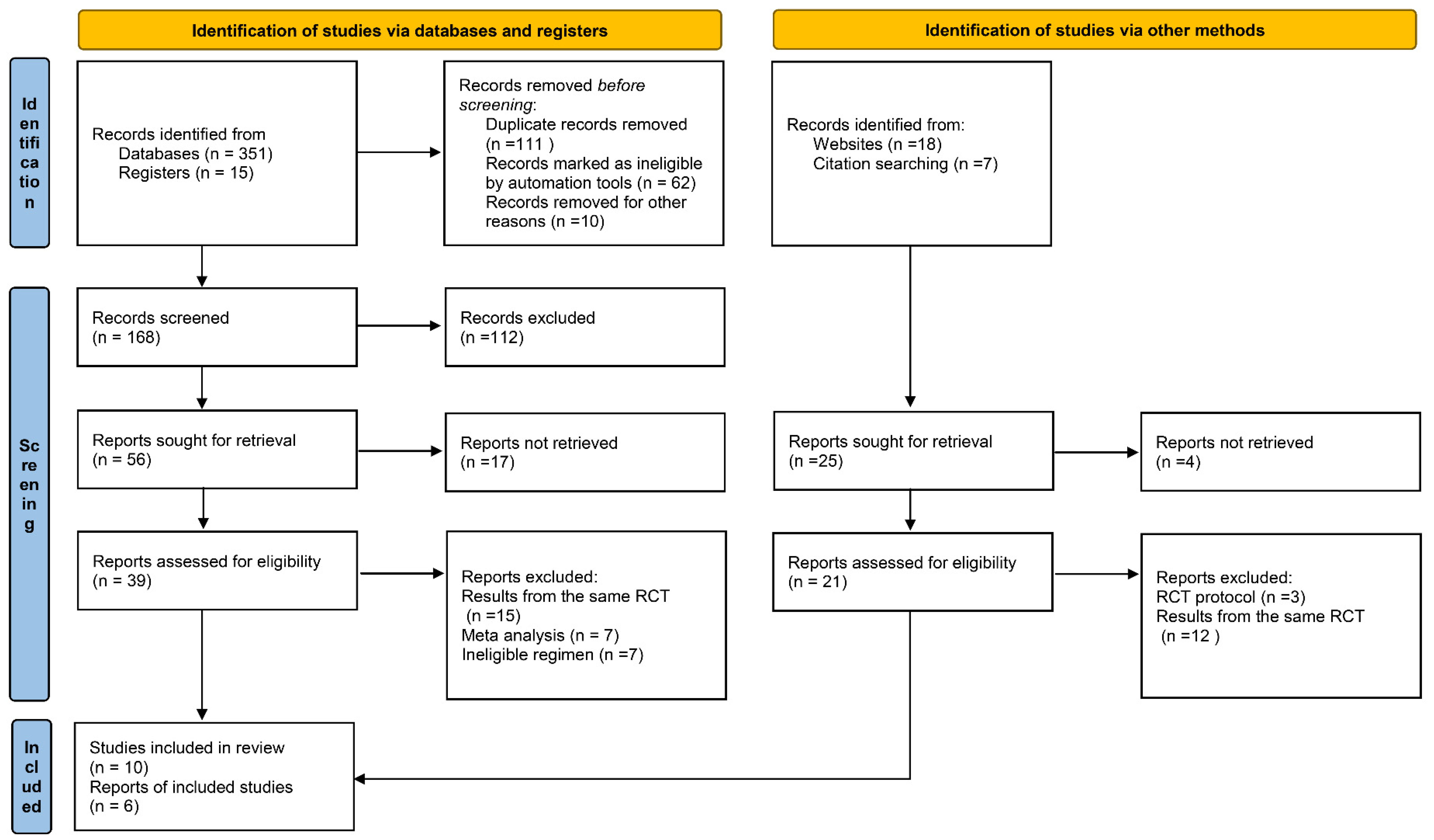

| Trial | BEVERLY [31] | CTONG 1509 [32] | JO25567 [33] | NEJ 026 [34] | RELAY [28] | Stinchcombe [35] | ETOP BOOSTER [30] | WJOG 8175L [36] | WJOG 917L [29] | KITAGAWA [37] | CTONG 1706 [38] | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author | Maria et al. | Zhou et al. | Yamamoto et al. | Saito et al. | Nakagawa et al. | Stinchcombe et al. | Soo et al. | Toi et al. | Kenmotsu et al. | Kitagawa et al. | Zhao et al. | |||||||||||
| Year | 2021 | 2019 | 2021 | 2019 PFS; | 2019 | 2019 | 2021 ESMO poster | 2020 ESMO | 2021 ESMO | 2019 | 2021 | |||||||||||
| ESMO | 2020 OS | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | Phase 3 RCT | Phase 3 RCT | Phase 2 RCT | Phase 3 RCT | Phase 3 RCT | Phase 2 RCT | Phase 2 RCT | Phase 2 RCT | Phase 2 RCT | Phase 2 RCT | Phase 3 RCT | |||||||||||
| Intervention | Erlotinib | Erlotinib + Bevacizumab | Erlotinib | Erlotinib + Bevacizumab | Erlotinib | Erlotinib + Bevacizumab | Erlotinib | Erlotinib+ Bevacizumab | Erlotinib | Erlotinib + Ramuicirumab | Erlotinib | Erlotinib + Ramuicirumab | Osimertinib | Osimertinib + Ramuicirumab | Osimertinib | Osimertinib + bevacizumab | Osimertinib | Osimertinib + bevacizumab | Gefitinib | Gefitinib + Bevacizumab | Apatinib + Gefitinib | Placebo + Gefitinib |
| Sample size | 80 | 80 | 154 | 157 | 77 | 75 | 112 | 112 | 221 | 225 | 45 | 43 | 77 | 78 | 41 | 40 | 61 | 61 | 10 | 6 | 157 | 156 |
| Patient character | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (median) | 67.7 | 65.9 | 57 | 59 | 67 | 67 | 68 | 67 | 64 | 65 | 63 | 65 | 67 | 70 | 68 | 66 | 67 | 72.5 | 73.5 | 57 | 60 | |
| Male (%) | 38% | 35% | 38% | 38% | 34% | 40% | 35% | 37% | 37% | 37% | 31% | 28% | 38% | 41% | 40% | 38% | 39% | 30% | 17% | 42% | 40% | |
| ECOG 0~1 (%) | 95% | 98% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 99% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | NA | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | % | 100% | 100% | |
| Brain metastasis (%) | NA | NA | 31% | 28% | NA | NA | 32% | 32% | NA | NA | 31% | 26% | NA | 22% | 30% | NA | NA | NA | NA | 33% | 26% | |
| Stage IV (%) | 94% | 96% | 86% | 90% | 81% | 80% | 75% | 73% | 84% | 87% | 100% | 100% | 98% | 63% | 83% | 75% | 79% | 90% | 100% | 97% | 95% | |
| Smoking, ever (%) | 54% | 43% | NA | NA | 42% | 43% | 43% | 42% | 32% | 29% | 40% | 49% | 40% | 49% | 48% | 51% | 38% | 20% | 33% | 27% | 22% | |
| Outcome | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| PFS (months, median) | 9.7 | 15.4 | 11.3 | 18 | 9.8 | 16.4 | 13.3 | 16.9 | 12.4 | 19.4 | 13.5 | 17.9 | 12.3 | 15.4 | 13.5 | 9.4 | 20.2 | 22.1 | 15.1 | 5.4 | 13.7 | 10% |
| PFS (HR, 95% CI ) | 0.60 (0.42–0.85) | 0.55 (0.41–0.75) | 0.52 (0.35–0.76) | 0.61 (0.41, 0.88) | 0.59 (0.46–0.76) | 0.81 (0.50–1.31) | 0.96 (0.69–1.36) | 1.44 (1.00–2.07) | 0.86 (0.53–1.40) | NA | 0.71 (0.54–0.95) | |||||||||||
| OS (months, median) | 23 | 28.4 | NA | NA | 47 | 47.4 | 46.2 | 50.7 | NA | NA | 50.6 | 32.4 | 24.3 | 24 | 22.1 | NR | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not mature | Not mature |
| OS (HR, 95% CI ) | 0.70, (0.46–1.10) | NA | 0.81 (0.53–1.24) | 1.00 (0.68–1.47) | NA | 1.41 (0.71–2.80) | HR 1.03; (95% CI 0.67–1.56; p = 0.91) | p = 0.96 | NA | NA | HR for OS was 1.10 (95% CI: 0.72–1.67, p = 0.66). | |||||||||||
| ORR (%) | 50.00% | 70.00% | 84.70% | 86.30% | 64.00% | 69.00% | 66.00% | 72.00% | 76.00% | 75.00% | 83.00% | 81.00% | 55.00% | 55.00% | 5400.00% | 6800.00% | 86.00% | 82.00% | 44.00% | 50.00% | 77.10% | 73.70% |
| AE, Gr >= 3; (%) | NA | NA | 26% | 55% | 53% | 91% | 46% | 88% | 54% | 72% | NA | NA | 18% | 47% | NA | NA | 48% | 56% | NA | NA | 84% | 38% |
| Discontinued due to AE (%) | NA | NA | 3% | 7% | 18% | 16% | 7% | 29% | 11% | 13% | NA | 26% | 4% | 25% | 31% | 35% | 26.70% | 55.70% | NA | NA | 29% | 5% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, T.-H.; Chen, H.-L.; Chang, H.-M.; Wu, C.-M.; Wu, K.-L.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Wei, P.-J.; Chen, C.-L.; Liu, H.-L.; Hung, J.-Y.; et al. Impact of Smoking Status in Combination Treatment with EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Anti-Angiogenic Agents in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Susceptible EGFR Mutations: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123366
Lee T-H, Chen H-L, Chang H-M, Wu C-M, Wu K-L, Kuo C-Y, Wei P-J, Chen C-L, Liu H-L, Hung J-Y, et al. Impact of Smoking Status in Combination Treatment with EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Anti-Angiogenic Agents in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Susceptible EGFR Mutations: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(12):3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123366
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Tai-Huang, Hsiao-Ling Chen, Hsiu-Mei Chang, Chiou-Mei Wu, Kuan-Li Wu, Chia-Yu Kuo, Po-Ju Wei, Chin-Ling Chen, Hui-Lin Liu, Jen-Yu Hung, and et al. 2022. "Impact of Smoking Status in Combination Treatment with EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Anti-Angiogenic Agents in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Susceptible EGFR Mutations: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 12: 3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123366
APA StyleLee, T.-H., Chen, H.-L., Chang, H.-M., Wu, C.-M., Wu, K.-L., Kuo, C.-Y., Wei, P.-J., Chen, C.-L., Liu, H.-L., Hung, J.-Y., Yang, C.-J., & Chong, I.-W. (2022). Impact of Smoking Status in Combination Treatment with EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Anti-Angiogenic Agents in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Susceptible EGFR Mutations: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(12), 3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123366






