Influence of Selected Air Pollutants on Mortality and Pneumonia Burden in Three Polish Cities over the Years 2011–2018
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Warsaw: NO2—3 stations, O3—3–4 stations, PM10—3–4 stations, PM2.5—2–4 stations
- Cracow: NO2—3–4 stations, O3—1 station, PM10—4 stations, PM2.5—3–4 stations
- Tricity: NO2—9 stations, O3—3–4 stations, PM10—8–9 stations, PM2.5—1 station
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Data Collection, Aggregation and Analyses
2.2.2. General Linear Models (GLMs)
2.2.3. Identification of the Periodic Structure
2.2.4. Model’s Identification and Diagnostic
3. Results
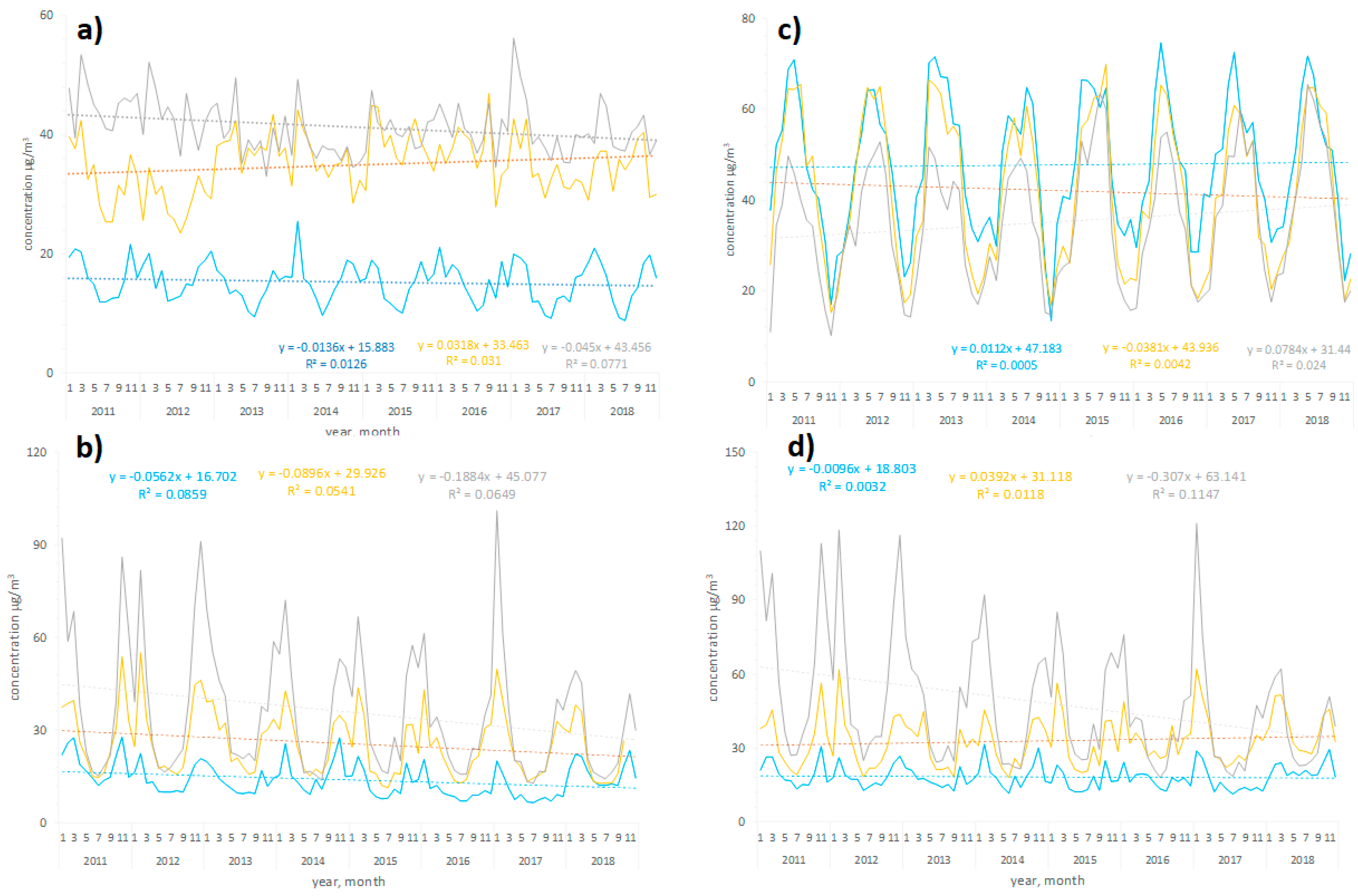
3.1. Air Pollution Profile in Warsaw, Tricity, and Cracow in 2011–2018
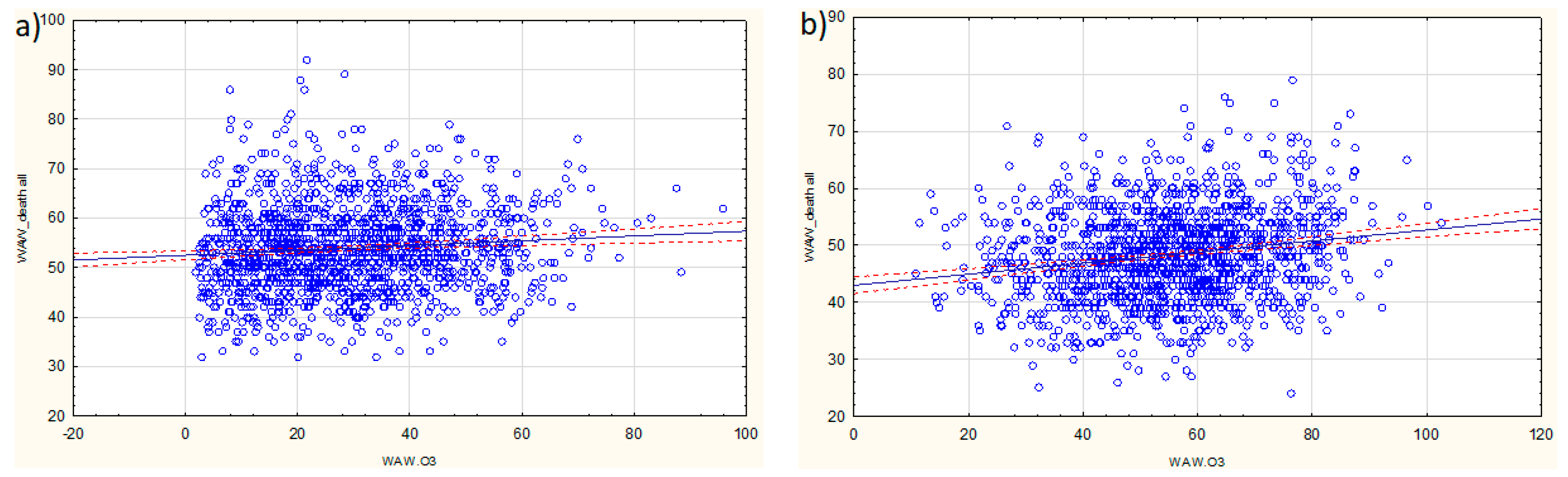
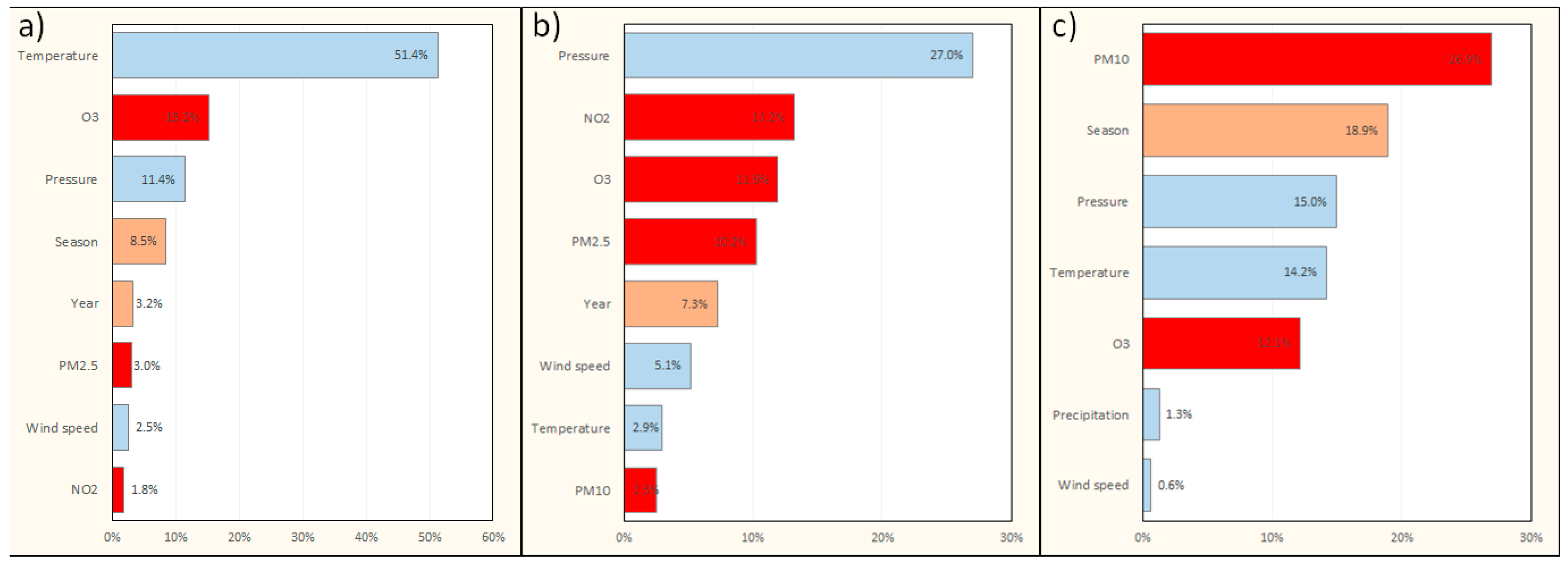
3.2. Models for All-Cause Deaths
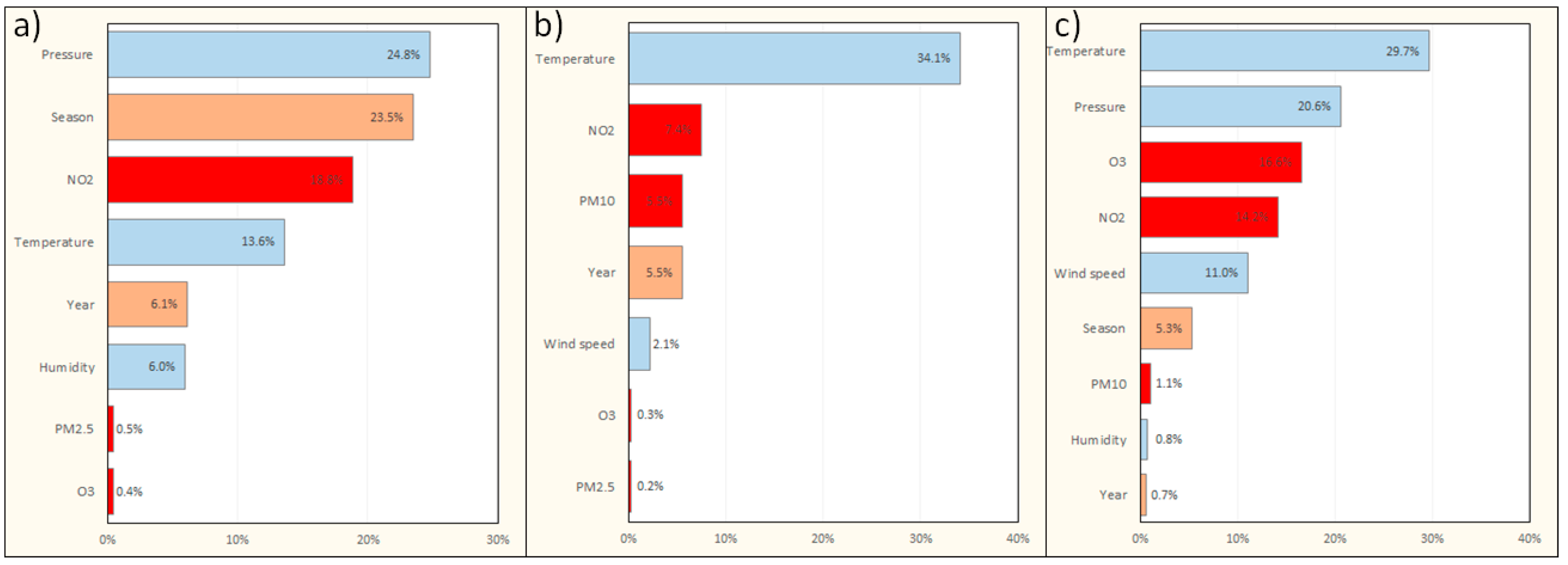
3.3. Models for Pneumonia-Related Hospitalizations
3.4. Models for Pneumonia-Related Hospitalizations and for All-Cause Deaths with Interactions and Lags
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Health Effects Institute. State of Global Air 2020; Special Report; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: www.stateofglobalair.org/sites/default/files/documents/2020-10/soga-2020-report.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Schultz, E.S.; Litonjua, A.A.; Melén, E. Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution on Lung Function in Children. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2017, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milanzi, E.B.; Koppelman, G.H.; Smit, H.A.; Wijga, A.H.; Oldenwening, M.; Vonk, J.M.; Brunekreef, B.; Gehring, U. Air pollution exposure and lung function until age 16 years: The PIAMA birth cohort study. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soliński, M.; Dąbrowiecki, P.; Badyda, A.J.; Adamkiewicz, Ł.; Kołtowski, Ł. Assessment of the Effects of Air Pollution on Lung Ventilation Efficiency of School Children—Interim Analysis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, A7224. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, M.; Schikowski, T.; Carsin, A.E.; Cai, Y.; Jacquemin, B.; Sanchez, M.; Vierkötter, A.; Marcon, A.; Keidel, D.; Sugiri, D.; et al. Adult lung function and long-term air pollution exposure. ESCAPE: A multicentre cohort study and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badyda, A.; Gayer, A.; Czechowski, P.O.; Majewski, G.; Dąbrowiecki, P. Pulmonary function and incidence of selected respiratory diseases depending on the exposure to ambient PM10. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giani, P.; Castruccio, S.; Anav, A.; Howard, D.; Hu, W.; Crippa, P. Short-term and long-term health impacts of air pollution reductions from COVID-19 lockdowns in China and Europe: A modelling study. Lancet 2020, 4, e474–e482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunekreef, B.; Holgate, S.T. Air pollution and health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, H.R.; Spix, C.; Medina, S.; Schouten, J.P.; Castellsague, J.; Rossi, G.; Zmirou, D.; Touloumi, G.; Wojtyniak, B.; Ponka, A.; et al. Air pollution and daily admissions for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in 6 European cities: Results from the APHEA project. Eur. Respir. J. 1997, 10, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samoli, E.; Aga, E.; Touloumi, G.; Nisiotis, K.; Forsberg, B.; Lefranc, A.; Pekkanen, J.; Wojtyniak, B.; Schindler, C.; Niclu, E.; et al. Short-term effects of nitrogen dioxide on mortality: An analysis within the APHEA project. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badyda, A.; Dąbrowiecki, P. Smog episode in Poland in January 2017 as a risk factor of increased hospital admissions due to respiratory and cardiovascular exacerbations. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, PA2630. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency. Air Quality in Europe—2020 Report; European Environment Agency: Luxembourg, 2020; Available online: www.eea.europa.eu/publications/air-quality-in-europe-2020-report/at_download/file (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Ministry of Climate. Poland’s Informative Inventory Report 2020. Submission under the UN ECE Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution and Directive (EU) 2016/2284; Air Pollutant Emissions in Poland 1990–2018; The National Centre for Emissions Management: Warsaw, Poland, 2020. Available online: webdab01.umweltbundesamt.at/download/submissions2020/PL_IIR2020.zip?cgiproxy_skip=1 (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Badyda, A.; Majewski, G.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Dąbrowiecki, P. Air pollution—What do we breathe in Poland? Lekarz. Wojskowy 2017, 95, 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Badyda, A. Niska emisja—Zanieczyszczenia powietrza pochodzące z transportu i gospodarstw domowych. In A Chapter in the Monograph Jak Wpływa na nas Smog—Profilaktyka i Leczenie; Medical Education: Warsaw, Poland, 2020; ISBN 978-83-65471-63-5. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution (LRTAP); Treaty Series; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 13 November 1979; Volume 1302, p. 217. Available online: https://treaties.un.org/Pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=IND&mtdsg_no=XXVII-1&chapter=27&clang=_en (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- European Environment Agency. Air Pollutant Emissions Data Viewer (Gothenburg Protocol, LRTAP Convention). 1990–2019. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/dashboards/air-pollutant-emissions-data-viewer-4 (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Badyda, A.; Krawczyk, P.; Bihałowicz, J.S.; Bralewska, K.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Majewski, G.; Oberbek, P.; Marciniak, A.; Rogulski, M. Are BBQs Significantly Polluting Air in Poland? A Simple Comparison of Barbecues vs. Domestic Stoves and Boilers Emissions. Energies 2020, 13, 6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, G.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Rozbicka, K.; Rogula-Kopiec, P.; Mathews, B.; Brandyk, A. Concentration, Chemical Composition and Origin of PM1: Results from the First Long-term Measurement Campaign in Warsaw (Poland). Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 636–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ćwiek, K.; Majewski, G. Wpływ elementów meteorologicznych na kształtowanie się stężeń zanieczyszczeń powietrza na przykładzie Krakowa. Przegląd Nauk. Inżynieria I Kształtowanie Sr. 2015, 67, 54–66. [Google Scholar]
- Chief Inspectorate for Environmental Protection. Air Quality Assessment—Annual Air Quality Assessments. Available online: https://powietrze.gios.gov.pl/pjp/maps/air/quality/type/R (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on Ambient air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32008L0050&qid=1653677581275&from=PL (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Kuźma, Ł.; Struniawski, K.; Pogorzelski, S.; Bachórzewska-Gajewska, H.; Dobrzycki, S. Gender Differences in Association between Air Pollution and Daily Mortality in the Capital of the Green Lungs of Poland–Population-Based Study with 2,953,000 Person-Years of Follow-Up. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holnicki, P.; Tainio, M.; Kałuszko, A.; Nahorski, Z. Burden of Mortality and Disease Attributable to Multiple Air Pollutants in Warsaw, Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adamkiewicz, Ł.; Badyda, A.; Gayer, A.; Mucha, D. Disability Adjusted Life-Years in the assessment of health effects of traffic-related air pollution. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 834, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomenko, S.; Cirach, M.; Pereira-Barboza, E.; Mueller, N.; Barrera-Gómez, J.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; de Hoogh, K.; Hoek, G.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. Premature mortality due to air pollution in European cities: A health impact assessment. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e121–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/345329 (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Nazar, W.; Niedoszytko, M. Air Pollution in Poland: A 2022 Narrative Review with Focus on Respiratory Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czechowski, P.O.; Piksa, K.; Da̧browiecki, P.; Oniszczuk-Jastrząbek, A.; Czermański, E.; Owczarek, T.; Badyda, A.J.; Cirella, G.T. Financing Costs and Health Effects of Air Pollution in the Tri-City Agglomeration. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 831312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, A.A.; Gusev, B.A.; Leonenko, E.V.; Tamarovskaya, A.N.; Vasiliev, A.S.; Zaytcev, N.E.; Philippov, I.K. Graz Lagrangian Model (GRAL) for Pollutants Tracking and Estimating Sources Partial Contributions to Atmospheric Pollution in Highly Urbanized Areas. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holford, T.R.; Ebisu, K.; McKay, L.A.; Gent, J.F.; Triche, E.W.; Bracken, M.B.; Leaderer, B.P. Integrated exposure modeling: A model using GIS and GLM. Stat. Med. 2010, 29, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.M.; Teodoro, F.; Cerdeira, R.; Coelho, L.M.R.; Carvalho, M.G. Developing a methodology to predict PM10 urban concentrations using GLM. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 183, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiogna, M.; Gaetan, C. Dynamic Generalized Linear Models with Application to Environmental Epidemiology. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 2002, 51, 453–468. [Google Scholar]
- Demetriou, E.; Hadjistassou, C. Lowering mortality risks in urban areas by containing atmospheric pollution. Environ. Res. 2022, 211, 113096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, J. General Regression Models. In Bayesian and Frequentist Regression Methods; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 425–500. [Google Scholar]
- Ratajczak, A.; Badyda, A.; Czechowski, P.O.; Czarnecki, A.; Dubrawski, M.; Feleszko, W. Air Pollution Increases the Incidence of Upper Respiratory Tract Symptoms among Polish Children. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrotek, A.; Badyda, A.; Czechowski, P.O.; Owczarek, T.; Dąbrowiecki, P.; Jackowska, T. Air Pollutants’ Concentrations Are Associated with Increased Number of RSV Hospitalizations in Polish Children. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engardt, M.; Bergström, R.; Andersson, C. Climate and emission changes contributing to changes in near-surface ozone in Europe over the coming decades: Results from model studies. Ambio 2009, 38, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: An analysis of data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beelen, R.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Stafoggia, M.; Andersen, Z.J.; Weinmayr, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Wolf, K.; Samoli, E.; Fischer, P.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; et al. Effects of long-term exposure to air pollution on natural-cause mortality: An analysis of 22 European cohorts within the multicentre ESCAPE project. Lancet 2014, 383, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsouyanni, K.; Touloumi, G.; Samoli, E.; Gryparis, A.; Le Tertre, A.; Monopolis, Y.; Rossi, G.; Zmirou, D.; Ballester, F.; Boumghar, A.; et al. Confounding and effect modification in the short-term effects of ambient particles on total mortality: Results from 29 European cities within the APHEA2 project. Epidemiology 2001, 12, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhong, L.; Bi, X.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Zhu, T.; Huang, W. Systematic review of Chinese studies of short-term exposure to air pollution and daily mortality. Environ. Int. 2013, 54, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samoli, E.; Analitis, A.; Touloumi, G.; Schwartz, J.; Anderson, H.R.; Sunyer, J.; Bisanti, L.; Zmirou, D.; Vonk, J.M.; Pekkanen, J.; et al. Estimating the exposure-response relationships between particulate matter and mortality within the APHEA multicity project. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadogeorgou, G.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Braun, D.; Zanobetti, A. Low Levels of Air Pollution and Health: Effect Estimates, Methodological Challenges, and Future Directions. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2019, 6, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J.; Samoli, E.; Gryparis, A.; Touloumi, G.; Peacock, J.; Anderson, R.H.; Le Tertre, A.; Bobros, J.; Celko, M.; et al. The temporal pattern of respiratory and heart disease mortality in response to air pollution. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Environment Agency. Europe’s Urban Air Quality—Re-Assessing Implementation Challenges in Cities; EEA Report No 24/2018; European Environment Agency: Luxembourg, 2018; Available online: www.eea.europa.eu/publications/europes-urban-air-quality/at_download/file (accessed on 23 March 2021). [CrossRef]
- Faustini, A.; Rapp, R.; Forastiere, F. Nitrogen dioxide and mortality: Review and meta-analysis of long-term studies. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seaton, A.; Dennekamp, M. Hypothesis: III health associated with low concentrations of nitrogen dioxide—An effect of ultrafine particles? Thorax 2003, 58, 1012–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Samoli, E.; Wong, C.M.; Huang, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Kan, H. Associations between short-term exposure to nitrogen dioxide and mortality in 17 Chinese cities: The China Air Pollution and Health Effects Study (CAPES). Environ. Int. 2012, 45, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Disease Burden and Mortality Estimates. Global Health Estimates 2016: Estimated Deaths by Age, Sex, and Cause; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GHE2016_Deaths_Global_2000_2016.xls?ua=1 (accessed on 23 March 2021). [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.S. Nitrogen dioxide exposure and airway responsiveness in individuals with asthma. Inhal. Toxicol. 2015, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barck, C.; Lundahl, J.; Halldén, G.; Bylin, G. Brief exposures to NO2 augment the allergic inflammation in asthmatics. Environ. Res. 2005, 97, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezratty, V.; Guillossou, G.; Neukirch, C.; Dehoux, M.; Koscielny, S.; Bonay, M.; Cabanes, P.A.; Samet, J.M.; Mure, P.; Ropert, L.; et al. Repeated nitrogen dioxide exposures and eosinophilic airway inflammation in asthmatics: A randomized crossover study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robison, T.W.; Kim, K.-J. Dual effect of nitrogen dioxide on barrier properties of guinea pig tracheobronchial epithelial monolayers cultured in an air interface. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1995, 44, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spannhake, E.W.; Reddy, S.P.M.; Jacoby, D.B.; Yu, X.Y.; Saatian, B.; Tian, J. Synergism between rhinovirus infection and oxidant pollutant exposure enhances airway epithelial cell cytokine production. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacIntyre, E.A.; Gehring, U.; Mölter, A.; Fuertes, E.; Klümper, C.; Krämer, U.; Quass, U.; Hoffmann, B.; Gascon, M.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Air pollution and respiratory infections during early childhood: An analysis of 10 European birth cohorts within the ESCAPE project. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halonen, J.I.; Lanki, T.; Yli-Tuomi, T.; Tiittanen, P.; Kulmala, M.; Pekkanen, J. Particulate air pollution and acute cardiorespiratory hospital admissions and mortality among the elderly. Epidemiology 2009, 20, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Host, S.; Larrieu, S.; Pascal, L.; Blanchard, M.; Declercq, C.; Fabre, P.; Jusot, J.F.; Chardon, B.; Le Tertre, A.; Wagner, V.; et al. Short-term associations between fine and coarse particles and hospital admissions for cardiorespiratory diseases in six French cities. Occup. Environ. Med. 2008, 65, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleudi, V.; Faustini, A.; Stafoggia, M.; Cattani, G.; Marconi, A.; Perucci, C.A.; Forastiere, F. Impact of fine and ultrafine particles on emergency hospital admissions for cardiac and respiratory diseases. Epidemiology 2010, 21, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Tian, L.W.; Pun, V.C.; Ho, K.F.; Wong, T.W.; Yu, I.T.S. Coarse particulate matter associated with increased risk of emergency hospital admissions for pneumonia in Hong Kong. Thorax 2014, 69, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Sario, M.; Katsouyanni, K.; Michelozzi, P. Climate change, extreme weather events, air pollution and respiratory health in Europe. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 826–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanobetti, A.; Peters, A. Disentangling interactions between atmospheric pollution and weather. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2015, 69, 613–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, R.M.; Heal, M.R.; O’Connor, F.M. Climate change impacts on human health over Europe through its effect on air quality. Environ. Health 2017, 16 (Suppl. 1), 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gryparis, A.; Forsberg, B.; Katsouyanni, K.; Analitis, A.; Touloumi, G.; Schwartz, J.; Samoli, E.; Medina, S.; Anderson, H.R.; Niciu, E.M.; et al. Acute effects of ozone on mortality from the “Air Pollution and Health: A European Approach” project. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, D.J.; Winner, D.A. Effect of climate change on air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wichmann, H.E.; Mueller, W.; Allhoff, P.; Beckmann, M.; Bocter, N.; Csicsaky, M.J.; Jung, M.; Molik, B.; Schoeneberg, G. Health effects during a smog episode in West Germany in 1985. Environ. Health Perspect. 1989, 79, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Warsaw | Cracow | Tricity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population † | 1,790,658 | 779,115 | 752,974 |
| Population density, per km2 † | 3462 | 2384 | 1811 |
| Geographical location | Central lowlands | Foothills | Coastal plain |
| Weather conditions § | |||
| Temperature, °C | 9.5 (9.0–10.1) | 9.5 (9.0–10.1) | 8.7 (8.1–9.3) |
| Air humidity, % | 75.8 (73.8–77.9) | 77.0 (75.8–78.3) | 78.7 (78.2–79.3) |
| Wind speed, m/s | 2.9 (2.8–3.0) | 2.4 (2.4–2.5) | 3.9 (3.7–4.0) |
| Precipitation, mm # | 616.9 (515.9–717.8) | 699.8 (585.6–814.1) | 619.1 (491.2–746.9) |
| Atmospheric pressure, hPa ‡ | 1003.5 (1003.2–1003.8) | 988.1 (987.8–988.4) | 1007.1 (1006.8–1007.4) |
| Air pollution § | |||
| PM2.5, µg/m3 | 25.6 (25.0–26.2) | 35.8 (34.7–36.9) | 13.9 (13.6–14.3) |
| PM10, µg/m3 | 33.1 (32.4–33.7) | 48.1 (46.7–49.5) | 18.3 (17.9–18.7) |
| NO2, µg/m3 | 35.0 (34.6–35.4) | 41.3 (40.8–41.7) | 15.2 (14.9–15.5) |
| O3, µg/m3 | 42.1 (41.4–42.9) | 35.5 (34.8–36.2) | 47.8 (47.1–48.4) |
| Number of evaluated health outcomes in 2011–2018 | |||
| All-cause deaths | 149,418 | 59,127 | 62,771 |
| All-cause deaths (per 100,000 inhabitants) | 8404 | 7668 | 8,381 |
| Pneumonia-related hospitalizations | 45,046 | 20,165 | 12,350 |
| Pneumonia-related hospitalizations (per 100,000 inhabitants) | 2531 | 2612 | 1649 |
| Air Pollutant | EU Limit Values * | Annual WHO AQG # | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| μg/m3 | ||||
| Annual | Daily | Annual | Daily | |
| PM2.5, µg/m3 | 25 | n.a. | 5 | 15 |
| PM10, µg/m3 | 40 | 50 | 15 | 45 |
| NO2, µg/m3 | 40 | n.a. | 10 | 25 |
| O3, µg/m3 | n.a. | 120 † | 60 § | 100 ‡ |
| Warsaw | Cracow | Tricity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 (inter.) | 24.0% | 9.9% | 12.7% |
| R2 (univ.) | 19.7% | 9.4% | 11.2% |
| df | 2800 | 2860 | 2888 |
| Year | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| Season | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| NO2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| O3 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| PM10 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| PM2.5 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Pressure | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Wind | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Temperature | 4 | 1 | 2 |
| Humidity | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Precipitation | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Interactions: | O3 × temperature | Season × humidity | O3 × PM10 |
| Pressure × temperature | Pressure | Season | |
| PM2.5 × wind | PM2.5 × wind | Pressure × temperature | |
| Season × O3 | NO2 × O3 | Year × pressure | |
| Year × PM10 | Pressure × temperature | Year × temperature | |
| NO2 × humidity | Year × PM10 | PM10 × precipitation | |
| PM10 × precipitation | NO2 × humidity | Year × wind | |
| PM10 × temperature | Year × O3 | ||
| Season | |||
| Season × NO2 | |||
| Season × pressure | |||
| Year × temperature | |||
| Year × wind | |||
| Single factors: | Season | Year | Season |
| O3 | Season | O3 | |
| PM10 | NO2 | Year | |
| Year | Pressure | Temperature | |
| Temperature | Wind | Humidity | |
| Pressure | Temperature | NO2 | |
| PM2.5 | PM10 | ||
| O3 |
| Warsaw | Cracow | Tricity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 (inter.) | 45.8% | 29.8% | 17.4% |
| R2 (univ.) | 40.8% | 26.1% | 16.7% |
| df | 2800 | 2860 | 2888 |
| Year | 5 | 5 | 1 |
| Season | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| NO2 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| O3 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| PM10 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| PM2.5 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Pressure | 4 | 0 | 2 |
| Wind | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Temperature | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| Humidity | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Precipitation | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Interactions: | Season × humidity | Temperature × humidity | Pressure × temperature |
| NO2 × pressure | NO2 × humidity | Season × O3 | |
| NO2 × wind | Season | NO2 × O3 | |
| Season × PM10 | PM10 × temperature | Wind × temperature | |
| NO2 × temperature | Season × PM10 | Pressure | |
| Pressure | Season × humidity | PM10 × wind | |
| Pressure × temperature | Season × temperature | NO2 × wind | |
| PM2.5 × temperature | Wind × temperature | NO2 × humidity | |
| Year × O3 | Year × O3 | Year × temperature | |
| Season × temperature | Year × temperature | ||
| Year × temperature | Year × PM10 | ||
| Year × wind | NO2 × wind | ||
| Year | Year × PM2.5 | ||
| Year × pressure | Year × wind | ||
| Single factors: | Temperature | NO2 | NO2 |
| NO2 | Temperature | Temperature | |
| Season | Season | Season | |
| Wind | Wind | PM10 | |
| Pressure | Pressure | O3 | |
| Year | Year | Wind | |
| Pressure | |||
| Year |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dąbrowiecki, P.; Badyda, A.; Chciałowski, A.; Czechowski, P.O.; Wrotek, A. Influence of Selected Air Pollutants on Mortality and Pneumonia Burden in Three Polish Cities over the Years 2011–2018. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3084. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113084
Dąbrowiecki P, Badyda A, Chciałowski A, Czechowski PO, Wrotek A. Influence of Selected Air Pollutants on Mortality and Pneumonia Burden in Three Polish Cities over the Years 2011–2018. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(11):3084. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113084
Chicago/Turabian StyleDąbrowiecki, Piotr, Artur Badyda, Andrzej Chciałowski, Piotr Oskar Czechowski, and August Wrotek. 2022. "Influence of Selected Air Pollutants on Mortality and Pneumonia Burden in Three Polish Cities over the Years 2011–2018" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 11: 3084. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113084
APA StyleDąbrowiecki, P., Badyda, A., Chciałowski, A., Czechowski, P. O., & Wrotek, A. (2022). Influence of Selected Air Pollutants on Mortality and Pneumonia Burden in Three Polish Cities over the Years 2011–2018. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(11), 3084. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113084








