Relationship between ABO Blood Group Distribution and COVID-19 Infection in Patients Admitted to the ICU: A Multicenter Observational Spanish Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
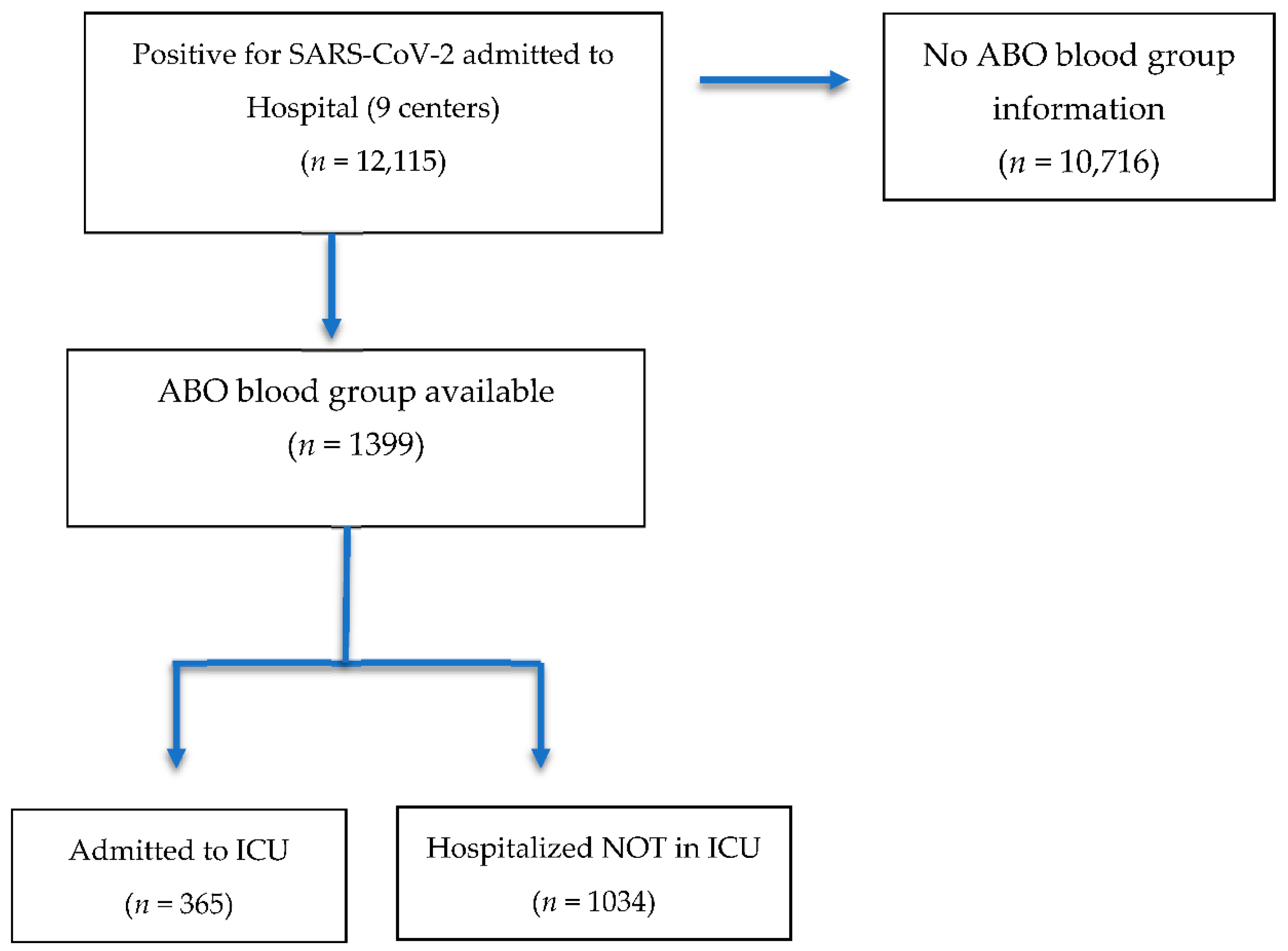
2.1. Study Design and Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Data Collection and Confidentiality
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Z.; Mc Googan, J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72314 case from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas-Rojo, J.; Antón-Santos, J.; Millán-Núñez-Cortés, J.; Lumbreras-Bermejo, C.; Ramos-Rincón, J.; Roy-Vallejo, E.; Artero-Mora, A.; Arnalich-Fernández, F.; García-Bruñén, J.; Vargas-Núñez, J.; et al. Clinical characteristics of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Spain: Results from the SEMI-COVID-19 Registry. Rev. Clín. Esp. 2020, 220, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.; Hirsch, J.S.; Narasimhan, M.; Crawford, J.M.; McGinn, T.; Davidson, K.W.; the Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA 2020, 323, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pozo-Herce, P.; Garrido-García, R.; Santolalla-Arnedo, I.; Gea-Caballero, V.; García-Molina, P.; de Viñaspre-Hernández, R.R.; Rodríguez-Velasco, F.J.; Juárez-Vela, R. Psychological Impact on the Nursing Professionals of the Rioja Health Service (Spain) Due to the SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santolalla-Arnedo, I.; Del Pozo-Herce, P.; De Viñaspre-Hernandez, R.R.; Gea-Caballero, V.; Juarez-Vela, R.; Gil-Fernandez, G.; Garrido-Garcia, R.; Echaniz-Serrano, E.; Czapla, M.; Rodriguez-Velasco, F.J. Psychological impact on care professionals due to the SARS-CoV-2 virus in Spain. Int. Nurs. Rev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Esteban, E.M.; Quintana-Diaz, M.; Ramírez-Cervantes, K.L.; Benayas-Peña, I.; Silva-Obregón, A.; Magallón-Botaya, R.; Santolalla-Arnedo, I.; Juárez-Vela, R.; Gea-Caballero, V. Outcomes of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 according to level of frailty. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grupo Cooperativo Internacional de Medicina Transfusional. Inmunohematología Básica y Aplicada, 1st ed.; GCIAMT, Grupo Cooperativo Internacional de Medicina Transfusional: Bogotá, Colombia, 2014; ISBN 978-958-46-4106-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gilmiyarova, F.N.; Kolotyeva, N.A.; Kuzmicheva, V.I.; Gusyakova, O.A.; Borodina, I.A.; Baisheva, G.M.; Selezneva, I.A. Blood Group and Human Diseases (Review Of Literature). Russ. Clin. Lab. Diagn. 2020, 65, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, D.; Gu, D.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; et al. Relationship between the ABO Blood Group and the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Susceptibility. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Cai, Y.; Deng, A.; Yang, M. Association between ABO blood groups and risk of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietz, M.; Tatonetti, N.P. Testing the association between blood type and COVID-19 infection, intubation, and death. medRxiv 2020, 3, 32511586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellinghaus, D.; Degenhardt, F.; Bujanda, L.; Buti, M.; Albillos, A.; Invernizzi, P.; Fernández, J.; Prati, D.; Baselli, G.; Asselta, R.; et al. The ABO blood group locus and a chromosome 3 gene cluster associate with SARS-CoV-2 respiratory failure in an Italian-Spanish genome-wide association analysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1522–1534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Enguita-Germán, M.; Librero, J.; Leache, L.; Gutiérrez-Valencia, M.; Tamayo, I.; Jericó, C.; Gorricho, J.; García-Erce, J.A. Role of the AB0 blood group in COVID-19 infection and complications: A population-based study. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Valencia, M.; Leache, L.; Librero, J.; Jericó, C.; Germán, M.E.; García-Erce, J.A. ABO blood group and risk of COVID -19 infection and complications: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transfusion 2021, 62, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalba Marcos, S.; Antelo, M.L.; Galbete, A.; Etayo, M.; Ongay, E.; García-Erce, J.A. Infection and thrombosis associated with COVID-19: Possible role of the ABO blood group. Med. Clin. 2020, 155, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Cheng, G.; Chui, C.H.; Lau, F.Y.; Chan, P.K.S.; Margaret, H.L.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Wong, R.S.M. ABO blood group and susceptibility to severe acute respiratory syndrome. JAMA 2005, 293, 1450–1451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Fan, H.; Lu, D.; Huang, F.; Xi, M.; Li, Z.; Tang, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, N.; Liu, Z.; et al. Association between ABO blood groups and clinical outcome of coronavirus disease 2019: Evidence from two cohorts. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Li, P.; Yu, Q. Relationship between ABO blood group distribution and clinical characteristics in patients with COVID-19. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 509, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Li, D.-J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, F. Association Between ABO Blood Group System and COVID-19 Susceptibility in Wuhan. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzik, S.; Eliason, K.; Morris, E.B.; Kaufman, R.M.; North, C.M. COVID-19 and ABO blood groups. Transfusion 2020, 60, 1883–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaf, R.K.; Al-Samkari, H.; Brenner, S.K.; Gupta, S.; Leaf, D. ABO phenotype and death in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudin, L.; Janvier, F.; Bylicki, O.; Dutasta, F. ABO blood groups are not associated with risk of acquiring the SARS-CoV-2 infection in young adults. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2841–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latz, C.A.; Decarlo, C.; Boitano, L.; Png, C.Y.M.; Patell, R.; Conrad, M.F.; Eagleton, M.; Dua, A. Blood type and outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenti, L.; Villa, S.; Baselli, G.; Temporiti, R.; Bandera, A.; Scudeller, L.; Prati, D. Association of ABO blood group and secretor phenotype with severe COVID-19. Transfusion 2020, 60, 3067–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaylacı, S.; Dheir, H.; Işsever, K.; Genc, A.B.; Şenocak, D.; Kocayigit, H.; Guclu, E.; Suner, K.; Ekerbicer, H.; Koroglu, M. The effect of abo and rh blood group antigens on admission to intensive care unit and mortality in patients with COVID-19 infection. Rev. Assoc. Médica Bras. 2020, 66, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, E.; Fontán-Vela, M.; Valencia, J.; Fernandez-Jimenez, I.; Álvaro-Alonso, E.A.; Izquierdo-García, E.; Cebas, A.L.; Ruiz-Elvira, E.G.; Troya, J.; Tebar-Martinez, A.J.; et al. Characteristics, complications and outcomes among 1549 patients hospitalised with COVID-19 in a secondary hospital in Madrid, Spain: A retrospective case series study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e042398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-Diaz, E.; Llopis, J.; Parra, R.; Roig, I.; Ferrer, G.; Grifols, J.; Millan, A.; Ene, G.; Ramiro, L.; Maglio, L.; et al. Relationship between the ABO blood group and COVID-19 susceptibility, severity and mortality in two cohorts of patients. Blood Transfus. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, M.; Glingani, C.; Del Fante, C.; Capuzzo, M.; Di Stasi, V.; Rastrelli, G.; Vignozzi, L.; De Donno, G.; Perotti, C. The protective effect of O blood type against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Vox Sang. 2020, 116, 249–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.G.; Schull, M.J.; Vermeulen, M.J.; Park, A.L. Association Between ABO and Rh Blood Groups and SARS-CoV-2 Infection or Severe COVID-19 Illness. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmaz, I.; Araç, S. ABO blood groups in COVID-19 patients; Cross-sectional study. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2020, 75, e13927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendu, J.L.; Breiman, A.; Rocher, J.; Dion, M.; Ruvoën-Clouet, N. ABO Blood Types and COVID-19: Spurious, Anecdotal, or Truly Important Relationships? A Reasoned Review of Available Data. Viruses 2021, 13, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patients No-ICU (n = 1034) | Patients ICU (n = 365) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| Male | 547 (52.9) | 260 (71.2) |
| Female | 487 (47.1) | 105 (28.8) |
| Age (years) | 81 (15) | 66 (15) |
| ABO Blood Group, n (%) | ||
| A | 478 (46.2) | 170 (46.6) |
| B | 75 (7.3) | 39 (10.7) |
| AB | 36 (3.5) | 14 (3.8) |
| O | 445 (43) | 142 (38.9) |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | ||
| Hypertension | 699 (67.6) | 186 (51) |
| Diabetes | 313 (30.3) | 91 (24.9) |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) | 331 (32) | 114 (34.2) |
| Cardiovascular disease | 404 (39.1) | 58 (15.9) |
| Obstructive lung disease | 199 (19.2) | 64 (17.5) |
| Malignancy | 208 (20.1) | 50 (13.7) |
| Laboratory, median [IQR] | ||
| Lymphocytes (×106/L) | 0.80 [0.78] | 0.47 [0.40] |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 101.7 [148.9] | 255.40 [216.6] |
| D-dimer (ng/mL) | 1392.5 [2238] | 9039 [21,010] |
| Thrombotic complications, n (%) | 32 (3.1) | 77 (21.1) |
| Mortality, n (%) | ||
| Exitus | 363 (35.1) | 157 (43) |
| ABO Blood Group | Patients No ICU n (%) | General Population n(%) | OR (IC 95%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | 445 (43.0) | 87,605 (48.0) | 1 † |
| A | 478 (46.2) | 78,402 (43.0) | 1.20 (1.05–1.36) * |
| B | 75 (7.3) | 11,725 (6.4) | 1.26 (0.99–1.60) |
| AB | 36 (3.5) | 4652 (2.6) | 1.52 (1.08–2.13) * |
| Total | 1034 (100.0) | 182,384 (100) |
| ABO Blood Group | Patients ICU n (%) | General Population n (%) | OR (IC 95%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | 142 (38.9) | 87,605 (48.0) | 1 † |
| A | 170 (46.6) | 78,402 (43.0) | 1.33 (1.07–1.67) * |
| B | 39 (10.7) | 11,725 (6.4) | 2.05 (1.44–2.92) * |
| AB | 14 (3.8) | 4652 (2.6) | 1.85 (1.07–3.20) * |
| Totals | 365 (100.0) | 182,384 (100) |
| ABO Blood Group | Patients ICU n (%) | Patients No ICU n (%) | OR (IC 95%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | 142 (38.9) | 445 (43.0) | 1 † |
| A | 170 (46.6) | 478 (46.2) | 1.08 (0.89–1.32) |
| B | 39 (10.7) | 75 (7.3) | 1.41 (1.05–1.89) * |
| AB | 14 (3.8) | 36 (3.5) | 1.16 (0.73–1.85) |
| Totals | 365 (100.0) | 1034 (100.0) |
| ABO Blood Group | Admitted to ICU | Adjusted OR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 170 (46.6) | ----- | ----- | 0.018 |
| B | 39 (10.7) | 1.27 | [0.55–2.90] | 0.577 |
| AB | 14 (3.8) | 0.60 | [0.17–2.08] | 0.416 |
| O | 142 (38.9) | 0.52 | [0.33–0.81] | 0.004 * |
| Age | 0.91 | [0.89–0.93] | <0.001 ** | |
| Sex | 0.52 | [0.33–0.82] | 0.005 * | |
| Hypertension | 0.74 | [0.46–1.18] | 0.204 | |
| Diabetes | 1.17 | [0.73–1.85] | 0.517 | |
| Obesity | 1.57 | [0.97–2.53] | 0.065 | |
| Cardiovascular disease | 0.38 | [0.23–0.64] | <0.001 ** | |
| Obstructive lung disease | 1.06 | [0.63–1.78] | 0.825 | |
| Malignancy | 0.88 | [0.68–1.12] | 0.298 | |
| Lymphocytes | 0.33 | [0.22–0.50] | <0.001 ** | |
| C-reactive protein | 1.00 | [1.00–1.00] | <0.001 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jericó, C.; Zalba-Marcos, S.; Quintana-Díaz, M.; López-Villar, O.; Santolalla-Arnedo, I.; Abad-Motos, A.; Laso-Morales, M.J.; Sancho, E.; Subirà, M.; Bassas, E.; et al. Relationship between ABO Blood Group Distribution and COVID-19 Infection in Patients Admitted to the ICU: A Multicenter Observational Spanish Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113042
Jericó C, Zalba-Marcos S, Quintana-Díaz M, López-Villar O, Santolalla-Arnedo I, Abad-Motos A, Laso-Morales MJ, Sancho E, Subirà M, Bassas E, et al. Relationship between ABO Blood Group Distribution and COVID-19 Infection in Patients Admitted to the ICU: A Multicenter Observational Spanish Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(11):3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113042
Chicago/Turabian StyleJericó, Carlos, Saioa Zalba-Marcos, Manuel Quintana-Díaz, Olga López-Villar, Iván Santolalla-Arnedo, Ane Abad-Motos, María Jesús Laso-Morales, Esther Sancho, Maricel Subirà, Eva Bassas, and et al. 2022. "Relationship between ABO Blood Group Distribution and COVID-19 Infection in Patients Admitted to the ICU: A Multicenter Observational Spanish Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 11: 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113042
APA StyleJericó, C., Zalba-Marcos, S., Quintana-Díaz, M., López-Villar, O., Santolalla-Arnedo, I., Abad-Motos, A., Laso-Morales, M. J., Sancho, E., Subirà, M., Bassas, E., Ruiz de Viñaspre-Hernández, R., Juárez-Vela, R., & García-Erce, J. A. (2022). Relationship between ABO Blood Group Distribution and COVID-19 Infection in Patients Admitted to the ICU: A Multicenter Observational Spanish Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(11), 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113042








