The Effect of Low-Dose Dexmedetomidine on Pain and Inflammation in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Anesthesia and Surgery
2.2. Blood Sampling and Laboratory Data Collection
2.3. Postoperative Management
2.4. Primary Endpoints and Secondary Endpoints
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics and Operative Details
3.2. Perioperative Profile (Postoperative Pain and Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting)
3.3. Inflammatory Response
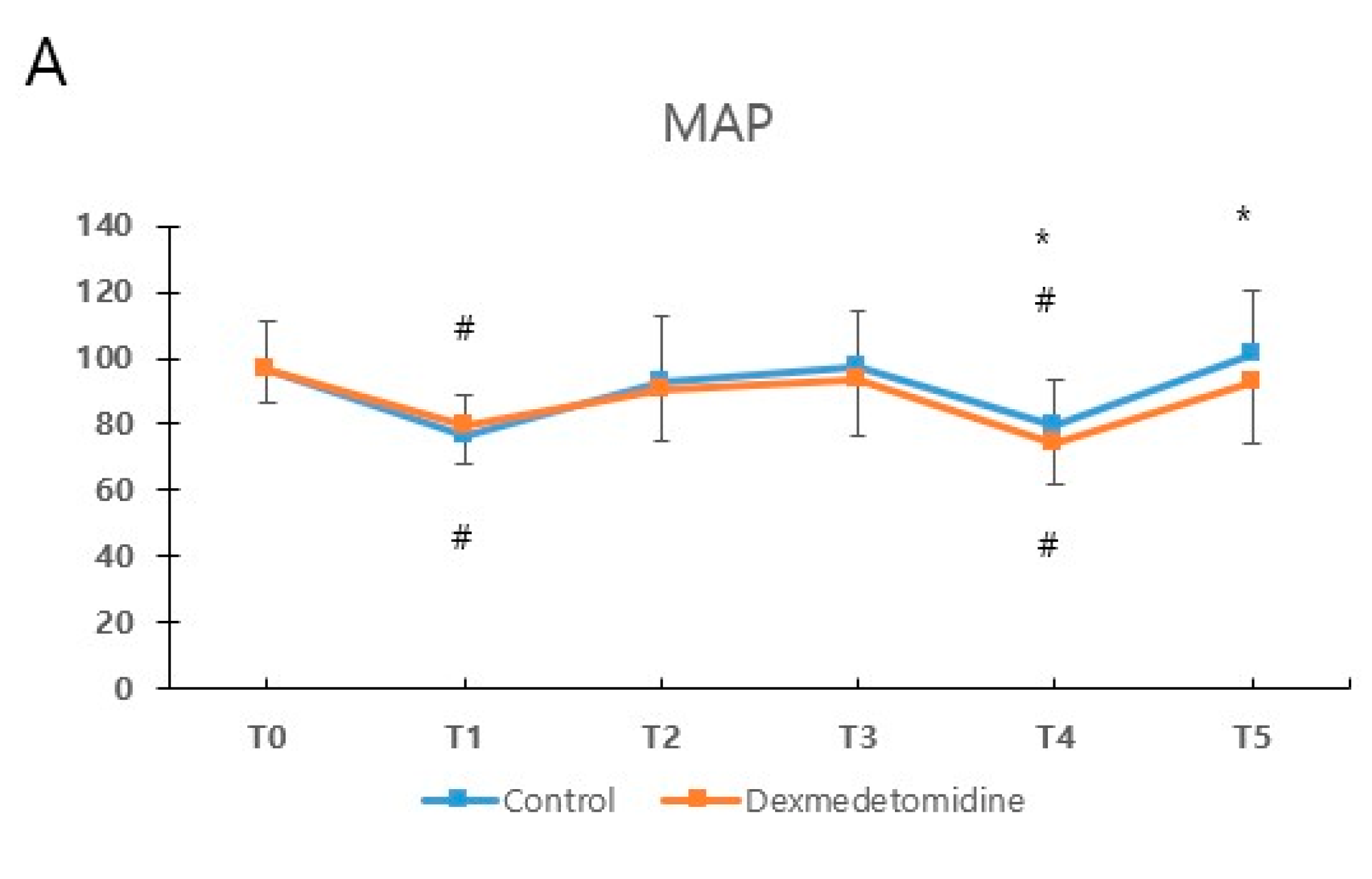
3.4. Vital Signs during Anesthesia and Surgery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| CRP | c-related peptide |
| IL | interleukin |
| IV | intravenous |
| PACU | post-anesthesia care unit |
| PCA | patient-controlled analgesia |
| PONV | postoperative nausea and vomiting |
| VAS | visual analog scale |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Aarts, J.W.; Nieboer, T.E.; Johnson, N.; Tavender, E.; Garry, R.; Mol, B.W.; Kluivers, K.B. Surgical approach to hysterectomy for benign gynaecological disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, Cd003677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.B.; Bevil, K.; Giles, D.L. Preemptive Analgesia in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2018, 26, 198–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartley, E.J.; Fillingim, R.B. Sex differences in pain: A brief review of clinical and experimental findings. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandsborg, B.; Nikolajsen, L.; Hansen, C.T.; Kehlet, H.; Jensen, T.S. Risk Factors for Chronic Pain after HysterectomyA Nationwide Questionnaire and Database Study. Anesthesiol. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2007, 106, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Bhana, N.; Goa, K.L.; McClellan, K.J. Dexmedetomidine. Drugs 2000, 59, 263–268; discussion 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.P.; Valinetti, E.A.; Bandeira, D.; Bertacchi, M.F.; Simoes, C.M.; Auler, J.O., Jr. Effects of preanesthetic administration of midazolam, clonidine, or dexmedetomidine on postoperative pain and anxiety in children. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2007, 17, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvan, E.G.; Oc, B.; Uzun, S.; Karabulut, E.; Coskun, F.; Aypar, U. Dexmedetomidine and postoperative shivering in patients undergoing elective abdominal hysterectomy. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2008, 25, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, Y.; Tian, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, A.; Gao, C. Anti-inflammatory effects of perioperative dexmedetomidine administered as an adjunct to general anesthesia: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Yang, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y. Comparison of the pro-postoperative analgesia of intraoperative dexmedetomidine with and without loading dose following general anesthesia: A prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Medicine 2017, 96, e6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Kim, B.I.; Byun, S.H.; Kim, E.; Sung, S.Y.; Jung, J.Y. Cardiac arrest in a patient with anterior fascicular block after administration of dexmedetomidine with spinal anesthesia: A case report. Medicine 2016, 95, e5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielka, K.; Kuchyn, I.; Babych, V.; Martycshenko, K.; Inozemtsev, O. Dexmedetomidine infusion as an analgesic adjuvant during laparoscopic small es, Cyrillicholecystectomy: A randomized controlled study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.N.; Kong, M.; Qi, B.; Ge, D.J. Comparison of the morphine-sparing effect of intraoperative dexmedetomidine with and without loading dose following general anesthesia in multiple-fracture patients: A prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Medicine 2016, 95, e4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, J.W.; Sebel, P.S.; Fisher, D.M. Development and Clinical Application of Electroencephalographic Bispectrum Monitoring. Anesthesiology 2000, 93, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Park, C.; Kim, J.; Ki, Y.; Cha, S.H.; Kim, J.Y. Effect of Low-pressure Pulmonary Recruitment Maneuver on Postlaparoscopic Shoulder Pain: Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2020, 27, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzer, O.; Moitra, V.; Sladen, R.N. Pharmacology of sedative-analgesic agents: Dexmedetomidine, remifentanil, ketamine, volatile anesthetics, and the role of peripheral mu antagonists. Crit. Care Clin. 2009, 25, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.N.; Purdon, P.L.; Van Dort, C.J. General anesthesia and altered states of arousal: A systems neuroscience analysis. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 601–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, L.E.; Lu, J.; Guo, T.; Saper, C.B.; Franks, N.P.; Maze, M. The α2-Adrenoceptor Agonist Dexmedetomidine Converges on an Endogenous Sleep-promoting Pathway to Exert Its Sedative Effects. Anesthesiology 2003, 98, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, N.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, F.; Ding, C. Effect of Intravenous Dexmedetomidine During General Anesthesia on Acute Postoperative Pain in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. J. Pain. 2018, 34, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, T.J.; Hall, J.E.; Barney, J.A.; Uhrich, T.D.; Colinco, M.D. The effects of increasing plasma concentrations of dexmedetomidine in humans. Anesthesiology 2000, 93, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.J.; Qi, B.; Tang, G.; Li, J.Y. Intraoperative Dexmedetomidine Promotes Postoperative Analgesia and Recovery in Patients after Abdominal Hysterectomy: A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.S.; Tsui, B.C. Impact of anesthesia for cancer surgery: Continuing professional development. Can. J. Anaesth. 2013, 60, 1248–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruickshank, A.M.; Fraser, W.D.; Burns, H.J.; Van Damme, J.; Shenkin, A. Response of serum interleukin-6 in patients undergoing elective surgery of varying severity. Clin. Sci. 1990, 79, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, L.; Jing, S.; Wang, X. Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Perioperative Stress Response and Immune Function in Patients With Tumors. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820977542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povoa, P. C-reactive protein: A valuable marker of sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2002, 28, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Honda, I.; Suzuki, H.; Murakami, M.; Matsukawa, S.; Hashimoto, Y. Interleukin-10 production during and after upper abdominal surgery. J. Clin. Anesth. 1998, 10, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, A.; Haile, M.; Kline, R.; Didehvar, S.; Babu, R.; Martiniuk, F.; Urban, M. The effect of intraoperative infusion of dexmedetomidine on the quality of recovery after major spinal surgery. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2013, 25, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulow, N.M.; Colpo, E.; Pereira, R.P.; Correa, E.F.; Waczuk, E.P.; Duarte, M.F.; Rocha, J.B. Dexmedetomidine decreases the inflammatory response to myocardial surgery under mini-cardiopulmonary bypass. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2016, 49, e4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Lu, Y.F.; Wang, M.L.; Chen, J.S.; Hsu, Y.C.; Yang, F.S.; Cheng, Y.J. Effects of Dexmedetomidine Infusion on Inflammatory Responses and Injury of Lung Tidal Volume Changes during One-Lung Ventilation in Thoracoscopic Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 2575910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, J.B.; Maze, M.; Haack, C.; Azarnoff, D.L.; Vuorilehto, L.; Shafer, S.L. Computer-controlled infusion of intravenous dexmedetomidine hydrochloride in adult human volunteers. Anesthesiology 1993, 78, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, A.D.; Pennick, V.; Bombardier, C.; van Tulder, M. 2009 updated method guidelines for systematic reviews in the Cochrane Back Review Group. Spine 2009, 34, 1929–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hu, H.M.; Edelman, A.L.; Brummett, C.M.; Englesbe, M.J.; Waljee, J.F.; Smerage, J.B.; Griggs, J.J.; Nathan, H.; Jeruss, J.S.; et al. New Persistent Opioid Use among Patients with Cancer after Curative-Intent Surgery. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 4042–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henzi, I.; Walder, B.; Tramèr, M.R. Dexamethasone for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: A quantitative systematic review. Anesth. Analg. 2000, 90, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhen, T.; Cidlowski, J.A. Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids--new mechanisms for old drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, T.; Paech, M.; Law, D.; Muchatuta, N.A.; French, M.; Ho, K.M. Intraoperative dexamethasone alters immune cell populations in patients undergoing elective laparoscopic gynaecological surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Control (n = 41) | Dexmedetomidine (n = 47) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 46.6 (5.1) | 45.3 (4.9) | 0.23 |
| Height | 159.3 (4.7) | 159.3 (4.4) | 0.99 |
| Weight | 60.4 (8.9) | 63.0 (10.3) | 0.21 |
| BMI, Kg/m2 | 23.8 (3.4) | 24.8 (3.9) | 0.19 |
| ASA physical status I/II | 18/23 | 26/21 | 0.29 |
| Cesarean delivery history | 21 (51%) | 17 (36%) | 0.16 |
| Abdominal surgery history | 14 (34%) | 10 (21%) | 0.18 |
| Intraoperative fluid, mL | 1320.7 (527.9) | 1253.2 (479.5) | 0.53 |
| Estimated blood loss, mL | 300.0 [100.0–1300.0] | 200.0 [50.0–1700.0] | 0.60 |
| Transfusion | 4 (10%) | 3 (6%) | 0.70 |
| Insertion of drain | 17 (42%) | 15 (32%) | 0.35 |
| Duration of operation (min) | 108.5 (53.5) | 107.3 (54.2) | 0.92 |
| Duration of anesthesia (min) | 141.3 (55.4) | 141.7 (55.8) | 0.98 |
| Duration of emergence (min) | 5.8 (1.9) | 6.4 (2.2) | 0.16 |
| Control (n = 41) | Dexmedetomidine (n = 47) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pain | |||
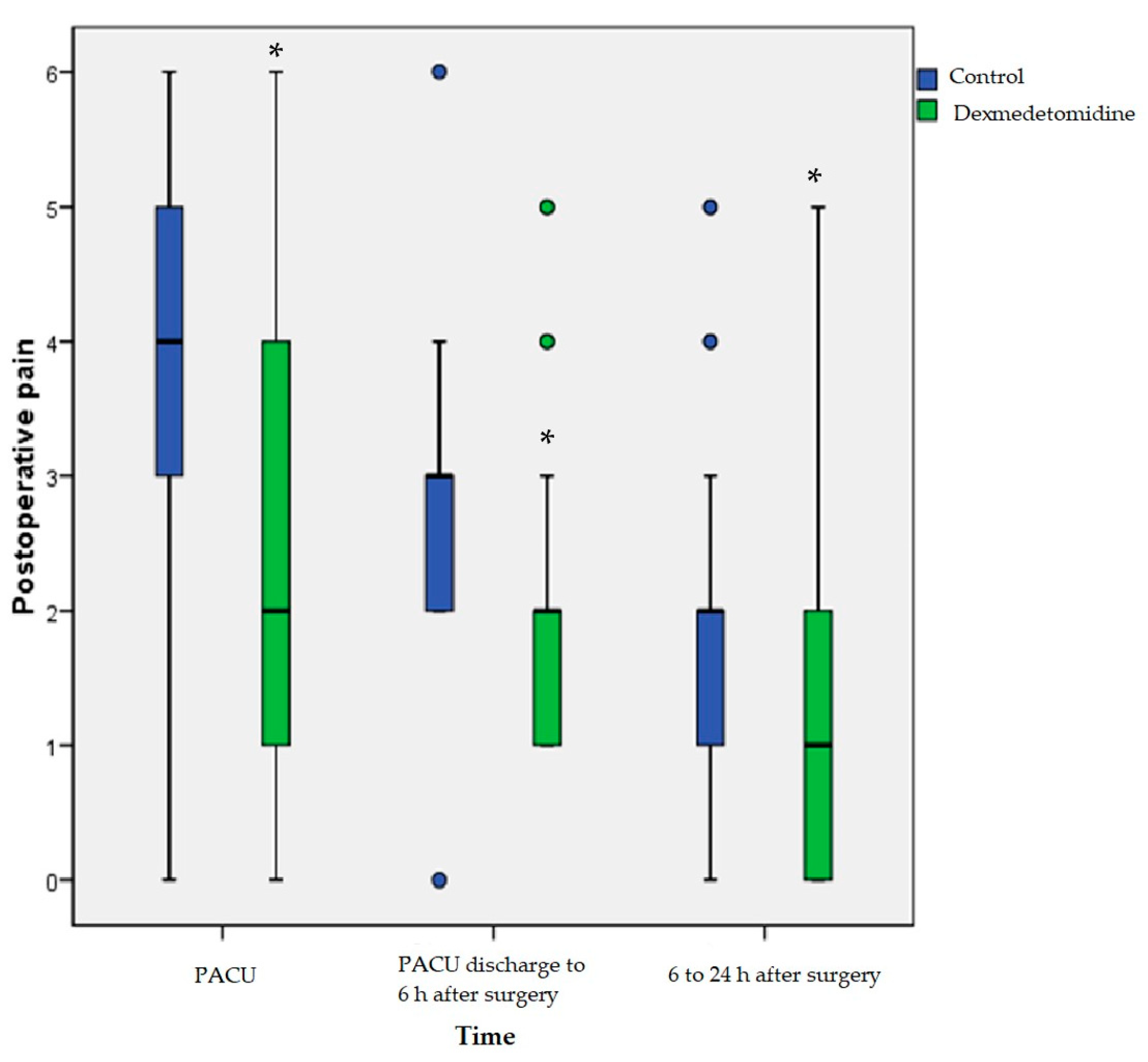
| PACU | 4 [3–5] | 2 [1–4] | <0.001 |
| PACU discharge to 6 h after surgery | 3 [2–3] | 2 [1–2] | <0.001 |
| 6 to 24 h after surgery | 2 [1–2] | 1 [1–2] | <0.01 |
| Rescue analgesic | |||
| PACU Fentanyl (ug) | 29.3 (29.5) | 16.0 (25.8) | 0.03 |
| PACU discharge to 6 h after surgery | 3 (7%) | 4 (9%) | 1.00 |
| 6 to 24 h after surgery | 5 (12%) | 8 (17%) | 0.52 |
| PONV | |||
| PACU | 3 (7%) | 2 (4%) | 0.66 |
| PACU discharge to 6 h after surgery | 13 (32%) | 6 (13%) | 0.03 |
| 6 to 24 h after surgery | 12 (29%) | 5 (11%) | 0.03 |
| Antiemetic | |||
| PACU | 3 (7%) | 2 (4%) | 0.66 |
| PACU discharge to 6 h after surgery | 6 (15%) | 4 (9%) | 0.37 |
| 6 to 24 h after surgery | 1 (2%) | 3 (6%) | 0.62 |
| Side effect | |||
| PACU | <0.01 | ||
| Hypotension | 0 (0%) | 7 (15%) | 0.01 |
| Bradycardia | 0 (0%) | 4 (9%) | 0.12 |
| Shivering | 2 (5%) | 0 (0%) | 0.21 |
| Hypertension | 1 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 0.47 |
| PACU discharge to 6 h after surgery | 0.47 | ||
| Dizziness | 1 (2%) | 0 (0%) | |
| 6 to 24 h after surgery | 0.47 | ||
| Dizziness | 1 (2%) | 0 (0%) | |
| RSS score at PACU | |||
| PACU arrival 2/3/4 | 10/29/2 | 20/24/3 | 0.16 |
| 30 min after PACU arrival 2/3 | 39/2 | 44/3 | 1.00 |
| Duration of PACU stay (minutes) | 54.1 (19.1) | 54.3 (15.4) | 0.66 |
| Control (n = 41) | Dexmedetomidine (n = 47) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | |||
| After induction | 0.50 [0.43–0.72] | 0.57 [0.44–0.79] | 0.35 |
| End of surgery | 0.42 [0.30–0.52] | 0.45 [0.35–0.55] | 0.38 |
| POD 1 | 0.44 [0.35–0.59] | 0.46 [0.28–0.62] | 0.97 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | |||
| After induction | 0.45 [0.00–1.68] | 0.33 [0.00–1.51] | 0.92 |
| End of surgery | 4.43 [2.14–19.41] | 7.98 [3.19–11.35] | 0.75 |
| POD 1 | 8.53 [4.07–16.43] | 7.07 [4.15–16.67] | 0.77 |
| IL-10 (pg/mL) | |||
| After induction | 2.14 [0.58–4.23] | 2.50 [0.00–4.85] | 0.84 |
| End of surgery | 16.34 [7.45–34.21] | 16.14 [5.79–32.65] | 0.62 |
| POD 1 | 2.98 [1.07–5.44] | 2.37 [0.44–5.22] | 0.65 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | |||
| After induction | 0.05 [0.03–0.10] | 0.05 [0.03–0.11] | 0.76 |
| POD 1 | 0.68 [0.42–1.33] | 0.52 [0.28–1.06] | 0.38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Hwang, H.W.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, C.; Kim, J.Y. The Effect of Low-Dose Dexmedetomidine on Pain and Inflammation in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Hysterectomy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102802
Lee J, Hwang HW, Jeong J-Y, Kim YM, Park C, Kim JY. The Effect of Low-Dose Dexmedetomidine on Pain and Inflammation in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Hysterectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(10):2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102802
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jiyoung, He Won Hwang, Ju-Yeon Jeong, Yong Min Kim, Chunghyun Park, and Jong Yeop Kim. 2022. "The Effect of Low-Dose Dexmedetomidine on Pain and Inflammation in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Hysterectomy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 10: 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102802
APA StyleLee, J., Hwang, H. W., Jeong, J.-Y., Kim, Y. M., Park, C., & Kim, J. Y. (2022). The Effect of Low-Dose Dexmedetomidine on Pain and Inflammation in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Hysterectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(10), 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102802






