Differences in Postural Balance, Pain Sensitivity and Depression between Individuals with Acute and Chronic Back Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Assessments
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bank, P.J.; Peper, C.L.; Marinus, J.; Beek, P.J.; van Hilten, J.J. Motor dysfunction of complex regional pain syndrome is related to impaired central processing of proprioceptive. J. Pain 2013, 14, 1460–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, L.H.; Sauer, J.F.; Yuan, S.L.; Sousa, A.; Mango, P.C.; Marques, A.P. Postural control and balance self-efficacy in women with fibromyalgia. Are there differences? Eur. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 51, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Stanton, T.R.; Leake, H.B.; Chalmers, K.J.; Moseley, G.L. Evidence of impaired proprioception in chronic idiopathic neck pain: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Phys. Ther. 2016, 96, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.; Bassi, A.R.; Brandao, M.P.; Silva, A.G. Do patients with chronic neck pain have distorted body image and tactile dysfunction? Eur. J. Phys. 2017, 19, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, V.; Kankaanpää, M.; Luukkonen, M.; Kansanen, M.; Hänninen, O.; Airaksinen, O.; Taimela, S. Lumbar paraspinal muscle function, perception of lumbar position, and postural control in disc herniation-related back pain. Spine 2003, 28, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigkanos, C.; Gaskell, L.; Smirniotou, A.; Tsigkanos, G. Static and dynamic balance deficiencies in chronic low back pain. J. Back Musculoskelet. 2016, 29, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wand, B.M.; O’Connell, N.E. Chronic non-specific low back pain–subgroups or a single mechanism? BMC Musculoskel. Dis. 2008, 25, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ruhe, A.; Fejer, R.; Walker, B. Center of pressure excursion as a measure of balance performance in patients with non-specific low back pain compared to healthy controls: A systematic review of the literature. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, K.; Brumagne, S.; Dankaerts, W.; Kiers, H.; Janssens, L. Decreased variability in postural control strategies in young people with non-specific low back pain is associated with altered proprioceptive reweighting. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, N.W.; Brauer, S.G.; Hodges, P.W. Hip strategy for balance control in quiet standing is reduced in people with low back pain. Spine 2004, 29, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipko, T.; Kuczynski, M. Intensity of chronic pain modifies postural control in low back patients. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massé-Alarie, H.; Flamand, V.H.; Moffet, H.; Schneider, C. Corticomotor control of deep abdominal muscles in chronic low back pain and anticipatory postural adjustments. Exp. Brain Res. 2012, 218, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keogh, E.; Book, K.; Thomas, J.; Giddins, G.; Eccleston, C. Predicting pain and disability in patients with hand fractures: Comparing pain anxiety, anxiety sensitivity and pain catastrophizing. Eur. J. Pain. 2010, 14, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, M.A.; Gallinati, J.L.; Clark, M.E. Conceptualizing and treating comorbid chronic pain and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Pain Res. Treat. 2013, 2013, 174728. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.Y. A Brain Signature to Differentiate Acute and Chronic Pain in Rats. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pastor, C.; Álvarez-Solís, G.A. The Romberg test. Rev. Mex. Neuroci. 2014, 15, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gea, J.; Muñoz, M.A.; Costa, I.; Ciria, L.F.; Miranda, J.G.; Montoya, P. Viewing pain and happy faces elicited similar changes in postural body sway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104381. [Google Scholar]
- Holley, A.L.; Wilson, A.C.; Palermo, T.M. Predictors of the transition from acute to persistent musculoskeletal pain in children and adolescents: A prospective study. Pain 2017, 18, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berubé, M.; Choinière, M.; Laflamme, Y.G.; Gélinas, C. Acute to chronic pain transition in extremity trauma: A narrative review for future preventive interventions. Int. J. Orthop Trauma Nurs. 2016, 23, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Vallabhajosula, S.; Zahodne, L.B.; Bowers, D.; Okun, M.S.; Fernández, H.H.; Hass, C.J. Correlations of apathy and depression with postural instability in Parkinson disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 338, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, M.M.; Lin, S.I.; Close, J.C.; Lord, S.R. Depressive symptoms in addition to visual impairment, reduced strength and poor balance predict falls in older Taiwanese people. Age Ageing 2012, 41, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Deschamps, T.; Thomas-Ollivier, V.; Sauvaget, A.; Bulteau, S.; Fortes-Bourbousson, M.; Vachon, H. Balance characteristics in patients with major depression after a two-month walking exercise program. Gait Posture 2015, 42, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louw, Q.A.; Morris, L.D.; Grimmer-Somers, K. The prevalence of low back pain in Africa: A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2007, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobscha, S.K.; Corson, K.; Perrin, N.A.; Hanson, G.C.; Leibowitz, R.Q.; Doak, M.N.; Dickinson, K.C.; Sullivan, M.D.; Gerrity, M.S. Collaborative care for chronic pain in primary care: A cluster randomized trial. JAMA 2009, 301, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sá, S.; Silva, A.G. Repositioning error, pressure pain threshold, catastrophizing and anxiety in adolescents with chronic idiopathic neck pain. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2017, 30, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backonja, M.M.; Attal, N.; Baron, R.; Bouhassira, D.; Drangholt, M.; Dyck, P.J.; Edwards, R.R.; Freeman, R.; Gracely, R.; Haanpaa, M.H.; et al. Value of quantitative sensory testing in neurological and pain disorders: NeuPSIG consensus. Pain 2013, 154, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, N.; Credicio, B.C.; Nogueria, L.P.; Salles, R.M.; Souza, L.G.; Vale, M.; Cavalcanti, M.; Bomfim, J.P.; Vivas, J.G. Free instrument for measurements of motion. Rev. Bras. Ensino Fís. 2013, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Puta, C.; Schulz, B.; Schoeler, S.; Magerl, W.; Gabriel, B.; Gabriel, H.H.; Miltner, W.H.; Weiss, T. Somatosensory Abnormalities for Painful and Innocuous Stimuli at the Back and at a Site Distinct from the Region of Pain in Chronic Back Pain Patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, W.W.; Wen, R.Y.; Naghdechi, L.; Vanle, B.; Dang, J.; Knosp, M.; Dascal, J.; Marcia, L.; Gohar, Y.; Eskander, L.; et al. Pain and Depression: A Systematic Review. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2018, 26, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, H.; Sánchez, J.A.; Estevez, M.M.; Molina, T.; Cortes, J.L.; Alfaro, A. Depression and Pain: Use of Antidepressants. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 384–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, H. Analgesic Mechanisms of Antidepressants for Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartley, E.J.; Fillingim, R.B. Sex differences in pain: A brief review of clinical and experimental findings. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dance, A. Why the sexes don’t feel pain the same way. Nature 2019, 567, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salk, R.H.; Hyde, J.S.; Abramson, L.Y. Gender differences in depression in representative national samples: Meta-analyses of diagnoses and symptoms. Psychol. Bull. 2017, 143, 783–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
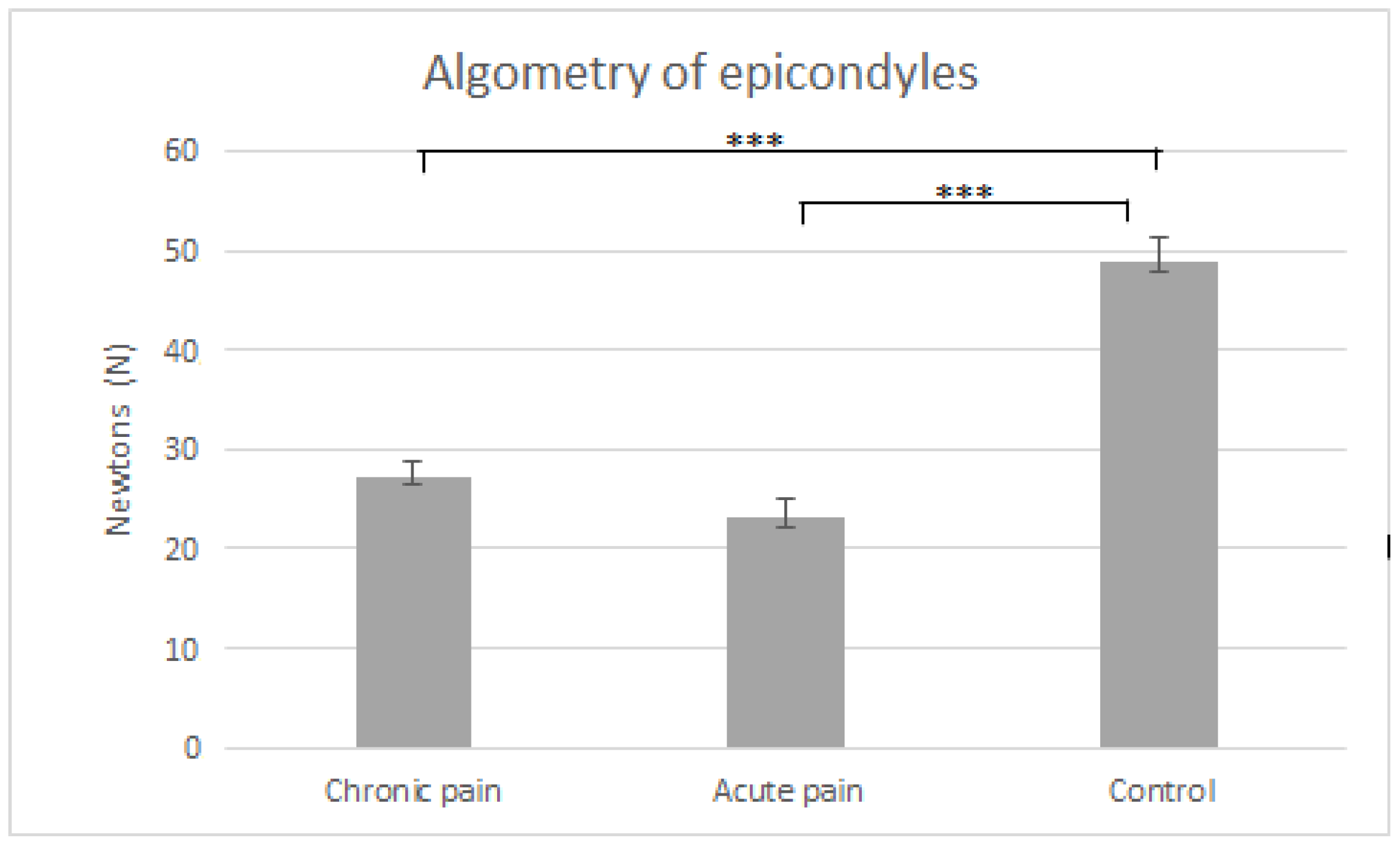
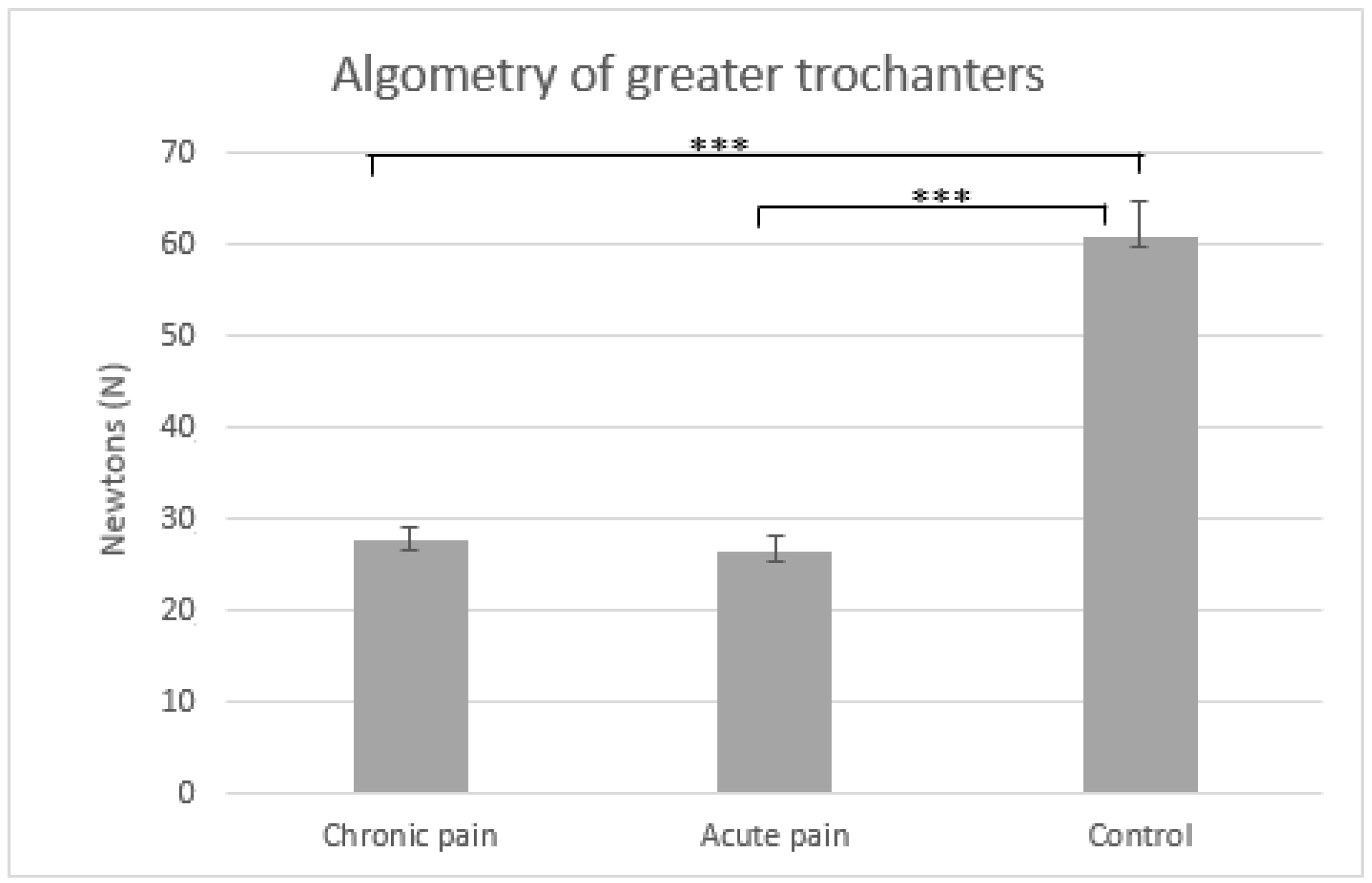

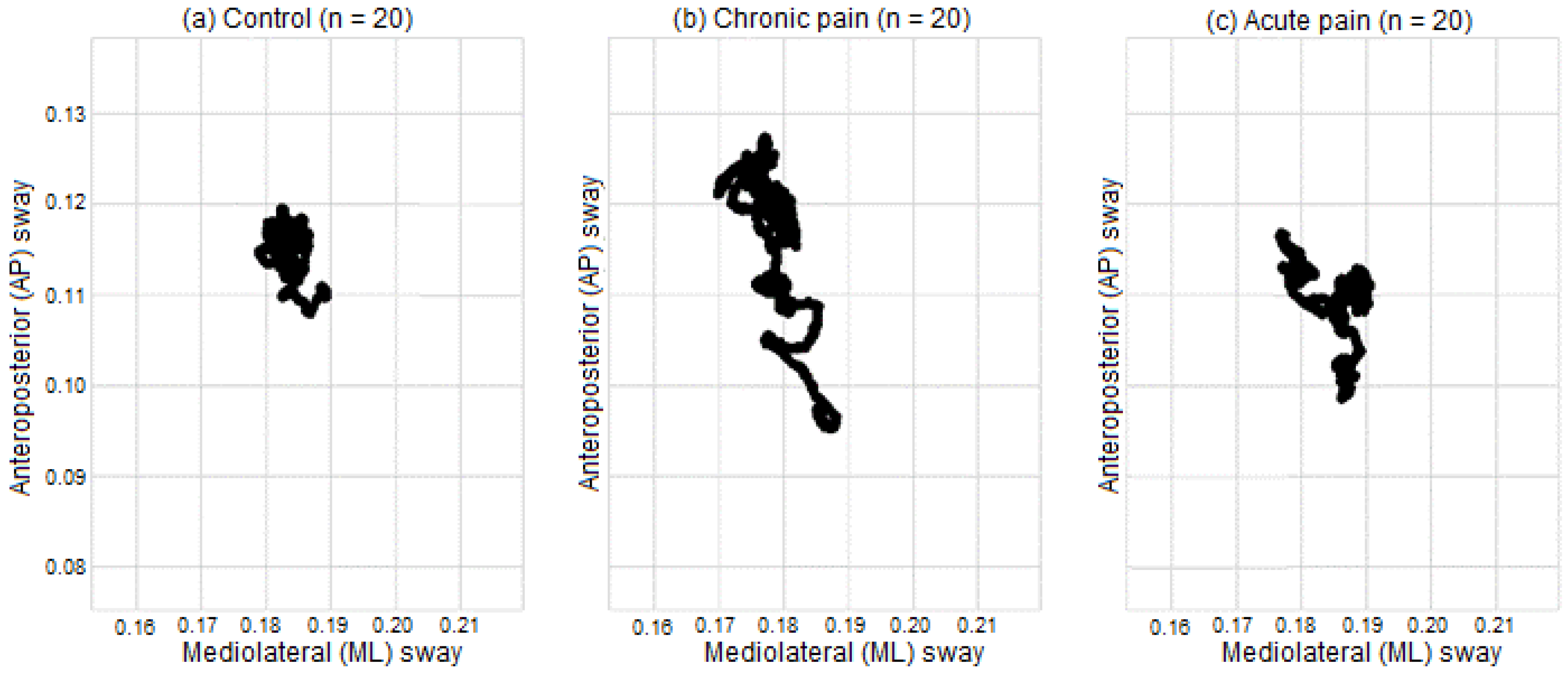
| Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic Pain (n = 20) | Acute Pain (n = 20) | Control (n = 20) | ||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Significance Level | |
| Age (years) | 40.8 (1.44) | 37.9 (1.32) | 40.75 (1.63) | 0.28 |
| Pain duration (months) | 29.1 (2.54) | 1.07 (0.07) | 0 | p < 0.001 |
| BMI | 21.97 (1.54) | 19.81 (0.75) | 21.11 (0.81) | 0.38 |
| Height (centimeters) | 167.65 (2.01) | 170.5 (2.11) | 171.45 (1.71) | 0.36 |
| Weight (kilograms) | 61.2 (3.97) | 58.1 (2.56) | 60.25 (1.84) | 0.75 |
| Gender (women) | n = 10 | n = 9 | n = 10 | 0.98 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mingorance, J.A.; Montoya, P.; Vivas Miranda, J.G.; Riquelme, I. Differences in Postural Balance, Pain Sensitivity and Depression between Individuals with Acute and Chronic Back Pain. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102700
Mingorance JA, Montoya P, Vivas Miranda JG, Riquelme I. Differences in Postural Balance, Pain Sensitivity and Depression between Individuals with Acute and Chronic Back Pain. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(10):2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102700
Chicago/Turabian StyleMingorance, José Antonio, Pedro Montoya, José García Vivas Miranda, and Inmaculada Riquelme. 2022. "Differences in Postural Balance, Pain Sensitivity and Depression between Individuals with Acute and Chronic Back Pain" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 10: 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102700
APA StyleMingorance, J. A., Montoya, P., Vivas Miranda, J. G., & Riquelme, I. (2022). Differences in Postural Balance, Pain Sensitivity and Depression between Individuals with Acute and Chronic Back Pain. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(10), 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102700







