The Offprint of an Abnormal Pre-Parotidectomy Electrodiagnostic Finding in a Normally Functioning Facial Nerve: Correlation with Intraoperative Findings, Histology and Postoperative Facial Nerve Function †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vander Poorten, V.; Bradley, P.J.; Takes, R.P.; Rinaldo, A.; Woolgar, J.A.; Ferlito, A. Diagnosis and management of parotid carcinoma with a special focus on recent advances in molecular biology. Head Neck 2012, 34, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, D.; Overgaard, J.; Sogaard, H.; Elbrond, O.; Overgaard, M. Malignant parotid tumors in 110 consecutive patients: Treatment results and prognosis. Laryngoscope 1992, 102, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Klussmann, J.P.; Schroeder, U.; Quante, G.; Jungehuelsing, M.; Stennert, E. Primary Parotid Malignoma Surgery in Patients with Normal Preoperative Facial Nerve Function: Outcome and Long-Term Postoperative Facial Nerve Function. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiertel-Krawczuk, A.; Huber, J.; Wojtysiak, M.; Golusiński, W.; Pieńkowski, P.; Golusinski, P. Correlations between the clinical, histological and neurophysiological examinations in patients before and after parotid gland tumor surgery: Verification of facial nerve transmission. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2015, 272, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimoni, C.; Lombardi, L.; Gastaldo, E.; Stacchini, M.; Pastore, A. Preoperative and Postoperative Electroneurographic Facial Nerve Monitoring in Patients with Parotid Tumors. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003, 129, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantsopoulos, K.; Psychogios, G.; Agaimy, A.; Künzel, J.; Zenk, J.; Iro, H.; Bohr, C. Inflamed benign tumors of the parotid gland: Diagnostic pitfalls from a potentially misleading entity. Head Neck 2013, 37, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Volk, G.F.; Olsen, K.D.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Silver, C.E.; Zafereo, M.E.; Rinaldo, A.; Randolph, G.W.; Simo, R.; Shaha, A.R.; et al. Facial nerve electrodiagnostics for patients with facial palsy: A clinical practice guideline. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 277, 1855–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendet, E.; Talmi, Y.P.; Kronenberg, J. Preoperative electroneurography (ENoG) in parotid surgery: Assessment of facial nerve outcome and involvement by tumor—A preliminary study. Head Neck 1998, 20, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AJCC Cancer Staging Manual; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2017.
- Volk, G.F.; Pantel, M.; Guntinas-Lichius, O. Modern concepts in facial nerve reconstruction. Head Face Med. 2010, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, J.W.; Brackmann, D.E. Facial Nerve Grading System. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 1985, 93, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayani, Y.; Haginomori, S.-I.; Wada, S.-I.; Nakano, H.; Inaka, Y.; Ozaki, A.; Ichihara, T.; Inui, T.; Kawata, R. Optimal current intensity for supramaximal stimulation during electroneurography for facial palsy. Auris Nasus Larynx 2021, 48, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaveling, S.; Steenvoorde, P.; Da Costa, S.A. Treatment of Postparotidectomy Fistulae with Fibrin Glue. Acta Medica 2006, 49, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Skevas, A.T.; Danielides, V.G.; Assimakopoulos, D.A. The role of the facial nerve latency test in the prognosis of Bell’s palsy. Laryngoscope 1990, 100, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros, J.L.; Nobrega, J.A.; de Andrade, L.A.; Juliano, Y. Facial nerve electroneurography. Variability in normal subjects. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 1996, 54, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ayani, Y.; Haginomori, S.-I.; Wada, S.-I.; Nakano, H.; Hamada, M.; Ichihara, T.; Inui, T.; Inaka, Y.; Ozaki, A.; Kawata, R. Latency shift in compound muscle action potentials during electroneurography in facial palsy. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2019, 276, 3281–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, M.; Kennett, R. Turns amplitude analysis of the orbicularis oculi and oris muscles. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 2550–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willison, R.G. Analysis of electrical activity in healthy and dystrophic muscle in man. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1964, 27, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stålberg, E.; Nandedkar, S.D.; Sanders, D.B.; Falck, B. Quantitative Motor Unit Potential Analysis. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1996, 13, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bär, B.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Iro, H. Paradigm shift in surgery for benign parotid tumors: 19 years of experience with almost 3000 cases. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 1941–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntinas–Lichius, O. The facial nerve in the presence of a head and neck neoplasm: Assessment and outcome after surgical management. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 12, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte-Mattler, W.J.; Grimm, T. Common and not so common nerve entrapment syndromes: Diagnostics, clinical aspects and therapy. Nervenarzt 2015, 86, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmus, H.; Martini, A.-K. Nerve compression syndromes of the upper extremity. Z. Orthopädie Unf. 2010, 148, 611. [Google Scholar]
- Mantsopoulos, K.; Koch, M.; Iro, H. Extracapsular dissection as sole therapy for small low-grade malignant tumors of the parotid gland. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 1804–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantsopoulos, K.; Mueller, S.; Goncalves, M.; Koch, M.; Iro, H. Completion surgery after extracapsular dissection of low-grade parotid gland malignant tumors. Head Neck 2019, 41, 3383–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantsopoulos, K.; Velegrakis, S.; Iro, H. Unexpected Detection of Parotid Gland Malignancy during Primary Extracapsular Dissection. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2015, 152, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Silver, C.E.; Thielker, J.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Bradford, C.R.; De Bree, R.; Kowalski, L.P.; Olsen, K.D.; Quer, M.; Rinaldo, A.; et al. Management of the facial nerve in parotid cancer: Preservation or resection and reconstruction. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2018, 275, 2615–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stitik, T.P.; Foye, P.; Nadler, S.F. Electromyography in craniomaxillofacial trauma. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Trauma 1999, 5, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A. The utility of interference pattern analysis. Muscle Nerve 2000, 23, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karandreas, N.; Kararizou, E.; Papagianni, A.; Zambelis, T.; Kokotis, P. Turns-amplitude analysis in normal and myopathic facial muscles. Muscle Nerve 2010, 43, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J. Differentiation between neurogenic and myogenic lesions of facial muscles by turn/amplitude analysis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 1400–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

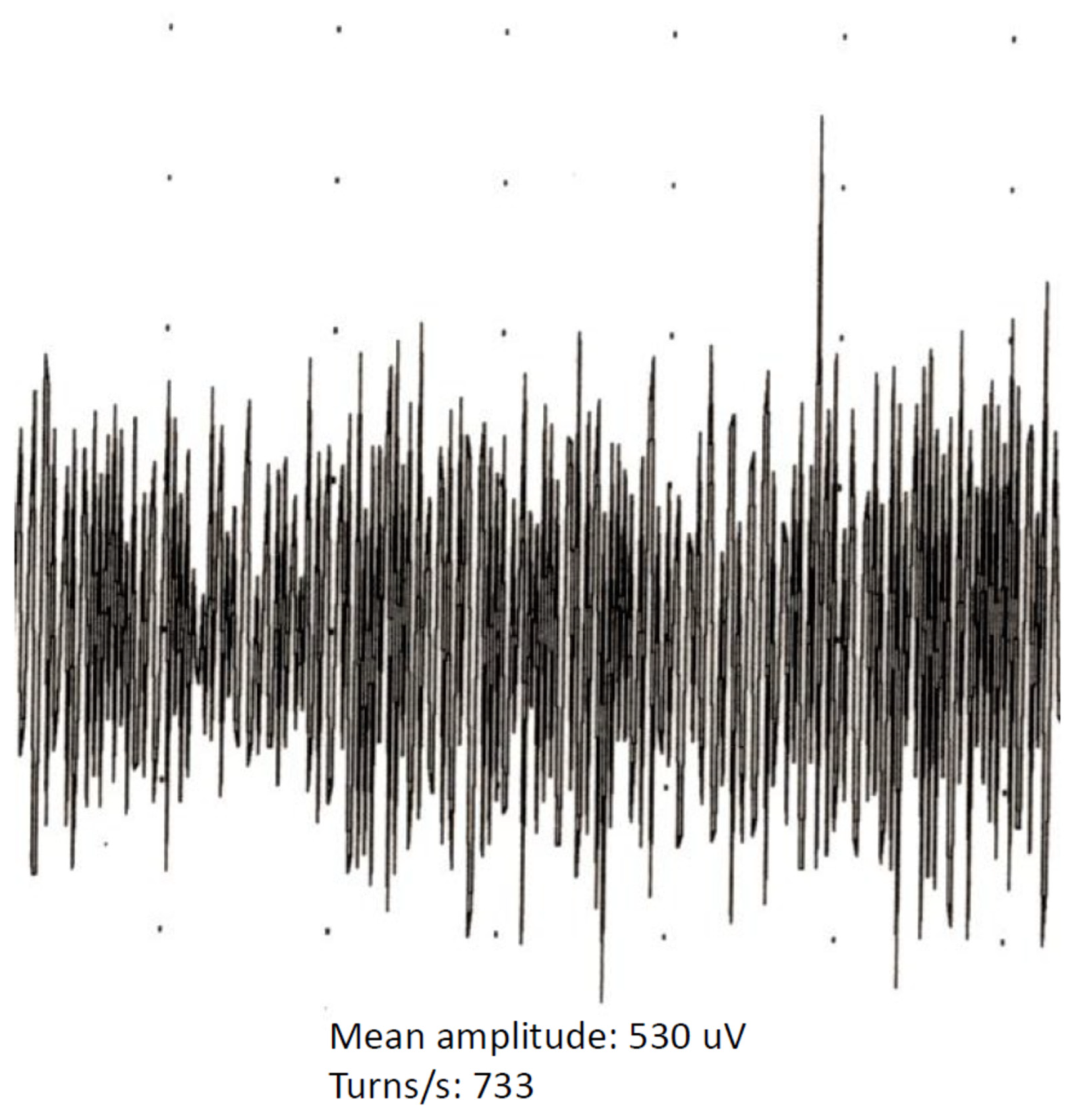
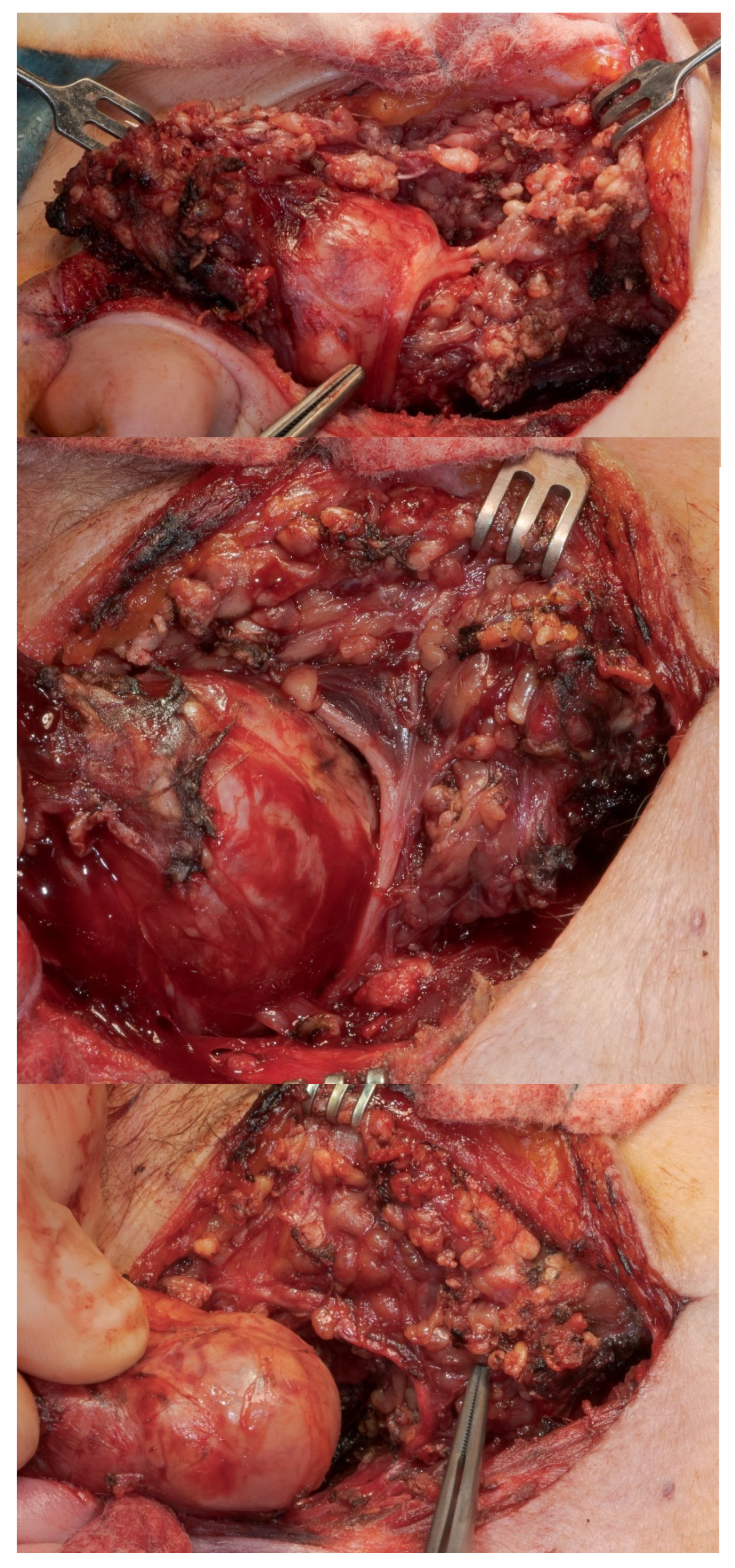
| Histology | Number of Cases | % |
|---|---|---|
| Cystadenolymphoma (“Warthin’s tumor”) | 108 | 48.6 |
| Pleomorphic adenoma | 72 | 32.5 |
| Basal cell adenoma | 10 | 4.5 |
| Oncocytic adenoma | 7 | 3.2 |
| Chronic sialadenitis | 6 | 2.7 |
| Lymphoepithelial cyst | 4 | 1.8 |
| Parotid cyst | 4 | 1.8 |
| Lymphadenitis | 3 | 1.4 |
| Oncocytic hyperplasia | 3 | 1.4 |
| Myoepithelioma | 2 | 0.9 |
| Abscess | 1 | 0.5 |
| Monomorphic adenoma | 1 | 0.5 |
| Schwannoma | 1 | 0.5 |
| Total | 222 | 100 |
| Histology | Number of Cases | % |
|---|---|---|
| “Low-grade” mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 4 | 6.3 |
| “Low-grade” acinic cell carcinoma | 4 | 6.3 |
| Salivary duct carcinoma (ex-pleomorphic adenoma) | 4 | 6.3 |
| Salivary duct carcinoma (“de novo”) | 2 | 3.2 |
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma | 2 | 3.2 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 2 | 3.2 |
| Dedifferentiated acinic cell carcinoma | 1 | 1.6 |
| Dedifferentiated mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 1 | 1.6 |
| “Low-grade” basal cell adenocarcinoma | 1 | 1.6 |
| “Low-grade” intraductal carcinoma (“intercalated cell” type) | 1 | 1.6 |
| Undifferentiated large cell carcinoma | 1 | 1.6 |
| Epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma | 1 | 1.6 |
| Lymphoma | 12 | 19 |
| Malignant melanoma | 3 | 4.8 |
| Merkel cell carcinoma | 2 | 3.2 |
| Parotid gland metastasis from breast cancer | 1 | 1.6 |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 21 | 33.3 |
| Total | 63 | 100 |
| Histology | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors | Total | |
| Pattern of nerve involvement | |||
| Displacement | 154 | 31 | 185 |
| Infiltration | 1 | 16 | 17 |
| No tumor–nerve interface | 67 | 16 | 83 |
| Total | 222 | 63 | 285 |
| No Facial Nerve Infiltration | Facial Nerve Infiltration | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean number of turns/second (±SD) | 871.9 ± 369.6 | 723.8 ± 304.7 | 0.04 |
| Mean amplitude (±SD) | 3684.9 ± 1685.2 | 3420.6 ± 2007.5 | 0.274 |
| Mean turns/amplitude ratio | 0.26 ± 0.10 | 0.25 ± 0.09 | 0.4 |
| Direct Postoperative Phase | Last Presentation | Direct Postoperative Phase | Last Presentation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| House–Brackmann | Displacement | No Tumor Nerve Contact | ||
| I | 113 | 160 | 72 | 79 |
| II | 47 | 19 | 9 | 3 |
| III | 15 | 3 | 0 | 1 |
| IV | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| V | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| VI | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katheder, V.; Sievert, M.; Müller, S.K.; Thimsen, V.; Gostian, A.-O.; Balk, M.; Rupp, R.; Iro, H.; Mantsopoulos, K. The Offprint of an Abnormal Pre-Parotidectomy Electrodiagnostic Finding in a Normally Functioning Facial Nerve: Correlation with Intraoperative Findings, Histology and Postoperative Facial Nerve Function. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010248
Katheder V, Sievert M, Müller SK, Thimsen V, Gostian A-O, Balk M, Rupp R, Iro H, Mantsopoulos K. The Offprint of an Abnormal Pre-Parotidectomy Electrodiagnostic Finding in a Normally Functioning Facial Nerve: Correlation with Intraoperative Findings, Histology and Postoperative Facial Nerve Function. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(1):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010248
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatheder, Verena, Matti Sievert, Sarina Katrin Müller, Vivian Thimsen, Antoniu-Oreste Gostian, Matthias Balk, Robin Rupp, Heinrich Iro, and Konstantinos Mantsopoulos. 2022. "The Offprint of an Abnormal Pre-Parotidectomy Electrodiagnostic Finding in a Normally Functioning Facial Nerve: Correlation with Intraoperative Findings, Histology and Postoperative Facial Nerve Function" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 1: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010248
APA StyleKatheder, V., Sievert, M., Müller, S. K., Thimsen, V., Gostian, A.-O., Balk, M., Rupp, R., Iro, H., & Mantsopoulos, K. (2022). The Offprint of an Abnormal Pre-Parotidectomy Electrodiagnostic Finding in a Normally Functioning Facial Nerve: Correlation with Intraoperative Findings, Histology and Postoperative Facial Nerve Function. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(1), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010248







