Cognitive Impairement in Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension: Highlights on Physiopathology, Diagnosis and Management
Abstract
1. Criteria for the Literature’s Selection
2. Definition
3. Historical Point and Pathophysiology
4. Prevalence of HE
5. Diagnosis
5.1. Diagnosis of Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy
5.2. Diagnosis of Covert Hepatic Encephalopathy
6. Treatment
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ginés, P.; Quintero, E.; Arroyo, V.; Terés, J.; Bruguera, M.; Rimola, A.; Caballería, J.; Rodés, J.; Rozman, C. Compensated cirrhosis: Natural history and prognostic factors. Hepatology 1987, 7, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilstrup, H.; Amodio, P.; Bajaj, J.; Cordoba, J.; Ferenci, P.; Mullen, K.D.; Weissenborn, K.; Wong, P. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014, 60, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichoż-Lach, H.; Michalak, A. Current pathogenetic aspects of hepatic encephalopathy and noncirrhotic hyperammonemic encephalopathy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.C. Portal-systemic collaterals and hepatic encephalopathy. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2012, 75, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sherlock, S.; Summerskill, W.H.; White, L.P.; Phear, E.A. Portal-systemic encephalopathy: Neurological complications of liver disease. Lancet 1954, 267, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, R.F. The neurobiology of hepatic encephalopathy. Semin. Liver Dis. 1996, 16, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norenberg, M.D. Astrocytic-ammonia interactions in hepatic encephalopathy. Semin. Liver Dis. 1996, 16, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, T.J.; Trochsler, M.I.; Bridgewater, F.H.; Maddern, G.J. Systematic review of congenital and acquired portal-systemic shunts in otherwise normal livers. Br. J. Surg. 2014, 101, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laleman, W.; Simon-Talero, M.; Maleux, G.; Perez, M.; Ameloot, K.; Soriano, G.; Villalba, J.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Barrufet, M.; Jalan, R.; et al. Embolization of large spontaneous portosystemic shunts for refractory hepatic encephalopathy: A multicenter survey on safety and efficacy. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2448–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Kim, K.W.; Han, S.; Lee, J.; Lim, Y.S. Improvement in survival associated with embolisation of spontaneous portosystemic shunt in patients with recurrent hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, O.; Nardelli, S.; Moscucci, F.; Pasquale, C.; Ridola, L.; Merli, M. Hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Clin. Liver Dis. 2012, 16, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, K.M.; Rohrbach, B.W. Association of breed with the diagnosis of congenital portosystemic shunts in dogs: 2400 Cases (1980–2002). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 223, 1636–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindfelt, B.; Plum, F.; Duffy, T.E. Effects of acute ammonia intoxication on cerebral metabolism in rats with portacaval shunts. J. Clin. Investig. 1977, 59, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, R.F.; Girard, G.; Giguère, J.F. Regional differences in the capacity for ammonia removal by brain following portacaval anastomosis. J. Neurochem. 1988, 51, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gow, A.G.; Marques, A.I.; Yool, D.A.; Crawford, K.; Warman, S.M.; Eckersall, P.D.; Jalan, R.; Mellanby, R.J. Dogs with congenital porto-systemic shunting (cPSS) and hepatic encephalopathy have higher serum concentrations of C-reactive protein than asymptomatic dogs with cPSS. Metab. Brain Dis. 2012, 27, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tivers, M.S.; Handel, I.; Gow, A.G.; Lipscomb, V.J.; Jalan, R.; Mellanby, R.J. Hyperammonemia and systemic inflammatory response syndrome predicts presence of hepatic encephalopathy in dogs with congenital portosystemic shunts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e82303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskin, N.H.; Price, J.B.; Fishman, R.A. Portal-Systemic Encephalopathy due to congenital intrahepatic shunts. N. Engl. J. Med. 1964, 270, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A. Portal-systemic encephalopathy in non-cirrhotic patients: Classification of clinical types, diagnosis and treatment. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 15, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, S.; Nardelli, S.; Ridola, L.; Riggio, O. Causes and Management of Non-cirrhotic Portal Hypertension. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2020, 22, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association For The Study Of The Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Vascular diseases of the liver. J. Hepatol. 2015, 64, 179–202. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, R.; Sarin, S.K. Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension-diagnosis and management. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gottardi, A.; Rautou, P.E.; Schouten, J.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Leebeek, F.; Trebicka, J.; Murad, S.D.; Vilgrain, V.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Nery, F.; et al. Porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: Proposal and description of a novel entity. Lancet. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrey, D.; Meunier, L.; Valla, D.; Hillaire, S.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Dutheil, D.; Plessier, A.; Bureau, C. Drug induced liver injury and vascular liver disease. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2020, 44, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payancé, A.; Ceccaldi, P.F.; De Raucourt, E.; Valla, D.; Hillaire, S.; Dutheil, D.; Plessier, A. Pregnancy and vascular liver diseases: Vascular liver diseases: Position papers from the francophone network for vascular liver diseases, the French Association for the Study of the Liver (AFEF), and ERN-rare liver. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2020, 44, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Rameshbabu, C.S. Collateral pathways in portal hypertension. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2012, 2, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; Mejias, M.; Angermayr, B.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Rodés, J.; Bosch, J. Inhibition of VEGF receptor-2 decreases the development of hyperdynamic splanchnic circulation and portal-systemic collateral vessels in portal hypertensive rats. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Singh, P.; Chawla, Y.; Duseja, A.; Dhiman, R.K.; Suri, S. Magnetic resonance imaging of brain in patients with cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 2793–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, D.; Krieger, S.; Jansen, O.; Gass, P.; Theilmann, L.; Lichtnecker, H. Manganese and chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet 1995, 346, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourier-Layrargues, G.; Spahr, L.; Butterworth, R.F. Increased manganese concentrations in palladium of cirrhotic patients. Lancet Lett. 1995, 345, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Sato, M.; Yoshikawa, A.; Kimura, M.; Sonomura, T.; Terada, M. Brain MR imaging in patients with hepatic cirrhosis: Relationship between high intensity signal in basal ganglia on T1-weighted images and elemental concentrations in the brain. Neuroradiology 1997, 39, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, R.A.; Zesiewicz, T.A.; Rosemurgy, A.S.; Martinez, C.; Olanow, C.W. Manganese intoxication and chronic liver failure. Ann. Neurol. 1994, 44, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.; Butterworth, R.F.; Zayed, J.; Normandin, L.; Todd, K.; Mic-halak, A. Manganese deposition in basal ganglia structures results from both portal-systemic shunting and liver dysfunction. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, R.G. Manganese. Intoxications of the nervous system. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; De Wolff, F.A., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 20, pp. 303–322. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, D.V.; Agarwal, M.L.; Narang, A.P.; Samanta, A.K.; Chhuttani, P.N. Ammonia tolerance test in liver disease with special reference to non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis. Indian J. Med. Res. 1979, 70, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nolte, W.; Wiltfang, J.; Schindler, C.G.; Unterberg, K.; Finkenstaedt, M.; Niedmann, P.D. Bright basal ganglia in T1 weighted magnetic resonance images are frequent in patients with portal vein thrombosis without liver cirrhosis and not suggestive of hepatic encephalopathy. J. Hepatol. 1998, 29, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, B.C.; Puri, V.; Sarin, S.K. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with extrahepatic portal vein obstruction. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, B.C.; Puri, V.; Sarin, S.K. Natural history of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with extrahepatic portal vein obstruction. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, B.C. Lactulose for minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with extrahepatic portal vein obstruction. Saudi. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yachha, S.K.; Thomas, M.A.; Saraswat, V.A.; Gupta, R.K.J. Pro-inflammatory cytokines are raised in extrahepatic portal venous obstruction, with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Srivastava, A.; Srivastava, A.; Thomas, M.A.; Agarwal, J.; Pandey, C.M.; Lal, R.; Yachha, S.K.; Saraswat, V.A.; Gupta, R.K. Encephalopathy assessment in children with extra-hepatic portal vein obstruction with MR, psychometry, and critical flicker frequency. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antiga, L.; Dacchille, P.; Boniver, C.; Poledri, S.; Schiff, S.; Zancan, L.; Amodio, P. Clues for minimal hepatic encephalopathy in children with noncirrhotic portal hypertension. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Lal, R.; Yachha, S.K.; Thomas, M.A.; Saraswat, V.A.; Gupta, R.K. Effect of surgical portosystemic shunt on prevalence of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in children with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction: Assessment by magnetic resonance imaging and psychometry. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siramolpiwat, S.; Seijo, S.; Miquel, R.; Berzigotti, A.; Garcia-Criado, A.; Darnell, A.; Turon, F.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Bosch, J.; Garcia-Pagán, J.C. Idiopathic portal hypertension: Natural history and long-term outcome. Hepatology 2014, 59, 2276–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, V.; Gioia, S.; Lucatelli, P.; Nardelli, S.; Pasquale, C.; Sobrinho, S.N.; Pentassuglio, I.; Greco, F.; De Santis, A.; Merli, M.; et al. The assessment of covert hepatic encephalopathy: Focus on the Scan battery. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissonnette, J.; Garcia-Pagán, J.C.; Albillos, A.; Turon, F.; Ferreira, C.; Tellez, L.; Nault, J.C.; Carbonell, N.; Cervoni, J.P.; Abdel Rehim, M.; et al. Role of the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the management of severe complications of portal hypertension in idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension. Hepatology 2016, 64, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; He, W.T.; Chen, D.S.; Hu, D.H. Analysis of influencing factors on hepatic encephalopathy in patients with non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi = Chin. J. Hepatol. 2019, 27, 673–676. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Li, K.; He, C.; Luo, B.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Guo, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; et al. TIPSS for variceal bleeding in patients with idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension: Comparison with patients who have cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimura, T.; Tsuji, Y.; Ibayashi, H.; Sakai, H.; Nawata, H. Portal-systemic shunting in a patient with normal portal vain pressures and histological evidence of idiopathic portal hypertension. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1996, 11, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Lee, A.; Callender, M.; Loughrey, M.; Quah, S.P.; Dinsmore, W.W. Hepatic encephalopathy as an unusual late complication of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt insertion for non-cirrhotic portal hypertension caused by nodular regenerative hyperplasia in an HIV-positive patient on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Int. J. STD AIDS 2010, 21, 71–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ridola, L.; Riggio, O.; Gioia, S.; Faccioli, J.; Nardelli, S. Clinical management of type C hepatic encephalopathy. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Cordoba, J.; Mullen, K.D.; Amodio, P.; Shawcross, D.L.; Butterworth, R.F.; Morgan, M.Y.; International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN). Review article: The design of clinical trials in hepatic encephalopathy—an International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN) consensus statement. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanfilian, B.V.; Park, T.; Senatore, F.; Rustgi, V.K. Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 24, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Lauridsen, M.; Tapper, E.B.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Rahimi, R.S.; Tandon, P.; Shawcross, D.L.; Thabut, D.; Dhiman, R.K.; Romero-Gomez, M.; et al. Important Unresolved Questions in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: An ISHEN Consensus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnese, S.; Schiff, S.; Turco, M.; Bonato, C.A.; Ridola, L.; Gatta, A.; Nousbaum, J.B.; Riggio, O.; Merkel, C.; Amodio, P. Simple tools for complex syndromes: A three-level difficulty test for hepatic encephalopathy. Dig. Liver Dis. 2012, 44, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashi, M.; Igarashi, M.; Hino, S.; Goto, N.; Okuda, K. Chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy with normal portal vein pressure possibly due to noncirrhotic portal fibrosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1984, 29, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
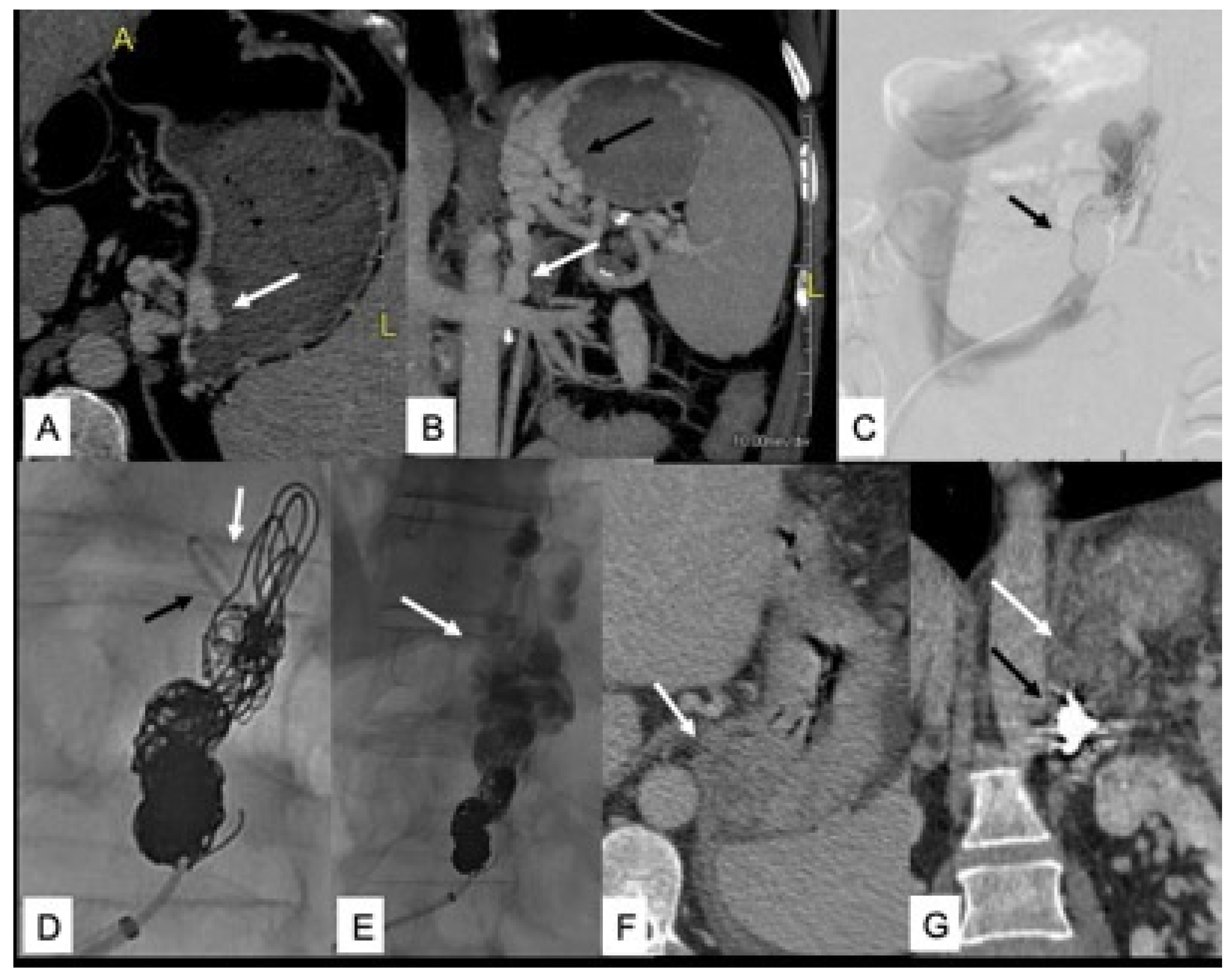
- Nardelli, S.; Gioia, S.; Ridola, L.; Riggio, O. Radiological Intervention for Shunt Related Encephalopathy. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2018, 8, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hashimoto, D.; Igarashi, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kumaoka, H.; Takagi, M.; Kawamura, K.; Koide, S.; Sasada, Y.; et al. An inferior mesenteric-caval shunt via the internal iliac vein with portosystemic encephalopathy. Intern. Med. 2001, 40, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogal, S.S.; Hu, A.; Bandi, R.; Shaikh, O. Novel therapy for non-cirrhotic hyperammonemia due to a spontaneous splenorenal shunt. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8288–8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice guideline by the European Association for the Study of the Liver and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 642–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnese, S.; Russo, F.P.; Amodio, P.; Burra, P.; Gasbarrini, A.; Loguercio, C.; Marchesini, G.; Merli, M.; Ponziani, F.R.; Riggio, O.; et al. Hepatic encephalopathy 2018, A clinical practice guideline by the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF). Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Karaksy, H.M.; Afifi, O.; Bakry, A.; Kader, A.A.; Saber, N. A pilot study using lactulose in management of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in children with extrahepatic portal vein obstruction. World J. Pediatr. 2017, 13, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year | N° of Patients | Type of NCPH | Prevalence of HE | Type of HE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sharma et al., 2008 [36] | 34 | PVT | 37.3% | MHE |
| Sharma et al., 2012 [38] | 70 | PVT | 43% | MHE |
| Srivastava et al., 2011 [39] | 20 | PVT | 60% | MHE |
| Yadav et al., 2010 [40] | 22 | PVT | 32% | MHE |
| D’Antiga et al., 2014 [41] | 13 | PVT | 45% | MHE |
| Srivastava et al., 2010 [42] | 42 | PVT | 36% | MHE |
| Siramolpiwat et al., 2014 [43] | 84 | PSVD | 7% | OHE |
| Nicoletti et al., 2016 [44] | 51 | PVT and PSVD | 34% (PVT)/25% (PSVD) 5.7% (PVT)/12.5% (PSVD) | MHE OHE |
| Bissonnette et al., 2016 [45] | 41 | PSVD | 31% | OHE |
| Liu et al., 2019 [46] | 150 | PSVD | 4.7% 32.7% | OHE MHE |
| Lv et al., 2019 [47] | 76 | PSVD | 16% | OHE |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gioia, S.; Nardelli, S.; Riggio, O.; Faccioli, J.; Ridola, L. Cognitive Impairement in Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension: Highlights on Physiopathology, Diagnosis and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010101
Gioia S, Nardelli S, Riggio O, Faccioli J, Ridola L. Cognitive Impairement in Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension: Highlights on Physiopathology, Diagnosis and Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(1):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010101
Chicago/Turabian StyleGioia, Stefania, Silvia Nardelli, Oliviero Riggio, Jessica Faccioli, and Lorenzo Ridola. 2022. "Cognitive Impairement in Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension: Highlights on Physiopathology, Diagnosis and Management" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 1: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010101
APA StyleGioia, S., Nardelli, S., Riggio, O., Faccioli, J., & Ridola, L. (2022). Cognitive Impairement in Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension: Highlights on Physiopathology, Diagnosis and Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(1), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010101






