Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma: Epidemiology and Genetic Susceptibility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology of RMS
2.1. Trends in Incidence
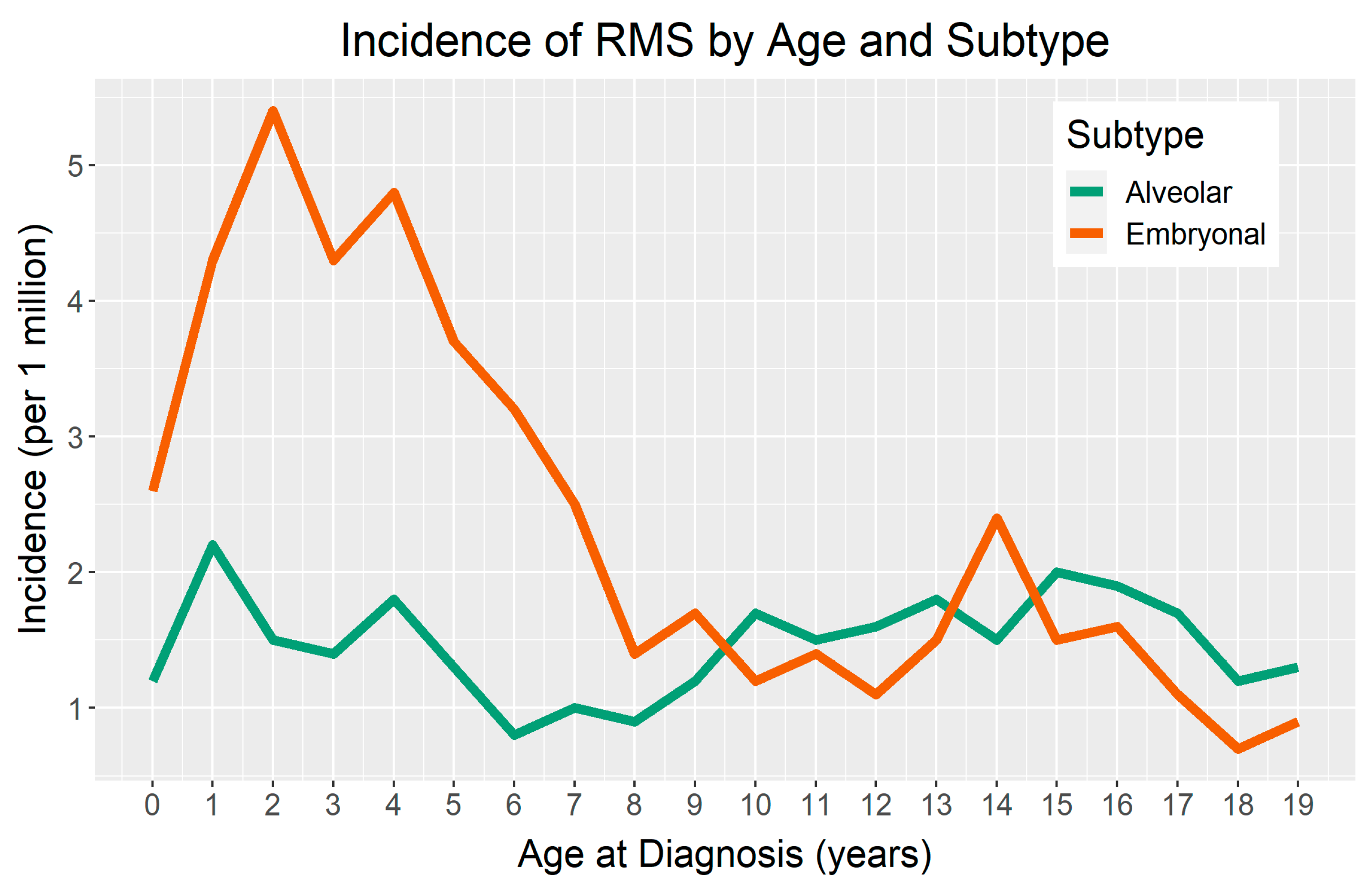
2.2. Incidence by Age and Sex
2.3. Global Incidence
2.4. Incidence by Race and Ethnicity
3. Non-Genetic Risk Factors
3.1. Parental Exposures
3.1.1. Parental Age
3.1.2. Additional Parental Exposures
3.2. Perinatal and Birth Characteristics
3.2.1. Birth Weight and Birth Term
3.2.2. Birth Defects
3.3. Exposures during Childhood
3.3.1. Immune-Related Factors
3.3.2. Additional Childhood Exposures
| Risk Factor | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | No. of Cases | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parental exposures | |||
| Parental age | |||
| Each 5-year increase in maternal age | 1.19 (1.05–1.34) * | 556 | [30] |
| Recreational drug use | |||
| Maternal | 3.1 (1.4–6.7) * | 322 | [32] |
| Paternal | 2.0 (1.3–3.3) * | 322 | [32] |
| Prenatal diagnostic radiation | 1.9 (1.1–3.4) * | 319 | [34] |
| Occupational exposures | |||
| Agent Orange exposure | 1.72 (0.55–5.41) | 319 | [36] |
| Electromagnetic fields | 1.67 (1.22–2.28) * | 1923 | [37] |
| Perinatal/birth characteristics | |||
| Birth weight | |||
| Overall RMS a, each 500 g increase | 1.18 (1.09–1.29) * | 583 | [38] |
| ERMS b, each 500 g increase | 1.27 (1.14–1.42) * | 363 | [38] |
| ARMS c, ≥4000 g | 2.41 (1.09–5.35) * | 66 | [49] |
| ARMS, <2500 g | 4.46 (1.41–14.1) * | 66 | [49] |
| Preterm birth | |||
| Overall RMS, GA d <37 weeks | 1.74 (1.08–2.79) *,e | 198 | [31] |
| ERMS, GA <37 weeks | 1.97 (0.98–3.94) e | 198 | [31] |
| Childhood exposures | |||
| Allergies | 0.60 (0.41–0.87) * | 322 | [40] |
| Hives | 0.61(0.38–0.97) * | 322 | [40] |
| Incomplete immunizations | 5.30 (2.47–11.33) * | 322 | [47] |
| Breastfeeding, ≥12 months | 0.36 (0.18–0.70) * | 322 | [40] |
4. Future Directions
5. Genetic Risk
5.1. Autosomal Dominant Mendelian Disorders
5.1.1. Li–Fraumeni Syndrome (LFS)
5.1.2. Costello Syndrome (CS)
5.1.3. Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1)
5.1.4. Noonan Syndrome (NS)
5.1.5. DICER1 Tumor Syndrome
5.1.6. Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome (RTS)
5.1.7. Retinoblastoma (RB)
5.2. Autosomal Recessive Mendelian Disorders
5.2.1. Constitutional Mismatch Repair Deficiency (CMMRD)
5.2.2. Fanconi Anemia (FA)
5.2.3. Mosaic Variegated Aneuploidy Syndrome (MVA)
5.3. Epigenetic Mechanisms
Beckwith–Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS)
6. Large-scale Pediatric Cancer Germline Genetics Studies
Large-Scale RMS-Specific Studies
7. Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Thompson, T.D.; Miller, J.W.; Pollack, L.A.; Stewart, S.L. Cancer Incidence Among Children and Adolescents in the United States, 2001–2003. Pediatrics 2008, 121, e1470–e1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurney, J.; Young, J.; Roffers, S.; Smith, M.; Bunin, G. Soft Tissue Sarcomas. In Cancer Incidence and Survival among Children and Adolescents: United States SEER Program 1975–1995; Ries, L., Smith, M., Gurney, J., Linet, M., Tamra, T., Young, J., Bunin, G., Eds.; National Cancer Institute, SEER Program: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1999; pp. 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, D.A.; King, J.; Tai, E.; Buchanan, N.; Ajani, U.A.; Li, J. Cancer Incidence Rates and Trends Among Children and Adolescents in the United States, 2001–2009. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e945–e955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawkins, D.S.; Spunt, S.L.; Skapek, S.X. Children’s Oncology Group’s 2013 Blueprint for Research: Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malempati, S.; Hawkins, D.S. Rhabdomyosarcoma: Review of the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) soft-tissue Sarcoma committee experience and rationale for current COG studies. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 59, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kashi, V.P.; Hatley, M.E.; Galindo, R.L. Probing for a deeper understanding of rhabdomyosarcoma: Insights from complementary model systems. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charytonowicz, E.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Matushansky, I.; Ziman, M. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: Is the cell of origin a mesenchymal stem cell? Cancer Lett. 2009, 279, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linardic, C.M.; Naini, S.; Herndon, J.E.; Kesserwan, C.; Qualman, S.J.; Counter, C.M. The PAX3-FKHR Fusion Gene of Rhabdomyosarcoma Cooperates with Loss of p16INK4A to Promote Bypass of Cellular Senescence. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6691–6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keller, C.; Arenkiel, B.R.; Coffin, C.M.; El-Bardeesy, N.; Depinho, R.A.; Capecchi, M.R. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcomas in conditional Pax3:Fkhr mice: Cooperativity of Ink4a/ARF and Trp53 loss of function. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2614–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drummond, C.J.; Hanna, J.A.; Garcia, M.R.; Devine, D.J.; Heyrana, A.J.; Finkelstein, D.; Rehg, J.E.; Hatley, M.E. Hedgehog Pathway Drives Fusion-Negative Rhabdomyosarcoma Initiated from Non-myogenic Endothelial Progenitors. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 108–124.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ognjanovic, S.; Linabery, A.M.; Charbonneau, B.; Ross, J.A. Trends in childhood rhabdomyosarcoma incidence and survival in the United States, 1975–2005. Cancer 2009, 115, 4218–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rudzinski, E.R.; Anderson, J.R.; Hawkins, D.S.; Skapek, S.X.; Parham, D.M.; Teot, L.A. The World Health Organization Classification of Skeletal Muscle Tumors in Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2015, 139, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhee, D.S.; Rodeberg, D.A.; Baertschiger, R.M.; Aldrink, J.H.; Lautz, T.B.; Grant, C.; Meyers, R.L.; Tracy, E.T.; Christison-Lagay, E.R.; Glick, R.D.; et al. Update on pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the APSA Cancer Committee. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 55, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbitts, E.; Chi, Y.; Hawkins, D.S.; Barr, F.G.; Bradley, J.A.; Dasgupta, R.; Meyer, W.H.; Rodeberg, D.A.; Rudzinski, E.R.; Spunt, S.L.; et al. Refinement of risk stratification for childhood rhabdomyosarcoma using FOXO1 fusion status in addition to established clinical outcome predictors: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 6437–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudzinski, E.R.; Kelsey, A.; Vokuhl, C.; Linardic, C.M.; Shipley, J.; Hettmer, S.; Koscielniak, E.; Hawkins, D.S.; Bisogno, G. Pathology of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: A consensus opinion document from the Children’s Oncology Group, European Paediatric Soft Tissue Sarcoma Study Group, and the Cooperative Weichteilsarkom Studiengruppe. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e28798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Cancer Institute: Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/ (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Linabery, A.M.; Ross, J.A. Trends in childhood cancer incidence in the U.S. (1992–2004). Cancer 2007, 112, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, Z.J.; Yeh, J.M.; Bhakta, N.; Frazier, A.L.; Atun, R. Estimating the total incidence of global childhood cancer: A simulation-based analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altekruse, S.; Kosary, C.; Krapcho, M.; Neyman, N.; Aminou, R.; Waldron, W.; Ruhl, J.; Howlader, N.; Tatalovich, Z.; Cho, H.; et al. Age-Adjusted and Age-Specific SEER Cancer Incidence Rates. In SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2018; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Valberg, M.; Grotmol, T.; Tretli, S.; Veierød, M.B.; Devesa, S.S.; Aalen, O.O. Frailty modeling of age-incidence curves of osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma among individuals younger than 40 years. Stat. Med. 2012, 31, 3731–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, L.A.; Richardson, M.; Kehm, R.D.; McLaughlin, C.C.; Mueller, B.A.; Chow, E.J.; Spector, L.G. The association between sex and most childhood cancers is not mediated by birthweight. Cancer Epidemiol. 2018, 57, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorak, M.T.; Ekarpuzoglu, E. Gender Differences in Cancer Susceptibility: An Inadequately Addressed Issue. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pastore, G.; Peris-Bonet, R.; Carli, M.; Martínez-García, C.; de Toledo, J.S.; Steliarova-Foucher, E. Childhood soft tissue sarcomas incidence and survival in European children (1978–1997): Report from the Automated Childhood Cancer Information System project. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 2136–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lychou, S.E.; Gustafsson, G.G.; Ljungman, G.E. Higher rates of metastatic disease may explain the declining trend in Swedish paediatric rhabdomyosarcoma survival rates. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 105, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, P.-P.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, C.-F.; Gu, K.; Jin, F.; Lu, W. Time trends and characteristics of childhood cancer among children age 0-14 in Shanghai. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2009, 53, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, K.; Ito, Y.; Magadi, W.; Bonaventure, A.; Stiller, C.A.; Katanoda, K.; Matsuda, T.; Miyashiro, I.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; Rachet, B. Childhood cancer incidence and survival in Japan and England: A population-based study (1993–2010). Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefan, C.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Liu, B.; Parkin, D.M. Cancer of childhood in sub-Saharan Africa. Ecancermedicalscience 2017, 11, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkin, D.M.; Stefan, C. Editorial: Childhood Cancer in sub-Saharan Africa. Ecancermedicalscience 2017, 11, ed69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jawad, M.U.; Cheung, M.C.; Min, E.S.; Schneiderbauer, M.M.; Koniaris, L.G.; Scully, S.P. Ewing sarcoma demonstrates racial disparities in incidence-related and sex-related differences in outcome. Cancer 2009, 115, 3526–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.J.; Carozza, S.E.; Chow, E.J.; Fox, E.E.; Horel, S.; McLaughlin, C.C.; Mueller, B.A.; Puumala, S.E.; Reynolds, P.; Von Behren, J.; et al. Parental Age and Risk of Childhood Cancer. Epidemiology 2009, 20, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lupo, P.J.; Luna-Gierke, R.E.; Chambers, T.M.; Tavelin, B.; Scheurer, M.E.; Melin, B.; Papworth, K. Perinatal and familial risk factors for soft tissue sarcomas in childhood through young adulthood: A population-based assessment in 4 million live births. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grufferman, S.; Schwartz, A.G.; Ruymann, F.B.; Maurer, H.M. Parents’ use of cocaine and marijuana and increased risk of rhabdomyosarcoma in their children. Cancer Causes Control. 1993, 4, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Rumrich, I.K.; Viluksela, M.; Vähäkangas, K.; Gissler, M.; Surcel, H.-M.; Hänninen, O. Maternal Smoking and the Risk of Cancer in Early Life–A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grufferman, S.; Ruymann, F.; Ognjanovic, S.; Erhardt, E.B.; Maurer, H.M. Prenatal X-ray Exposure and Rhabdomyosarcoma in Children: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hicks, N.; Zack, M.; Caldwell, G.G.; Fernbach, D.J.; Falletta, J.M. Childhood cancer and occupational radiation exposure in parents. Cancer 1984, 53, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grufferman, S.; Lupo, P.J.; Vogel, R.I.; Danysh, H.E.; Erhardt, E.B.; Ognjanovic, S. Parental Military Service, Agent Orange Exposure, and the Risk of Rhabdomyosarcoma in Offspring. J. Pediatr. 2014, 165, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kendall, G.M.; Bunch, K.J.; Stiller, C.A.; Vincent, T.J.; Murphy, M.F.G. Case–control study of paternal occupational exposures and childhood bone tumours and soft-tissue sarcomas in Great Britain, 1962–2010. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ognjanovic, S.; Carozza, E.S.; Chow, E.J.; Fox, E.E.; Horel, S.; McLaughlin, C.C.; Mueller, A.B.; Puumala, S.; Reynolds, P.; Von Behren, J.; et al. Birth characteristics and the risk of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma based on histological subtype. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 102, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, L.M.; McCauley, K.; Ma, X.; Wiemels, J.L.; Chokkalingam, A.P.; Metayer, C. Birth weight, fetal growth, and risk of pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma: An updated record linkage study in California. Ann. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupo, P.J.; Zhou, R.; Skapek, S.X.; Hawkins, D.S.; Spector, L.G.; Scheurer, M.E.; Okcu, M.F.; Melin, B.; Papworth, K.; Erhardt, E.B.; et al. Allergies, atopy, immune-related factors and childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the children’s oncology group. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Ritz, B.; Ognjanovic, S.; Lombardi, C.A.; Wilhelm, M.; Heck, J.E. Early Life Factors and Risk of Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma. Front. Public Health 2013, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spector, L.G.; Birch, J. The epidemiology of hepatoblastoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 59, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, F.D.; Watkins, B.T.; Roberts, D.J.; Tucker, T.C.; Shen, T.; Flood, T.J. Birth Weight and Risk of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Arizona, Illinois, and Kentucky. South. Med. J. 2018, 111, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, P.J.; Schraw, J.M.; Desrosiers, T.A.; Nembhard, W.N.; Langlois, P.H.; Canfield, M.A.; Copeland, G.; Meyer, R.E.; Brown, A.L.; Chambers, T.M.; et al. Association Between Birth Defects and Cancer Risk Among Children and Adolescents in a Population-Based Assessment of 10 Million Live Births. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daltveit, D.S.; Klungsøyr, K.; Engeland, A.; Ekbom, A.; Gissler, M.; Glimelius, I.; Grotmol, T.; Madanat-Harjuoja, L.; Ording, A.G.; Sæther, S.M.M.; et al. Cancer risk in individuals with major birth defects: Large Nordic population based case-control study among children, adolescents, and adults. BMJ 2020, 371, m4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Grufferman, S.; Khoury, M.J.; Schwartz, A.G.; Kowalski, J.; Ruymann, F.B.; Maurer, H.M. Association of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma with neurofibromatosis type i and birth defects. Genet. Epidemiol. 1995, 12, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sankaran, H.; Danysh, H.E.; Scheurer, M.E.; Okcu, M.F.; Skapek, S.X.; Hawkins, D.S.; Spector, L.G.; Erhardt, E.B.; Grufferman, S.; Lupo, P.J. The Role of Childhood Infections and Immunizations on Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oddsberg, J. Environmental Factors in the Etiology of Esophageal Atresia. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 52, S4–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, P.J.; Danysh, H.E.; Skapek, S.X.; Hawkins, D.S.; Spector, L.G.; Zhou, R.; Okcu, M.F.; Papworth, K.; Erhardt, E.B.; Grufferman, S. Maternal and birth characteristics and childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer Causes Control. 2014, 25, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupo, P.J.; Danysh, H.E.; Plon, S.E.; Curtin, K.; Malkin, D.; Hettmer, S.; Hawkins, D.S.; Skapek, S.X.; Spector, L.G.; Papworth, K.; et al. Family history of cancer and childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group and the Utah Population Database. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kratz, C.P.; Achatz, M.I.; Brugières, L.; Frebourg, T.; Garber, J.E.; Greer, M.-L.C.; Hansford, J.R.; Janeway, K.A.; Kohlmann, W.K.; McGee, R.; et al. Cancer Screening Recommendations for Individuals with Li-Fraumeni Syndrome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, e38–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.P. Soft-Tissue Sarcomas, Breast Cancer, and Other Neoplasms. Ann. Intern. Med. 1969, 71, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diller, L.; Sexsmith, E.; Gottlieb, A.; Li, F.P.; Malkin, D. Germline p53 mutations are frequently detected in young children with rhabdomyosarcoma. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognjanovic, S.; Olivier, M.; Bergemann, T.L.; Hainaut, P. Sarcomas in TP53 germline mutation carriers. Cancer 2012, 118, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettmer, S.; Archer, N.M.; Somers, G.R.; Novokmet, A.; Wagers, A.J.; Diller, L.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Teot, L.A.; Malkin, D. Anaplastic rhabdomyosarcoma inTP53germline mutation carriers. Cancer 2014, 120, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rauen, K.A. The RASopathies. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2013, 14, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gripp, K.W.; Rauen, K.A. Costello Syndrome. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kratz, C.P.; Rapisuwon, S.; Reed, H.; Hasle, H.; Rosenberg, P.S. Cancer in Noonan, Costello, cardiofaciocutaneous and LEOPARD syndromes. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2011, 157, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratz, C.P.; Franke, L.; Peters, H.M.; Kohlschmidt, N.; Kazmierczak, B.; Finckh, U.; Bier, A.; Eichhorn, B.W.; De Blank, C.M.; Kraus, C.; et al. Cancer spectrum and frequency among children with Noonan, Costello, and cardio-facio-cutaneous syndromes. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, J. Neurofibromatosis 1. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bollag, G.; Clapp, D.W.; Shih, S.; Adler, F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Thompson, P.; Lange, B.J.; Freedman, M.H.; McCormick, F.; Jacks, T.; et al. Loss of NF1 results in activation of the Ras signaling pathway and leads to aberrant growth in haematopoietic cells. Nat. Genet. 1996, 12, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, K.W.; Cost, N.G.; Schultz, K.A.P.; Svihovec, S.; Suttman, A. Germline predisposition to genitourinary rhabdomyosarcoma. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2020, 9, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.G.R.; Salvador, H.; Chang, V.Y.; Erez, A.; Voss, S.D.; Schneider, K.W.; Scott, H.S.; Plon, S.E.; Tabori, U. Cancer and Central Nervous System Tumor Surveillance in Pediatric Neurofibromatosis 1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, e46–e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crucis, A.; Richer, W.; Brugières, L.; Bergeron, C.; Marie-Cardine, A.; Stephan, J.-L.; Girard, P.; Corradini, N.; Munzer, M.; Lacour, B.; et al. Rhabdomyosarcomas in children with neurofibromatosis type I: A national historical cohort. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, C. Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jongmans, M.C.J.; Hoogerbrugge, P.M.; Hilkens, L.; Flucke, U.; Van Der Burgt, I.; Noordam, K.; Ruiterkamp-Versteeg, M.; Yntema, H.G.; Nillesen, W.M.; Ligtenberg, M.J.L.; et al. Noonan syndrome, the SOS1 gene and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2010, 49, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denayer, E.E.; Devriendt, K.K.; De Ravel, T.; Van Buggenhout, G.G.; Smeets, E.E.; Francois, I.; Sznajer, Y.; Craen, M.M.; Leventopoulos, G.G.; Mutesa, L.L.; et al. Tumor spectrum in children with Noonan syndrome andSOS1orRAF1mutations. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2009, 49, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, K.A.P.; Stewart, D.R.; Kamihara, J.; Bauer, A.J.; Merideth, M.A.; Stratton, P.; Huryn, L.A.; Harris, A.K.; Doros, L.; Field, A. DICER1 Tumor Predisposition Summary Genetic Counseling. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, J.C.; Jorcyk, C.L.; Oxford, J.T. DICER1 Syndrome: DICER1 Mutations in Rare Cancers. Cancers 2018, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultz, K.A.P.; Stewart, D.R.; Kamihara, J.; Bauer, A.J.; Merideth, M.A.; Stratton, P.; Huryn, L.A.; Harris, A.K.; Doros, L.; Field, A.; et al. DICER1 Tumor Predisposition. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes, W.D.; Priest, J.R.; Duchaine, T.F. DICER1: Mutations, microRNAs and mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, L.E.; Perkins, S.M.; Pfeifer, J.D.; Ma, C.; Chen, Y.; Dewees, T.; Grigsby, P.W. BRAF V600E mutational status in pediatric thyroid cancer. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.R.; Best, A.F.; Williams, G.M.; Harney, L.A.; Carr, A.G.; Harris, A.K.; Kratz, C.P.; Dehner, L.P.; Messinger, Y.H.; Rosenberg, P.S.; et al. Neoplasm Risk Among Individuals with a Pathogenic Germline Variant in DICER1. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobel, R.A.; Woerner, S. Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome andnasopharyngeal rhabdomyosarcoma. J. Pediatr. 1981, 99, 1000–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.W.; Rubinstein, J.H. Tumors in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1995, 56, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, D.R.; Gallie, B.L. Retinoblastoma. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi, K.; Oda, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Tamiya, S.; Takahira, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Tajiri, T.; Taguchi, T.; Suita, S.; Tsuneyoshi, M. Alterations of RB1 gene in embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: Special reference to utility of pRB immunoreactivity in differential diagnosis of rhabdomyosarcoma subtype. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 134, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temming, P.; Arendt, M.; Viehmann, A.; Eisele, L.; Le Guin, C.H.D.; Schündeln, M.M.; Biewald, E.; Astrahantseff, K.; Wieland, R.; Bornfeld, N.; et al. Incidence of second cancers after radiotherapy and systemic chemotherapy in heritable retinoblastoma survivors: A report from the German reference center. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinerman, R.A.; Tucker, M.A.; Abramson, D.H.; Seddon, J.M.; Tarone, R.E.; Fraumeni, J.F. Risk of Soft Tissue Sarcomas by Individual Subtype in Survivors of Hereditary Retinoblastoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebulla, C.M.; Kleinerman, R.A.; Alegret, A.; Kulak, A.; Dubovy, S.R.; Hess, D.J.; Murray, T.G. Rapid appearance of rhabdomyosarcoma after radiation and chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: A clinicopathologic correlation. Retin. Cases Brief. Rep. 2009, 3, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabori, U.; Hansford, J.R.; Achatz, M.I.; Kratz, C.P.; Plon, S.E.; Frebourg, T.; Brugières, L. Clinical Management and Tumor Surveillance Recommendations of Inherited Mismatch Repair Deficiency in Childhood. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, e32–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lavoine, N.; Colas, C.; Muleris, M.; Bodo, S.; Duval, A.; Entz-Werle, N.; Coulet, F.; Cabaret, O.; Andreiuolo, F.; Charpy, C.; et al. Constitutional mismatch repair deficiency syndrome: Clinical description in a French cohort. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 52, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, C.P.; Holter, S.; Etzler, J.; Lauten, M.; Pollett, A.; Niemeyer, C.M.; Gallinger, S.; Wimmer, K. Rhabdomyosarcoma in patients with constitutional mismatch-repair-deficiency syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 46, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, P.A.; Tolar, J. Fanconi Anemia. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Malric, A.; Defachelles, A.-S.; Leblanc, T.; Lescoeur, B.; Lacour, B.; Peuchmaur, M.; Maurage, C.-A.; Pierron, G.; Guillemot, D.; D’Enghien, C.D.; et al. Fanconi anemia and solid malignancies in childhood: A national retrospective study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Leasure, J.M.; Chronowski, C.; Geier, B.; Bondra, K.; Duan, W.; Hensley, L.A.; Villalona-Calero, M.; Li, N.; Vergis, A.M.; et al. FANCD2 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target and Biomarker in Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma Harboring the PAX3–FOXO1 Fusion Gene. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3884–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacquemont, S.; Bocéno, M.; Rival, J.M.; Méchinaud, F.; David, A. High risk of malignancy in mosaic variegated aneuploidy syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 109, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanks, S.; Coleman, K.; Reid, S.; Plaja, A.; Firth, H.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Kidd, A.; Méhes, K.; Nash, R.; Robin, N.; et al. Constitutional aneuploidy and cancer predisposition caused by biallelic mutations in BUB1B. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuman, C.; Beckwith, J.B.; Weksberg, R. Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.C.; Squire, J.A.; Thorner, P.; Zielenska, M.; Shuman, C.; Grant, R.; Chitayat, D.; Nishikawa, J.L.; Weksberg, R. Association of Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma with the Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2001, 4, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo-Avila, C.; Gooch, W.M. Neoplasms associated with the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Perspect. Pediatr. Pathol. 1976, 3, 255–272. [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan, W.; Sanders, D.W.; Grosfeld, J.L.; Plumley, A.D.; Rescorla, F.J.; Scherer, L.; West, K.W.; Breitfeld, P.P. Favorable outcome in children with Beckwith-Wiedeman syndrome and intraabdominal malignant tumors. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1995, 30, 1042–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aideyan, U.; Kao, S. Case report: Urinary bladder rhabdomyosarcoma associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Clin. Radiol. 1998, 53, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussa, A.; Molinatto, C.; Baldassarre, G.; Riberi, E.; Russo, S.; Larizza, L.; Riccio, A.; Ferrero, G.B. Cancer Risk in Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Outlining a Novel (Epi)Genotype Specific Histotype Targeted Screening Protocol. J. Pediatr. 2016, 176, 142–149.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, S.M.; Vansenne, F.; Kadouch, D.J.M.; Ibrahim, A.; Bliek, J.; Hopman, S.; Mannens, M.M.; Merks, J.H.M.; Maher, E.R.; Hennekam, R.C. Phenotype, cancer risk, and surveillance in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome depending on molecular genetic subgroups. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part. A 2016, 170, 2248–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsons, D.W.; Roy, A.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Scollon, S.; Bergstrom, K.; Kerstein, R.A.; Gutierrez, S.; Petersen, A.K.; Bavle, A.; et al. Diagnostic Yield of Clinical Tumor and Germline Whole-Exome Sequencing for Children with Solid Tumors. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Walsh, M.F.; Wu, G.; Edmonson, M.N.; Gruber, T.A.; Easton, J.; Hedges, D.; Aman, P.; Zhou, X.; Yergeau, D.A.; et al. Germline Mutations in Predisposition Genes in Pediatric Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2336–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mody, R.J.; Wu, Y.-M.; Lonigro, R.J.; Cao, X.; Roychowdhury, S.; Vats, P.; Frank, K.M.; Prensner, J.R.; Asangani, A.I.; Palanisamy, N.; et al. Integrative Clinical Sequencing in the Management of Refractory or Relapsed Cancer in Youth. JAMA 2015, 314, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sisoudiya, S.D.; Martin-Giacalone, A.B.; Khayat, M.M.; Dugan-Perez, S.; Marquez-Do, A.D.; Scheurer, E.M.; Muzny, D.; Boerwinkle, E.; Gibbs, A.R.; et al. Germline Cancer Predisposition Variants in Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Light, N.; Subasri, V.; Young, E.L.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Barkauskas, D.A.; Hall, D.; Lupo, P.J.; Patidar, R.; Maese, L.D.; et al. Pathogenic Germline Variants in Cancer Susceptibility Genes in Children and Young Adults with Rhabdomyosarcoma. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2021, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünewald, T.G.P.; Bernard, V.; Gilardi-Hebenstreit, P.; Raynal, V.; Surdez, D.; Aynaud, M.-M.; Mirabeau, O.; Cidre-Aranaz, F.; Tirode, F.; Zaidi, S.; et al. Chimeric EWSR1-FLI1 regulates the Ewing sarcoma susceptibility gene EGR2 via a GGAA microsatellite. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musa, J.; Cidre-Aranaz, F.; Aynaud, M.-M.; Orth, M.F.; Knott, M.M.L.; Mirabeau, O.; Mazor, G.; Varon, M.; Hölting, T.L.B.; Grossetête, S.; et al. Cooperation of cancer drivers with regulatory germline variants shapes clinical outcomes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Northcott, P.A.; Robinson, G.W.; Kratz, C.P.; Mabbott, D.J.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Clifford, S.C.; Rutkowski, S.; Ellison, D.W.; Malkin, D.; Taylor, M.D.; et al. Medulloblastoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.-X.; Finckenstein, F.G.; Abdueva, D.A.; Shahbazian, V.; Chung, B.; Weinberg, K.I.; Triche, T.J.; Shimada, H.; Anderson, M.J. Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cells Expressing PAX-FKHR form Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcomas by Cooperating with Secondary Mutations. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6587–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Linardic, C.M.; Downie, D.L.; Qualman, S.; Bentley, R.C.; Counter, C.M. Genetic Modeling of Human Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4490–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langenau, D.M.; Keefe, M.D.; Storer, N.Y.; Guyon, J.R.; Kutok, J.L.; Le, X.; Goessling, W.; Neuberg, D.S.; Kunkel, L.M.; Zon, L.I. Effects of RAS on the genesis of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, A.P.-Y.; Devidas, M.; Lee, S.H.R.; Cao, X.; Pei, D.; Borowitz, M.; Wood, B.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Dai, Y.; et al. Association of GATA3 Polymorphisms with Minimal Residual Disease and Relapse Risk in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020, 113, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Cao, X.; Devidas, M.; Yang, W.; Cheng, C.; Dai, Y.; Carroll, A.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhang, H.; Moriyama, T.; et al. TP53 Germline Variations Influence the Predisposition and Prognosis of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perez-Andreu, V.; Roberts, K.G.; Harvey, R.C.; Yang, W.; Cheng, C.; Pei, D.; Xu, H.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Shuyu, E.; Yew-Suang Lim, J.; et al. Inherited GATA3 variants are associated with Ph-like childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and risk of relapse. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1494–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thavaneswaran, S.; Rath, E.; Tucker, K.; Joshua, A.M.; Hess, D.; Pinese, M.; Ballinger, M.L.; Thomas, D.M. Therapeutic implications of germline genetic findings in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, P.J.; Spector, L.G. Cancer Progress and Priorities: Childhood Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin-Giacalone, B.A.; Weinstein, P.A.; Plon, S.E.; Lupo, P.J. Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma: Epidemiology and Genetic Susceptibility. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10092028
Martin-Giacalone BA, Weinstein PA, Plon SE, Lupo PJ. Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma: Epidemiology and Genetic Susceptibility. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(9):2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10092028
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin-Giacalone, Bailey A., P. Adam Weinstein, Sharon E. Plon, and Philip J. Lupo. 2021. "Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma: Epidemiology and Genetic Susceptibility" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 9: 2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10092028
APA StyleMartin-Giacalone, B. A., Weinstein, P. A., Plon, S. E., & Lupo, P. J. (2021). Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma: Epidemiology and Genetic Susceptibility. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(9), 2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10092028







