A New Outlook on the Ability to Accumulate an Iodine Contrast Agent in Solid Lung Tumors Based on Virtual Monochromatic Images in Dual Energy Computed Tomography (DECT): Analysis in Two Phases of Contrast Enhancement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. CT Scanning Parameters
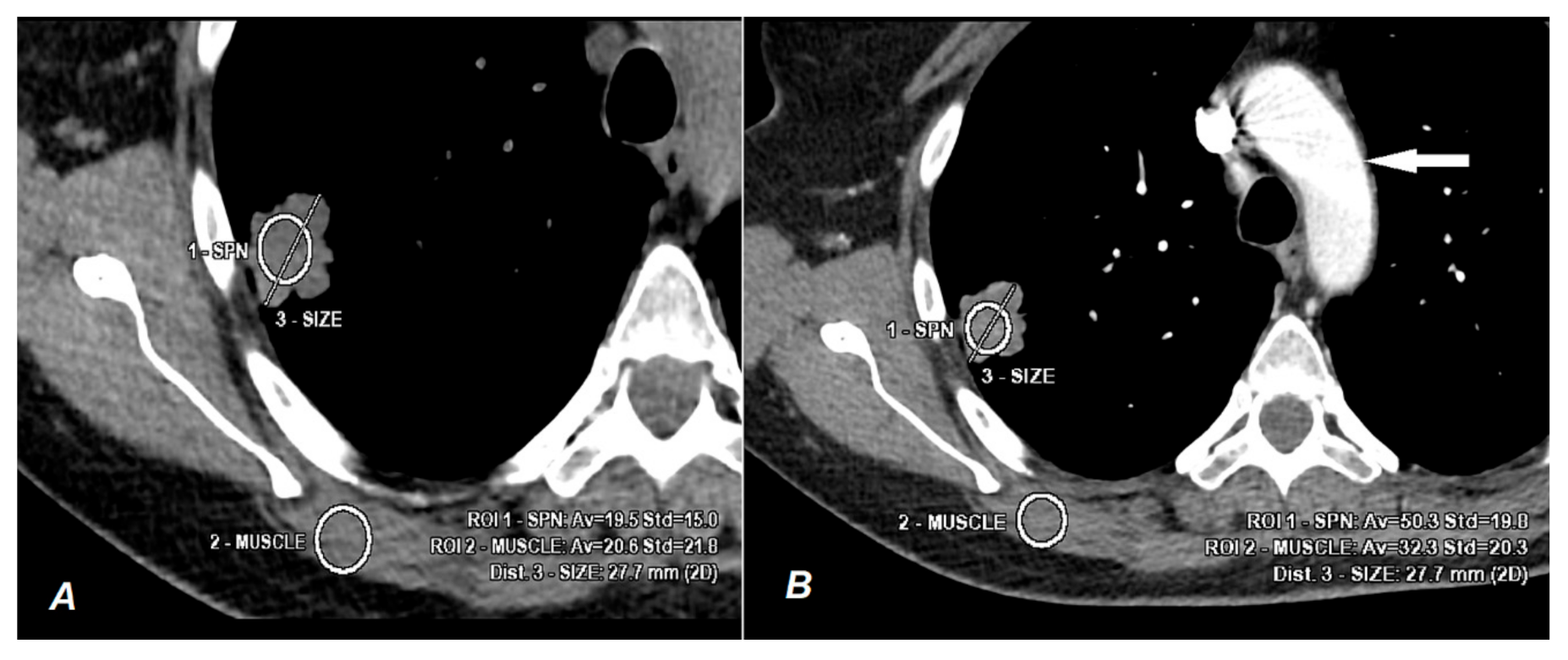
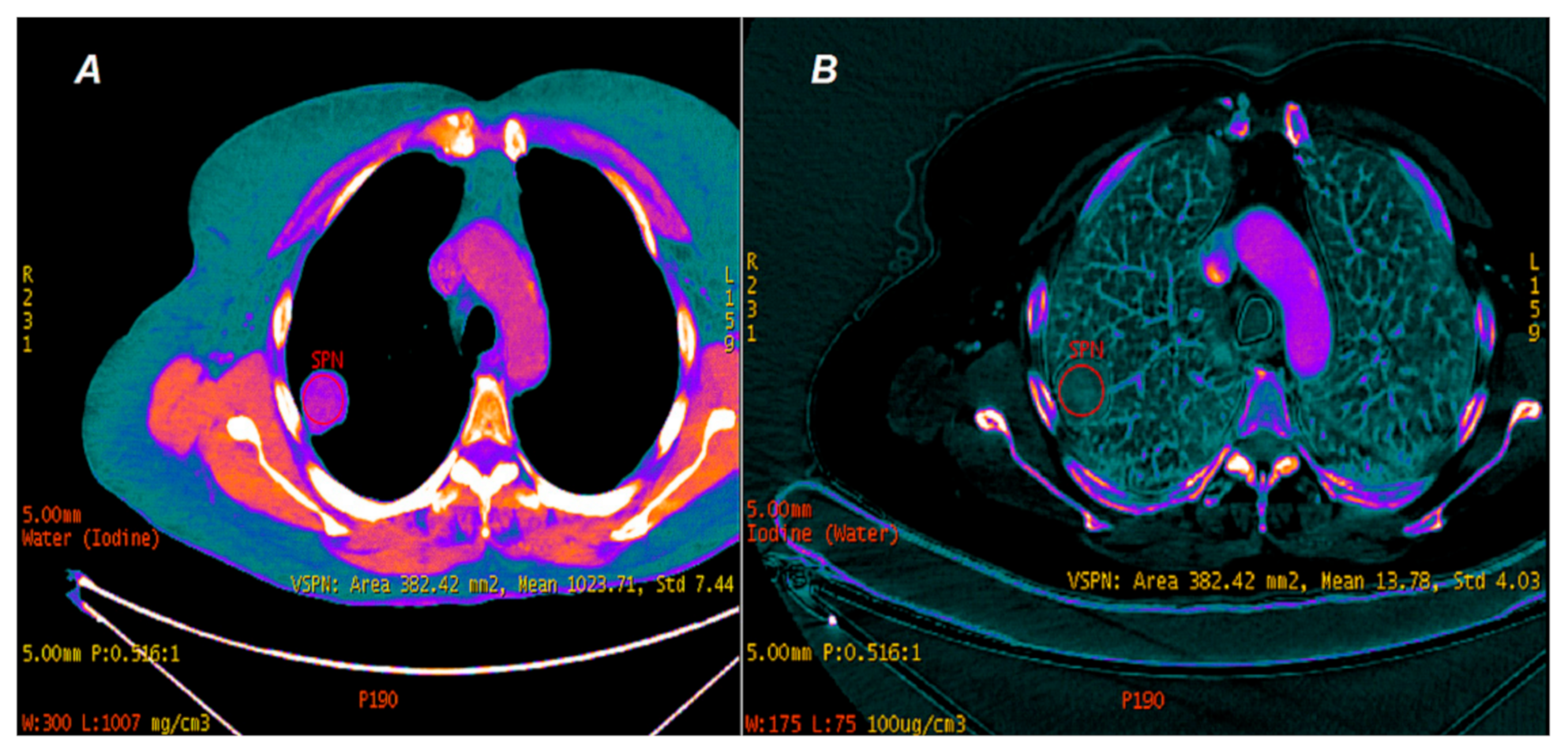
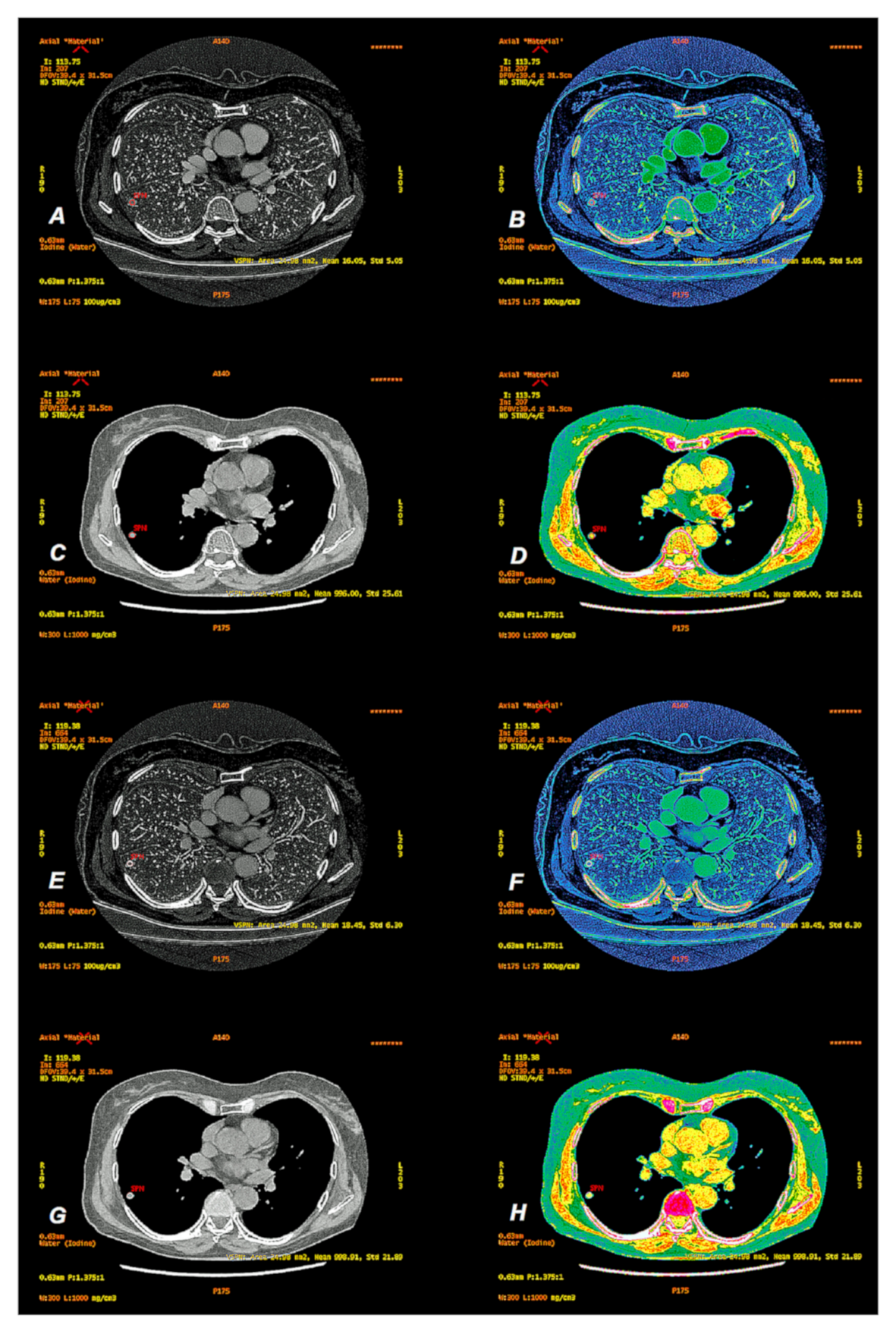
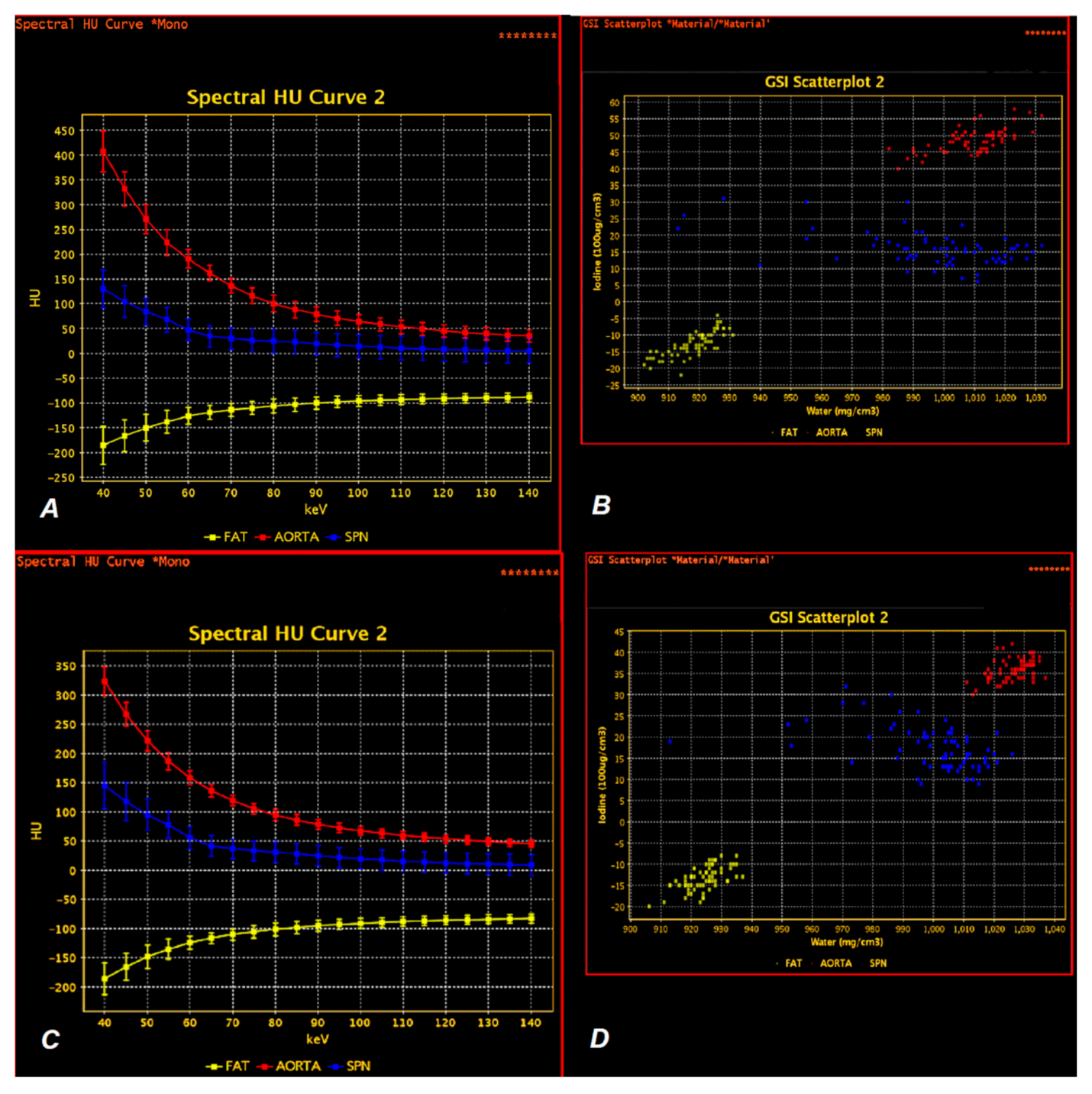
2.3. Data Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Radiation Dose
3.1.1. Photon Interaction with Iodine Contrast Agent Accumulated in Lung Tumors
3.1.2. Comparison of Iodine Concentration in IC Maps, Water Concentration (WC) and Radiation Absorption in Lung Tumors in AP and VP of DECT Examination
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Röntgen, W.C. On a New Kind of Rays. Science 1896, 3, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST X-ray Form Factor, Attenuation and Scattering Tables Form Page. Available online: https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/FFast/html/form.html (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- Artico, M.; Spoletini, M.; Fumagalli, L.; Biagioni, F.; Ryskalin, L.; Fornai, F.; Salvati, M.; Frati, A.; Pastore, F.S.; Taurone, S. Egas Moniz: 90 Years (1927–2017) from Cerebral Angiography. Front. Neuroanat. 2017, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessl, E.; Proksa, R. K-Edge Imaging in X-ray Computed Tomography Using Multi-Bin Photon Counting Detectors. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 4679–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halttunen, N.; Lerouge, F.; Chaput, F.; Vandamme, M.; Karpati, S.; Si-Mohamed, S.; Sigovan, M.; Boussel, L.; Chereul, E.; Douek, P.; et al. Hybrid Nano-GdF3 Contrast Media Allows Pre-Clinical in Vivo Element-Specific K-Edge Imaging and Quantification. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sülzle, D.; Bauser, M.; Frenzel, T.; Jost, G.; Pietsch, H.; Schäfer, M.; Berger, M.; Hassfeld, J.; Schmitt-Willich, H. New Tungsten Cluster Based Contrast Agents for X-ray Computed Tomography. J. Clust. Sci. 2015, 26, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.E.; Macovski, A. Energy-Selective Reconstructions in X-ray Computerized Tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 1976, 21, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrandino, M.N.; Pierre, S.A.; Simmons, W.N.; Paulson, E.K.; Albala, D.M.; Preminger, G.M. First Prize (Tie): Dual-Energy Computed Tomography with Advanced Postimage Acquisition Data Processing: Improved Determination of Urinary Stone Composition. J. Endourol. 2010, 24, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spek, A.; Strittmatter, F.; Graser, A.; Kufer, P.; Stief, C.; Staehler, M. Dual Energy Can Accurately Differentiate Uric Acid-Containing Urinary Calculi from Calcium Stones. World J. Urol. 2016, 34, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.; Henes, J.C.; Fuld, M.K.; Fishman, E.K.; Horger, M.S. Dual-Energy Computed Tomography of the Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Noninvasive Diagnosis of Gout and Quantification of Monosodium Urate in Tendons and Ligaments. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2016, 20, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-R.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, N.R.; Lee, S.-H. Detection of Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Crystal Deposition Disease by Dual-Energy Computed Tomography. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, B.; Kuehling, K.; Kromen, W.; Siebenhandl, P.; Kerl, M.J.; Vogl, T.J.; Bauer, R. Automatic Bone Removal Technique in Whole-Body Dual-Energy CT Angiography: Performance and Image Quality. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, W646–W650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, R.; De Man, B.; Gupta, R. Dual-Energy Computed Tomography: Physical Principles, Approaches to Scanning, Usage, and Implementation: Part 1. Neuroimaging Clin. 2017, 27, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, A.; Parker, R.A.; Manjunathan, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Shah, G.V.; Mukherji, S.K. Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Neck Pathologies: Preliminary Experience Using Spectral Computed Tomography. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2013, 37, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomerantz, S.R.; Kamalian, S.; Zhang, D.; Gupta, R.; Rapalino, O.; Sahani, D.V.; Lev, M.H. Virtual Monochromatic Reconstruction of Dual-Energy Unenhanced Head CT at 65–75 KeV Maximizes Image Quality Compared with Conventional Polychromatic CT. Radiology 2013, 266, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.; Gupta, R.; Levental, M.; Yu, E.; Curtin, H.D.; Forghani, R. Optimal Virtual Monochromatic Images for Evaluation of Normal Tissues and Head and Neck Cancer Using Dual-Energy CT. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forghani, R. Advanced Dual-Energy CT for Head and Neck Cancer Imaging. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2015, 15, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, R. An Update on Advanced Dual-Energy CT for Head and Neck Cancer Imaging. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2019, 19, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, M.; Kawai, T.; Ito, M.; Ogawa, M.; Ohashi, K.; Hara, M.; Shibamoto, Y. Split-Bolus CT-Urography Using Dual-Energy CT: Feasibility, Image Quality and Dose Reduction. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 3160–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Hsu, J.-S.; Jaw, T.-S.; Shih, M.-C.P.; Lee, L.-J.; Tsai, T.-H.; Liu, G.-C. Split-Bolus Portal Venous Phase Dual-Energy CT Urography: Protocol Design, Image Quality, and Dose Reduction. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 205, W492–W501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidinger, B.H.; Anderson, K.R.; Moriarty, E.M.; Costa, D.B.; Gangadharan, S.P.; VanderLaan, P.A.; Bankier, A.A. Size Measurement and T-Staging of Lung Adenocarcinomas Manifesting as Solid Nodules ≤ 30 Mm on CT: Radiology-Pathology Correlation. Acad. Radiol. 2017, 24, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, A.P.; Muenzel, D.; Dangelmaier, J.; Braren, R.; Pfeiffer, F.; Rummeny, E.J.; Noël, P.B.; Fingerle, A.A. Dual-Layer Spectral Computed Tomography: Virtual Non-Contrast in Comparison to True Non-Contrast Images. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 104, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications of Angiogenesis. Nature 2011, 473, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swensen, S.J.; Brown, L.R.; Colby, T.V.; Weaver, A.L. Pulmonary Nodules: CT Evaluation of Enhancement with Iodinated Contrast Material. Radiology 1995, 194, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, P.; Dwamena, B.A.; Kelly, A.M.; Carlos, R.C. Solitary Pulmonary Nodules: Meta-Analytic Comparison of Cross-Sectional Imaging Modalities for Diagnosis of Malignancy. Radiology 2008, 246, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, E.J.; Song, J.-W.; Seo, J.B.; Krauss, B.; Jang, Y.M.; Song, K.-S. Clinical Utility of Dual-Energy CT in the Evaluation of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules: Initial Experience. Radiology 2008, 249, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudarski, S.; Hagelstein, C.; Weis, M.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Apfaltrer, P. Dual-Energy Snap-Shot Perfusion CT in Suspect Pulmonary Nodules and Masses and for Lung Cancer Staging. Eur. J. Radiol. 2015, 84, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.-Q.; Xin, Y.-K.; Jing, Y.; Li, G.-F.; Wang, S.-M.; Rong, W.-C.; Xiao, G.; Lei, X.-B.; Li, B.; Hu, Y.-C.; et al. Iodine Quantification Using Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Differentiating Thymic Tumors. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2018, 42, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennartz, S.; Le Blanc, M.; Zopfs, D.; Große Hokamp, N.; Abdullayev, N.; Laukamp, K.R.; Haneder, S.; Borggrefe, J.; Maintz, D.; Persigehl, T. Dual-Energy CT–Derived Iodine Maps: Use in Assessing Pleural Carcinomatosis. Radiology 2019, 290, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Su, G.-Y.; Hu, H.; Ge, Y.-Q.; Si, Y.; Shen, M.-P.; Xu, X.-Q.; Wu, F.-Y. Radiomics Analysis of Dual-Energy CT-Derived Iodine Maps for Diagnosing Metastatic Cervical Lymph Nodes in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6251–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Duan, J.; Li, C.; Sun, H.; Wang, W. Correlation of Iodine Uptake and Perfusion Parameters between Dual-Energy CT Imaging and First-Pass Dual-Input Perfusion CT in Lung Cancer. Medicine 2017, 96, e7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-J.; Kim, S.H.; Bae, J.S.; Jeon, S.K.; Han, J.K. Can Quantitative Iodine Parameters on DECT Replace Perfusion CT Parameters in Colorectal Cancers? Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 4775–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordic, S.; Puippe, G.D.; Krauss, B.; Klotz, E.; Desbiolles, L.; Lesurtel, M.; Müllhaupt, B.; Pfammatter, T.; Alkadhi, H. Correlation between Dual-Energy and Perfusion CT in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Radiology 2016, 280, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, J.; Lee, S.M.; Do, K.-H.; Lee, J.B.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.-G.; Seo, J.B. Prognostic Value of Radiomic Analysis of Iodine Overlay Maps from Dual-Energy Computed Tomography in Patients with Resectable Lung Cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaup, M.; Scholtz, J.-E.; Engler, A.; Albrecht, M.H.; Bauer, R.W.; Matthias Kerl, J.; Beeres, M.; Lehnert, T.; Vogl, T.J.; Wichmann, J.L. Dual-Energy Computed Tomography Virtual Monoenergetic Imaging of Lung Cancer: Assessment of Optimal Energy Levels. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2016, 40, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Jinzaki, M.; Tanami, Y.; Ueno, A.; Yamada, M.; Kuribayashi, S. Virtual Monochromatic Spectral Imaging with Fast Kilovoltage Switching: Improved Image Quality as Compared with That Obtained with Conventional 120-KVp CT. Radiology 2011, 259, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, M.H.; Trommer, J.; Wichmann, J.L.; Scholtz, J.-E.; Martin, S.S.; Lehnert, T.; Vogl, T.J.; Bodelle, B. Comprehensive Comparison of Virtual Monoenergetic and Linearly Blended Reconstruction Techniques in Third-Generation Dual-Source Dual-Energy Computed Tomography Angiography of the Thorax and Abdomen. Investig. Radiol. 2016, 51, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, J.L.; Nöske, E.-M.; Kraft, J.; Burck, I.; Wagenblast, J.; Eckardt, A.; Frellesen, C.; Kerl, J.M.; Bauer, R.W.; Bodelle, B.; et al. Virtual Monoenergetic Dual-Energy Computed Tomography: Optimization of Kiloelectron Volt Settings in Head and Neck Cancer. Investig. Radiol. 2014, 49, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-J.; Liu, W.; Jin, Z.-Y.; Xue, H.-D.; Wang, Y.-N.; Yu, S.-H.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.-C. Improved Visualization of Gastric Cancer and Increased Diagnostic Performance in Lesion Depiction and Depth Identification Using Monoenergetic Reconstructions from a Novel Dual-Layer Spectral Detector CT. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, e140–e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, R.; Kelly, H.; Yu, E.; Belair, M.; Létourneau-Guillon, L.; Le, H.; Proulx, F.; Ong, T.; Tan, X.; Curtin, H.D.; et al. Low-Energy Virtual Monochromatic Dual-Energy Computed Tomography Images for the Evaluation of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Study of Tumor Visibility Compared with Single-Energy Computed Tomography and User Acceptance. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2017, 41, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenga, L.; Lange, M.; Arendt, C.T.; Yel, I.; Booz, C.; Durden, J.; Leithner, D.; Vogl, T.J.; Albrecht, M.H.; Martin, S.S. Can Dual-Energy CT-Based Virtual Monoenergetic Imaging Improve the Assessment of Hypodense Liver Metastases in Patients With Hepatic Steatosis? Acad. Radiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zopfs, D.; Laukamp, K.R.; Pinto dos Santos, D.; Sokolowski, M.; Große Hokamp, N.; Maintz, D.; Borggrefe, J.; Persigehl, T.; Lennartz, S. Low-KeV Virtual Monoenergetic Imaging Reconstructions of Excretory Phase Spectral Dual-Energy CT in Patients with Urothelial Carcinoma: A Feasibility Study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 116, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, W.U.; Yemin, X.U.; Yongshun, H.A.N.; Xiaofeng, T.A.O. Clinical Application of Gemstone Spectral CT Imaging for Reducing Orbital Metal Artifacts. J. Tissue Eng. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellenberg, R.H.H.; Boomsma, M.F.; van Osch, J.A.C.; Vlassenbroek, A.; Milles, J.; Edens, M.A.; Streekstra, G.J.; Slump, C.H.; Maas, M. Quantifying Metal Artefact Reduction Using Virtual Monochromatic Dual-Layer Detector Spectral CT Imaging in Unilateral and Bilateral Total Hip Prostheses. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 88, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Suo, S.-T.; Zhang, F.; Cheng, J.-J.; Wu, H.-W. Correlation between Dual-Energy Spectral CT Imaging Parameters and Pathological Grades of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 412.e1–412.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zou, H.; Yuan, A.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zuo, M.; Gong, L. A Single Enhanced Dual-Energy CT Scan May Distinguish Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma From Adenocarcinoma During the Venous Phase. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.J.; Gao, J.; Wang, G.L.; Zhang, C.Q.; Shi, H.; Deng, K. Correlation between Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Quantitative Dual-Energy Spectral CT in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Radiol. 2016, 71, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Atom | Z Number | K-Edge Energy (keV) | Absorption |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | 1.36000 × 10−2 | Compton scattering |
| Carbon (Ca) | 6 | 2.83800 × 10−1 | Compton scattering |
| Nitrogen (N) | 7 | 4.01600 × 10−1 | Compton scattering |
| Oxygen (O) | 8 | 5.32000 × 10−1 | Compton scattering |
| Fluorine (F) | 9 | 6.85400 × 10−1 | Compton scattering |
| Sodium (Na) | 11 | 1.07210 × 100 | Compton scattering |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 12 | 1.30500 × 100 | Compton scattering |
| Potassium (K) | 19 | 3.60740 × 100 | Compton scattering |
| Calcium (Ca) | 20 | 4.03810 × 100 | Compton scattering |
| Iron (Fe) | 26 | 7.11200 × 100 | Compton scattering |
| Iodine (I) * | 53 | 3.31694 × 101 | Photoelectric effect |
| Barium (Ba) * | 57 | 3.74406 × 101 | Photoelectric effect |
| Gadolinium (Gd) * | 64 | 5.02391 × 101 | Photoelectric effect |
| Patients (n = 66) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age (y), mean ± SD | 66 ± 11 | |
| Sex (male/female) | 43/23 | |
| Size (mm) ± SD | 21.2 ± 7 | |
| Histopathology (n) | Adenocarcinoma | 22 |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 18 | |
| Inflammatory infiltrations | 11 | |
| Sarcoidosis | 5 | |
| Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma | 3 | |
| Fibroma | 2 | |
| Squamous cell (95%) and neuroendocrine ca. | 1 | |
| Small cell carcinoma | 1 | |
| Hamartoma | 1 | |
| Hematoma | 1 | |
| Tuberculoma | 1 | |
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| 98 patients with a solid lung tumor Written consent for DECT examination with arterial and venous phase (AP and VP) | Exclusion criteria for CT examination (n = 14) |
| Family history of lung cancer (n = 5) Kidney failure (n = 5) Contrast media hypersensitivity (n = 3) Lack of patient’s consent (n = 1) Pregnancy (n = 0) | |
| 84 patients | Exclusion criteria for analysis (n = 18) |
| Lesion of a long-axis diameter larger than 30 mm (n = 8) “Ground-glass” lesion (n = 6) Lack of histopathological confirmation of diagnosis (n = 4) | |
| 66 patients |
| Parameter | Time 35 s. (AP) Mean ± SD * Median, 95% CI | Time 90 s. (VP) Mean ± SD * Median, 95% CI | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
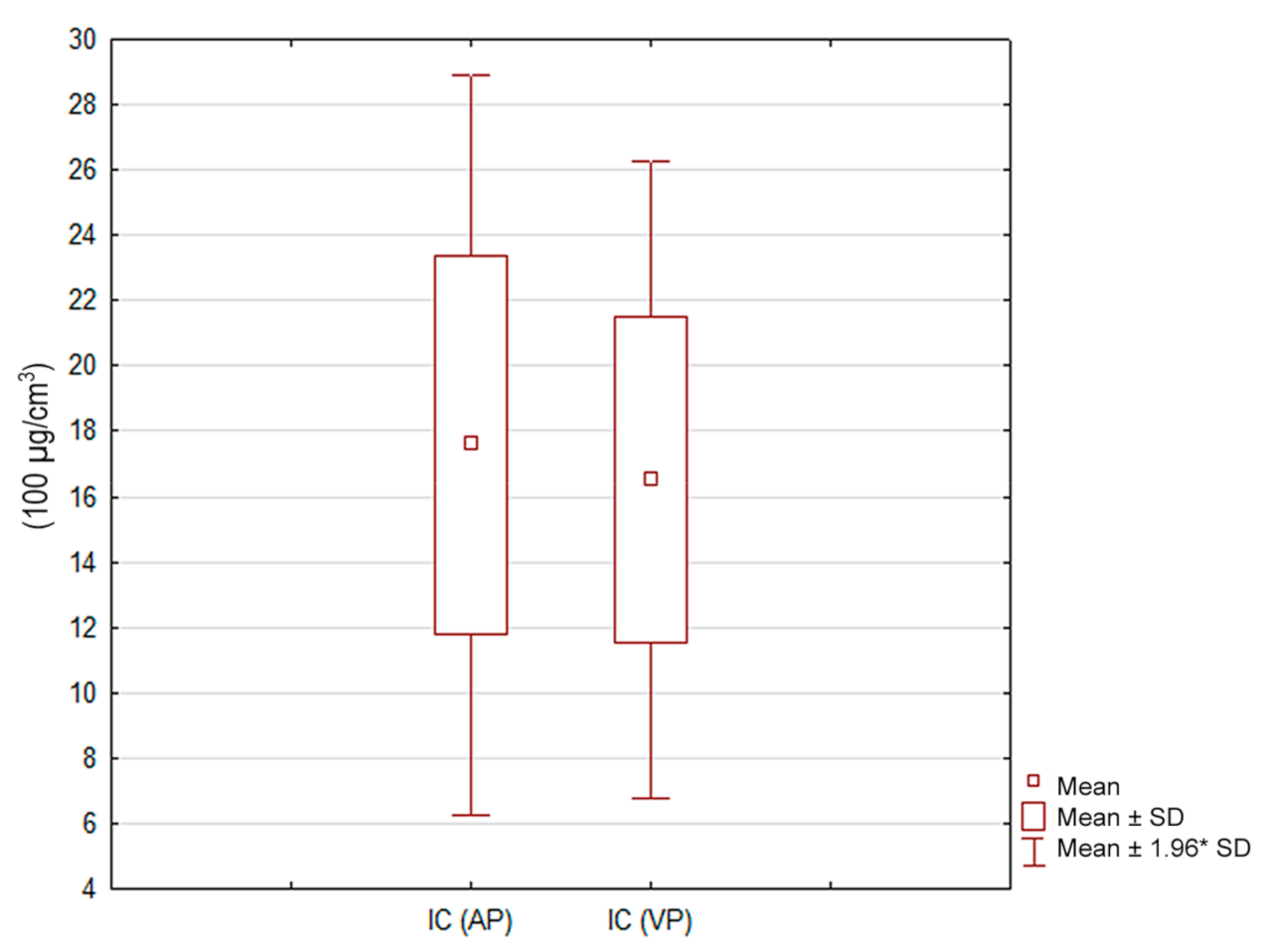
| IC (100 µg/cm3) | 17.6 | 5.8 | 16.5 | 4.98 | 0.25 |
| WC (mg/cm3) | 1010.6 * | 15–21.3 * | 1012 * | 10.9–15.4 * | 0.74 |
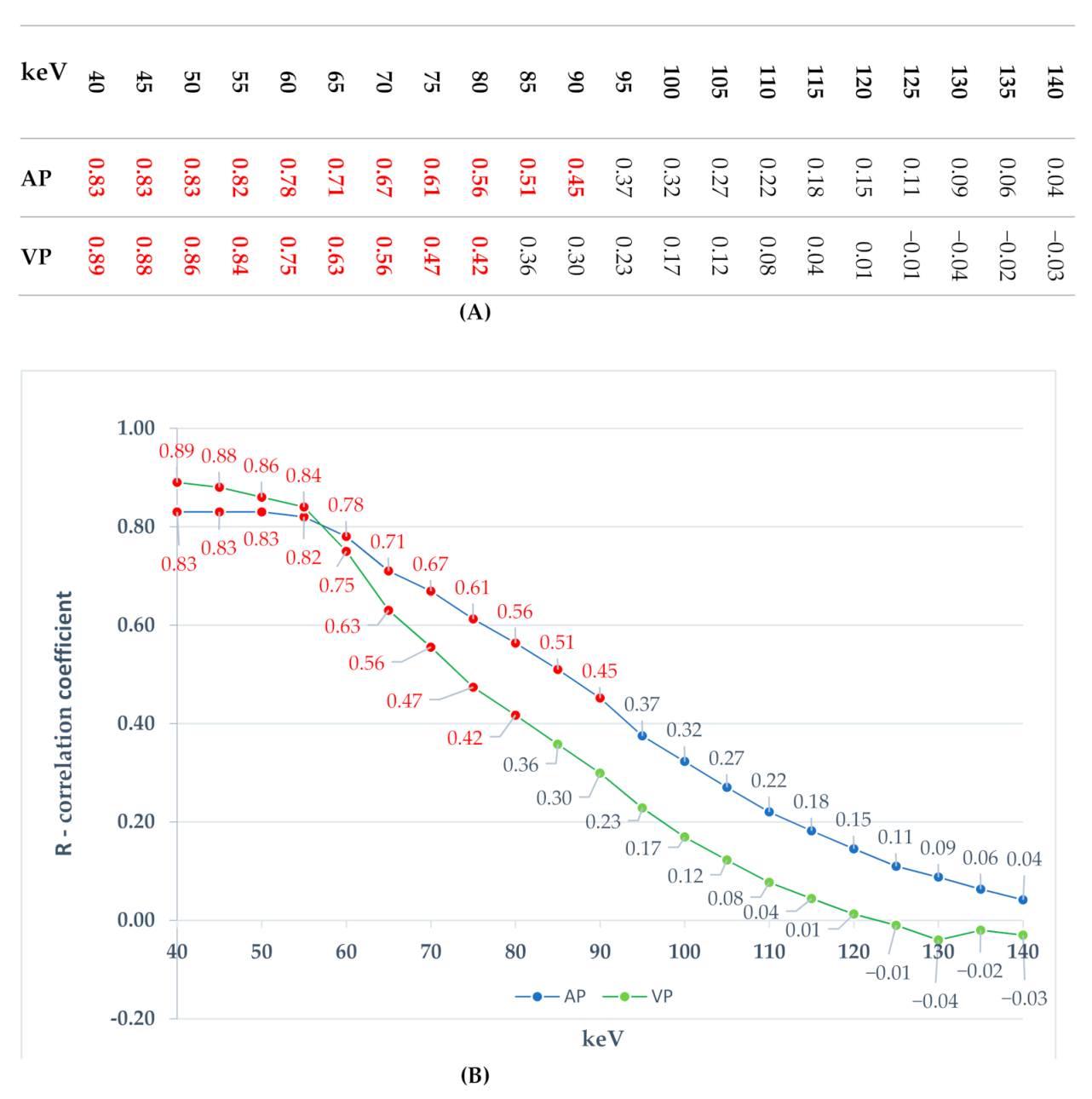
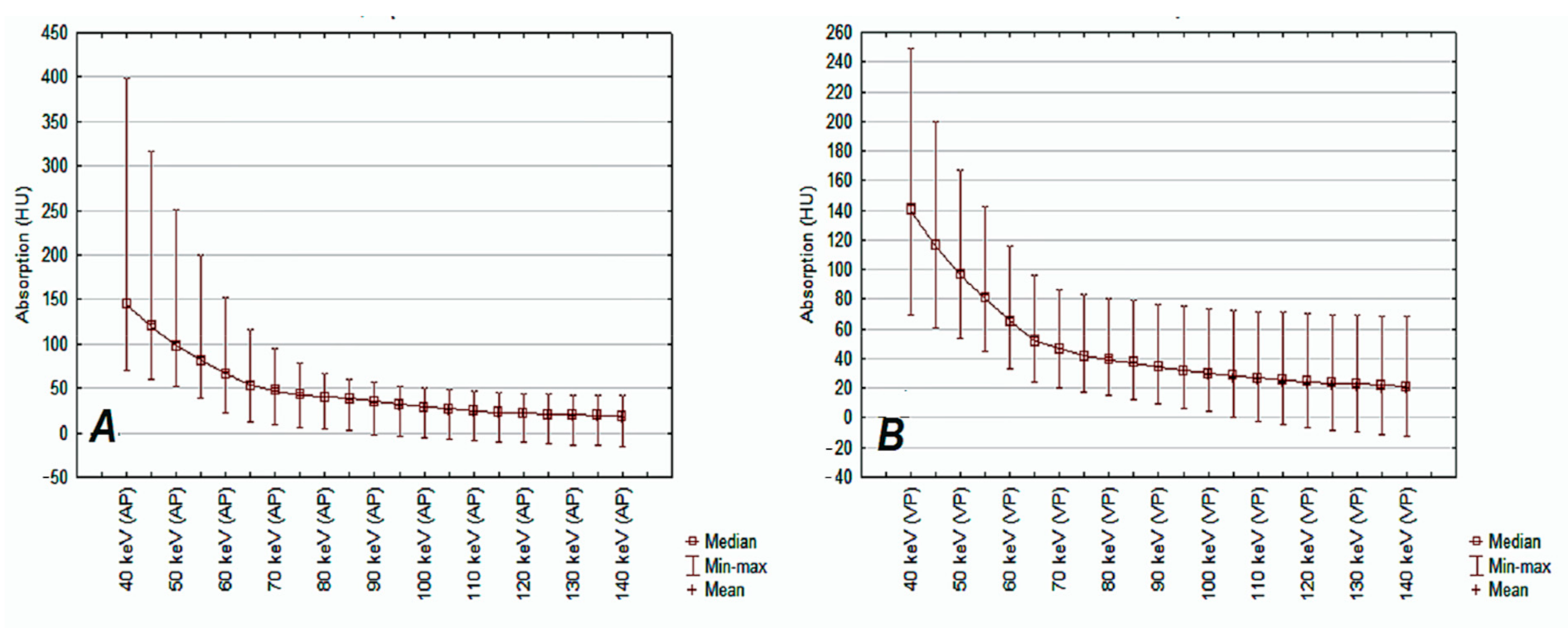
| 40 keV | 149.1 | 58.3 | 144.5 | 44.3 | 0.17 |
| 45 keV | 122.3 | 46.6 | 119.0 | 35.4 | 0.06 |
| 50 keV | 100.7 | 37.4 | 98.6 | 28.5 | 0.10 |
| 55 keV | 84.1 | 30.5 | 82.8 | 23.4 | 0.39 |
| 60 keV | 67.6 | 25.1 | 66.8 | 19.5 | 0.53 |
| 65 keV | 55.8 | 21.4 | 55.4 | 17.2 | 0.71 |
| 70 keV | 49.3 | 18.5 | 49.3 | 15.5 | 0.99 |
| 75 keV | 44.0 | 16.5 | 44.3 | 14.3 | 0.91 |
| 80 keV | 40.1 | 15.1 | 40.8 | 13.5 | 0.78 |
| 85 keV | 36.6 | 14.5 | 37.5 | 13.0 | 0.72 |
| 90 keV | 32.9 | 13.9 | 34.2 | 12.8 | 0.58 |
| 95 keV | 29.7 | 13.5 | 31.3 | 12.7 | 0.48 |
| 100 keV | 27.5 | 13.4 | 29.0 | 12.7 | 0.50 |
| 105 keV | 25.5 | 13.3 | 27.1 | 12.8 | 0.46 |
| 110 keV | 23.6 | 13.3 | 25.4 | 12.9 | 0.44 |
| 115 keV | 22.2 | 13.3 | 24.0 | 12.9 | 0.42 |
| 120 keV | 20.9 | 13.3 | 22.8 | 13.0 | 0.41 |
| 125 keV | 19.9 | 13.2 | 21.8 | 13.1 | 0.42 |
| 130 keV | 18.8 | 13.4 | 21.0 | 13.4 | 0.35 |
| 135 keV | 17.9 | 13.3 | 19.9 | 13.3 | 0.26 |
| 140 keV | 17.4 | 13.3 | 19.3 | 13.3 | 0.39 |
| Correlation | R = | R2 = | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC SPN (AP) (100 µg/cm3)/ Age (Y) | All | 0.29 | All | 0.08 | 0.018 |
| Man | 0.23 | Man | 0.05 | 0.133 | |
| Woman | 0.33 | Woman | 0.10 | 0.127 | |
| IC SPN (AP) (100 µg/cm3)/ Body mass (kg) | All | 0.12 | All | 0.02 | 0.326 |
| Man | 0.03 | Man | 0.00 | 0.848 | |
| Woman | 0.12 | Woman | 0.01 | 0.577 | |
| IC SPN (VP) (100 µg/cm3)/ Age (Y) | All | 0.32 | All | 0.10 | 0.007 |
| Man | 0.27 | Man | 0.07 | 0.074 | |
| Woman | 0.33 | Woman | 0.11 | 0.118 | |
| IC SPN (VP) (100 µg/cm3)/ Body mass (kg) | All | 0.15 | All | 0.02 | 0.215 |
| Man | 0.02 | Man | 0.00 | 0.914 | |
| Woman | 0.09 | Woman | 0.00 | 0.694 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zegadło, A.; Żabicka, M.; Różyk, A.; Więsik-Szewczyk, E. A New Outlook on the Ability to Accumulate an Iodine Contrast Agent in Solid Lung Tumors Based on Virtual Monochromatic Images in Dual Energy Computed Tomography (DECT): Analysis in Two Phases of Contrast Enhancement. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091870
Zegadło A, Żabicka M, Różyk A, Więsik-Szewczyk E. A New Outlook on the Ability to Accumulate an Iodine Contrast Agent in Solid Lung Tumors Based on Virtual Monochromatic Images in Dual Energy Computed Tomography (DECT): Analysis in Two Phases of Contrast Enhancement. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(9):1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091870
Chicago/Turabian StyleZegadło, Arkadiusz, Magdalena Żabicka, Aleksandra Różyk, and Ewa Więsik-Szewczyk. 2021. "A New Outlook on the Ability to Accumulate an Iodine Contrast Agent in Solid Lung Tumors Based on Virtual Monochromatic Images in Dual Energy Computed Tomography (DECT): Analysis in Two Phases of Contrast Enhancement" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 9: 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091870
APA StyleZegadło, A., Żabicka, M., Różyk, A., & Więsik-Szewczyk, E. (2021). A New Outlook on the Ability to Accumulate an Iodine Contrast Agent in Solid Lung Tumors Based on Virtual Monochromatic Images in Dual Energy Computed Tomography (DECT): Analysis in Two Phases of Contrast Enhancement. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(9), 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091870






