SARS-CoV-2 Renal Impairment in Critical Care: An Observational Study of 42 Cases (Kidney COVID)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Definitions
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethics and Approval and Consent to Participate
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Kidney Abnormalities during ICU Stay
3.3. Kidney Abnormalities on ICU Discharge
3.4. Prognosis Associated with AKI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, W.; Ni, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.; Ou, C.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019(COVID-19) outbreak in China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phua, J.; Weng, L.; Ling, L.; Egi, M.; Lim, C.M.; Divatia, J.V.; Shrestha, B.R.; Arabi, Y.M.; Ng, J.; Gomersall, C.D.; et al. Intensive care management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Challenges and recommendations. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatraju, P.K.; Ghassemieh, B.J.; Nichols, M.; Kim, R.; Jerome, K.R.; Nalla, A.K.; Greninger, A.L.; Pipavath, S.; Wurfel, M.M.; Evans, L.; et al. Covid-19 in Critically Ill Patients in the Seattle Region—Case Series. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72314 Cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arentz, M.; Yim, E.; Klaff, L.; Lokhandwala, S.; Riedo, F.X.; Chong, M.; Lee, M. Characteristics and Outcomes of 21 Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 in Washington State. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1612–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thakur, V.; Ratho, R.K.; Kumar, P.; Bhatia, S.K.; Bora, I.; Mohi, G.K.; Saxena, S.K.; Devi, M.; Yadav, D.; Mehariya, S. Multi-Organ Involvement in COVID-19: Beyond Pulmonary Manifestations. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manganelli, F.; Vargas, M.; Iovino, A.; Iacovazzo, C.; Santoro, L.; Servillo, G. Brainstem involvement and respiratory failure in COVID-19. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 1663–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarre, P.; Dumas, G.; Dupont, T.; Darmon, M.; Azoulay, E.; Zafrani, L. Acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.J.; Luo, Y.; Phua, K.; Choong, A.M.T.L. Acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 647–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Yu, C.; Ma, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; Yao, Y.; et al. Renal Involvement and Early Prognosis in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, S.H.; Kopp, J.B. COVID-19–Associated Collapsing Glomerulopathy: An Emerging Entity. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.W.; Xu, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, W.; Wang, L.-H.; Cui, X.G. gang Identification of a potential mechanism of acute kidney injury during the COVID-19 outbreak: A study based on single-cell transcriptome analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, H.; Yang, M.; Wan, C.; Yi, L.X.; Tang, F.; Zhu, H.Y.; Yi, F.; Yang, H.C.; Fogo, A.B.; Nie, X.; et al. Renal histopathological analysis of 26 postmortem findings of patients with COVID-19 in China. Kidney Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capuano, I.; Buonanno, P.; Riccio, E.; Pisani, A. Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19 Pandemic. Nephron 2020, 144, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmon, M.; Clec’h, C.; Adrie, C.; Argaud, L.; Allaouchiche, B.; Azoulay, E.; Bouadma, L.; Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; Haouache, H.; Schwebel, C.; et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome and risk of AKI among critically ill patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNicholas, B.A.; Rezoagli, E.; Pham, T.; Madotto, F.; Guiard, E.; Fanelli, V.; Bellani, G.; Griffin, M.D.; Ranieri, M.; Laffey, J.G. Impact of Early Acute Kidney Injury on Management and Outcome in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Secondary Analysis of a Multicenter Observational Study. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 47, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Shu, H.; Xia, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Fang, M.; et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin definition. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summary of Recommendation Statements. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 8–12. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Ge, S.; Xu, G. Kidney disease is associated with in-hospital death of patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, S.H.; Shen, C. Augmented renal clearance in critical illness: An important consideration in drug dosing. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robins, J.M.; Hernán, M.Á.; Brumback, B. Marginal structural models and causal inference in epidemiology. Epidemiology 2000, 11, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulouse, E.; Masseguin, C.; Lafont, B.; McGurk, G.; Harbonn, A.; Roberts, J.A.; Granier, S.; Dupeyron, A.; Bazin, J.E. French legal approach to clinical research. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2018, 37, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Revel, M.P.; Parkar, A.P.; Prosch, H.; Silva, M.; Sverzellati, N.; Gleeson, F.; Brady, A. COVID-19 patients and the radiology department–advice from the European Society of Radiology (ESR) and the European Society of Thoracic Imaging (ESTI). Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4903–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grasselli, G.; Zangrillo, A.; Zanella, A.; Antonelli, M.; Cabrini, L.; Castelli, A.; Cereda, D.; Coluccello, A.; Foti, G.; Fumagalli, R.; et al. Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, S.; Hirsch, J.S.; Narasimhan, M.; Crawford, J.M.; McGinn, T.; Davidson, K.W.; Barnaby, D.P.; Barnaby, D.P.; Becker, L.B.; Chelico, J.D.; et al. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes among 5700 Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoulay, E.; Lemiale, V.; Mourvillier, B.; Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; Schwebel, C.; Ruckly, S.; Argaud, L.; Cohen, Y.; Souweine, B.; Papazian, L.; et al. Management and outcomes of acute respiratory distress syndrome patients with and without comorbid conditions. Intensive Care Med. 2018, 44, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, O.; Gaut, J.P.; Watanabe, E.; To, K.; Fagley, R.E.; Sato, B.; Jarman, S.; Efimov, I.R.; Janks, D.L.; Srivastava, A.; et al. Mechanisms of cardiac and renal dysfunction in patients dying of sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Gomez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury revisited: Pathophysiology, prevention and future therapies. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2014, 20, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michard, F.; Vieillard-Baron, A. Critically ill patients with COVID-19: Are they hemodynamically unstable and do we know why? Intensive Care Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.S.; Wang, C.Y.; Pan, S.C.; Huang, T.M.; Lin, M.C.; Lai, C.F.; Wu, C.H.; Wu, V.C.; Chien, K.L.; Ko, W.J.; et al. Risk of developing severe sepsis after acute kidney injury: A population-based cohort study. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellomo, R.; Ronco, C.; Mehta, R.L.; Asfar, P.; Boisramé-Helms, J.; Darmon, M.; Diehl, J.L.; Duranteau, J.; Hoste, E.A.J.; Olivier, J.B.; et al. Acute kidney injury in the ICU: From injury to recovery: Reports from the 5th Paris International Conference. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, S.; Imai, K.; Kawano, S.; Ikeda, M.; Kodama, T.; Miyoshi, K.; Obinata, H.; Mimura, S.; Kodera, T.; Kitagaki, M.; et al. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in 104 people with SARS-CoV-2 infection on the Diamond Princess cruise ship: A retrospective analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, E.J.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; Bacon, S.; Bates, C.; Morton, C.E.; Curtis, H.J.; Mehrkar, A.; Evans, D.; Inglesby, P.; et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 2020, 584, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.L.; Kalra, P.R.; Petrie, M.C.; Mark, P.B.; Tomlinson, L.A.; Tomson, C.R.V. Change in renal function associated with drug treatment in heart failure: National guidance. Heart 2019, 105, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, M.J.D.; McAuley, D.F.; Perkins, G.D.; Barrett, N.; Blackwood, B.; Boyle, A.; Chee, N.; Connolly, B.; Dark, P.; Finney, S.; et al. Guidelines on the management of acute respiratory distress syndrome. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leisman, D.E.; Deutschman, C.S.; Legrand, M. Facing COVID-19 in the ICU: Vascular dysfunction, thrombosis, and dysregulated inflammation. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1105–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.S.; Ng, J.H.; Ross, D.W.; Sharma, P.; Shah, H.H.; Barnett, R.L.; Hazzan, A.D.; Fishbane, S.; Jhaveri, K.D. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19. Kidney Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joannidis, M.; Forni, L.G.; Klein, S.J.; Honore, P.M.; Kashani, K.; Ostermann, M.; Prowle, J.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Cantaluppi, V.; Darmon, M.; et al. Lung–kidney interactions in critically ill patients: Consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 21 Workgroup. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 654–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panitchote, A.; Mehkri, O.; Hasting, A.; Hanane, T.; Demirjian, S.; Torbic, H.; Mireles-Cabodevila, E.; Krishnan, S.; Duggal, A. Factors associated with acute kidney injury in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimes-Stigare, C.; Frumento, P.; Bottai, M.; Mårtensson, J.; Martling, C.R.; Walther, S.M.; Karlström, G.; Bell, M. Evolution of chronic renal impairment and long-term mortality after de novo acute kidney injury in the critically ill; a Swedish multi-centre cohort study. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bilbao-Meseguer, I.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Barrasa, H.; Isla, A.; Solinís, M.Á. Augmented Renal Clearance in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udy, A.A.; Dulhunty, J.M.; Roberts, J.A.; Davis, J.S.; Webb, S.A.R.; Bellomo, R.; Gomersall, C.; Shirwadkar, C.; Eastwood, G.M.; Myburgh, J.; et al. Association between augmented renal clearance and clinical outcomes in patients receiving β-lactam antibiotic therapy by continuous or intermittent infusion: A nested cohort study of the BLING-II randomised, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.A.; Lipman, J. Optimal doripenem dosing simulations in critically ill nosocomial pneumonia patients with obesity, augmented renal clearance, and decreased bacterial susceptibility. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.Y.; Park, B.H.; Hong, S.B.; Koh, Y.; Suh, G.Y.; Jeon, K.; Koh, S.O.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Choi, H.S.; et al. Acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with pandemic influenza A pneumonia 2009 in Korea: A multicenter study. J. Crit. Care 2011, 26, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villacrés, S.M.; Medar, S.S.; Aydin, S.I. Acute Kidney Injury in Children with Acute Respiratory Failure. Clin. Pediatr. (Phila). 2018, 57, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Overall (n = 42) | Non-AKI (n = 18) | AKI (n = 24) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic and Clinical Data | ||||
| Age (years) | 61.50 (54.25, 65.00) | 60.50 (49.75, 66.00) | 61.50 (55.50, 65.00) | 0.684 |
| Male (%) | 34 (81.0) | 15 (83.3) | 19 (79.2) | 1.000 |
| BMI (kg·m−2) | 27.25 (24.30, 30.00) | 25.10 (23.80, 27.10) | 29.40 (27.40, 30.90) | 0.009 |
| No comorbidities (%) | 17 (40.5) | 7 (38.9) | 10 (41.7) | 1.000 |
| CKD (%) | 7 (16.7) | 2 (11.1) | 5 (20.8) | 0.679 |
| SOFA score | 7.00 (4.00, 9.75) | 4.50 (3.00, 8.50) | 8.00 (6.00, 11.25) | 0.134 |
| Biological Data | ||||
| CRP (mg·L−1) | 246.15(144.88, 300.20) | 167.00 (140.52, 275.75) | 274.30 (213.85, 330.12) | 0.045 |
| Procalcitonin (ng·mL−1) | 1.01 (0.29, 2.50) | 0.27 (0.13, 0.91) | 1.56 (0.62, 3.70) | 0.015 |
| Confirmed concurrent infection | 12 (28.6) | 1 (5.6) | 11 (45.8) | 0.005 |
| GFR by MDRD (mL·min−1) | 87.72 (64.71, 117.29) | 91.80 (72.38, 135.85) | 82.47 (54.53, 102.27) | 0.213 |
| Creatinine (µmol·L−1) | 76.50 (61.75, 100.75) | 74.50 (54.25, 93.50) | 82.00 (69.25, 118.50) | 0.208 |
| ARC (%) | 10 (23.8) | 6 (33.3) | 4 (16.7) | 0.281 |
| pH | 7.41 (7.34, 7.47) | 7.44 (7.40, 7.48) | 7.35 (7.29, 7.44) | 0.024 |
| PEEP (cm H2O) | 12.00 (8.25, 12.00) | 8.00 (8.00, 12.00) | 12.00 (10.00, 14.00) | 0.027 |
| PaCO2 (mm Hg) | 40.00 (34.00, 44.00) | 35.00 (32.25, 40.75) | 42.00 (35.00, 47.50) | 0.027 |
| PaO2/FiO2 Ratio | 140.00 (103.75, 172.86) | 112.50 (95.75, 148.25) | 148.00 (113.12, 182.86) | 0.124 |
| Radiological Characteristic | ||||
| European Society of Radiology score | ||||
| Grade 1 | 1 (3.8) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | 0.958 |
| Grade 2 | 5 (19.2) | 2 (18.2) | 3 (20.0) | |
| Grade 3 | 7 (26.9) | 4 (36.4) | 3 (20.0) | |
| Grade 4 | 11 (42.3) | 4 (36.4) | 7 (46.7) | |
| Grade 5 | 2 (7.7) | 1 (9.1) | 1 (6.7) | |
| Overall (n = 34) | Non-AKI (n = 15) | AKI (n = 19) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days from ICU admission | 8.00 (6.00, 10.00) | 8.00 (6.00, 10.00) | 8.00 (5.50, 10.00) | 0.958 |
| Creatinine clearance (mL·min−1) | 96.21 (67.69, 126.41) | 126.41 (105.48, 157.48) | 68.73 (41.52, 86.17) | <0.001 |
| ARC (%) | 9 (31.0) | 7 (53.8) | 2 (12.5) | 0.041 |
| KDIGO (%) | 0.002 | |||
| 0 | 24 (70.6) | 15 (100.0) | 9 (47.4) | |
| 1 | 4 (11.8) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (21.1) | |
| 2 | 1 (2.9) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.3) | |
| 3 | 5 (14.7) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (26.3) | |
| Renal Impairment | ||||
| Hypovolemia (%) | 15 (48.4) | 8 (57.1) | 7 (41.2) | 0.479 |
| Intrinsic kidney injury (%) | 0.211 | |||
| Glomerular | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
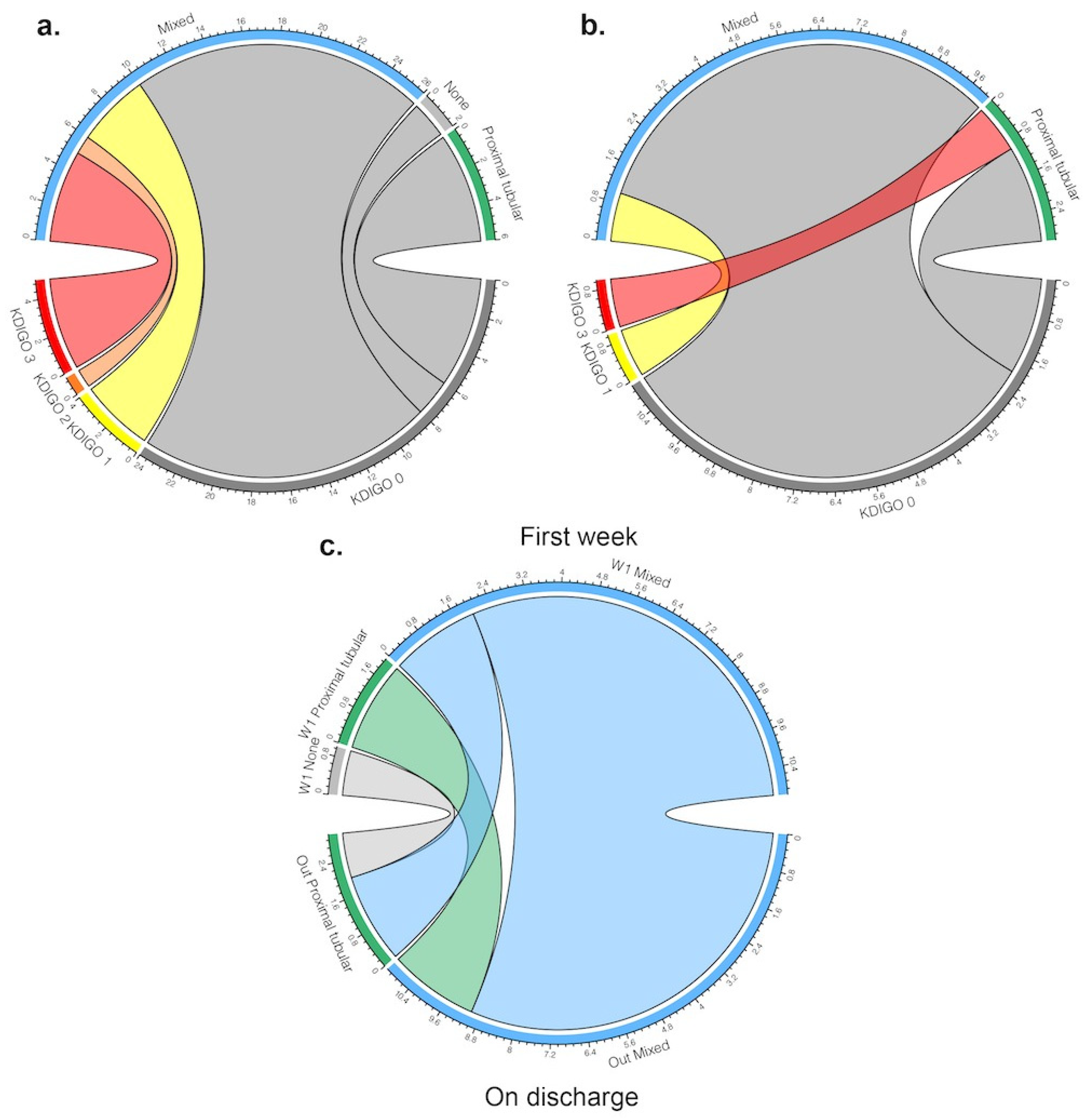
| Mixed | 26 (76.5) | 10 (66.7) | 16 (84.2) | |
| Proximal tubular | 6 (17.6) | 3 (20.0) | 3 (15.8) | |
| Tubular acidosis | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| None | 2 (5.9) | 2 (13.3) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Overall (n = 16) | Non-AKI (n = 7) | AKI (n = 9) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days from ICU admission | 20.00 (15.75, 23.25) | 20.00 (15.00, 22.50) | 20.00 (19.00, 23.00) | 0.749 |
| Creatinine clearance (mL·min−1) | 113.49 (69.30, 142.07) | 139.90 (81.20, 143.75) | 101.11 (50.37, 133.69) | 0.372 |
| ARC (%) | 6 (50.0) | 3 (60.0) | 3 (42.9) | 1.000 |
| KDIGO (%) | 0.070 | |||
| 0 | 10 (71.4) | 7 (100.0) | 3 (42.9) | |
| 1 | 2 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (28.6) | |
| 2 | 1 (7.1) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (14.3) | |
| 3 | 1 (7.1) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (14.3) | |
| Renal Impairment | ||||
| Hypovolemia (%) | 5 (35.7) | 2 (28.6) | 3 (42.9) | 1.000 |
| Intrinsic kidney injury (%) | 1.000 | |||
| Glomerular | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Mixed | 12 (75.0) | 5 (71.4) | 7 (77.8) | |
| Proximal tubular | 4 (25.0) | 2 (28.6) | 2 (22.2) | |
| Tubular acidosis | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| None | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Overall (n = 42) | Non-AKI (n = 18) | AKI (n = 24) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kidney Function during ICU Stay | ||||
| ARC (%) | 23 (54.8) | 16 (88.9) | 7 (29.2) | <0.001 |
| KDIGO | ||||
| KDIGO 0 (%) | 18 (42.9) | 18 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| KDIGO 1 (%) | 12 (28.6) | 0 (0.0) | 12 (50.0) | |
| KDIGO 2 (%) | 3 (7.1) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (12.5) | |
| KDIGO 3 (%) | 9 (21.4) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (37.5) | |
| Organ Support during ICU Stay | ||||
| Length of mechanical ventilation (days) | 19.00 (11.00, 28.00) | 17.00 (6.25, 23.75) | 22.00 (12.00, 34.00) | 0.173 |
| Norepinephrine (patients) | 33 (80.5) | 14 (77.8) | 19 (82.6) | 0.713 |
| Dobutamine | 1 (2.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.2) | 1.000 |
| Catecholamine duration (days) | 5.00 (1.00, 10.00) | 2.00 (1.00, 5.50) | 7.00 (3.50, 14.50) | 0.022 |
| Dialysis (%) | 9 (21.4) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (37.5) | 0.005 |
| Septic shock | 13 (31.0) | 2 (11.1) | 11 (45.8) | 0.021 |
| Infection during ICU stay | 28 (66.7) | 7 (38.9) | 21 (87.5) | 0.002 |
| Prognosis | ||||
| Creatinine clearance < 60 mL·min−1 on ICU discharge (%) | 11 (27.5) | 0 (0.0) | 11 (45.8) | 0.001 |
| ICU LOS (days) | 19.50 (14.00, 33.25) | 20.00 (13.75, 30.75) | 19.50 (15.50, 36.25) | 0.507 |
| ICU mortality (%) | 8 (19.0) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (33.3) | 0.007 |
| Outcome | Factor | Crude | IPTW | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value * | ||
| AKI | CKD | 2.11 (0.39–16.11) | 0.41 | 5.97 (2.1–19.69) | 0.00149 |
| Diabetes | 1.17 (0.28–5.32) | 0.834 | 0.86 (0.36–2.01) | 0.722 | |
| Chronic high blood pressure | 1.06 (0.31–3.67) | 0.929 | 0.75 (0.32–1.76) | 0.514 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molina Barragan, A.-M.; Pardo, E.; Galichon, P.; Hantala, N.; Gianinazzi, A.-C.; Darrivere, L.; Tsai, E.S.; Garnier, M.; Bonnet, F.; Fieux, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Renal Impairment in Critical Care: An Observational Study of 42 Cases (Kidney COVID). J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081571
Molina Barragan A-M, Pardo E, Galichon P, Hantala N, Gianinazzi A-C, Darrivere L, Tsai ES, Garnier M, Bonnet F, Fieux F, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Renal Impairment in Critical Care: An Observational Study of 42 Cases (Kidney COVID). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(8):1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081571
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolina Barragan, Antoine-Marie, Emmanuel Pardo, Pierre Galichon, Nicolas Hantala, Anne-Charlotte Gianinazzi, Lucie Darrivere, Eileen S. Tsai, Marc Garnier, Francis Bonnet, Fabienne Fieux, and et al. 2021. "SARS-CoV-2 Renal Impairment in Critical Care: An Observational Study of 42 Cases (Kidney COVID)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 8: 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081571
APA StyleMolina Barragan, A.-M., Pardo, E., Galichon, P., Hantala, N., Gianinazzi, A.-C., Darrivere, L., Tsai, E. S., Garnier, M., Bonnet, F., Fieux, F., & Verdonk, F. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 Renal Impairment in Critical Care: An Observational Study of 42 Cases (Kidney COVID). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(8), 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081571






