Flecainide How and When: A Practical Guide in Supraventricular Arrhythmias
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Flecainide Pharmacology
2.1. Pharmacokinetics
2.2. Pharmacodynamics
2.3. Controlled Release Flecainide
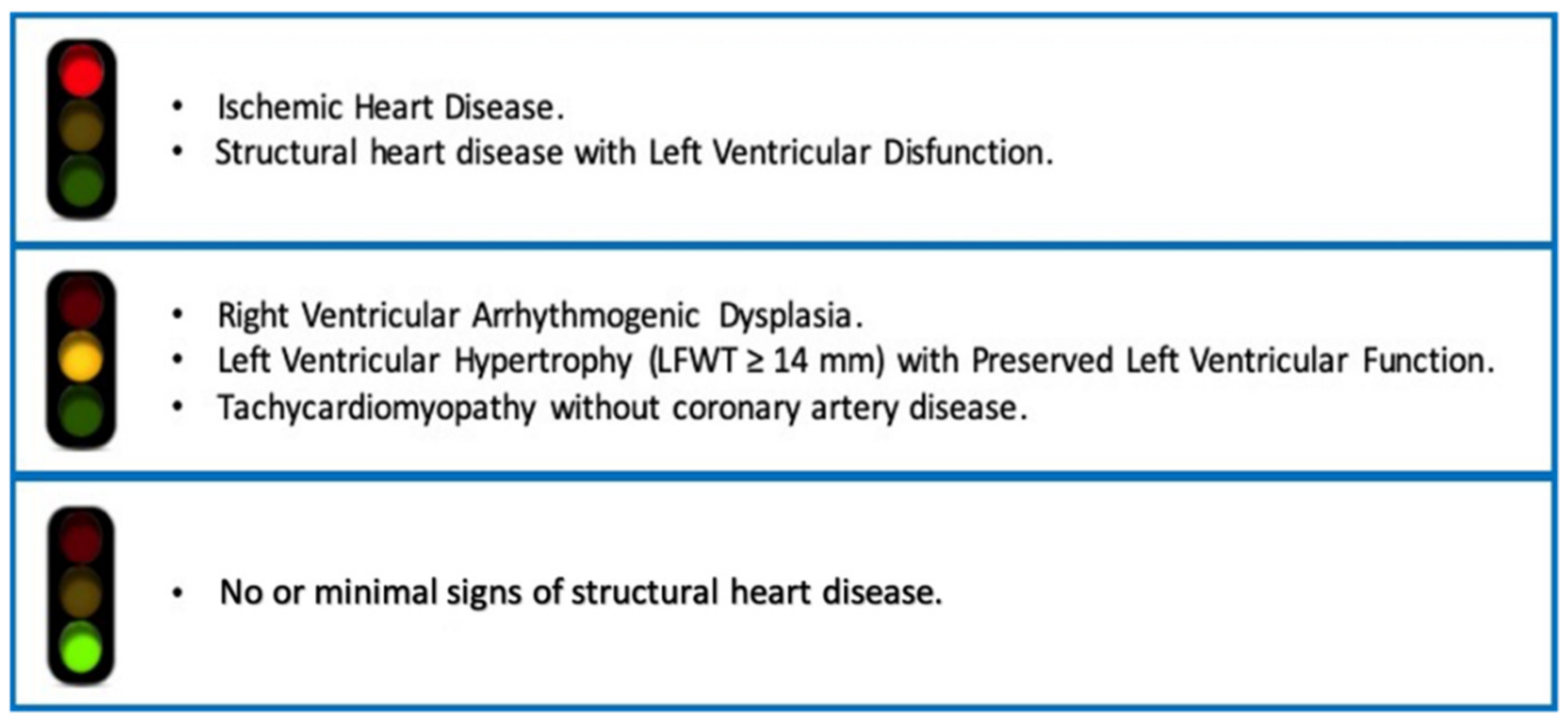
3. What Does “Structural Heart Disease” Mean? A Critical View
4. Safety Data
4.1. Patients with Pacemaker and Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator
4.2. Patients with Sinus Bradycardia and/or AV-IV Conduction Disturbances
4.3. Flecainide in Association with Other Antiarrhythmic Drugs
4.4. Flecainide in Pregnancy and in Pediatric Population
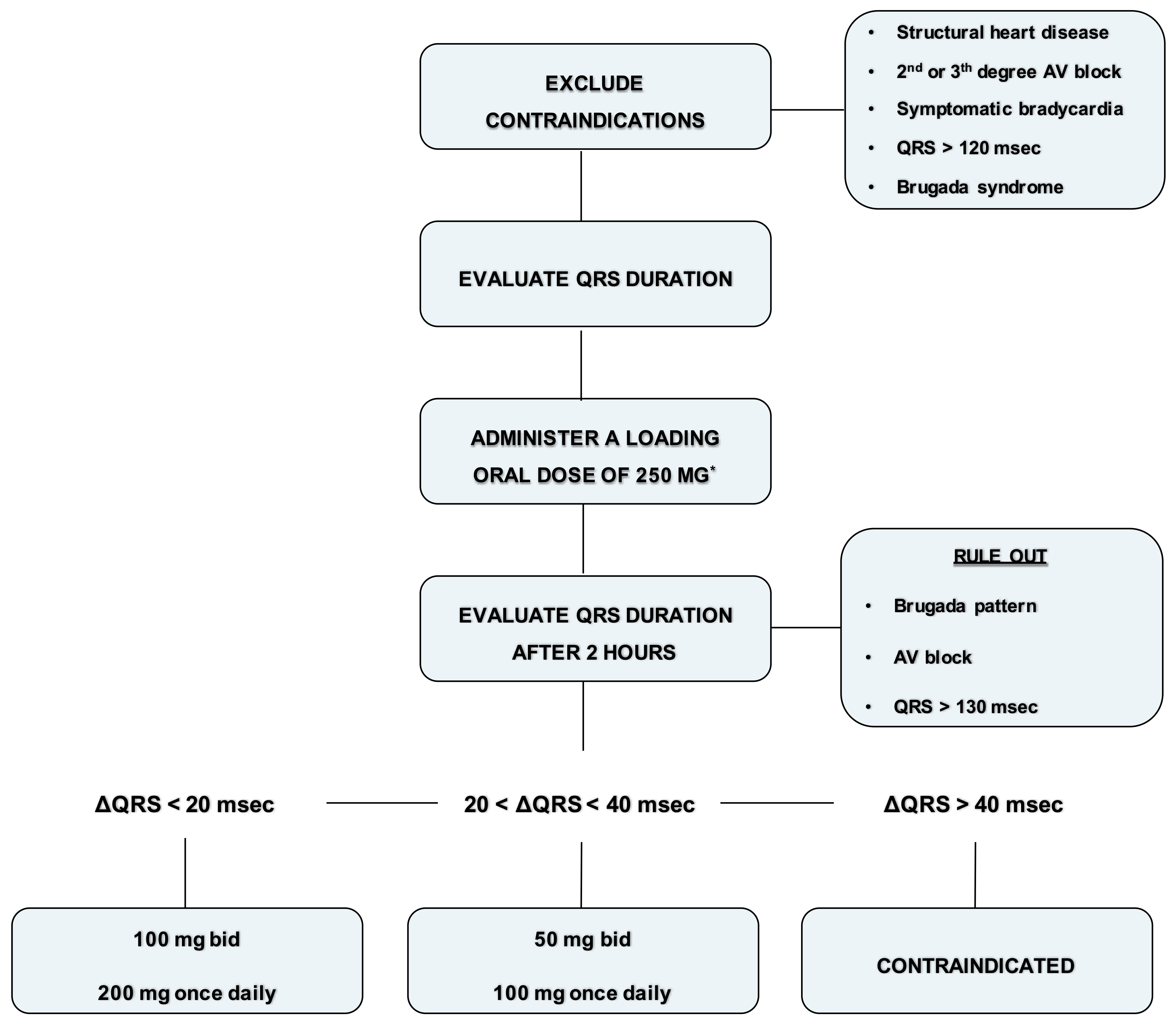
5. Vademecum for the Management of Flecainide
- Exclude contraindications (structural heart disease, symptomatic bradycardia, second degree or superior AV block, QRS > 120 ms or Brugada syndrome).
- Record an ECG with a paper speed of 50 mm/sec and calculate the QRS duration (1 mm = 20 ms).
- Administer a loading oral dose of 250 mg (200 mg if the weight is lower than 70 kg).
- At plasma concentration peak, after 90–120 min, evaluate blood pressure and record an ECG with a paper speed of 50 mm/s and calculate the QRS duration.
- Rule out Brugada ECG pattern and AV block.
- If the QRS duration is increased within 20 ms, prescribe 100 mg twice daily or 200 mg once daily. Check again the ECG after one week.
- If the QRS duration is increased between 20 and 40 ms or is wider than 120 ms, prescribe 50 mg twice daily or 100 mg once daily. Check again the ECG after 5 days.
- If the QRS duration is increased more than 40 ms or is wider than 130 ms, or a Brugada pattern is detected, consider flecainide contraindicated in that patient.
6. Flecainide in Atrial Fibrillation
6.1. Flecainide in Converting Recent Onset of Atrial Fibrillation
6.2. Pre-Treatment with Flecainide in Patients Undergoing Electrical Cardioversion
6.3. Flecainide in Long Term Rhythm Control
7. Flecainide in Other Supraventricular Arrhythmias
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | Atrial Fibrillation |
| AMI | Acute Myocardial Infarction |
| AV | AtrioVentricular |
| IV | IntraVentricular |
| LV | Left Ventricular |
| SVT | SupraVentricular Tachycardia |
| VT | Ventricular Tachycardia |
References
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation Developed in Collaboration with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, ehaa612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Rocca, D.G.; Mohanty, S.; Trivedi, C.; Biase, L.D.; Natale, A. Percutaneous Treatment of Non-Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: A Paradigm Shift from Pulmonary Vein to Non-Pulmonary Vein Trigger Ablation? Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. Rev. 2018, 7, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwlaat, R.; Capucci, A.; Camm, A.J.; Olsson, S.B.; Andresen, D.; Davies, D.W.; Cobbe, S.; Breithardt, G.; Le Heuzey, J.-Y.; Prins, M.H.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation Management: A Prospective Survey in ESC Member Countries. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 2422–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saksena, S.; Slee, A.; Waldo, A.L.; Freemantle, N.; Reynolds, M.; Rosenberg, Y.; Rathod, S.; Grant, S.; Thomas, E.; Wyse, D.G. Cardiovascular Outcomes in the AFFIRM Trial (Atrial Fibrillation Follow-Up Investigation of Rhythm Management). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 1975–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen LaPointe, N.M.; Dai, D.; Thomas, L.; Piccini, J.P.; Peterson, E.D.; Al-Khatib, S.M. Comparisons of Hospitalization Rates Among Younger Atrial Fibrillation Patients Receiving Different Antiarrhythmic Drugs. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2015, 8, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echt, D.S.; Liebson, P.R.; Mitchell, L.B.; Peters, R.W.; Obias-Manno, D.; Barker, A.H.; Arensberg, D.; Baker, A.; Friedman, L.; Greene, H.L.; et al. Mortality and Morbidity in Patients Receiving Encainide, Flecainide, or Placebo: The Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conard, G.J.; Ober, R.E. Metabolism of Flecainide. Am. J. Cardiol. 1984, 53, B41–B51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L.; Stewart, J.R.; Perry, B.A.; Van Hamersveld, D.D.; Johnson, T.A.; Conard, G.J.; Chang, S.F.; Kvam, D.C.; Pitt, B. Oral Flecainide Acetate for the Treatment of Ventricular Arrhythmias. N. Engl. J. Med. 1981, 305, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjandra-Maga, T.; Verbesselt, R.; Hecken, A.; Mullie, A.; Schepper, P. Flecainide: Single and Multiple Oral Dose Kinetics, Absolute Bioavailability and Effect of Food and Antacid in Man. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1986, 22, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, B.; Heel, R.C. Flecainide A Preliminary Review of Its Pharmacodynamic Properties and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 1985, 29, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephson, M.A.; Ikeda, N.; Singh, B.N. Effects of Flecainide on Ventricular Function: Clinical and Experimental Correlations. Am. J. Cardiol. 1984, 53, B95–B100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.J.; Williams, E.M.V. Voltage- and Time-Dependent Depression of Maximum Rate of Depolarisation of Guinea-Pig Ventricular Action Potentials by Two New Antiarrhythmic Drugs, Flecainide and Lorcainide. Cardiovasc. Res. 1983, 17, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anno, T.; Hondeghem, L.M. Interactions of Flecainide with Guinea Pig Cardiac Sodium Channels. Importance of Activation Unblocking to the Voltage Dependence of Recovery. Circ. Res. 1990, 66, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Follmer, C.H.; Colatsky, T.J. Block of Delayed Rectifier Potassium Current, IK, by Flecainide and E-4031 in Cat Ventricular Myocytes. Circulation 1990, 82, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo, J. Pharmacology of Cardiac Potassium Channels. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 62, 9–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Nademanee, K.; Josephson, M.A.; Ikeda, N.; Venkatesh, N.; Kannan, R. The Electrophysiology and Pharmacology of Verapamil, Flecainide, and Amiodarone: Correlations with Clinical Effects and Antiarrhythmic Actions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1984, 432, 210–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, D.; Imtiaz, M.S.; van Helden, D.F.; Knollmann, B.C.; Laver, D.R. Multiple Modes of Ryanodine Receptor 2 Inhibition by Flecainide. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 86, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhiddin, K.A.; Turner, P.; Blackett, A. Effect of Flecainide on Cardiac Output. Clin. Pharm. 1985, 37, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, V.; Vandormael, M.; Collignon, P.; Kulbertus, H.E. Hemodynamic Effects of a New Antiarrhythmic Agent, Flecainide (R-818), in Coronary Heart Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 1983, 51, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, H.J.; Roden, D.M.; Maffucci, R.J.; Vesper, B.S.; Conard, G.J.; Higgins, S.B.; Oates, J.A.; Smith, R.F.; Woosley, R.L. Suppression of Resistant Ventricular Arrhythmias by Twice Daily Dosing with Flecainide. Am. J. Cardiol. 1981, 48, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, M.; Haugland, J.M.; Granrud, G.; Conard, G.J.; Asinger, R.W.; Mikell, F.L.; Krejci, J. Suppression of Ventricular Ectopic Depolarizations by Flecainide Acetate, a New Antiarrhythmic Agent. Circulation 1982, 65, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josephson, M.A.; Kaul, S.; Hopkins, J.; Kvam, D.; Singh, B.N. Hemodynamic Effects of Intravenous Flecainide Relative to the Level of Ventricular Function in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Am. Heart J. 1985, 109, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paola, A.A.V.; Horowitz, L.N.; Morganroth, J.; Senior, S.; Spielman, S.R.; Greenspan, A.M.; Kay, H.R. Influence of Left Ventricular Dysfunction on Flecainide Therapy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1987, 9, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Coumel, P.; Maison-Blanche, P.; Tarral, E.; Périer, A.; Milliez, P.; Leenhardt, A. Pharmacodynamic Equivalence of Two Flecainide Acetate Formulations in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation by QRS Analysis of Ambulatory Electrocardiogram. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2003, 41, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennezé, L.; Tarral, E.; Ducloux, N.; Funck-Brentano, C. Pharmacokinetics and Electrocardiographic Effects of a New Controlled-Release Form of Flecainide Acetate: Comparison with the Standard Form and Influence of the CYP2D6 Polymorphism. Clin. Pharm. 2002, 72, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L.; Platia, E.V.; Hallstrom, A.; Henthorn, R.W.; Buckingham, T.A.; Carlson, M.D.; Carson, P.E. Interaction of Baseline Characteristics with the Hazard of Encainide, Flecainide, and Moricizine Therapy in Patients with Myocardial Infarction. A Possible Explanation for Increased Mortality in the Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial (CAST). Circulation 1994, 90, 2843–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, W.; Antzelevitch, C. Cellular and Ionic Basis for T-Wave Alternans under Long-QT Conditions. Circulation 1999, 99, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priori, S.G.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Mazzanti, A.; Blom, N.; Borggrefe, M.; Camm, J.; Elliott, P.M.; Fitzsimons, D.; Hatala, R.; Hindricks, G.; et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death: The Task Force for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 2793–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, N.; Della Rocca, D.G.; De Leon De La Cruz, N.S.; Manheimer, E.D.; Magnocavallo, M.; Lavalle, C.; Gianni, C.; Mohanty, S.; Trivedi, C.; Al-Ahmad, A.; et al. Catheter Ablation of Life-Threatening Ventricular Arrhythmias in Athletes. Medicina 2021, 57, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorin, E.; Taub, R.; Medina, A.; Flint, N.; Viskin, S.; Benhorin, J. Long-Term Flecainide Therapy in Type 3 Long QT Syndrome. EP Eur. 2018, 20, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, M.C.; Mustin, D.; Supple, G.; Schaller, R.D.; Santangeli, P.; Arkles, J.; Lin, D.; Muser, D.; Dixit, S.; Nazarian, S.; et al. Class IC Antiarrhythmic Drugs for Suspected Premature Ventricular Contraction–Induced Cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm. 2018, 15, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Rocca, D.G.; Santini, L.; Forleo, G.B.; Sanniti, A.; Del Prete, A.; Lavalle, C.; Di Biase, L.; Natale, A.; Romeo, F. Novel Perspectives on Arrhythmia-Induced Cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations and an Update on Invasive Management Strategies. Cardiol. Rev. 2015, 23, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, S.; Gerstenfeld, E.P.; Svetlichnaya, Y.; Scheinman, M.M. Use of Flecainide in Combination Antiarrhythmic Therapy in Patients with Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm. 2017, 14, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, R.; Houghtaling, P.L.; Tchou, M.; Niebauer, M.J.; Lindsay, B.D.; Tchou, P.J.; Chung, M.K. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Antiarrhythmic Drugs in Atrial Fibrillation: Impact on Mortality: Lvh, Antiarrhythmic Drugs, and Mortality. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2014, 37, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roden, D.M.; Woosley, R.L. Flecainide. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platia, E.V.; Estes, N.A.M.; Heine, D.L.; Griffith, L.S.C.; Garan, H.; Ruskin, J.N.; Reid, P.R. Flecainide: Electrophysiologic and Antiarrhythmic Properties in Refractory Ventricular Tachycardia. Am. J. Cardiol. 1985, 55, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crijns, H.J.; van Gelder, I.C.; Lie, K.I. Supraventricular Tachycardia Mimicking Ventricular Tachycardia during Flecainide Treatment. Am. J. Cardiol. 1988, 62, 1303–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriani, G.; Diemberger, I.; Biffi, M.; Martignani, C.; Branzi, A. Pharmacological Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation: Current Management and Treatment Options. Drugs 2004, 64, 2741–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehling, M. Meta-Analysis of Flecainide Safety in Patients with Supraventricular Arrhythmias. Arzneimittelforschung 2011, 52, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gentzkow, G.D.; Sullivan, J.Y. Extracardiac Adverse Effects of Flecainide. Am. J. Cardiol. 1984, 53, B101–B105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohnloser, S.H.; Dorian, P.; Roberts, R.; Gent, M.; Israel, C.W.; Fain, E.; Champagne, J.; Connolly, S.J. Effect of Amiodarone and Sotalol on Ventricular Defibrillation Threshold: The Optimal Pharmacological Therapy in Cardioverter Defibrillator Patients (OPTIC) Trial. Circulation 2006, 114, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfatto, G.; Zaza, A.; Forster, M.; Sodowick, B.; Danilo, P.; Rosen, M.R. Electrophysiologic, Inotropic and Antiarrhythmic Effects of Propafenone, 5-Hydroxypropafenone and N-Depropylpropafenone. J. Pharm. Exp. 1988, 246, 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Capucci, A.; Botto, G.; Molon, G.; Spampinato, A.; Favale, S.; Proclemer, A.; Porfilio, A.; Marotta, T.; Vimercati, M.; Boriani, G. The Drug and Pace Health CliNical Evaluation (DAPHNE) Study: A Randomized Trial Comparing Sotalol versus β-Blockers to Treat Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Brady-Tachycardia Syndrome Implanted with an Antitachycardia Pacemaker. Am. Heart J. 2008, 156, 373.e1–373.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funck, R.C.; Boriani, G.; Manolis, A.S.; Püererfellner, H.; Mont, L.; Tukkie, R.; Pisapia, A.; Israel, C.W.; Grovale, N.; Grammatico, A.; et al. The MINERVA Study Design and Rationale: A Controlled Randomized Trial to Assess the Clinical Benefit of Minimizing Ventricular Pacing in Pacemaker Patients with Atrial Tachyarrhythmias. Am. Heart J. 2008, 156, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavalle, C.; Ricci, R.P.; Santini, M. Atrial Tachyarrhythmias and Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy: Clinical and Therapeutic Implications. Heart 2010, 96, 1174–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, I.; Guarnieri, T.; Kupersmith, J. Implanted Automatic Defibrillators: Effects of Drugs and Pacemakers. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1988, 11, 2250–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alboni, P.; Paparella, N.; Cappato, R.; Candini, G.C. Direct and Autonomically Mediated Effects of Oral Flecainide. Am. J. Cardiol. 1988, 61, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellestrand, K.J.; Nathan, A.W.; Bexton, R.S.; Camm, A.J. Electrophysiologic Effects of Flecainide Acetate on Sinus Node Function, Anomalous Atrioventricular Connections, and Pacemaker Thresholds. Am. J. Cardiol. 1984, 53, B30–B38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L.; Lutz, J.R.; Allison, S.B. Electrophysiologic and Antiarrhythmic Effects of Oral Flecainide in Patients with Inducible Ventricular Tachycardia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1983, 2, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touboul, P.; Atallah, G.; Gressard, A.; Kirkorian, G. Effects of Amiodarone on Sinus Node in Man. Br. Heart J. 1979, 42, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mary-Rabine, L.; Telerman, M. Long Term Evaluation of Flecainide Acetate in Supraventricular Tachyarrhythmias. Acta Cardiol. 1988, 43, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Shea, P.; Lal, R.; Kim, S.S.; Schechtman, K.; Ruffy, R. Flecainide and Amiodarone Interaction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1986, 7, 1127–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumel, P.; Chouty, F.; Slama, R. Logic and Empiricism in the Selection of Antiarrhythmic Agents: The Role of Drug Combinations. Drugs 1985, 29, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capucci, A.; Piangerelli, L.; Ricciotti, J.; Gabrielli, D.; Guerra, F. Flecainide–Metoprolol Combination Reduces Atrial Fibrillation Clinical Recurrences and Improves Tolerability at 1-Year Follow-up in Persistent Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation. Europace 2016, 18, 1698–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.P.; Holtzman, J.L. Interaction of Flecainide with Digoxin and Propranolol. Am. J. Cardiol. 1984, 53, B52–B57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, T.C.; Nolan, P.E. Antiarrhythmic Agents: Drug Interactions of Clinical Significance. Drug Saf. 2000, 23, 509–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtzman, J.L.; Finley, D.; Mottonen, L.; Berry, D.A.; Ekholm, B.P.; Kvam, D.C.; McQuinn, R.L.; Miller, A.M. The Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Interaction between Single Doses of Flecainide Acetate and Verapamil: Effects on Cardiac Function and Drug Clearance. Clin. Pharm. 1989, 46, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugada, J.; Katritsis, D.G.; Arbelo, E.; Arribas, F.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Calkins, H.; Corrado, D.; Deftereos, S.G.; Diller, G.-P.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Supraventricular TachycardiaThe Task Force for the Management of Patients with Supraventricular Tachycardia of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 655–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugada, J.; Blom, N.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Deanfield, J.; Janousek, J.; Abrams, D.; Bauersfeld, U.; Brugada, R.; Drago, F.; et al. Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Therapy for Arrhythmias in the Pediatric Population: EHRA and AEPC-Arrhythmia Working Group Joint Consensus Statement. EP Eur. 2013, 15, 1337–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.C.; Garson, A. Supraventricular Tachycardia Due to Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome in Children: Early Disappearance and Late Recurrence. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1990, 16, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.; Silver, E.S. Management of Supraventricular Tachycardia in Infants. Pediatr. Drugs 2017, 19, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.E.; Schweikert, R.A.; Saliba, W.I.; Burkhardt, J.D.; Kilikaslan, F.; Saad, E.; Natale, A. Brief Communication: Atrial–Esophageal Fistulas after Radiofrequency Ablation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 144, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.; Arora, G.; Tudorascu, D.L.; Hickey, R.W.; Saladino, R.A.; Manole, M.D. Acute Management of Refractory and Unstable Pediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia. J. Pediatr. 2017, 181, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo, J.; Le Heuzey, J.-Y.; Mabo, P. Narrow Therapeutic Index Drugs: A Clinical Pharmacological Consideration to Flecainide. Eur. J. Clin. Pharm. 2015, 71, 549–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Marcos, F.J.; García-Garmendia, J.L.; Ortega-Carpio, A.; Fernández-Gómez, J.M.; Santos, J.M.; Camacho, C. Comparison of Intravenous Flecainide, Propafenone, and Amiodarone for Conversion of Acute Atrial Fibrillation to Sinus Rhythm. Am. J. Cardiol. 2000, 86, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriani, G. Oral Propafenone To Convert Recent-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with and without Underlying Heart Disease: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 1997, 126, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucci, A.; Boriani, G.; Botto, G.L.; Lenzi, T.; Rubino, I.; Falcone, C.; Trisolino, G.; Della Casa, S.; Binetti, N.; Cavazza, M.; et al. Conversion of Recent-Onset Atrial Fibrillation by a Single Oral Loading Dose of Propafenone or Flecainide. Am. J. Cardiol. 1994, 74, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crijns, H.J.G.M.; Van Wijk, L.M.; Van Gilst, W.H.; Kingma, J.H.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Lie, K.I. Acute Conversion of Atrial Fibrillation to Sinus Rhythm: Clinical Efficacy of Flecainide Acetate. Comparison of Two Regimens. Eur. Heart J. 1988, 9, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriani, G.; Bifft, M.; Capucci, A.; Botto, G.; Broffoni, T.; Ongari, M.; Trisolino, G.; Rubino, I.; Sanguinetti, M.; Branzi, A.; et al. Conversion of Recent-Onset Atrial Fibrillation to Sinus Rhythm: Effects of Different Drug Protocols. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1998, 21, 2470–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capucci, A.; Lenzi, T.; Boriani, G.; Trisolino, G.; Binetti, N.; Cavazza, M.; Fontana, G.; Magnani, B. Effectiveness of Loading Oral Flecainide for Converting Recent-Onset Atrial Fibrillation to Sinus Rhythm in Patients without Organic Heart Disease or with Only Systemic Hypertension. Am. J. Cardiol. 1992, 70, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, S.; Fattore, L.; Toscano, G.; Corsini, F.; Coppo, A.; Catanzaro, M.; Romano, A.; Martone, A.; Caccavale, F.; Iodice, E.; et al. Effectiveness and side effects of the treatment with propafenone and flecainide for recent-onset atrial fibrillation. Ital. Heart J. Suppl. 2001, 2, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.A. Oral Loading Single Dose Flecainide for Pharmacological Cardioversion of Recent-Onset Atrial Fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2003, 87, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, P.; Durand-Dubief, A.; Burri, H.; Cucherat, M.; Kirkorian, G.; Touboul, P. Amiodarone versus Placebo and Class Ic Drugs for Cardioversion of Recent-Onset Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alboni, P.; Botto, G.L.; Baldi, N.; Luzi, M.; Russo, V.; Gianfranchi, L.; Marchi, P.; Calzolari, M.; Solano, A.; Baroffio, R.; et al. Outpatient Treatment of Recent-Onset Atrial Fibrillation with the “Pill-in-the-Pocket” Approach. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2384–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valembois, L.; Audureau, E.; Takeda, A.; Jarzebowski, W.; Belmin, J.; Lafuente-Lafuente, C. Antiarrhythmics for Maintaining Sinus Rhythm after Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvage, S.C.; Chandrasekharan, K.H.; Jeevaratnam, K.; Dulhunty, A.F.; Thompson, A.J.; Jackson, A.P.; Huang, C.L.-H. Multiple Targets for Flecainide Action: Implications for Cardiac Arrhythmogenesis. Br. J. Pharm. 2018, 175, 1260–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.G.; MacGillivray, J.; Macle, L.; Yao, R.J.R.; Bennett, M.; Fordyce, C.B.; Hawkins, N.; Krahn, A.; Jue, J.; Ramanathan, K.; et al. Clinical Effectiveness of a Systematic “Pill-in-the-Pocket” Approach for the Management of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2018, 15, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alboni, P.; Botto, G.L.; Boriani, G.; Russo, G.; Pacchioni, F.; Iori, M.; Pasanisi, G.; Mancini, M.; Mariconti, B.; Capucci, A. Intravenous Administration of Flecainide or Propafenone in Patients with Recent-Onset Atrial Fibrillation Does Not Predict Adverse Effects during “pill-in-the-Pocket” Treatment. Heart 2010, 96, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echt, D.S.; Ruskin, J.N. Use of Flecainide for the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2020, 125, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, V.E.; Marín, F.; Mainar, L.; Gómez-Aldaraví, R.; Martínez, J.G.; Chorro, F.J.; Román, P.; Sogorb, F. Effects of Pretreatment with Intravenous Flecainide on Efficacy of External Cardioversion of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2004, 27, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriani, G.; Biffi, M.; Capucci, A.; Bronzetti, G.; Ayers, G.M.; Zannoli, R.; Branzi, A.; Magnani, B. Favorable Effects of Flecainide in Transvenous Internal Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1999, 33, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimienti, M.; Cullen, M.T.; Casadei, G. Safety of Flecainide versus Propafenone for the Long-Term Management of Symptomatic Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachyarrhythmias. Eur. Heart J. 1995, 16, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulizia, M.; Mangiameli, S.; Orazi, S.; Chiarandà, G.; Piccione, G.; Di Giovanni, N.; Colletti, A.; Pensabene, O.; Lisi, F.; Vasquez, L.; et al. A Randomized Comparison of Amiodarone and Class IC Antiarrhythmic Drugs to Treat Atrial Fibrillation in Patients Paced for Sinus Node Disease: The Prevention Investigation and Treatment: A Group for Observation and Research on Atrial Arrhythmias (PITAGORA) Trial. Am. Heart J. 2008, 155, 100.e1–100.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, P.; Camm, A.J.; Goette, A.; Brandes, A.; Eckardt, L.; Elvan, A.; Fetsch, T.; van Gelder, I.C.; Haase, D.; Haegeli, L.M.; et al. Early Rhythm-Control Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The AFFIRM Investigators. Relationships Between Sinus Rhythm, Treatment, and Survival in the Atrial Fibrillation Follow-Up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) Study. Circulation 2004, 109, 1509–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forleo, G.B.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Lavalle, C.; Mantica, M.; Papavasileiou, L.P.; Ribatti, V.; Panattoni, G.; Santini, L.; Natale, A.; Biase, L.D. A Patient with Asymptomatic Cerebral Lesions During AF Ablation: How Much Should We Worry? J. Atr. Fibrillation 2016, 8, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Natale, A.; Yang, R.; Trivedi, C.; Romero, J.; Briceno, D.; Mohanty, S.; Alviz, I.; Natale, V.; Sanchez, J.; et al. Is Transesophageal Echocardiography Necessary in Patients Undergoing Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation on an Uninterrupted Direct Oral Anticoagulant Regimen? Results from a Prospective Multicenter Registry. Heart Rhythm. 2020, 17, 2093–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Ogunbayo, G.; Elayi, S.C.; Darrat, Y.; Rios, S.A.; Diaz, J.C.; Alviz, I.; Cerna, L.; Gabr, M.; Chernobelsky, E.; et al. Safety of Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation in the Octogenarian Population. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2019, 30, 2686–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Rocca, D.G.; Mohanty, S.; Mohanty, P.; Trivedi, C.; Gianni, C.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Burkhardt, J.D.; Gallinghouse, G.J.; Hranitzky, P.; Sanchez, J.E.; et al. Long-term Outcomes of Catheter Ablation in Patients with Longstanding Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Lasting Less than 2 Years. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Trivedi, C.; Gianni, C.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Morris, E.H.; Burkhardt, J.D.; Sanchez, J.E.; Horton, R.; Gallinghouse, G.J.; Hongo, R.; et al. Procedural Findings and Ablation Outcome in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Referred after Two or More Failed Catheter Ablations. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2017, 28, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemantle, N.; Lafuente-Lafuente, C.; Mitchell, S.; Eckert, L.; Reynolds, M. Mixed Treatment Comparison of Dronedarone, Amiodarone, Sotalol, Flecainide, and Propafenone, for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation. Europace 2011, 13, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, P.; Andresen, D.; Bosch, R.; Borggrefe, M.; Meinertz, T.; Parade, U.; Ravens, U.; Samol, A.; Steinbeck, G.; Treszl, A.; et al. Short-Term versus Long-Term Antiarrhythmic Drug Treatment after Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation (Flec-SL): A Prospective, Randomised, Open-Label, Blinded Endpoint Assessment Trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Rocca, D.G.; Tarantino, N.; Trivedi, C.; Mohanty, S.; Anannab, A.; Salwan, A.S.; Gianni, C.; Bassiouny, M.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Romero, J.; et al. Non-pulmonary Vein Triggers in Nonparoxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: Implications of Pathophysiology for Catheter Ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 2154–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allot, E.; Denjoy, I. Comparison of the Safety and Efficacy of Flecamide versus Propafenone in Hospital Out-Patients with Symptomatic Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter. Am. J. Cardiol. 1996, 77, 66A–71A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccarelli, G.V.; Dorian, P.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Coumel, P. Prospective Comparison of Flecainide versus Quinidine for the Treatment of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter. Am. J. Cardiol. 1996, 77, 53A–59A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carunchio, A.; Fera, M.S.; Mazza, A.; Burattini, M.; Greco, G.; Galati, A.; Ceci, V. A comparison between flecainide and sotalol in the prevention of recurrences of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. G. Ital. Cardiol. 1995, 25, 51–68. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wijk, L.M.; den Heijer, P.; Crijns, H.J.; van Gilst, W.H.; Lie, K.I. Flecainide Versus Quinidine in the Prevention of Paroxysms of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1989, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henthorn, R.W.; Waldo, A.L.; Anderson, J.L.; Gilbert, E.M.; Alpert, B.L.; Bhandari, A.K.; Hawkinson, R.W.; Pritchett, E.L. Flecainide Acetate Prevents Recurrence of Symptomatic Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia. The Flecainide Supraventricular Tachycardia Study Group. Circulation 1991, 83, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett, E.L.C. Propafenone Treatment of Symptomatic Paroxysmal Supraventricular Arrhythmias: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial in Patients Tolerating Oral Therapy. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991, 114, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Scheinman, M.M.; Aliot, E.M.; Alpert, J.S.; Calkins, H.; Camm, A.J.; Campbell, W.B.; Haines, D.E.; Kuck, K.H.; Lerman, B.B.; et al. ACC/AHA/ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Supraventricular Arrhythmias—Executive Summary. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 1493–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crijns, H.J.G.M.; den Heijer, P.; van Wijk, L.M.; Lie, K.I. Successful Use of Flecainide in Atrial Fibrillation with Rapid Ventricular Rate in the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome. Am. Heart J. 1988, 115, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandozi, C.; Galeazzi, M.; Lavalle, C.; Ficili, S.; Russo, M.; Santini, M. Navx-Guided Cryoablation of Atrial Tachycardia Inside the Left Atrial Appendage. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol. J. 2011, 10, 556–561. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett, E.L.C.; DaTorre, S.D.; Platt, M.L.; McCarville, S.E.; Hougham, A.J. Flecainide Acetate Treatment of Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia and Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: Dose-Response Studies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1991, 17, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katritsis, D.G.; Boriani, G.; Cosio, F.G.; Hindricks, G.; Jaïs, P.; Josephson, M.E.; Keegan, R.; Kim, Y.-H.; Knight, B.P.; Kuck, K.-H.; et al. European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) Consensus Document on the Management of Supraventricular Arrhythmias, Endorsed by Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), and Sociedad Latinoamericana de Estimulación Cardiaca y Electrofisiologia (SOLAECE). EP Eur. 2017, 19, 465–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, C.; Sanchez, J.E.; Mohanty, S.; Trivedi, C.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Burkhardt, J.D.; Gallinghouse, G.J.; Hranitzky, P.M.; Horton, R.P.; et al. Isolation of the Superior Vena Cava from the Right Atrial Posterior Wall: A Novel Ablation Approach. Ep Eur. 2018, 20, e124–e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietersen, A.H.; Hellemann, H. Usefulness of Flecainide for Prevention of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation and Flutter. Am. J. Cardiol. 1991, 67, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SVT | Recommended Dose | Administration Route |
|---|---|---|
| Atrial Fibrillation (Restoration of sinus rhythm) | 200–300 mg 2 mg/kg | Oral Intravenous |
| Atrial Fibrillation (Maintenance of sinus rhythm) | 100–200 mg bid 200 mg once daily | Oral |
| AVNRT/AVRT | 50–150 mg bid | Oral |
| Focal Atrial Tachycardia | 50–150 mg bid | Oral |
| Adverse Event | Incidence | Indication |
|---|---|---|
| Drug induced Brugada | <1% | Discontinue |
| QRS increased more than 40 ms or wider than 130 ms | <1% | Discontinue |
| QRS increased more than 20 ms | 1–2% | Reduce Dosage |
| Bradyarrhythmia, sinus pause, AV block | 1–2% | Discontinue |
| Hypotension | 3–5% (mostly with IV) | Reduce Dosage |
| 1:1 atrial flutter | 3–5% | Discontinue and consider ablate CTI dependent-flutter |
| Worsening heart failure | <1% | Discontinue |
| Extracardiac effects (dizziness, tremor, nausea) | 1–2% | Reduce Dosage |
| Study | Population in Flecainide Arm | AF Duration | Flecainide | Reversion Rate | Adverse Event |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Martínez-Marcos et al. [65] | 50 | ≤2 d | Intravenous (2 mg/kg followed by 1 mg/kg at 8 h if not in sinus rhythm) | 1 h → 58% 8 h → 82% 12 h → 90% | Transient junctional rhythm: 4% Atrial flutter: 2% Symptomatic hypotension:2% Paresthesia: 4% Total: 12% |
| Capucci et al. [67] | 58 | ≤7 d | Single oral dose (300 mg) | 3 h → 59% 8 h → 78% | Transient junctional rhythm:1.7% Atrial flutter: 3.4% |
| Crijns et al. [68] | 13 | ≤24 h | Intravenous (2 mg/kg up to 150 mg) | 3 h → 77% | - |
| Boriani et al. [69] | 69 | ≤7 d | Single oral dose (300 mg) | 1 h → 13% 3 h → 57% 8 h → 75% | - |
| Capucci et al. [70] | 22 | ≤7 d | Single oral dose (300 mg) | 8 h → 91% 24 h → 95% | no |
| Romano et al. [71] | 138 | ≤3 d | Intravenous | 1 h → 73% 3 h → 80% 6 h → 86% 24 h → 90% | - |
| Author | n. Patient | Type of AF | Compared Treatment | Endpoint of AF Recurrence | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chimienti et al. [82] | 200 | Paroxysmal | Flecainide vs. Propafenone | Palpitation recurrence on days 15, 30, 90, 180, 270, 360 | No difference between flecainide and propafenone |
| Gulizia et al. [83] | 176 with PMK | Paroxysmal | Ic AAD vs. Amiodarone | Time to first occurrence of death, atrial cardioversion, cardiovascular hospitalization or change of AAD | IC AAD non inferior to Amiodarone. Similar AT recurrences |
| Naccarelli et al. [95] | 239 | Paroxysmal | Flecainide vs. Quinidine | AF recurrence at 12 months | Flecainide similar efficacy to quinidine but better tolerated |
| Allot et al. [94] | 97 | Paroxysmal | Flecainide vs. Propafenone | AF recurrence at 12 months | Flecainide similar efficacy to propafenone |
| Carunchio et al. [96] | 66 | Paroxysmal | Flecainide vs. Sotalolo vs. Placebo | AF recurrence at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months | Flecainide similar efficacy to sotalol and superior to placebo |
| van Wijk et al. [97] | 26 | Paroxysmal | Flecainide vs. Quinidine | AF recurrence during 3-months follow-up period | Flecainide superior to quinidine |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lavalle, C.; Magnocavallo, M.; Straito, M.; Santini, L.; Forleo, G.B.; Grimaldi, M.; Badagliacca, R.; Lanata, L.; Ricci, R.P. Flecainide How and When: A Practical Guide in Supraventricular Arrhythmias. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071456
Lavalle C, Magnocavallo M, Straito M, Santini L, Forleo GB, Grimaldi M, Badagliacca R, Lanata L, Ricci RP. Flecainide How and When: A Practical Guide in Supraventricular Arrhythmias. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(7):1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071456
Chicago/Turabian StyleLavalle, Carlo, Michele Magnocavallo, Martina Straito, Luca Santini, Giovanni Battista Forleo, Massimo Grimaldi, Roberto Badagliacca, Luigi Lanata, and Renato Pietro Ricci. 2021. "Flecainide How and When: A Practical Guide in Supraventricular Arrhythmias" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 7: 1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071456
APA StyleLavalle, C., Magnocavallo, M., Straito, M., Santini, L., Forleo, G. B., Grimaldi, M., Badagliacca, R., Lanata, L., & Ricci, R. P. (2021). Flecainide How and When: A Practical Guide in Supraventricular Arrhythmias. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(7), 1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071456









