Hypertension and Related Comorbidities as Potential Risk Factors for COVID-19 Hospitalization and Severity: A Prospective Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
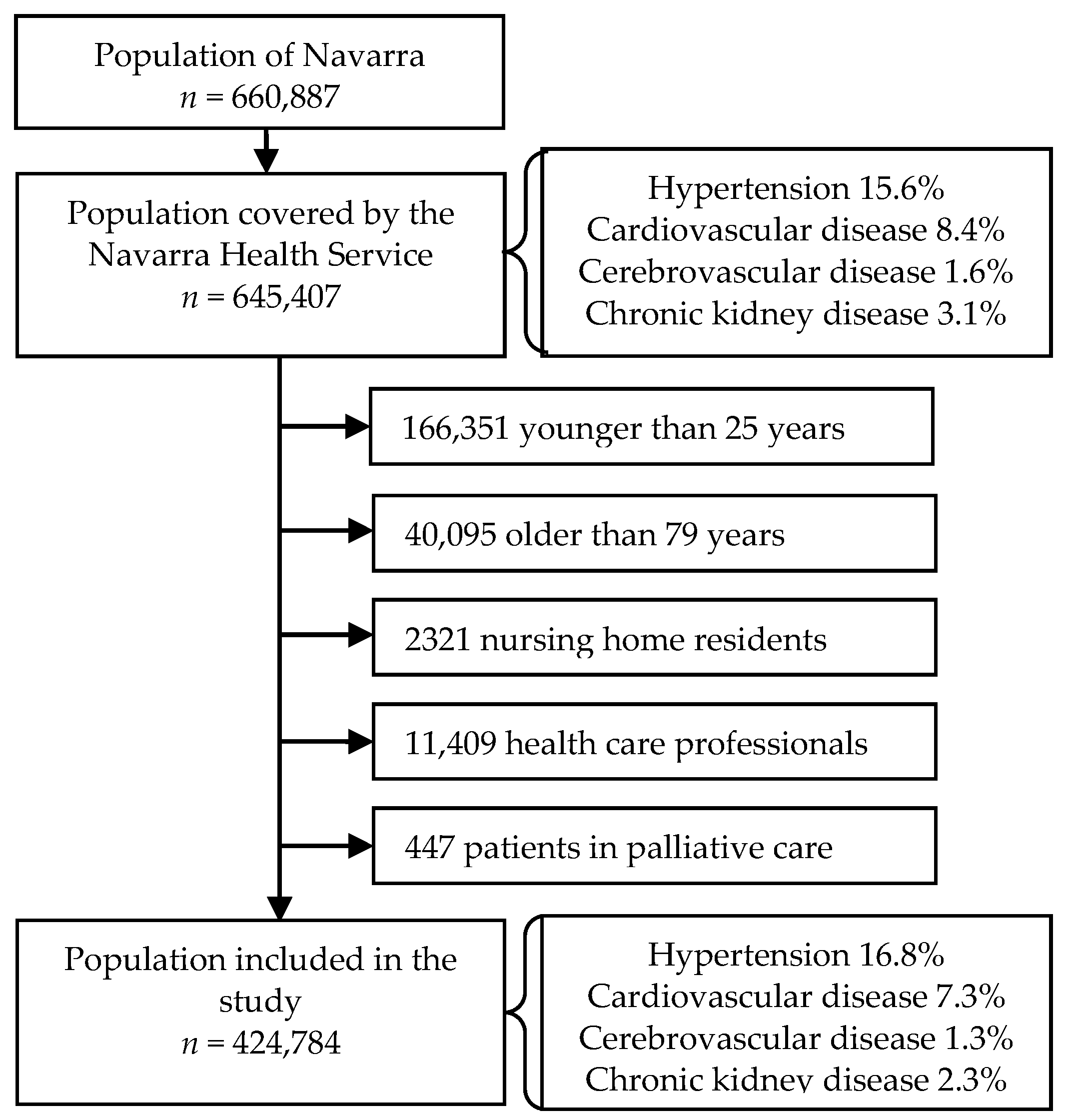
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. COVID-19 Hospitalization and Severe Outcomes
3.3. Hypertension, Related Conditions, and Risk for COVID-19 Outcomes
3.4. Effect on Severe Outcomes among COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report—51. 2020. Available online: www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200311-sitrep-51-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=1ba62e57_10 (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami, A.; Javanmardi, F.; Pirbonyeh, N.; Akbari, A. Prevalence of Underlying Diseases in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2020, 8, e35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Gou, X.; Pu, K.; Chen, Z.; Guo, Q.; Ji, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Gillies, C.L.; Singh, R.; Singh, A.; Chudasama, Y.; Coles, B.; Seidu, S.; Zaccardi, F.; Davies, M.J.; Khunti, K. Prevalence of co-morbidities and their association with mortality in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabi, F.A.; Al Zoubi, M.S.; Kasasbeh, G.A.; Salameh, D.M.; Al-Nasser, A.D. SARS-CoV-2 and Coronavirus Disease 2019: What We Know So Far. Pathogens 2020, 9, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Mao, Y.; Chen, G. Risk factors for 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) patients progressing to critical illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging 2020, 12, 12410–12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, K.; Salunke, A.; Pathak, S.K.; Pandey, A.; Doctor, C.; Puj, K.; Sharma, M.; Jain, A.; Warikoo, V. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the impact of various comorbidities on serious events. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, E.; Zoli, M.; Gonzalez-Freire, M.; Salive, M.E.; Studenski, S.A.; Ferrucci, L. Aging and Multimorbidity: New Tasks, Priorities, and Frontiers for Integrated Gerontological and Clinical Research. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Peng, F.; Xu, B.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Peng, J.; Li, Q.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e16–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Gu, J.; Zhang, P.; Xu, Y.; Ye, J.; Wang, Z.; Ye, D.; Pan, W.; et al. Comparison of clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 at different ages. Aging 2020, 12, 10070–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, L.; Garg, S.; O’Halloran, A.; Whitaker, M.; Pham, H.; Anderson, E.J.; Armistead, I.; Bennett, N.M.; Billing, L.; Como-Sabetti, K.; et al. Risk Factors for Intensive Care Unit Admission and In-hospital Mortality among Hospitalized Adults Identified through the U.S. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)-Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iaccarino, G.; Grassi, G.; Borghi, C.; Ferri, C.; Salvetti, M.; Volpe, M.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Minuz, P.; Muiesan, M.L.; Mulatero, P.; et al. Age and Multimorbidity Predict Death among COVID-19 Patients. Hypertension 2020, 76, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, M.J.; Baldwin, M.R.; Abrams, D.; Jacobson, S.D.; Meyer, B.J.; Balough, E.M.; Aaron, J.G.; Claassen, J.; Rabbani, L.E.; Hastie, J.; et al. Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.d.C.M.; Mattos, L.R.; Raposo, L.M. Risk Factors for Hospitalization and Mortality due to COVID-19 in Espírito Santo State, Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Ge, S.; Xu, G. Kidney disease is associated with in-hospital death of patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, E.J.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; Bacon, S.; Bates, C.; Morton, C.E.; Curtis, H.J.; Mehrkar, A.; Evans, D.; Inglesby, P.; et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 2020, 584, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Data & Statistics. Available online: www.cdc.gov/datastatistics/index.html (accessed on 22 July 2020).
- Harbers, M.M.; Achterberg, P.W. Information, Indicators and Data on the Prevalence of Chronic Diseases in the European Union. 2012. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/major_chronic_diseases/docs/eu_chronicdiseases_data_information_31072012_en.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Moreno-Iribas, C.; Sayon-Orea, C.; Delfrade, J.; Ardanaz, E.; Gorricho, J.; Burgui, R.; Nuin, M.; Guevara, M. Validity of type 2 diabetes diagnosis in a population-based electronic health record database. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2017, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Classification Committee of WONCA. International Classification of Primary Care—Revised, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Case Definition for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), as of 29 May 2020. Available online: www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/surveillance/case-definition (accessed on 31 May 2020).
- Wang, X.; Fang, X.; Cai, Z.; Wu, X.; Gao, X.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Comorbid Chronic Diseases and Acute Organ Injuries Are Strongly Correlated with Disease Severity and Mortality among COVID-19 Patients: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Research 2020, 2020, 2402961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Galdamez, D.R.; González-Block, M.Á.; Romo-Dueñas, D.K.; Lima-Morales, R.; Hernández-Vicente, I.A.; Lumbreras-Guzmán, M.; Méndez-Hernández, P. Increased Risk of Hospitalization and Death in Patients with COVID-19 and Pre-existing Noncommunicable Diseases and Modifiable Risk Factors in Mexico. Arch. Med. Res. 2020, 51, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.-J.; Liang, W.-H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H.-R.; Chen, Z.-S.; Li, Y.-M.; Liu, X.-Q.; Chen, R.-C.; Tang, C.-L.; Wang, T.; et al. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: A nationwide analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figliozzi, S.; Masci, P.G.; Ahmadi, N.; Tondi, L.; Koutli, E.; Aimo, A.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Dimopoulos, M.-A.; Caforio, A.L.P.; Georgiopoulos, G. Predictors of adverse prognosis in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2020, 50, e13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.L.; Gianos, E.; Barish, M.A.; Chatterjee, S.; Kohn, N.; Lesser, M.; Giannis, D.; Coppa, K.; Hirsch, J.; McGinn, T.; et al. Prevalence and Predictors of Venous Thromboembolism or Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Thromb. Haemost. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiga, M.; Wang, D.W.; Han, Y.; Lewis, D.B.; Wu, J.C. COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease: From basic mechanisms to clinical perspectives. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inciardi, R.M.; Solomon, S.D.; Ridker, P.M.; Metra, M. Coronavirus 2019 Disease (COVID-19), Systemic Inflammation, and Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e017756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafi, A.M.A.; Shaikh, S.A.; Shirke, M.M.; Iddawela, S.; Harky, A. Cardiac manifestations in COVID-19 patients-A systematic review. J. Card. Surg. 2020, 35, 1988–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słomka, A.; Kowalewski, M.; Żekanowska, E. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID–19): A Short Review on Hematological Manifestations. Pathogens 2020, 9, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Laukkanen, J.A. Renal complications in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Med. 2020, 52, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Socio-Demographic and Clinical Variables | Hypertension | Cardiovascular Disease | Cerebrovascular Disease | Chronic Kidney Disease | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | |
| Population, number | 353,461 | 71,323 | 393,779 | 31,005 | 419,136 | 5648 | 414,883 | 9901 |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Female | 50.5 | 44.1 | 50.3 | 37.5 | 49.6 | 36.8 | 49.6 | 38.7 |
| Male | 49.5 | 55.9 | 49.7 | 62.5 | 50.4 | 63.2 | 50.4 | 61.3 |
| Age, years | ||||||||
| 25–49 | 57.7 | 9.2 | 51.7 | 22.6 | 50.1 | 8.2 | 50.5 | 10.9 |
| 50–64 | 29.3 | 35.1 | 30.3 | 29.0 | 30.3 | 29.3 | 30.4 | 22.4 |
| 65–79 | 13.0 | 55.7 | 18.0 | 48.3 | 19.6 | 62.4 | 19.1 | 66.7 |
| Country of origin | ||||||||
| Spain | 79.6 | 90.3 | 80.7 | 90.9 | 81.3 | 92.0 | 81.2 | 92.7 |
| Other | 20.4 | 9.7 | 19.3 | 9.1 | 18.7 | 8.0 | 18.8 | 7.3 |
| Municipality population | ||||||||
| >100,000 | 31.8 | 32.4 | 31.8 | 33.6 | 31.9 | 33.6 | 31.8 | 34.1 |
| 5000–100,000 | 34.8 | 32.4 | 34.5 | 33.3 | 34.5 | 31.6 | 34.5 | 31.4 |
| <5000 | 33.4 | 35.1 | 33.7 | 33.1 | 33.7 | 34.9 | 33.7 | 34.6 |
| Annual taxable income level (€) | ||||||||
| None/dependent | 5.9 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 5.2 | 5.9 | 5.7 | 5.9 | 5.6 |
| <18,000 | 53.4 | 51.0 | 53.3 | 49.0 | 52.9 | 54.7 | 53.0 | 52.3 |
| 18,000–100,000 | 40.0 | 42.9 | 40.2 | 45.1 | 40.5 | 39.0 | 40.5 | 41.6 |
| >100,000 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.4 |
| Primary healthcare visits in prior 12 months | ||||||||
| 0 | 22.4 | 8.0 | 20.9 | 8.6 | 20.2 | 5.0 | 20.3 | 5.5 |
| 1–4 | 43.0 | 34.9 | 42.2 | 34.2 | 41.8 | 29.5 | 41.9 | 28.9 |
| 5–9 | 19.9 | 27.3 | 20.7 | 26.1 | 21.0 | 27.2 | 21.0 | 27.9 |
| >9 | 14.7 | 29.8 | 16.2 | 31.0 | 17.0 | 38.3 | 16.8 | 37.7 |
| Hospitalization in prior 12 months | 4.8 | 9.0 | 4.9 | 12.7 | 5.3 | 18.3 | 5.3 | 14.1 |
| Smoking status | ||||||||
| Current smoker | 11.7 | 29.0 | 13.9 | 23.3 | 14.4 | 25.7 | 14.3 | 28.5 |
| Former smoker | 3.7 | 11.4 | 4.5 | 11.6 | 4.9 | 13.4 | 4.8 | 12.1 |
| Never smoker | 17.5 | 20.6 | 17.9 | 20.4 | 18.0 | 22.9 | 18.0 | 18.6 |
| Unknown | 67.1 | 39.1 | 63.8 | 44.7 | 62.7 | 37.9 | 62.9 | 40.8 |
| Hypertension | 0 | 100.0 | 15.0 | 38.9 | 16.3 | 53.9 | 15.8 | 58.2 |
| Hypertension-related conditions | ||||||||
| Cardiovascular disease | 5.4 | 16.9 | 0 | 100.0 | 7.1 | 25.3 | 6.8 | 26.9 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 0.7 | 4.3 | 1.1 | 4.6 | 0 | 100.0 | 1.2 | 6.3 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 1.2 | 8.1 | 1.8 | 8.6 | 2.2 | 11.0 | 0 | 100.0 |
| Any other major chronic condition | 16.0 | 39.3 | 18.6 | 36.6 | 19.6 | 42.6 | 19.3 | 46.7 |
| Hospitalization | Severe Cases 2 | ICU Admission | Deaths | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study population | N | 1106 | 176 | 117 | 97 |
| Rate 1 | 260 | 41 | 28 | 23 | |
| Persons with HT | N | 354 | 85 | 52 | 55 |
| Rate 1 | 496 | 119 | 73 | 77 | |
| Persons without HT | N | 752 | 91 | 65 | 42 |
| Rate 1 | 213 | 26 | 18 | 12 | |
| HT vs all others | RR (95% CI) | 2.33 (2.06–2.65) | 4.63 (3.44–6.22) | 3.96 (2.75–5.71) | 6.49 (4.34–9.70) |
| Persons with CVD | N | 188 | 51 | 25 | 41 |
| Rate 1 | 606 | 164 | 81 | 132 | |
| Persons without CVD | N | 918 | 125 | 92 | 56 |
| Rate 1 | 233 | 32 | 23 | 14 | |
| CVD vs all others | RR (95% CI) | 2.60 (2.22–3.04) | 5.18 (3.74–7.18) | 3.45 (2.22–5.37) | 9.30 (6.22–13.91) |
| Persons with CBVD | N | 46 | 16 | 5 | 16 |
| Rate 1 | 814 | 283 | 89 | 283 | |
| Persons without CBVD | N | 1060 | 160 | 112 | 81 |
| Rate 1 | 253 | 38 | 27 | 19 | |
| CBVD vs all others | RR (95% CI) | 3.22 (2.40–4.33) | 7.42 (4.44–12.41) | 3.31 (1.35–8.11) | 14.66 (8.57–25.06) |
| Persons with CKD | N | 89 | 27 | 10 | 21 |
| Rate 1 | 899 | 273 | 101 | 212 | |
| Persons without CKD | N | 1017 | 149 | 107 | 76 |
| Rate 1 | 245 | 36 | 26 | 18 | |
| CKD vs all others | RR (95% CI) | 3.67 (2.95–4.55) | 7.59 (5.04–11.44) | 3.92 (2.05–7.49) | 11.58 (7.14–18.77) |
| Crude Analysis | Partially Adjusted Analysis 1 | Fully Adjusted Analysis 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR (95% CI) | p-Value | RR (95% CI) | p-Value | RR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Analysis of hospitalizations | ||||||
| Hypertension | 2.33 (2.06–2.65) | <0.001 | 1.22 (1.06–1.41) | 0.005 | 0.96 (0.83–1.12) | 0.622 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 2.60 (2.22–3.04) | <0.001 | 1.65 (1.40–1.94) | <0.001 | 1.33 (1.13–1.58) | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 3.22 (2.40–4.33) | <0.001 | 1.74 (1.29–2.35) | <0.001 | 1.41 (1.04–1.92) | 0.025 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 3.67 (2.95–4.55) | <0.001 | 1.97 (1.57–2.46) | <0.001 | 1.52 (1.21–1.91) | <0.001 |
| Analysis of severe cases 3 | ||||||
| Hypertension | 4.63 (3.44–6.22) | <0.001 | 1.53 (1.11–2.10) | 0.009 | 1.12 (0.80–1.56) | 0.517 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 5.18 (3.74–7.18) | <0.001 | 2.22 (1.58–3.12) | <0.001 | 1.61 (1.13–2.30) | 0.008 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 7.42 (4.44–12.41) | <0.001 | 2.60 (1.54–4.40) | <0.001 | 1.91 (1.13–3.25) | 0.016 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 7.59 (5.04–11.44) | <0.001 | 2.60 (1.70–3.99) | <0.001 | 1.78 (1.14–2.76) | 0.010 |
| Analysis of ICU admission | ||||||
| Hypertension | 3.96 (2.75–5.71) | <0.001 | 1.75 (1.18–2.59) | 0.005 | 1.38 (0.91–2.09) | 0.124 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 3.45 (2.22–5.37) | <0.001 | 1.84 (1.66–2.91) | 0.009 | 1.44 (0.90–2.31) | 0.131 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 3.31 (1.35–8.11) | 0.009 | 1.55 (0.63–3.84) | 0.341 | 1.18 (0.47–2.93) | 0.729 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 3.92 (2.05–7.49) | <0.001 | 1.88 (0.97–3.64) | 0.064 | 1.28 (0.65–2.53) | 0.476 |
| Analysis of exitus | ||||||
| Hypertension | 6.49 (4.34–9.70) | <0.001 | 1.53 (1.01–2.32) | 0.047 | 1.09 (0.70–1.67) | 0.734 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 9.30 (6.22–13.91) | <0.001 | 3.16 (2.08–4.79) | <0.001 | 2.17 (1.40–3.37) | 0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 14.66 (8.57–25.06) | <0.001 | 3.89 (2.25–6.73) | <0.001 | 2.76 (1.58–4.81) | <0.001 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 11.58 (8.57–18.77) | <0.001 | 2.87 (1.74–4.72) | <0.001 | 1.83 (1.09–3.07) | 0.022 |
| COVID-19 Outcome Evaluated | Crude Analysis | Partially-Adjusted Analysis 2 | Fully-Adjusted Analysis 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR (95% CI) | p-Value | RR (95% CI) | p-Value | RR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| People without hypertension-related conditions | ||||||
| Hospitalization | 2.01 (1.72–2.35) | <0.001 | 1.13 (0.95–1.34) | 0.167 | 0.95 (0.80–1.14) | 0.589 |
| Severe cases 1 | 3.61 (2.45–5.30) | <0.001 | 1.32 (0.87–1.98) | 0.189 | 1.10 (0.72–1.69) | 0.658 |
| ICU admission | 3.76 (2.44–5.80) | <0.001 | 1.68 (1.06–2.67) | 0.027 | 1.38 (0.85–2.23) | 0.192 |
| Exitus | 5.17 (2.90–9.24) | <0.001 | 1.33 (0.72–2.43) | 0.363 | 1.11 (0.59–2.07) | 0.751 |
| People with any hypertension-related condition | ||||||
| Hospitalization | 1.74 (1.36–2.23) | <0.001 | 1.20 (0.93–1.56) | 0.161 | 0.99 (0.76–1.30) | 0.958 |
| Severe cases 1 | 2.84 (1.69–4.78) | <0.001 | 1.58 (0.92–2.70) | 0.097 | 1.21 (0.70–2.10) | 0.499 |
| ICU admission | 2.35 (1.12–4.93) | 0.025 | 1.72 (0.79–3.75) | 0.174 | 1.46 (0.65–3.26) | 0.361 |
| Exitus | 2.72 (1.52–4.86) | 0.001 | 1.31 (0.73–2.38) | 0.365 | 1.05 (0.57–1.92) | 0.885 |
| Chronic Condition Evaluated | Crude Analysis | Partial-Adjusted Analysis 2 | Fully-Adjusted Analysis 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR (95% CI) | p-Value | RR (95% CI) | p-Value | RR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Severe cases | ||||||
| Hypertension | 1.98 (1.48–2.67) | <0.001 | 1.31 (0.96–1.79) | 0.092 | 1.19 (0.86–1.65) | 0.298 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 1.99 (1.44–2.76) | <0.001 | 1.20 (0.84–1.72) | 0.321 | 1.14 (0.79–1.65) | 0.474 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 2.30 (1.38–3.85) | 0.002 | 1.34 (0.78–2.30) | 0.289 | 1.26 (0.73–2.18) | 0.407 |
| Chronic renal disease | 2.07 (1.37–3.12) | <0.001 | 1.21 (0.78–1.87) | 0.392 | 1.13 (0.73–1.76) | 0.581 |
| ICU admission | ||||||
| Hypertension | 1.70 (1.18–2.45) | 0.004 | 1.42 (0.96–2.10) | 0.077 | 1.42 (0.94–2.13) | 0.095 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 1.33 (0.85–2.06) | 0.210 | 1.07 (0.66–1.72) | 0.790 | 1.05 (0.64–1.70) | 0.856 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 1.03 (0.42–2.52) | 0.951 | 0.91 (0.36–2.30) | 0.850 | 0.87 (0.34–2.23) | 0.778 |
| Chronic renal disease | 1.07 (0.56–2.04) | 0.842 | 0.86 (0.44–1.69) | 0.662 | 0.82 (0.41–1.62) | 0.565 |
| Exitus | ||||||
| Hypertension | 2.78 (1.86–4.16) | <0.001 | 1.38 (0.91–2.09) | 0.131 | 1.15 (0.75–1.79) | 0.518 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 3.58 (2.39–5.35) | <0.001 | 1.84 (1.21–2.81) | 0.005 | 1.45 (0.92–2.30) | 0.111 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 4.55 (2.66–7.78) | <0.001 | 2.23 (1.27–3.91) | 0.005 | 1.80 (1.00–3.23) | 0.049 |
| Chronic renal disease | 3.16 (1.95–5.12) | <0.001 | 1.51 (0.92–2.50) | 0.105 | 1.10 (0.65–1.86) | 0.714 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fresán, U.; Guevara, M.; Trobajo-Sanmartín, C.; Burgui, C.; Ezpeleta, C.; Castilla, J. Hypertension and Related Comorbidities as Potential Risk Factors for COVID-19 Hospitalization and Severity: A Prospective Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061194
Fresán U, Guevara M, Trobajo-Sanmartín C, Burgui C, Ezpeleta C, Castilla J. Hypertension and Related Comorbidities as Potential Risk Factors for COVID-19 Hospitalization and Severity: A Prospective Population-Based Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(6):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061194
Chicago/Turabian StyleFresán, Ujué, Marcela Guevara, Camino Trobajo-Sanmartín, Cristina Burgui, Carmen Ezpeleta, and Jesús Castilla. 2021. "Hypertension and Related Comorbidities as Potential Risk Factors for COVID-19 Hospitalization and Severity: A Prospective Population-Based Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 6: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061194
APA StyleFresán, U., Guevara, M., Trobajo-Sanmartín, C., Burgui, C., Ezpeleta, C., & Castilla, J. (2021). Hypertension and Related Comorbidities as Potential Risk Factors for COVID-19 Hospitalization and Severity: A Prospective Population-Based Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(6), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061194






