Smell and Taste Loss Recovery Time in COVID-19 Patients and Disease Severity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
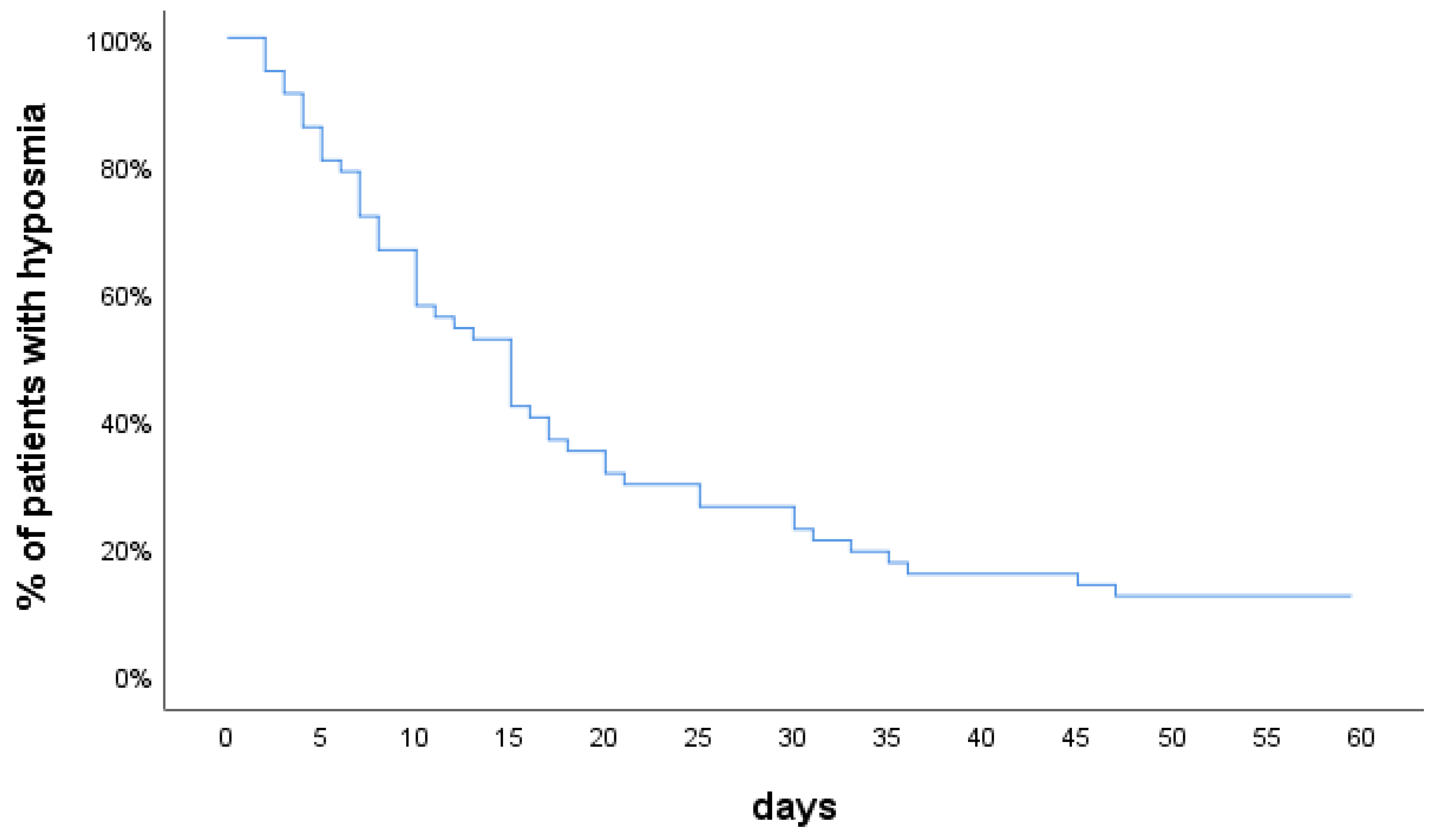
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Von Bartheld, C.S.; Hagen, M.M.; Butowt, R. Prevalence of Chemosensory Dysfunction in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Reveals Significant Ethnic Differences. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 2944–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, A.R.; Gengler, I.; Speth, M.M. Olfactory Dysfunction: A Highly Prevalent Symptom of COVID-19 with Public Health Significance. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2020, 163, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, B.; Arshamian, A.; Ravia, A.; Mishor, E.; Snitz, K.; Shushan, S.; Roth, Y.; Perl, O.; Honigstein, D.; Weissgross, R.; et al. Relationship between odor intensity estimates and COVID-19 prevalence prediction in a Swedish population. Chem. Sens. 2020, 45, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Printza, A.; Katotomichelakis, M.; Metallidis, S.; Panagopoulos, P.; Sarafidou, A.; Petrakis, V.; Constantinidis, J. The clinical course of smell and taste loss in COVID-19 hospitalized patients. Hippokratia 2020, 24, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Journe, F.; Hans, S.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Mustin, V.; Beckers, E.; Vaira, L.A.; De Riu, G.; Hopkins, C.; Saussez, S. Severity of Anosmia as an Early Symptom of COVID-19 Infection May Predict Lasting Loss of Smell. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 582802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerkin, R.C.; Ohla, K.; Veldhuizen, M.G.; Joseph, P.V.; E Kelly, C.; Bakke, A.J.; E Steele, K.; Farruggia, M.C.; Pellegrino, R.; Pepino, M.Y.; et al. Recent smell loss is the best predictor of COVID-19 among individuals with recent respiratory symptoms. Chem. Senses 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Vaira, L.; Hopkins, C.; Petrocelli, M.; Lechien, J.R.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Salzano, G.; Cucurullo, M.; A Salzano, F.; Saussez, S.; Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; et al. Smell and taste recovery in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: A 60-day objective and prospective study. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2020, 134, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Printza, A.; Constantinidis, J. The role of self-reported smell and taste disorders in suspected COVID-19. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 277, 2625–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.A.; Elsherif, H.S.; Abdel-Hamid, A.S.; Elzayat, S. Early recovery patterns of olfactory disorders in COVID-19 patients; a clinical cohort study. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 41, 102725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almqvist, J.; Granberg, T.; Tzortzakakis, A.; Klironomos, S.; Kollia, E.; Öhberg, C.; Martin, R.; Piehl, F.; Ouellette, R.; Ineichen, B.V. Neurological manifestations of coronavirus infections—A systematic review. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 2057–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wostyn, P. COVID-19 and chronic fatigue syndrome: Is the worst yet to come? Med. Hypotheses 2021, 146, 110469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: Who.int/publications/i/item/clinical-management-of-covid-19 (accessed on 29 June 2020).
- Speth, M.; Singer-Cornelius, T.; Oberle, M.; Gengler, I.; Brockmeier, S.; Sedaghat, A. Time scale for resolution of olfactory dysfunction in COVID-19. Rhinol. J. 2020, 58, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.H.; Faraji, F.; Bs, D.P.P.; Ostrander, B.T.; DeConde, A.S. Self-reported olfactory loss associates with outpatient clinical course in COVID-19. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020, 10, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzatenta, A.; Neri, G.; D’Ardes, D.; De Luca, C.; Marinari, S.; Porreca, E.; Cipollone, F.; Vecchiet, J.; Falcicchia, C.; Panichi, V.; et al. Smell and Taste in Severe CoViD-19: Self-Reported vs. Testing. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 589409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moein, S.T.; Hashemian, S.M.; Mansourafshar, B.; Khorram-Tousi, A.; Tabarsi, P.; Doty, R.L. Smell dysfunction: A biomarker for COVID-19. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020, 10, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samimi Ardestani, S.H.; Mohammadi Ardehali, M.; Rabbani Anari, M.; Rahmaty, B.; Erfanian, R.; Akbari, M.; Motedayen, Z.; Samimi Niya, F.; Aminloo, R.; Farahbakhsh, F.; et al. The coronavirus disease 2019: The prevalence, prognosis, and recovery from olfactory dysfunction (OD). Acta Otolaryngol. 2020, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speth, M.M.; Singer-Cornelius, T.; Oberle, M.; Gengler, I.; Brockmeier, S.J.; Sedaghat, A.R. Olfactory Dysfunction and Sinonasal Symptomatology in COVID-19: Prevalence, Severity, Timing, and Associated Characteristics. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2020, 163, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altundag, A.; Saatci, O.; Sanli, D.E.T.; Duz, O.A.; Sanli, A.N.; Olmuscelik, O.; Temirbekov, D.; Kandemirli, S.G.; Karaaltin, A.B. The temporal course of COVID-19 anosmia and relation to other clinical symptoms. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, M.; Liu, J.; Counsell, N.; Ta, N.H.; Rocke, J.; Anmolsingh, R.; Eynon-Lewis, N.; Paun, S.; Hopkins, C.; Khwaja, S.; et al. Course of symptoms for loss of sense of smell and taste over time in one thousand forty-one healthcare workers during the Covid-19 pandemic: Our experience. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2020, 46, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, C.; Surda, P.; Vaira, L.; Lechien, J.; Safarian, M.; Saussez, S.; Kumar, N. Six month follow-up of self-reported loss of smell during the COVID-19 pandemic. Rhinol. J. 2021, 59, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.S.; Kristiansen, M.F.; Hanusson, K.D.; Danielsen, M.E.; Gaini, S.; Strøm, M.; Weihe, P. Long COVID in the Faroe Islands—A longitudinal study among non-hospitalized patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 30, ciaa1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidler, A.; Karpinski, T.M. SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 Comparison of Three Emerging Coronaviruses. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2020, 13, e103744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavem, K.; Ghanima, W.; Olsen, M.K.; Gilboe, H.M.; Einvik, G. Persistent symptoms 1.5–6 months after COVID-19 in non-hospitalised subjects: A population-based cohort study. Thorax 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hintschich, C.A.; Wenzel, J.J.; Hummel, T.; Hankir, M.K.; Kühnel, T.; Vielsmeier, V.; Bohr, C. Psychophysical tests reveal impaired olfaction but preserved gustation in COVID-19 patients. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020, 10, 1105–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmier, J.K.; Halpern, M.T. Patient recall and recall bias of health state and health status. Expert Rev. Pharm. Outcomes Res. 2004, 4, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| During Your COVID-19 Illness | |
|---|---|
| 1. Did you experience loss/impairment of smell? | The severity in an ordinal scale 0–4 |
| 2. Did you experience loss/impairment of taste? | The severity in an ordinal scale 0–4 |
| 3. Did you experience nasal congestion/obstruction? | The severity in an ordinal scale 0–4 |
| 4. Did you experience rhinorrhea? | The severity in an ordinal scale 0–4 |
| 5. When did you first notice the loss of smell? | Before/After diagnosis |
| 6. Did the loss/impairment of smell resolve and when? | Yes ● No Days from onset |
| 7. Did the loss/impairment of taste resolve and when? | Yes ● No Days from onset |
| 8. Are you smoking? | Yes ● No ● Ex-smoker ● Electronic |
| 9. Do you have a history of allergic rhinitis? | Yes ● No |
| 10. Do you have a history of chronic rhinosinusitis? | Yes ● No |
| Patients, n = 150, n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 18–89 |
| Mean ± SD | 51.6 ± 16.8 |
| Sex | |
| Male | 93 (62) |
| Female | 57 (38) |
| Smoking | 21 (14) |
| Allergic rhinitis | 11 (7) |
| Chronic rhinosinusitis | 3 (2) |
| Comorbidities | |
| No medical history | 86 (57) |
| Hypertension | 30 (20) |
| Diabetes | 16 (11) |
| Cardiopathy | 9 (6) |
| Covid-19 severity | |
| Mild | 56 (37) |
| Moderate | 50 (33) |
| Severe | 34 (23) |
| Critical (ICU-treated) | 10 (7) |
| Hospitalized | 94 (63) |
| Patients (n = 140), n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Smell loss | 57 (41) |
| Taste loss | 53 (38) |
| Smell and taste loss | 48 (34) |
| Nasal obstruction | 16 (11) |
| Rhinorrhea | 13 (9) |
| Allergic rhinitis | 11 (8) |
| Chronic rhinosinusitis | 3 (2) |
| Smell loss severity | |
| Mild | 3 (5) |
| Moderate | 12 (21) |
| Severe | 11 (19) |
| Extremely severe (anosmia) | 31 (54) |
| Taste loss severity | |
| Mild | 3 (6) |
| Moderate | 11 (21) |
| Severe | 7 (5) |
| Extremely severe | 32 (61) |
| Smell loss recovery | 50 (88) |
| Taste loss recovery | 42 (79) |
| Hyposmia before other symptoms | 15 (26) |
| Smell loss duration (days), median (IQR) | 11.5 (13.3) |
| Taste loss duration (days), median (IQR) | 10 (8) |
| Smell Loss Prevalence Patients; n (%) | p | Hyposmia Duration Days; Mean ± SD | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COVID-19 Disease Severity | 0.327 | 0.756 ** | ||
| Mild Moderate Severe | 19 (33) 23 (46) 15 (44) | 13.5 ± 8.3 14.1 ± 12 16.9 ± 13.2 | ||
| Sex | 0.327 | 0.874 *** | ||
| Male Female | 33 (38) 24 (44) | 14.1 ± 9.2 15.7 ± 13.9 |
| Recovery Rates Patients; n (%) | p | Days to Recovery Mean ± SD | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smell loss severity | 0.396 | 0.04 | ||
| Moderate Severe Extremely severe | 10 (83) 11 (100) 27 (87) | 9 ± 6.8 21.2 ± 12.5 14.7 ± 10.3 | ||
| Taste loss severity | 0.51 | 0.084 | ||
| Moderate Severe Extremely severe | 8 (73) 6 (85) 28 (88) | 8.5 ± 7 15.8 ± 12.8 14.8 ± 10.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Printza, A.; Katotomichelakis, M.; Valsamidis, K.; Metallidis, S.; Panagopoulos, P.; Panopoulou, M.; Petrakis, V.; Constantinidis, J. Smell and Taste Loss Recovery Time in COVID-19 Patients and Disease Severity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050966
Printza A, Katotomichelakis M, Valsamidis K, Metallidis S, Panagopoulos P, Panopoulou M, Petrakis V, Constantinidis J. Smell and Taste Loss Recovery Time in COVID-19 Patients and Disease Severity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(5):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050966
Chicago/Turabian StylePrintza, Athanasia, Mihalis Katotomichelakis, Konstantinos Valsamidis, Symeon Metallidis, Periklis Panagopoulos, Maria Panopoulou, Vasilis Petrakis, and Jannis Constantinidis. 2021. "Smell and Taste Loss Recovery Time in COVID-19 Patients and Disease Severity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 5: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050966
APA StylePrintza, A., Katotomichelakis, M., Valsamidis, K., Metallidis, S., Panagopoulos, P., Panopoulou, M., Petrakis, V., & Constantinidis, J. (2021). Smell and Taste Loss Recovery Time in COVID-19 Patients and Disease Severity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(5), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050966










