Elevated CSF LRG and Decreased Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment
2.2. Frontal Cortical Biopsy Sampling
2.3. The CSF Sampling
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics Statement
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, R.D.; Fisher, C.M.; Hakim, S.; Ojemann, R.G.; Sweet, W.H. Symptomatic Occult Hydrocephalus with Normal Cerebrospinal-Fluid Pressure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1965, 273, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, E.; Ishikawa, M.; Kato, T.; Kazui, H.; Miyake, H.; Miyajima, M.; Nakajima, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Kuriyama, N.; Tokuda, T.; et al. Guidelines for Management of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Second Edition. Neurol. Medico Chir. 2012, 52, 775–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toma, A.K.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Stapleton, S.; Kitchen, N.D.; Watkins, L.D. Systematic review of the outcome of shunt surgery in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 1977–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eide, P.K.; Sorteberg, W. Outcome of Surgery for Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Role of Preoperative Static and Pulsatile Intracranial Pressure. World Neurosurg. 2016, 86, 186–193.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivisto, A.M.; Alafuzoff, I.; Savolainen, S.; Sutela, A.; Rummukainen, J.; Kurki, M.; Jääskeläinen, J.E.; Soininen, H.; Rinne, J.; Leinonen, V. Poor Cognitive Outcome in Shunt-Responsive Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2013, 72, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyykkö, O.T.; Nerg, O.; Niskasaari, H.-M.; Niskasaari, T.; Koivisto, A.M.; Hiltunen, M.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Rauramaa, T.; Kojoukhova, M.; Alafuzoff, I.; et al. Incidence, Comorbidities, and Mortality in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. World Neurosurg. 2018, 112, e624–e631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräutigam, K.; Vakis, A.; Tsitsipanis, C. Pathogenesis of idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A review of knowledge. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 61, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; Blennow, K.; Breteler, M.M.B.; de Strooper, B.; Frisoni, G.B.; Salloway, S.; Van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2016, 388, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, J.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Ishikawa, M.; Kristensen, B.; Leinonen, V.; Mori, E.; Owler, B.K.; Tullberg, M.; A Williams, M.; Relkin, N.R. Influence of comorbidities in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus—Research and clinical care. A report of the ISHCSF task force on comorbidities in INPH. Fluids Barriers CNS 2013, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luikku, A.J.; Hall, A.; Nerg, O.; Koivisto, A.M.; Hiltunen, M.; Helisalmi, S.; Herukka, S.-K.; Junkkari, A.; Sutela, A.; Kojoukhova, M.; et al. Predicting Development of Alzheimer’s Disease in Patients with Shunted Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 71, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Miyajima, M.; Ogino, I.; Akiba, C.; Kawamura, K.; Kamohara, C.; Fusegi, K.; Harada, Y.; Hara, T.; Sugano, H.; et al. Preoperative Phosphorylated Tau Concentration in the Cerebrospinal Fluid Can Predict Cognitive Function Three Years after Shunt Surgery in Patients with Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 66, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, H.; Baudner, S. Isolation and characterization of an unknown, leucine-rich 3.1-S-alpha2-glycoprotein from human serum (author’s transl). Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 1977, 358, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirai, R.; Hirano, F.; Ohkura, N.; Ikeda, K.; Inoue, S. Up-regulation of the expression of leucine-rich α2-glycoprotein in hepatocytes by the mediators of acute-phase response. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 382, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, M.; Nakajima, M.; Motoi, Y.; Moriya, M.; Sugano, H.; Ogino, I.; Nakamura, E.; Tada, N.; Kunichika, M.; Arai, H. Leucine-Rich α2-Glycoprotein Is a Novel Biomarker of Neurodegenerative Disease in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid and Causes Neurodegeneration in Mouse Cerebral Cortex. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Miyajima, M.; Mineki, R.; Taka, H.; Murayama, K.; Arai, H. Analysis of potential diagnostic biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus by proteomics. Acta Neurochir. 2006, 148, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Miyajima, M.; Ogino, I.; Watanabe, M.; Miyata, H.; Karagiozov, K.L.; Arai, H.; Hagiwara, Y.; Segawa, T.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. Leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein is a marker for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir. 2011, 153, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relkin, N.; Marmarou, A.; Klinge, P.; Bergsneider, M.; Black, P.M. Diagnosing Idiopathic Normal-pressure Hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2005, 57, S2–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junkkari, A.; Luikku, A.J.; Danner, N.; Jyrkkänen, H.K.; Rauramaa, T.; Korhonen, V.E.; Koivisto, A.M.; Nerg, O.; Kojoukhova, M.; Huttunen, T.J.; et al. The Kuopio idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus protocol: Initial outcome of 175 patients. Fluids Barriers CNS 2019, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, Y.; Kazui, H.; Yoshida, T.; Kito, Y.; Kimura, N.; Tokunaga, H.; Ogino, A.; Miyake, H.; Ishikawa, M.; Takeda, M. Validation of Grading Scale for Evaluating Symptoms of Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2007, 25, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppala, T.T.; Nerg, O.; Koivisto, A.M.; Rummukainen, J.; Puli, L.; Zetterberg, H.; Pyykko, O.T.; Helisalmi, S.; Alafuzoff, I.; Hiltunen, M.; et al. CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer disease correlate with cortical brain biopsy findings. Neurology 2012, 78, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leinonen, V.; Rauramaa, T.; Johansson, J.; Bottelbergs, A.; Tesseur, I.; Van Der Ark, P.; Pemberton, D.; Koivisto, A.M.; Jääskeläinen, J.E.; Hiltunen, M.; et al. S-[18F]THK-5117-PET and [11C]PIB-PET Imaging in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus in Relation to Confirmed Amyloid-β Plaques and Tau in Brain Biopsies. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 64, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkonen, N.; Herukka, S.-K.; Huilaja, L.; Kokki, M.; Koivisto, A.M.; Hartikainen, P.; Remes, A.M.; Tasanen, K. Increased Levels of the Bullous Pemphigoid BP180 Autoantibody Are Associated with More Severe Dementia in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junkkari, A.; Häyrinen, A.; Rauramaa, T.; Sintonen, H.; Nerg, O.; Koivisto, A.M.; Roine, R.P.; Viinamäki, H.; Soininen, H.; Luikku, A.; et al. Health-related quality-of-life outcome in patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus—A 1-year follow-up study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppsson, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Wikkelsø, C. Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: Pathophysiology and diagnosis by CSF biomarkers. Neurology 2013, 80, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppsson, A.; Wikkelsö, C.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Constantinescu, R.; Remes, A.M.; Herukka, S.-K.; Rauramaa, T.; Nagga, K.; Leinonen, V.; et al. CSF biomarkers distinguish idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus from its mimics. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff-Radford, N.R. Alzheimer CSF biomarkers may be misleading in normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurology 2014, 83, 1573–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, Y.; Bundo, M.; Sugiura, S.; Kamita, M.; Ono, M.; Hattori, K.; Yoshida, S.; Goto, Y.-I.; Urakami, K.; Niida, S. PTPRQ as a potential biomarker for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3034–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, M.; Rauramaa, T.; Mäkinen, P.M.; Hiltunen, M.; Herukka, S.; Kokki, M.; Musialowicz, T.; Jyrkkänen, H.; Danner, N.; Junkkari, A.; et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type Q in cerebrospinal fluid reflects ependymal cell dysfunction and is a potential biomarker for adult chronic hydrocephalus. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, B.; Lautner, R.; Andreasson, U.; Öhrfelt, A.; Portelius, E.; Bjerke, M.; Hölttä, M.; Rosén, C.; Olsson, C.; Strobel, G.; et al. CSF and blood biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
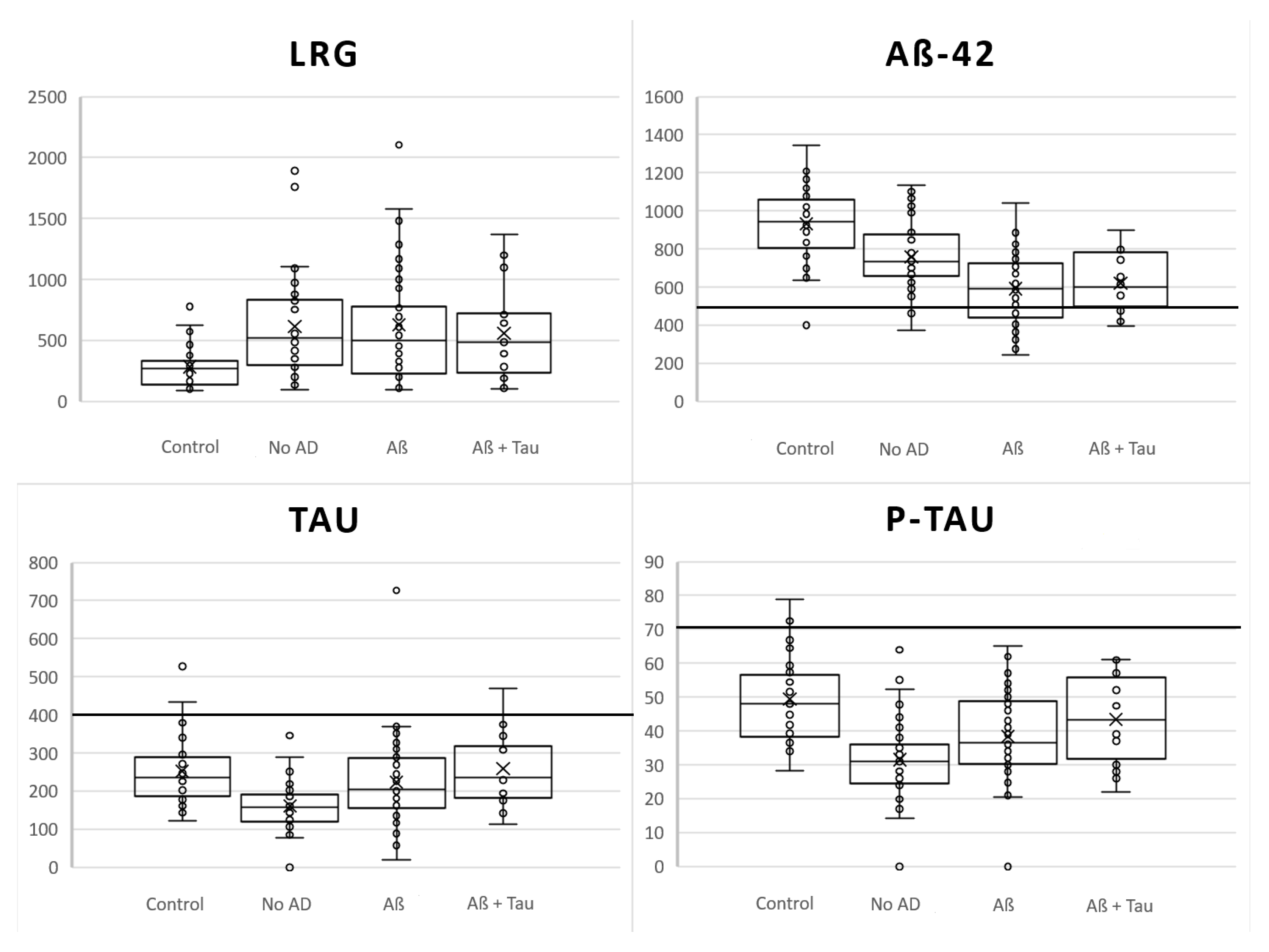
| Category | Control | iNPH No-AD | iNPH Aβ | iNPH Aβ+Tau | Pooled iNPH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 33 | 48 | 52 | 16 | 119 | |
| Age | Mean (SD) | 73 (4) | 73 (6) | 76 (5) * | 81 (3) ** | 75 (6) * |
| MMSE | Median (IQR) | 28 (27–29) | 24 (22–27) ** | 23 (18–26) ** | 20 (16–24) ** | 24 (19–26) ** |
| LRG pg/mL | Mean (SD) | 283.0 (170.5) | 614.1 (418.1) * | 625.3 (493.0) * | 558.6 (384.3) | 610.1 (440.7) ** |
| Aβ1-42 pg/mL | Mean (SD) | 933.2 (194.9) | 757.3 (167.7) ** | 591.5 (182.3) ** | 622.0 (153.8) ** | 658.8 (189.4) ** |
| Tau pg/mL | Mean (SD) | 252.3 (89.2) | 160.3 (59.5) ** | 223.7 (110.3) | 259.1 (95.2) | 199.7 (97.3) ** |
| P-Tau181 pg/mL | Mean (SD) | 49.4 (12.5) | 31.5 (11.4) ** | 38.4 (14.1) ** | 43.4 (13.1) | 35.5 (14.2) ** |
| Variable | Regression Coefficient | Odds Ratio | 95% C.I. for OR |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRG * | 0.00317 | 1.00318 | 1.000682–1.00567 |
| Aβ1-42 * | −0.00577 | 0.994 | 0.991–0.997 |
| P-Tau181 * | −0.0518 | 0.950 | 0.910–0.990 |
| Excluded variables ** | |||
| Age | 0.091 | 1.095 | 0.978–1.227 |
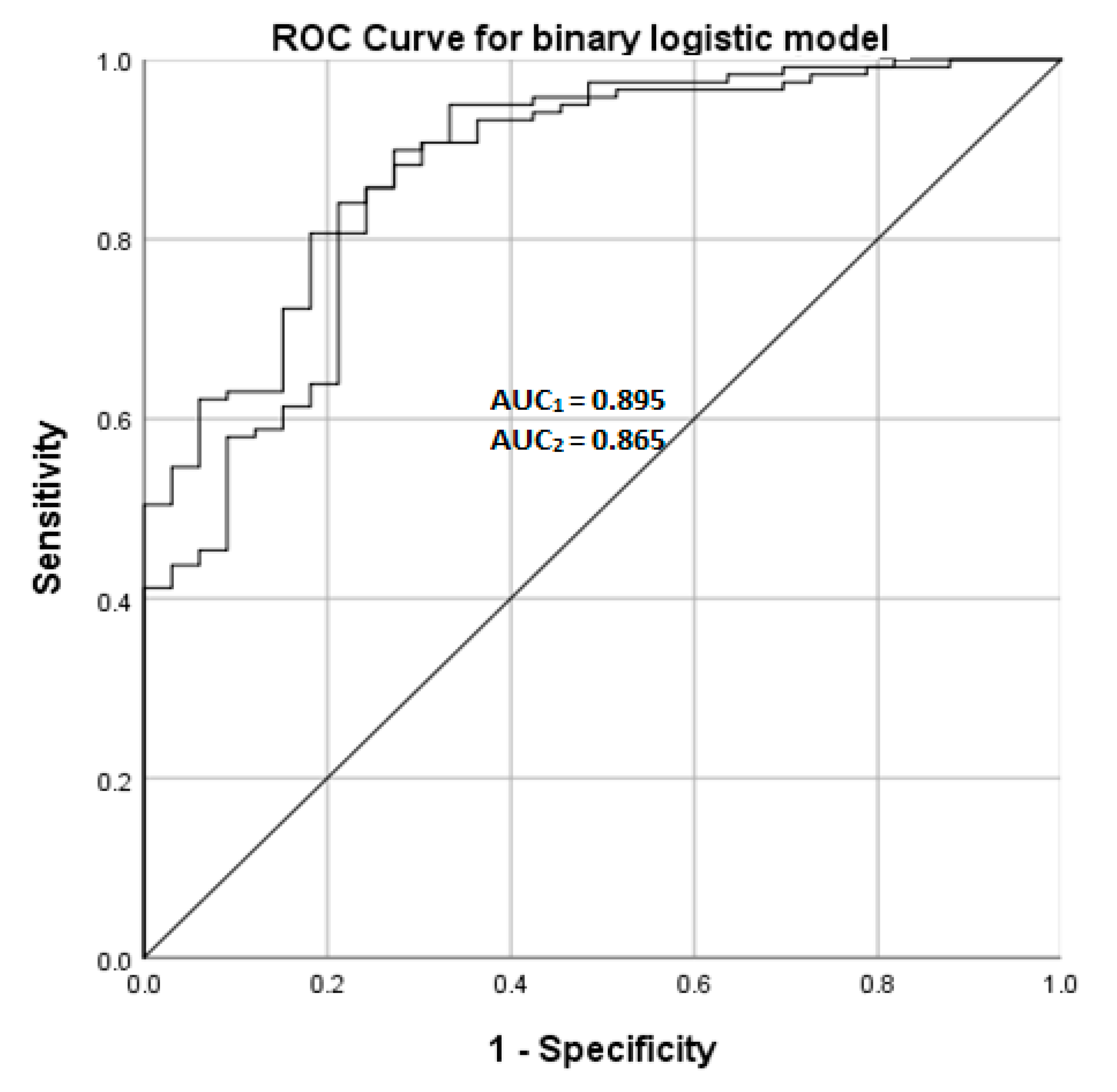
| Model value1 | Specificity | Sensitivity | ROC AUC (95% C.I.) |
| 54.5% | 95.8% | 0.895 (0.837–0.952) | |
| Variable | Regression Coefficient | Odds Ratio | 95% C.I for OR |
| Aβ1-42 * | −0.00632 | 0.994 | 0.991–0.996 |
| P-Tau181 * | −0.0542 | 0.947 | 0.910–0.986 |
| Excluded variables ** | |||
| - | |||
| Model value2 | Specificity | Sensitivity | ROC AUC (95% C.I.) |
| 48.5% | 95.8% | 0.865 (0.795—0.934) |
| Category | No-AD | Aβ | p * | Aβ and Tau | p * | Tau ** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 48 | 52 | 16 | 3 | |||
| Age | Mean (SD) | 73 (6) | 76 (5) | 81 (3) | 71 (2) | ||
| MMSE | Median (IQR) | 24 (22–27) | 23 (18–26) | 20 (16–24) | 20 (14–22) | ||
| LRG pg/mL | Mean (SD) | 614.1 (418.1) | 625.3 (493.0) | 0.98 | 558.6 (384.3) | 0.71 | 557.2 (120.4) |
| Aβ1-42 pg/mL | Mean (SD) | 757.3 (167.7) | 591.5 (182.3) | <0.001 | 622.0 (153.8) | 0.059 | 445.8 (44.7) |
| Tau pg/mL | Mean (SD) | 160.3 (59.5) | 223.7 (110.3) | 0.015 | 259.1 (95.2) | 0.71 | 96.1 (26.7) |
| P-Tau181 pg/mL | Mean (SD) | 31.5 (11.4) | 38.4 (14.1) | 0.067 | 43.4 (13.1) | 0.032 | 6.3 (11.0) |
| NPHGS-baseline | Median (IQR) | 6 (4–8) | 7 (4–10) | 8 (4–9.5) | 10 (10–12) | ||
| NPHGS-change | Median (IQR) | −1 (−3–0) | −1 (−2–0) | 1 (−1–2) | −1 (-2–1) |
| Category | Likelihood Ratio Test | Parameter Estimates | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vs Aβ-Pathology | Vs Aβ + Tau | ||||
| Parameter | −2 Log | Chi-Square | p | p | p |
| Variable | |||||
| LRG | 156.6 | 1.1 | 0.58 | 0.325 | 0.876 |
| Aβ1-42 | 193.3 | 37.7 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| P-tau181 | 180.3 | 24.8 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| iNPHGS-change | 164.9 | 9.4 | 0.009 | 0.90 | 0.009 |
| Category | Non-Responder | Responder | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 27 | 91 | ||
| Age | Mean (SD) | 77 (4) | 75 (6) | 0.031 |
| MMSE | Median (IQR) | 21 (16–26) | 24 (20–27) | 0.051 |
| LRG pg/ml | Mean (SD) | 652.7 (439.0) | 599.0 (445.1) | 0.636 |
| Aβ1-42 pg/ml | Mean (SD) | 617.5 (172.7) | 673.9 (192.2) | 0.263 |
| Tau pg/ml | Mean (SD) | 211.3 (75.9) | 190.4 (86.8) | 0.822 |
| P-tau181 pg/ml | Mean (SD) | 38.3 (12.2) | 34.7 (14.8) | 0.683 |
| NPHGS-baseline | Median (IQR) | 8 (4–10) | 6 (4–9) | |
| NPHGS-change | Median (IQR) | 0 (−1–1) | −1 (−3–0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vanninen, A.; Nakajima, M.; Miyajima, M.; Rauramaa, T.; Kokki, M.; Musialowicz, T.; Mäkinen, P.M.; Herukka, S.-K.; Koivisto, A.M.; Jääskeläinen, J.E.; et al. Elevated CSF LRG and Decreased Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051105
Vanninen A, Nakajima M, Miyajima M, Rauramaa T, Kokki M, Musialowicz T, Mäkinen PM, Herukka S-K, Koivisto AM, Jääskeläinen JE, et al. Elevated CSF LRG and Decreased Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(5):1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051105
Chicago/Turabian StyleVanninen, Aleksi, Madoka Nakajima, Masakazu Miyajima, Tuomas Rauramaa, Merja Kokki, Tadeusz Musialowicz, Petra M. Mäkinen, Sanna-Kaisa Herukka, Anne M. Koivisto, Juha E. Jääskeläinen, and et al. 2021. "Elevated CSF LRG and Decreased Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 5: 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051105
APA StyleVanninen, A., Nakajima, M., Miyajima, M., Rauramaa, T., Kokki, M., Musialowicz, T., Mäkinen, P. M., Herukka, S.-K., Koivisto, A. M., Jääskeläinen, J. E., Hiltunen, M., & Leinonen, V. (2021). Elevated CSF LRG and Decreased Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(5), 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051105







